Research Progress on the Stability and Durability of Ag/AgCl Prepared by Anodic Chlorination Method for Chloride Ion Sensors in Cement-Based Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Working Principle of Ag/AgCl as ISEs
3. Fabrication Methods of Ag/AgCl ISEs
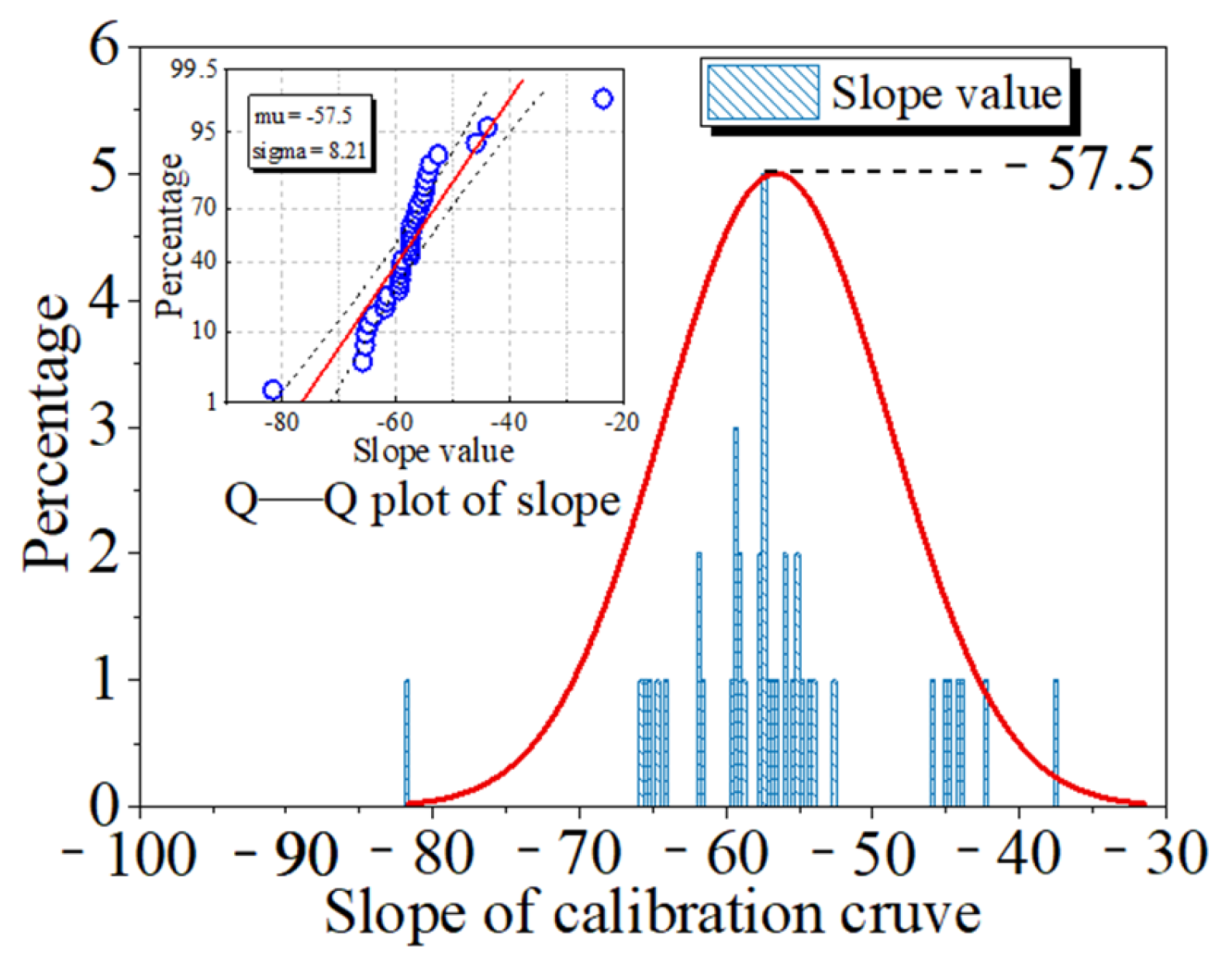
3.1. Anodic Chlorination
3.2. Calibration
4. The Stability of Ag/AgCl ISEs Used to Monitor Chloride in Concrete
4.1. Potential Interference
4.1.1. Liquid Junction Potential
4.1.2. Diffusion Potential
4.1.3. Membrane Potential
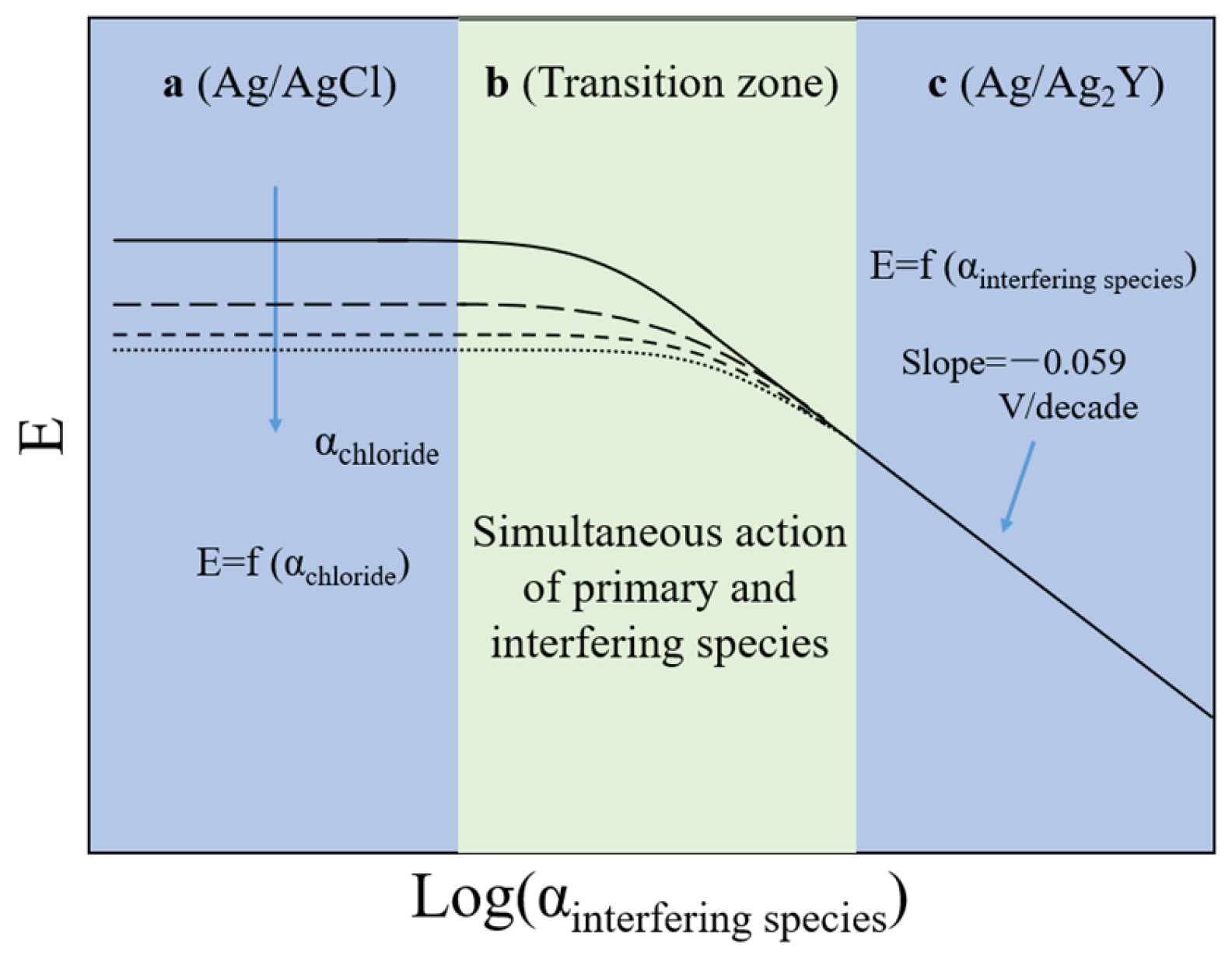
4.2. Ion Interference
4.2.1. Sulfion and Sulfate Ions
4.2.2. Halide Ions
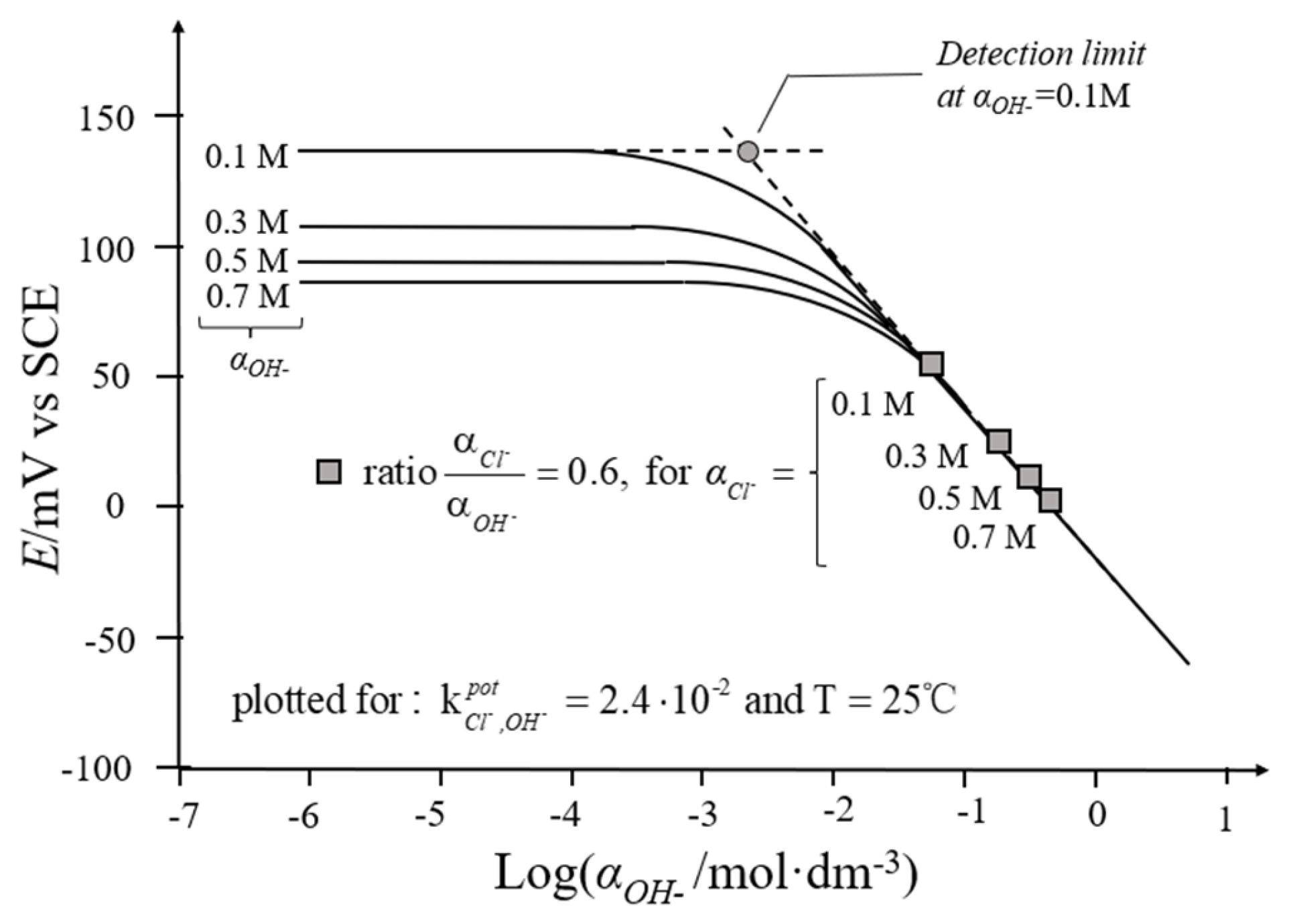
4.2.3. Hydroxide Ions
4.2.4. Ion Selectivity Coefficient
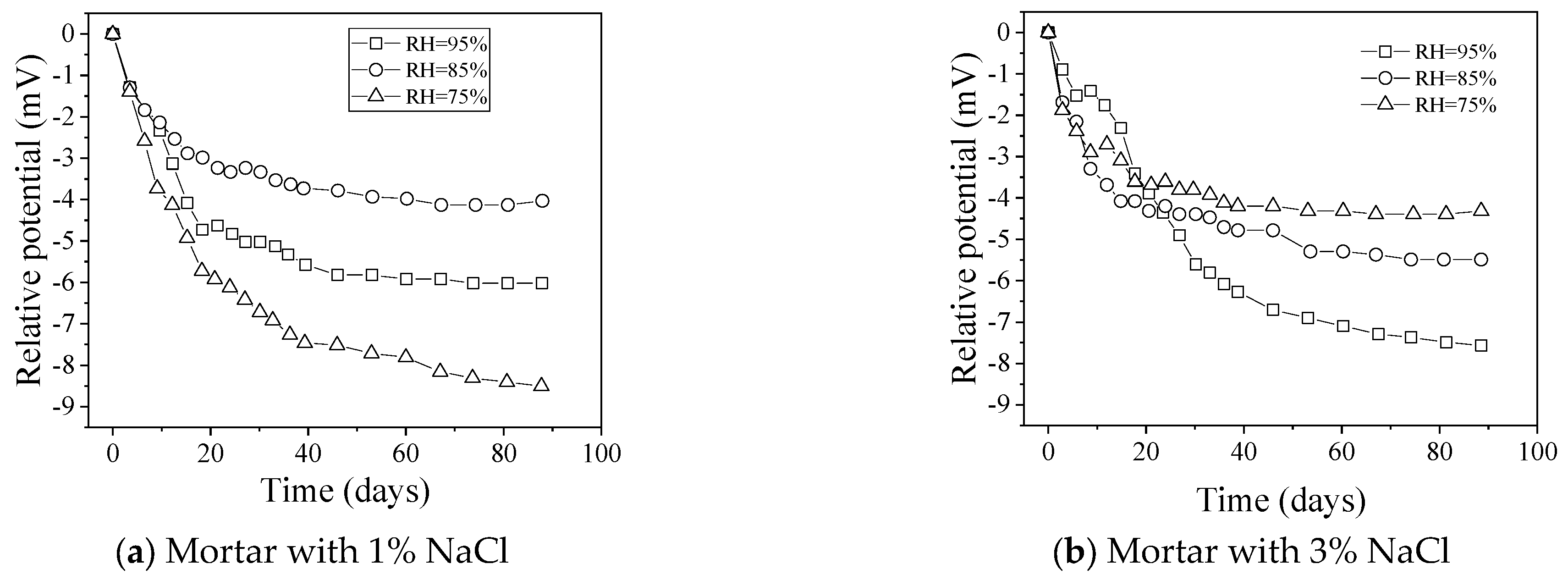
4.3. Temperature and Humidity
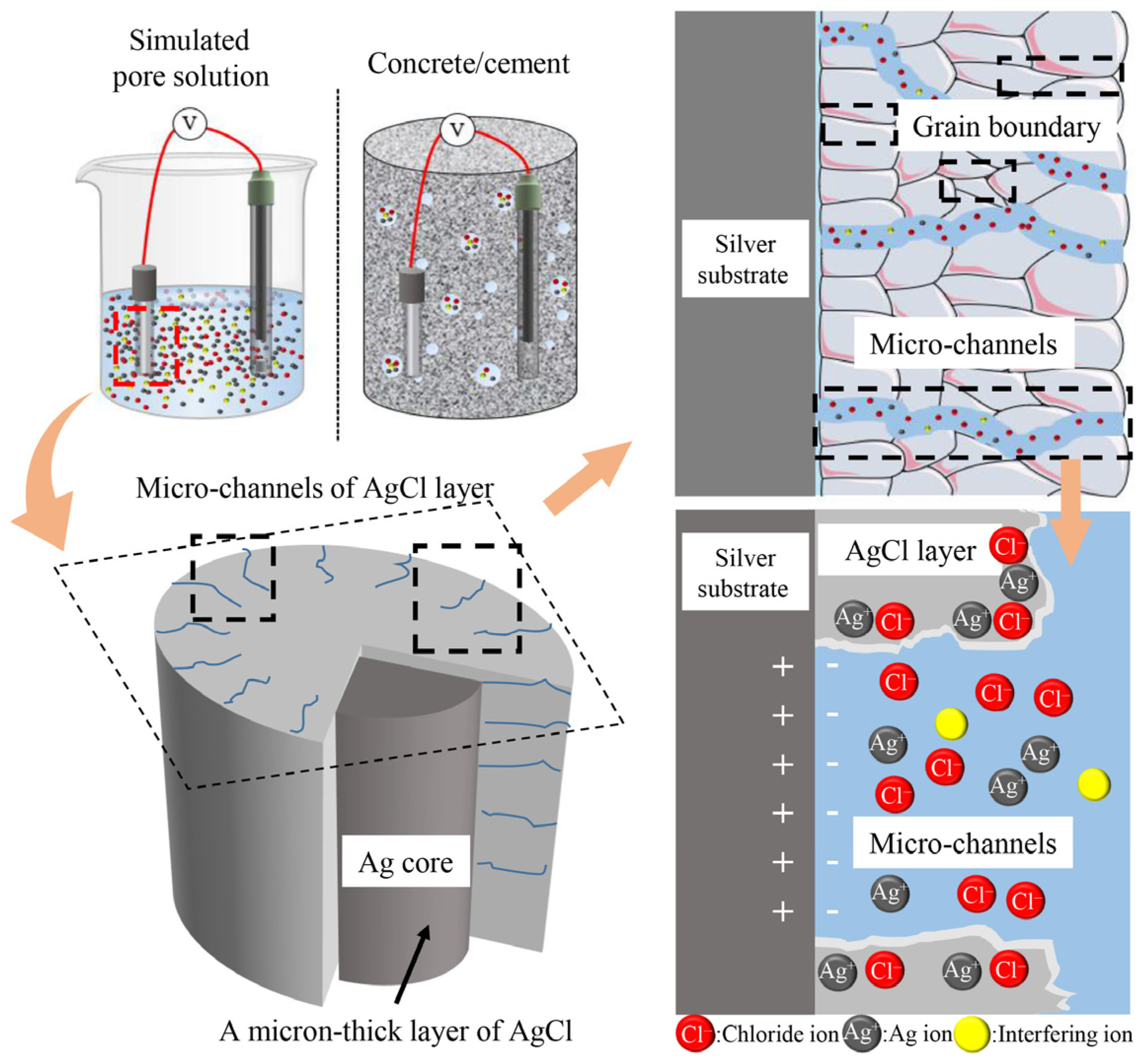
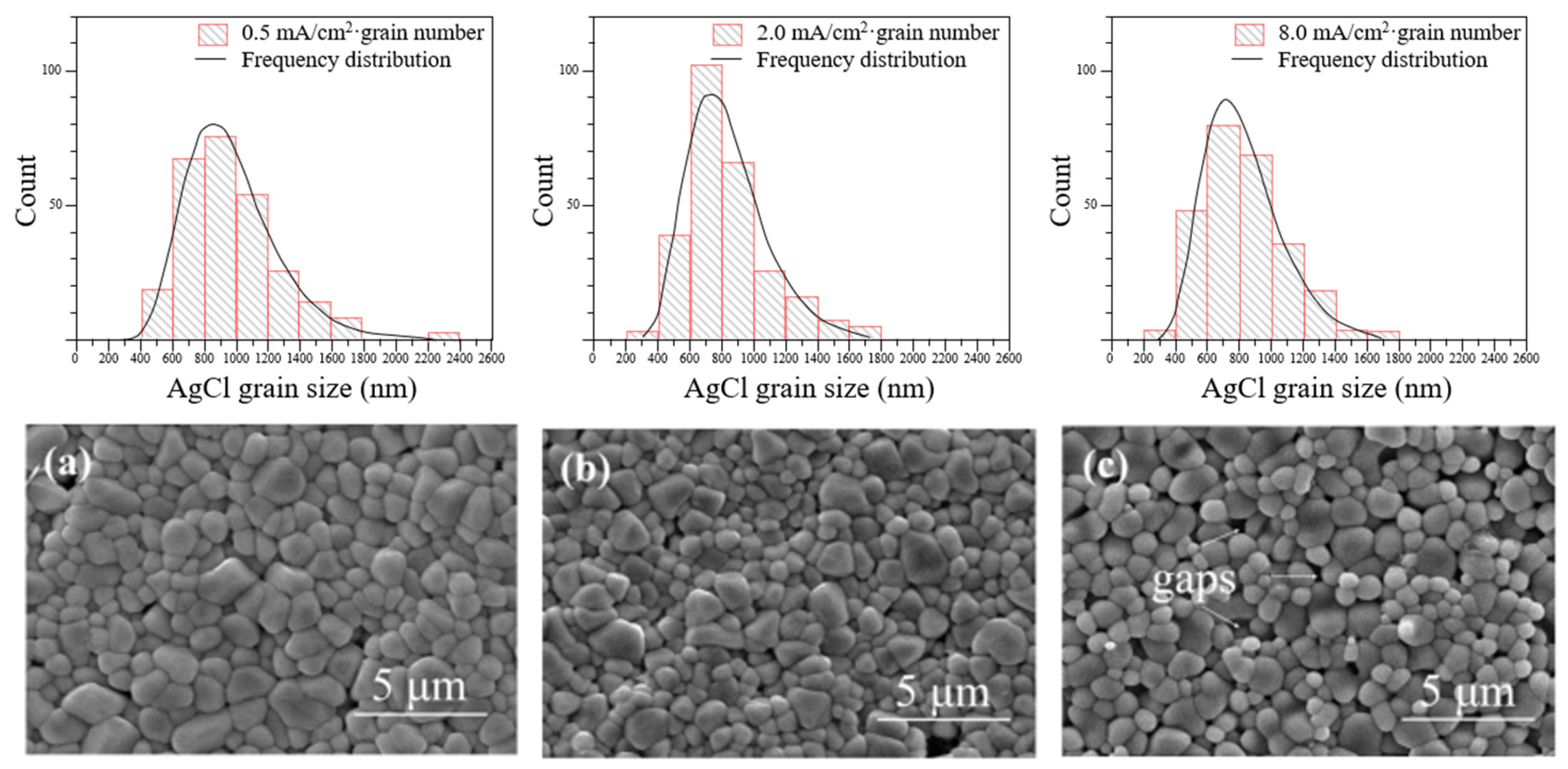
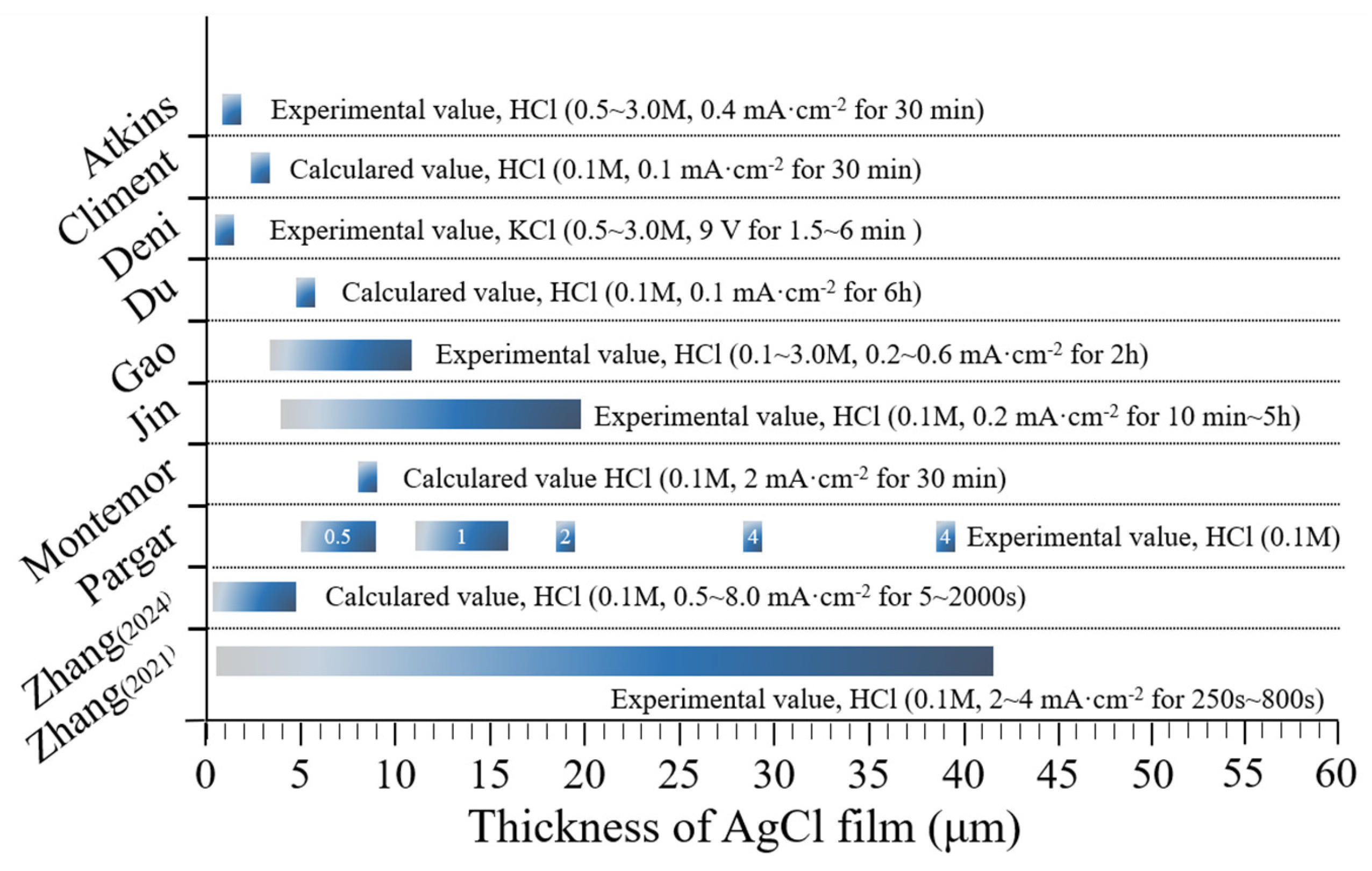
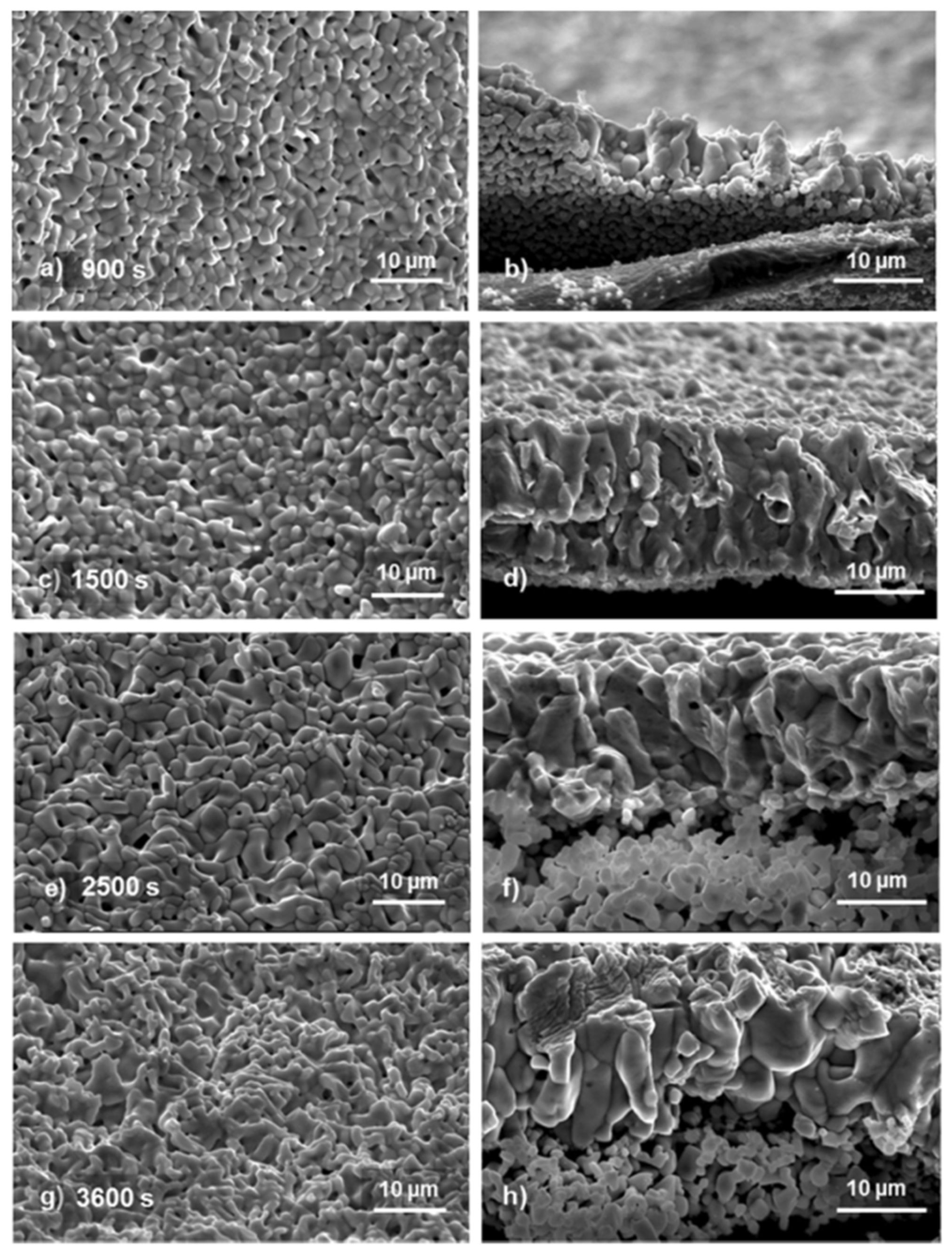
4.4. Effect of AgCl Film Properties on Stability of Ag/AgCl ISE
5. The Durability of Ag/AgCl ISEs Used to Monitor Chloride in Concrete
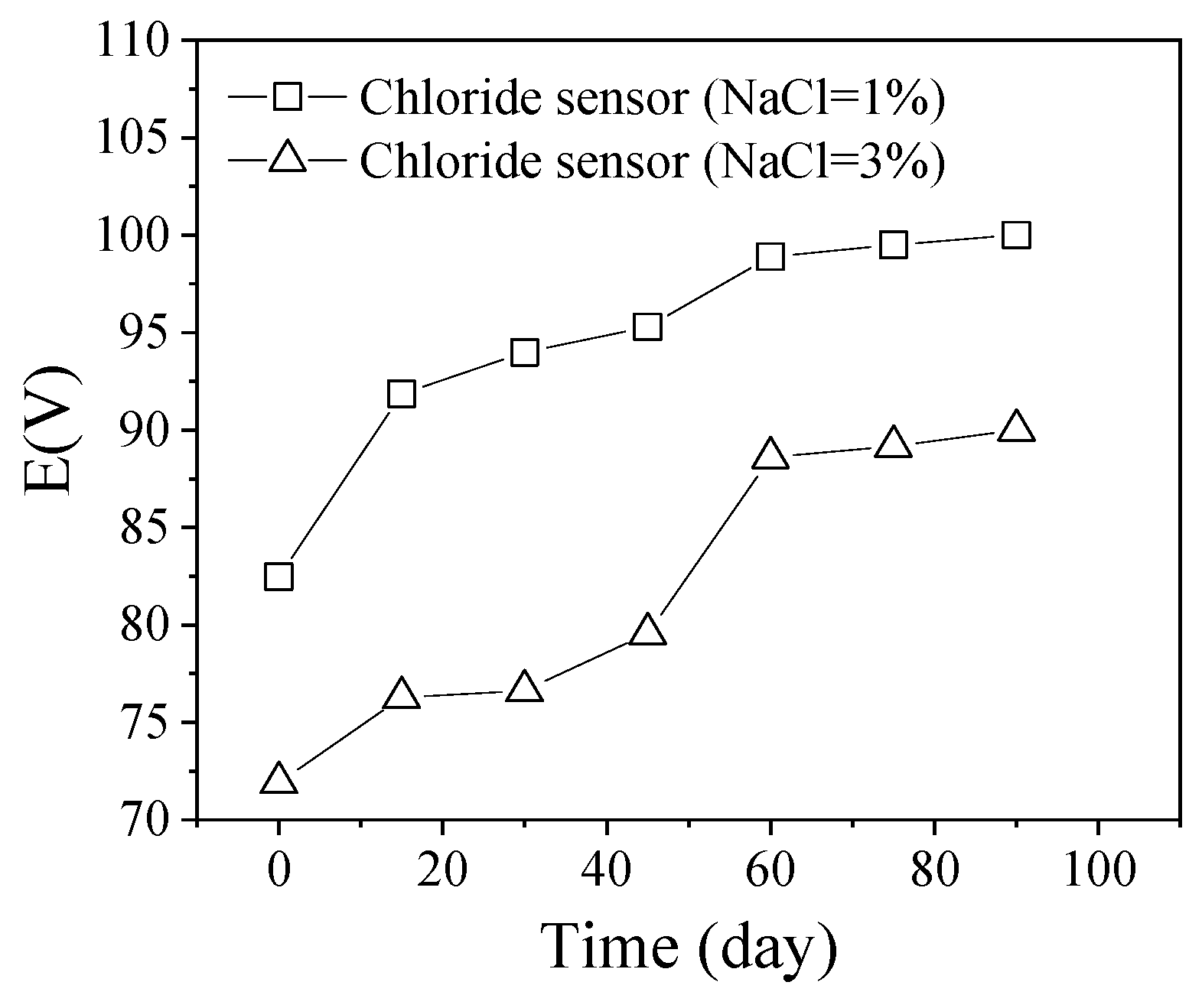
5.1. Applications of Ag/AgCl ISEs for Long-Term Monitoring in Cement-Based Materials
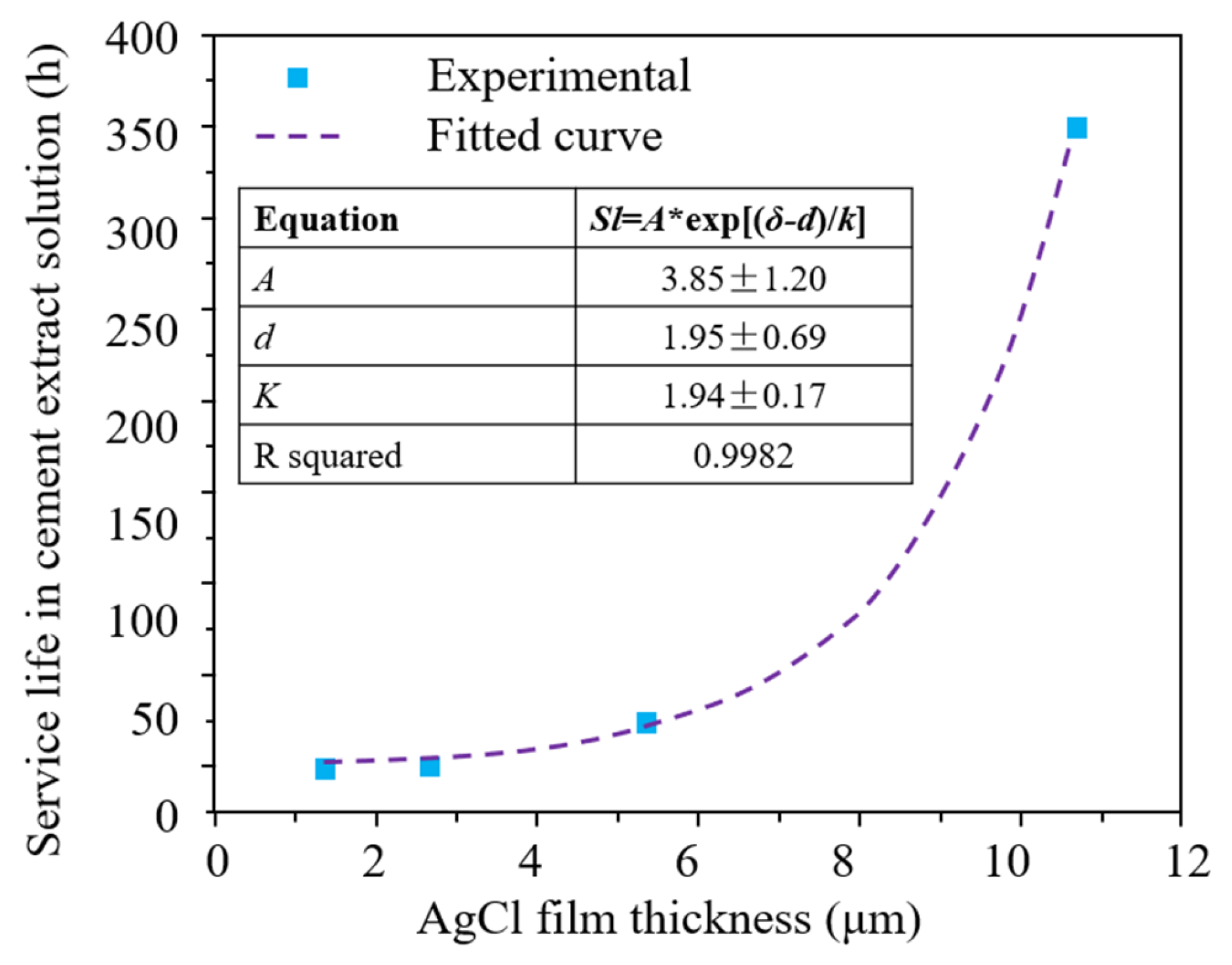
5.2. Reason for Durability Failure
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
- -
- The influence of environmental factors, including temperature, interfering ions, and alkalinity, on the performance of Ag/AgCl ISEs is systematically analyzed in this work. Temperature may lead to potential shifts, and this disadvantage can be overcome with temperature correction. Influences of interfering ions on the stability of the Ag/AgCl ISEs used to monitor chloride in concrete are derived from the membrane potential and insoluble silver salt, which should be considered only as interfering ions over a certain high concentration. Errors often appear in such high-alkalinity materials, such as concrete, with low concentrations of chloride due to the formation of AgOH on the surface of Ag/AgCl ISEs, leading to a lower potential than the theoretical values. However, when chloride concentration reaches a certain level, the electrode is no longer affected by alkalinity.
- -
- The microstructure of AgCl films, depending on the fabrication methods, plays a crucial role in the test errors; thus, selecting and improving the fabrication process to improve the electrode performance is the basis of reducing the test error. Besides, the calculated content based on Ag/AgCl ISEs is slightly lower than the actual chloride concentration, which is attributed to the diffusion potential, liquid junction potential, and membrane potential. It is noted that the change in concrete humidity may induce a distinct test error. Due to the differences in testing methods, the test results of electrodes vary greatly. Therefore, it is necessary to promote the standardization process of electrode preparation and use.
- -
- The Ag/AgCl ISEs can be used in cement-based materials by half-cell potentiometric measurement. The durability studies of Ag/AgCl ISEs in cement-based materials vary significantly, ranging from 20 to 550 days. The long-term durability of Ag/AgCl ISEs is related to the AgCl film corrosion caused by dissolution and exfoliation. The AgCl thickness, interfering ion, especially OH−, and the bonding between the AgCl film and Ag substrate will influence the durability life of Ag/AgCl ISEs.
- -
- Although long-term durability is necessary for Ag/AgCl ISEs to be used as in situ monitoring sensors, the relevant research enhancing long-term durability is still limited. To enhance the stability and durability of the electrode, its chemical stability in complex environments can be improved by modifying the microstructure and coating materials of the electrode. Given that the electrode test results are influenced by many factors, but the influence of multiple factors on the electrode results is still unclear, research can be carried out through methods such as machine learning.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ann, K.; Song, H. Chloride threshold level for corrosion of steel in concrete. Corros. Sci. 2007, 49, 4113–4133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.; Vennesland, Ø. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete—A review. Cement Concrete Res. 2009, 39, 1122–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yan, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Li, J. Chloride threshold value and initial corrosion time of steel bars in concrete exposed to saline soil environments. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 267, 120979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wittmann, F.; Vogel, M.; Müller, H.; Zhao, T. Influence of freeze-thaw cycles on capillary absorption and chloride penetration into concrete. Cement Concrete Res. 2017, 100, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, J.; Wei, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhuang, Z.; Zhao, T. Experimental and theoretical investigation of chloride ingress into concrete exposed to real marine environment. Cement Concrete Comp. 2022, 130, 104511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Cong, Y.; Vogel, M.; Liu, Z.; Müller, H.; Zhu, Y. Steel reinforcement corrosion in concrete under combined actions: The role of freeze-thaw cycles, chloride ingress, and surface impregnation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, D.; Yu, L.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Jia, H.; Wu, Z.; Bao, J.; Liu, J.; Xi, X.; Su, L. A state-of-the-art on electromagnetic and mechanical properties of electromagnetic waves absorbing cementitious composites. Cement Concrete Comp. 2024, 157, 105889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Zhang, Z. A state-of-the-art review on Ag/AgCl ion-selective electrode used for non-destructive chloride detection in concrete. Compos. Part. B-Eng. 2020, 200, 108289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B.; Zimmermann, L.; Böhni, H. Non destructive determination of the free chloride content in cement-based materials. Mater. Corros. 2015, 54, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Qi, L.; Wang, H. Antifreezing Ag/AgCl reference electrodes: Fabrication and applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 666, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, C.; Scantlebury, J.; Nedwell, P.; Blatch, S. Monitoring chloride concentrations in hardened cement pastes using ion selective electrodes. Cement Concrete Res. 1996, 26, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.; Almeraya, F.; Barrios, C.; Gaona, C.; Núnez, R.; López, I. Effect of cathodic protection on steel–concrete bond strength using ion migration measurements. Cement Concrete Comp. 2012, 34, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Climent, M.; Viqueira, E.; Vera, G.; López-Atalaya, M. Analysis of acid-soluble chloride in cement, mortar, and concrete by potentiometric titration without filtration steps. Cement Concrete Res. 1999, 29, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Maruta, T.; Yamane, T.; Kiba, N. Simultaneous determination of fluorine, chlorine and bromine in cement with ion chromatography after pyrolysis. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2009, 640, 106–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millar, S.; Kruschwitz, S.; Wilsch, G. Determination of total chloride content in cement pastes with laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy (LIBS). Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 117, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vera, G.; Climent, M.; Antón, C.; Hidalgo, A.; Andrade, C. Determination of the selectivity coefficient of a chloride ion selective electrode in alkaline media simulating the cement paste pore solution. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 639, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, C.; Nishiwaki, T.; Tanabe, T.; Oohashi, T.; Hamasaki, H.; Hikishima, S.; Tanaka, A.; Arita, K.; Fujii, S.; Sato, D. Non-destructive testing of reinforced concrete structures using sub-terahertz reflected waves. Dev. Built Environ. 2024, 18, 100423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mattarneh, H. Determination of chloride content in concrete using near-and far-field microwave non-destructive methods. Corros. Sci. 2016, 105, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Fan, L.; Zhao, X.; Huang, H. Development and evaluation of fluorescent optical fiber sensors for chloride ion measurement in actual mortar pore solutions. Measurement 2025, 253, 117554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.; Phua, S.; Aw, T. Differences in serum chloride measurements by direct potentiometry and indirect potentiometry may affect anion gap calculation. Pathology 2019, 51, 111–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, Y.; Liu, Z.; Gao, X. Methods for optimization of the original signal in laser induced breakdown spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part B Spectrosc. 2024, 218, 106982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Furukawa, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Minagawa, H. Non-destructive chemical analysis of water and chlorine content in cement paste using near-infrared spectroscopy. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Y.; Pargar, F.; Koleva, D.; van Breugel, K.; Olthuis, W.; van den Berg, A. Non-destructive measurement of chloride ions concentration in concrete–A comparative analysis of limitations and prospects. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Jiang, L.; Tao, D.; Bai, S. Characterization of Ag/AgCl electrode manufactured by immersion in sodium hypochloride acid for monitoring chloride content in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 122, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, P.; Leese, R.; Brown, R. An improved approach for fabricating Ag/AgCl reference electrodes. Electrochim. Acta. 2012, 71, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prkić, A.; Vukušić, T.; Mitar, I.; Giljanović, J.; Sokol, V.; Bošković, P. New sensor based on AgCl containing iron oxide or zinc oxide nanoparticles for chloride determination. Int. J. Electrochem. Sc. 2019, 14, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Jin, X.; Wang, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, G. A quartz sealed Ag/AgCl reference electrode for CaCl2 based molten salts. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 579, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Lin, C.; Hu, R.; Li, L.; Du, R. Effective monitoring of corrosion in reinforcing steel in concrete constructions by a multifunctional sensor. Electrochim. Acta. 2011, 56, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargar, F.; Koleva, V.; Breugel, K. Determination of chloride content in cementitious materials: From fundamental Aspects to application of Ag/AgCl chloride sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Hong, S.; Yang, S. A solid-state thin-film Ag/AgCl reference electrode coated with graphene oxide and its use in a pH sensor. Sensors 2015, 15, 6469–6482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Xu, Y.; Chu, H. Investigation on the performance characteristics of chloride selective electrode in concrete. Ionics 2015, 21, 2981–2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzini, B.; Giovannelli, G.; Mele, C. Electrochemical dynamics and structure of the Ag/AgCl interface in chloride-containing aqueous solutions. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2007, 201, 4619–4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, H.; Thirsk, H.; Wynne, J. A study of the behaviour of polarized electrodes. Part I.—The silver/silver halide system. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1951, 47, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhad, P.; Hristo, K.; Koleva, D.; Klaas, V. Potentiometric response of Ag/AgCl chloride sensors in model alkaline medium. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ibernón, A.; Gasch, I.; Romero, J.; Soto, J. New use of an Ag electrode and a potentiodynamic method to control the presence of chlorides in porous media like concrete. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 488, 144230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemor, M.; Alves, J.; Simoes, A.; Fernandes, J.; Lourenço, Z.; Costa, A. Multiprobe chloride sensor for in situ monitoring of reinforced concrete structures. Cement Concrete Comp. 2006, 28, 233–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguí, F.; Angst, U.; Caruso, F.; Elsener, B. Ag/AgCl ion-selective electrodes in neutral and alkaline environments containing interfering ions. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 2637–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Polder, R. Spatial variability of chloride in concrete within homogeneously exposed areas. Cement Concrete Res. 2014, 56, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkins, C.; Carter, M.; Scantlebury, J. Sources of error in using silver/silver chloride electrodes to monitor chloride activity in concrete. Cement Concrete Res. 2001, 31, 1207–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janata, J. Principles of Chemical Sensors; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Koryta, J. Theory and applications of ion-selective electrodes. Part 8. Anal. Chim. Acta 1990, 233, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Xu, Z.; Huang, H.; Yin, S.; Ma, Y. Degradation process of Ag/AgCl chloride-sensing electrode in cement extract with low chloride concentration. Corros. Sci. 2022, 198, 110107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.; Bower, V. Standard potential of the silver-silver-chloride electrode from 0 to 95 °C and the thermodynamic properties of dilute hydrochloric acid solutions. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1954, 53, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, D.; Kumar, P.; Sloan, E. A new technique for hydrate thermal diffusivity measurements. Int. J. Thermophys. 2005, 26, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öijerholm, J.; Forsberg, S.; Hermansson, H.; Ullberg, M. Relation between the SHE and the internal Ag/AgCl reference electrode at high temperatures. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Lu, J.; Liu, P.; Tong, H. The electrochemical formation and reduction of a thick AgCl deposition layer on a silver substrate. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2003, 542, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birss, V.; Smith, C. The anodic behavior of silver in chloride solutions—I. The formation and reduction of thin silver chloride films. Electrochim. Acta 1987, 32, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Gao, G.; Chu, H.; Xiong, C. Electrochemical characterization of a solid embeddable Ag/AgCl reference electrode for corrosion monitoring in reinforced concrete. Electrochemistry 2014, 82, 1040–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, I.; Huang, R. Fabrication and characterization of a new planar solid-state reference electrode for ISFET sensors. Thin Solid. Film 2002, 406, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C. Preparation and Characterization of AgCl-MnO2 Chloride Sensor. Master’s Thesis, School of Civil Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao, China, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Bai, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chu, H. Review on research of threshold chloride concentration of reinforcing steel corrosion in concrete. Adv. Sci. Techn Water Reso 2015, 35, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, H.; Payer, J. The effect of silver chloride formation on the kinetics of silver dissolution in chloride solution. Electro Chim. Acta. 2011, 56, 2781–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J.; Liu, S.; Guo, Y. Influence of AgCl film resistance on stability and potential response of Ag/AgCl chloride-sense electrode in simulated concrete pore solution. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 478, 143839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, A.; Vera, G.; Climent, M.; Andrade, C.; Alonso, C. Measurements of chloride activity coefficients in real Portland cement paste pore solutions. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2001, 84, 3008–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.; Vennesland, Ø. Potentiometric determination of the chloride ion activity in cement based materials. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2010, 40, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.; Yeon, J.; Hwang, J.; Hong, C.; Song, K. A calibration technique for an Ag/AgCl reference electrode utilizing the relationship between the electrical conductivity and the KCl concentration of the internal electrolyte. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2009, 39, 2587–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Long, Y.; Tang, S. Simulation of low-heat Portland cement permeability and thermal conductivity using thermodynamics. Eng. Transp. 2024, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deni, S.; Faisal, R.; Sagir, A. Optimization strategy of Ag/AgCl thin film electrodes approached by chlorination process for electrochemical response materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 240, 122294. [Google Scholar]
- Climent, M.; Viqueira, E.; López, M. Embeddable Ag/AgCl sensors for in-situ monitoring chloride contents in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1996, 26, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, R.; Hu, R.; Huang, R.; Lin, C. In situ measurement of Cl— concentrations and pH at the reinforcing steel/concrete interface by combination sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3179–3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. In-Suit Monitoring of Chloride ion Concentration in Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Lu, S. Preparation of chloride ion selective electrode and its potential response to different chloride solutions representing concrete environments. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 675, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, K.; Du, Z.; Zhao, T. Application of Ag/AgCl sensor for chloride monitoring of mortar under dry-wet cycles. Sensors 2020, 20, 1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, S.; You, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, F.; Geng, G. Probing transformation of Ag/AgCl chloride-sensing electrode interface in concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2025, 246, 112747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Dechiruji, H.; Selberg, J.; Pansodtee, P.; Mathews, J.; Wu, C. Bioelectronic control of chloride ions and concentration with Ag/AgCl contacts. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 091106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M. Measuring of chloride diffusivity in cement paste using Ag/AgCl probe. Concrete 2012, 11, 36–39. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, D.; Jiang, L.; Jin, M. A method of preparation of Ag/AgCl chloride selective electrode. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2018, 33, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M.; Atkinson, J. A review of screen-printed silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) reference electrodes potentially suitable for environmental potentiometric sensors. Sensor Actuat A-Phys. 2017, 267, 106–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargar, F.; Kolev, H.; Koleva, D.; Breugel, K. Microstructure, surface chemistry and electrochemical response of Ag/AgCl sensors in alkaline media. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 7527–7550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Vennesland, Ø.; Myrdal, R. Diffusion potentials as source of error in electrochemical measurements in concrete. Mater. Struct. 2009, 42, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angst, U.; Vennesland, Ø. Detecting critical chloride content in concrete using embedded ion selective electrodes–effect of liquid junction and membrane potentials. Mater. Corros. 2009, 60, 638–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, M.; Jiang, L.; Xu, J.; Chu, H.; Tao, D.; Bai, S.; Jia, Y. Electrochemical characterization of solid Ag/AgCl reference electrode with different electrolytes for corrosion monitoring of steel in concrete. Electrochemistry 2016, 84, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollivier, J.; Maso, J.; Bourdette, B. Interfacial transition zone in concrete. Adv. Cem. Based Mater. 1995, 2, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowell, R.; Lian, R.; Shkrob, I.; Bartels, D.; Chen, X.; Bradforth, S. Ultrafast dynamics for electron photodetachment from aqueous hydroxide. J. Chem. Phys. 2004, 120, 11712–11725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannes, E.; Koosha, E.; Esben, T. Impedimetric detection of chloride ions using two symmetric Ag/AgCl electrodes. Electrochim. Acta 2024, 503, 144864. [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes, R.; Buck, R. Competitive ion-exchange evaluation of the bromide interference on anodized silver/silver chloride electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1980, 113, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulanicki, A.; Lewenstam, A. Interpretation of selectivity coefficients of solid-state ion-selective electrodes by means of the diffusion-layer model. Talanta 1977, 24, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yuan, H.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, J.; Cao, F. A highly sensitive, long-time stable Ag/AgCl ultra-micro sensor for in situ monitoring chloride ions inside the crevice using SECM. Talanta 2024, 274, 126026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shreir, L. Corrosion: Metal/Environment Reactions; Newnes-Butterworths: Oxford, UK, 1976; Volume I. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z. A Research of Chloride Ion Sensor Embedded in Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Ding, Q.; Hou, D.; Xiong, C.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, G. Influence of hoop restraint on microstructure and phase composite of cement paste filled steel tube under external sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 366, 130195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Ukrainczyk, N.; Mu, S.; Zhang, Y.; De, S. Numerical study on the chemical and electrochemical coupling mechanisms for concrete under combined chloride-sulfate attack. Cement Concrete Res. 2024, 175, 107368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Saout, G.; Haha, M.; Figi, R.; Wieland, E. Hydration of a low-alkali CEM III/B–SiO2 cement (LAC). Cement Concrete Res. 2012, 42, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pargar, F.; Koleva, D.; Breugel van, K. Potentiometric response of Ag/AgCl sensor in Portland and slag cement pastes. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Concrete Modelling and Materials Behaviour in Honor of Professor Klaas van Breugel, Rilem, Delft, The Netherlands, 27–28 August 2018; pp. 214–221. [Google Scholar]
- Femenias, S.; Angst, U.; Elsener, B. Monitoring chloride concentrations in concrete by means of Ag/AgCl ion-selective electrodes. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Concrete Repair, Rehabilitation and Retrofitting (ICCRRR-4), Leipzig, Germany, 5–7 October 2015; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016; pp. 861–869. [Google Scholar]
- Pargar, F. The application of Ag/AgCl electrodes as chloride sensors in cementitious materials. Mater. Environ. 2018, 10, 4233. [Google Scholar]
- Klasens, H.; Goossen, J. The iodide interference with silver chloride electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 1977, 88, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, D.; Yee, D. Behaviour of Ag/AgCl electrodes in solutions containing both Cl− and I−. Electrochim. Acta 1969, 14, 1143–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svegl, F.; Kalcher, K.; Grosse, Y.; Balonis, M.; Bobrowski, A. Detection of chlorides in pore water of cement based materials by potentiometric sensors. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2006, 35, 232–237. [Google Scholar]
- Duffó, G.; Farina, S.; Giordano, C. Characterization of solid embeddable reference electrodes for corrosion monitoring in reinforced concrete structures. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1010–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.; Kayyali, O. Free and water soluble chloride in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 1995, 25, 531–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, A.; Ferra, M.; Bandeira, M. Activity coefficients of potassium chloride in aqueous solutions of potassium chloride and potassium phthalate. Port. Electrochim. Act. 2006, 24, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R. The activity coefficient of potassium chloride in aqueous solutions at 0° from electromotive force and freezing point data. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 3279–3282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morf, W.; Kahr, G.; Simon, W. Theoretical treatment of the selectivity and detection limit of silver compound membrane electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1974, 46, 1538–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morf, W. The Principles of Ion-Selective Electrodes and of Membrane Transport; Elsevier Science: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 154–162. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhurst, D.; Appelo, C. Description of input and examples for PHREEQC version 3—A computer program for speciation, batch-reaction, one-dimensional transport, and inverse geochemical calculations. USGS Tech. Methods 2013, 6, 418–497. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, G.; Rigdon, L.; Meisenheimer, R.; Frazer, J. Selectivity parameters of homogeneous solid-state chloride ion-selective electrodes and the surface morphology of silver chloride-silver sulphide discs under simulated interference conditions. Analyst 1981, 106, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulanicki, A.; Lewenstam, A. Variability of selectivity coefficients of solid-state ion-selective electrodes. Talanta 1982, 29, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindner, E.; Umezawa, Y. Performance evaluation criteria for preparation and measurement of macro-and microfabricated ion-selective electrodes (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleksandar, R.; Shane, P.; Eric, B.; Diamond, D. Guidelines for improving the lower detection limit of ion-selective electrodes: A systematic approach. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 144–154. [Google Scholar]
- Shreir, L. Corrosion: Corrosion Control; Newnes: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dobos, D. A Handbook for Electrochemists in Industry and Universities; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, H.; Cao, L.; Cao, X.; Yu, S.; Huang, M. Experimental investigation of chloride ion monitoring in concrete considering the coupling effect of temperature and humidity. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 98, 111155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrieal, V.; Giaan, A.; Carlos, V.; Pablo, R.; María, T. Composites: A novel alternative to construct solid state Ag/AgCl reference electrodes. Sens. Actuat B-Chem. 2005, 110, 264–270. [Google Scholar]
- Jaya, S.; Rao, T.; Rao, G. Anodic-stripping voltammetric determination of arsenic at a copper-coated glassy-carbon electrode. Talanta 1987, 34, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jovi, B.; Jovi, V.; Drai, D. Kinetics of chloride ion adsorption and the mechanism of AgCl layer formation on the (111), (100) and (110) faces of silver. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1995, 399, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, R.; Ma, Y.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Yu, Q. Relationship between microstructure of AgCl film and electrochemical behavior of Ag/AgCl electrode for chloride detection. Corros. Sci. 2021, 184, 109393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacInnes, D. Reference Electrodes. Theory and Practice, J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1962, 84, 503–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, J.; Peng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L. Thermodynamics-based simulations of the hydration of low-heat Portland cement and the compensatory effect of magnesium oxide admixtures. J. Zhejiang Univ. -Sci. A 2025, 26, 305–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W. Application of Ag/AgCl chloride sensor in concrete. J. Funct. Mater. 2010, 41, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Gbandour, M. Effect of the temperature on the composition and electro-chemical behaviour of electro deposited MnO2 electrodes. Z. Phys. Chem. 1981, 262, 514–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, S.; Saraswathy, V.; Madhavamayandi, A.; Thangavel, K.; Palaniswamy, N. Evaluation of embeddable potential sensor for corrosion monitoring in concrete structures. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 7248–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Fu, H.; Tian, L.; Du, Z.; Wang, P. Embeddable chloride sensor for monitoring chloride penetration into cement mortar. Sensors 2024, 24, 2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Feng, X.; Qu, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, R.; Zhou, Q.; He, A.; Zhang, H.; Chen, S. An array sensor for monitoring the chloride concentration profile in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 478, 141419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, A.; Wang, H. Electrochemical investigation on the effect of chloride ion concentration on the corrosion of concrete reinforcement using in-situ nano-Ag/AgCl electrode. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 66, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Progress in in-situ electrochemical monitoring techniques for chloride ions in concrete structures. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, C.; Wang, Q.; Yin, C.; Li, X.; Yang, R.; Shen, X.; Xin, W. Shape-engineering and mechanism investigation of AgCl microcrystals. Crystals 2025, 15, 451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Hao, J.; Dong, Z. Preparation and Properties of Solid-state Chloride Ion Selective Electrode for Detecting Chloride Ions in Concrete. Corros. Sci. Prot. Technol. 2015, 27, 211–218. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, M.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, Q. Monitoring chloride ion penetration in concrete with different mineral admixtures based on embedded chloride ion selective electrodes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 143, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, W. Steel reinforcement corrosion in concrete–an overview of some fundamentals. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Gehlen, C.; Angst, U.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Yao, Y. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete-An updated review considering Chinese experience. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 117, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ye, Z.; Muthumani, A.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, H. A Corrosion Monitoring System for Existing Reinforced Concrete Structure; Alaska University Transportation Center, Oregon Department of Transportation: Washington, DC, USA, 2015; pp. 26–33. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.; Chu, H.; Shi, J.; Yang, L.; Long, B.; Xu, Y.; Li, W. Study of polypyrrole coating on the performance improvement of Ag/AgCl chloride ion sensor in highly alkaline concrete environments. Mater. Corros. 2025, 76, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Interfering Ions | Exposure Time to the Solution | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| I− | 86.5 | Not specified | [41] |
| 2.9 × 106 | Theoretical model | [94] | |
| 1~2.1 × 106 | Theoretical model | [95] | |
| 3~14 | <1 day | [87] | |
| 1.8 × 102~2.2 × 106 | <1 day | [96,97] | |
| 86.5~1.8 × 106 | <1 day | [98] | |
| Br− | 3.63 × 102 | Theoretical model | [94] |
| 1~3.5 × 102 | Theoretical model | [95] | |
| 1.2 | Not specified | [41] | |
| 1.1 × 102~3.5 × 102 | <1 day | [97,98] | |
| 2.1~3.3 × 102 | <1 day | [98] | |
| , | 2.04 × 1015 | Not specified | [94] |
| 4.73 × 10−8 | Not specified | [94] | |
| OH− | 2.4 × 10−2 | Not specified | [41] |
| 9.33 × 10−3 | Theoretical model | [94,95] | |
| 10−2 | Theoretical model | [95] | |
| ≈10−2 | Theoretical model | [95] | |
| 4 × 10−3 | >6 months | [65] | |
| ≈10−2 | Not specified | [16] | |
| 2 × 10−3~9.1 × 10−3 | <1 day | [97,98] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Lei, D.; Wang, P.; Bao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, T.; Guo, W. Research Progress on the Stability and Durability of Ag/AgCl Prepared by Anodic Chlorination Method for Chloride Ion Sensors in Cement-Based Materials. Buildings 2025, 15, 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132290
Tian Y, Lei D, Wang P, Bao J, Wang Y, Zhao T, Guo W. Research Progress on the Stability and Durability of Ag/AgCl Prepared by Anodic Chlorination Method for Chloride Ion Sensors in Cement-Based Materials. Buildings. 2025; 15(13):2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132290
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yupeng, Dongyi Lei, Penggang Wang, Jiuwen Bao, Yanru Wang, Tiejun Zhao, and Weina Guo. 2025. "Research Progress on the Stability and Durability of Ag/AgCl Prepared by Anodic Chlorination Method for Chloride Ion Sensors in Cement-Based Materials" Buildings 15, no. 13: 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132290
APA StyleTian, Y., Lei, D., Wang, P., Bao, J., Wang, Y., Zhao, T., & Guo, W. (2025). Research Progress on the Stability and Durability of Ag/AgCl Prepared by Anodic Chlorination Method for Chloride Ion Sensors in Cement-Based Materials. Buildings, 15(13), 2290. https://doi.org/10.3390/buildings15132290








