Abstract
Resource depletion and food waste accumulation represent a tremendous socio-economic and environmental problem. One promising strategy involves the use of byproducts derived from food waste as ingredients for cosmetic products. The aim of this work is to propose clementine peels and olive leaf extracts as value-added bioproducts for a cosmetic cream. Extracts were obtained by super critical extraction showing an antioxidant activity of ca. 25%. No cytotoxic effects of the extracts were recorded on keratinocyte cells up to a concentration of 4% v/v ratio within 24 h. The incorporation of clementine peels and olive leaf extracts into creams did not compromise their stability, as demonstrated by Turbiscan analyses at room and extreme (40 °C) storage conditions. The safety profiles of the final cosmetic formulations were further in vivo demonstrated on human volunteers. We analyzed the trans-epidermal water loss and variation of the skin’s erythematous index, which showed profiles that almost overlapped with the negative control. Moreover, rheological analysis of the resulting creams evidences their suitable spreadability with similar pseudoplastic profiles, although a slight reduction of viscosity was recorded by improving the extracts’ concentrations. The proposed approach highlights the advantage of combining byproduct resources and supercritical fluid extraction to obtain a safe and eco-friendly face cream.
1. Introduction
In 2023, it was estimated that more than 58 million Kg of food waste was produced in the European Union, which corresponds to 131 Kg/inhabitant per year (Eurostat, 2023, https://food.ec.europa.eu/index_en, accessed on 14 February 2024), thus representing a critical socio-economic and environmental problem [1,2]. The development of new approaches to obtaining biomaterials from food waste is an urgent priority, and several strategies have been put in place to develop a circular economy able to reduce environmental degradation and resource depletion [3,4,5]. In this context, the use of byproduct-derived compounds for the cosmetic industry represents a promising alternative to conventional approaches [6,7]. In line with this approach, this study evaluates the use of clementine peels and olive leaf extract (CPE and OLE, respectively) for cosmetic purposes, emphasizing their role as ingredients for the production of face cream.
Clementine peels and olive leaf extracts offer multiple beneficial features, thus making them suitable raw materials for use in the cosmetic industry [8,9,10,11]. The main bioactive compounds of these byproducts’ extracts are polyphenols, which serve as forefront bioactive molecules for plants defending themselves against pathogens and stress conditions [12]. The inclusion of polyphenols derived from clementine peel and olive leaf extracts in cosmetic products offers several advantages for skincare. These compounds, renowned for their potent antioxidant properties, effectively neutralize free radicals that can cause premature aging and skin damage [13,14]. Additionally, their anti-inflammatory properties make them valuable compounds to treat irritated skin, thus reducing redness and promoting a more even complexion [15,16,17,18]. Polyphenols also exhibit remarkable skin-brightening effects, helping to reduce the appearance of dark spots and hyperpigmentation [19,20] and support collagen production, thus improving elasticity and contributing to a tighter and more youthful-looking skin texture [21]. With their multifaceted benefits, clementine peel and olive leaf extracts are suitable ingredients for cosmetic products, offering natural solutions to several skin concerns. Apart from their skin benefits, the inclusion of citrus peels and olive leaf extracts in cosmetic products also represents a valuable approach to obtain sustainable cosmetic formulations. In fact, the many potentials in polyphenols make these extracts proper candidates as natural components, thus reducing the side effects associated with synthetic ingredients [10,22,23].
The integration of clementine peels and olive leaf extracts aligns with the goals of sustainable cosmetic manufacturing, thus minimizing the environmental impact of this ever-growing industry. Moreover, their abundance as byproduct of the food industries highlights their potential contribution to the circular economy, creating value-added bioactive ingredients [24,25].
Another interesting, but still not much explored, re-use of waste concerns the water used in the process of obtaining fibers from citrus or other fruits, or from washing processes, or from other passages of the food production chain. This water waste contains many compounds potentially beneficial both from a technological and health-related point of view, as well as being able to be used as an added value for a cosmetic formulation, for example providing a light and pleasant fragrance similar to the fruit from which it is obtained [26].
Extraction procedures can be also optimized to maximize the resource’s efficacy and minimize its environmental impact. In this attempt, supercritical fluid extraction processes represent a valid alternative to the conventional ones [27]. Supercritical carbon dioxide (CO2) extraction is a highly efficient and environmentally friendly technique that uses CO2 in its supercritical state [28]. One significant advantage of this technique is the ability to modify the nature and the percentage of the co-solvent, thus obtaining a purer and more concentrated target molecules extract, while leaving behind unwanted impurities [29]. Moreover, supercritical CO2 extraction operates at lower temperatures compared to conventional methods, minimizing the risk of thermal degradation and preserving the integrity of sensitive bioactive compounds [27]. Additionally, CO2 is non-toxic and readily available, making it a safer and more sustainable alternative to the chemical solvents commonly used in extraction processes. Overall, supercritical CO2 extraction presents a superior approach to obtaining high-quality extracts from clementine peels and olive leaves to be used to develop products with enhanced efficacy and sustainability.
The main goal of this study is to elucidate the multifaceted benefits of incorporating clementine peels and olive leaf extracts into face cream, emphasizing their pivotal role in advancing the principles of a circulating economy in the cosmetic field. To further minimize the environmental impact of the realized product, a supercritical fluid extraction technique was used, thus reducing the environmental footprint, and preserving at the same time the integrity of thermo-sensitive compounds. For making the final cosmetic product more appealing to a hypothetical consumer, the cream was naturally perfumed using bergamot water waste. The described advantages underscore the significance of combining byproducts as a resource and eco-friendly supercritical fluid extraction processes in cosmetic products development.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
Glutamate Emulsifier Olivoil was kindly provided by Kalichem (Brescia, Italy). Sweet Almond Oil USP, Ceteareth 25, Xantan Gum was purchased by A.C.E.F. A supply of dl-α-Tocopheryl Acetate was obtained from Roche (Milan, Italy). Rutin, oleuropein, hesperidin, naringin, apigenin, sodium nitrite, aluminum chloride, sodium hydroxide, gallic acid (GA), L-ascorbic acid, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) for chemical analyses, sodium dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), trypan Bleu dye solution (0.4% v/v), 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-3,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT), and glycerol were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany). Clementine peels taken from industrial processing waste were kindly offered by the Company Medi Mais Calabra of Corigliano-Rossano (Cosenza, Italy). Olive leaves from Olea europea and bergamot wastewater were provided by a local factory. Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium, fetal bovine serum, and penicillin (100 UI/mL)-streptomycin (100 µg/mL) solution (1% v/v) were purchased from S.I.A.L. Group (Rome, Italy). Trypsin/EDTA 1× was purchased from GIBCO (Invitrogen Corporation, Giuliano Milanese, Milan, Italy). NCTC244 cells were provided by “Istituto Zooprofilattico di Modena e Reggio Emilia” (Modena, Italy). All materials and solvents used for the study were of analytical grade and do not require further purification processes.
2.2. Extracts Preparation and Characterization
Before performing the extractive procedures, the olive leaves were individually removed from the wooden twigs, washed, dried, and ground with a mortar, while the clementine waste material was used as it was supplied.
The extracts were obtained using a supercritical CO2 extractor (SFE Process—SFE 100 mL—Tomblaine, France) using 90 g of raw material for every extraction. The chiller was set at a temperature between 0 °C and 5 °C, while the extraction vial was set at 40 °C. In each extraction, 600–800 g of CO2 was consumed, with the CO2 pressure set at ~250 bar and ethanol used as the co-solvent with a flow rate of 20 mL/min for extracts collection. Each extractive procedure required approximately 20% w/v of ethanol compared to the carbon dioxide consumed. Subsequently, the volume of ethanol was reduced by a rotary evaporator (Rotavapor Buchi, Flawil, Switzerland) equipped with a vacuum pump, with the aim of increasing the concentration of bioactive molecules. The obtained samples were centrifuged (2000× g—10 min—4 °C), filtered through 0.22 µm cellulose filters, and stored in the freezer at −20 °C before all analyses.
All extracts were characterized in terms of total phenolic content (TPC), total flavonoids content (TFC), and antioxidant activity (DPPH assay) using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (ThermoScientific, Rosano, Milan, Italy—Genesys® 150), while the analytical profile of the molecules contained in the extracts was obtained by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC), as better described below.
2.3. Total Phenolic Content
The polyphenolic profile of the extracts, including hydrolysable tannins, was obtained as previously described in the literature with slight modifications [30]. Briefly, 100 µL of extract was mixed with 500 µL of Folin-Ciocalteu’s phenol reagent and 1 mL of sodium carbonate (5% w/v). The obtained mixtures were vortexed, incubated 25 min in the dark, and their absorbance (Abs) acquired at wavelength (λ) of 760 nm. Gallic acid was used as the reference molecule, with a concentration between 0.1 and 0.5 mg/mL. The total phenolic content of the extract was finally described as gallic acid equivalent (GAE mg/mL).
2.4. Total Flavonoid Content
The TFC in the extracts was quantified according to a colorimetric approach recently described [30]. Briefly, 1 mL of the sample, properly diluted, was incubated with 60 µL of sodium nitrite solution (5% w/v) and 120 µL aluminum chloride (10% w/v). After 5 min of incubation, 0.40 mL of sodium hydroxide (1 M) were added to the sample to neutralize its pH. The final volume of each sample was 2 mL. A suitable calibration curve was obtained using a mixture of flavonoids standard molecules in equal weight ratio.
2.5. Antioxidant Activity of the Extracts
The antioxidant activity of our extracts was estimated using a DPPH assay and described as the inhibition percentage of free radicals (I%) as commonly described [31]. DPPH solution and L-ascorbic acid solution (5 mg/mL) were used as the negative and positive controls, respectively. Methanol was used as a blank for the analyses. The percentage of radical scavenging activity was normalized as a function of the extracts’ concentrations and finally calculated using the following equation:
where A0 = Absorbance of negative control and A1 = Absorbance of extracts/standards.
I(%) = ((A0 − A1)/A0) × 100
2.6. HPLC Analyses
The HPLC apparatus consisted of a ThermoFisher Scientific Vanquish System Base equipped with a quaternary pump and a UV/VIS variable wavelength detector (ThermoFisher Scientific—Rosano, MI, Italy). The mixtures were separated by an Acclaim® 120 reverse phase C18 column (100 mm–4.6 mm–5 µm particle size).
The mobile phase consisted of different ratios of acetonitrile (ACN) and phosphoric acid (10 nM) or formic acid (0.1% v/v) aqueous solutions for flavonoids or oleuropein quantification, respectively. The column temperature was 25 °C and the absorbance acquired at wavelength 260–270 nm or 254–280 nm, respectively, for flavonoids or oleuropein detection. Chromatograms were compared with retention times of rutin, naringin, hesperidin, oleuropein, and apigenin standard solutions. Suitable calibration curves (r2 > 0.98 in all cases) were used to identify the molecules contained in the samples. The extracts (20 µL) were injected into an HPLC apparatus. The total acquisition time never exceeded 30 min.
2.7. In Vitro Studies on NCTC2544 Cells
The cytotoxicity of clementine peels and olive leaf extract (CPE and OLE, respectively), was evaluated on human keratinocytes (NCTC2544), considered as a model of a cutaneous cell line. The results of cell viability were determined using the MTT assay [32]. Cells were seeded at a density of 7 × 103 cells/well in 96-well plates and incubated for 24 h. Subsequently, the cells were treated with 100 µL of fresh media with OLE or CPE added at different concentrations (0.5%, 1%, 2% v/v) or combined (1%, 2%, 4% v/v, final concentration). Ethanol was used as the control and tested at several concentrations equivalent to those used for extracts during the study (0.5–4% v/v). After treatment, 10 µL of the MTT solution (5 mg/mL dissolved in PBS solution) were added to each well, and the plates were incubated for 3 h. Ethanol-DMSO solution (50:50 v/v, 100 µL/well) was used to dissolve precipitated formazan salts using an orbital shaker (IKA® KS 130 Control, IKA® WERKE GMBH & Co., Staufen, Germany). Cell viability was quantified using a Varioskan™ LUX microplate reader (Thermo Fischer Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), according to the following equation:
where Abs T and Abs C represent the absorbance values of a treated and untreated cell, respectively.
2.8. Preparation of Proposed Face Creams
The compositions of empty and citrus and olive leaf extract-loaded face creams are reported in Table 1.

Table 1.
Quali-quantitative composition of prepared formulations.
All ingredients of phase A and phase B were collected in two different beakers and heated to a temperature of 72 ± 1 °C using a multi-point heating magnetic stirrer (AM4 Digital PRO, VELP Scientifica, Usmate, MB, Italy). When the required temperature wasreached, phase B was added to the phase A under homogenization at 2000 rpm using a high shear mixer Silverson® L4TR. The mixing was continued until a homogeneous emulsion was obtained and the temperature of emulsion had reduced to around 40 °C. Finally, phase C, containing the preservative Kemipur 100 and OLE and CPE (in the case of the 2%, 3%, and 4% OLE-CPE Formulations) were added to the cooled emulsion. The same protocol was performed to prepare emulsions in the presence of natural extracts. The formulations were kept at rest for 24 h at room temperature to ensure a suitable equilibration of the emulsions, and then all characterization studies were carried out as described below [33].
2.9. Microrheological Evaluation of Empty and Citrus and Olive Leaf Extracts-Loaded Face Creams Using Diffusing Wave Spectroscopy (DWS)
Microrheological characterization of all formulations was carried out using diffusing wave spectroscopy and the Rheolaser Master™ (Formulaction, Alfatest, Milano, MI, Italy). This technique exploits the Brownian motion of particles in the sample to define their viscoelastic features. The samples were loaded into suitable glass vials (20 mL for each sample) and the light intensity was detected for all durations of analysis (1 h). The software RheoSoft Master 1.4.0.0. permitted us to obtain some microrheological parameters of the analysed samples such as the mean square displacement (MSD), elasticity index, and solid liquid balance (SLB).
2.10. Dynamic Rheological Characterization of Empty and Citrus and Olive Leaf Extracts-Loaded Face Creams Using Kinexus Rotational Rheometer
A Kinexus Pro+ Rotational Rheometer (Malvern Panalytical Ltd., Spectris plc, Malvern, UK) was used for in-depth characterizing of the formulations from the rheological point of view. Knowing the rheological behavior of semisolid formulations when they are solicited is of fundamental importance, above all for cosmetic purposes. The tool is equipped with cone-plate geometries (40 mm diameter; 2° angle) [34]. For all analyses, a fixed gap between the upper and lower geometries was pre-set at 1 mm, and the temperature was maintained constant at pre-fixed values: 25.00 ± 0.01 °C and 40.00 ± 0.01 °C, as a function of experimental design. The functionality of the tool was guaranteed by a compressed air flow (2 bar) that was pre-filtered through fine and superfine Clearpoint filters (Beko, Atlanta, GA, USA), which permitted us to obtain the pressure needed to perform the analysis. For the rheological investigation, each sample was carefully and gently loaded on the lower measuring geometry, and then the upper geometry was lowered at a very slow speed. Preliminary tests of sweep strain tests (0.01–100%, and 1 Hz of frequency) were carried out to define the suitable experimental conditions and to maintain the subsequent rheological measurements within the linear viscoelasticity region (LVR).
Two different types of rheological analysis were carried out on empty and citrus and olive leaf extract-loaded face creams: (i) viscosity studies as a function of shear rate (from 0.1 s−1 to 100 s−1), and (ii) oscillatory tests with a frequency sweep (from 0.1 Hz to 10 Hz) at controlled shear stress equal to 1 Pa.
2.11. Stability Studies
The long-term stability of emulsions was investigated using a Turbiscan Lab® (Formulaction, L’Union, France) [35]. Cylindrical glass vials were filled with samples and any variations in transmission (ΔT) and backscattering (ΔBS) profiles were recorded over time. Measurements were collected up to 1 h at 25 ± 1 °C and 40 ± 1 °C. Values of ΔT and ΔBS were plotted as mean values ± standard deviation. The diameter kinetics profiles of the formulations were also investigated using Turbiscan Lab® and reported as a function of time. The destabilization kinetic profiles of emulsions were determined using Turbiscan Stability Index (TSI) values, and different formulations were compared each other [36].
2.12. Microscopy Studies
A Morphologi G3-S microscope equipped with a Nikon® CFI 60 Brightfield/Darkfield optical system was used to investigate the emulsions’ structure. Each emulsion was diluted with water (~5 mg/mL) and a drop of the diluted sample was placed on a slide and covered using a cover slip (20 × 20 mm, Syntesys, Padova, Italy). Microscopies were performed at 20× magnification and images were exported as TIFF using the Morphologi software v. 8.30 package (Malvern Panalytical, Worcestershire, UK).
2.13. In Vivo Studies on Healthy Human Volunteers
2.13.1. Transepidermal Water Loss (TEWL)
The skin tolerability of the formulations was evaluated on 16 healthy human volunteers (mean age 27 ± 9) using a C+ K Multi Probe Adapter equipped with a Tewameter® TM300 probe (Courage & Khazak, Cologne, Germany). This probe uses two pairs of sensors to measure temperature and humidity to assess transepidermal water loss (TEWL), which is a worldwide-accepted measurement to recognize any damage to the skin water barrier [37]. Volunteers were accommodated for 20 min in a day surgery room (24 ± 1 °C, 40–50% RH) and informed about the experimental procedures. After giving their written consent, volunteers were enrolled in the study and five sites were marked on their forearms using a circular template (1 cm2). The sites were traced on skin regions lacking discolorations and comedones, and sites were separated by at least 2 cm to avoid any interference between formulations. The first site was treated with 200 µL of saline solution, used as a negative control. The second site was treated with 200 mg of empty formulation. The last three sites were treated with 200 mg of formulations containing both OLE and CPE (2%, 3%, and 4% OLE-CPE Formulations). TEWL values were recorded 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h after application and expressed as g/h·m2.
2.13.2. X-Rite
The X-Rite Ci62 (X-Rite Incorporated, Grandville, MI, USA) was used to detect any variations of skin color following the cutaneous application of emulsions [32]. Since melanin and hemoglobin play a key role in defining skin color, these two chromophores were monitored during the study [38]. Baseline values of erythema index (E.I.) were collected from each site demarcated on the forearm of each volunteer according to the scheme previously reported (Section 2.13.1. After 0, 1, 2, 4, 6, and 8 h had passed since the application of the samples, any variation in E.I. values was recorded according to the following equation:
where 1/R is the inverse value of reflectance measured at different wavelengths (510, 540, 560, 580, 610 nm) linked to hemoglobin and melanin.
Data are reported as ΔE.I. and were obtained by subtracting the E.I. value recorded at each time point from that of the baseline at the same site.
2.14. Skin Feeling
After testing the skin tolerability, volunteers were divided into two groups (8 for each group) and were asked to apply two different formulations and to express their primary and secondary skin feelings [39]. A single blind procedure was used for the study, and only the operator was aware what formulations the volunteer was applying. Participants filled out an anonymous questionnaire evaluating primary and secondary skin feelings from −5 to +5, indicating a “very low/absent” to “very nice/excellent” feeling, respectively [40]. All the studies performed on human volunteers were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Committee of the University of Catanzaro “Magna Graecia” (Approval number: 392/2019).
2.15. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using a one-way ANOVA test. A Bonferroni t-test was used to confirm the results, and the probability was set at * p < 0.05. The analysis was carried out using GraphPad Prism v8 software (San Diego, CA, USA) and Excel (Office 2010).
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Extracts
The use of different analytical methods made it possible to characterize the chemical profile of the extracts obtained via supercritical CO2 as well as their antioxidant activity against free radicals. The results obtained in every single analysis are listed and summarized in Table 2.

Table 2.
Chemical characterization of extracts.
The olive leaf extracts showed a total phenolic content of 0.0903 ± 0.0035 mg/mL (GAE) and a flavonoids concentration of 0.2164 ± 0.762 mg/mL, which gave them an antioxidant power of 23.23 ± 1.47%I. The clementine waste extracts, on the other hand, contained gallic acid-like polyphenols equal to 0.330 ± 0.017 mg/mL GAE and a flavonoids concentration of 0.8844 ± 0.0796 mg/mL, showing an antioxidant activity of 25.86 ± 3.07%I (Table 2).
Interestingly, despite the phenolic and flavonoid contents of the CPE being three and four times higher, respectively, than the OLE, the antioxidant activity levels of the two extracts were almost overlapping. The results obtained can be explained by the differences in chemical structure of the molecules contained in the extracts. In fact, antioxidant activity is a unique and characteristic property of each molecule, affected by the insaturations and functional groups contained in the molecules as well as by their spatial location, factors that have an overall impact on their chemical reactivity and therefore the tendency to interact with other circulating molecules [41,42].
In agreement with our hypothesis, the HPLC analyses showed the presence of different molecules in the extracts. Indeed, in decreasing order, the CPE contained hesperidin (679.88 ± 59.29 ppm), naringin (28.16 ± 2.13 ppm), and rutin (25.97 ± 1.10 ppm), while the OLE contained only 7.44 ± 0.52 ppm of oleuropein (Table 2). Interestingly, in contrast to the scientific literature, our OLE did not contain rutin, a flavanol that is generally detectable in olive leaf extract [43]. However, the presence and concentration of bioactive molecules in plants is susceptible to numerous variations. In fact, various external and seasonal parameters influence the concentration of the molecules, as well as the genetic and geographical profile of the species. These parameters are known to significantly influence the vegetative activity and metabolic processes of plants, as previously assumed by Al Foraih M. and Williams C.A. and their respective co-workers [44,45].
3.2. In Vitro Cytotoxic Effects
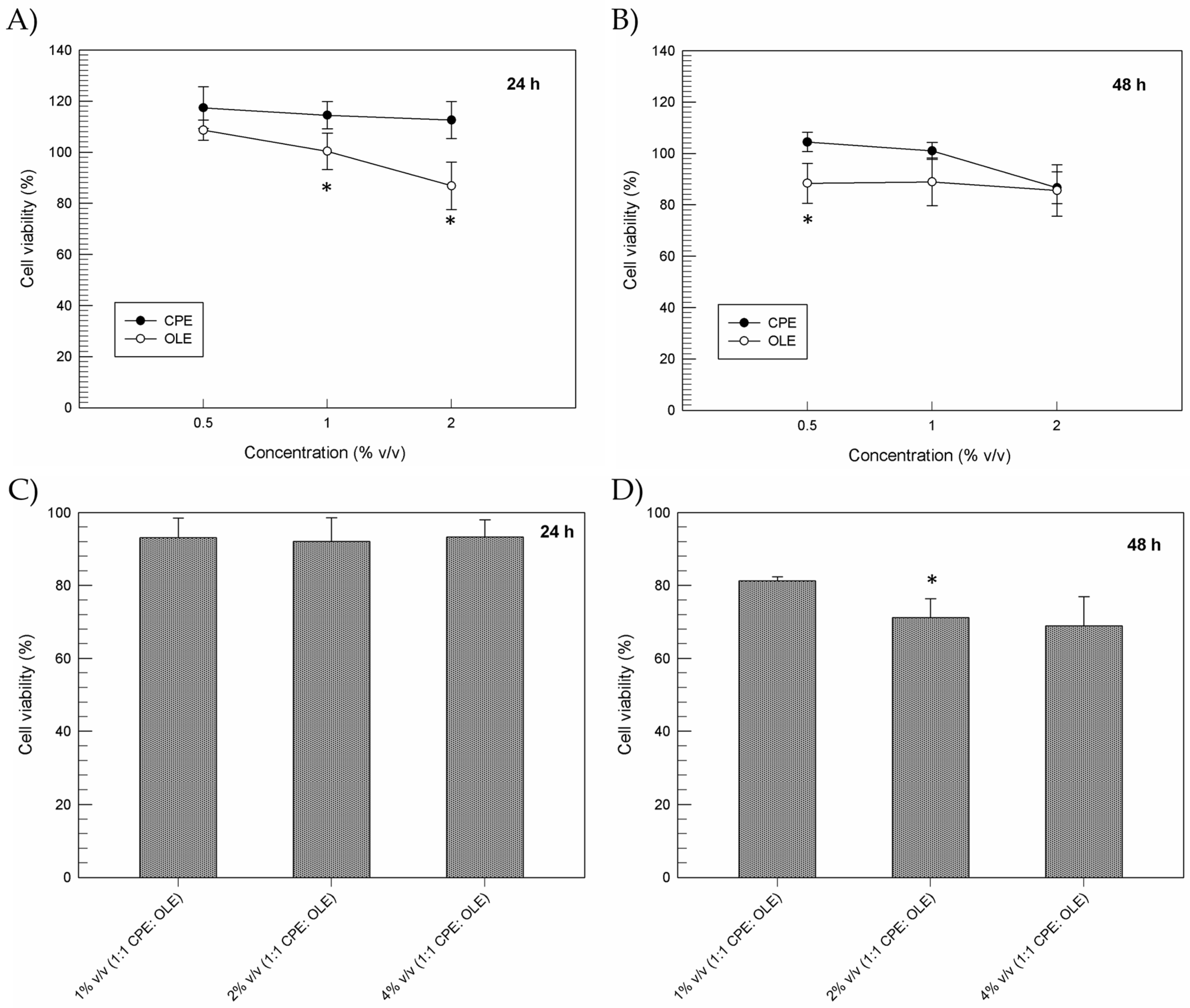
The MTT cell proliferation assay allowed us to detect cellular metabolic activity as an indicator of cell viability, proliferation, and cytotoxicity [46]. Figure 1A,B shows that CPE and OLE as single agents do not induce any relevant variation in cell viability percentages of normal keratinocytes after up to 48 h, even at the highest concentration tested (2% w/v). Indeed, cell viability values higher than 80% were recorded for all the samples tested. A slight pro-proliferative effect was also shown by CPE at the different concentrations tested up to 24 h after treatment. These data are in very good agreement with the pro-proliferative effect previously reported from Chung J.H. et al. and Gunes S. et al. for green tea and spirulina platensis extracts, respectively, on human keratinocytes [47,48].
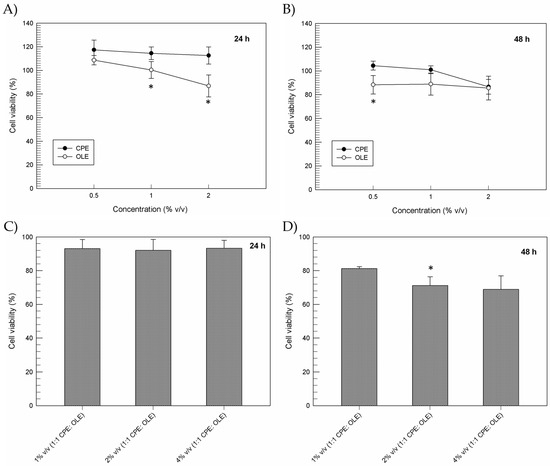
Figure 1.
In vitro cytotoxic effect of CPE and OLE as single agents (A,B) or combined (C,D) on human keratinocytes. Results are reported as a function of incubation time and extract concentration. Data are normalized with respect to the cytotoxic effect of ethanol at the same concentrations used for the extracts. Results are the average of three independent experiments ± SD. * p < 0.05.
Figure 1C,D show the results obtained from a combined treatment using CPE and OLE at an increasing final concentration (1–4% v/v, 1:1 ratio). As can be seen, the combination of both extracts did not induce relevant cytotoxic effects on human keratinocytes, keeping values above 90% up to 24 h after treatment and proving the great safety of the extracts tested (Figure 1C). Formulation 1% v/v (1:1 CPE:OLE) guaranteed a high safety profile even up to 48 h after exposure to the cells, while increasing concentrations of the extracts (final concentrations 2% or 4%) reported lower cell viability percentages (~70%). This effect could be due to some compounds present in olive leaf extracts, such as oleuropein, hydroxytyrosol, and oleocanthal, which can interfere with cell proliferation processes, blocking cell division or inducing apoptosis through different mechanisms [49,50,51]. The simultaneous presence of the organic acids contained in CPE, i.e., citric acid, could alter the stability of these compounds as well as causing combined effects on oxidative stress and increased cytotoxic effects. For this reason, OLE was kept at 0.5% v/v in all the realized emulsions in order to exploit beneficial effects, thus preventing cytotoxic effects.
3.3. In-Depth Characterization of Empty and Citrus and Olive Leaf Extracts-Loaded Face Creams
For the cosmetic application of natural extracts obtained from clementine peel from industrial processing waste and olive leaves as waste material, an optimized face cream formulation was chosen. The empty formulation, and consequently the citrus and olive leaf extracts (CPE-OLE)-loaded formulations, were prepared with an easy laboratory process based on the homogenization and emulsification of their components. The composition of formulations permitted us to obtain O/W emulsions that were apparently stable, pleasant in appearance and smell, and offered a good apparent spreadability. To better and more scientifically characterize all of the prepared emulsions, a deep analysis was carried out in terms of stability, microrheological, and dynamic rheological investigation. Another aim was to evaluate how the presence of increasing percentages of natural extracts could influence and modify the physico-chemical properties of emulsions.
3.3.1. Microrheological Investigation of Empty and Clementine Peels and Olive Leaf Extracts-Loaded Face Creams
The comparison between different formulations can be carried out through a microrheological investigation using a Rheolaser Master™, which permits the researcher to characterize the formulations at rest, without inducing a solicitation and without disrupting or forcing the sample to flow. This technique is called diffusing wave spectroscopy (DWS), similar to dynamic light scattering, and provides information about the internal structure of analyzed samples based on the Brownian movements of emulsion droplets, taking into account that internal structure can limit this movement [52]. Starting from these purposes, the microrheological profiles of the four prepared formulations were analyzed as a function of temperature; 25 °C for room conditions and 40 °C as an example of extreme storage conditions.
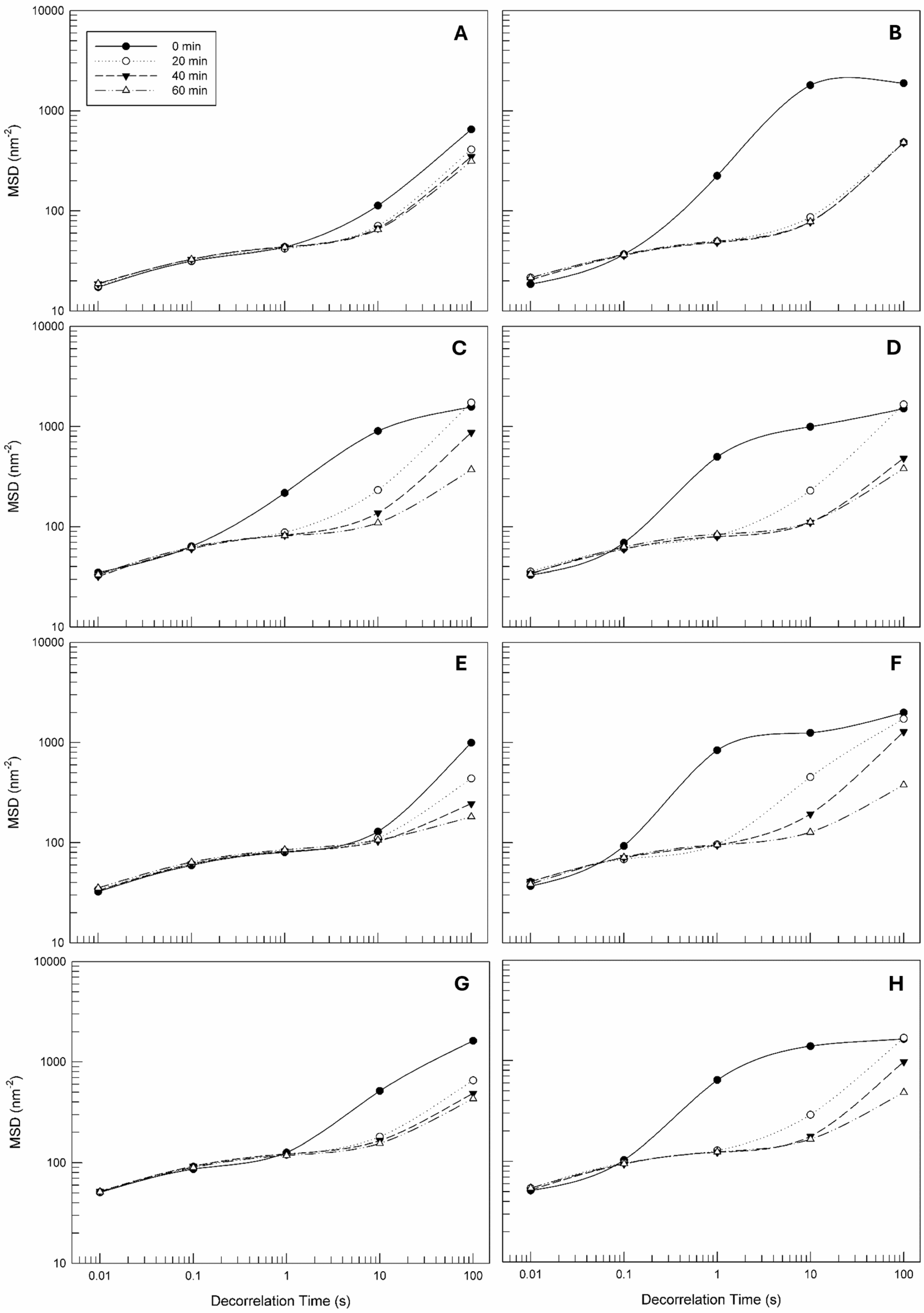
The first parameter obtained from the Rheolaser Master™ was a Mean Square Displacement (MSD) curve of each formulation. The slope of an MSD curve is related to the elasticity and viscosity of the sample. In detail, the movement of particles (in this case of droplets) within samples can induce a deformation of speckle images, and the entity of the induced deformation is recorded from a specific detector [53]. When the sample can be considered soft or fluid, the particles within its structure are characterized by more freedom of movement. In this case, the slope of the resulting MSD curve is directly proportional to the viscosity of the sample. In other cases, when the sample is characterized by a hard structure, the Brownian movement of the particles is strongly limited, and the MSD curves tend to decrease until a plateau is reached [54].
Figure 2 shows the MSD curves of all of the formulations analyzed both at 25 °C and 40 °C at different aging times (0 min, 20 min, 40 min, and 60 min). Comparing them, it is possible to note that no marked differences between the samples’ structures and behavior are present when the samples are analyzed at room temperature. In fact, the MSD curves of all of the samples tended to decrease during the analysis time. The progressive reduction of MSD curves, until the plateau was reached, highlights the observation that the droplets within samples have a certain freedom of movement. We can assume that the three-dimensional internal structures of the prepared emulsions are sufficiently soft to permits it, at least at rest. Comparing the microrheological profiles of each sample analyzed at different temperatures, it is possible to note that the increased temperature induced a slowing down of plateau achievement, showing a greater freedom of movement of droplets within emulsions at 40 °C with respect to the same samples analyzed at 25 °C.
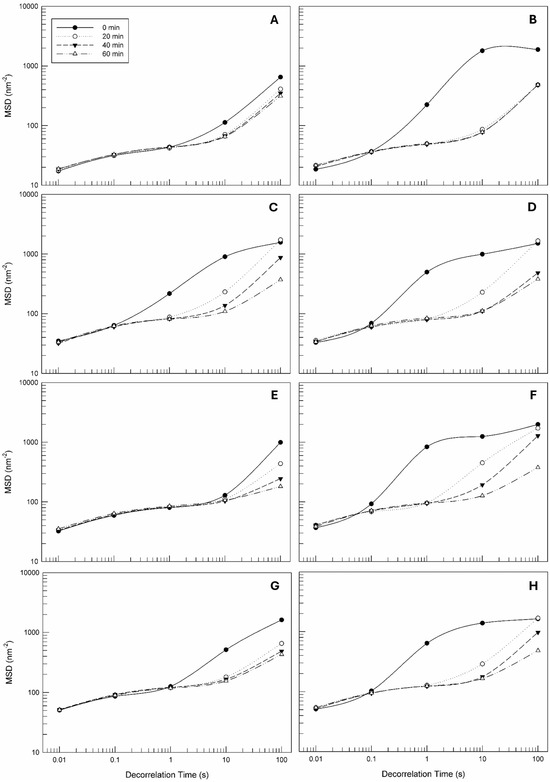
Figure 2.
Mean square displacement (MSD) curves as a function of decorrelation time (s) of empty and OLE-CPE formulations. The illustrated results are representative of three independent experiments. Legend: Empty Formulation at 25 °C (A) and 40 °C (B); 2% OLE-CPE Formulation at 25 °C (C) and 40 °C (D); 3% OLE-CPE Formulation at 25 °C (E) and 40 °C (F); 4% OLE-CPE Formulation at 25 °C (G) and 40 °C (H).
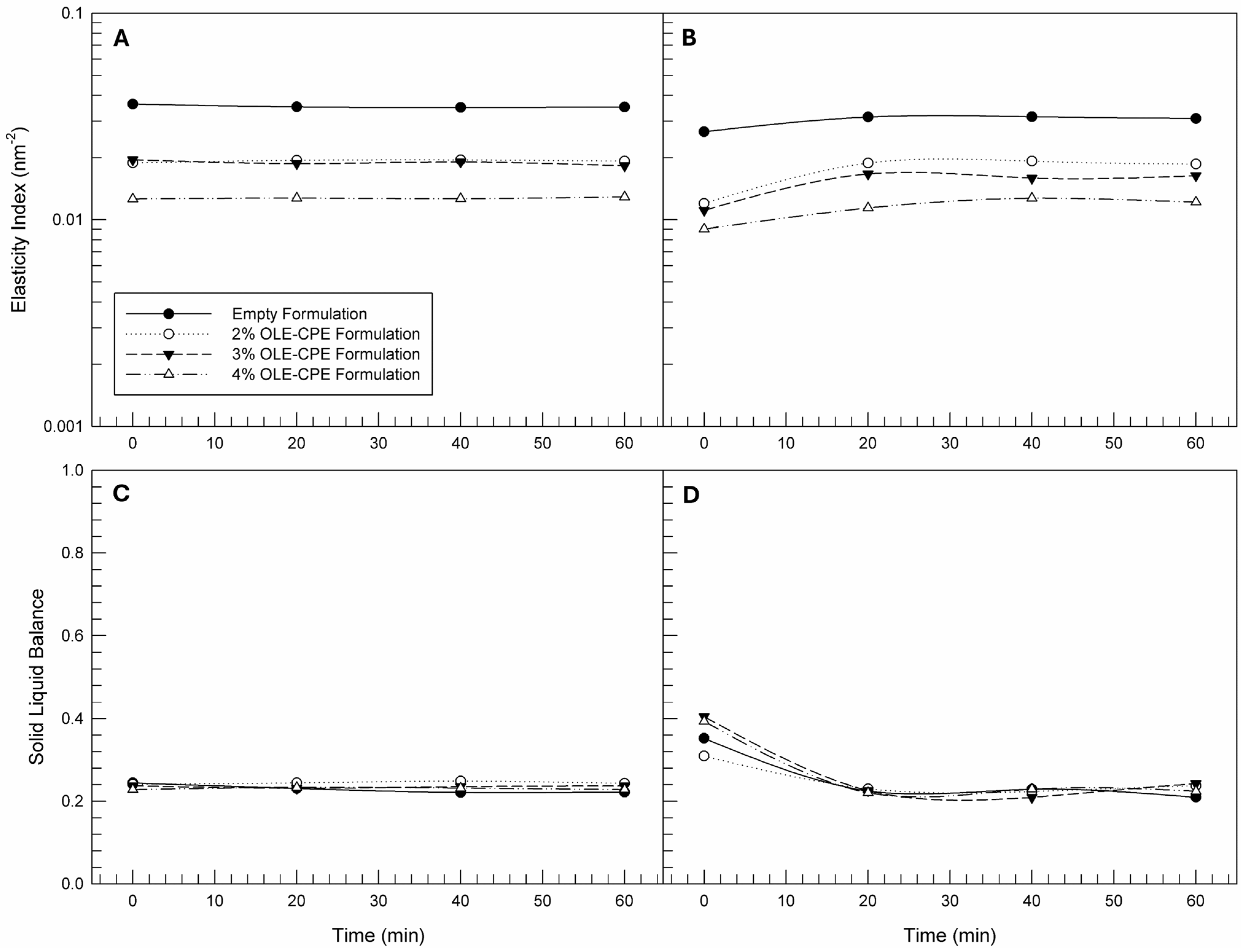
Starting from the MSD curves, other microrheological parameters can be obtained thanks to the software package RheoSoft Master 1.4.0.0. These parameters are the elasticity index (nm−2) and SLB. The Elasticity Index curves reported in Figure 3A,B permit us to appreciate the small differences that are difficult to find in the MSD curves (Figure 2). Generally, an increase in elasticity index values corresponds to a reduction in the particles’ movement within emulsion structures [55]. From the data reported in Figure 3A, it can be noted that the empty formulation was characterized by greater values of Elasticity Index (mean Elasticity Index value equal to 0.035 ± 0.00 nm−2) with respect to formulations prepared with increasing concentrations of natural extracts when analyzed at room temperature. Moreover, there do not seem to be any differences between the Elasticity Index profiles of 2% and 3% OLE-CPE formulations. On the contrary, the presence of the highest natural extract concentrations in a formulation resulted in the lowest elasticity values. Interpreting these data, we can assume that the presence of the extracts induces a reduction in the hardness of the internal structure of the formulations and, consequently, the oily droplets could better move within the three-dimensional network of the emulsion. In fact, as the concentration of the extracts increases, the movement of the droplets appears to be freer, resulting in a mean elasticity index value equal to 0.013 ± 0.00 nm−2 in the 4% OLE-CPE formulation.
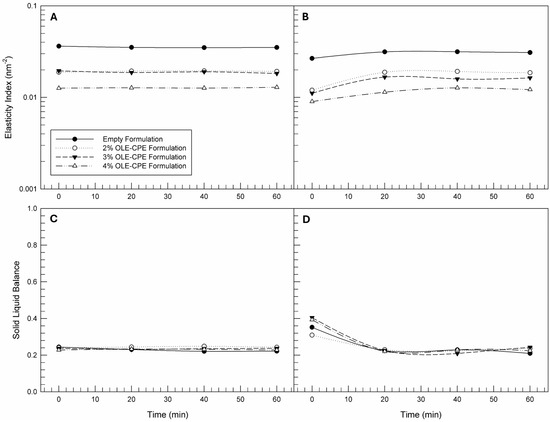
Figure 3.
Elasticity Index and Solid Liquid Balance curves as a function time of formulations analyzed at different temperatures. The illustrated results were representative of three independent experiments. Legend: Elasticity profiles at 25 °C (A) and 40 °C (B); Solid Liquid Balance profiles at 25 °C (C) and 40 °C (D).
The other mentioned microrheological parameter is the SLB, which corresponds to the ratio between the liquid-like and solid-like behavior of the analyzed sample [56]. For some types of samples, SLB can indicate the gelling point, the adhesiveness, and spreadability. SLB is a dimensionless parameter that can have values between 0 and 1; for 0 < SLB < 0.5, the sample is characterized by predominantly solid behavior, while for 0.5 < SLB < 1 the sample is characterized by predominantly liquid behavior. Crucial is a value of SLB equal to 0.5, because it indicates that a transformation from a liquid to a solid (or vice versa) occurred. In our study, no formulation underwent a transition, because the SLB values all remained below the value of 0.5, as shown in Figure 3C,D. Regardless of the presence or absence of extracts within the formulations, all of the samples showed a predominantly solid behavior, with SLB values between 0 and 0.5.
The increase in the analysis temperature (up to 40 °C) did not induce an alteration in either the Elasticity Index or the SLB profiles, confirming that the prepared emulsions are able to resist at temperature changes when they are maintained at rest and analyzed from a microrheological point of view.
3.3.2. Dynamic Rheological Characterization of Empty and Citrus and Olive Leaf Extracts-Loaded Face Creams
The previously mentioned microrheological characterization permitted us to observe the behavior of the samples at rest, without any solicitation and without inducing a structural modification. When a formulation is designed for topical application and above all for being spread on skin, a crucial aspect to consider is its dynamic rheological behavior and its responsiveness to specific solicitation [57]. For this purpose, two different rheological analysis were carried out on empty and OLE-CPE extracts-loaded formulations, i.e., viscosity evaluation in rotational mode and oscillatory test with frequency sweep.
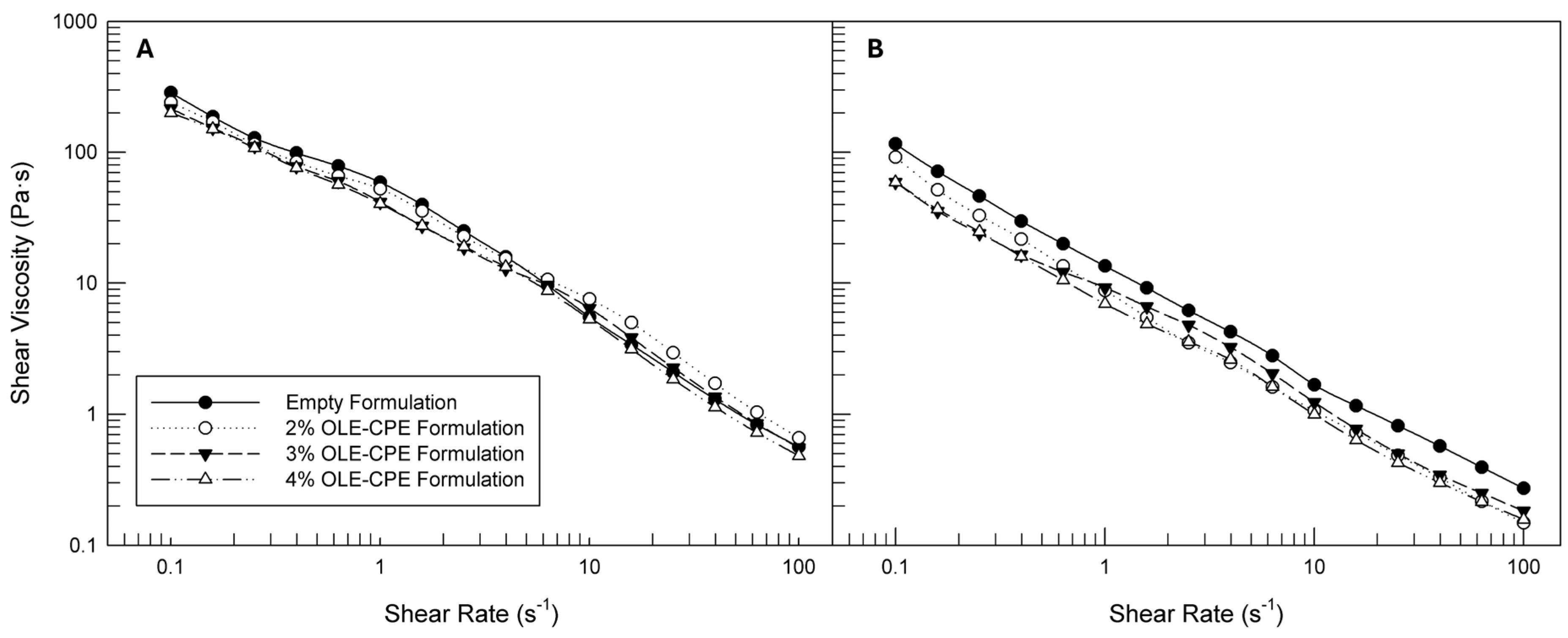
In the Figure 4 the rheological profiles as shear viscosity versus shear rate are reported for all of the characterized formulations. As we can see, regardless of the analysis temperature, all samples showed a non-Newtonian behavior, modifying their structures and adapting them to the induced flow. In fact, the samples’ viscosity decreases when the shear rate is increased. This pseudoplastic flow behavior is important because it is correlated with the spreadability of cosmetic products [58]. Moreover, observing Figure 4, the slope of the viscosity curves seems to be comparable for all of the analyzed samples. Comparing instead Figure 4A,B, it can be noted that the rheological behavior of formulations with and without extracts did not change when the temperature was increased, but a certain reduction in shear viscosity values occurred (Table 3), confirming a fluidizing effect of the temperature on the prepared emulsions.
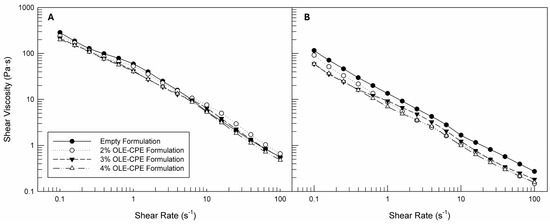
Figure 4.
Rheological profiles (shear viscosity versus shear rate) of empty and OLE-CPE formulations analyzed at 25 °C (A) and 40 °C (B). The illustrated results are representative of three independent experiments.

Table 3.
Shear rate-dependent viscosity (Pa·s) for empty and OLE-CPE Formulations at different shear rates. Values are reported as the average of three independent experiments ± standard deviation.
Observing Table 3, it is also possible to note that the presence of increasing percentages of natural extracts in the formulations induced a statistically significant reduction in viscosity values, above all at the lowest shear rate, while not modifying the rheological behavior of the formulations.
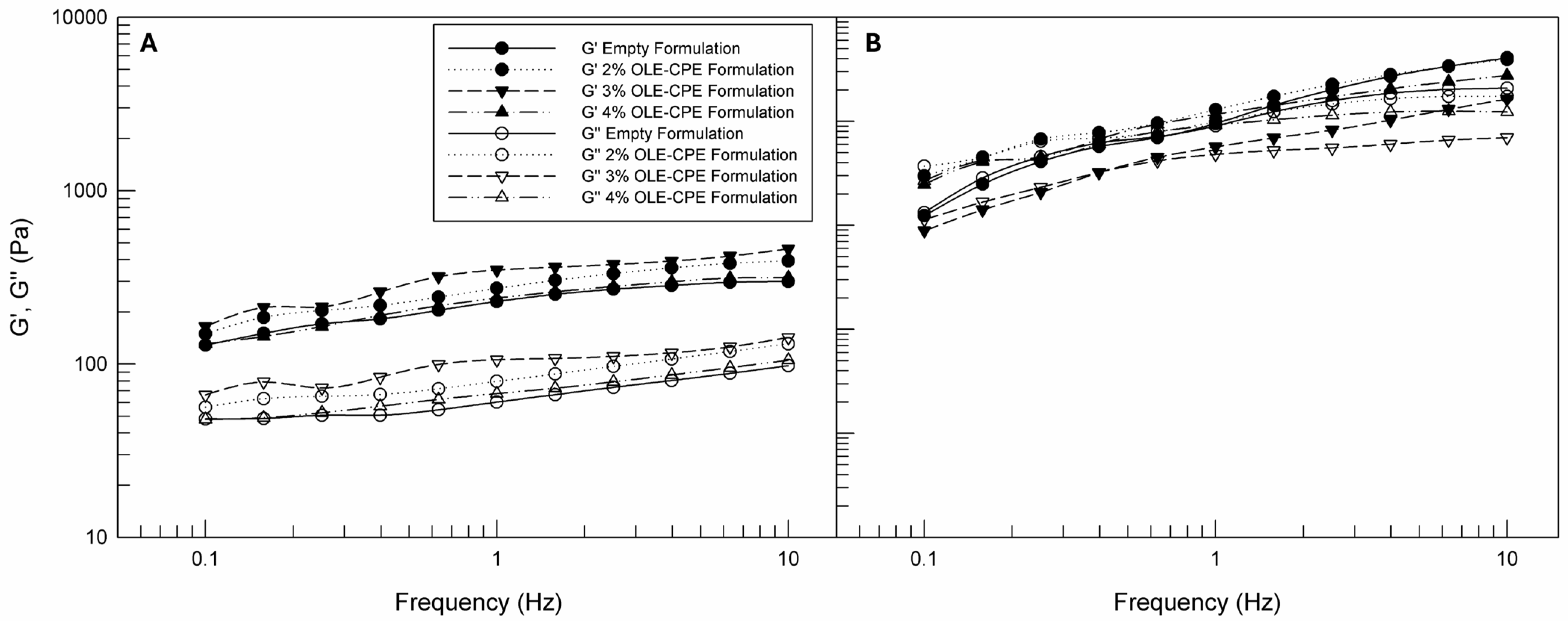
Finally, rheological oscillation tests were carried out on all formulationd to determine the G′ and G″ values as a function of frequency and temperature, inducing sinusoidal periodic deformations on the material. G′ is defined as the elastic or storage modulus, while G″ is the viscous or loss modulus; when G′ is greater than G″, the induced deformation is elastic and recoverable, and the sample appears as a solid-like material. On the other hand, when G′ is greater than G″ the sample shows a predominantly solid-like behavior [59]. In Figure 5A,B, the values of G′ and G″ were reported. For all samples, the values of G′ were greater than G″, indicating that the elastic behavior of the formulations was maintained in the frequency range of the analysis and confirming the resistance of the emulsions’ structure to the oscillatory solicitation. This is an important result, because it permits us to assume that the formulations will resist and maintain their structure during storage, commercial distribution, and use. In this case, the effects of temperature increase are more evident when compared to shear viscosity curves (Figure 4). When the temperature was increased from 25 °C to 40 °C, both the G′ and G″ moduli increased. It is probable that the increased fluidity of empty and OLE-CPE formulations due to heating could allow better mobility of the droplets in the material, resulting in an increase in both moduli. Moreover, the reduction in viscosity could promote the formation or reorientation of internal structures, which would contribute to the material’s resistance to deformation. As a result, the values of G′ and G″ increase. Considering the obtained rheological data, we can conclude that the prepared formulations were suitable for skin spreading due to their responses to the induced flow. They are characterized by an internal structure able to resist induced deformation.
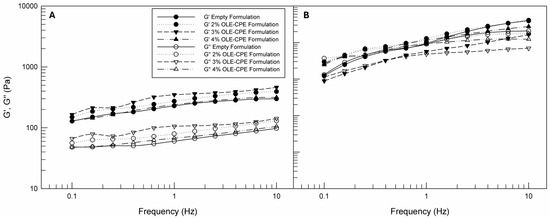
Figure 5.
G′ and G″ moduli (Pa) curves as a function of frequency (Hz) of empty and OLE-CPE formulations analyzed at 25 °C (A) and 40 °C (B). The illustrated results were representative of three independent experiments.
3.4. Stability Studies on Emulsions
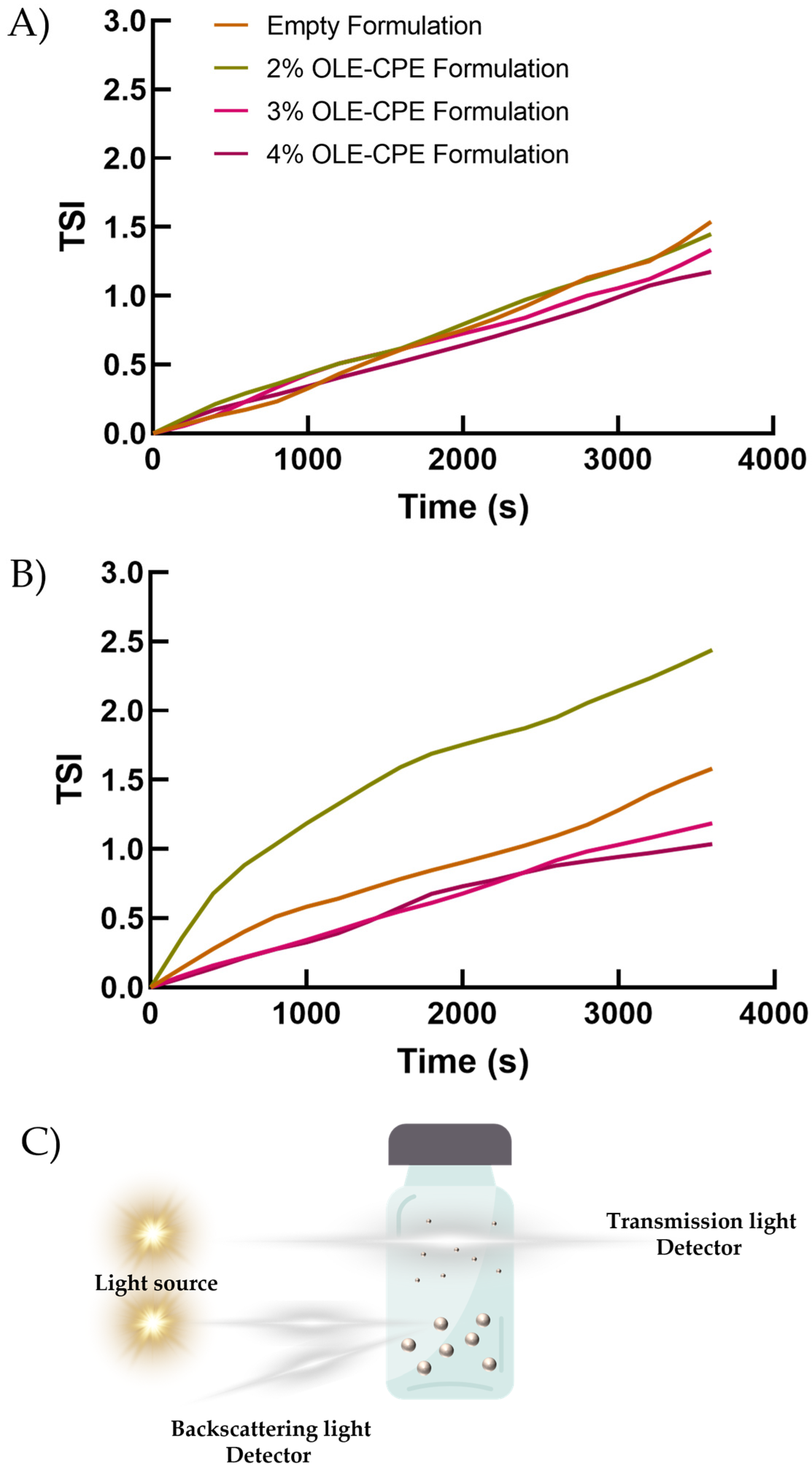
The long-term stability of the emulsions was studied using the multiple light scattering technology of Turbiscan Lab®. All the formulations displayed great stability profiles, which were not compromised by the addition of OLE and CPE during the preparation phase. Values of ΔT and ΔBS were between ±2% regardless of the amount of extracts used (Figure S1), thus indicating the absence of any creaming, flocculation, or sedimentation phenomena [60]. This result was further confirmed by TSI analyses that showed the absence of relevant variations in TSI values between the empty formulation and the formulations containing OLE and CPE (Figure 6). In detail, all of the formulations displayed overlapping profiles at 25 °C, thus confirming the lack of destabilizing phenomena induced by the addition of the extracts during preparation (Figure 6A). Contrarily, a slight increase in TSI values was reported at 40 °C for the formulation containing the smallest amount or no extracts (Figure 6B), thus indicating a lower stability compared to the other formulations tested [61].
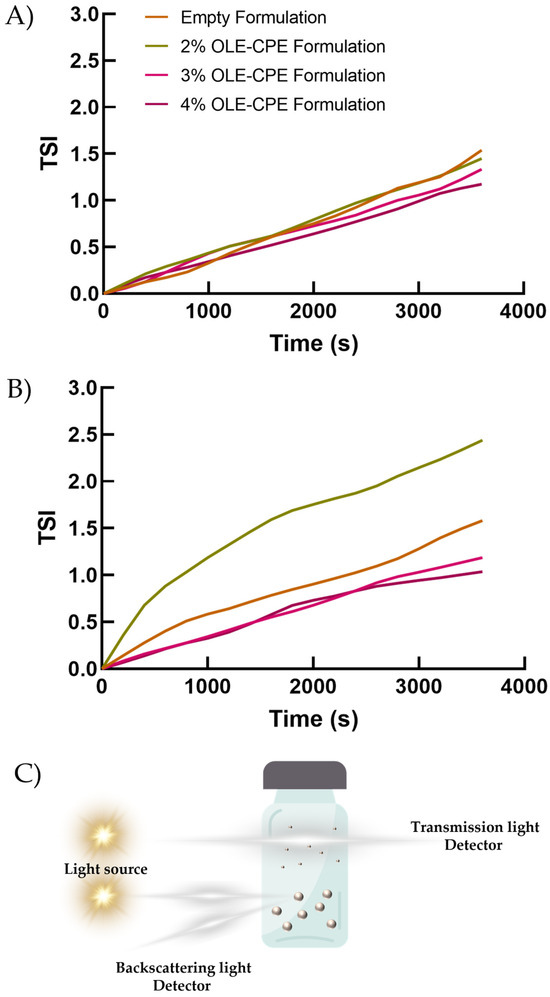
Figure 6.
Turbiscan analysis of emulsions. The kinetic destabilization profiles are reported as a function of time (0–60 min) and temperature (25 °C and 40 °C for Panel (A,B), respectively). The results are representative of three analyses carried out on three different batches of each formulation. Panel (C) is a graphic representation of the working principles of the Turbiscan Lab analyzer. Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.
Turbiscan Lab® also provided information on the diameter kinetic profiles of the emulsions, demonstrating the maintenance of globule size (5.5–6.5 µm) for the entire duration of the analysis performed at 25 °C, which is an indicator of high stability (Figure S2A). Contrarily, a slight increase in diameter of both the empty formulation and that containing 2% CPE-OLE was obtained during the first 20 min of the analysis performed at 40 °C (Figure S2B), subsequently reaching a dimensional plateau. These effects confirmed the results of TSI, leading to the hypothesis of a stabilizing effect of the extracts. The sizes of the emulsion globules were also confirmed by microscopy studies, reporting diameters lower than 10 µm for all the analyzed samples regardless of their composition (Figure S3).
3.5. In Vivo Evaluation of Cutaneous Tolerability and Feelings Induced by Emulsions
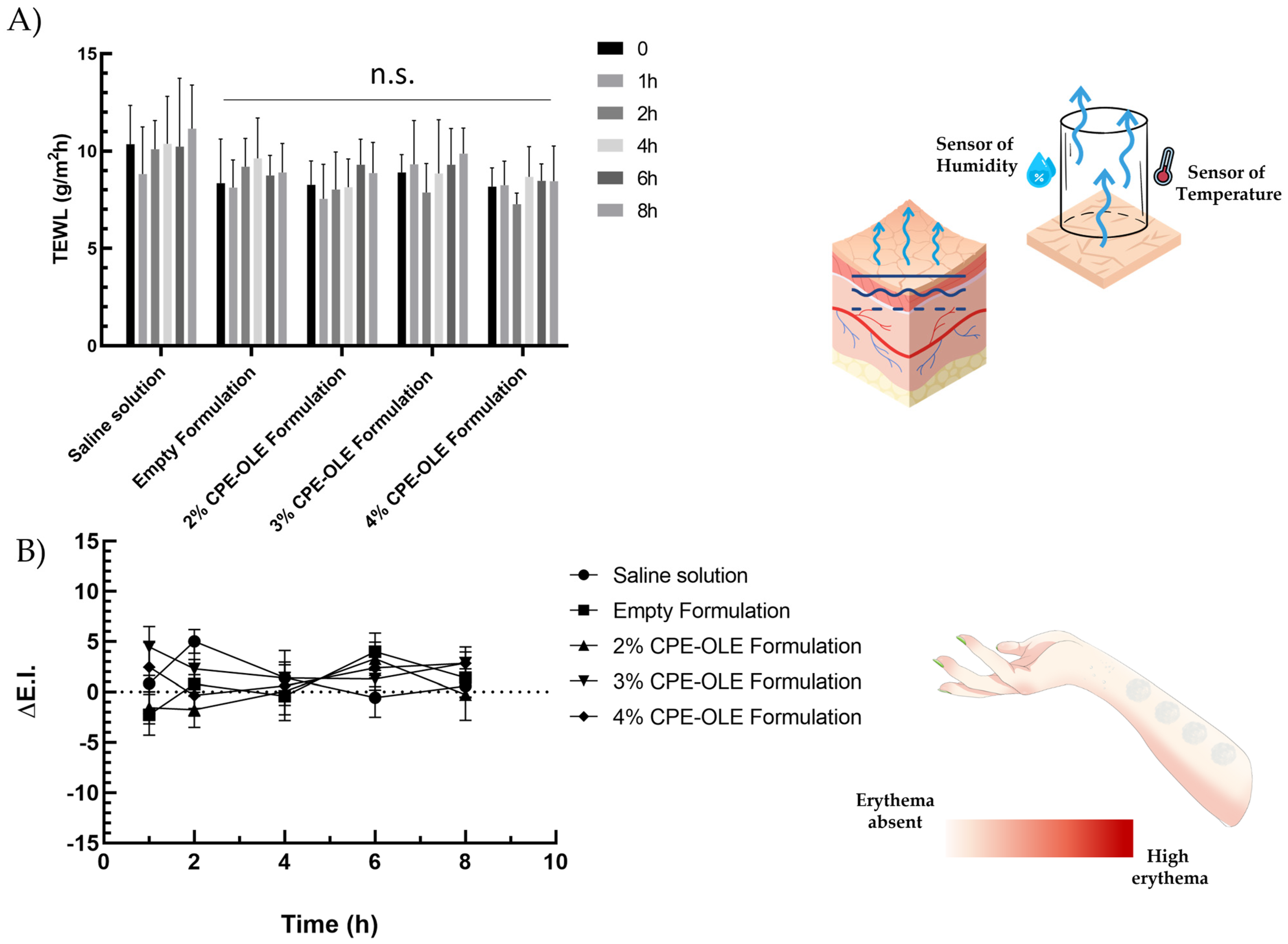
Cutaneous tolerability represents a fundamental requirement for the appeal of the face cream. The monitoring of the TEWL and increase in erythematous index after application of the cream represent two non-invasive strategies that allow the evaluation of the safety profile of the proposed formulations. TEWL quantifies the water loss from the outermost skin layer. Higher TEWL values can indicate a disruption in the skin’s protective barrier [37]. Figure 7A shows the skin tolerability of emulsions expressed as TEWL values over varying exposure times (0–8 h). Saline solution (0.9% NaCl w/v) was used as a control during the study. Neither the empty formulations nor those containing extracts caused increases in TEWL values, which is a very good marker of an intact skin barrier function. TEWL values below 11 were reported for all of the formulations tested and were in very good agreement with those normally recorded for healthy skin [62]. Rather, a slight decrease in TEWL values was recorded in the results obtained from emulsions in comparison to those obtained from the saline solution. This effect could be due to a film-forming potential of the cream, creating a protective layer on the skin, as well as a hydrating effect on the part of the oils contained in the emulsion, which overall reduce the loss of transepidermal water [63].
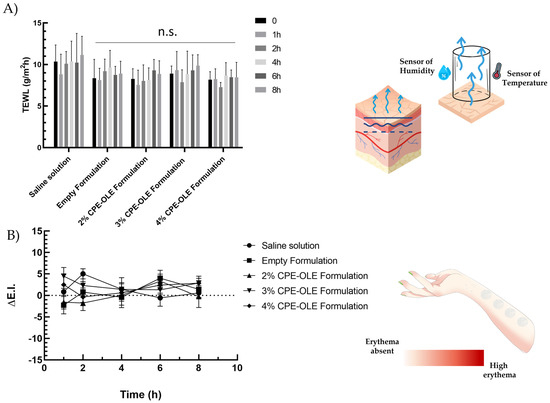
Figure 7.
Studies of skin tolerability on human volunteers. Panel (A) shows the values of TEWL after topical administration of the empty formulation or formulations containing 2%, 3%, or 4% CPE-OLE. Panel (B) shows the variation of erythematous index values after the administration of empty formulations or formulations containing CPE-OLE. Saline solution (NaCl 0.9% w/v) was used as a control for both studies. n.s. = not significant. Parts of the figure were drawn using pictures from Servier Medical Art. Servier Medical Art by Servier is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.
The results of skin tolerability were further confirmed by reflectance spectroscopy studies using X-Rite Ci62 to assess any occurrence of cutaneous erythema following the application of the emulsions. Figure 7B shows the results of skin tolerance as variations of erythema index values (ΔE.I.) compared to baseline values. All of the samples tested did not lead to relevant changes in erythema index values, remaining in the same range of variation as the sites treated with saline solution alone. The data confirmed the great safety of the tested formulations, regardless of the quantity of extracts loaded in the formulation. The lack of relevant changes in the erythematous index toward more negative values was also a sign of a lack of opacification after application of the cream, with an attractive potential for the user.
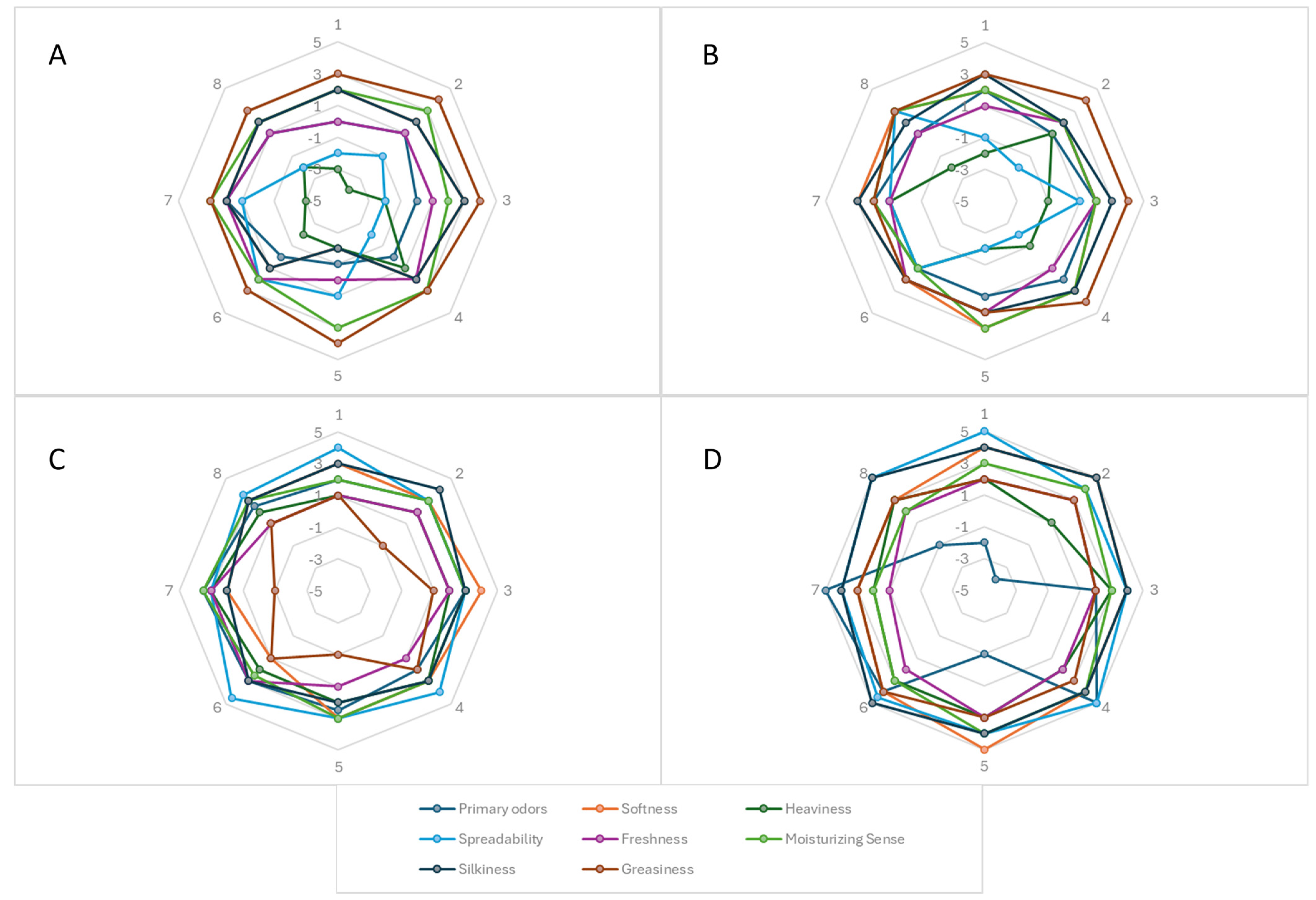
The volunteers enrolled in the in vivo studies were invited to complete a confidential survey on their primary (softness, heaviness, spreadability, freshness) and secondary (moisturizing sense, silkiness, greasiness) sensations experienced during and after applying the empty formulations or those that contained 2–4% of CPE-OLE [40]. Volunteers gave a rating between +5 and −5 to each formulation, and the results were collected into a radar diagram (Figure 8). Overall, the formulations were highly appreciated by all candidates, and primary odors appeared pleasant for all samples due to the presence of bergamot water and extracts in the formulations. However, some parameters were very different between the investigated emulsions. In detail, spreadability and silkiness were more appreciated, with increased amounts of OLE and CPE in the preparation, which agrees with the results reported in our rheological studies.
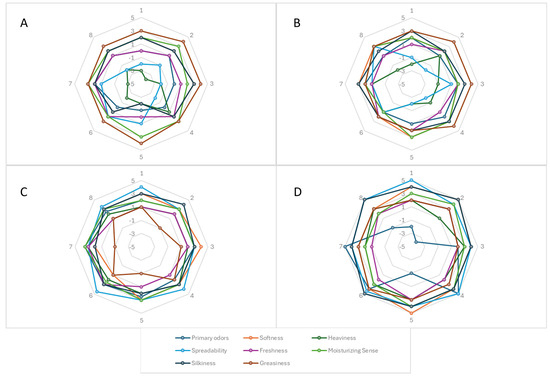
Figure 8.
Radar diagram of skin feelings after cutaneous application of emulsions. Human volunteers were asked to rate primary and secondary skin feelings through an anonymous questionnaire. Panel (A) refers to the empty formulation; panels (B–D) refer to the formulations containing 2%, 3%, and 4% CPE-OLE, respectively.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we proposed the use of clementine peels and olive leaf extracts as value-added food-waste-derived ingredients for face cream. Extracts were obtained using a carbon dioxide supercritical fluid extraction technique and showed suitable antioxidant features, with an antioxidant activity of ca. 25%. The inclusion of these ingredients in the proposed cosmetic results in stable creams, as demonstrated by Turbiscan analyses at room temperature and extreme storage conditions, i.e., 25 and 40 °C, respectively. Both extracts demonstrated safe profiles in vitro on NCTC human keratinocytes, without any significant cytotoxic effect after up to 48 h of incubation at extract concentrations ranging between 1 and 2% v/v. The resulting face creams embedded with clementine peel and olive leaf extracts showed proper spreadability and demonstrated pseudoplastic behavior under dynamic rheological analysis. Similar trends were recorded for the investigated creams regardless of the extract concentrations added, although a slight progressive reduction of overall viscosity was found by increasing their concentration. The safety profiles of the creams were investigated in vivo, showing no significant variations of TEWL and erythematous index in healthy volunteers with respect to a negative control. The positive feedback received from healthy human volunteers confirmed the potential use of these cosmetic formulations, since the OLE-CPE formulations were described as suitably spreadable, with a good texture and a pleasant fragrance provided by bergamot wastewater. The proposed approach highlights the re-use of food waste byproducts as ingredients in the cosmetic field in order to develop a circular economy able to provide value-added biomaterials while at the same time reducing environmental impacts and resource depletion.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/cosmetics11020041/s1, Figure S1: Turbiscan analysis of emulsions. Transmitted and backscattered signals recorded at 25 °C (A,B) or 40 °C (C,D) are reported as a function of sample height (mm). Figure S2: Diameter kinetic profiles of emulsions. Data of average diameter are reported as a function of time (0–1 h) and temperature (25 °C and 40 °C for Panel (A) and (B), respectively). Figure S3: Microscopies of emulsions. (A) refers to Empty formulation; (B–D) refer to Formulations containing 2%, 3% and 4% CPE-OLE, respectively.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.P.; methodology, O.I.P. and S.M.; validation, D.P.; investigation, A.M., N.d. and R.M.; data curation, M.C.C. and A.S.; writing—original draft preparation, A.M., M.C.C. and N.d.; writing—review and editing, R.M., S.M. and O.I.P.; supervision, D.P.; funding acquisition, D.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Next Generation EU-Italian NRRP, Mission 4, Component 2, Investment 1.5, call for the creation and strengthening of ‘Innovation Ecosystems’, building ‘Territorial R&D Leaders’ (Directorial Decree n. 2021/3277)—project Tech4You—Technologies for climate change adaptation and quality of life improvement, n. ECS0000009. This work reflects only the authors’ views and opinions, neither the Ministry for University and Research nor the European Commission can be considered responsible for them.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee of Committee of University of Catanzaro “Magna Graecia” (Approval number: 392/2019).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon request. The data are not publicly available due to privacy.
Acknowledgments
We thank the Company Medi Mais Calabra of Corigliano-Rossano (Cosenza, Italy) for providing the citrus peel waste used for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Huang, C.-H.; Liu, S.-M.; Hsu, N.-Y. Understanding global food surplus and food waste to tackle economic and environmental sustainability. Sustainability 2020, 12, 2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Chiu, S.-Y.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Lu, L.-C.; Huang, K.-Y. Agricultural production efficiency, food consumption, and food waste in the European countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, B.; Mohanta, Y.K.; Reddy, C.N.; Reddy, S.D.M.; Mandal, S.K.; Yadavalli, R.; Sarma, H. Valorization of agro-industrial biowaste to biomaterials: An innovative circular bioeconomy approach. Circ. Econ. 2023, 2, 100050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.C.; Sharma, R.; Debnath, S.; Nayak, P.K.; Roy, R.; Sharma, M.; Inbaraj, B.S.; Sridhar, K. Recent advances in production of sustainable and biodegradable polymers from agro-food waste: Applications in tissue engineering and regenerative medicines. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 129129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrapani, G.; Zare, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Biomaterials from the value-added food wastes. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2022, 19, 101181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morganti, P.; Gao, X.; Vukovic, N.; Gagliardini, A.; Lohani, A.; Morganti, G. Food loss and food waste for green cosmetics and medical devices for a cleaner planet. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondello, A.; Salomone, R.; Mondello, G. Exploring circular economy in the cosmetic industry: Insights from a literature review. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2024, 105, 107443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, A.C.; Paiva, J.P.; Diniz, R.R.; Dos Anjos, V.M.; Silva, A.B.S.; Pinto, A.V.; Dos Santos, E.P.; Leitão, A.C.; Cabral, L.M.; Rodrigues, C.R. Photoprotection assessment of olive (Olea europaea L.) leaves extract standardized to oleuropein: In vitro and in silico approach for improved sunscreens. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2019, 193, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Mejía, E.; Rosales-Conrado, N.; León-González, M.E.; Madrid, Y. Citrus peels waste as a source of value-added compounds: Extraction and quantification of bioactive polyphenols. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.L.; Gondim, S.; Gómez-García, R.; Ribeiro, T.; Pintado, M. Olive leaf phenolic extract from two Portuguese cultivars–bioactivities for potential food and cosmetic application. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leporini, M.; Loizzo, M.R.; Sicari, V.; Pellicanò, T.M.; Reitano, A.; Dugay, A.; Deguin, B.; Tundis, R. Citrus× clementina Hort. juice enriched with its by-products (peels and leaves): Chemical composition, in vitro bioactivity, and impact of processing. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevete, G.; Carvalho, L.G.; del Carmen Razola-Diaz, M.; Verardo, V.; Mancini, G.; Fiore, A.; Mazzonna, M. Ultrasound assisted extraction and liposome encapsulation of olive leaves and orange peels: How to transform biomass waste into valuable resources with antimicrobial activity. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2024, 102, 106765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe-Fuentes, I.; Uribe, E.; López, J.; Contreras, D.; Poblete, J. A study of dried mandarin (Clementina orogrande) peel applying supercritical carbon dioxide using co-solvent: Influence on oil extraction, phenolic compounds, and antioxidant activity. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2022, 46, e16116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Márquez, J.M.; Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Varela-López, A.; Puentes, J.G.; Pino-García, R.D.; Sánchez-González, C.; Elio, I.; Battino, M.; García, R. Exploring the antioxidant, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory potential of olive leaf extracts from Spain, Portugal, Greece, and Italy. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanitphakdeedecha, R.; Ng, J.N.C.; Junsuwan, N.; Phaitoonwattanakij, S.; Phothong, W.; Eimpunth, S.; Manuskiatti, W. Efficacy of olive leaf extract–containing cream for facial rejuvenation: A pilot study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qabaha, K.; Al-Rimawi, F.; Qasem, A.; Naser, S.A. Oleuropein is responsible for the major anti-inflammatory effects of olive leaf extract. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zillich, O.; Schweiggert-Weisz, U.; Eisner, P.; Kerscher, M. Polyphenols as active ingredients for cosmetic products. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, C.V.; Pintado, M. Hesperidin from Orange Peel as a Promising Skincare Bioactive: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiefer, S.; Weibel, M.; Smits, J.; Juch, M.; Tiedke, J.; Herbst, N. Citrus flavonoids with skin lightening effects–Safety and efficacy studies. Int. J. Appl. Sci. 2010, 132, 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Boo, Y.C. Human skin lightening efficacy of resveratrol and its analogs: From in vitro studies to cosmetic applications. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Nosoudi, N.; Karamched, S.; Parasaram, V.; Vyavahare, N. Polyphenol treatments increase elastin and collagen deposition by human dermal fibroblasts; Implications to improve skin health. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2021, 102, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casquete, R.; Castro, S.M.; Martín, A.; Ruiz-Moyano, S.; Saraiva, J.A.; Córdoba, M.G.; Teixeira, P. Evaluation of the effect of high pressure on total phenolic content, antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of citrus peels. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2015, 31, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.X.; Wang, H.C.; Chu, Y.L.; Wu, Y.Z.; Liao, J.A.; Su, Z.Y. Essential oil from Citrus depressa peel exhibits antimicrobial, antioxidant and cancer chemopreventive effects. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2024. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, G.; Iesce, M.R.; Naviglio, D.; Ciaravolo, M.; Vitale, E.; Arena, C. Comparative studies on different citrus cultivars: A revaluation of waste mandarin components. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berbel, J.; Posadillo, A. Review and analysis of alternatives for the valorisation of agro-industrial olive oil by-products. Sustainability 2018, 10, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viuda-Martos, M.; Ruiz-Navajas, Y.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J. Effect of adding citrus waste water, thyme and oregano essential oil on the chemical, physical and sensory characteristics of a bologna sausage. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2009, 10, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaw, K.-Y.; Parat, M.-O.; Shaw, P.N.; Falconer, J.R. Solvent supercritical fluid technologies to extract bioactive compounds from natural sources: A review. Molecules 2017, 22, 1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Elmaaty, T.; Sayed-Ahmed, K.; Magdi, M.; Elsisi, H. An eco-friendly method of extracting alizarin from Rubia tinctorum roots under supercritical carbon dioxide and its application to wool dyeing. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radzali, S.A.; Markom, M.; Saleh, N.M. Co-solvent selection for supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) of phenolic compounds from Labisia pumila. Molecules 2020, 25, 5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mare, R.; Pujia, R.; Maurotti, S.; Greco, S.; Cardamone, A.; Coppoletta, A.R.; Bonacci, S.; Procopio, A.; Pujia, A. Assessment of Mediterranean Citrus Peel Flavonoids and Their Antioxidant Capacity Using an Innovative UV-Vis Spectrophotometric Approach. Plants 2023, 12, 4046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mare, R.; Maurotti, S.; Ferro, Y.; Galluccio, A.; Arturi, F.; Romeo, S.; Procopio, A.; Musolino, V.; Mollace, V.; Montalcini, T. A rapid and cheap method for extracting and quantifying lycopene content in tomato sauces: Effects of lycopene micellar delivery on human osteoblast-like cells. Nutrients 2022, 14, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, M.C.; Barone, A.; Mancuso, A.; Torella, D.; Paolino, D. Rutin-loaded nanovesicles for improved stability and enhanced topical efficacy of natural compound. J. Funct. Biomater. 2021, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, A.; Tarsitano, M.; Udongo, B.P.; Cristiano, M.C.; Torella, D.; Paolino, D.; Fresta, M. A comparison between silicone-free and silicone-based emulsions: Technological features and in vivo evaluation. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2022, 44, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, J.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Sun, J.; Ding, J. Thermogel loaded with low-dose paclitaxel as a facile coating to alleviate periprosthetic fibrous capsule formation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 30235–30246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Kang, W.; Wang, X.; Meng, L. Influence of water content and temperature on stability of W/O crude oil emulsion. Pet. Sci. Technol. 2013, 31, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Qi, X.; Ren, T.; Huang, Y.; Keller, A.A.; Wang, H.; Wu, B.; Jin, H.; Li, F. Heteroaggregation of CeO2 and TiO2 engineered nanoparticles in the aqueous phase: Application of turbiscan stability index and fluorescence excitation-emission matrix (EEM) spectra. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 533, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardien, K.L.; Baas, D.C.; de Vet, H.C.; Middelkoop, E. Transepidermal water loss measured with the Tewameter TM300 in burn scars. Burns 2016, 42, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matts, P.; Dykes, P.; Marks, R. The distribution of melanin in skin determined in vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 2007, 156, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moravkova, T.; Stern, P. Rheological and textural properties of cosmetic emulsions. Appl. Rheol. 2011, 21, 35200. [Google Scholar]
- Bekker, M.; Webber, G.; Louw, N. Relating rheological measurements to primary and secondary skin feeling when mineral-based and Fischer–Tropsch wax-based cosmetic emulsions and jellies are applied to the skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Wilson, A.M.; Glossman-Mitnik, D. Theoretical study of the molecular properties and chemical reactivity of (+)-catechin and (−)-epicatechin related to their antioxidant ability. J. Mol. Struct. THEOCHEM 2006, 761, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parcheta, M.; Świsłocka, R.; Orzechowska, S.; Akimowicz, M.; Choińska, R.; Lewandowski, W. Recent developments in effective antioxidants: The structure and antioxidant properties. Materials 2021, 14, 1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, J.J.; Alcaraz, M.; Benavente-García, O. Antioxidant and radioprotective effects of olive leaf extract. In Olives and Olive Oil in Health and Disease Prevention; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 951–958. [Google Scholar]
- Al Foraih, M.; Hyatt, S.L.; Naumovski, N.; Alasmari, H.A. Seasonal Variations in Dietary Flavonoid Content of Edible Plants. J. High Inst. Public Health 2023, 53, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.A.; Richardson, J.; Greenham, J.; Eagles, J. Correlations between leaf flavonoids, taxonomy and plant geography in the genus Disporum. Phytochemistry 1993, 34, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-García, J.; Lehocký, M.; Humpolíček, P.; Sáha, P. HaCaT keratinocytes response on antimicrobial atelocollagen substrates: Extent of cytotoxicity, cell viability and proliferation. J. Funct. Biomater. 2014, 5, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, J.H.; Han, J.H.; Hwang, E.J.; Seo, J.Y.; Cho, K.H.; Kim, K.H.; Youn, J.I.; Eun, H.C. Dual mechanisms of green tea extract-induced cell survival in human epidermal keratinocytes. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunes, S.; Tamburaci, S.; Dalay, M.C.; Deliloglu Gurhan, I. In vitro evaluation of Spirulina platensis extract incorporated skin cream with its wound healing and antioxidant activities. Pharm. Biol. 2017, 55, 1824–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goren, L.; Zhang, G.; Kaushik, S.; Breslin, P.A.; Du, Y.-C.N.; Foster, D.A. (−)-Oleocanthal and (−)-oleocanthal-rich olive oils induce lysosomal membrane permeabilization in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Q.; Cao, S.; Du, L. Mitochondria-mediated apoptosis was induced by oleuropein in H1299 cells involving activation of p38 MAP kinase. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 5480–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, F.; Di Sano, C.; Barbieri, G. The hydroxytyrosol induces the death for apoptosis of human melanoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhauser, S.; Fattahi, E.; Geier, D.; Becker, T. Non-invasive rheology measurement employing diode laser imaging. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Qiu, S.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Yin, L. Physical stability, microstructure and micro-rheological properties of water-in-oil-in-water (W/O/W) emulsions stabilized by porcine gelatin. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristiano, M.C.; Froiio, F.; Mancuso, A.; De Gaetano, F.; Ventura, C.A.; Fresta, M.; Paolino, D. The Rheolaser Master™ and Kinexus rotational rheometer® to evaluate the influence of topical drug delivery systems on rheological features of topical poloxamer gel. Molecules 2020, 25, 1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degrand, L.; Michon, C.; Bosc, V. New insights into the study of the destabilization of oil-in-water emulsions with dextran sulfate provided by the use of light scattering methods. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 848–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wu, T.; Liu, R.; Liang, B.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, E.; Zhang, M. Effects of superfine grinding and microparticulation on the surface hydrophobicity of whey protein concentrate and its relation to emulsions stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2015, 51, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estanqueiro, M.; Amaral, M.; Sousa Lobo, J. Comparison between sensory and instrumental characterization of topical formulations: Impact of thickening agents. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2016, 38, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaspar, L.; Campos, P.M. Rheological behavior and the SPF of sunscreens. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 250, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsaros, G.; Tsoukala, M.; Giannoglou, M.; Taoukis, P. Effect of storage on the rheological and viscoelastic properties of mayonnaise emulsions of different oil droplet size. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calienni, M.N.; Prieto, M.J.; Couto, V.M.; de Paula, E.; de VaAlonso, S.; Montanari, J. 5-Fluorouracil-loaded ultradeformable liposomes for skin therapy. AIP Conf. Proc. 2018, 1990, 020024. [Google Scholar]
- Trujillo-Cayado, L.; Alfaro, M.; Muñoz, J. Effects of ethoxylated fatty acid alkanolamide concentration and processing on d-limonene emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 536, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, T.; Ibrahim, A.; Maddern, G.; Caplash, Y.; Wagstaff, M. Devices measuring transepidermal water loss: A systematic review of measurement properties. Ski. Res. Technol. 2022, 28, 497–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, C.; Han, J.; Cho, J.; Suh, K.; Nam, G. Analysis of electrical property changes of skin by oil-in-water emulsion components. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 402–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).