Quantification of Cisplatin Encapsulated in Nanomedicine: An Overview
Abstract
1. Introduction
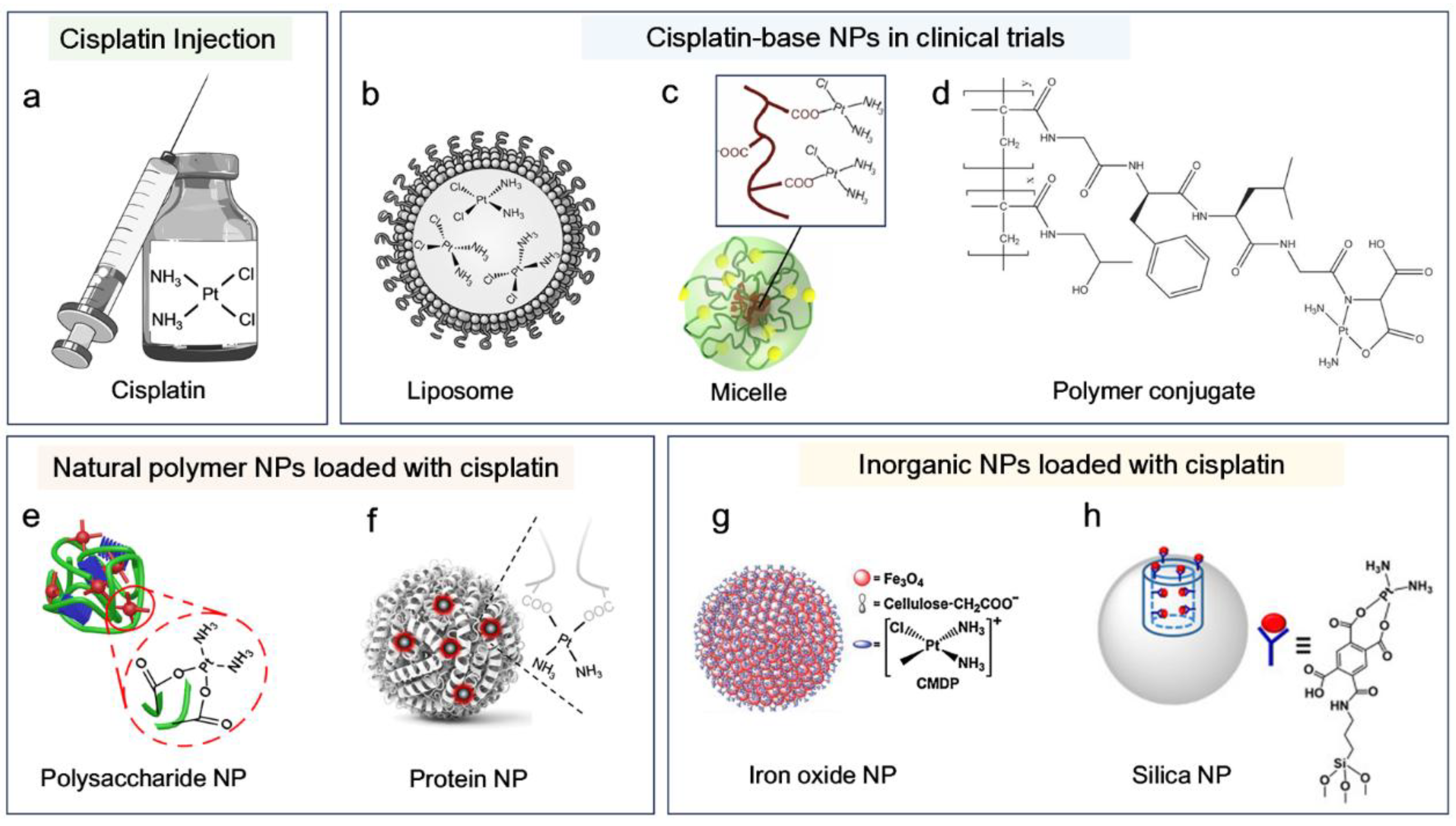
2. Cisplatin-Based Nanomedicine
2.1. Nanomedicine-Based Strategies to Enhance Cisplatin Therapy
2.2. Advances in Cisplatin-Based Nanomedicine
3. Determination of Cisplatin Loaded in NPs
3.1. The Importance of Accurate Determination of Cisplatin in Nanomedicine
3.2. The Main Strategies Used for Quantification of Cisplatin in NPs
3.2.1. Spectrophotometric Method
3.2.2. HPLC Techniques
3.2.3. Quantitative Analysis of Pt Element
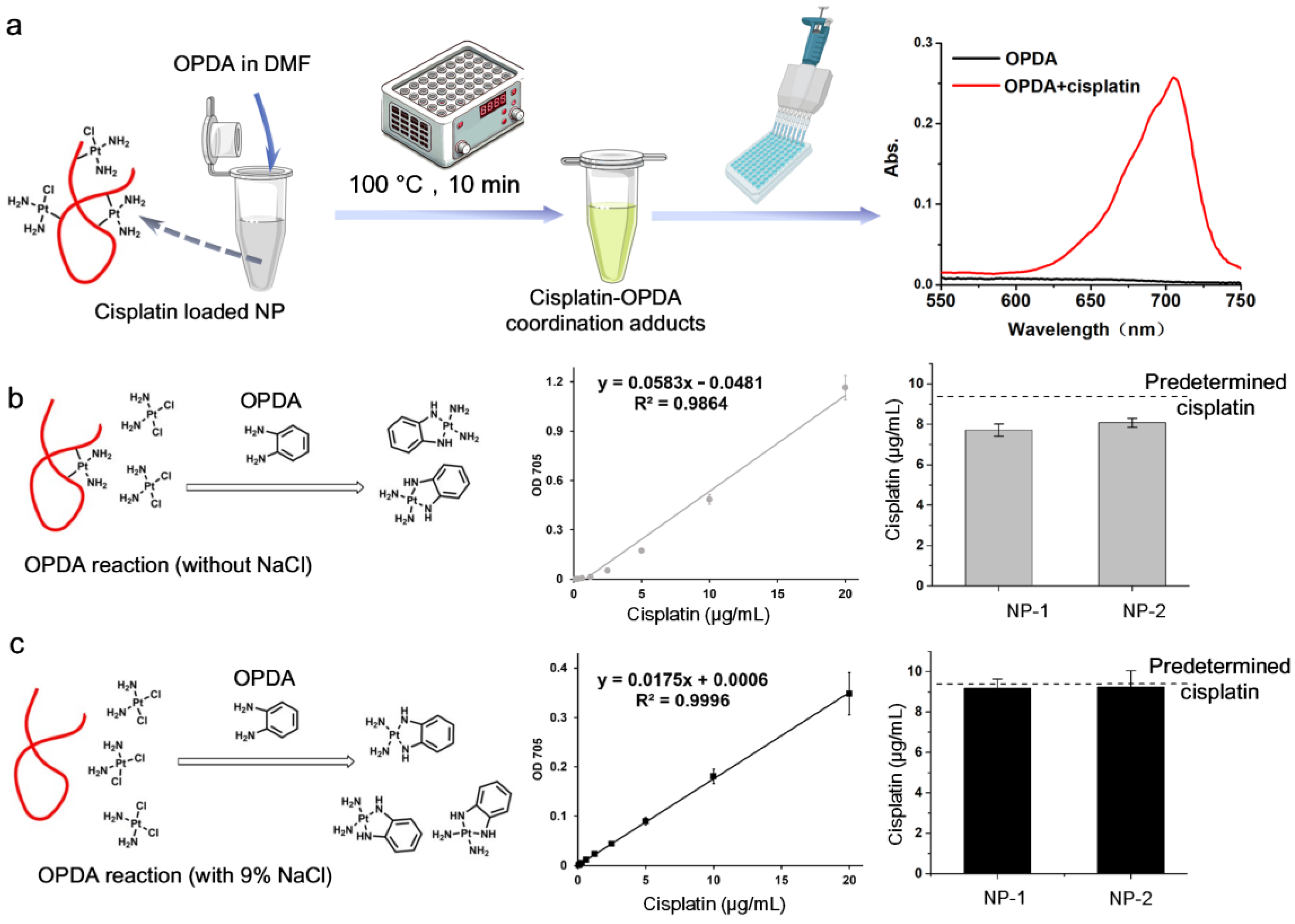
3.2.4. Spectrophotometric Determination Based on Cisplatin’s Derivatizing Reaction
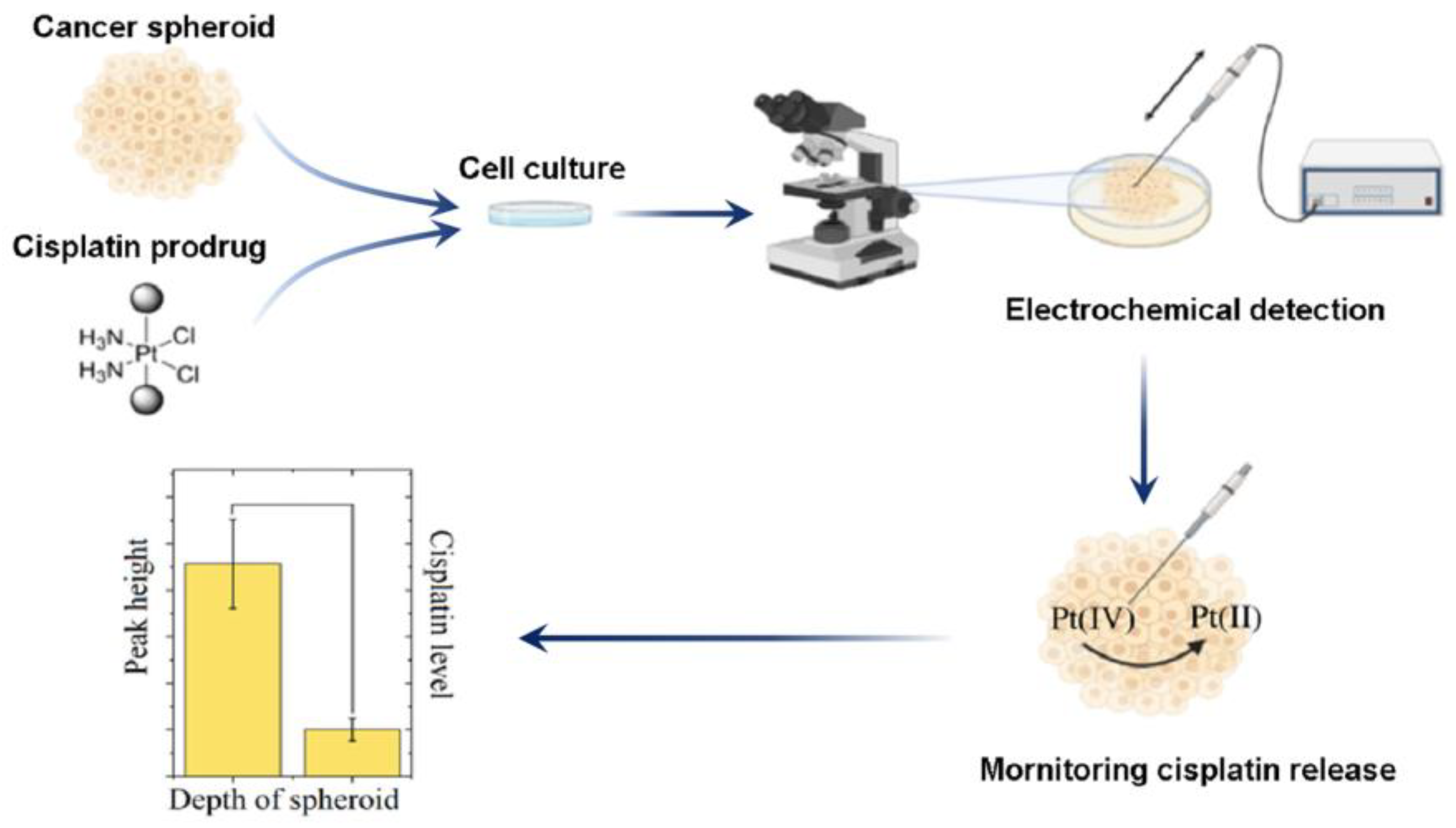
3.2.5. Electrochemical Determination
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. The next generation of platinum drugs: Targeted Pt (II) agents, nanoparticle delivery, and Pt (IV) prodrugs. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 3436–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S. Cisplatin: The first metal based anticancer drug. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 88, 102925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnstone, T.C.; Suntharalingam, K.; Lippard, S.J. Third row transition metals for the treatment of cancer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2015, 373, 20140185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, L.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, F.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F. Advances in toxicological research of the anticancer drug cisplatin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2019, 32, 1469–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinho, N.; Santos, T.C.; Florindo, H.F.; Silva, L.C. Cisplatin-membrane interactions and their influence on platinum complexes activity and toxicity. Front. Physiol. 2019, 9, 1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kryczka, J.; Kryczka, J.; Czarnecka-Chrebelska, K.H.; Brzeziańska-Lasota, E. Molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance induced by cisplatin in NSCLC cancer therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Brenner, C.; Szabadkai, G.; Harel-Bellan, A.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Systems biology of cisplatin resistance: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi, L.; Senovilla, L.; Vitale, I.; Michels, J.; Martins, I.; Kepp, O.; Castedo, M.; Kroemer, G. Molecular mechanisms of cisplatin resistance. Oncogene 2012, 31, 1869–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tung, C.-H. Redox-responsive cisplatin nanogels for anticancer drug delivery. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 8367–8370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulikas, T.; Pantos, A.; Bellis, E.; Christofis, P. Designing platinum compounds in cancer: Structures and mechanisms. Cancer Ther. 2007, 5, 537–583. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Miura, Y.; Mochida, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Toh, K.; Anraku, Y.; Melo, V.; Liu, X.; Ishii, T.; Nagano, O. Glucose transporter 1-mediated vascular translocation of nanomedicines enhances accumulation and efficacy in solid tumors. J. Control. Release 2019, 301, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Cano, C.; Hannon, M.J. Novel and emerging approaches for the delivery of metallo-drugs. Dalton Trans. 2009, 48, 10702–10711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Tung, C.-H. Beyond chemotherapeutics: Cisplatin as a temporary buckle to fabricate drug-loaded nanogels. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, A.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, J.; Ding, X.; Chen, Y.; Du, J.; Wei, S.; Sun, H.; Xu, J.; Yu, S. Bioresponsive cisplatin crosslinked albumin hydrogel served for efficient cancer combination therapy. Nano Res. 2023, 16, 2762–2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Li, C.; Dai, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Hou, Z.; Lin, J. Inorganic nanocarriers for platinum drug delivery. Mater. Today 2015, 18, 554–564. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.S.; Jung, M.H.; Lee, Y.-S.; Bae, J.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Ha, C.-S. Functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles with excellent cytotoxicity against various cancer cells for pH-responsive and controlled drug delivery. Mater. Des. 2019, 184, 108187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surnar, B.; Sharma, K.; Jayakannan, M. Core–shell polymer nanoparticles for prevention of GSH drug detoxification and cisplatin delivery to breast cancer cells. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 17964–17979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Wen, P.; Li, J.; Kataoka, K. Targeted nanomedicine in cisplatin-based cancer therapeutics. J. Control. Release 2022, 345, 709–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Jun, E.; Chang, H.; Yhee, J.Y.; Koh, E.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Jung, J.Y.; Jeong, E.J.; Lee, J.W.; Shim, M.K. Prediction the clinical EPR effect of nanoparticles in patient-derived xenograft models. J. Control. Release 2022, 351, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, P.; Wang, Y.; Wei, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, B.; Xiao, H.; Song, H.; Mao, X. Nanoparticle-based drug delivery systems with platinum drugs for overcoming cancer drug resistance. J. Mater. Chem. B 2021, 9, 5173–5194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, H.; Wu, T.; Yu, B.; Cong, H.; Shen, Y. Nanodrugs based on co-delivery strategies to combat cisplatin resistance. J. Control. Release 2024, 370, 14–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourmadadi, M.; Eshaghi, M.M.; Rahmani, E.; Ajalli, N.; Bakhshi, S.; Mirkhaef, H.; Lasemi, M.V.; Rahdar, A.; Behzadmehr, R.; Diez-Pascual, A.M. Cisplatin-loaded nanoformulations for cancer therapy: A comprehensive review. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 77, 103928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, X.; Kagan, L. Physiologically-Based Modeling and Interspecies Prediction of Cisplatin Pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 113, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tung, C.-H. Cisplatin cross-linked multifunctional nanodrugplexes for combination therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 8547–8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, G.; Curcio, M.; Cirillo, G.; Spizzirri, U.G.; Besharat, Z.M.; Abballe, L.; Vacca, A.; Iemma, F.; Picci, N.; Ferretti, E. Albumin nanoparticles for glutathione-responsive release of cisplatin: New opportunities for medulloblastoma. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 517, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sala, L.; Perecko, T.; Mestek, O.; Pinkas, D.; Homola, T.; Kocisek, J. Cisplatin-cross-linked DNA origami nanostructures for drug delivery applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 13267–13275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkesh, K.; Heidari, R.; Iranpour, P.; Azarpira, N.; Ahmadi, F.; Mohammadi-Samani, S.; Farjadian, F. Theranostic hyaluronan coated EDTA modified magnetic mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted delivery of cisplatin. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 77, 103903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boztepe, T.; Castro, G.R.; León, I.E. Lipid, polymeric, inorganic-based drug delivery applications for platinum-based anticancer drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 605, 120788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zajda, J.; Wróblewska, A.; Ruzik, L.; Matczuk, M. Methodology for characterization of platinum-based drug’s targeted delivery nanosystems. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahednezhad, F.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Shahbazi Mojarrad, J.; Valizadeh, H. The latest advances of cisplatin liposomal formulations: Essentials for preparation and analysis. Expert. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 523–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrichi, H.; Kouki, N.; Tar, H. Analytical methods for the quantification of cisplatin, carboplatin, and oxaliplatin in various matrices over the last two decades. Curr. Pharm. Anal. 2022, 18, 455–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Huang, Y.; Ren, C.; Xiong, S.; Guo, X.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, L.; Huang, Z. Construction of Cisplatin-18-Crown-6 Complexes Through Supramolecular Chemistry to Improve Solubility, Stability, and Antitumor Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahednezhad, F.; Zakeri-Milani, P.; Mojarrad, J.S.; Sarfraz, M.; Mahmoudian, M.; Baradaran, B.; Valizadeh, H. Acetyl carnitine modified liposomes elevate cisplatin uptake in macrophage and cancer cells. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.H.; Tian, M.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, Y.N. Preparation of novel cisplatin-conjugated hollow gold nanospheres for targeting cervical cancer. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 16475–16484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, S.V.; Prakash, T. Kinetics of cisplatin release by in-vitro using poly (D, L-Lactide) coated Fe3O4 Nanocarriers. IEEE Trans. NanoBiosci. 2013, 12, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.G.; Hanafy, N.A.; Ali, R.A.; El-Monem, D.D.A.; El-Shafiey, S.H.; El-Magd, M.A. Unveiling the therapeutic potential of anthocyanin/cisplatin-loaded chitosan nanoparticles against breast and liver cancers. Cancer Nanotechnol. 2024, 15, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iram, S.; Zahera, M.; Wahid, I.; Baker, A.; Raish, M.; Khan, A.; Ali, N.; Ahmad, S.; Khan, M.S. Cisplatin bioconjugated enzymatic GNPs amplify the effect of cisplatin with acquiescence. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.; Zhu, J.; Ismail, M.A.; Li, B. Dual encapsulation and sequential release of cisplatin and vitamin E from soy polysaccharides and β-cyclodextrin bioadhesive hydrogel nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 273, 133240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iram, S.; Zahera, M.; Khan, S.; Khan, I.; Syed, A.; Ansary, A.A.; Ameen, F.; Shair, O.H.; Khan, M.S. Gold nanoconjugates reinforce the potency of conjugated cisplatin and doxorubicin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 160, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.D.; Telma, K.A.; Chang, K.-E.; Lee, T.D.; Madigan, J.P.; Lloyd, J.R.; Goldlust, I.S.; Hoeschele, J.D.; Gottesman, M.M. Say no to DMSO: Dimethylsulfoxide inactivates cisplatin, carboplatin, and other platinum complexes. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3913–3922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.; Cheriyamundath, S.; Madassery, J. Dimethyl sulfoxide inactivates the anticancer effect of cisplatin against human myelogenous leukemia cell lines in in vitro assays. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 322–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kai, M.P.; Keeler, A.W.; Perry, J.L.; Reuter, K.G.; Luft, J.C.; O’Neal, S.K.; Zamboni, W.C.; DeSimone, J.M. Evaluation of drug loading, pharmacokinetic behavior, and toxicity of a cisplatin-containing hydrogel nanoparticle. J. Control. Release 2015, 204, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arenas, M.; Martín, J.; Santos, J.L.; Aparicio, I.; Fernández-Sanfrancisco, O.; Alonso, E. Comparison of different techniques for the determination of platinized cytostatic drugs in urine samples. Molecules 2022, 27, 8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosch, M.E.; Sánchez, A.R.; Rojas, F.S.; Ojeda, C.B. Analytical methodologies for the determination of cisplatin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Flores, A.; Jurado, R.; Garcia-Lopez, P. A high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for determination of cisplatin in plasma, cancer cell, and tumor samples. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2005, 52, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toro-Córdova, A.; Ledezma-Gallegos, F.; Mondragon-Fuentes, L.; Jurado, R.; Medina, L.A.; Pérez-Rojas, J.M.; Garcia-Lopez, P. Determination of liposomal cisplatin by high-performance liquid chromatography and its application in pharmacokinetic studies. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 1016–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Du, Z.; Wang, P.; Guo, H.; Zhang, H.; Lei, X.; Ren, F. 2-deoxyglucose-modified folate derivative: Self-assembling nanoparticle able to load cisplatin. Molecules 2019, 24, 1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Tang, Q.; Xue, W.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. The preparation and characterization of folate-conjugated human serum albumin magnetic cisplatin nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Res. 2010, 24, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meermann, B.; Sperling, M. Hyphenated techniques as tools for speciation analysis of metal-based pharmaceuticals: Developments and applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1501–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planeta, K.; Kubala-Kukus, A.; Drozdz, A.; Matusiak, K.; Setkowicz, Z.; Chwiej, J. The assessment of the usability of selected instrumental techniques for the elemental analysis of biomedical samples. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Gao, M.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhang, W. Harnessing the CD44-targeted delivery of self-assembled hyaluronan nanogel to reverse the antagonism between Cisplatin and Gefitinib in NSCLC cancer therapy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2024, 344, 122521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Deng, H.; Gao, M.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, R.; Hou, W.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W. Radiotherapy potentiates the P-selectin targeted cancer drug delivery based on a cisplatin and mitoxantrone coassembled fucoidan nanogel. ACS Mater. Lett. 2023, 5, 2843–2851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Romero, L.; Díez, P.; Montes-Bayón, M. Bioanalytical strategies to evaluate cisplatin nanodelivery systems: From synthesis to incorporation in individual cells and biological response. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2024, 237, 115760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Trujillo, S.; Jiménez-Moreno, M.; Rodríguez-Fariñas, N.; Rodríguez Martín-Doimeadios, R.C. Critical evaluation of the potential of ICP-MS-based systems in toxicological studies of metallic nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2024, 416, 2657–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riisom, M.; Gammelgaard, B.; Lambert, I.H.; Stürup, S. Development and validation of an ICP-MS method for quantification of total carbon and platinum in cell samples and comparison of open-vessel and microwave-assisted acid digestion methods. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 158, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Kinsella, J.M.; Jandial, D.D.; Howell, S.B.; Sailor, M.J. Cisplatin-loaded porous Si microparticles capped by electroless deposition of platinum. Small 2011, 7, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bełdzińska, P.; Galikowska-Bogut, B.; Zakrzewski, M.; Bury, K.; Jamrógiewicz, M.; Wyrzykowski, D.; Gołuński, G.; Sądej, R.; Piosik, J. Platinum as both a drug and its modulator–Do platinum nanoparticles influence cisplatin activity? Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2025, 407, 111365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golla, E.D.; Ayres, G.H. Spectrophotometric determination of platinum with o-phenylenediamine. Talanta 1973, 20, 199–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anilanmert, B.; Yalçin, G.; Ariöz, F.; Dölen, E. The spectrophotometric determination of cisplatin in urine, using o-phenylenediamine as derivatizing agent. Anal. Lett. 2001, 34, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basotra, M.; Singh, S.K.; Gulati, M. Development and validation of a simple and sensitive spectrometric method for estimation of cisplatin hydrochloride in tablet dosage forms: Application to dissolution studies. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2013, 2013, 936254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talele, D.; Patel, D. Spectrophotometric Determination of Cisplatin Using Derivatizing Agent. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Nanotechnol. 2023, 16, 6504–6511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catanzaro, D.; Nicolosi, S.; Cocetta, V.; Salvalaio, M.; Pagetta, A.; Ragazzi, E.; Montopoli, M.; Pasut, G. Cisplatin liposome and 6-amino nicotinamide combination to overcome drug resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vhora, I.; Khatri, N.; Desai, J.; Thakkar, H.P. Caprylate-conjugated cisplatin for the development of novel liposomal formulation. AAPS Pharmscitech 2014, 15, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Li, Y.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Xi, F. Supramolecular hydrogels from cisplatin-loaded block copolymer nanoparticles and α-cyclodextrins with a stepwise delivery property. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 3086–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Luo, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, B.; Luo, K.; Lan, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, S. DOTA functionalized cross-linked small-molecule micelles for theranostics combining magnetic resonance imaging and chemotherapy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 3402–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Su, M. Polydopamine nanoparticles for combined chemo-and photothermal cancer therapy. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amreddy, N.; Babu, A.; Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y.D.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Chemo-biologic combinatorial drug delivery using folate receptor-targeted dendrimer nanoparticles for lung cancer treatment. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Du, B.; Gao, M.; Tung, C.-H. A hybrid nanogel to preserve lysosome integrity for fluorescence imaging. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 16442–16451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tung, C.-H. Lysosome enlargement enhanced photochemotherapy using a multifunctional nanogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4343–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tung, C.H. Sequence-Independent DNA Nanogel as a Potential Drug Carrier. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2017, 38, 1700366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, H.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, W. Facile preparation of toluidine blue-loaded DNA nanogels for anticancer photodynamic therapy. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2023, 11, 1180448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varache, M.; Bezverkhyy, I.; Weber, G.; Saviot, L.; Chassagnon, R.; Baras, F.; Bouyer, F. Loading of cisplatin into mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Effect of surface functionalization. Langmuir 2019, 35, 8984–8995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong-Thi, N.-H.; Nguyen, N.H.; Nguyen, D.T.D.; Tang, T.N.; Nguyen, T.H.; Nguyen, D.H. pH-responsive delivery of Platinum-based drugs through the surface modification of heparin on mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Eur. Polym. J. 2023, 185, 111818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrlova, J.; Potesil, D.; Zehnalek, J.; Sures, B.; Adam, V.; Trnkova, L.; Kizek, R. Cisplatin electrochemical biosensor. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 5169–5173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; He, X.; Chen, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Conformational switch for cisplatin with hemin/G-quadruplex DNAzyme supersandwich structure. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaneev, A.N.; Gorelkin, P.V.; Krasnovskaya, O.O.; Akasov, R.A.; Spector, D.V.; Lopatukhina, E.V.; Timoshenko, R.V.; Garanina, A.S.; Zhang, Y.; Salikhov, S.V. In vitro/in vivo electrochemical detection of Pt (II) species. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 4901–4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, H.R.S.; da Silva, J.S.; de Oliveira Farias, E.A.; Teixeira, P.R.S.; Eiras, C.; Nunes, L.C.C. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors for the analysis of antineoplastic drugs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 108, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theyagarajan, K.; Sruthi, V.P.; Satija, J.; Senthilkumar, S.; Kim, Y.-J. Materials and design strategies for the electrochemical detection of antineoplastic drugs: Progress and perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2024, 161, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dospivova, D.; Smerkova, K.; Ryvolova, M.; Hynek, D.; Adam, V.; Kopel, P.; Stiborova, M.; Eckschlager, T.; Hubalek, J.; Kizek, R. Catalytic electrochemical analysis of platinum in Pt-DNA adducts. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2012, 7, 3072–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizkova, S.; Adam, V.; Petrlova, J.; Zitka, O.; Stejskal, K.; Zehnalek, J.; Sures, B.; Trnkova, L.; Beklova, M.; Kizek, R. A Suggestion of Electrochemical Biosensor for Study of Platinum (II)-DNA Interactions. Electroanal. Int. J. Devoted Fundam. Pract. Asp. Electroanal. 2007, 19, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascini, M.; Bagni, G.; Pietro, M.L.D.; Ravera, M.; Baracco, S.; Osella, D. Electrochemical biosensor evaluation of the interaction between DNA and metallo-drugs. Biometals 2006, 19, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, E.L.; Gooding, J.J. The electrochemical monitoring of the perturbation of charge transfer through DNA by cisplatin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8950–8951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lai, R.Y. Tunable signal-off and signal-on electrochemical cisplatin sensor. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 9984–9989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Arroyo-Currás, N. Nucleic Acid-based Electrochemical Sensors Facilitate the Study of DNA Binding by Platinum (II)-based Antineoplastics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202312402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Materon, E.M.; Wong, A.; Klein, S.I.; Liu, J.; Sotomayor, M.D. Multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified screen-printed electrodes for cisplatin detection. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 158, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholivand, M.B.; Ahmadi, E.; Mavaei, M. A novel voltammetric sensor based on graphene quantum dots-thionine/nano-porous glassy carbon electrode for detection of cisplatin as an anti-cancer drug. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 299, 126975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumngern, S.; Choosang, J.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Numnuam, A. Voltammetric sensor for an anti-cancer drug cisplatin based on bismuth nanoparticles/graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 2024, 267, 125147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrag, C.; Noroozifar, M.; Kerman, K. Ultralight 3D Graphene Oxide Aerogel Decorated with Pd–Fe Nanoparticles for the Simultaneous Detection of Eight Biomolecules. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 27502–27514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Miguel, L.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G.; Caudron, E.; Arpinati, L.; Doménech-Carbó, A.; Ponchel, G. Bone-targeted cisplatin-complexed poly (γ-benzyl-L-glutamate)–poly (glutamic acid) block polymer nanoparticles: An electrochemical approach. ChemElectroChem 2015, 2, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, L.; Popa, I.; Noiray, M.; Caudron, E.; Arpinati, L.; Desmaele, D.; Cebrián-Torrejón, G.; Doménech-Carbó, A.; Ponchel, G. Osteotropic polypeptide nanoparticles with dual hydroxyapatite binding properties and controlled cisplatin delivery. Pharm. Res. 2015, 32, 1794–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spector, D.V.; Erofeev, A.S.; Gorelkin, P.V.; Vaneev, A.N.; Akasov, R.A.; Ul’yanovskiy, N.V.; Nikitina, V.N.; Semkina, A.S.; Vlasova, K.Y.; Soldatov, M.A. Electrochemical Detection of a Novel Pt (IV) Prodrug with the Metronidazole Axial Ligand in the Hypoxic Area. Inorg. Chem. 2022, 61, 14705–14717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krasnovskaya, O.O.; Akasov, R.A.; Spector, D.V.; Pavlov, K.G.; Bubley, A.A.; Kuzmin, V.A.; Kostyukov, A.A.; Khaydukov, E.V.; Lopatukhina, E.V.; Semkina, A.S. Photoinduced Reduction of Novel Dual-Action Riboplatin Pt (IV) Prodrug. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 12882–12894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Methods | Principle | Measurement Time | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectrophotometric method | UV-Vis absorbance | <10 min | Simple, cheap | Low sensitivity and specificity |
| HPLC/HPLC-MS | Chromatographic separation and detection | ~20–60 min | High specificity, structure determination (with MS) | Sample pretreatment, sophisticated instrumentation |
| ICP-MS/OES | Elemental analysis of Pt | ~10–30 min | Excellent sensitivity and accuracy | Sample pretreatment, sophisticated instrumentation, detection of the ion form of Pt |
| OPDA method | Derivatization of cisplatin with OPDA | ~20 min | Simple, cheap, user-friendly | Interference by sulfurs/thiols |
| Electrochemical determination | Redox activity of Pt (II) | ~10 min | Ease of operation, cheap, rapid detection | Sample pretreatment, interference by other electroactive species, less used for cisplatin nanomedicine |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Wen, T.; Deng, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, H.; Chang, H.; Xu, H.; Zhang, W. Quantification of Cisplatin Encapsulated in Nanomedicine: An Overview. Biosensors 2025, 15, 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050293
Zhang Z, Chen J, Wen T, Deng H, Zhang Y, Guo H, Chang H, Xu H, Zhang W. Quantification of Cisplatin Encapsulated in Nanomedicine: An Overview. Biosensors. 2025; 15(5):293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050293
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ziwen, Jiayu Chen, Tao Wen, Hong Deng, Yiyi Zhang, Hua Guo, Hui Chang, Haiyan Xu, and Weiqi Zhang. 2025. "Quantification of Cisplatin Encapsulated in Nanomedicine: An Overview" Biosensors 15, no. 5: 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050293
APA StyleZhang, Z., Chen, J., Wen, T., Deng, H., Zhang, Y., Guo, H., Chang, H., Xu, H., & Zhang, W. (2025). Quantification of Cisplatin Encapsulated in Nanomedicine: An Overview. Biosensors, 15(5), 293. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050293






