Enzyme-Based Solid-Phase Electrochemiluminescence Sensors with Stable, Anchored Emitters for Sensitive Glucose Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Measurements and Instrumentations
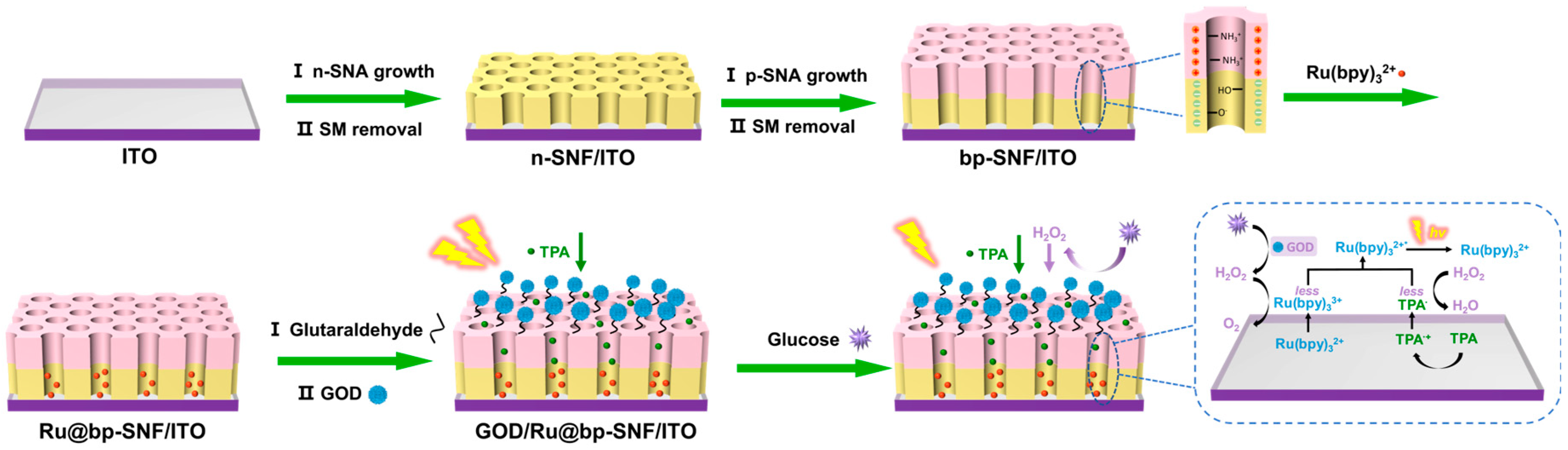
2.3. Growth of Bilayer SNA on the Electrode Surface
2.4. Preparation of Enzyme Electrode and Immobilization of ECL Emitter
2.5. Detection of Glucose
3. Results and Discussion
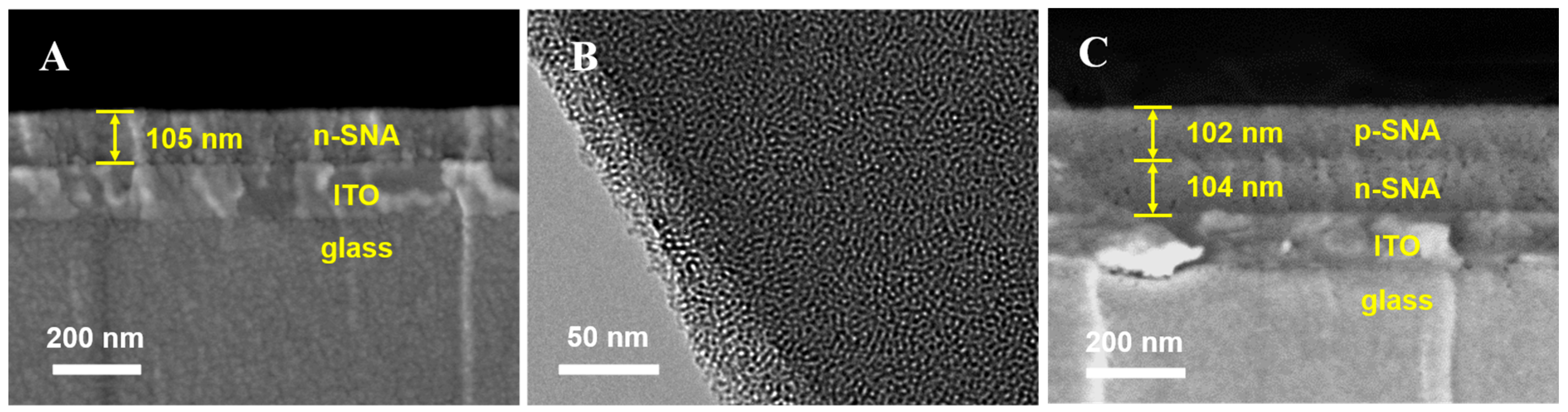
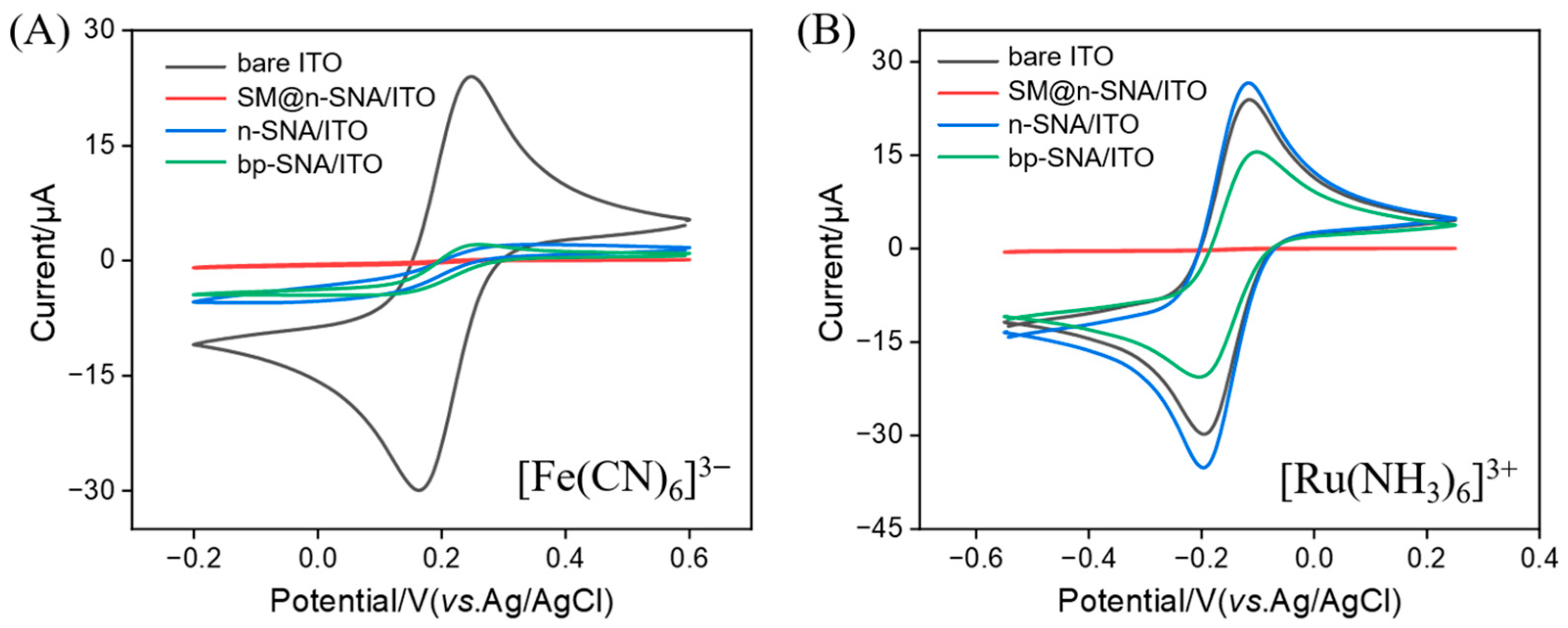
3.1. Preparation of Bipolar Bilayer SNA and Characterization of bp-SNA-Modified Electrode
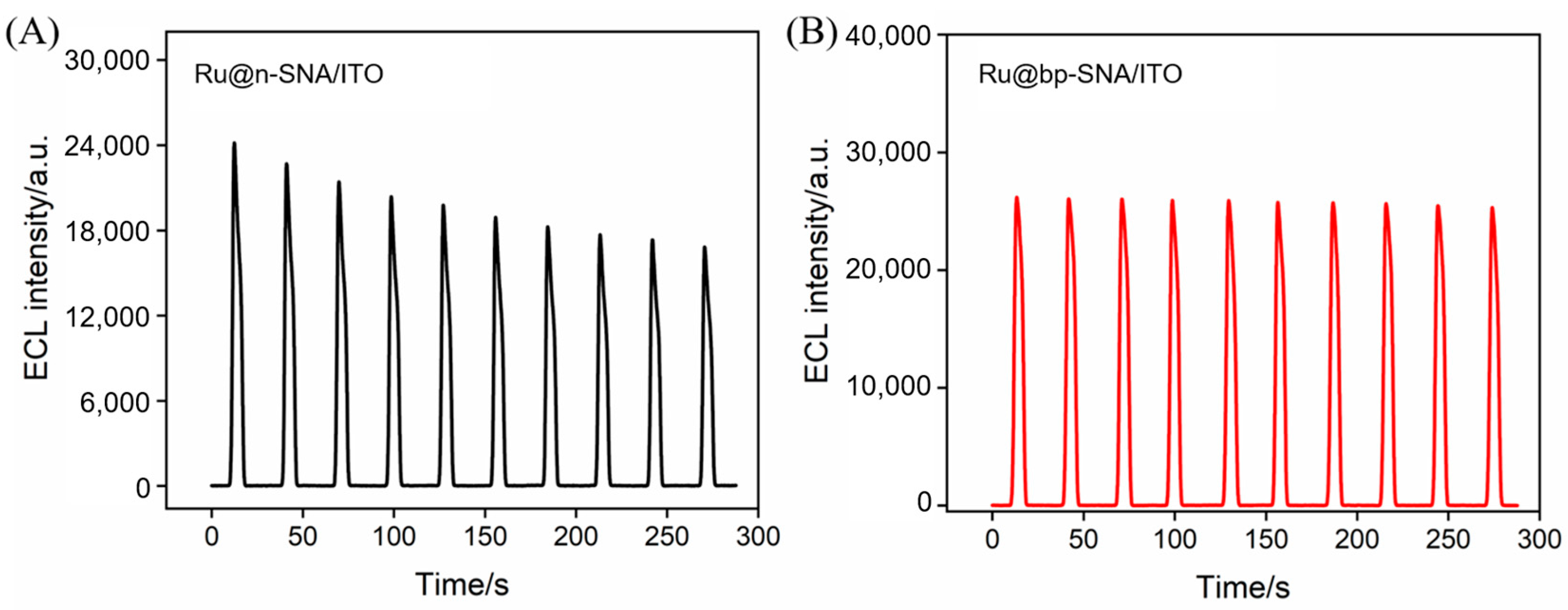
3.2. Stability of Ru(bpy)32+ Enriched in bp-SNA
3.3. Interface Characteristics and ECL Signal on the Fabrication of Enzyme Electrodes
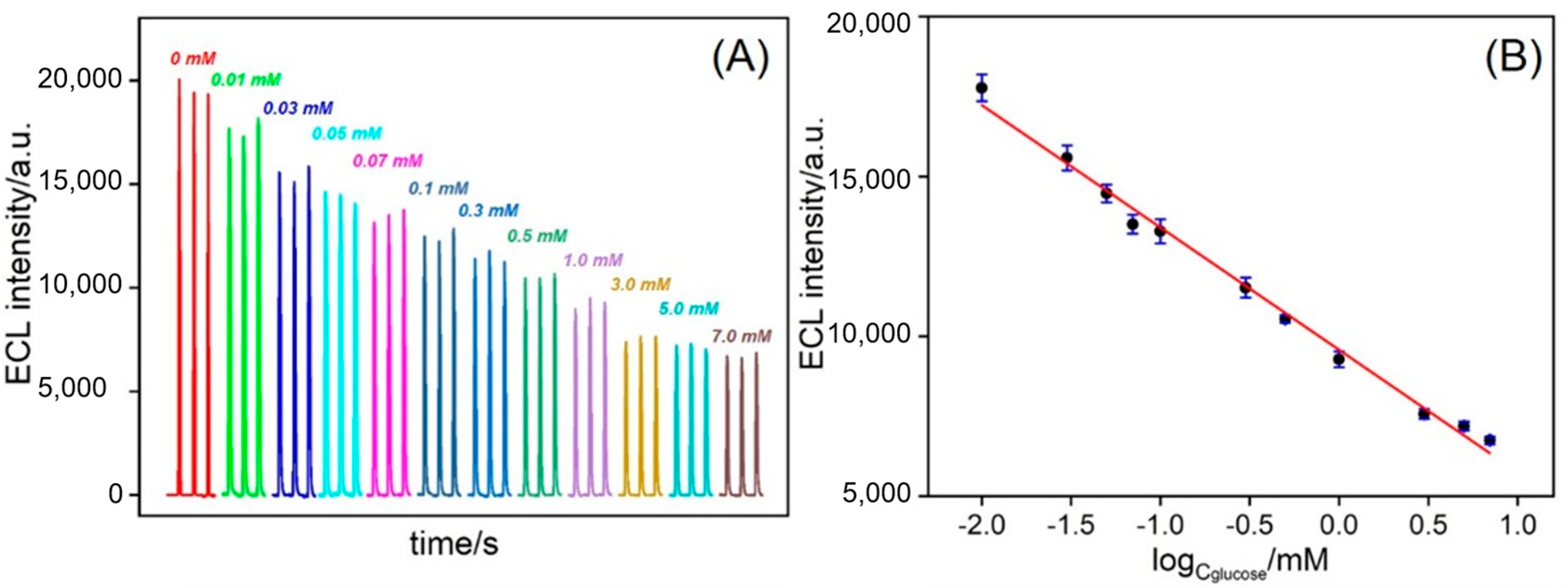
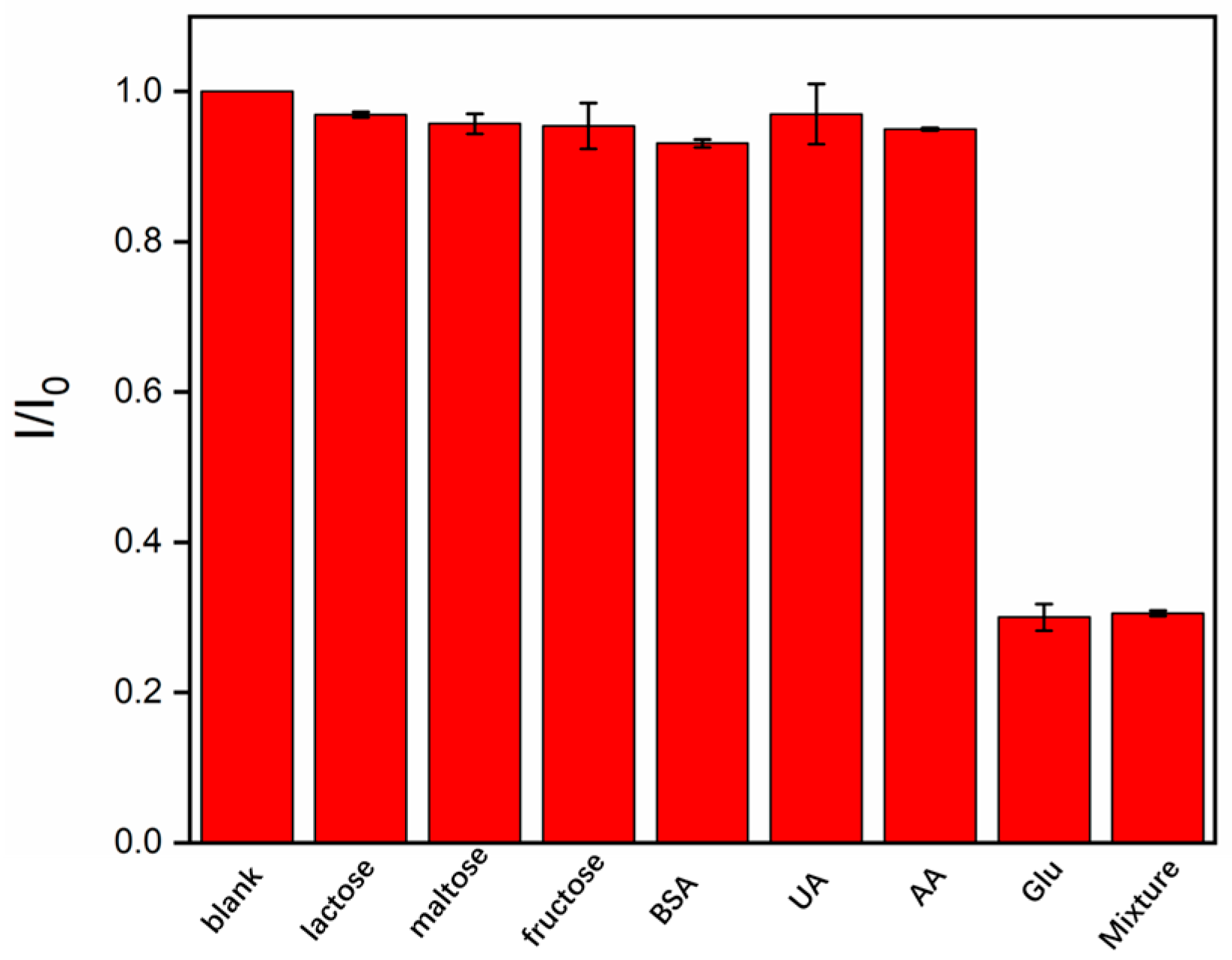
3.4. ECL Detection of Glucose and Detection Selectivity
3.5. Analysis of Real Sample
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jarnda, K.V.; Wang, D.; Qurrat Ul, A.; Anaman, R.; Johnson, V.E.; Roberts, G.P.; Johnson, P.S.; Jallawide, B.W., Jr.; Kai, T.; Ding, P. Recent advances in electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensor for the detection of glucose in tears and saliva: A review. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2023, 363, 114778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huu Do, H.; Kim, S.Y.; Le, Q.V. Development of non-precious metal oxide-based electrodes for enzyme-free glucose detection: A review. Microchem. J. 2023, 193, 109202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Maurya, K.K.; Malviya, M. Recent progress on nanomaterial-based electrochemical sensors for glucose detection in human body fluids. Microchim. Acta 2025, 192, 110–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Guidance on Global Monitoring for Diabetes Prevention and Control: Framework, Indicators and Application; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240102248 (accessed on 24 December 2024).
- International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2025; The International Diabetes Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2025; Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/idf-diabetes-atlas-2025 (accessed on 7 April 2025).
- Wang, S.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, Y.; Huang, K.; Cheng, N. Recent advances in personal glucose meter-based biosensors for food safety hazard detection. Foods 2023, 12, 3947–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, C.; Park, J.-K.; Lee, H.-J.; Yun, G.-H.; Yook, J.-G. Non-invasive fluidic glucose detection based on dual microwave complementary split Ring resonators with a switching circuit for environmental effect elimination. IEEE. Sens. J. 2020, 20, 8520–8527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Asif, M.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, F.; Liu, H.; Xia, B.Y. Noble metal construction for electrochemical nonenzymatic glucose detection. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 8, 2200272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X. Glucose detection through surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy: A review. Aanl. Chim. Acta 2022, 1206, 339226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Gong, J.; Wang, Z.; Tan, X.; Li, H. Self-assembled all-inclusive organic-inorganic nanoparticles enable cascade reaction for the detection of glucose. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Ding, Z.; Li, Y.; Xi, F.; Liu, J. Magnetic nanozyme based on loading nitrogen-doped carbon dots on mesoporous Fe3O4 nanoparticles for the colorimetric detection of glucose. Molecules 2023, 28, 4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, M.; Xi, F. Highly active nanozyme based on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots and iron ion nanocomposite for selective colorimetric detection of hydroquinone. Talanta 2025, 281, 126817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harun-Or-Rashid, M.; Aktar, M.N.; Preda, V.; Nasiri, N. Advances in electrochemical sensors for real-time glucose monitoring. Sens. Diagn. 2024, 3, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czarnik, A.W.; James, T.D. Fluorescent chemosensors in the creation of a commercially available continuous glucose monitor. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 6320–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, J.; Sun, H.; Li, J.; Deng, L.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, H.; Feng, D.; Huang, X.; Zhang, J.; Li, X. Tilted fiber Bragg grating sensor based on surface plasmon resonance and electrospinning for glucose detection. Microchem. J. 2024, 204, 110978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Zhang, C.; Wu, X.; Qian, X.; Sun, H.; He, M.; Guo, C. Research progress on biomimetic nanomaterials for electrochemical glucose sensors. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naikoo, G.A.; Arshad, F.; Hassan, I.U.; Omar, F.B.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Mustaqeem, M.; Saleh, T.A. Trends in bimetallic nanomaterials and methods for fourth-generation glucose sensors. TrAC Trend Anal. Chem. 2023, 162, 117042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Qi, W.; Xu, G. Recent advances in electrochemiluminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 3117–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Gu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Xi, F. Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of luminol at neutral medium using nanochannel-confined Co3O4 nanozyme for highly sensitive detection of tumor biomarker. Microchem. J. 2025, 209, 112903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Sensitive detection of biomarker in gingival crevicular fluid based on enhanced electrochemiluminescence by nanochannel-confined Co3O4 nanocatalyst. Biosensors 2025, 15, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zou, Y.; Ru, H.; Yan, F.; Liu, J. Silica nanochannels as nanoreactors for the confined synthesis of Ag NPs to boost electrochemical stripping chemiluminescence of the luminol-O2 system for the sensitive aptasensor. Anal. Chem. 2024, 96, 10264–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Liu, J.; Mou, Y. Nanochannel confined graphene quantum dots/platinum nanoparticles boosts electrochemiluminescence of luminal-O2 system for sensitive immunoassay. Talanta 2025, 285, 127223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Lin, J.; Gao, X.; Xi, F. Nanochannel-confined Ni(OH)2-CeO2 composite nanozyme boosts electrochemiluminescence of luminol-dissolved oxygen for immunosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 280, 117451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Yu, R.; Xi, F. Enhanced electrochemiluminescence of luminol and-dissolved oxygen by nanochannel-confined Au nanomaterials for sensitive immunoassay of carcinoembryonic antigen. Molecules 2024, 29, 4880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, J. Solid electrochemiluminescence sensor by immobilization of emitter ruthenium(ii)tris(bipyridine) in bipolar silica nanochannel film for sensitive detection of oxalate in serum and urine. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 390–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Han, Q.; Xi, F. The fabrication of a probe-integrated electrochemiluminescence aptasensor based on double-layered nanochannel array with opposite charges for the sensitive determination of C-reactive protein. Molecules 2023, 28, 7867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmawati, I.; Einaga, Y.; Ivandini, T.A.; Fiorani, A. Enzymatic biosensors with electrochemiluminescence transduction. ChemElectroChem 2022, 9, e202200175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Xu, G. Applications and trends in electrochemiluminescence. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3275–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wu, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Chi, Y.; Chen, G. A highly performing electrochemiluminescent biosensor for glucose based on a polyelectrolyte-chitosan modified electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 4582–4586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Wee, A.S.H.; Park, E.B.; Hwang, J.; Kim, S.J.; Jeong, H.Y.; Khine, M.T.; Pujar, P.; Lee, J.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. Enhancing nonenzymatic glucose detection through cobalt-substituted hafnia. Adv. Sci. 2025, 12, e2408687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezanejade Bardajee, G.; Rahimi Chahrogh, A.; Monfared, A. Fabrication of Glucose Fluorescent Aptasensor Based on CdTe Quantum Dots. J. Fluoresc. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, Y.; Liu, J. Facile synthesis of iron and nitrogen co-doped carbon dot nanozyme as highly efficient peroxidase mimics for visualized detection of metabolites. Molecules 2023, 28, 6064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiba, N.; Miwa, T.; Tachibana, M.; Tani, K.; Koizumi, H. Chemiluminometric sensor for simultaneous determination of l-glutamate and l-lysine with immobilized oxidases in a flow injection system. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Su, B.; Song, X.; Chen, Q.-A.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Recent advances in electrochemiluminescent enzyme biosensors. TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2011, 30, 665–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, T.; Giaretta, J.; Zulli, R.; Rath, R.J.; Farajikhah, S.; Talebian, S.; Dehghani, F. Covalent immobilization: A review from an enzyme perspective. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 503, 158054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.; Zhu, Q.; Qiao, X.; Shi, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Lin, E.; Cheng, P.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Y. Fast production of covalent organic frameworks for covalent enzyme immobilization with boosted enzymatic catalysis by solar-driven photothermal effect. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 64, e202416550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Yu, L.; Ye, J.; Yan, M.; Peng, Y.; Huang, J.; Yang, X. A ratiometric electrochemiluminescence strategy based on two-dimensional nanomaterial-nucleic acid interactions for biosensing and logic gates operation. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 178, 113022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Gong, J.; Han, Q.; Hu, W.; Yan, F.; Liu, J. Nanogold amplified electrochemiluminescence/electrochemistry in bipolar silica nanochannel array for ultrasensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2 pseudoviruses. Talanta 2024, 277, 126319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, J. Highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor based on methylene blue-reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites as signal probes for IL-6 detection in gingival crevicular fluid samples. Front. Chem. 2025, 13, 1549927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Yang, L.; Liu, J.; Liu, J. Electrochemical sensor nanoarchitectonics for sensitive detection of uric acid in human whole blood based on screen-printed carbon electrode equipped with vertically-ordered mesoporous silica-nanochannel film. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Qin, D. Label-free homogeneous electrochemical aptasensor based on size exclusion/charge-selective permeability of nanochannel arrays and 2D nanorecognitive probe for sensitive detection of alpha-fetoprotein. Molecules 2023, 28, 6935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Xing, J. Homogeneous electrochemical aptamer sensor based on two-dimensional nanocomposite probe and nanochannel modified electrode for sensitive detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Molecules 2023, 28, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Luo, X.; Xi, F. Probe-integrated electrochemical immunosensor based on electrostatic nanocage array for reagentless and sensitive detection of tumor biomarker. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1121450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, S.; Xi, F. Homogeneous aptasensor with electrochemical and electrochemiluminescence dual detection channels enabled by nanochannel-based probe enrichment and DNase I cleavage for tumor biomarker detection. Molecules 2025, 30, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wu, J.; Luo, T.; Liu, J.; Xi, F.; Zhang, W. Solid-phase electrochemiluminescence immunosensing platform based on bipolar nanochannel array film for sensitive detection of carbohydrate antigen 125. Front. Chem. 2024, 12, 1493368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Zheng, Y.; An, L.; Liu, J. Ultrasensitive immunosensor for prostate-specific antigen based on enhanced electrochemiluminescence by vertically ordered mesoporous silica-nanochannel film. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 851178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Yao, L.; Chen, K.; Su, B. Silica nanochannel membranes for electrochemical analysis and molecular sieving: A comprehensive review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 50, 424–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, T.; Liu, J. Electrochemical/electrochemiluminescence sensors based on vertically-ordered mesoporous silica films for biomedical analytical applications. ChemBioChem 2024, 25, e202400320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Zhang, C.; Xi, F.; Su, D.; Zhang, W. Direct and sensitive electrochemical determination of total antioxidant capacity in foods using nanochannel-based enrichment of redox probes. Molecules 2024, 29, 2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Yang, L.; Huang, H.; Lv, N.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y. Nanochannel array on electrochemically polarized screen printed carbon electrode for rapid and sensitive electrochemical determination of clozapine in human whole blood. Molecules 2022, 27, 2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Ding, Y.; Su, R.; Lu, D.; Tang, H.; Xi, F. Silica nanochannel array film supported by ß-cyclodextrin-functionalized graphene modified gold film electrode for sensitive and direct electroanalysis of acetaminophen. Front. Chem. 2022, 9, 812086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhang, T.; Tang, H.; Liu, J. Novel electrochemical and electrochemiluminescence dual-modality sensing platform for sensitive determination of antimicrobial peptides based on probe encapsulated liposome and nanochannel array electrode. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 962736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Tang, H.; Xi, F. Sensitive electrochemical detection of p-nitrophenol by pre-activated glassy carbon electrode integrated with silica nanochannel array film. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 954748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yan, F.; Xi, F. A dual-functional antibiofouling and signal amplification sensing platform enabling accurate analysis in complicated biological samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 439, 137856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Su, R.; Xi, F. Sensitive detection of noradrenaline in human whole blood based on Au nanoparticles embedded vertically-ordered silica nanochannels modified pre-activated glassy carbon electrodes. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1126213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Xuan, L.; Gong, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Xi, F.; Chen, J. Three-dimensional macroscopic graphene supported vertically-ordered mesoporous silica-nanochannel film for direct and ultrasensitive detection of uric acid in serum. Talanta 2022, 238, 123027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walcarius, A.; Sibottier, E.; Etienne, M.; Ghanbaja, J. Electrochemically assisted self-assembly of mesoporous silica thin films. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Lin, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, J.; Tang, H. Equipment of vertically-ordered mesoporous silica film on electrochemically pretreated three-dimensional graphene electrodes for sensitive detection of methidazine in urine. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Gu, X.; He, L.; Xi, F. A highly sensitive immunosensor based on nanochannel-confined nano-gold enhanced electrochemiluminescence for procalcitonin detection. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1274424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Tao, D.; Hasebe, Y.; Zhang, Z. Electrochemical evaluation of sulfide mineral modified glassy carbon electrode as novel mediated glucose biosensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 894, 115357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auria-Luna, F.; Foss, F.W.; Molina-Canteras, J.; Velazco-Cabral, I.; Marauri, A.; Larumbe, A.; Aparicio, B.; Vázquez, J.L.; Alberro, N.; Arrastia, I.; et al. Supramolecular chemistry in solution and solid–gas interfaces: Synthesis and photophysical properties of monocolor and bicolor fluorescent sensors for barium tagging in neutrinoless double beta decay. RSC Appl. Interfaces 2025, 2, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altay, D.N.; Yagar, H.; Ozcan, H.M. A new ITO-based Aβ42 biosensor for early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioelectrochemistry 2023, 153, 108501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, C.; Xi, F. Disposable amperometric label-free immunosensor on chitosan–graphene-modified patterned ITO electrodes for prostate specific antigen. Molecules 2022, 27, 5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Xu, S.; Xi, F. Disposal immunosensor for sensitive electrochemical detection of prostate-specific antigen based on amino-rich nanochannels array-modified patterned indium tin oxide electrode. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Chen, Z.; Xu, H.; Zhang, A. Sensitive electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer (ECL-RET) between Ru(bpy)32+ and Au nanorod for hydrogen peroxide detection. Sci. China Chem. 2016, 60, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Zu, Y. Emission of tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(ii) by coreactant electrogenerated chemiluminescence: From O2-insensitive to highly O2-sensitive. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 12049–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Sample | Added (mM) | Detected (mM) | RSD (%, n = 3) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fetal bovine serum a | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.7 | 100.0 |
| 0.50 | 0.48 | 0.3 | 96.2 | |
| 1.00 | 1.02 | 2.0 | 102.5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, C.; Zheng, Y.; Yan, F.; Xu, L. Enzyme-Based Solid-Phase Electrochemiluminescence Sensors with Stable, Anchored Emitters for Sensitive Glucose Detection. Biosensors 2025, 15, 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050332
Wei C, Zheng Y, Yan F, Xu L. Enzyme-Based Solid-Phase Electrochemiluminescence Sensors with Stable, Anchored Emitters for Sensitive Glucose Detection. Biosensors. 2025; 15(5):332. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050332
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Chunyin, Yanyan Zheng, Fei Yan, and Lifang Xu. 2025. "Enzyme-Based Solid-Phase Electrochemiluminescence Sensors with Stable, Anchored Emitters for Sensitive Glucose Detection" Biosensors 15, no. 5: 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050332
APA StyleWei, C., Zheng, Y., Yan, F., & Xu, L. (2025). Enzyme-Based Solid-Phase Electrochemiluminescence Sensors with Stable, Anchored Emitters for Sensitive Glucose Detection. Biosensors, 15(5), 332. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios15050332





