A Real Option Pricing Decision of Construction Project under Group Bidding Environment
Abstract
1. Introduction
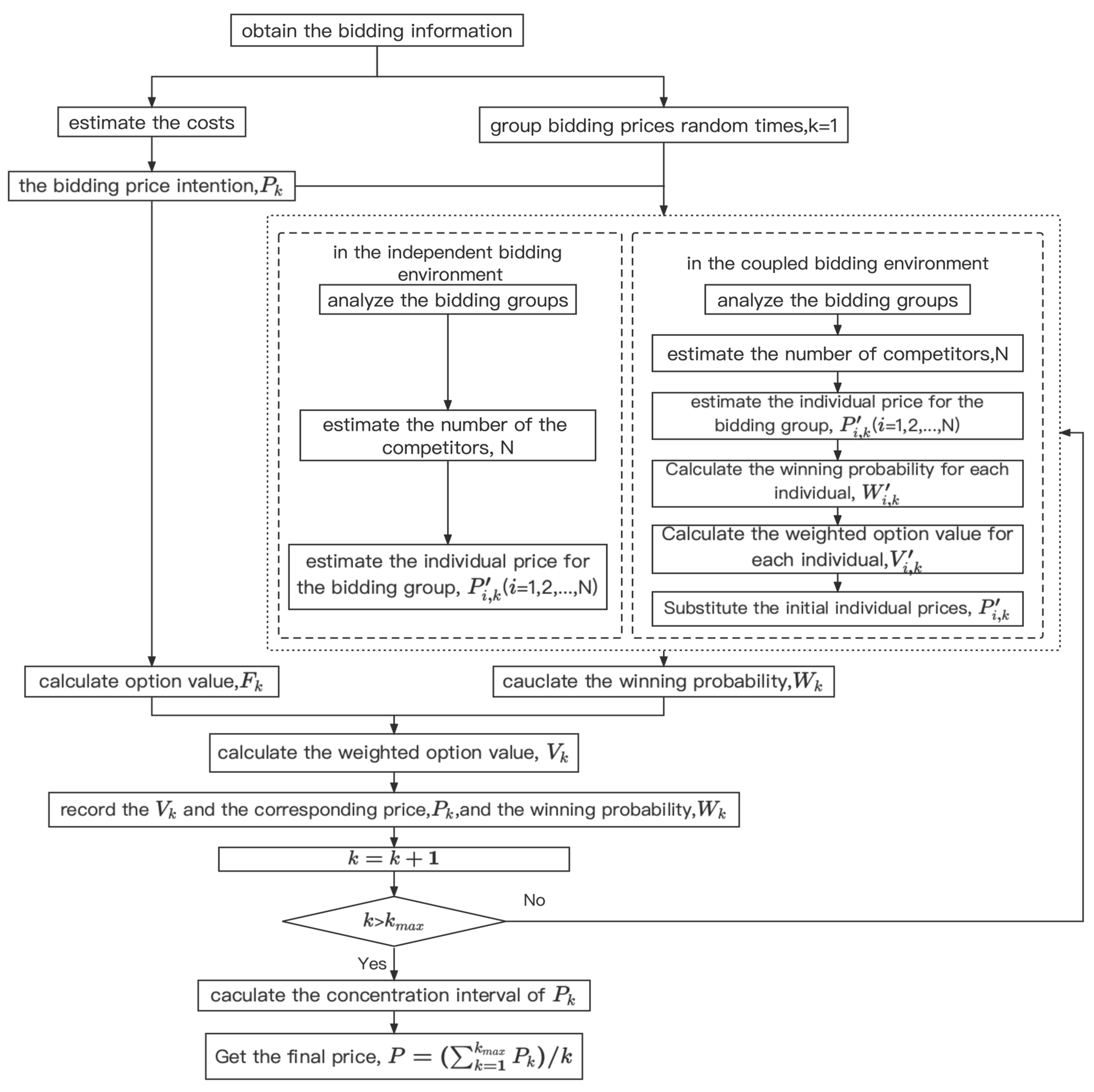
2. A Real Option Pricing Decision Model under Group Bidding Environments
2.1. Assumptions
- (1)
- The enterprises need to consider the external competitive environments when determining the bid price.
- (2)
- The external competitive environment can be assumed to be the independent and the coupled bidding environment. The independent bidding environment refers to the application of this research method only by the bidding enterprises themselves, and the coupled bidding environment means that the external environment all adopts the independent bidding price method.
- (3)
- The historical bid-winning data of the external competitive environment is publicly available.
- (4)
- In the group-independent bidding environment, the individual price decisions in the external competitive environment are independent of each other, and the group price follows the random distribution. In the group coupling bidding environment, it is believed that individual price guesses the group price outside itself and determines its optimal price through group price coupling.
- (5)
- The competition environment is equitable, and there are no behaviors that violate the law or morality such as vicious competition.
2.2. The Option Value Calculation
2.3. The Winning Probability and the Weighted Option Value Calculation
2.3.1. The Winning Probability Calculation
2.3.2. The Weighted Option Value Calculation
2.4. The Model Framework
3. The Model Application and Analysis
3.1. Example Background
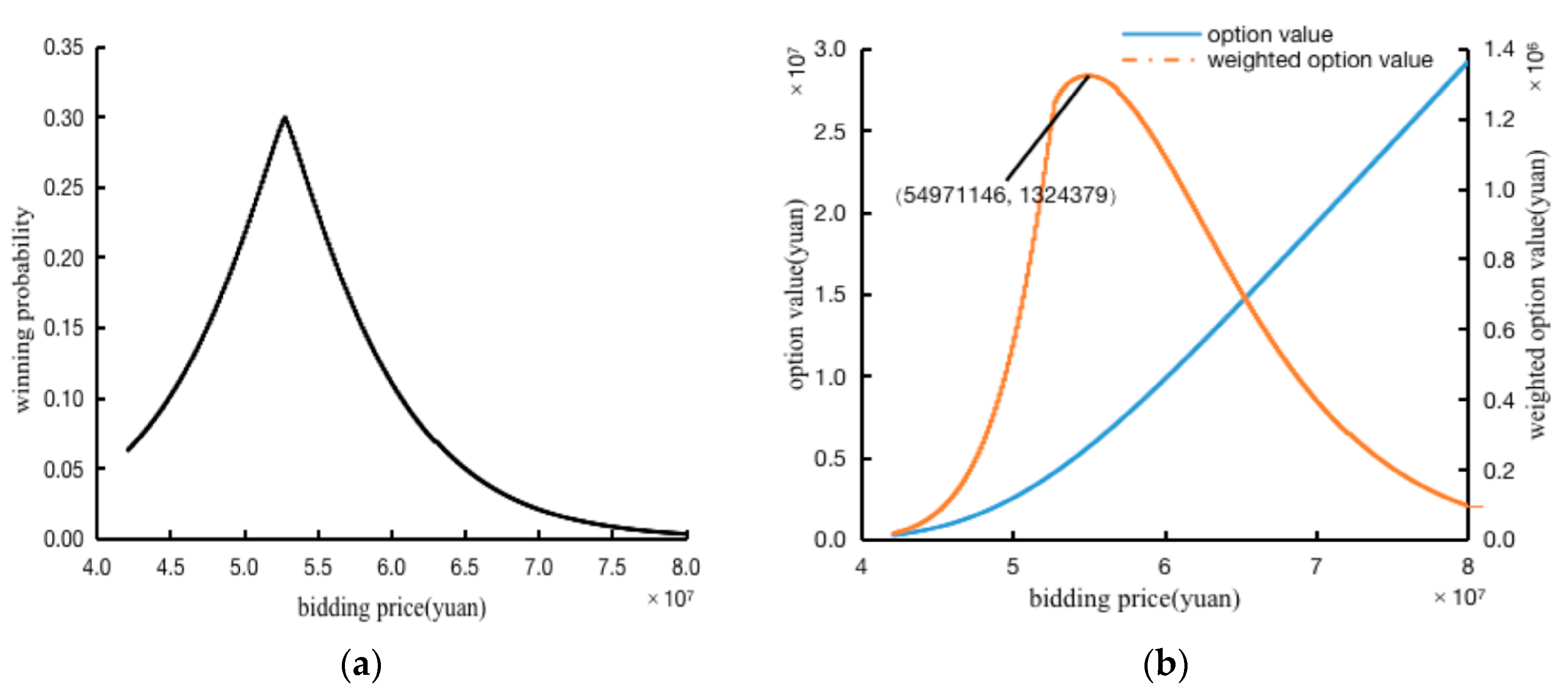
3.2. Simulation Results Analysis in the Independent Bidding Environment
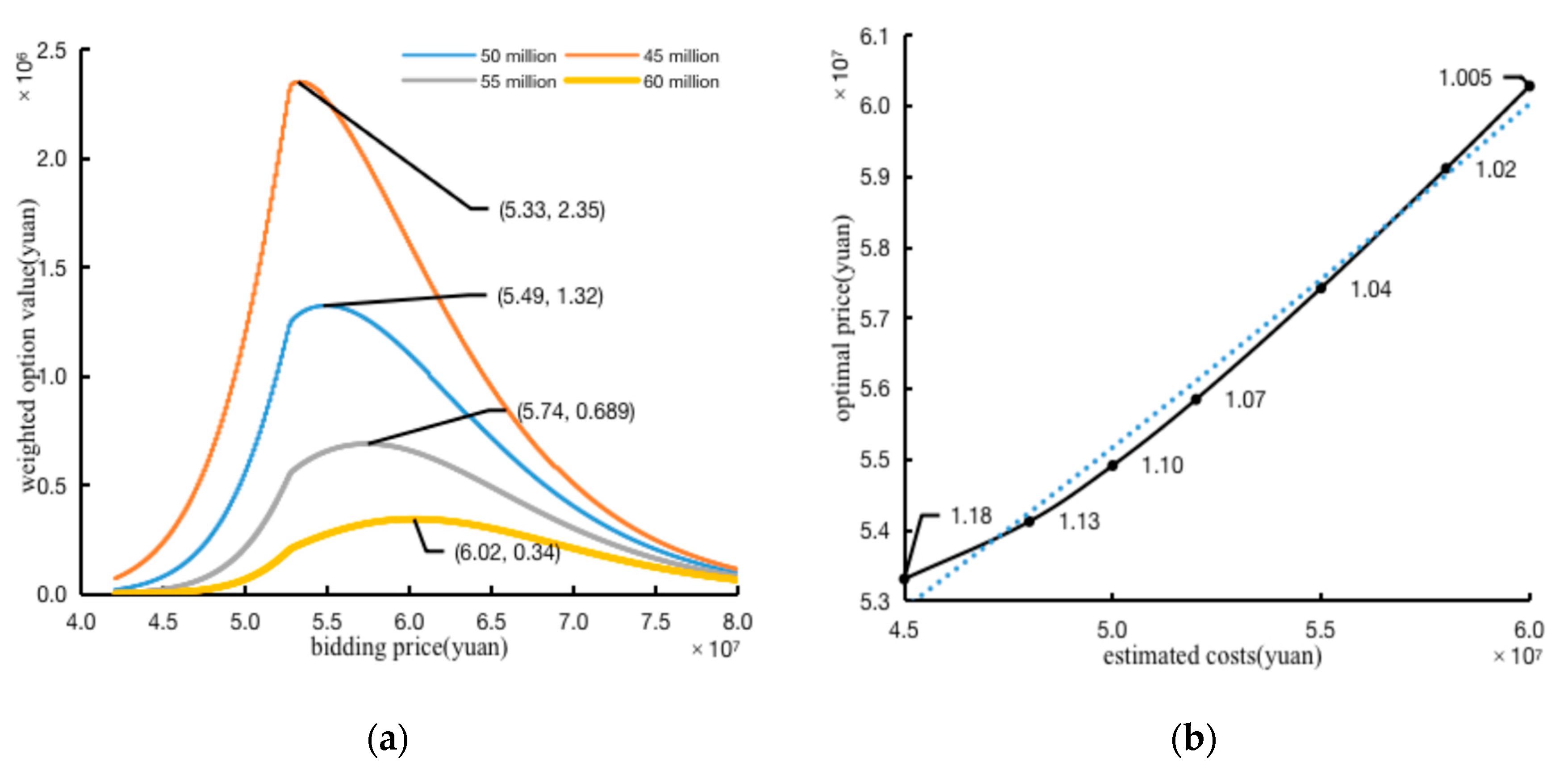
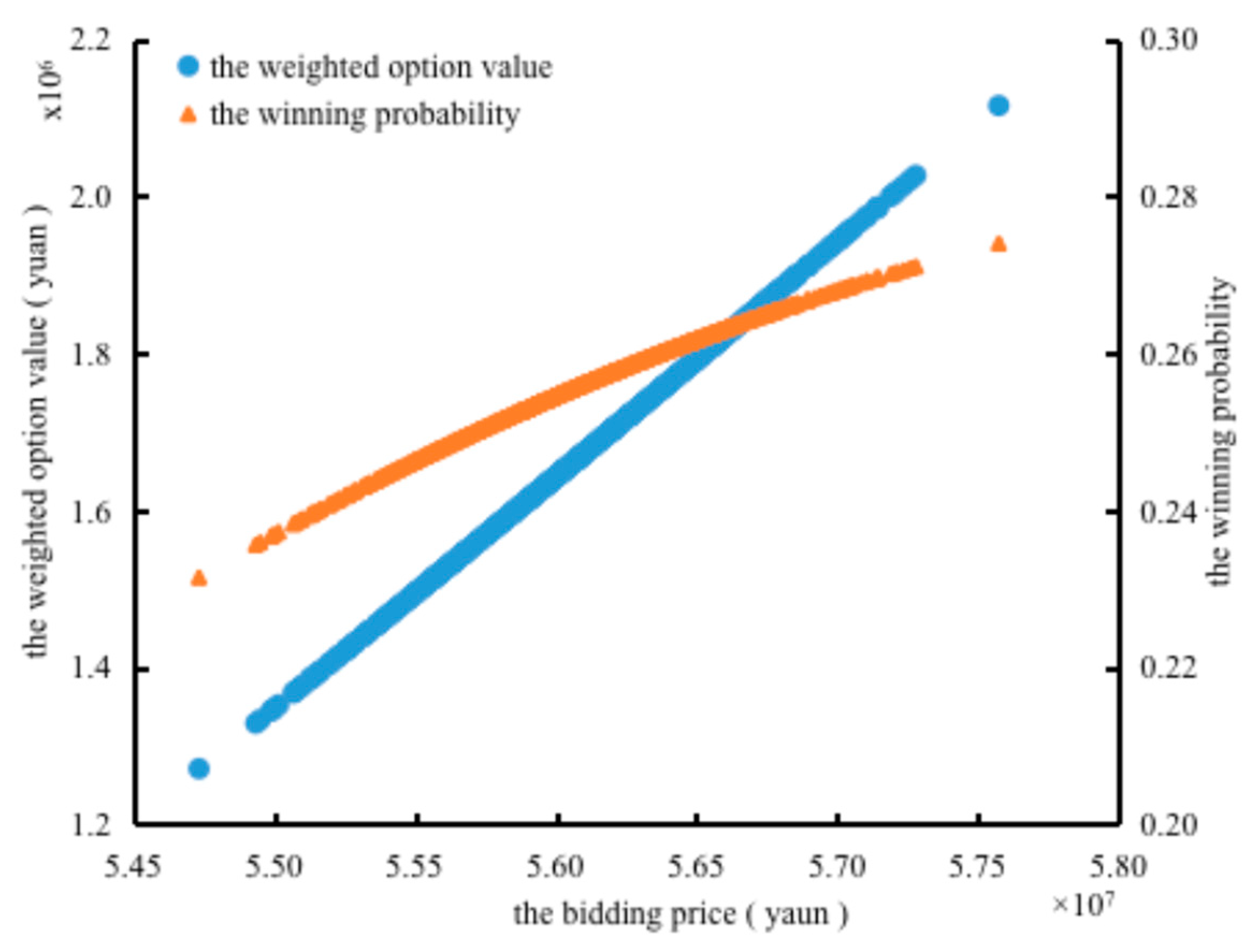
3.2.1. The Optimal Bidding Price Analysis
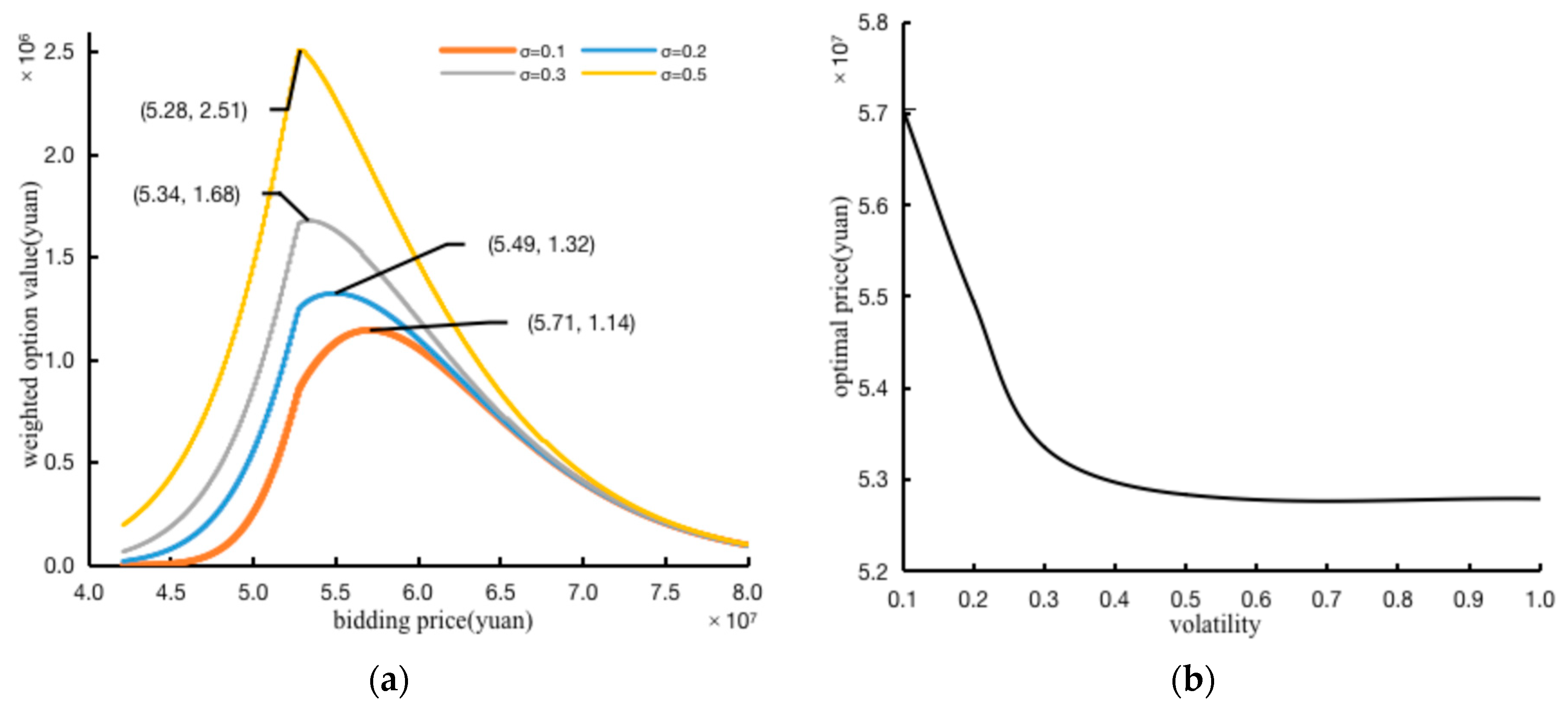
3.2.2. The Sensitivity Analysis of Parameters
- (1)
- Sensitivity analysis of the volatility level
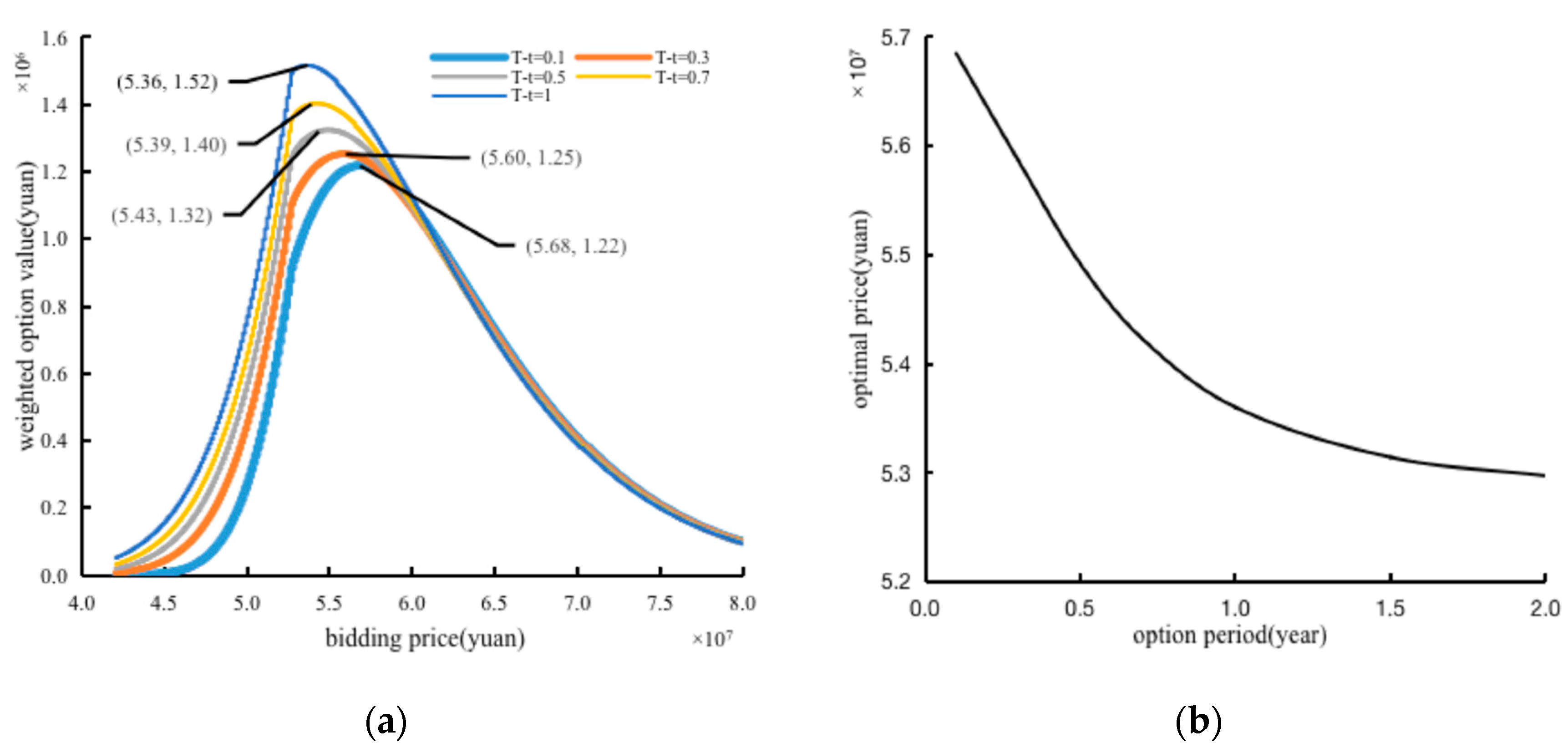
- (2)
- The Sensitivity Analysis of The Option Period
- (3)
- The Sensitivity Analysis of The Estimated Costs
- (4)
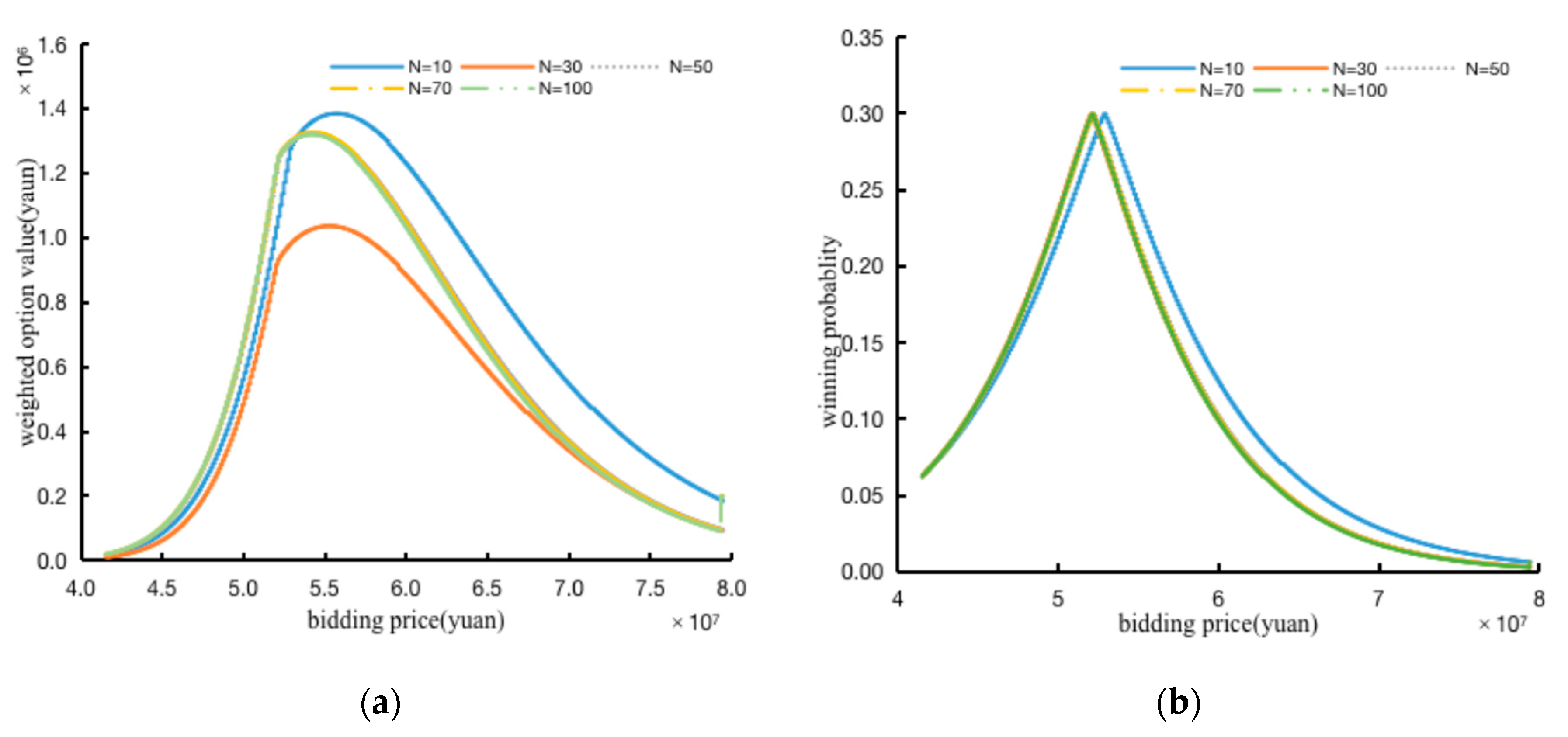
- The Sensitivity Analysis of The Number of Competitors
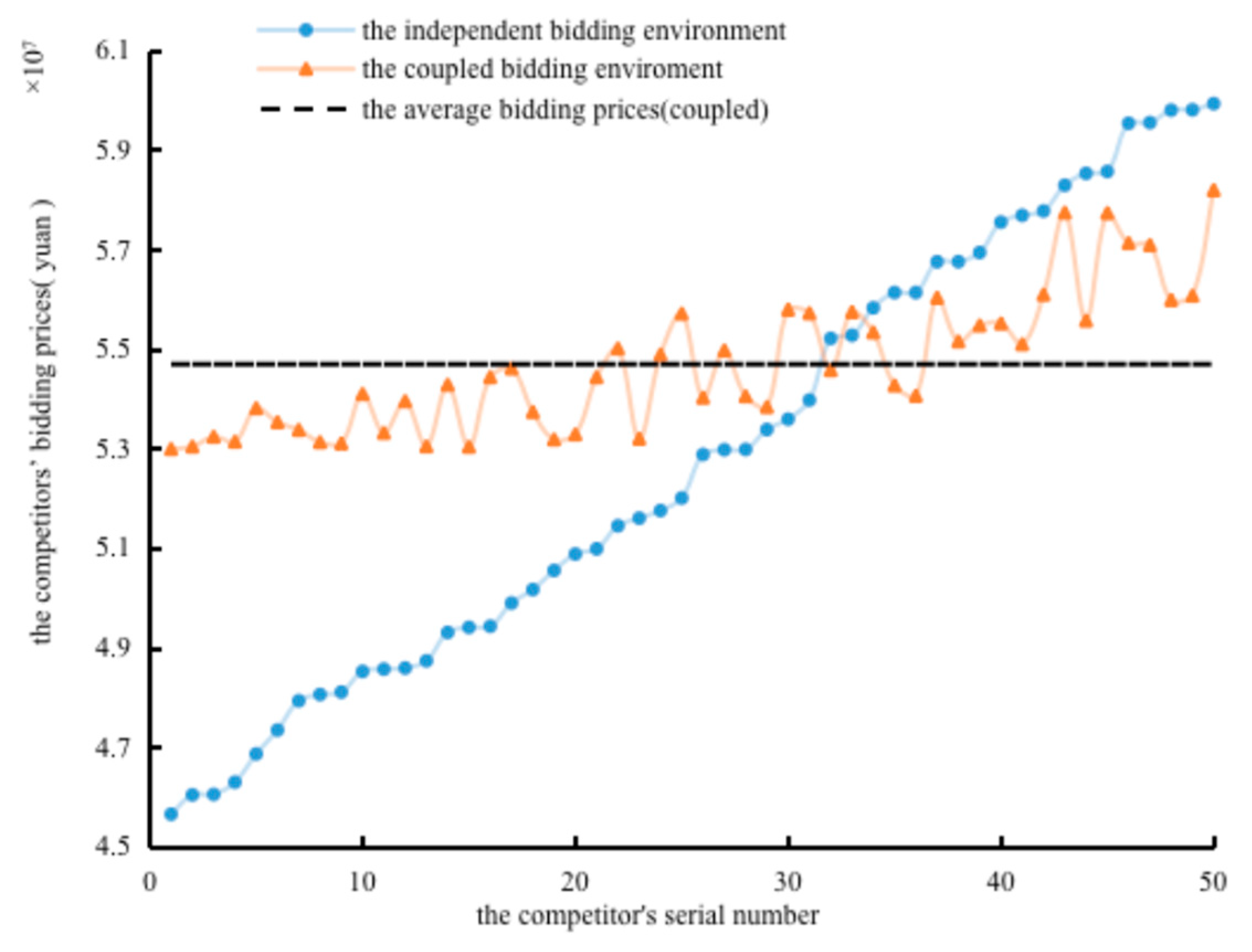
3.3. Simulation Results Analysis in the Coupled Bidding Environment
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kagel, J.H.; Levin, D. Common Value Auctions and the Winner’s Curse; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Yin, Z.H.; Deng, S.J.; Wei, Y.N.; Qian, W.; Li, Z. Why is below average bid auction preferred in procurement? South China J. Econ. 2018, 37, 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou, P.G.; Leu, S.S. Average-bid method—Competitive bidding strategy. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 1993, 119, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.T. Equilibrium Bidding Behaviors and Collusion Incentives in BAMs. South China J. Econ. 2010, 246, 46–62. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.T.; Zhang, Y.G.; Lu, Y.F. An Experimental Study on Average-price-win Auction: The Tradeoff between Avoiding Winner’s Curse and Cutting Price. Ind. Econ. Rev. 2011, 12, 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, L.A. Competitive-bidding strategy. Oper. Res. 1956, 4, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davatgaran, V.; Saniei, M.; Mortazavi, S.S. Optimal bidding strategy for an energy hub in energy market. Energy 2018, 148, 482–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rastegar, H.; Arbab, S.B.; Mirmohammadi, S.H.; Bajegani, E.A. Stochastic programming model for bidding price decision in construction projects. J. Constr. Eng. Manag. 2021, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Ishii, N.; Muraki, M. A sequential competitive bidding strategy considering inaccurate cost estimates. Omega 2014, 42, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.H. Research on the Application of the Maneuver Tree of Tendering and Bidding. Commer. Res. 2002, 8, 84–85. [Google Scholar]
- Christodoulou, S. Bid mark-up selection using artificial neural networks and an entropy metric. Eng. Constr. Archit. Manag. 2010, 17, 424–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, O.; Elhakeem, A. Simulating the winning bid: A generalized approach for optimum markup estimation. Autom. Constr. 2012, 22, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, L.P.; Tan, Q.M.; Ge, Y. Study on Strategies Making of Project Offering Based on Game Model and Fuzzy Forecasting. J. Ind. Eng. Eng. Manag. 2002, 16, 94–96. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Fu, H.Y. Research on evolution game of multi-stakeholder collusion in project bidding. J. Railw. Sci. Eng. 2019, 16, 2378–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaad, R.; Ahmed, M.O.; El-Adaway, I.H.; Elsayegh, A.; Nadendla, V.S.S. Comparing the Impact of Learning in Bidding Decision-Making Processes Using Algorithmic Game Theory. J. Manag. Eng. 2020, 37, 04020099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.P.; Wang, W.D.; An, J. Optimal Price Decision of Bidding Based on Prospect Theory. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Inf. Manag. Eng. 2012, 34, 353–356. [Google Scholar]
- You, T.H.; Cao, B.B. A Method for Bid Price Decision Making Considering Bidder’s Psychological Behaviors and Normal Distribution. J. Eng. Manag. 2017, 31, 19–23. [Google Scholar]
- Engelbrecht-Wiggans, R.; Katok, E. Regret and Feedback Information in First-Price Sealed-Bid Auctions. Manag. Sci. 2008, 54, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.D.; Zou, Q.L. Risk Analysis and Evaluation of Hydropower EPC Project Cost Based on Entropy Weight. Water Resour. Power 2015, 33, 168–171. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.Q.; Zhan, W.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Wang, S.Y. Methods for Bidding under Risk. Oper. Res. Manag. Sci. 2002, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Biancardi, M.; Bufalo, M.; Di Bari, A.; Villani, G. Flexibility to switch project size: A real option application for photovoltaic investment valuation. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2023, 116, 106869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, D.Q. A real options model for renewable energy investment with application to solar photovoltaic power generation in China. Energy Econ. 2016, 59, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Fang, N.; Wang, Y.; Long, T.; Deng, S.; Xue, M.; Deng, B. Value evaluation of mining right based on fuzzy real options. Resour. Policy 2022, 78, 102818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Assereto, M. Deferring real options with solar renewable energy certificates. Glob. Financ. J. 2022, 55, 100795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.; Meng, X.; He, H.; Wang, L.; Gao, J. Towards Optimized ARMGs’ Low-Carbon Transition Investment Decision Based on Real Options. Energies 2022, 15, 5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, F.; Scholes, M. The pricing of options and corporate libilities. J. Political Econ. 1973, 81, 637–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | Value | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Ct | CNY 50 million | estimated investment costs |
| σ | 20% | estimated costs volatility level |
| r | 1% | risk-free rate of return |
| T − t | 0.5 years | The option period |
| n | 1.1 | calibration parameter |
| b | 10 | calibration parameter |
| u | 0.3 | calibration parameter |
| N | 50 | Number of competitors |
| Pi | - | the bidding price of the i-th competitor |
| Prices (CNY Ten Million) | Average | Maximum | Minimum | Median | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Numbers | |||||
| 10 | 5.279 | 5.693 | 4.806 | 5.291 | |
| 30 | 5.279 | 5.842 | 4.710 | 5.231 | |
| 50 | 5.279 | 5.992 | 4.564 | 5.243 | |
| 70 | 5.279 | 5.856 | 4.686 | 5.292 | |
| 100 | 5.279 | 5.992 | 4.564 | 5.243 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Zhu, C. A Real Option Pricing Decision of Construction Project under Group Bidding Environment. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13021130
Liu M, Zhu C. A Real Option Pricing Decision of Construction Project under Group Bidding Environment. Applied Sciences. 2023; 13(2):1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13021130
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Mengkai, and Chenwei Zhu. 2023. "A Real Option Pricing Decision of Construction Project under Group Bidding Environment" Applied Sciences 13, no. 2: 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13021130
APA StyleLiu, M., & Zhu, C. (2023). A Real Option Pricing Decision of Construction Project under Group Bidding Environment. Applied Sciences, 13(2), 1130. https://doi.org/10.3390/app13021130






