A Thermal Model for Carbon Nanotube Interconnects
Abstract
:1. Introduction
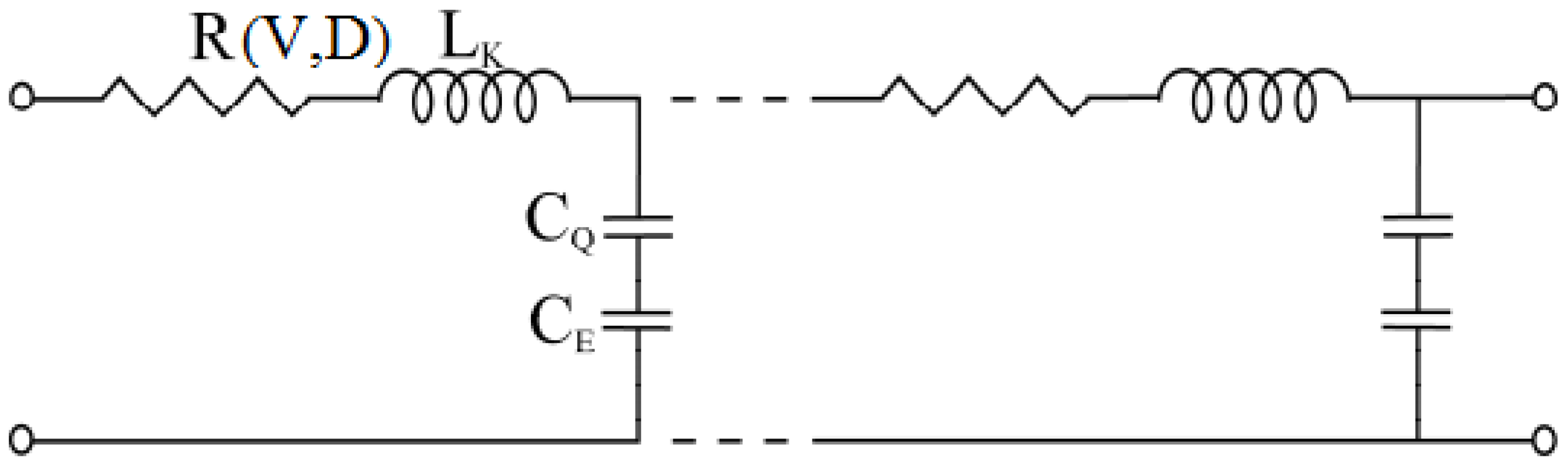
2. Electrical and Thermal Transport Model






 is optical phonon energy and its typical value varies from 0.16 eV to 0.20 eV [19]. In our work, we have taken this value as 0.16 eV. Occupancy function of optical phonon increases as temperature increases which eventually decreases optical phonon absorption component (λop,abs) of electron mean free path. Optical phonon emission process has two components, one is for the absorbed energy (
is optical phonon energy and its typical value varies from 0.16 eV to 0.20 eV [19]. In our work, we have taken this value as 0.16 eV. Occupancy function of optical phonon increases as temperature increases which eventually decreases optical phonon absorption component (λop,abs) of electron mean free path. Optical phonon emission process has two components, one is for the absorbed energy (  ) and another (
) and another (  ) is for the electric field across the SWCNT length. Both of these components are expressed as follows [19],
) is for the electric field across the SWCNT length. Both of these components are expressed as follows [19],


 ) depends on both the electric field (V/l) and temperature (T). The effective mean free path can now be calculated by Matthiessen’s rule as follows,
) depends on both the electric field (V/l) and temperature (T). The effective mean free path can now be calculated by Matthiessen’s rule as follows,












3. Results and Discussion

- Consider differential length of CNT and calculate mean free path as well as differential resistance for differential element using Equations (10) and (19). Estimate total resistance of SWCNT by summing all differential resistances.
- Calculate I2R per unit length for heat generation and then use Equation (21) to get temperature profile over the CNT length.
- Use current temperature profile as the initial temperature for next iteration. Repeat steps 1 to 4 until convergence is obtained.
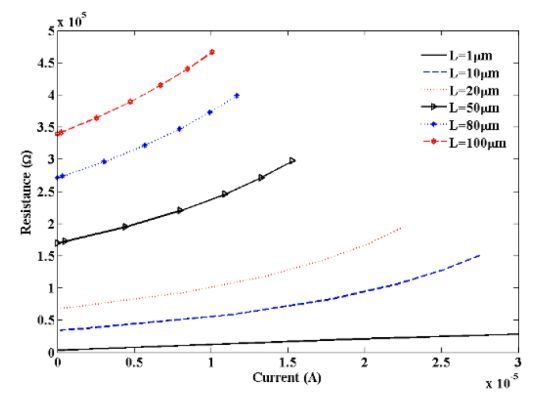
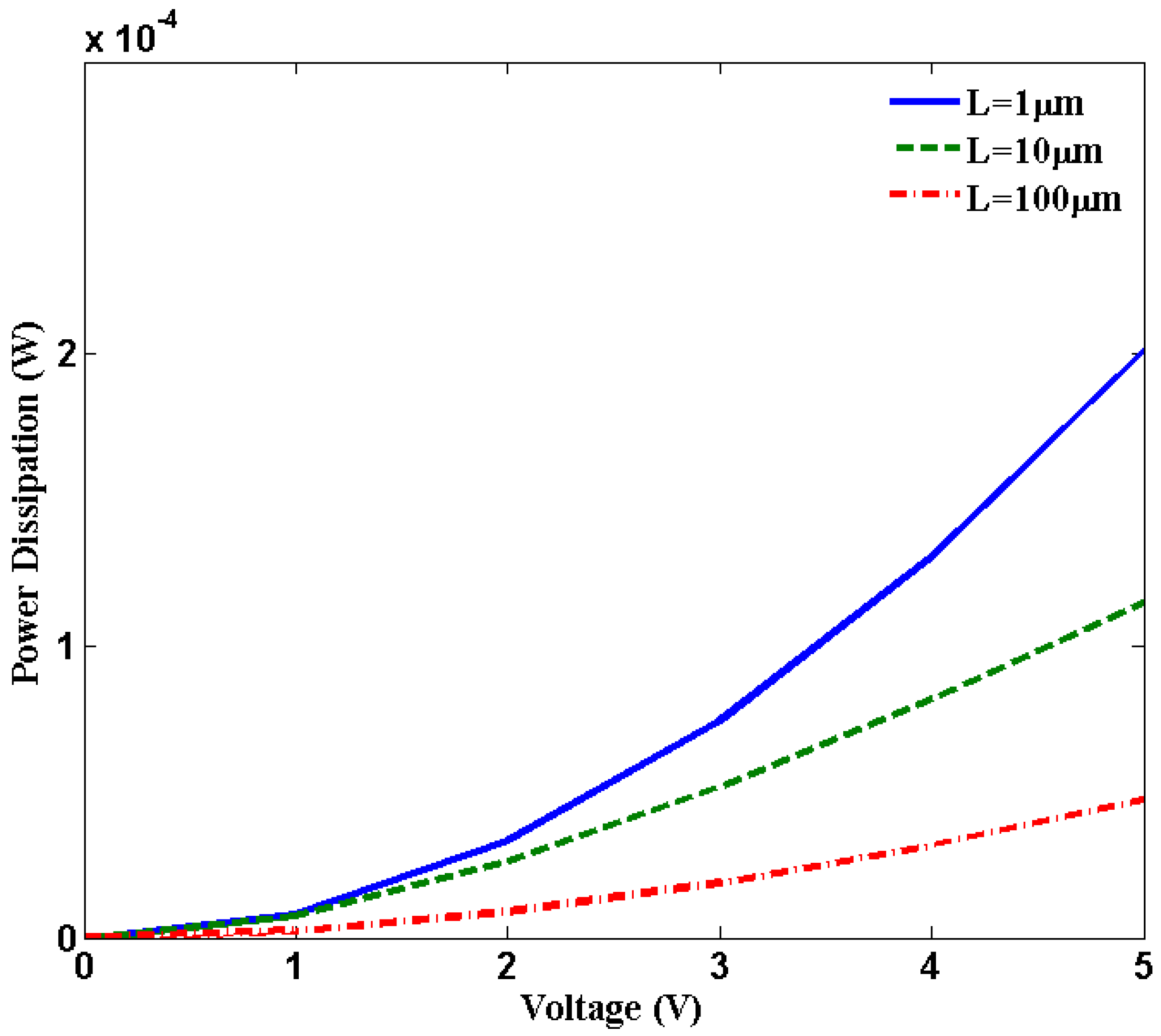
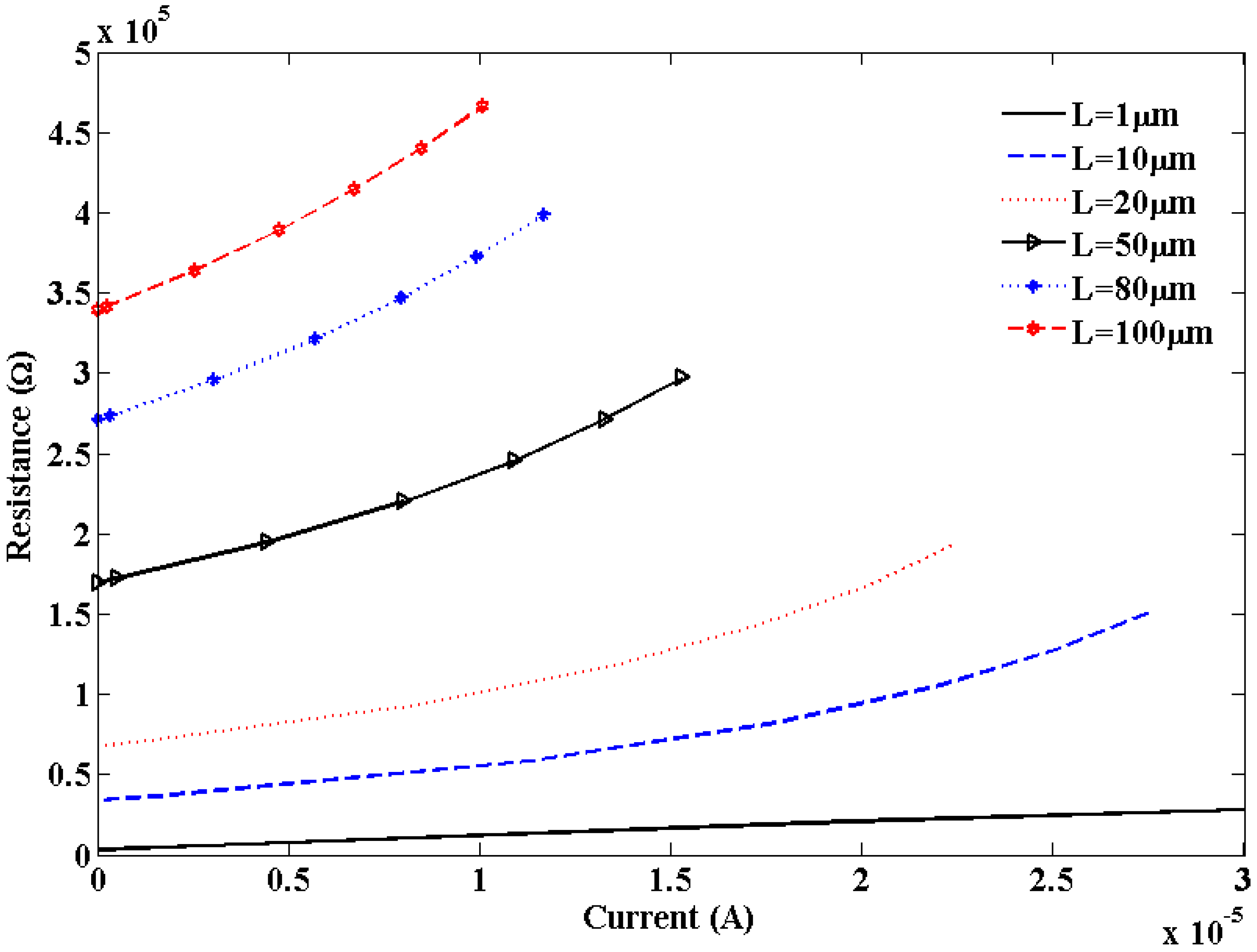
 decreases with increase in bias voltage which contributes to decrease in effective mean free path (λeff). The total resistance increases with decreasing effective scattering length. This increase in resistance contributes to increase in Joule heating.
decreases with increase in bias voltage which contributes to decrease in effective mean free path (λeff). The total resistance increases with decreasing effective scattering length. This increase in resistance contributes to increase in Joule heating.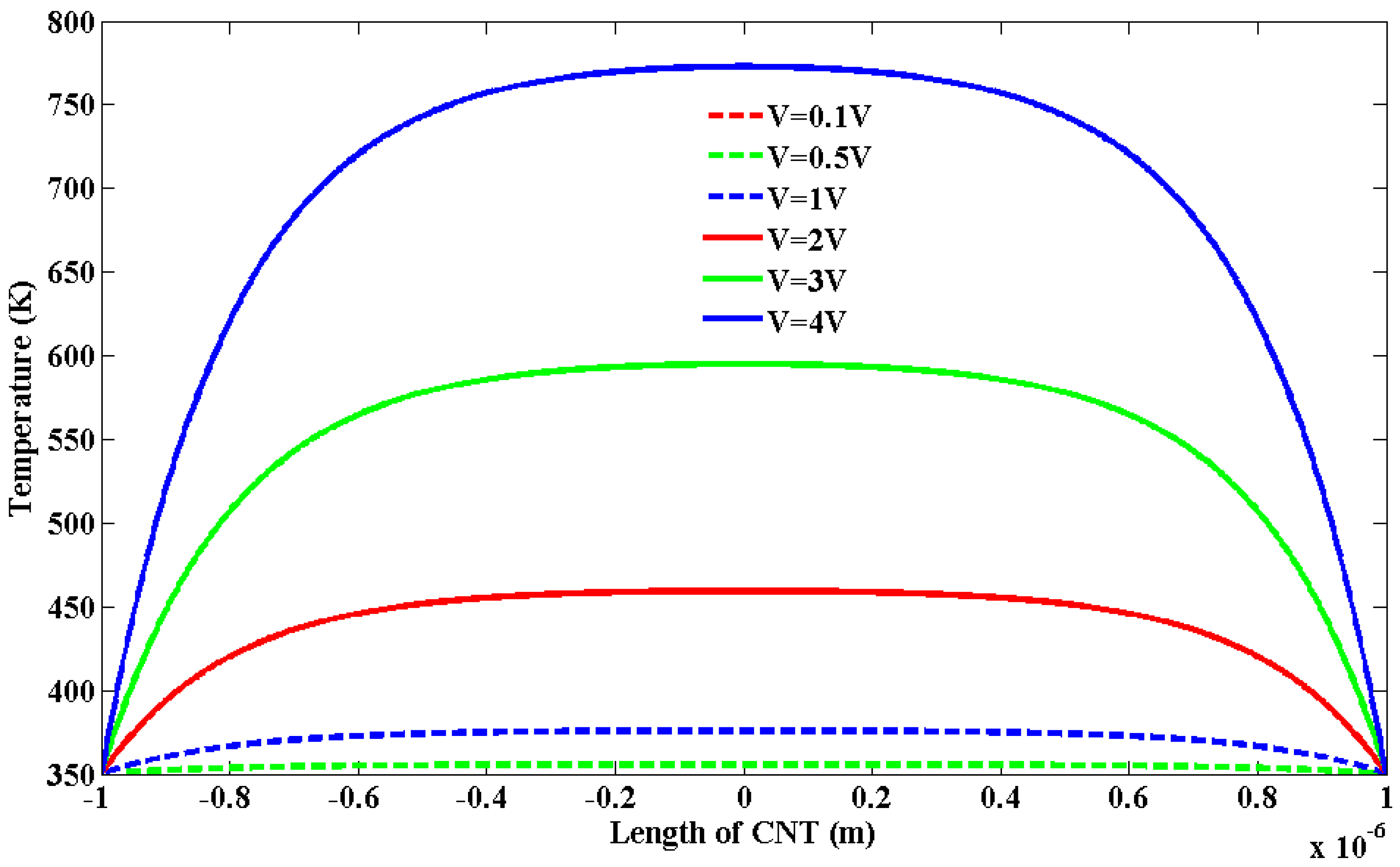
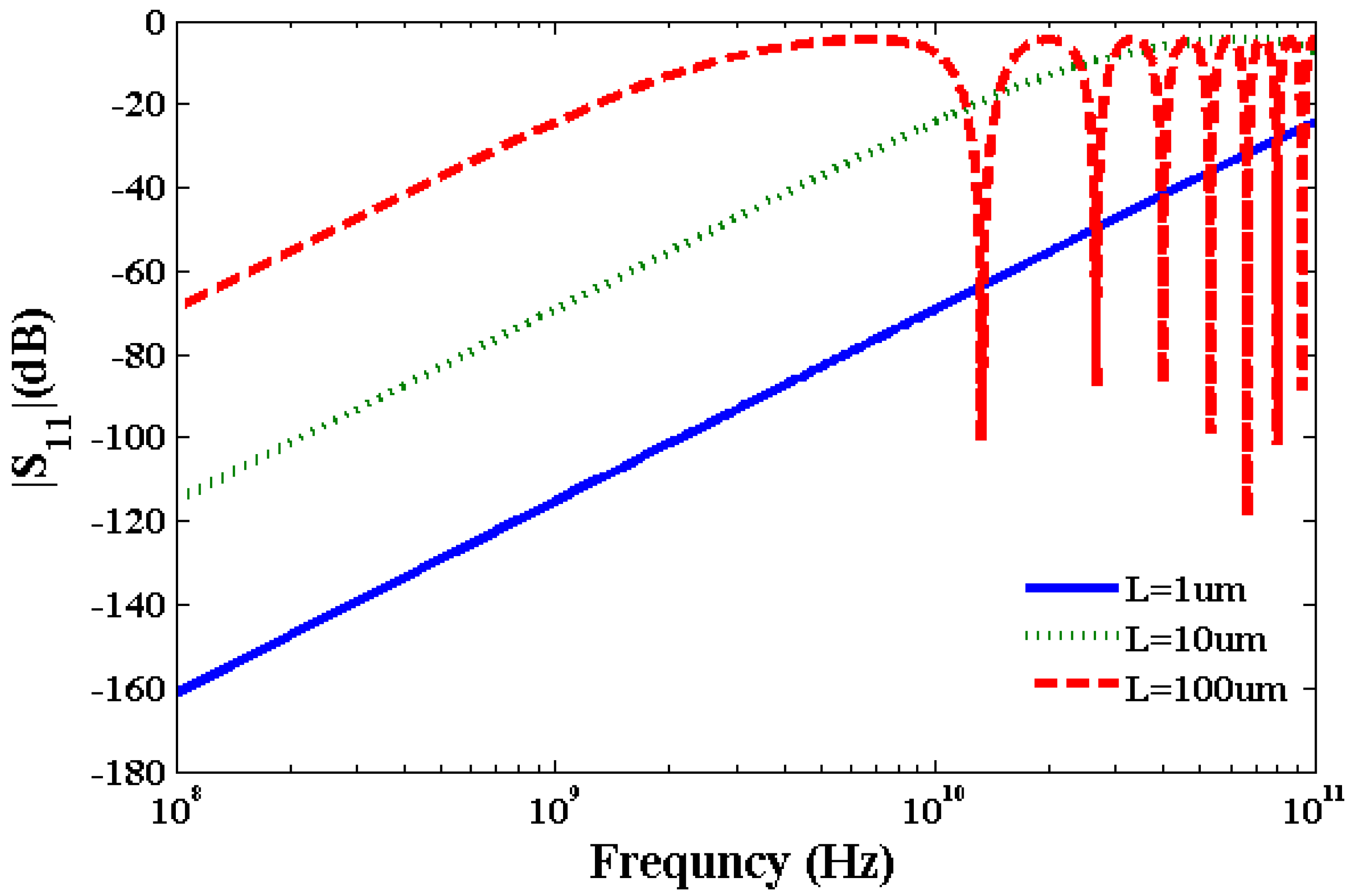

| Length of SWCNT (µm) | Band Width (GHz) without Scattering [16] | Band Width (GHz) with Scattering |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1000 | 120 |
| 10 | 110 | 11 |
| 100 | 30 | 1.0 |

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ryu, C.; Kwon, K.-W.; Loke, A.L.S.; Lee, H.; Nogami, T.; Dubin, V.M.; Kavari, R.A.; Ray, G.W.; Wong, S.S. Microstructure and reliability of copper interconnects. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 1999, 46, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, K.-H.; Kapur, P.; Saraswat, K.C. Compact performance models and comparison for gigascale on-chip global interconnect technologies. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 2009, 56, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, C.; Srivastava, N.; Banerjee, K. Carbon nanomaterials for next-generation interconnects and passives: Physics, status, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Electron. Dev. 2009, 56, 1799–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon. Nature 1991, 354, 56–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselman, M.; Hauck, S. The future of integrated circuits: A survey of nanoelectronics. Proc. IEEE 2010, 98, 11–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffucci, A. Carbon nanotubes in nanopackaging applications. IEEE Nanotechnol. Mag. 2009, 3, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiariello, A.G.; Miano, G.; Maffucci, A. Carbon Nanotube Bundles as Nanoscale Chip to Package Interconnects. In Proceedings of 9th IEEE Conference on Nanotechnology (IEEE-NANO 2009), Genoa, Italy, 26–30 July 2009; pp. 58–61.
- Ting, J.-H.; Chiu, C.-C.; Huang, F.-Y. Carbon nanotube array vias for interconnect applications. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 2009, 27, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, N.; Kureshi, A.K.; Hasan, M.; Arslan, T. Carbon Nanotube Interconnects for Low-Power High-Speed Applications. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS 2009), Taipei, Taiwan, 24–27 May 2009; pp. 2273–2276.
- Stan, M.R.D.; Ghosh, A.; Tseng, F. Graphene Devices, Interconnect and Circuits. In Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS 2009), Taipei, Taiwan, 24–27 May 2009; pp. 69–72.
- Santini, C.A.; Volodin, A.; Haesendonck, C.V.; Gendt, S.D.; Groeseneken, G.; Vereecken, P.M. Carbon nanotube–carbon nanotube contacts as an alternative towards low resistance horizontal interconnects. Carbon 2011, 49, 4004–4012. [Google Scholar]
- Santini, C.A.; Vereecken, P.M.; Haesendonck, C.V. Growth of carbon nanotube branches by electrochemical decoration of carbon nanotubes. Mater. Lett. 2012, 88, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, P.J. Lüttinger Liquid Theory as a model of the gigahertz electrical properties of carbon nanotubes. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2002, 1, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salahuddin, S.; Lundstrom, M.; Datta, S. Transport effects on signal propagation in quantum wires. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2005, 52, 1734–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffucci, A.; Miano, G.; Villone, F. A transmission line model for metallic carbon nanotube interconnects. Int. J. Circuit Theory Appl. 2008, 36, 31–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Srivastava, A. A model for carbon nanotube interconnects. Int. J. Circ. Theor. Appl. 2010, 38, 559–575. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, A.; Xu, Y.; Sharma, A.K. Carbon nanotubes for next generation very large scale integration interconnects. J. Nanophotonics. 2010, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Pop, E.; Mann, D.; Reifenberg, J.; Goodson, K.; Dai, H. Electro-Thermal Transport in Metallic Single-Wall Carbon Nanotubes for Interconnect Applications. In Proceedings of Electron Devices Meeting, Washington, DC, USA, 5 December 2005. [CrossRef]
- Pop, E.; Mann, D.A.; Goodson, K.E.; Dai, H. Electrical and thermal transport in metallic single-wall carbon nanotubes on insulating substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeemi, A.; Meindl, J.D. Impact of electron-phonon scattering on the performance of carbon nanotube interconnects for GSI. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2005, 26, 476–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeemi, A.; Meindl, J.D. Physical modeling of temperature coefficient of resistance for single- and multi-wall carbon nanotube interconnects. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2007, 28, 135–138. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.Y.; She, J.C.; Chen, J.; Deng, S.Z.; Xu, N.S.; Bishop, H.; Huq, S.E.; Wang, L.; Zhong, D.Y.; Wang, E.G.; et al. Mechanism responsible for initiating carbon nanotube vacuum breakdown. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 93, 075501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, C. From Surface Plasmon Resonance Based Sensors to Carbon Nanotube Based Sensors. Ph.D. Thesis, Katholieke Universiteit, Leuven, Belgium, April 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kitsuki, H.; Yamada, T.; Fabris, D.; Jameson, J.R.; Wilhite, P.; Suzuki, M.; Yang, C.Y. Length dependence of current-induced breakdown in carbon nanofiber interconnects. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 173110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Saito, T.; Fabris, D.; Yang, C.Y. Electrothermal analysis of breakdown in carbon nanofiber interconnects. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2009, 30, 469–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, S.; Jiang, J.; Torres, L.; Saito, R. Charge transport in carbon nanotubes: Quantum effects of electron–phonon coupling. J. Phys.Condens. Matter 2007, 19, 183203–183223. [Google Scholar]
- Slepyan, G.Y.; Maksimenko, S.A.; Lakhtakia, A.; Yevtushenko, O.; Gusakov, A.V. Electrodynamics of carbon nanotubes: Dynamic conductivity, impedance boundary conditions, and surface wave propagation. Phys. Rev. B 1999, 60, 17136–17149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carslaw, H.S.; Jaeger, J.C. Conduction of Heat in Solids; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1959. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, T.; Madriz, F.R.; Yang, C.Y. Inductance in one dimensional nanostructures. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2009, 56, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Veen, M; Vereecke, B. Personal communication, Interuniversity Microelectronics Centre (IMEC): Leuven, Belgium, 2011.
© 2013 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohsin, K.M.; Srivastava, A.; Sharma, A.K.; Mayberry, C. A Thermal Model for Carbon Nanotube Interconnects. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 229-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3020229
Mohsin KM, Srivastava A, Sharma AK, Mayberry C. A Thermal Model for Carbon Nanotube Interconnects. Nanomaterials. 2013; 3(2):229-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3020229
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohsin, Kaji Muhammad, Ashok Srivastava, Ashwani K. Sharma, and Clay Mayberry. 2013. "A Thermal Model for Carbon Nanotube Interconnects" Nanomaterials 3, no. 2: 229-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3020229
APA StyleMohsin, K. M., Srivastava, A., Sharma, A. K., & Mayberry, C. (2013). A Thermal Model for Carbon Nanotube Interconnects. Nanomaterials, 3(2), 229-241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano3020229