1064 nm Q-Switched Fractional Laser for Transcutaneous Delivery of a Biostimulator: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of a Split-Face Study
Abstract
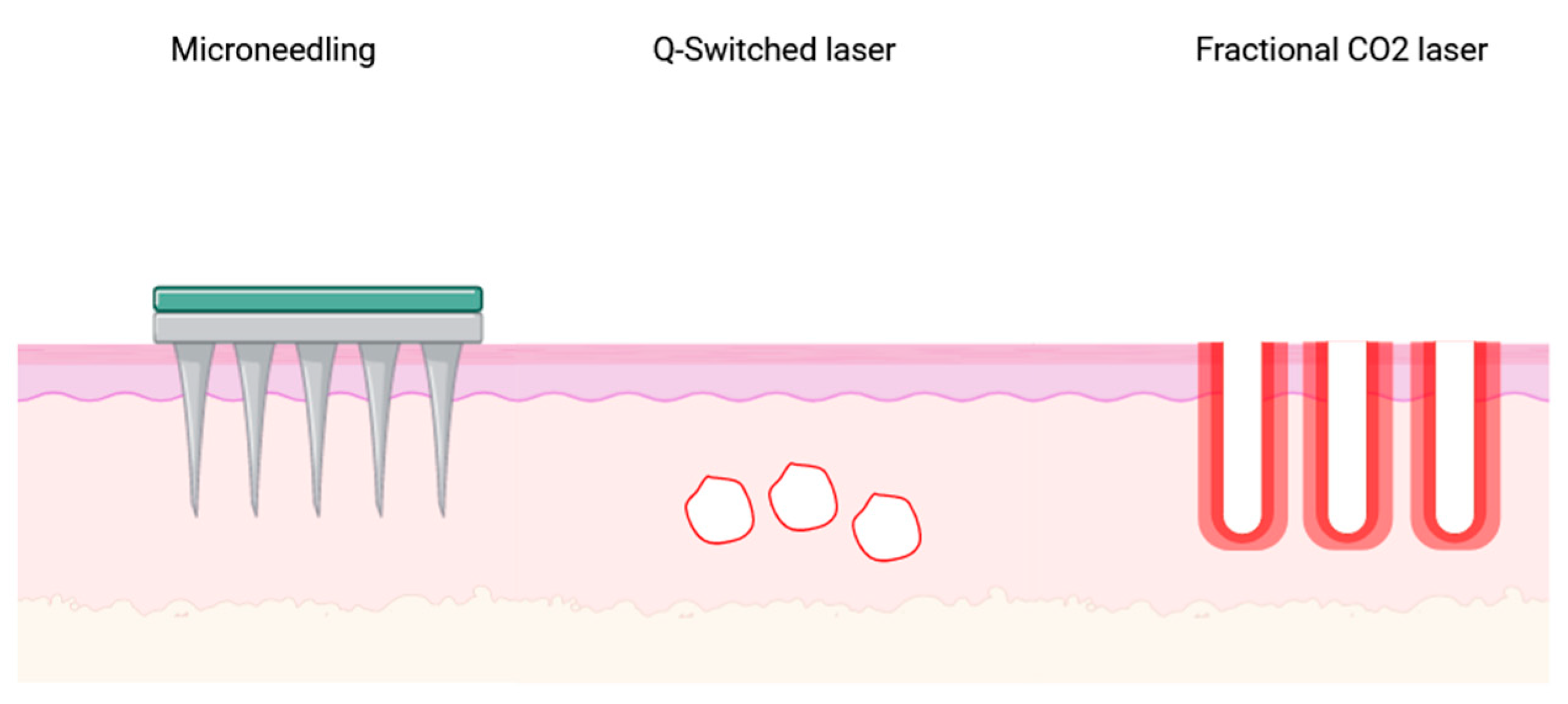
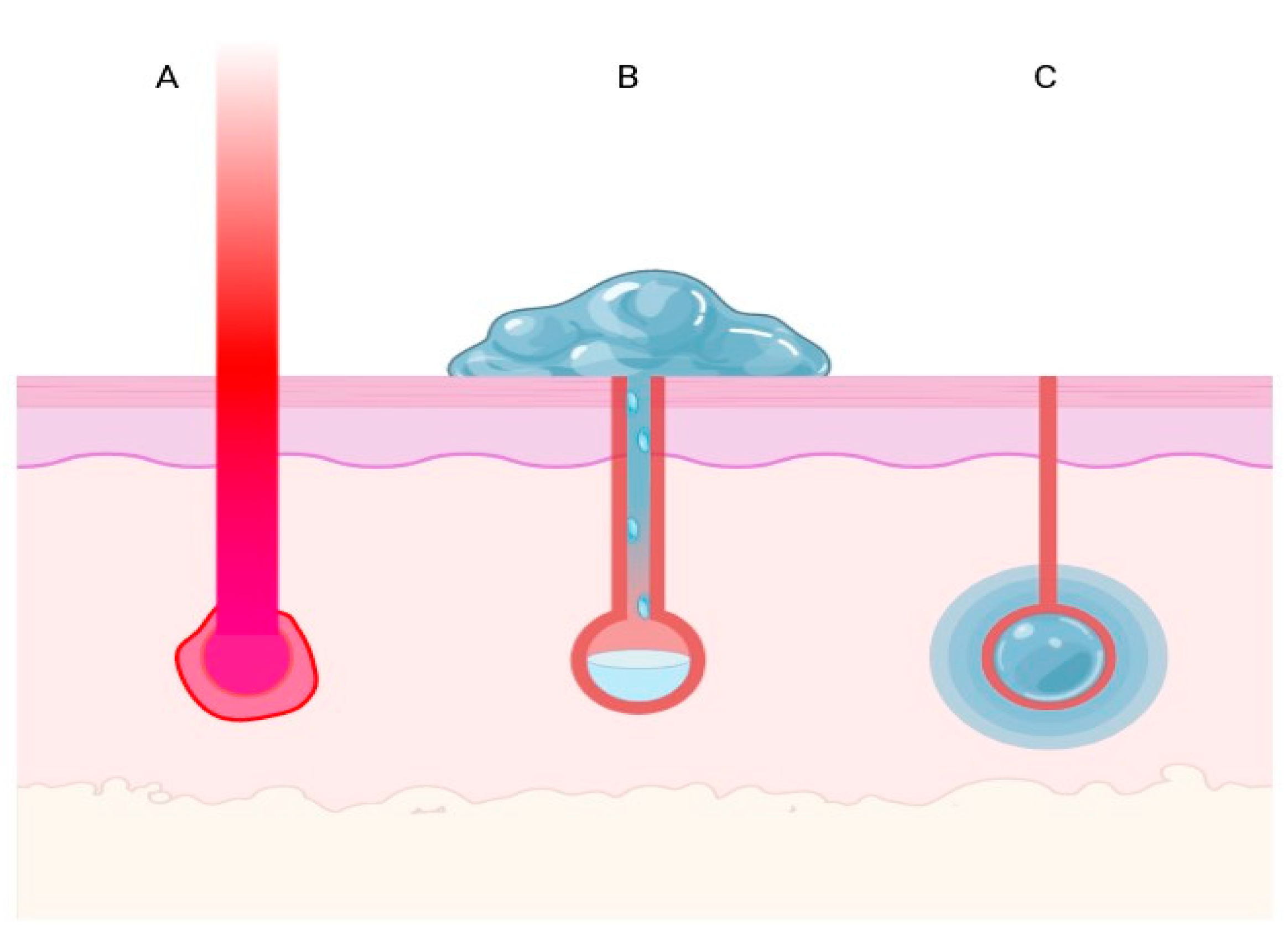
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
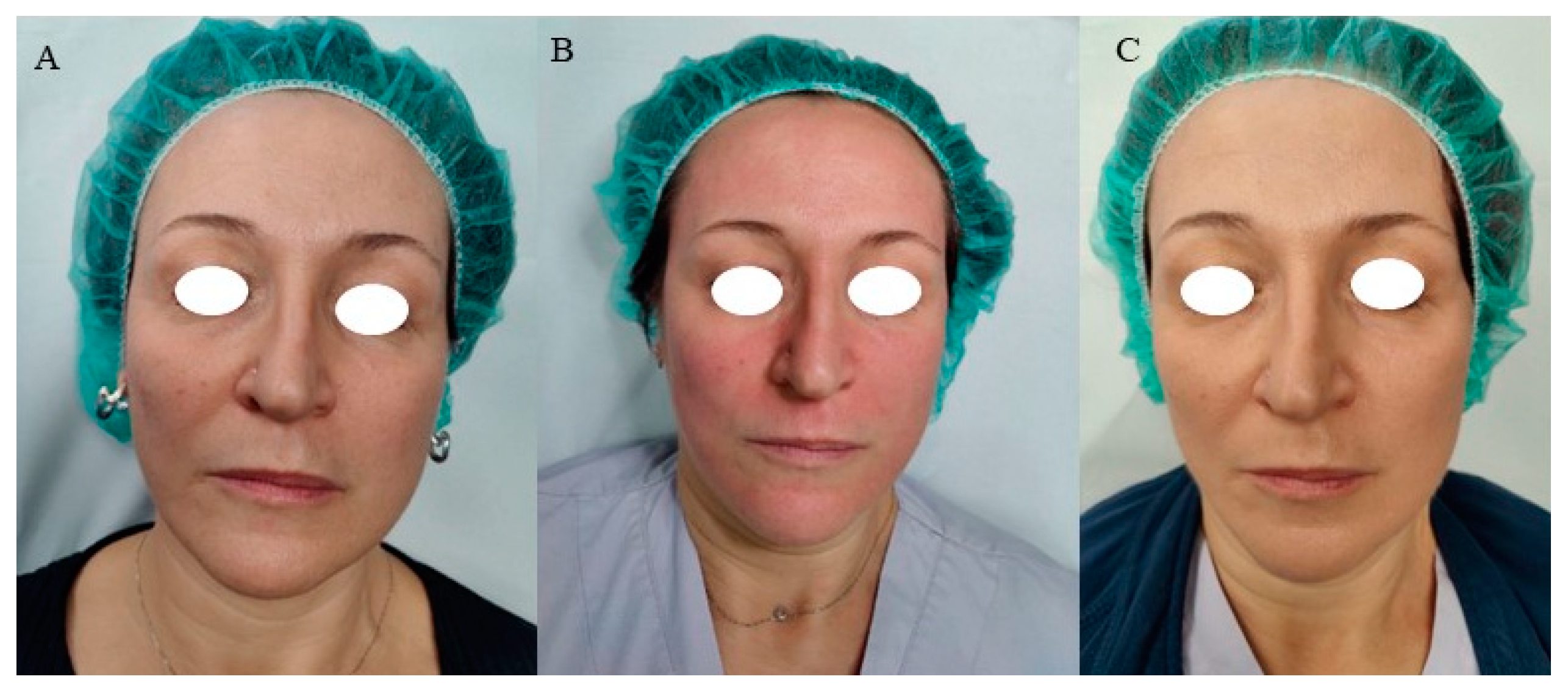
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schoellhammer, C.M.; Blankschtein, D.; Langer, R. Skin permeabilization for transdermal drug delivery: Recent advances and future prospects. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 393–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.B.; Martin, G.P.; Jones, S.A.; Akomeah, F.K. Dermal and transdermal drug delivery systems: Current and future prospects. Drug Deliv. 2006, 13, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivamani, R.K.; Liepmann, D.; Maibach, H.I. Microneedles and transdermal applications. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2007, 4, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkilani, A.Z.; McCrudden, M.T.C.; Donnelly, R.F. Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovative Pharmaceutical Developments Based on Disruption of the Barrier Properties of the stratum corneum. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 438–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waghule, T.; Singhvi, G.; Dubey, S.K.; Pandey, M.M.; Gupta, G.; Singh, M.; Dua, K. Microneedles: A smart approach and increasing potential for transdermal drug delivery system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1249–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labadie, J.G.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Worley, B.; Kang, B.Y.; Rakita, U.; Rigali, S.; Arndt, K.A.; Bernstein, E.; Brauer, J.A.; Chandra, S.; et al. Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Laser-Assisted Drug Delivery. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manstein, D.; Herron, G.S.; Sink, R.K.; Tanner, H.; Anderson, R.R. Fractional photothermolysis: A new concept for cutaneous remodeling using microscopic patterns of thermal injury. Lasers Surg. Med. 2004, 34, 426–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.H.S.; Smith, S.D. Laser-Assisted Drug Delivery: A Systematic Review of Safety and Adverse Events. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, J.; Yue, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zhu, D. 1064 nm-Nd:YAG lasers with different output modes enhancing transdermal delivery: Physical and physiological mechanisms. J. Biomed. Opt. 2013, 18, 61228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haedersdal, M.; Erlendsson, A.M.; Paasch, U.; Anderson, R.R. Translational medicine in the field of ablative fractional laser (AFXL)-assisted drug delivery: A critical review from basics to current clinical status. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2016, 74, 981–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waibel, J.S.; Rudnick, A.; Nousari, C.; Bhanusali, D.G. Fractional Ablative Laser Followed by Transdermal Acoustic Pressure Wave Device to Enhance the Drug Delivery of Aminolevulinic Acid: In Vivo Fluorescence Microscopy Study. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sklar, L.R.; Burnett, C.T.; Waibel, J.S.; Moy, R.L.; Ozog, D.M. Laser assisted drug delivery: A review of an evolving technology. Lasers Surg. Med. 2014, 46, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Fang, J.-Y. Lasers as an approach for promoting drug delivery via skin. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 599–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenande, E.; Anderson, R.R.; Haedersdal, M. Fundamentals of fractional laser-assisted drug delivery: An in-depth guide to experimental methodology and data interpretation. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 153, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haedersdal, M.; Sakamoto, F.H.; Farinelli, W.A.; Doukas, A.G.; Tam, J.; Anderson, R.R. Fractional CO(2) laser-assisted drug delivery. Lasers Surg. Med. 2010, 42, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prausnitz, M.R.; Langer, R. Transdermal drug delivery. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, J.; Loureiro, V.B. Fractional Non-ablative Laser and Drug Delivery. In Drug Delivery in Dermatology: Fundamental and Practical Applications; Kalil, C.L.P.V., Campos, V., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taudorf, E.H.; Haak, C.S.; Erlendsson, A.M.; Philipsen, P.A.; Anderson, R.R.; Paasch, U.; Haedersdal, M. Fractional ablative erbium YAG laser: Histological characterization of relationships between laser settings and micropore dimensions. Lasers Surg. Med. 2014, 46, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.K.; Jeong, K.H.; Kim, N.I.; Shin, M.K. Nonablative fractional laser as a tool to facilitate skin penetration of 5-aminolaevulinic acid with minimal skin disruption: A preliminary study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2014, 170, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalil, C.; Campos, V.B.; Reinehr, C.P.H.; Chaves, C.R.P. Laser toning and drug delivery: A pilot study using laser Q-switched laser 1064nm. Surg. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 8. Available online: https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:113503096 (accessed on 10 November 2023). [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Park, J.W.; Seo, S.J.; Park, K.Y. Evaluating the tolerance and efficacy of laser-assisted delivery of tranexamic acid, niacinamide, and kojic acid for melasma: A single center, prospective, split-face trial. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.K.; Li, K.; Seo, S.J.; Hong, C.K. A randomized, observer-blinded, comparison of combined 1064-nm Q-switched neodymium-doped yttrium-aluminium-garnet laser plus 30% glycolic acid peel vs. laser monotherapy to treat melasma. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2011, 36, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.I.; Shin, M.K.; Jeong, K.-H.; Suh, D.H.; Lee, S.J.; Oh, I.-H.; Lee, M.-H. A randomised comparative study of 1064 nm Neodymium-doped yttrium aluminium garnet (Nd:YAG) laser and topical antifungal treatment of onychomycosis. Mycoses 2016, 59, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyetakin-White, P.; Suggs, A.; Koo, B.; Matsui, M.S.; Yarosh, D.; Cooper, K.D.; Baron, E.D. Does poor sleep quality affect skin ageing? Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 40, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Q.Y.A.; Chew, F.T. Defining skin aging and its risk factors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijsten, T.E.C.; Sampogna, F.; Chren, M.-M.; Abeni, D.D. Testing and reducing skindex-29 using Rasch analysis: Skindex-17. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1244–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chren, M.M.; Lasek, R.J.; Quinn, L.M.; Mostow, E.N.; Zyzanski, S.J. Skindex, a quality-of-life measure for patients with skin disease: Reliability, validity, and responsiveness. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 107, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows 25.0 IBM Corp. (n.d.). IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0; IBM: Armonk, NY, USA, 2007; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- Zaleski-Larsen, L.A.; Fabi, S.G. Laser-Assisted Drug Delivery. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2016, 42, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegre-Sánchez, A.; Jiménez-Gómez, N.; Boixeda, P. Laser-Assisted Drug Delivery. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2018, 109, 858–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Voyer, J.; Li, Y.; Kang, X.; Chen, X. Laser microporation facilitates topical drug delivery: A comprehensive review about preclinical development and clinical application. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2023, 20, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searle, T.; Ali, F.R.; Al-Niaimi, F. Lessons Learned from the First Decade of Laser-Assisted Drug Delivery. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; He, H. A review of cosmetic skin delivery. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, M.; Hsu, T.-S.; Dover, J.S.; Wrone, D.A.; Arndt, K.A. Nonablative laser and light treatments: Histology and tissue effects—A review. Lasers Surg. Med. 2003, 33, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fatemi, A.; Weiss, M.A.; Weiss, R.A. Short-term histologic effects of nonablative resurfacing: Results with a dynamically cooled millisecond-domain 1320 nm Nd:YAG laser. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2002, 28, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanzi, E.L.; Alster, T.S. Comparison of a 1450-nm diode laser and a 1320-nm Nd:YAG laser in the treatment of atrophic facial scars: A prospective clinical and histologic study. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2004, 30, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippis, A.; Perfetto, B.; Guerrera, L.P.; Oliviero, G.; Baroni, A. Q-switched 1064 nm Nd-Yag nanosecond laser effects on skin barrier function and on molecular rejuvenation markers in keratinocyte-fibroblasts interaction. Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 34, 595–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Duan, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, Q.; Guo, B.; Xiang, S.; Jia, X.; He, L. The effect of Q-switched 1064-nm Nd: YAG laser on skin barrier and collagen synthesis via miR-663a to regulate TGFβ1/smad3/p38MAPK pathway. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 2021, 37, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifrach, H. Non-ablative laser treatment improves lip volume, texture, and color. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Laser Dermatol. 2022, 24, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.J.; Silapunt, S. Histologic evaluation of a Q-switched Nd:YAG laser in the nonablative treatment of wrinkles. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2001, 27, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, Y.; Ye, X.; Weng, Y.; Tong, Z.; Ren, Q. Effects of the 532-nm and 1,064-nm Q-switched Nd:YAG lasers on collagen turnover of cultured human skin fibroblasts: A comparative study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2010, 25, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watchmaker, L.E.; Watchmaker, J.D.; Callaghan, D.; Arndt, K.A.; Dover, J.S. The Unhappy Cosmetic Patient: Lessons From Unfavorable Online Reviews of Minimally and Noninvasive Cosmetic Procedures. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2020, 46, 1191–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, A.; Maisel, A.; Weil, A.; Iyengar, S.; Sacotte, K.; Lazaroff, J.M.; Kurumety, S.; Shaunfield, S.L.; Reynolds, K.A.; Poon, E.; et al. Patients believe that cosmetic procedures affect their quality of life: An interview study of patient-reported motivations. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2019, 80, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carroll, L.; Humphreys, T.R. LASER-tissue interactions. Clin. Dermatol. 2006, 24, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aust, M.C.; Knobloch, K.; Reimers, K.; Redeker, J.; Ipaktchi, R.; Altintas, M.A.; Gohritz, A.; Schwaiger, N.; Vogt, P.M. Percutaneous collagen induction therapy: An alternative treatment for burn scars. Burns 2010, 36, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šuca, H.; Zajíček, R.; Vodsloň, Z. Microneedling—A form of collagen induction therapy—Our first experiences. Acta Chir. Plast. 2017, 59, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Moftah, N.H.; El Khayyat, M.A.M.; Ragai, M.H.; Alaa, H. Carboxytherapy Versus Skin Microneedling in Treatment of Atrophic Postacne Scars: A Comparative Clinical, Histopathological, and Histometrical Study. Dermatol. Surg. Off. Publ. Am. Soc. Dermatol. Surg. 2018, 44, 1332–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| % | m (SD) | |
|---|---|---|
| Age | 44.87 (7.73) | |
| Female sex | 100 | |
| BMI | 21.58 (3.86) | |
| Smoking habit Yes | 66.7 | |
| Insomnia Yes | 55.6 |
| Mean | SD | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Skin Hydration baseline | 59.56 | 8.71 |
| Skin Hydration Laser + Drug 3-week FU | 67.30 | 5.45 | |
| 2 | Skin Elasticity baseline | 66.10 | 13.51 |
| Skin Elasticity Laser + Drug 3-week FU | 67.10 | 8.59 | |
| 3 | Skin Hydration Laser + Drug 3-week FU | 67.30 | 5.45 |
| Skin Hydration Only Laser 3-week FU | 59.60 | 7.47 | |
| 4 | Skin Elasticity Laser + Drug 3-week FU | 67.10 | 8.59 |
| Skin Elasticity Laser 3-week FU | 65.20 | 7.84 |
| Means | SD | 95% L.C.I. (df9) | 95% U.C.I. (df9) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skin Hydration baseline vs. Skin Hydration Laser + Drug 3-week FU | −7.740 | 4.201 | −10.745 | −4.734 | <0.001 |
| Skin Elasticity baseline vs. Skin Elasticity Laser + Drug 3-week FU | −1.000 | 11.175 | −8.994 | 6.994 | 0.784 |
| Skin Hydration Laser + Drug 3-week FU vs. Skin Hydration Only Laser 3-week FU | 7.700 | 4.667 | 4.360 | 11.039 | <0.001 |
| Skin Elasticity Laser + Drug 3-week FU vs. Skin Elasticity Laser 3-week FU | 1.900 | 2.846 | −0.135 | 3.935 | 0.064 |
| m (SD) | |
|---|---|
| Physical domain | 10.00 (12.472) |
| Psychosocial domain | 0.417 (1.318) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moro, F.; Camela, E.; Samela, T.; Pirrotta, L.; Pupa, M.B.; Zingoni, T.; Fusco, I.; Colonna, L. 1064 nm Q-Switched Fractional Laser for Transcutaneous Delivery of a Biostimulator: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of a Split-Face Study. Cosmetics 2024, 11, 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010014
Moro F, Camela E, Samela T, Pirrotta L, Pupa MB, Zingoni T, Fusco I, Colonna L. 1064 nm Q-Switched Fractional Laser for Transcutaneous Delivery of a Biostimulator: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of a Split-Face Study. Cosmetics. 2024; 11(1):14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010014
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoro, Francesco, Elisa Camela, Tonia Samela, Lia Pirrotta, Maria Beatrice Pupa, Tiziano Zingoni, Irene Fusco, and Laura Colonna. 2024. "1064 nm Q-Switched Fractional Laser for Transcutaneous Delivery of a Biostimulator: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of a Split-Face Study" Cosmetics 11, no. 1: 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010014
APA StyleMoro, F., Camela, E., Samela, T., Pirrotta, L., Pupa, M. B., Zingoni, T., Fusco, I., & Colonna, L. (2024). 1064 nm Q-Switched Fractional Laser for Transcutaneous Delivery of a Biostimulator: Efficacy and Safety Outcomes of a Split-Face Study. Cosmetics, 11(1), 14. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics11010014







