Thermal and Electrochemical Properties of Solid Polymer Electrolytes Prepared via Lithium Salt-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Polymerization
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Thermal and Electrochemical Parameters of Interest
2.1. Glass Transition Temperature
2.2. Ionic Conductivity
2.3. Transference Number
2.4. Electrochemical Stability Window
3. Varieties of Epoxide-Based Polymer Electrolyte
3.1. Polyether-Based
3.2. Silicone-Based Reagents
3.3. Amines (Jeffamines)
3.4. Plasticizers and Gel Electrodes
4. Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouchet, R.; Lascaud, S.; Rosso, M. An EIS Study of the Anode Li/PEO-LiTFSI of a Li Polymer Battery. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, A1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Xue, R.; Wang, F. The Mechanism of Lithium Ion Transport in Polyacrylonitrile-Based Polymer Electrolytes. Solid State Ion. 1996, 91, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Z.; He, D.; Xie, X. Poly(ethylene oxide)-based electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 19218–19253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Qu, W.; Guo, X.; Li, L.; Wu, F. The pursuit of solid-state electrolytes for lithium batteries: From comprehensive insight to emerging horizons. Mater. Horiz. 2016, 3, 487–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.W.A.; Donoso, J.P.; Magon, C.J.; Pernaut, J.M.; De Souza, P.P. NMR and DSC study of polymer electrolyte-Carbon Black composites. Solid State Ion. 2000, 136–137, 1181–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, W.T.; Liebig, A.; Cook, J.; Marsh, P.; Ciocanel, C.; Lindberg, G.E.; Browder, C.C. Development of a PEO-based lithium ion conductive epoxy resin polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 2018, 326, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Liang, X.; Chai, J.; Cui, Z.; Wang, Q.; He, W.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Feng, J. High Performance Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Rechargeable Batteries: A Self-Catalyzed Strategy toward Facile Synthesis. Adv. Sci. 2017, 4, 1700174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzberger, J.; Niederer, K.; Pohlit, H.; Seiwert, J.; Worm, M.; Wurm, F.R.; Frey, H. Polymerization of ethylene oxide, propylene oxide, and other alkylene oxides: Synthesis, novel polymer architectures, and bioconjugation. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 2170–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mindemark, J.; Lacey, M.J.; Bowden, T.; Brandell, D. Beyond PEO—Alternative host materials for Li+-conducting solid polymer electrolytes. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 114–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, J.R.; Shaji, I.; Ehteshami, N.; Thum, A.; Diddens, D.; Heuer, A.; Winter, M. Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Lithium Metal Battery via Thermally Induced Cationic Ring-Opening Polymerization (CROP) with an Insight into the Reaction Mechanism. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 3118–3133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, C.Y.; Wang, Z.-G. Ion transport in small-molecule and polymer electrolytes. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 153, 100903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier, N.; Lepage, D.; Zidani, R.; Prebe, A.; Ayme-Perrot, D.; Pellerin, C.; Dollé, M.; Rochefort, D. Crosslinked polyacrylonitrile-based elastomer used as gel polymer electrolyte in Li-ion battery applications. Appl. Energy Mater. 2020, 3, 1099–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, K.; Ding, F.; Liu, X. Recent advances in solid polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 4139–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Peng, X.; Song, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, Y.; Chen, D.; Wang, F. Cure and ionic conductivity of a two-component epoxy network polymer electrolyte. Solid State Ion. 1995, 76, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligon, S.C.; Liska, R.; Stampfl, J.; Gurr, M.; Mülhaupt, R. Polymers for 3D Printing and Customized Additive Manufacturing. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10212–10290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Genier, F.S.; Li, H.; Biria, S.; Hosein, I.D. A Solid Polymer Electrolyte from Cross-Linked Polytetrahydrofuran for Calcium Ion Conduction. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2019, 1, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachipudi, P.S.; Kittur, A.A.; Sajjan, A.M.; Kariduraganavar, M.Y. Synthesis and characterization of hybrid membranes using chitosan and 2-(3,4-epoxycyclohexyl) ethyltrimethoxysilane for pervaporation dehydration of isopropanol. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 441, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Zhu, C.; Huang, B.; Lu, M.; Yang, Y. Synthesis and electrochemical characterization of PEO-based polymer electrolytes with room temperature ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 5789–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changzhi, L.; Xinsheng, P.; Borong, Z.; Baochen, W. An all-solid-state lithium/polyaniline rechargeable cell. J. Power Sources 1992, 39, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, H.; Yin, Y.X.; Zeng, X.X.; Li, J.Y.; Shi, J.L.; Shi, Y.; Wen, R.; Guo, Y.G.; Wan, L.J. In-situ plasticized polymer electrolyte with double-network for flexible solid-state lithium-metal batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 10, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popall, M.; Andrei, M.; Kappel, J.; Kron, J.; Olma, K.; Olsowski, B. ORMOCERs as inorganic-organic electrolytes for new solid state lithium batteries and supercapacitors. Electrochim. Acta 1998, 43, 1155–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaretto, N.; Bittner, A.; Brinkmann, C.; Olsowski, B.E.; Schulz, J.; Seyfried, M.; Vezzù, K.; Popall, M.; Di Noto, V. Highly conducting 3D-hybrid polymer electrolytes for lithium batteries based on siloxane networks and cross-linked organic polar interphases. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 6339–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J. An all-solid-state lithium ion battery electrolyte membrane fabricated by hot-pressing method. J. Power Sources 2015, 284, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, J.F.; Aparicio, M.; Mosa, J. Covalent silica-PEO-LiTFSI hybrid solid electrolytes via sol-gel for Li-ion battery applications. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 213, 831–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, J. Agarose Based Solid Electrolyte for All-Solid-State Lithium Ion Batteries Working from −20 to 80 °C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2020, 167, 80519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, M.S.; Tanaka, M.; Kawakami, H. Free-standing polydimethylsiloxane-based cross-linked network solid polymer electrolytes for future lithium ion battery applications. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 307, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.T.; Tran, B.T.; Subramani, R.; Nguyen, H.T.T.; Rajamani, A.; Lee, M.Y.; Hou, S.S.; Lee, Y.L.; Teng, H. Free-standing polymer electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium batteries operated at room temperature. J. Power Sources 2020, 449, 227518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrieu, X.; Boeuve, J.P.; Vicédo, T. New conducting polymer networks. J. Power Sources 1993, 44, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Kuo, C.L.; Lin, C.L.; Kuo, P.L. Solid polymer electrolytes. IV. Preparation and characterization of novel crosslinked epoxy-siloxane polymer complexes as polymer electrolytes. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2002, 40, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.L.; Liang, W.J.; Chen, T.Y. Solid polymer electrolytes V: Microstructure and ionic conductivity of epoxide-crosslinked polyether networks doped with LiClO4. Polymer 2003, 44, 2957–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Yang, J.; Yu, Y.; Tian, F.; Zhang, B.; Feng, M.; Wang, S. The ionic conductivity, mechanical performance and morphology of two-phase structural electrolytes based on polyethylene glycol, epoxy resin and nano-silica. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 2017, 219, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guhathakurta, S.; Min, K. Lithium sulfonate promoted compatibilization in single ion conducting solid polymer electrolytes based on lithium salt of sulfonated polysulfone and polyether epoxy. Polymer 2010, 51, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, Q.; Huang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Xu, X. One-pot preparation of new copolymer electrolytes with tunable network structure for all-solid-state lithium battery. J. Power Sources 2016, 331, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, J.; Wei, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, Y.; Yao, X.; Xu, X. One-pot synthesis of crosslinked polymer electrolyte beyond 5V oxidation potential for all-solid-state lithium battery. J. Power Sources 2019, 431, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.J.; Chen, T.Y.; Kuo, P.L. Solid Polymer Electrolytes. VII. Preparation and Ionic Conductivity of Gelled Polymer Electrolytes Based on Poly(ethylene glycol) Diglycidyl Ether Cured with α,ω-Diamino Poly(propylene oxide). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 1264–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Sun, K.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, N.; Zhu, X. Polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) with crosslinked poly(ethylene glycol) for lithium batteries. Solid State Ion. 2009, 180, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Endo, T. Synthesis of Networked Polymers with Lithium Counter Cations from a Difuctional Epoxide Containing Poly(ethylene glycol) and an Epoxide Monomer Carrying a Lithium Sulfonate Salt Moiety. J. Polym. Sci. Part A-1 Polym. Chem. 2010, 48, 3113–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.K.; Jung, B.M.; Choi, U.H.; Lee, S.B. Ion Conduction and Viscoelastic Response of Epoxy-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes Containing Solvating Plastic Crystal Plasticizer. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2018, 219, 1700514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, U.H.; Jung, B.M. Ion Conduction, Dielectric and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes Containing Succinonitrile. Macromol. Res. 2018, 26, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, K.; Endo, T. Design and synthesis of ionic-conductive epoxy-based networked polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, B.G.; Silva, A.A.; Livi, S.; Duchet-Rumeau, J.; Gerard, J.F. New Epoxy/Jeffamine networks modified with ionic liquids. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, S.J.; Kim, T.; Jung, B.M.; Lee, S.B.; Choi, U.H. Multifunctional Epoxy-Based Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Solid-State Supercapacitors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35108–35117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, H.; Locascio, L.E. Polymer microfluidic devices. Talanta 2002, 56, 267–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoso, J.P.; Cavalcante, M.G.; Bonagamba, T.J.; Nascimento, O.R.; Panepucci, H. Magnetic resonance study of water absorption in some peo-lithium salt polymer electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 1995, 40, 2357–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moylan, J. Considerations for Measuring Glass Transition Temperature. Available online: https://www.element.com/nucleus/2017/08/15/18/45/considerations-for-measuring-glass-transition-temperature (accessed on 27 May 2020).
- Commarieu, B.; Paolella, A.; Collin-Martin, S.; Gagnon, C.; Vijh, A.; Guerfi, A.; Zaghib, K. Solid-to-liquid transition of polycarbonate solid electrolytes in Li-metal batteries. J. Power Sources 2019, 436, 226852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarlane, D.R.; Zhou, F.; Forsyth, M. Ion conductivity in amorphous polymer/salt mixtures. Solid State Ion. 1998, 113–115, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caradant, L.; Lepage, D.; Nicolle, P.; Prébé, A.; Aymé-Perrot, D.; Dollé, M. Effect of Li+Affinity on Ionic Conductivities in Melt-Blended Nitrile Rubber/Polyether. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 4943–4951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sturtevant, J.M. Biochemical applications of differential scanning calorimetry. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1987, 38, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Mindemark, J.; Edström, K.; Brandell, D. Polycarbonate-based solid polymer electrolytes for Li-ion batteries. Solid State Ion. 2014, 262, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foran, G.; Mankovsky, D.; Verdier, N.; Lepage, D.; Prébé, A.; Aymé-Perrot, D.; Dollé, M. The Impact of Absorbed Solvent on the Performance of Solid Polymer Electrolytes for Use in Solid-State Lithium Batteries. iScience 2020, 23, 101597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, J. Ionic Conductivity. In Comprehensive Polymer Science and Supplemants; Allen, G., Bevington, J.C., Eds.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 669–686. [Google Scholar]
- Schauser, N.S.; Nikolaev, A.; Richardson, P.M.; Xie, S.; Johnson, K.; Susca, E.M.; Wang, H.; Seshadri, R.; Clément, R.J.; Read de Alaniz, J.; et al. Glass Transition Temperature and Ion Binding Determine Conductivity and Lithium–Ion Transport in Polymer Electrolytes. ACS Macro Lett. 2020, 10, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, B.E.; Forbey, S.J.; Steuber, F.W.; Moore, R.B.; Madsen, L.A. Multiscale Lithium and Counterion Transport in an Electrospun Polymer-Gel Electrolyte. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 4481–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederichsen, K.M.; Buss, H.G.; McCloskey, B.D. The Compensation Effect in the Vogel-Tammann-Fulcher (VTF) Equation for Polymer-Based Electrolytes. Macromolecules 2017, 50, 3831–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldalur, I.; Armand, M.; Zhang, H. Jeffamine-Based Polymers for Rechargeable Batteries. Batter. Supercaps 2020, 3, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankovsky, D.; Lepage, D.; Caradant, L.; Lachal, M.; Ayme-Perrot, D.; Dolle, M. Water content in solid polymer electrolytes: The lost knowledge. ChemComm 2020, 56, 10167–10170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Yu, J.; He, K. Thermoplastic starch plasticized by glycerol as solid polymer electrolytes. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2006, 291, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesko, D.M.; Timachova, K.; Bhattacharya, R.; Smith, M.C.; Villaluenga, I.; Newman, J.; Balsara, N.P. Negative Transference Numbers in Poly(ethylene oxide)-Based Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, E3569–E3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, R.D.; Clarke, M.D. The effect of traces of water on PEO4.5LiCF3SO3 films. Solid State Ion. 1984, 11, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, K.D.; Self, J.; Diederichsen, K.M.; Wood, B.M.; McCloskey, B.D.; Persson, K.A. Ion Transport and the True Transference Number in Nonaqueous Polyelectrolyte Solutions for Lithium Ion Batteries. ACS Cent. Sci. 2019, 5, 1250–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.; Vincent, C.A.; Bruce, P.G. Electrochemical measurement of transference numbers in polymer electrolytes. Polymer 1987, 28, 2324–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruce, P.G.; Hardgrave, M.T.; Vincent, C.A. The determination of transference numbers in solid polymer electrolytes using the Hittorf method. Solid State Ion. 1992, 53–56, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsara, N.P.; Newman, J. Relationship between Steady-State Current in Symmetric Cells and Transference Number of Electrolytes Comprising Univalent and Multivalent Ions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A2720–A2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.; Fedkiw, P.S.; Khan, S.A. Transport Properties of Lithium Hectorite-Based Composite Electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, A667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pożyczka, K.; Marzantowicz, M.; Dygas, J.R.; Krok, F. Ionic conductivity and lithium transference number of poly(ethylene oxide):litfsi system. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 227, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chintapalli, M.; Timachova, K.; Olson, K.R.; Mecham, S.J.; Devaux, D.; Desimone, J.M.; Balsara, N.P. Relationship between Conductivity, Ion Diffusion, and Transference Number in Perfluoropolyether Electrolytes. Macromolecules 2016, 49, 3508–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Hassoun, J.; Panero, S.; Scrosati, B.; Tominaga, Y. Electrochemical properties of a poly(ethylene carbonate)-LiTFSI electrolyte containing a pyrrolidinium-based ionic liquid. Ionics 2015, 21, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Wang, X.; Yao, P.; Li, J.; Zhu, J. Towards high energy density lithium battery anodes: Silicon and lithium. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 7132–7148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Venkatram, S.; Kim, C.; Batra, R.; Chandrasekaran, A.; Ramprasad, R. Electrochemical Stability Window of Polymeric Electrolytes. Chem. Mater. 2019, 31, 4598–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Park, K.S. The Li-ion rechargeable battery: A perspective. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Jiang, M.; Gao, X.; Bao, D.; Sun, Q.; Holmes, N.; Duan, H.; Mukherjee, S.; Adair, K.; Zhao, C.; et al. Determining the limiting factor of the electrochemical stability window for PEO-based solid polymer electrolytes: Main chain or terminal –OH group? Energy Environ. Sci. 2020, 1318–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Downie, L.E.; Ma, L.; Qiu, W.; Dahn, J.R. Study of the Failure Mechanisms of LiNi0.8Mn0.1Co0.1O2 Cathode Material for Lithium Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A1401–A1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowe, A.W.; Dahn, J.R. Positive Electrode Materials in the Li-Mn-Ni-O System Exhibiting Anomalous Capacity Growth during Extended Cycling. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A308–A317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Burns, J.C.; Trussler, S.; Dahn, J.R. Precision Measurements of the Coulombic Efficiency of Lithium-Ion Batteries and of Electrode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2010, 157, A196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Shangguan, X.; Tian, S.; Zhou, X.; Cui, G. Siloxane-based polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 23, 466–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matkovska, L.; Iurzhenko, M.; Mamunya, Y.; Tkachenko, I.; Demchenko, V.; Synyuk, V.; Shadrin, A.; Boiteux, G. Structural Peculiarities of Ion-Conductive Organic-Inorganic Polymer Composites Based on Aliphatic Epoxy Resin and Salt of Lithium Perchlorate. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2017, 12, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, P.G. Solid State Electrochemistry; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; ISBN 0521400074. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez, J.; Mackanic, D.G.; Cui, Y.; Bao, Z. Designing polymers for advanced battery chemistries. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2019, 4, 312–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qu, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. The Challenge of Lithium Metal Anodes for Practical Applications. Small Methods 2019, 3, 1800551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.M.; Saikia, D.; Ho, S.Y.; Chen, M.C.; Kao, H.M. High ion-conducting solid polymer electrolytes based on blending hybrids derived from monoamine and diamine polyethers for lithium solid-state batteries. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 20373–20383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.C.; Chu, Y.T. Blend-Curing of Epoxies with Jeffamine® and Diethyltoluenediamine. J. Polym. Eng. 1996, 16, 51–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira da Silva, L.C.; Soares, B.G. New all solid-state polymer electrolyte based on epoxy resin and ionic liquid for high temperature applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, J. Gas Hydrate Control. In Petroleum Engineer’s Guide to Oil Field Chemicals and Fluids; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 405–413. [Google Scholar]
- Aldalur, I.; Zhang, H.; Piszcz, M.; Oteo, U.; Rodriguez-Martinez, L.M.; Shanmukaraj, D.; Rojo, T.; Armand, M. Jeffamine® based polymers as highly conductive polymer electrolytes and cathode binder materials for battery application. J. Power Sources 2017, 347, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motogami, K.; Mori, S. Ion-Conductive Polymer Electrolyte. European Patent Application 90303944.4, 17 October 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Aldalur, I.; Martinez-Ibañez, M.; Piszcz, M.; Rodriguez-Martinez, L.M.; Zhang, H.; Armand, M. Lowering the operational temperature of all-solid-state lithium polymer cell with highly conductive and interfacially robust solid polymer electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2018, 383, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.M.; Chang, P.C.; Chao, S.W.; Lee, C.H. 7Li NMR, ionic conductivity and self-diffusion coefficients of lithium ion and solvent of plasticized organic-inorganic hybrid electrolyte based on PPG-PEG-PPG diamine and alkoxysilanes. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 52, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Kim, T.; Choi, U.H. Tuning Morphology and Properties of Epoxy-Based Solid-State Polymer Electrolytes by Molecular Interaction for Flexible All-Solid-State Supercapacitors. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 3879–3892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Marsh, R. Polymer Batteries. SAE Trans. 1991, 100, 408–412. [Google Scholar]
- Greaves, T.L.; Drummond, C.J. Protic ionic liquids: Properties and applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 206–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazi, Z.A.; Sun, Z.; Sun, C.; Qi, F.; An, B.; Li, F.; Cheng, H.M. Key Aspects of Lithium Metal Anodes for Lithium Metal Batteries. Small 2019, 15, 1900687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K. Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11503–11618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
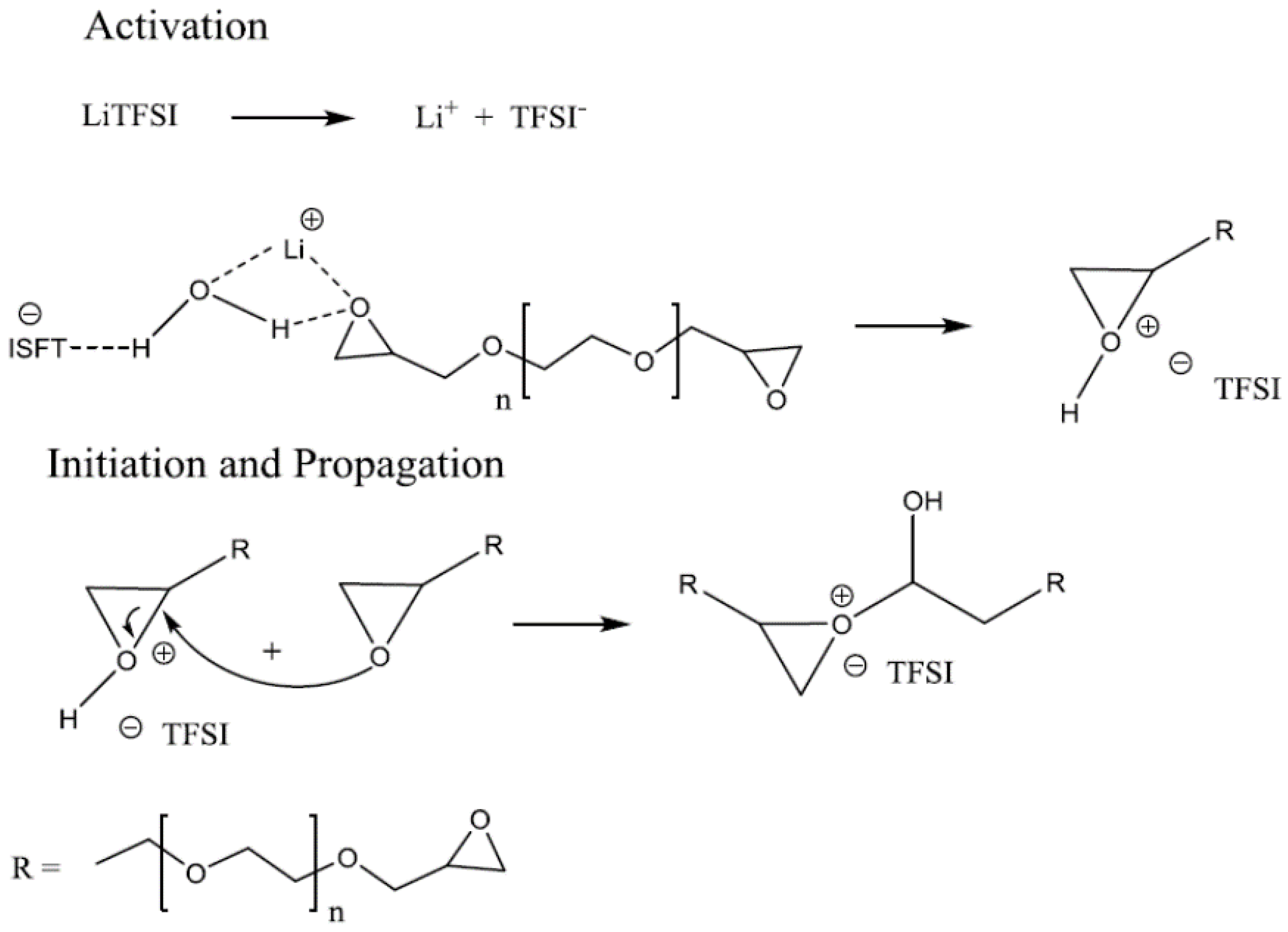
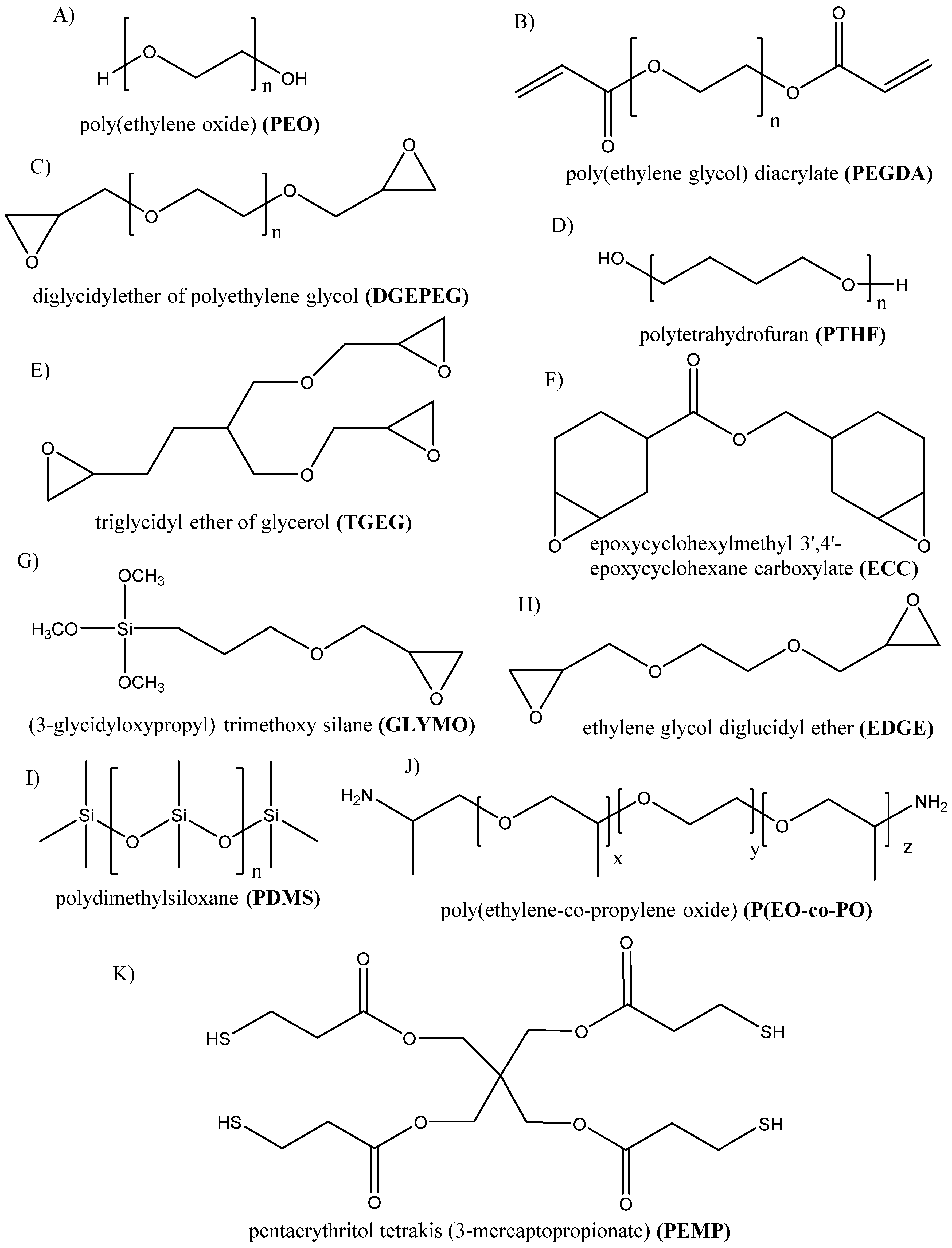
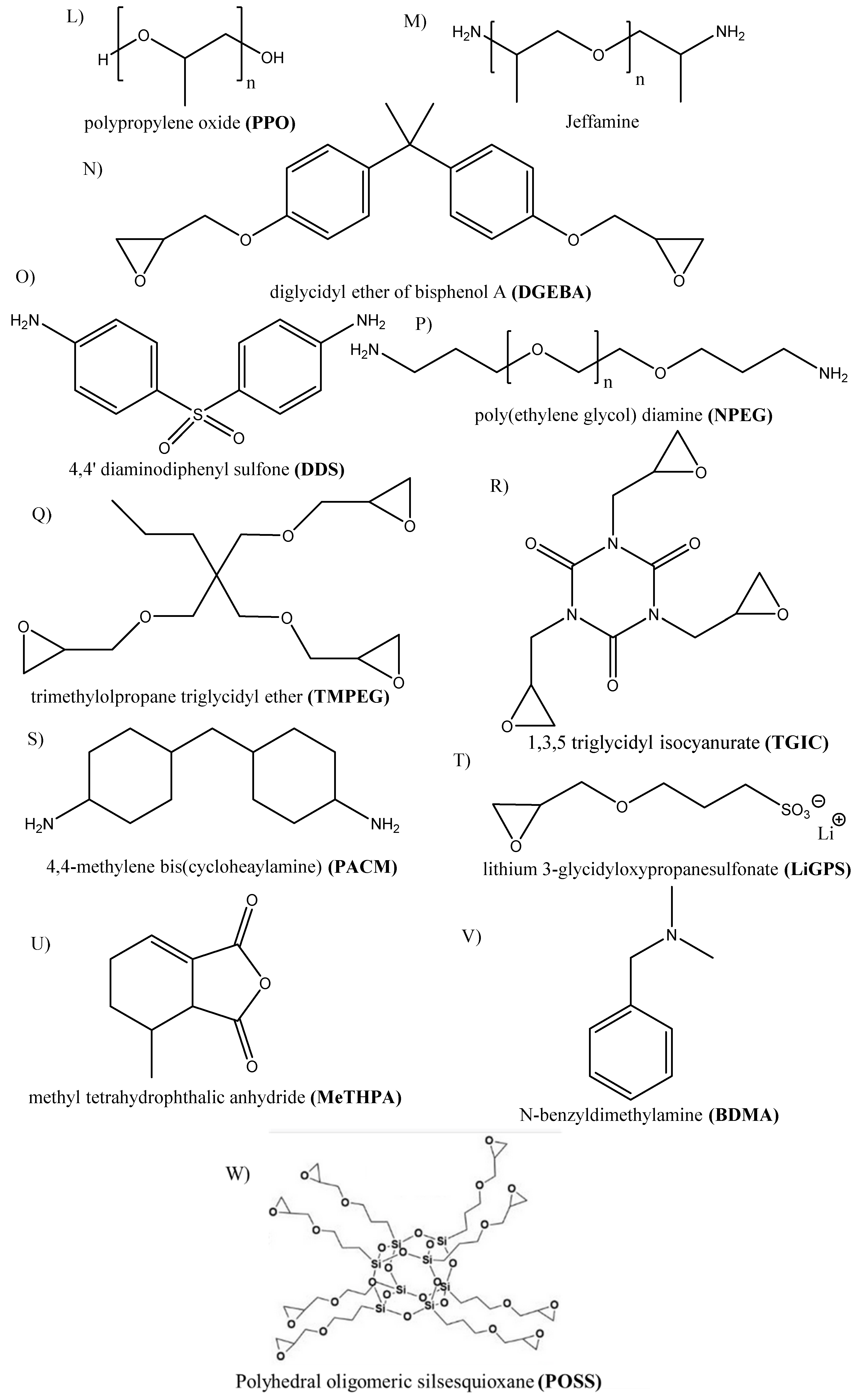
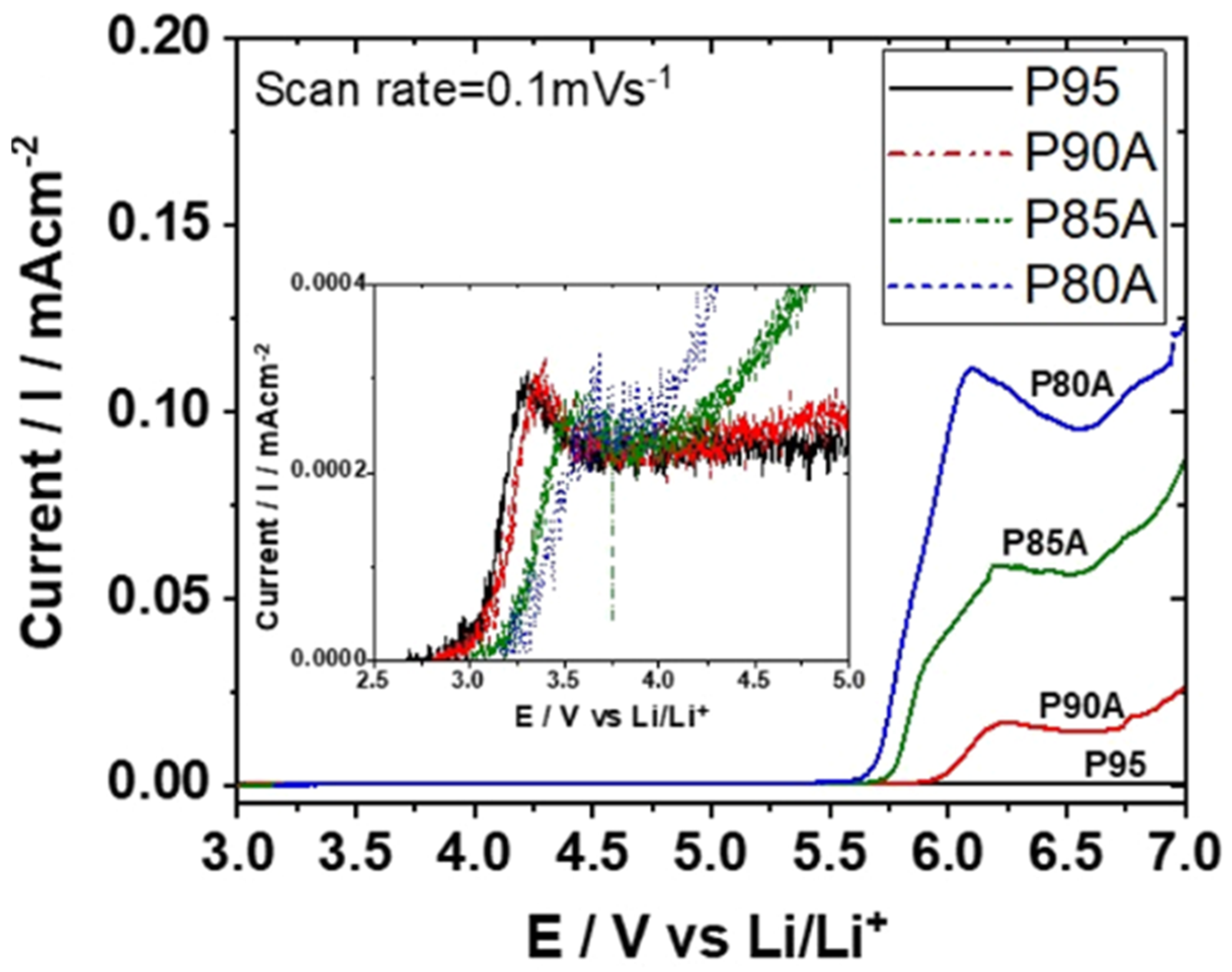
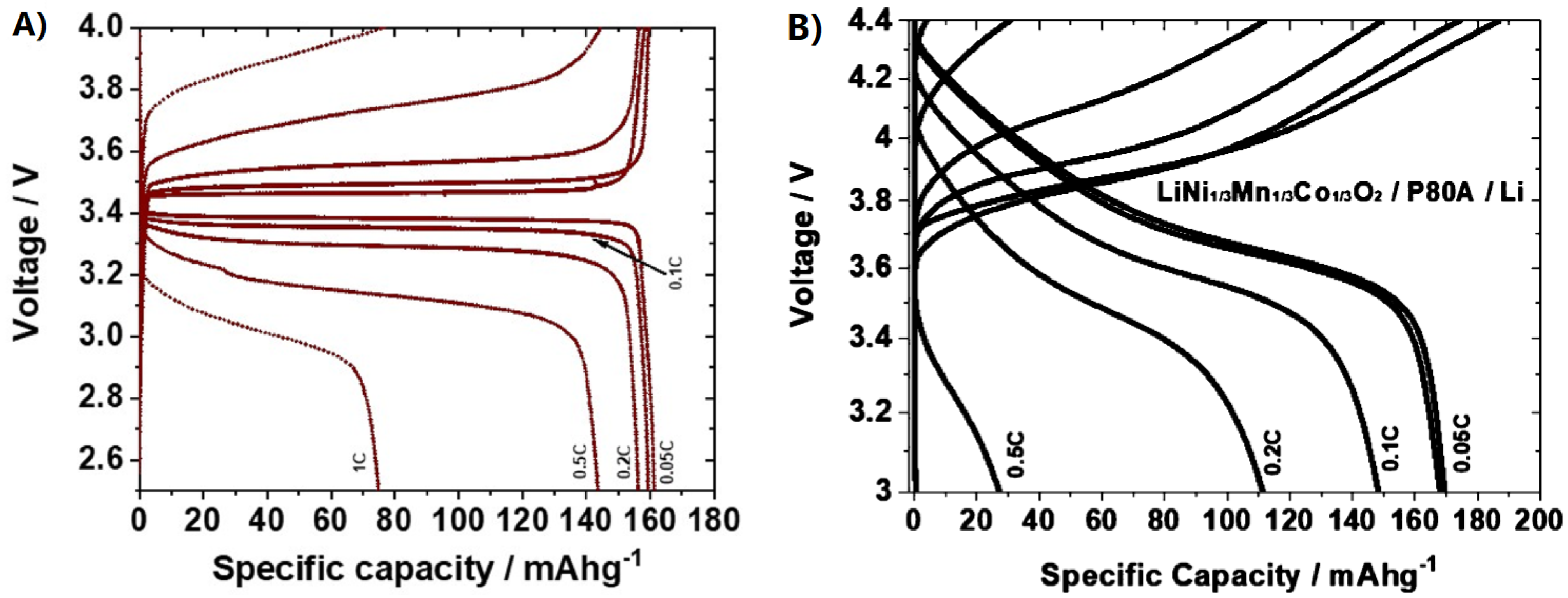
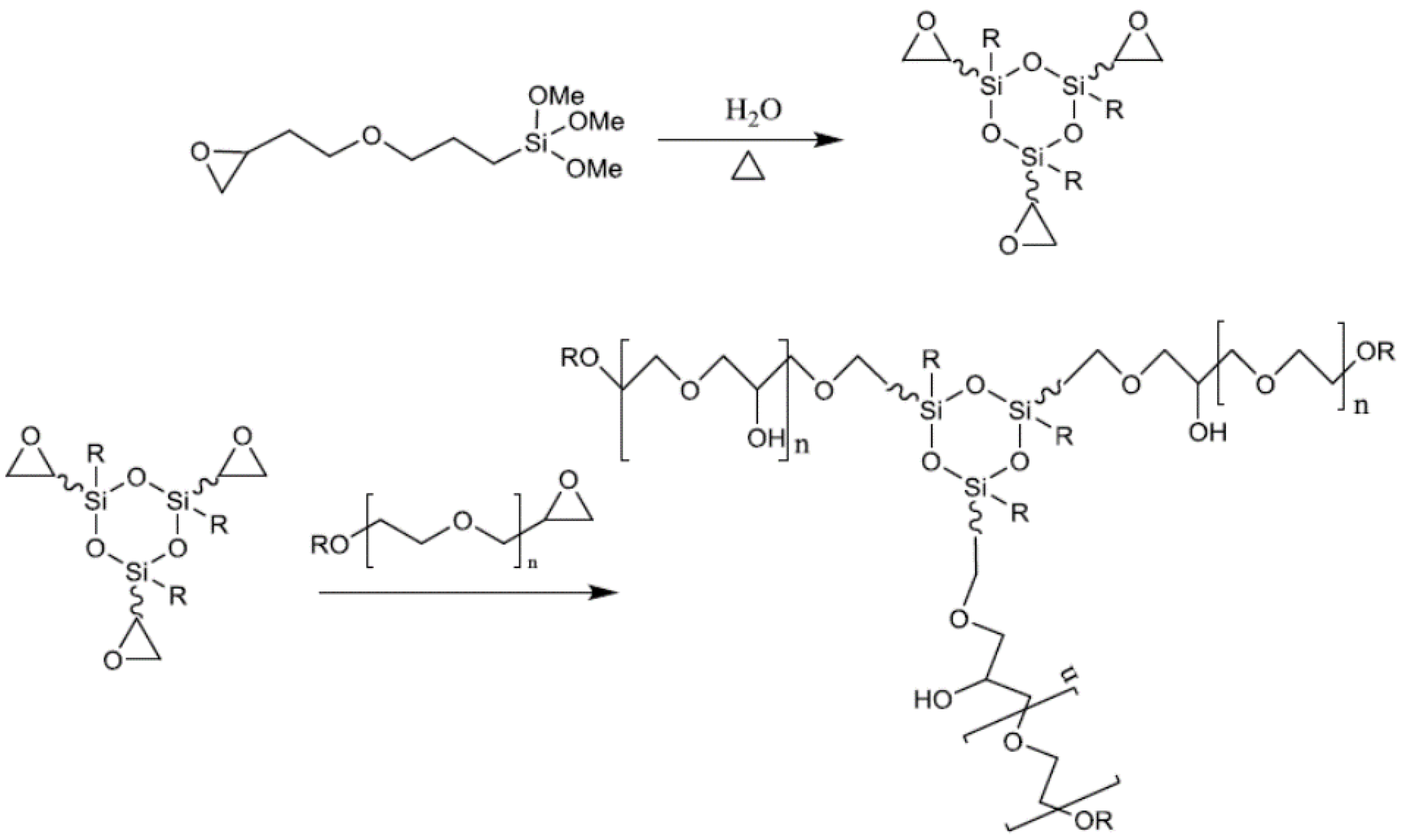
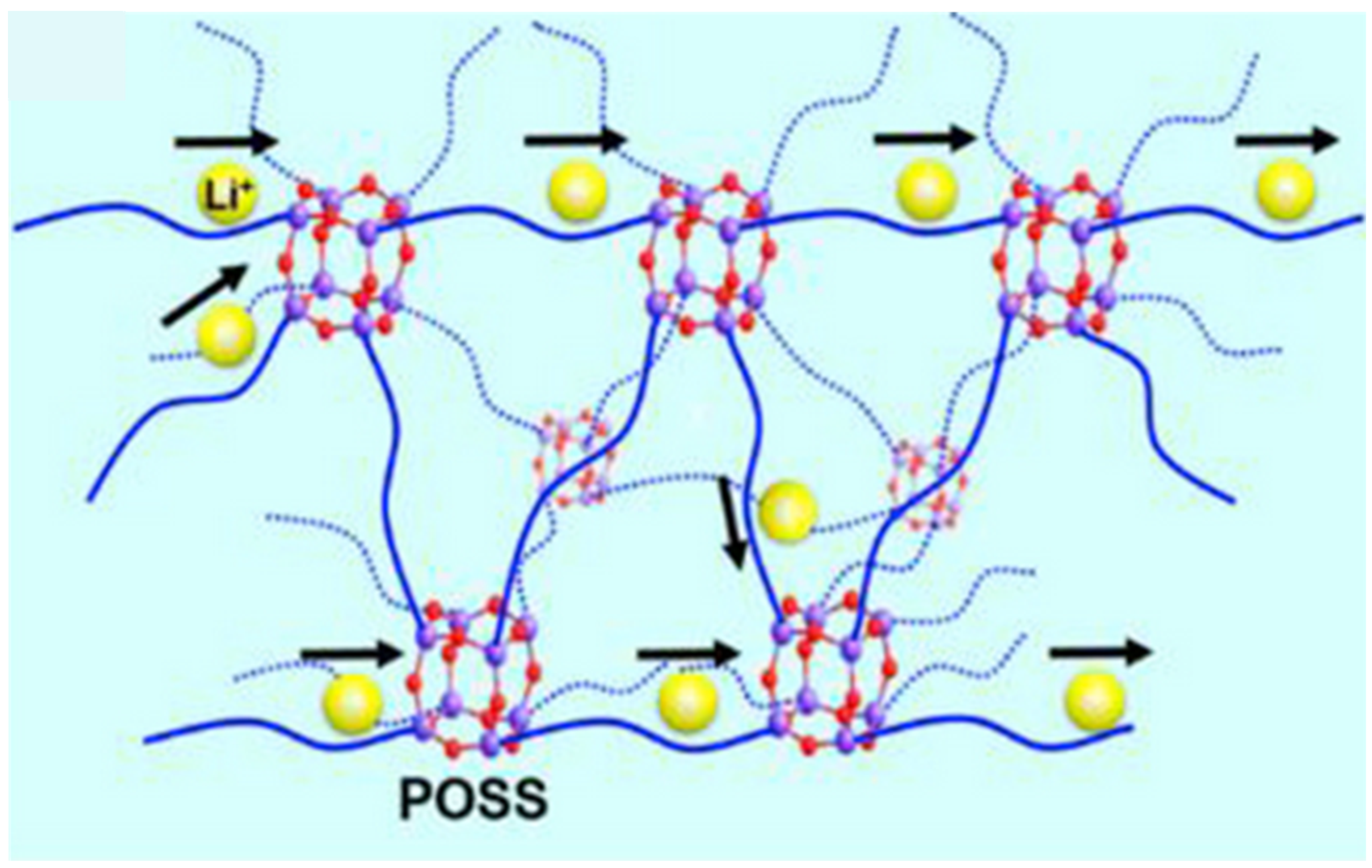
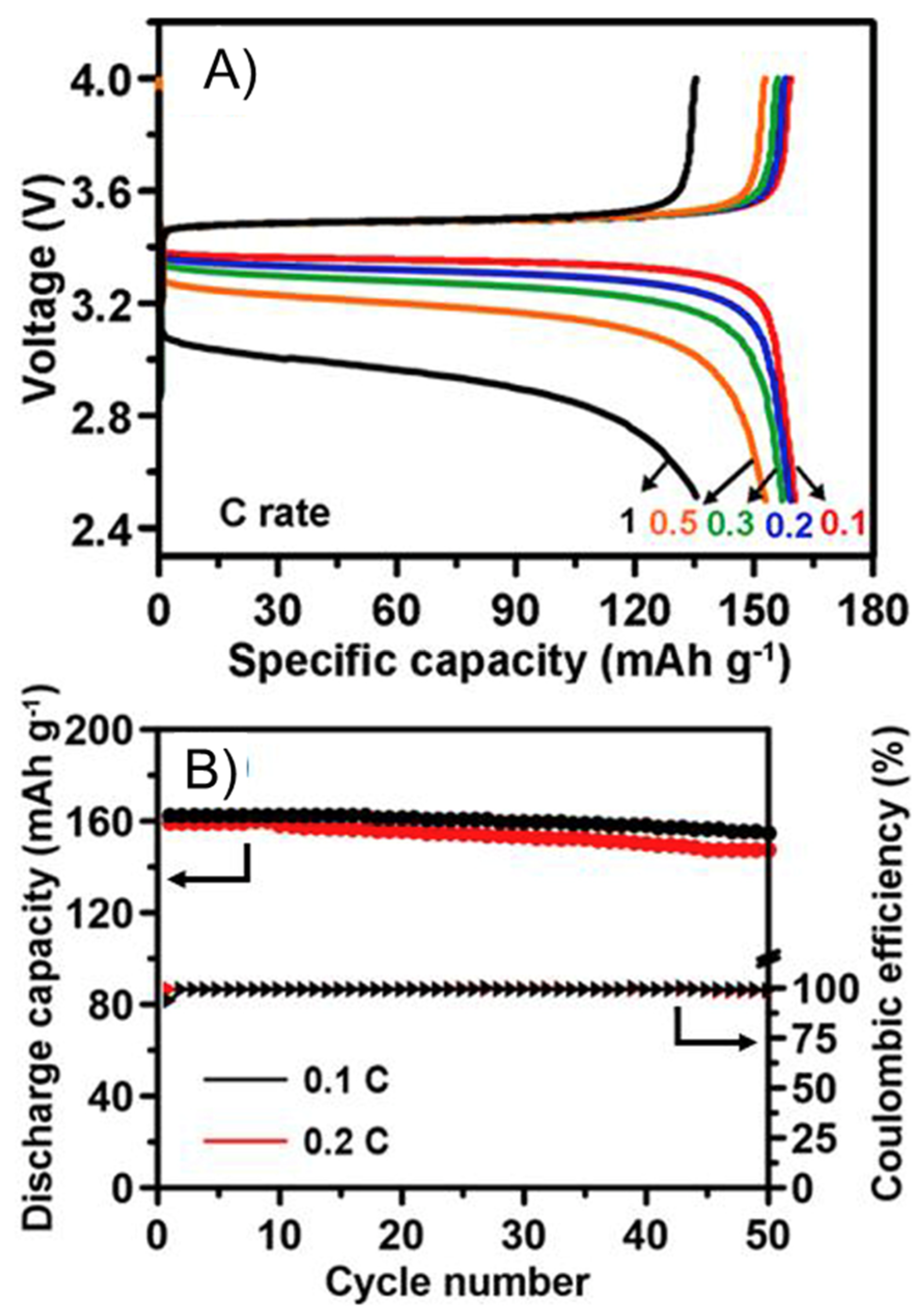
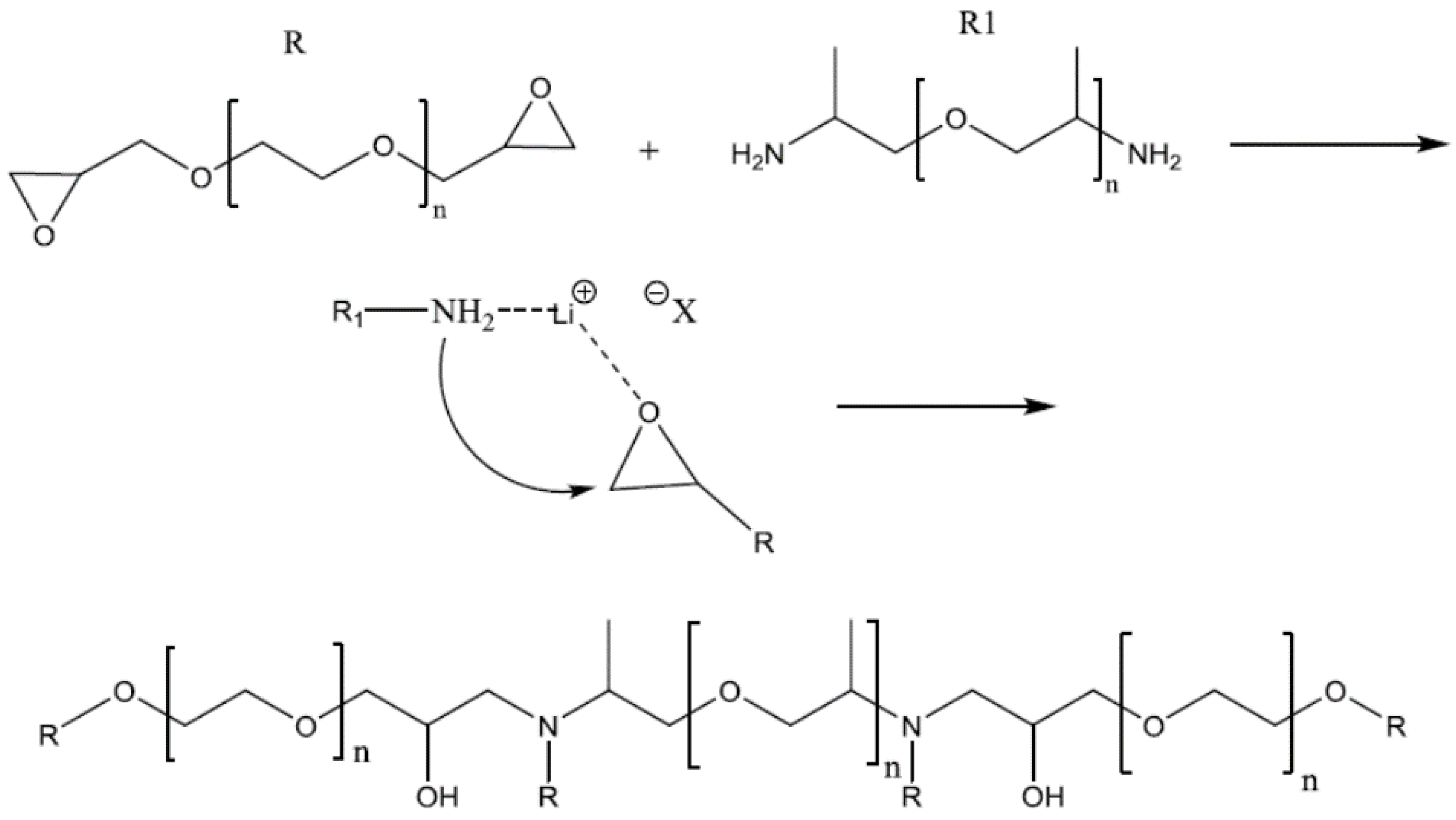
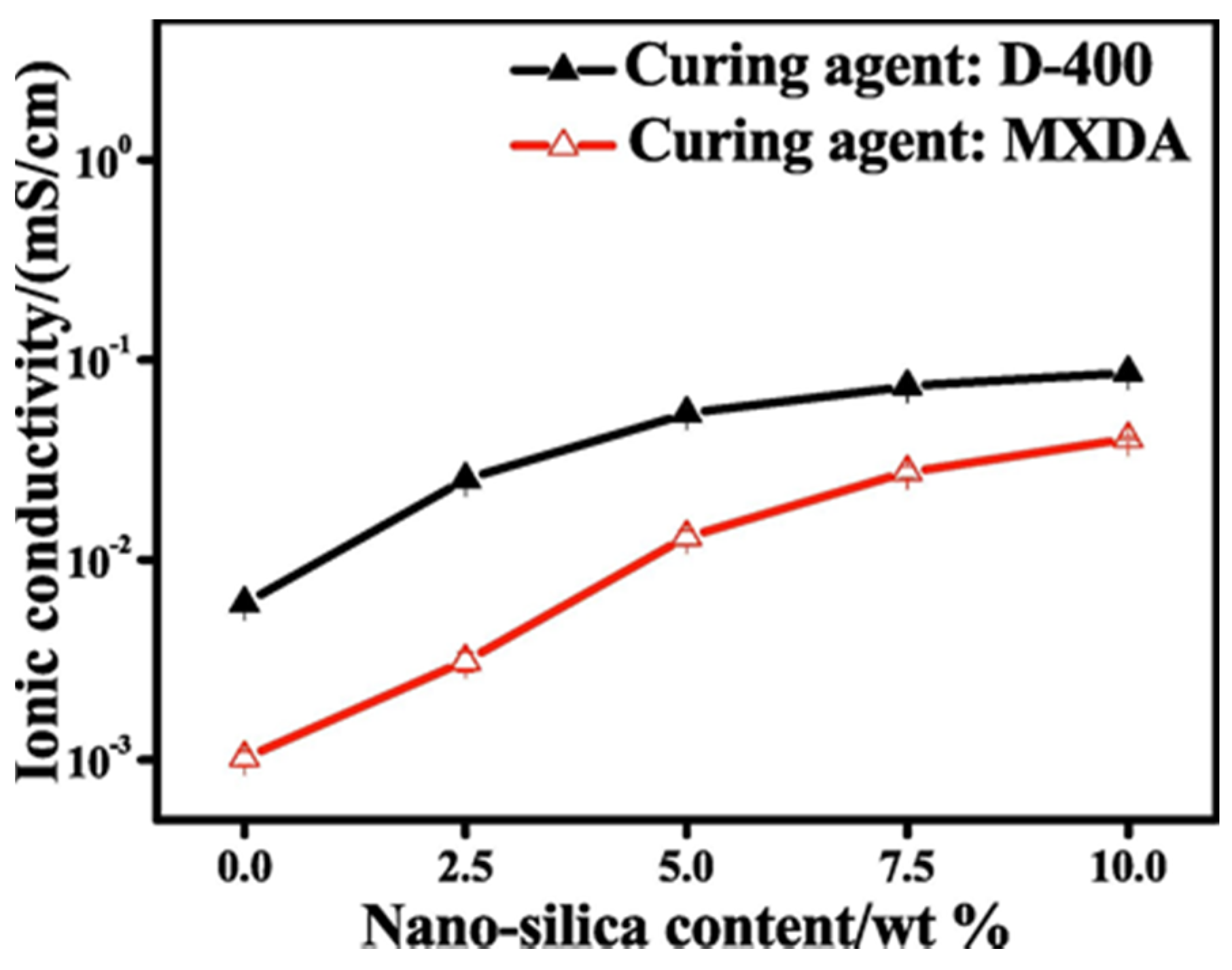
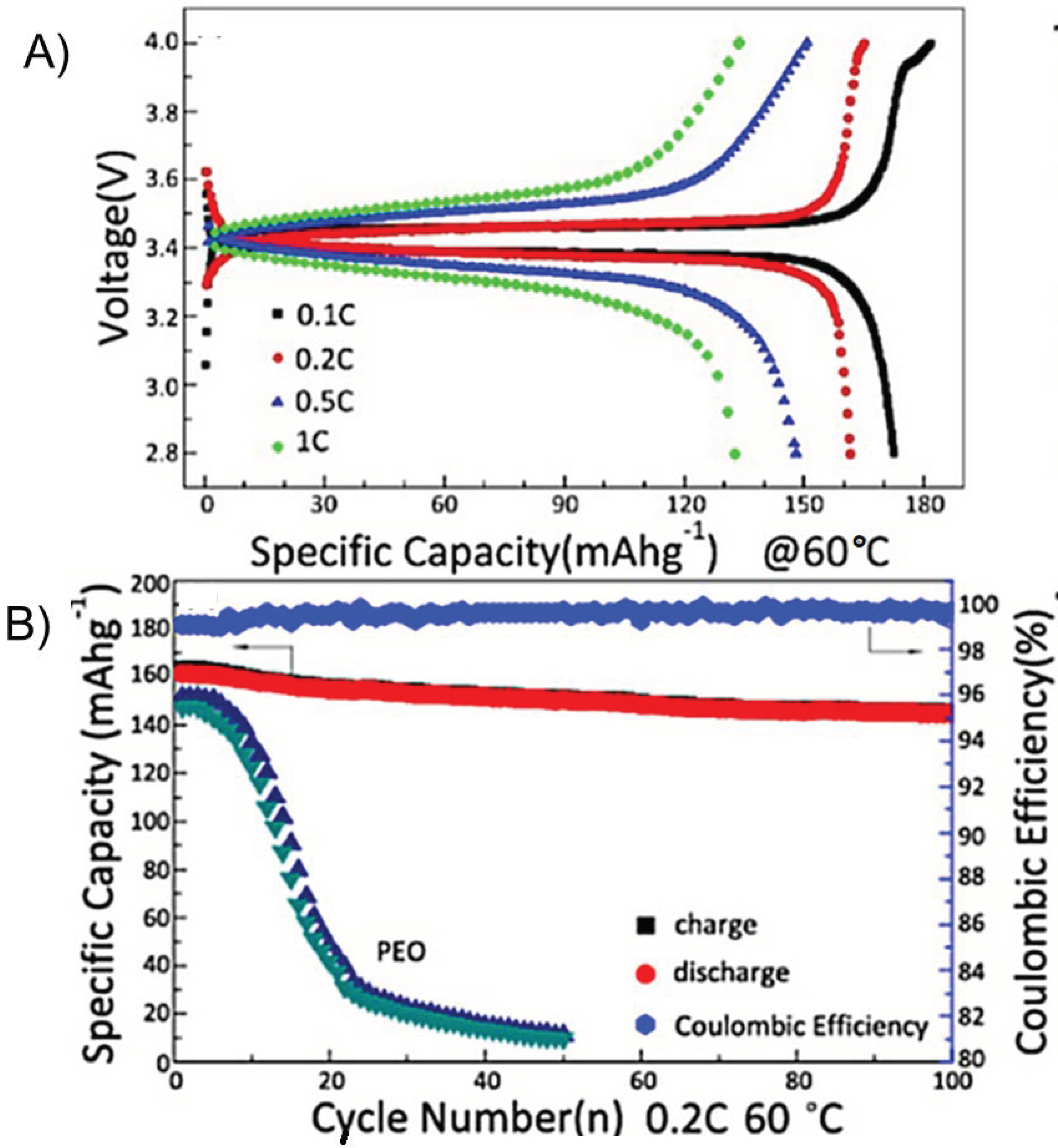

| Components | Salt, Plasticizer | Solvent | Tg (°C) | σ at RT (S/cm) | t+ | Stability vs. Li+/Li (V) and Cathode | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEO | LiTFSI | ACN | −40 | 4 × 10−7 | 0.40 | 4.8 * | Cheng [18] |
| Polyether-Based | |||||||
| PEO, epoxy resin | LiClO4 | none | n/a | ~10−6 | n/a | n/a | Changzhi [19] |
| DGEPEG, TGEG | LiClO4 | none | 0 | ~10−5 | n/a | n/a | Wu [14] |
| DGEPEG | LiDFOB | none | −43 | 8.9 × 10−5 | n/a | 4.5, LFP | Cui [7] |
| DGEPEG | LiTFSI, LiBF4 | none | −50 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 0.23 | 5.5, LFP and NMC | Nair [10] |
| DGEPEG, PEGDA | LiTFSI | none | −37 | 5.3 × 10−5 | n/a | 4.7, LFP | Duan [20] |
| PTHF, ECC | Ca(NO3)2 | none | −7 | ~10−4 | 0.36 | n/a | Wang [16] |
| Silicon-Based | |||||||
| GLYMO, DGEPEG | LiClO4 | none | −60 | 1.2 × 10−4 | n/a | n/a | Popall [21] |
| GLYMO, PEO-MO | LiClO4 | H2O | n/a | ~10−4 | 0.5 | 4.5 * | Boaretto [22] |
| GLYMO, PEO | LiTFSI | toluene | −45.5 | 5.56 × 10−5 | n/a | 3.75 | Han [23] |
| GLYMO, EDGE | LiTFSI | ethanol | −55 | 2.6 × 10−5 | 0.37 | 4.9, LTO | Vélez [24] |
| agarose, GLYMO | LiTFSI | NMP | n/a | 2.66 × 10−4 | 0.39 | 4.9, LFP | Liu [25] |
| PDMS, DGEPEG, PEMP | LiTFSI | ACN | −34 | ~10−6 | 0.2 | 5.3 * | Grewal [26] |
| POSS, P(EO-co-PO) | LiTFSI | THF | −43 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 0.62 | 5.4, LFP | Hsu [27] |
| Jeffamines | |||||||
| PPO Jeffamine, DGEPEG | LiClO4 | ACN | −56 | 4 × 10−5 | n/a | 4.6 * | Andrieu [28] |
| Jeffamine D2000, SG80 | LiClO4 | acetone | −41 | ~10−7 | n/a | n/a | Liang [29] |
| Jeffamine D400, DGEPEG | LiClO4 | acetone | −20 | ~10−7 | n/a | n/a | Kuo [30] |
| Jeffamine D400, DGEBA, PEG, nano silica | LiTf | none | 40–70 | 10−6–10−5 varies based on silica content | n/a | n/a | Feng [31] |
| DDS, DGEPEG | DDS is lithiated | DMAc | 40 | 10−8 | n/a | n/a | Guhathakurta [32] |
| NPEG, TMPEG | LiTFSI | THF | −40 | 1.1 × 10−4 | 0.27 | 5.4 * | Chen [33] |
| NPEG, TGIC | LiTFSI | ACN | −44 | 1.15 × 10−4 | 0.32 | 5.1 * | Chen [34] |
| Plasticizers and Gel Electrolytes | |||||||
| DGEPEG, DGEBA, Jeffamine D400 | LiClO4, PC | none | −40 | 3.1 × 10−5 | n/a | n/a | Liang [35] |
| PVDF-HFP DGEPEG, DIEPEG-PEI | LiPF6, EC, DMC | acetone H2O | n/a | 2.3 × 10−3 | n/a | 4.8 * | Ren [36] |
| DGEPEG, PEGBA, LiGPS | LiTFSI, PC | CH3OH | −55 | 9.2 × 10−3 | n/a | n/a | Matsumoto [37] |
| DGEPEG, PACM | LiTFSI, PC | none | 160 | 1.0 × 10−3 | n/a | n/a | Andrews [6] |
| DGEBA, BDMA | LiTFSI, SN | none | n/a | 10−2 | n/a | n/a | Jang [38] |
| YD-128 | LiTFSI, SN | none | n/a | 10−4 | n/a | n/a | Choi [39] |
| DGEPEG, DGEBA | LiTFSI, EMImFSI | none | n/a | 4.3 × 10−3 | n/a | n/a | Matsumoto [40] |
| Jaffamine D400, DGEBA | OdTPP or DOdIm | none | 50 | n/a | n/a | n/a | Soares [41] |
| DGEBA, DGEPEG, MeTHPA, Al2O3 | LiTFSI, BMIM-TFSI | none | 96 | 2.5 × 10−6 | n/a | n/a | Kwon [42] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Foran, G.; Verdier, N.; Lepage, D.; Prébé, A.; Aymé-Perrot, D.; Dollé, M. Thermal and Electrochemical Properties of Solid Polymer Electrolytes Prepared via Lithium Salt-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Polymerization. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041561
Foran G, Verdier N, Lepage D, Prébé A, Aymé-Perrot D, Dollé M. Thermal and Electrochemical Properties of Solid Polymer Electrolytes Prepared via Lithium Salt-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Polymerization. Applied Sciences. 2021; 11(4):1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041561
Chicago/Turabian StyleForan, Gabrielle, Nina Verdier, David Lepage, Arnaud Prébé, David Aymé-Perrot, and Mickaël Dollé. 2021. "Thermal and Electrochemical Properties of Solid Polymer Electrolytes Prepared via Lithium Salt-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Polymerization" Applied Sciences 11, no. 4: 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041561
APA StyleForan, G., Verdier, N., Lepage, D., Prébé, A., Aymé-Perrot, D., & Dollé, M. (2021). Thermal and Electrochemical Properties of Solid Polymer Electrolytes Prepared via Lithium Salt-Catalyzed Epoxide Ring Opening Polymerization. Applied Sciences, 11(4), 1561. https://doi.org/10.3390/app11041561







