Application Possibilities of Sustainable Nanostructured Silica-Based Materials in Cosmetics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of Sustainable Nanostructured Silica-Based Materials
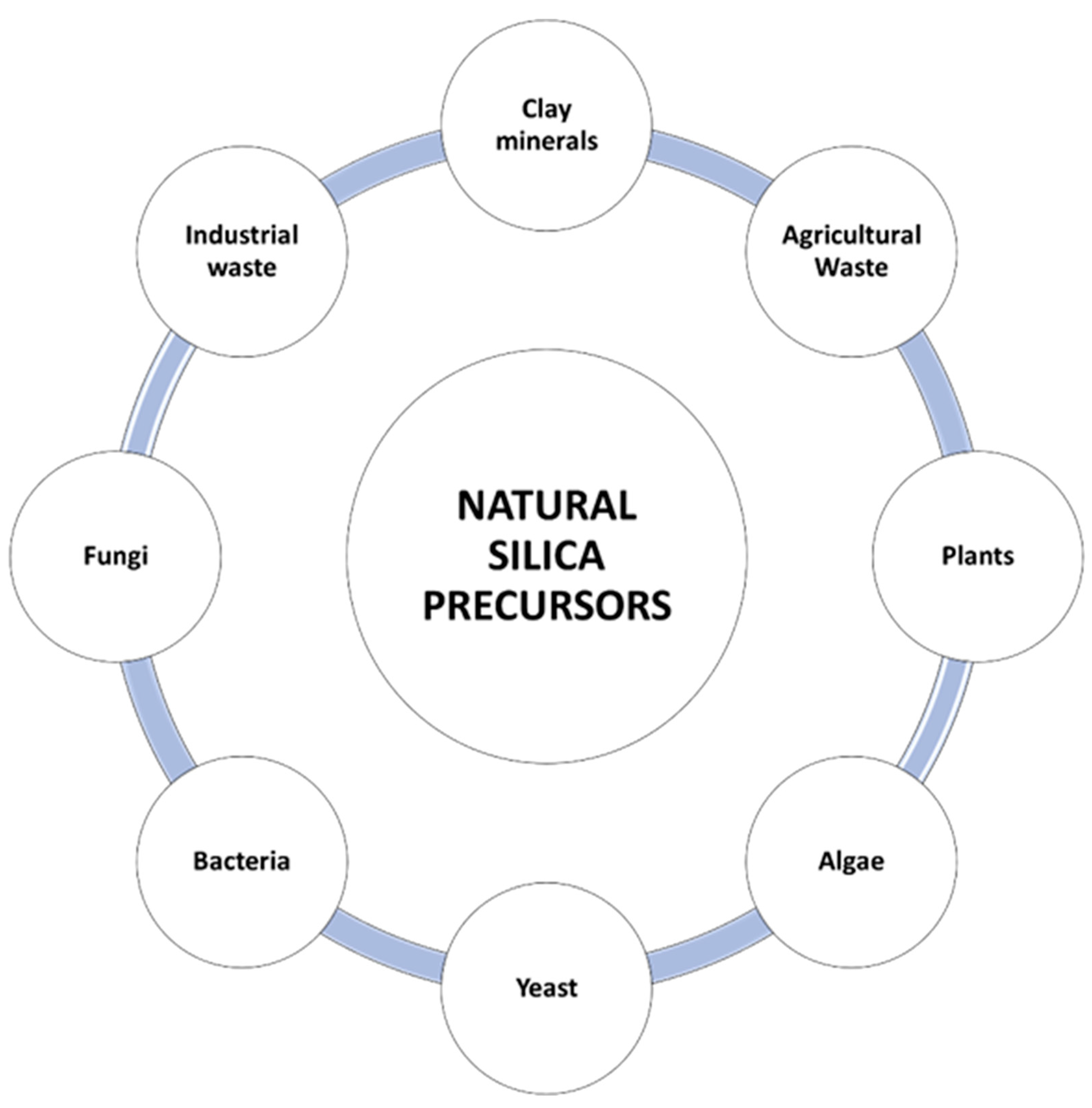
2.1. Clays/Minerals
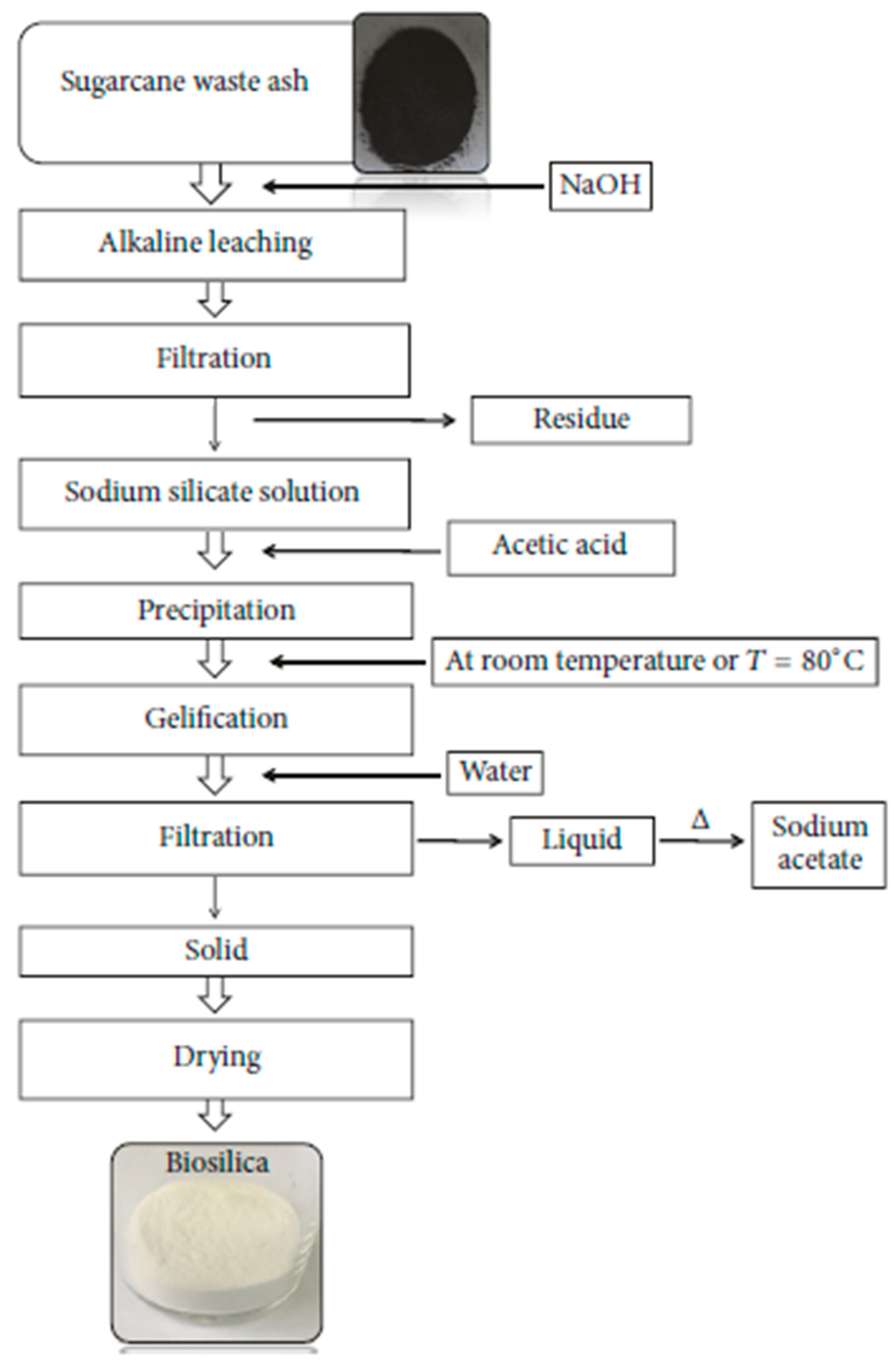
2.2. Agricultural Waste Products, Plants, and Industrial Waste
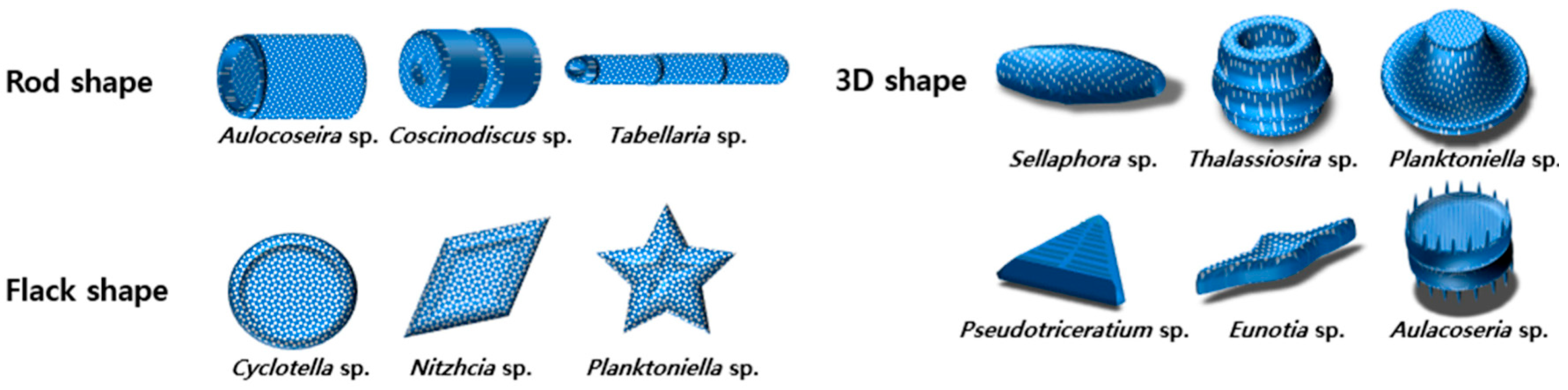
2.3. Algae
2.4. Bacteria and Yeast
2.5. Fungi
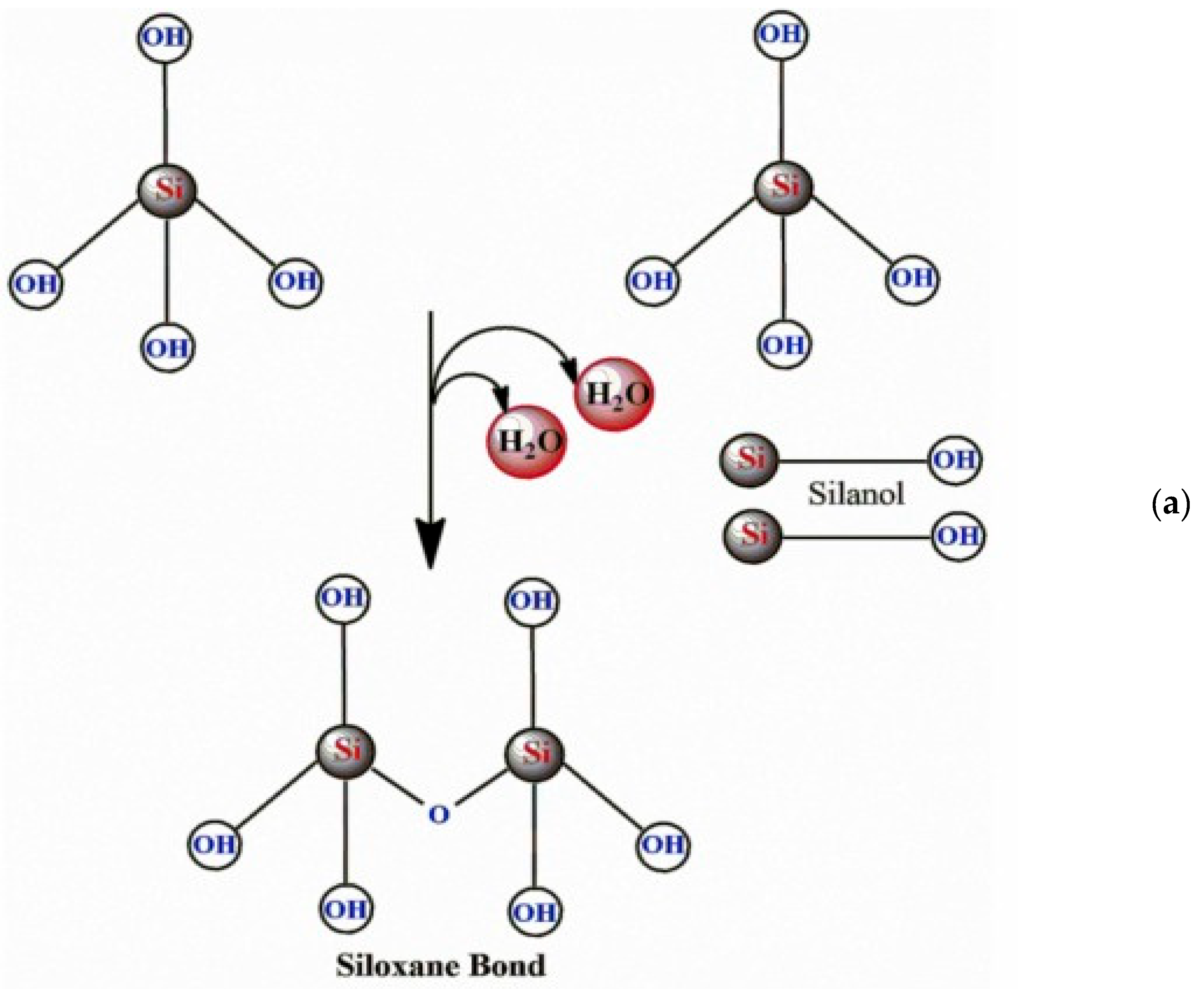
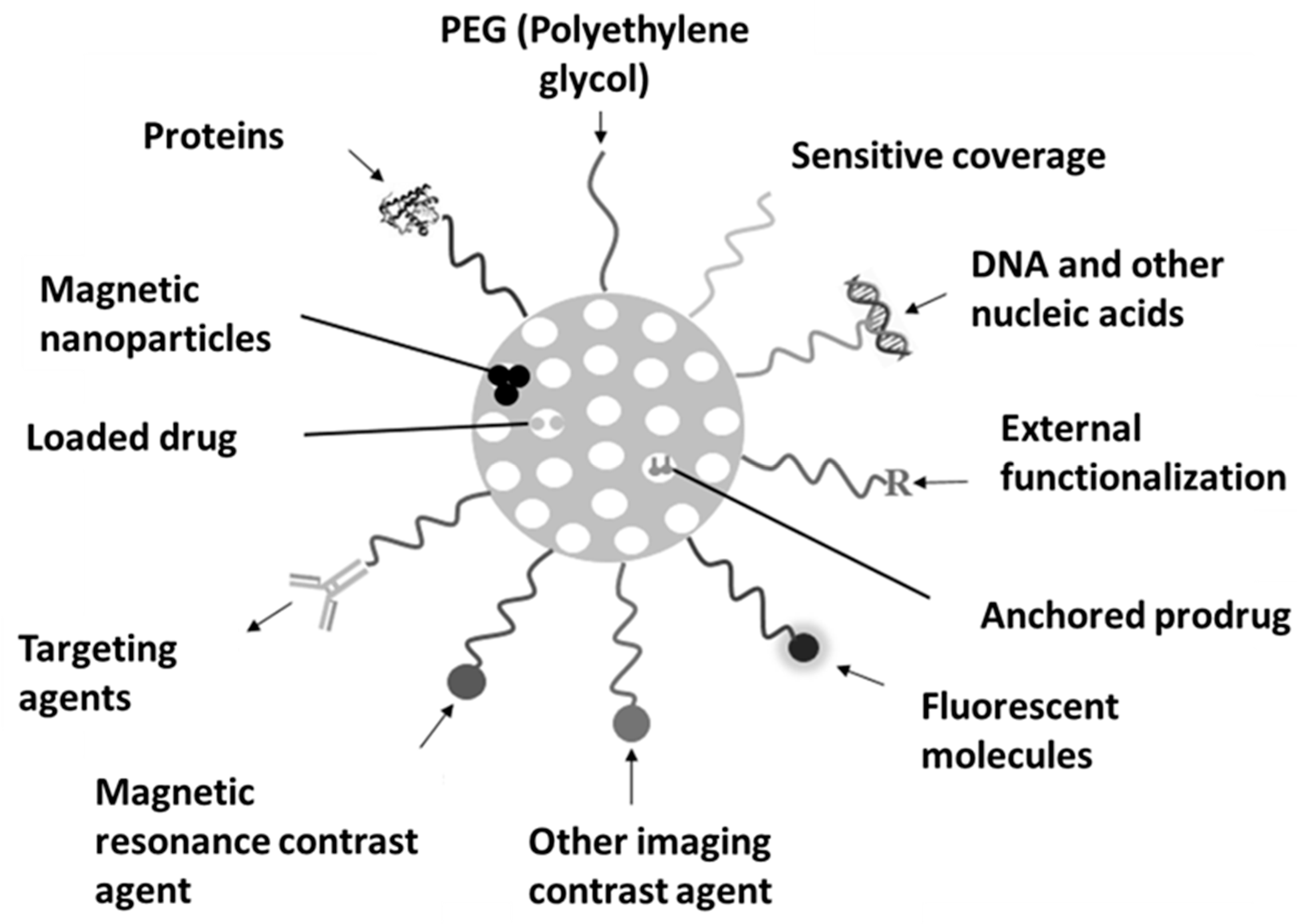
3. Modification Possibilities for Nanostructured Silica Materials
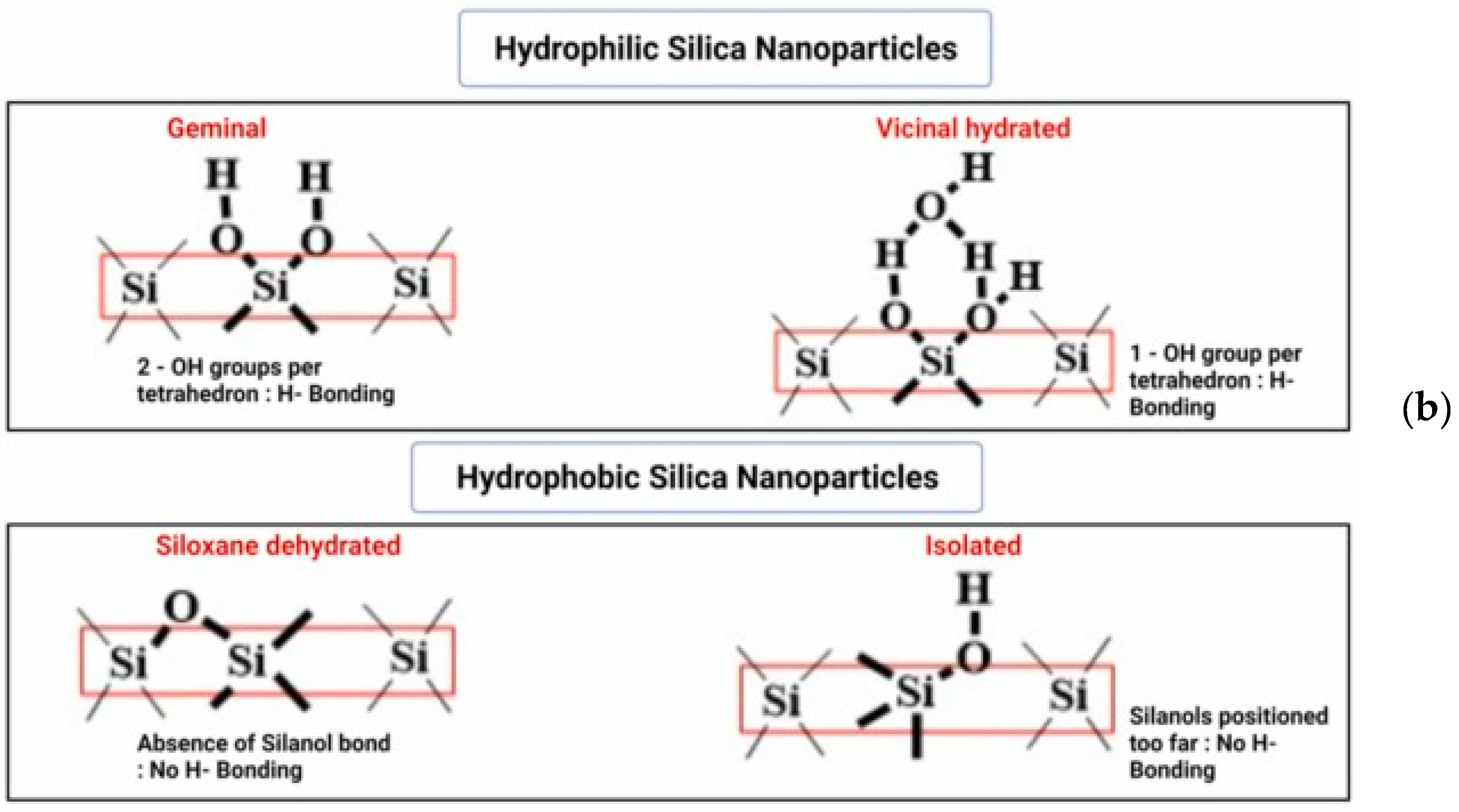
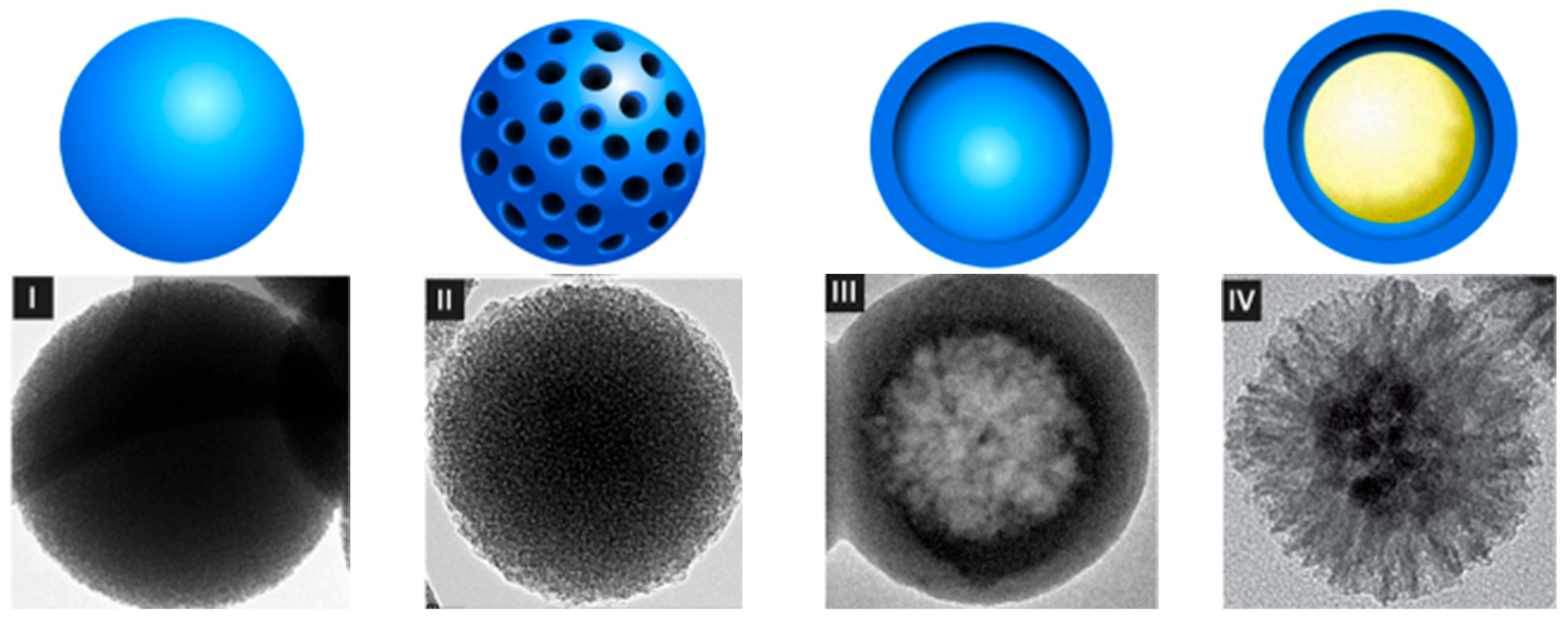
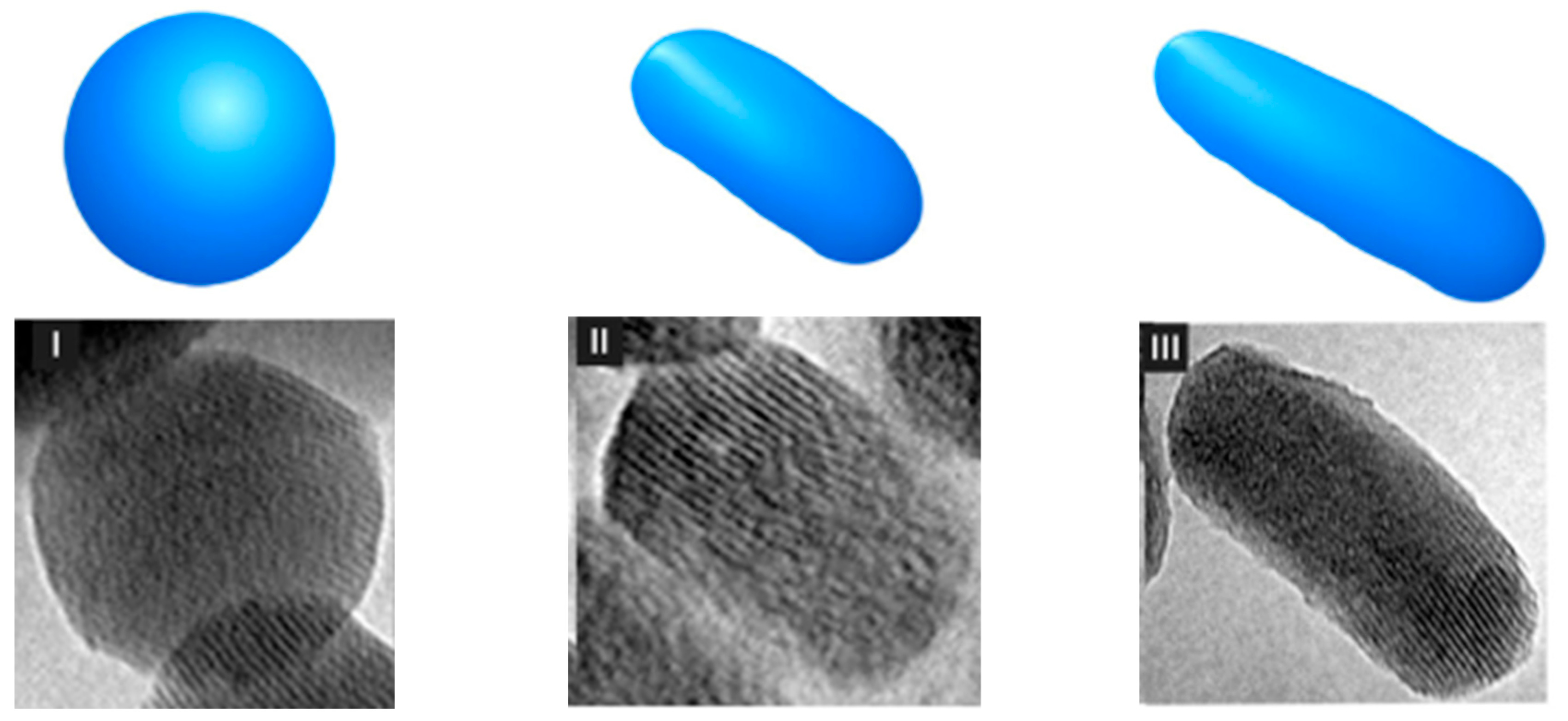
4. Characteristics of Nanostructured Silica Materials
5. Sustainable Nanostructured Silica Materials in Cosmetic Products
5.1. Potential Toxicity of Topical Formulations Containing Nanostructured Silica
5.2. Applications of Silica-Based Nanostructured Materials in Sustainable Cosmetics Products
6. Summary and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Götze, J.; Pan, Y.; Müller, A. Mineralogy and mineral chemistry of quartz: A review. Mineral. Mag. 2021, 85, 639–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, R.P.; Hochheim, S.; de Oliveira, C.C.; Riegel-Vidotti, I.C.; Marino, C.E.B. Skin interaction, permeation, and toxicity of silica nanoparticles: Challenges and recent therapeutic and cosmetic advances. Int. J. Pharm. 2022, 614, 121439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Mishra, P.; Biswas, G.; Bhakta, S. Greening the pathways: A comprehensive review of sustainable synthesis strategies for silica nanoparticles and their diverse applications. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11197–11216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Hableel, G.; Zhao, E.R.; Jokerst, J.V. Multifunctional nanomedicine with silica: Role of silica in nanoparticles for theranostic, imaging, and drug monitoring. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 521, 261–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, B.; Rom, W.N. Silica, Some Silicates, Coal Dust and Para-Aramid Fibrils. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, Volume 68; IARC: Lyon, France, 1997; Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/86 (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Sarkar, J.; Mridha, D.; Sarkar, J.; Orasugh, J.T.; Gangopadhyay, B.; Chattopadhyay, D.; Roychowdhury, T.; Acharya, K. Synthesis of nanosilica from agricultural wastes and its multifaceted applications: A review. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2021, 37, 102175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreeharsha, N.; Philip, M.; Krishna, S.S.; Viswanad, V.; Sahu, R.K.; Shiroorkar, P.N.; Aasif, A.H.; Fattepur, S.; Asdaq, S.M.B.; Nair, A.B.; et al. Multifunctional Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Oral Drug Delivery. Coatings 2022, 12, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallet-Regí, M.; Schüth, F.; Lozano, D.; Colilla, M.; Manzano, M. Engineering mesoporous silica nanoparticles for drug delivery: Where are we after two decades? Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5365–5451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvioni, L.; Morelli, L.; Ochoa, E.; Labra, M.; Fiandra, L.; Palugan, L.; Prosperi, D.; Colombo, M. The emerging role of nanotechnology in skincare. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 293, 102437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytianos, G.; Rahdar, A.; Kyzas, G.Z. Nanomaterials in cosmetics: Recent updates. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Agarwal, P.; Sebghatollahi, Z.; Mahato, N. Functional Nanostructured Materials in the Cosmetics Industry: A Review. ChemEngineering 2023, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verified Market Reports. Available online: https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/product/nano-silica-market-size-and-forecast/ (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Global Market Insights. Available online: https://www.gminsights.com/industry-analysis/green-silica-market (accessed on 10 June 2025).
- Shafiei, N.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Iravani, S. Green Synthesis of Silica and Silicon Nanoparticles and Their Biomedical and Catalytic Applications. Comments Inorg. Chem. 2021, 41, 317–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huston, M.; DeBella, M.; DiBella, M.; Gupta, A. Green Synthesis of Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stöber, W.; Fink, A.; Bohn, E. Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1968, 26, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlina, H.; Hasnidawani, J.; Norita, H.; Surip, S. Synthesis of SiO2 nanostructures using sol-gel method. Acta Phys. Pol. 2016, 129, 842–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, E.G.; Livotto, P.R.; do Santos, J.H.Z. Hybrid silica bearing different organosilanes produced by the modified Stöber method. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.F.; Alalaiwe, A.; Wang, P.W.; Fang, Y.P.; Fang, J.Y. UV filter entrapment in mesoporous silica hydrogel for skin protection against UVA with minimization of percutaneous absorption. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 122, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, G.; Su, H.; Wang, S. The combined method to synthesis silica nanoparticle by Stöber process. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2020, 96, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, N.; Khan, A.M.; Shujait, S.; Chaudhary, K.; Ikram, M.; Imran, M.; Haider, J.; Khan, M.; Khan, Q.; Maqbool, M. Synthesis of nanomaterials using various top-down and bottom-up approaches, influencing factors, advantages, and disadvantages: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 300, 102597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhadhrami, A.; Mohamed, G.G.; Sadek, A.H.; Ismail, S.H.; Ebnalwaled, A.A.; Almalki, A.S.A. Behavior of Silica Nanoparticles Synthesized from Rice Husk Ash by the Sol–Gel Method as a Photocatalytic and Antibacterial Agent. Materials 2022, 15, 8211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeelani, P.G.; Mulay, P.; Venkat, R.; Ramalingam, C. Multifaceted application of silica nanoparticles. A review. Silicon 2020, 12, 1337–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periakaruppan, R.; N, R.D.; Abed, S.A.; Vanathi, P.; Kumar, J.S. Production of Biogenic Silica Nanoparticles by Green Chemistry Approach and Assessment of their Physicochemical Properties and Effects on the Germination of Sorghum bicolor. Silicon 2023, 15, 4309–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meierhofer, F.; Fritsching, U. Synthesis of Metal Oxide Nanoparticles in Flame Sprays: Review on Process Technology, Modeling, and Diagnostics. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 5495–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janjua, T.I.; Cao, Y.; Kleitz, F.; Linden, M.; Yu, C.; Popat, A. Silica nanoparticles: A review of their safety and current strategies to overcome biological barriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 203, 115115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rex, A.; dos Santos, J.H.Z. The use of sol–gel processes in the development of supported catalysts. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2023, 105, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoushtari, M.S.; Hoey, D.; Biak, D.R.A.; Abdullah, N.; Kamarudin, S.; Zainuddin, H.S. Sol–gel-templated bioactive glass scaffold: A review. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 40, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, S.; Mahian, O.; Languri, E.M. Applications of nanofluids in condensing and evaporating systems. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Bayona, R.; Chu, C.; Liu, P.; Roberts, W.L. Flame Synthesis of Carbon and Metal-Oxide Nanoparticles: Flame Types, Effects of Combustion Parameters on Properties and Measurement Methods. Materials 2023, 16, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suman; Rani, G.; Siddharth; Choudhary, S.; Ahlawat, R. A comprehensive study on silica nanoparticles: Green synthesis and photodegradation of organic dyes. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2025, 23, 101049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.; Adhikari, N. An Overview on Common Organic Solvents and Their Toxicity. J. Pharm. Res. Int. 2019, 28, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, W.Y.; Amal, R.; Mädler, L. Flame spray pyrolysis: An enabling technology for nanoparticles design and fabrication. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 1324–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.M.; Kim, T.H.; Kim, K.S.; Kim, S.G. Hazard Identification of Powder Generated from a Chemical Vapor Deposition Process in the Semiconductor Manufacturing Industry. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2013, 10, D1–D5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amendola, V.; Meneghetti, M. What controls the composition and the structure of nanomaterials generated by laser ablation in liquid solution? Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 3027–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caramazana, P.; Dunne, P.; Gimeno-Fabra, M.; McKechnie, J.; Lester, E. A review of the environmental impact of nanomaterial synthesis using continuous flow hydrothermal synthesis. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 12, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourzahedi, L.; Eckelman, M.J. Comparative life cycle assessment of silver nanoparticle synthesis routes. Environ. Sci. Nano. 2015, 2, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegner, K.; Schimmöller, B.; Thiebaut, B.; Fernandez, C.; Rao, T.N. Pilot Plants for Industrial Nanoparticle Production by Flame Spray Pyrolysis. KONA Powder Part J. 2011, 29, 251–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.; Takuli, A.; Gupta, T.K.; Gupta, D. Rethinking Nanoparticle Synthesis: A Sustainable Approach vs. Traditional Methods. Chem. Asian J. 2024, 19, e202400701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Kanchi, S.; Bisetty, K. Biogenic synthesis of nanoparticles: A review. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 3576–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraj, A.; Kumar, V.; Sunder, R.; Parthasarathy, K.; Kasivelu, G. Commercial Yeast Extracts Mediated Green Synthesis of Silver Chloride Nanoparticles and their Anti-mycobacterial Activity. J. Clust. Sci. 2020, 31, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karande, S.D.; Jadhav, S.A.; Garud, H.B.; Kalantre, V.A.; Burungale, S.H.; Patil, P.S. Green and sustainable synthesis of silica nanoparticles. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2021, 6, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshnazar, S.M.; Asadi, A.; Holghoomi, R.; Abdolmaleki, A. Green Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles/Nanocomposites for Biomedical Applications: A Narraitive Review. Biochem. Suppl. Ser. Biomed. Chem. 2023, 17, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaeian, M.; Afjoul, H.; Shamloo, A.; Maleki, A.; Afjoul, N. Green Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticles From Olive Residue and Investigation of Their Anticancer Potential. Nanomedicine 2021, 16, 1581–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, M.; Dwibedi, V.; Sharma, S.; George, N. Biogenic silica nanoparticles from agro-waste: Properties, mechanism of extraction and applications in environmental sustainability. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Cheng, Z.; Tan, S.; Zhu, Q. Clay nanoparticles as pharmaceutical carriers in drug delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 18, 695–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, U.; Subhani, T.; Husain, S. Synthesis and characterization of silica nanoparticles from clay. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 4, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourhly, A.; Khachani, M.; Hamidi, A.; Kacimi, M.; Halim, M.; Arsalane, S. The synthesis and characterization of low-cost mesoporous silica SiO2 from local Pumice rock. Nanomater. Nanotechnol. 2015, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmadianti, S.; Hendronursito, Y. Synthesis of Silica Nanoparticle Made from Lampung Pumice Modified With Sonication Parameters for Size and Purity. J. Ris. Technol. Pencegah. 2023, 14, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ainomugisha, S.; Matovu, M.; Manga, M. Application of green agro-based nanoparticles in cement-based construction materials: A systematic review. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 87, 108955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuvaneshwari, S.; Hettiarachchi, H.; Meegoda, J.N. Crop residue burning in India: Policy challenges and potential solutions. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y. Rice husk silica derived nanomaterials for sustainable applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 453–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Dizaji, H.B.; Puttuswamy, H.; Sharma, S. Biogenic Nanosilica Synthesis Employing Agro-Waste Rice Straw and Its Application Study in Photocatalytic Degradation of Cationic Dye. Sustainability 2022, 14, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijaz, U.; Ahmed, T.; Rizwan, M.; Noman, M.; Shah, A.A.; Azeem, F.; Alharby, H.F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Alharbi, B.M.; Ali, S. Rice straw based silicon nanoparticles improve morphological and nutrient profile of rice plants under salinity stress by triggering physiological and genetic repair mechanisms. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 201, 107788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, N.A.; El-Sherbiny, M.; Alkharpotly, A.A.; Sayed, O.A.; Dawood, A.F.A.; Hossain, M.A.; Abdelrhim, A.S.; Dawood, M.F.A. Rice-husks synthesized-silica nanoparticles modulate silicon content, ionic homeostasis, and antioxidants defense under limited irrigation regime in eggplants. Plant Stress 2024, 11, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djafaripetroudy, S. Facile One-Pot Process for Extracting High-Purity and Homogenous Biogenic Silica Nanoparticles from Rice Husks. In Rice Husk Biomass. Sustainable Materials and Technology; Jawaid, M., Parmar, B., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zewide, Y.T.; Yemata, T.A.; Ayalew, A.A.; Kedir, H.J.; Tadesse, A.A.; Fekad, A.Y.; Shibesh, A.K.; Getie, F.A.; Tessema, T.D.; Wubieneh, T.A.; et al. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for experimental optimization in biogenic silica extraction from rice husk and straw ash. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seroka, N.S.; Taziwa, R.T.; Khotseng, L. Extraction and Synthesis of Silicon Nanoparticles (SiNPs) from Sugarcane Bagasse Ash: A Mini-Review. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.L.; Sairam, V.; Muruganandam, L.; Srinivasan, K. An overview of the influences of mechanical and chemical processing on sugarcane bagasse ash characterisation as a supplementary cementitious material. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 245, 118854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athinarayanan, J.; Periasamy, V.S.; Alhazmi, M.; Alshatwi, A.A. Synthesis and biocompatibility assessment of sugarcane bagasse-derived biogenic silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2015, 105, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, R.H.; Reis, T.V.D.S.; Rovani, S.; Fungaro, D.A. Green synthesis and characterization of biosilica produced from sugarcane waste ash. J. Chem. 2017, 1, 6129035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maseko, N.N.; Schneider, D.; Wassersleben, S.; Enke, D.; Iwarere, S.A.; Pocock, J.; Stark, A. The Production of Biogenic Silica from Different South African Agricultural Residues through a Thermo-Chemical Treatment Method. Sustainability 2021, 13, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.R.; Capeto, A.P.; Pereira, C.F.; Pedrosa, S.S.; Mota, I.F.; da Silva Burgal, J.; Pintado, A.I.; Pintado, M.E.; Oliveira, C.S.S.; Costa, P.; et al. Valorization of Sugarcane By-Products through Synthesis of Biogenic Amorphous Silica Microspheres for Sustainable Cosmetics. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 4201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anuar, M.; Fen, Y.; Zaid, M.; Matori, K.; Khaidir, R. Synthesis and structural properties of coconut husk as potential silica source. Results Phys. 2018, 11, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seroka, N.S.; Taziwa, R.; Khotseng, L. Green Synthesis of Crystalline Silica from Sugarcane Bagasse Ash: Physico-Chemical Properties. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agunsoye, J.O.; Adebisi, J.A.; Bello, S.A.; Haris, M.; Agboola, J.B.; Hassan, S.B. Synthesis of silicon nanoparticles from Cassava periderm by reduction method. Contrib. Pap. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Peng, S.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Cui, H. Silica nanoparticles loaded with caffeic acid to optimize the performance of cassava starch/sodium carboxymethyl cellulose film for meat packaging. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 241, 124591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindar, Y.; Ramli, Y.; Steven, S.; Restiawaty, E. Optimization of purity and yield of amorphous bio-silica of amorphous bio-silica nanoparticles synthesized from bamboo leaves. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 102, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velmurugan, G.; Chohan, J.S.; Babu, K.; Paramasivam, P.; Maranan, R. Biosynthesis of SiO2 nanoparticles from bamboo leaves for tanning wastewater treatment and mechanical properties of HMPC-SiO2 nanocomposite. Clean. Techn. Environ. Policy 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusaidi, N.; Abdullah, S.; Zarib, N. Structural analysis of silica extract from banana stems via acid leaching under different reaction time. Int. J. Eng. Adv. Technol. 2019, 9, 5858–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szumski, M.; Al Saoud, H.; Wojtczak, I.; Sprynskyy, M.; Gadzała-Kopciuch, R.; Bocian, S.; Dembek, M.; Potrzebowski, M.; Buszewski, B. Diatom biosilica for liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. 2025, 1741, 465603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.; Seo, Y.; Kwon, D.; Kang, S.; Yu, J.; Park, H.; Lee, S.D.; Lee, T. Recent Progress in Diatom Biosilica: A Natural Nanoporous Silica Material as Sustained Release Carrier. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramontano, C.; Chianese, G.; Terracciano, M.; de Stefano, L.; Rea, I. Nanostructured Biosilica of Diatoms: From Water World to Biomedical Applications. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, S.; Singh, M.; Paul, S.; Kar, S.; Bagchi, T.; Chavali, M.; Chandrasekhar, K. Sustainable Bio-Applications of Diatom Silica as Nanoarchitectonic Material. In Algae Refinery Up- and Downstream Processes; Mehariya, S., Verma, P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023; Chapter 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Bay, B.H.; Matsumoto, K. Harnessing Microalgae as Sustainable Cell Factories for Polyamine-Based Nanosilica for Biomedical Applications. Molecules 2025, 30, 1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprynskyy, M.; Pomastowski, P.; Hornowska, M.; Król, A.; Rafińska, K.; Buszewski, B. Naturally organic functionalized 3D biosilica from diatom microalgae. Mater. Des. 2017, 132, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.H.; Kim, D.H.; Youn, S.; Pack, S.P. Biomimetic Diatom Biosilica and Its Potential for Biomedical Applications and Prospects: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.R.; Wang, S.-C.; Maity, J.P.; Banerjee, P.; Dey, G.; Huang, Y.-H.; Bundschuh, J.; Hsiao, P.-G.; Chen, T.-H.; Chen, C.-Y. A novel BMSN (biologically synthesized mesoporous silica nanoparticles) material: Synthesis using a bacteria-mediated biosurfactant and characterization. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 32906–32916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.M.; Waqas, M.; Shahzad, R.; You, Y.H.; Asaf, S.; Khan, M.A.; Lee, K.-E.; Joo, G.-J.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, I.-J. Isolation and characterization of a novel silicate-solubilizing bacterial strain Burkholderia eburnea CS4-2 that promotes growth of japonica rice (Oryza sativa L. cv. Dongjin). Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 63, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-E.; Adhikari, A.; Kang, S.-M.; You, Y.-H.; Joo, G.-J.; Kim, J.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, I.-J. Isolation and Characterization of the High Silicate and Phosphate Solubilizing Novel Strain Enterobacter ludwigii GAK2 that Promotes Growth in Rice Plants. Agronomy 2019, 9, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, H.; Jafari, A.; Mousavi, S.; Darezereshki, E. Biosynthesis of silica nanoparticle using Saccharomyces cervisiae and its application on enhanced oil recovery. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 2020, 190, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, M.; Gil, S.; Gaviña, P.; Costero, A.M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles in Chemical Detection: From Small Species to Large Bio-Molecules. Sensors 2022, 22, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, M.A.; Abdelaziz, A.M.; Attia, M.S.; Saied, E.; Elganzory, H.H.; Hashem, A.H. Mycosynthesis of Silica Nanoparticles Using Aspergillus niger: Control of Alternaria solani Causing Early Blight Disease, Induction of Innate Immunity and Reducing of Oxidative Stress in Eggplant. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaabo, H.E.; Saied, E.; Hassan, S.E.D.; Mahdy, H.M.; Sultan, M.H. Penicillium oxalicum-mediated the green synthesis of silica nanoparticles: Characterization and environmental applications. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2025, 15, 5229–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanien, Y.A.; Mosleh, M.A.; Abdel-Razek, A.S.; El-Sayyad, G.S.; El-Hakim, E.H.; Borai, E.H. Green synthesis of SiO2 nanoparticles from Egyptian white sand using submerged and solid-state culture of fungi. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 14, 26159–26172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchanang, G.; Djangang, C.N.; Abi, C.F.; Moukouri, D.L.M.; Blanchart, P. Synthesis of reactive silica from kaolinitic clay: Effect of process parameters. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 207, 106087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielonka, A.; Zymanczyk-Duda, E.; Brzezinska-Rodak, M.; Duda, M.; Grzesiak, J.; Klimek-Ochab, M. Nanosilica synthesis mediated by Aspergillus parasiticus strain. Fungal Biol. 2018, 122, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Sun, H.; Luo, Z.; Sun, J.; Wen, Z. Preparation of low surface area SiO2 microsphere from wheat husk ash with a facile precipitation process. Mater. Lett. 2015, 156, 42–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefi, M.; Davar, F.; Hadadzadeh, H. Green synthesis of nanosilica by thermal decomposition of pine cones and pine needles. Adv. Powder Technol. 2015, 26, 1583–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauldhar, B.S.; Yadav, S.K. Turning waste to wealth: A direct process for recovery of nano-silica and lignin from paddy straw agro-waste. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 194, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pieła, A.; Zymanczyk-Duda, E.; Brzezinska-Rodak, M.; Duda, M.; Grzesiak, J.; Saeid, A.; Klimek-Ochab, M. Biogenic synthesis of silica nanoparticles from corn cobs husks. Dependence of the productivity on the method of raw material processing. Bioorg. Chem. 2020, 99, 103773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palanimuthu, V.; Periakaruppan, R.; Romanovski, V.; Bharathi, A.; Selvaraj, K.; Selvaraj, V.; Anukeerthana, S.; Nishanthi, R.; Vanajadevi, G. Synthesis and Structural Characterization of SiO2 Nanoparticles Using Extract of Gracilaria Crassa Via Green Chemistry Approach. ChemSusChem 2025, 14, e202400356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukosav, P.; Pašalić, L.; Bakarić, D.; Jurašin, D.D.; Radić, T.M. Interaction of Silica Nanoparticles with Microalgal Extracellular Polymers. Water 2023, 15, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetchinkina, E.; Loshchinina, E.; Kupryashina, M.; Burov, A.; Nikitina, V. Shape and Size Diversity of Gold, Silver, Selenium, and Silica Nanoparticles Prepared by Green Synthesis Using Fungi and Bacteria. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 17207–17218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, M.U.; Ali, S.; Ali, M.Y.; Tariq, I.; Nasrullah, U.; Pinnapreddy, S.R.; Wölk, C.; Bakowsky, U.; Brüßler, J. Enhanced efficacy and drug delivery with lipid coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles in cancer therapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2021, 165, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, L.; Du, Z.; Gao, Z. Synthetic methods of lipid-coated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug carriers. Biointerphases 2022, 17, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafisi, S.; Samadi, N.; Houshiar, M.; Maibach, H.I. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for enhanced lidocaine skin delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Mahrooqi, J.H.; Khutoryanskiy, V.V.; Williams, A.C. Thiolated and PEGylated silica nanoparticle delivery to hair follicles. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 593, 120130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shevchenko, V.Y.; Madison, A.E. Structure of Nanoparticles: I. Generalized Crystallography of Nanoparticles and Magic Numbers. Glass Phys. Chem. 2002, 28, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvarajan, V.; Obuobi, S.; Ee, P.L.R. Silica Nanoparticles-A Versatile Tool for the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzano, M.; Vallet-Regí, M. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 30, 1902634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.; Mohapatra, S.; Mishra, H.; Farooq, U.; Kumar, K.; Ansari, M.J.; Aldawsari, M.F.; Alalaiwe, A.S.; Mirza, M.A.; Iqbal, Z. Nanotechnology in Cosmetics and Cosmeceuticals—A Review of Latest Advancements. Gels 2022, 8, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filon, F.L.; Mauro, M.; Adami, G.; Bovenzi, M.; Crosera, M. Nanoparticles skin absorption: New aspects for a safety profile evaluation. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, M.; Aggett, P.; Aguilar, F.; Crebelli, R.; Dusemund, B.; Filipič, M.; Frutos, M.J.; Galtier, P.; Gott, D.; Gundert-Remy, U.; et al. EFSA ANS Panel (EFSA Panel on Food Additives and Nutrient Sources added to Food). Scientific Opinion on the re-evaluation of silicon dioxide (E 551) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2018, 16, 5088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCCS. The SCCS Notes of Guidance for the Testing of Cosmetic Ingredients and Their Safety Evaluation; 11th Revision; Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS): Luxembourg, 2021; pp. 20–22. Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/publications/sccs-notes-guidance-testing-cosmetic-ingredients-and-their-safety-evaluation-11th-revision_en (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Bosch, A.; Bott, J.; Warfving, N.; Nolde, J. Investigation on the skin penetration of synthetic amorphous silica (SAS) used in cosmetic products. Toxicol. Lett. 2024, 399 (Suppl. S1), 80–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, E.; Guo, M.; Heng, J.Y.Y. Synthetic amorphous silica: Environmental impacts of current industry and the benefit of biomass-derived silica. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 4244–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.R.; Neto, T.; Pedrosa, S.S.; Sousa, S.C.; Azevedo-Silva, J.; Tavares-Valente, D.; Mendes, A.; Pintado, M.E.; Fernandes, J.C.; Oliveira, A.L.S.; et al. Biogenic silica microparticles as a new and sustainable cosmetic ingredient: Assessment of performance and quality parameters. Colloids Surf. Biointerfaces 2023, 226, 113305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshatwi, A.A.; Athinarayanan, J.; Periasamy, V.S. Biocompatibility assessment of rice husk-derived biogenic silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 47, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niroumand, U.; Firouzabadi, N.; Goshtasbi, G.; Hassani, B.; Ghasemiyeh, P.; Mohammadi-Samani, S. The effect of size, morphology and surface properties of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on pharmacokinetic aspects and potential toxicity concerns, Front. Mater. 2023, 10, 1189463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bragato, C.; Mazzotta, R.; Persico, A.; Bengalli, R.; Ornelas, M.; Gomes, F.; Bonfanti, P.; Mantecca, P. Biocompatibility Analysis of Bio-Based and Synthetic Silica Nanoparticles during Early Zebrafish Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.J.; Seong, N.W.; So, B.J.; Seo, H.S.; Kim, J.H.; Hong, J.S.; Park, M.-K.; Kim, M.-S.; Kim, Y.-R.; Cho, K.-B.; et al. Evaluation of silica nanoparticle toxicity after topical exposure for 90 days. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9 (Suppl. S2), 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lérida-Viso, A.; Estepa-Fernández, A.; García-Fernández, A.; Martí-Centelles, V.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Biosafety of mesoporous silica nanoparticles; towards clinical translation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2023, 201, 115049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SCCS. Silica, Hydrated Silica and Silica Surface Modified with Alkyl Silylates (Nano Form); Opinion of the Independent Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS): Luxemburg, 2015; Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/publications/revision-opinion-silica-hydrated-silica-and-silica-surface-modified-alkyl-silylates-nano-form_en (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- SCCS. Guidance on the Safety Assessment of Nanomaterials in Cosmetics; 2nd Revision; Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety (SCCS): Luxemburg, 2023; Available online: https://health.ec.europa.eu/publications/sccs-guidance-safety-assessment-nanomaterials-cosmetics-2nd-revision_en (accessed on 28 April 2025).
- Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Kang, Y.; Chen, A.; Feng, X.; Shao, L. The toxicity of silica nanoparticles to the immune system. Nanomedicine 2018, 13, 1939–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, G.; Warncke, P.; Fischer, D.; Stranik, O.; Hall, A.J.; Gubala, V. Improving colloidal stability of silica nanoparticles when stored in responsive gel: Application and toxicity study. Nanotoxicology 2018, 12, 407–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, R.; Cheney, D.L.; Grunberger, J.W.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Jedrzkiewicz, J.; Isaacson, K.J.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Ghandehari, H. One year chronic toxicity evaluation of single dose intravenously administered silica nanoparticles in mice and their Ex vivo human hemocompatibility. J. Control. Release 2020, 324, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vareda, J.P.; García-González, C.A.; Valente, A.J.M.; Simón-Vázquez, R.; Stipetic, M.; Durães, L. Insights on toxicity, safe handling and disposal of silica aerogels and amorphous nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 1177–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, S.; Hu, X.; Sun, D.; Yang, J.; Yang, C.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Gu, X.; Li, M.; et al. Toxicity and mechanism of mesoporous silica nanoparticles in eyes. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 13637–13653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadpour, R.; Yazdimamaghani, M.; Cheney, D.L.; Jedrzkiewicz, J.; Ghandehari, H. Subchronic toxicity of silica nanoparticles as a function of size and porosity. J. Control. Release 2019, 304, 216–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, V.M.; Benjdir, M.; Montagne, P.; Pairon, J.-C.; Lanone, S.; Andujar, P. Pulmonary Toxicity of Silica Linked to Its Micro- or Nanometric Particle Size and Crystal Structure: A Review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puerari, R.C.; Ferrari, E.; Oscar, B.V.; Simioni, C.; Ouriques, L.C.; Vicentini, D.S.; Matias, W.G. Acute and chronic toxicity of amine-functionalized SiO2 nanostructures toward Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 212, 111979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Cheng, F.; Xue, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Du, Q.; Ge, D.; Sun, B. Surface modification of Stöber silica nanoparticles with controlled moiety densities determines their cytotoxicity profiles in macrophages. Langmuir 2019, 35, 14688–14695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nafisi, S.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Maibach, H.I. Measuring silica nanoparticles in the skin. In Agache’s Measuring the Skin; Humbert, P., Fanian, F., Maibach, H., Agache, P., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1141–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafuro, G.; Costantini, A.; Piatto, M.; Lucchetti, S.; Francescato, S.; Busata, L.; Baratto, G.; Semenzato, A. Eco-Designing Cosmetic Products while Preserving the Sensorial-Application Properties: An Instrumental Approach toward Sustainable Formulations. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H. Factors Enhancing Adhesion of Color Cosmetic Products to Skin: The Role of Pigments and Fillers. In Surface Science and Adhesion in Cosmetics; Mittal, K.L., Bui, H.S., Eds.; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 487–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drakontis, C.E.; Amin, S. Design of sustainable lip gloss formulation with biosurfactants and silica particles. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2020, 42, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, C.A.; Larsen, P.B.; Read, S.A.K.; Varet, J.; Hankin, S.M.; Lam, H.R. Assessment of Nano-Enabled Technologies in Cosmetics; The Danish Environmental Protection Agency: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Belostozky, A.; Bretler, S.; Kolitz-Domb, M.; Grinberg, I.; Margel, S. Solidification of oil liquids by encapsulation within porous hollow silica microspheres of narrow size distribution for pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 97, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Bao, H.; Jia, S.; Bao, Y.; Niu, Y.; Kou, X. Organic Hollow Mesoporous Silica as a Promising Sandalwood Essential Oil Carrier. Molecules 2021, 26, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.R.; Costa, A.H.; Azevedo-Silva, J.; Tavares-Valente, D.; Sousa, S.C.; Neto, T.; Pintado, M.E.; Madureira, A.R. Silica Microparticles from Sugarcane By-Products as an Encapsulation System for Retinoids Aimed at Topical Sustained Release. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, N.; Kısa, D.; Ceylan, Y.; Güçlü, E.; Şen, F. Biogenic synthesis of silica nanoparticles from industrial hemp waste for sustainable applications: Characterization and potential environmental benefits. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2024, 167, 112750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, G.P.; Barberia Roque, L.; Igal, K.; Gámez Espinosa, E.; Bellotti, N. Citronellol-functionalized natural silica: A biogenic approach for antifungal and antibacterial material applications Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1535787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebert, A.M.; Baglole, C.J.; Desimone, M.F.; Maysinger, D. Nanoengineered silica: Properties, applications and toxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 753–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyńczak, A.; Nowak, I.; Feliczak-Guzik, A. SBA-15-and SBA-16-Functionalized Silicas as New Carriers of Niacinamide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, T.; Khan, H.M.S.; Akhtar, N.; Hanan, H.; Hussain, M.D.; Kazi, M. Structural elucidation and development of azelaic acid loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles infused gel: Revolutionizing nanodrug delivery for cosmetics and pharmaceuticals. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wawrzyńczak, A.; Feliczak-Guzik, A.; Nowak, I. Nanosunscreens: From nanoencapsulated to nanosized cosmetic active forms. In Nanobiomaterials in Galenic Formulations and Cosmetics: Applications of Nanobiomaterials; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 25–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Liang, H.T.; Yang-Wang, Y.T.; Shih, C.J. Synthesis of hierarchically mesoporous silica with encapsulated avobenzone as a UV protection filter. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15846–15852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knežević, N.Ž.; Ilić, N.; Dokić, V.; Petrović, R.; Janaćković, D. Mesoporous Silica and Organosilica Nanomaterials as UV-Blocking Agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 20231–20236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kim, J.; Rahman, R.T.; Lee, D.J.; Lee, K.; Nam, Y.S. Plastic-free silica-titania-polyphenol heterojunction hybrids for efficient UV-to-blue light blocking and suppressed photochemical reactivity. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 431, 133790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Huangfu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zhou, C.; Rong, H.; Deng, L.; Dong, A.; Zhang, J. Solid SiO2-Sealed Mesoporous Silica for Synergistically Combined Use of Inorganic and Organic Filters to Achieve Safe and Effective Skin Protection from All-Band UV Radiation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 12209–12220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.; Kim, H.; Chang, H.; Park, W.; Hahn, S.K.; Kwon, W. Biocompatible organosilica nanoparticles with self-encapsulated phenyl motifs for effective UV protection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 9062–9069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.C.; Morais, F.; Simões, A.; Pereira, I.; Sequeira, J.A.D.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Veiga, F.; Ribeiro, A. Nanotechnology for the development of new cosmetic formulations. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 313–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raszewska-Famielec, M.; Flieger, J. Nanoparticles for Topical Application in the Treatment of Skin Dysfunctions—An Overview of Dermo-Cosmetic and Dermatological Products. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijai Selvaraj, K.S.; Periakaruppan, R.; Abhishekh, K.T.; Sathishkumar, K.; Das, M.N. Fabrication and Characterization of Cymodocea serrulata Extract-Mediated Silica Nanoparticles with Antioxidant Properties. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. 2025, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Periakaruppan, R.; Chandrasekaran, N.; Kumar, S.T.; Sasthri, G.; Al-Dayan, N. Green synthesis of silica nanoparticles using Enhalus acoroides: Characterization and antioxidant activity. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, A.; Maheen, S.; Khan, H.U.; Shafqat, S.S.; Irshad, M.; Aslam, I.; Rasul, A.; Bashir, S.; Zafar, M.N. Pharmaco-Technical Evaluation of Statistically Formulated and Optimized Dual Drug-Loaded Silica Nanoparticles for Improved Antifungal Efficacy and Wound Healing. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 8210–8225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baka, Z.A.M.; El-Sharkawy, A.M.; El-Zahed, M.M. Anti-Aspergillus Niger Action of Biosynthesized Silicon Dioxide Nanoparticles Alone or Combined with Matricaria Chamomilla L. Extract. J. Microb. Biotech. Food. Sci. 2024, 13, e10816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montazeri, M.; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M.; Nasrollahi, S.A.; Maibach, H.; Nafisi, S. Enhanced topical econazole antifungal efficacy by amine-functionalized silica nanoparticles. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2019, 43, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trendafilova, I.; Chimshirova, R.; Momekova, D.; Petkov, H.; Koseva, N.; Petrova, P.; Popova, M. Curcumin and Capsaicin-Loaded Ag-Modified Mesoporous Silica Carriers: A New Alternative in Skin Treatment. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Feng, J.; Ao, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, M.; Yu, C. Natural agents derived Pickering emulsion enabled by silica nanoparticles with enhanced antibacterial activity against drug-resistant bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2025, 678, 158–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzahosseinipour, M.; Khorsandi, K.; Hosseinzadeh, R.; Ghazaeian, M.; Shahidi, F.K. Antimicrobial photodynamic and wound healing activity of curcumin encapsulated in silica nanoparticles. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 29, 101639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pote, A.K.; Pande, V.V.; Patel, V.P.; Giri, M.A.; Bhalke, R.D.; Pund, A.U. Design & Development of Curcumin Loaded Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Decorated Mesoporous Silica Liquid Stitches: A Proof of Concept in Animals. Mater. Technol. 2020, 37, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Shi, T.; Wang, Y.; He, Z.; Mu, Z.; Cai, X.; Deng, H.; Shen, J.; Liu, F. Hybrid Hydrogel Loaded with Chlorhexidine⊂β-CD-MSN Composites as Wound Dressing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 1725–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamam, F.; Nasr, A. Curcumin-loaded mesoporous silica particles as wound healing agent: An In vivo study. Saudi J. Med. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkady, O.A.; Zaafan, M.A.; George, M.; Elsayed, N.A.; Ghaly Mettias, V.; Sameh Edward, V.; Saeed Ghataty, D. Metformin-loaded bioinspired mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted melanoma therapy: Nanotopographical design with in vitro and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Pharm. 2025, 674, 125499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahedi, P.; Ebrahimnejad, P.; Seyedabadi, M.; Babaei, A. Optimized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Delivery of Curcumin and Quercetin: Enhanced Skin Permeation and Cytotoxicity Against A375 Melanoma Cells. J. Clust. Sci. 2025, 36, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
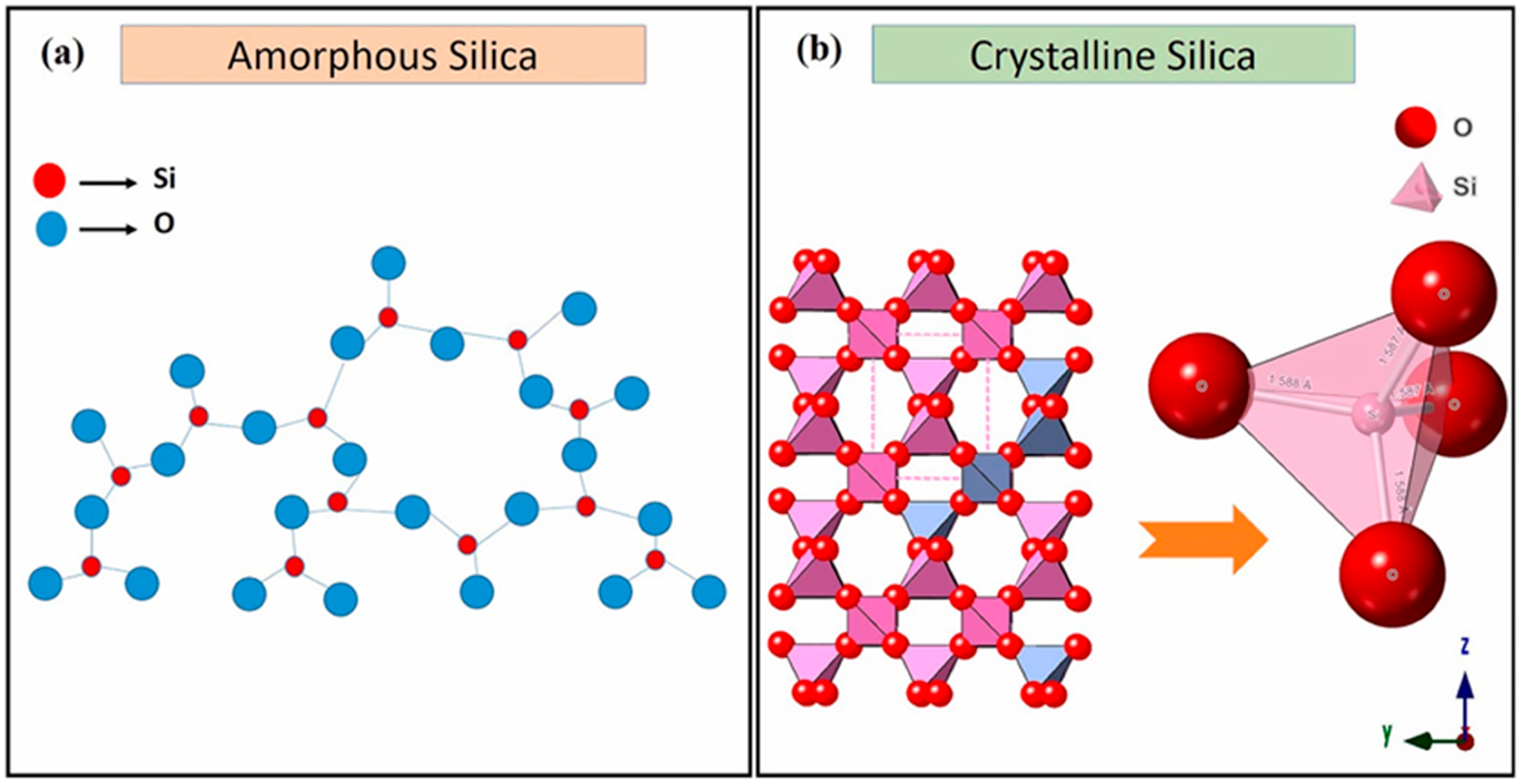
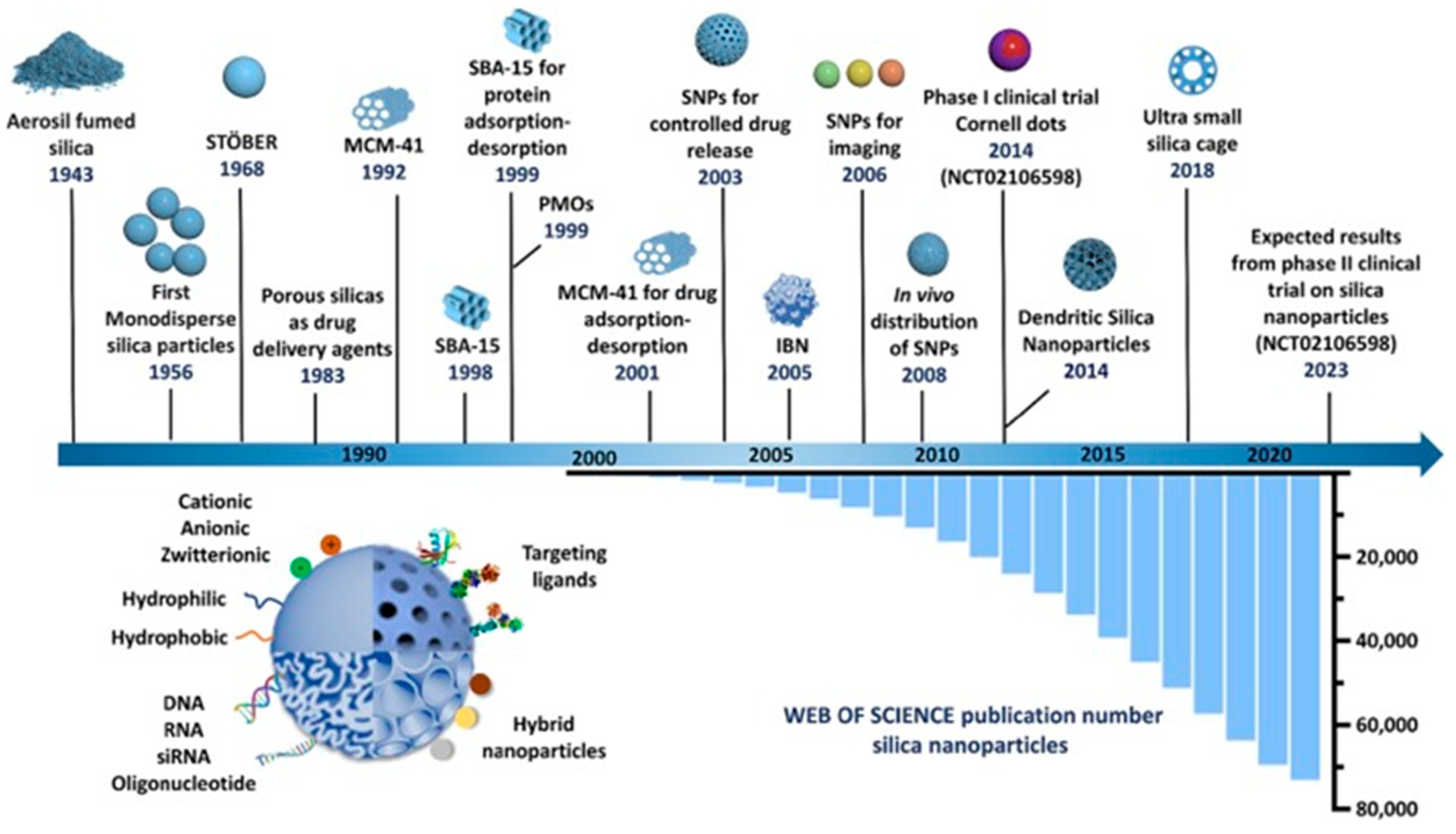
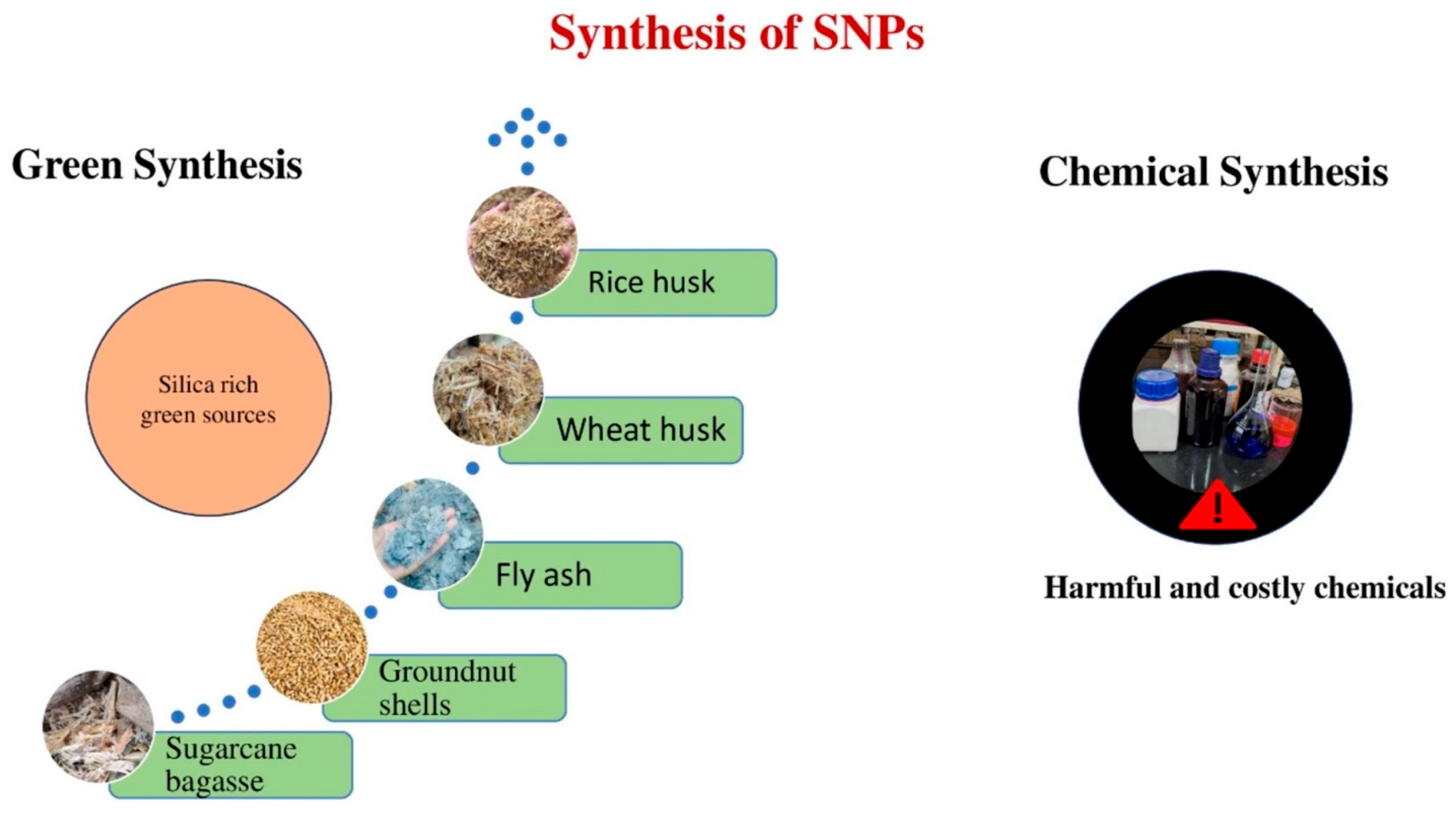
| Traditional Synthesis Methods | |
| Disadvantages | Advantages |
| The use of large amounts of organic solvents—negative impact on the nervous and reproductive systems of living organisms [32]. | Obtaining a wide range of nanoparticles with diverse properties [15]. |
| Use of high pressures and temperatures [33]. | Relative simplicity of procedures for nanoparticle synthesis with two main approaches: top-down and bottom-up [21]. |
| Generation of volatile vapors [34]. | Control over the morphology of nanoparticles [35]. |
| Excessive carbon dioxide production, contributing to the greenhouse effect [36,37]. | The ability to scale up processes [38]. |
| Ecological (Green) Synthesis Methods | |
| Disadvantages | Advantages |
| The impact of geographical differences on the acquisition of biological research material [39]. | The use of microorganisms (bacteria, yeast) and certain species of algae and plants as substrates for synthesis [40]. |
| Low reproducibility of the results [39]. | Ensuring that nanomaterials have the proper characteristics, e.g., antibacterial properties [41]. |
| Silica Source | Properties of SiNPS | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Clays/minerals | ||
| Bentonite | 69–223 nm | [47] |
| Kaolinitic clay | 21–30 nm; amorphous silica; homogeneous morphology with agglomerated particles. | [86] |
| Agricultural waste products, plants, and its industrial waste | ||
| Rice Husk | 400 nm; spherical particles. | [87] |
| Wheat husk | 100–200 nm; spherical particles. | [88] |
| Pine cone and pine needles | 30–60 nm; quasi spherical particles. | [89] |
| Paddy straw | 17 nm; spherical particles. | [90] |
| Corn cob husks | 40–70 nm; spherical particles. | [91] |
| Algae | ||
| Gracilaria crassa | 20–50 nm; amorphous; spherical particles. | [92] |
| Cylindrotheca closterium | 7–17 nm; spherical particles. | [93] |
| Bacteria and yeast | ||
| Azospirillum brasilense | 100–200 nm; spherical particles. | [94] |
| Fungi | ||
| Pleurotus ostreatus | 5–15 nm; spherical particles. | [94] |
| Lentinula edodes | 50–100 nm; spherical particles. | |
| Grifola frondosa | 5–15 nm; spherical particles. | |
| Ganoderma lucidum | 50–100 nm; spherical particles. | |
| Agaricus bisporus | 30–60 nm; mesoporous. | |
| Agaricus arvensis | 30–20 nm; spherical particles. | |
| Penicillium oxalicum | 20–50 nm; crystalline nature. | [84] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Latini, V.; Feliczak-Guzik, A.; Wawrzyńczak, A. Application Possibilities of Sustainable Nanostructured Silica-Based Materials in Cosmetics. Cosmetics 2025, 12, 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040134
Latini V, Feliczak-Guzik A, Wawrzyńczak A. Application Possibilities of Sustainable Nanostructured Silica-Based Materials in Cosmetics. Cosmetics. 2025; 12(4):134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040134
Chicago/Turabian StyleLatini, Veronica, Agnieszka Feliczak-Guzik, and Agata Wawrzyńczak. 2025. "Application Possibilities of Sustainable Nanostructured Silica-Based Materials in Cosmetics" Cosmetics 12, no. 4: 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040134
APA StyleLatini, V., Feliczak-Guzik, A., & Wawrzyńczak, A. (2025). Application Possibilities of Sustainable Nanostructured Silica-Based Materials in Cosmetics. Cosmetics, 12(4), 134. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics12040134







