Abstract
High-profile school shootings in recent years have fueled fear and uncertainty among stakeholders (e.g., parents, teachers, and students) and the public debate on gun control legislation nationwide. These fears are reflected in the public discourse and the academic community, which focuses their investigation on rampage school shootings. To address this gap in the empirical literature, the current study’s goal is twofold: (1) to contribute to the descriptive understanding of school shooting characteristics; and (2) address the gaps in the extant literature through examining the perpetrators relationship with the school on the total number of victims during a school shooting incident. Secondary data analysis was performed on the K-12 School Shooting database (K-12 SSDB). A negative binomial and descriptive analysis were conducted on the K-12 School Shooting database, established by the Naval Postgraduate School’s Center for Homeland Defense and Security (CHDS) in 2018, which has been recently updated to reflect recent incidents. The findings and policy implications of the findings are discussed in detail in the manuscript.
1. Introduction
High-profile school shootings in recent years have fueled fear and uncertainty among stakeholders (e.g., parents, teachers, and students) and the public debate on gun control legislation nationwide (Burton et al. 2021; Gammell et al. 2021; Schafer et al. 2018). Although rampage school shootings (i.e., indiscriminate shooting events unrelated to any other crime or incident, with at least four victims) are the rarest type of school shooting, these incidents have resulted in substantial media attention and public support for various target-hardening strategies implemented in schools nationwide (Livingston et al. 2019; Shultz et al. 2013). For instance, following the Columbine shooting, many schools increased security measures with public support to protect students (Aguado and Joseph 2023; Burton et al. 2021). Although support is contingent on party affiliation, some policymakers have suggested arming staff with firearms, assuming that armed staff can deter potential perpetrators or quickly subdue the perpetrators (Mooney et al. 2022; Stanford 2022). Overall, these incidents require the public and policymakers to consider policies and strategies to make schools and their surrounding communities safer.
School shootings are incidents that involve the discharge of a firearm on school grounds (Joseph et al. 2023). Most school shooting perpetrators have a previous relationship with the school and have been occurring in the U.S. for decades, causing physical and psychological harm to stakeholders and communities (Everytown for Gun Safety n.d.; Rajan et al. 2019; Reeping et al. 2022). Previous research has identified that community violence and school shootings share similar etiological pathways (e.g., gang presence, student disputes, teacher-student disputes, and socially disorganized neighborhoods) (Fridel 2019; Shultz et al. 2013). However, scant literature has investigated the perpetrator’s relationship to the school and school shooting severity. An empirical investigation into the topic will help researchers, stakeholders, and policymakers understand the various mechanisms that influence the severity of school shootings and develop/identify effective strategies to reduce the number of causalities. Therefore, the purpose of the current study is to examine the characteristics of school shootings and the perpetrators relationship with the school influence on the total number of victims.
2. Empirical Research on School Shootings
Although incidents are infrequent, most empirical research focuses on investigating rampage school shooting incidents and ignores general school shooting incidents (Freilich et al. 2022; Gammell et al. 2021; Holland et al. 2019; Joseph et al. 2023; Madfis 2017; Paradice 2017; Rocque and Duwe 2018). Research into school shootings is burgeoning and has identified that firearm type, shooting type, time period, school, and shooter characteristics (e.g., number of shooters, school level, school racial demographics, and shooter’s age) are associated with more causalities and fatalities in school shooting incidents (Gammell et al. 2021; Holland et al. 2019; Joseph et al. 2023; Livingston et al. 2019). Further, research has consistently found that access to firearms increases the severity and frequency of school shootings (Livingston et al. 2019; National Threat Assessment Center 2019, 2021; Newman et al. 2004). Several factors have been associated with school shooting severity within the extant literature. However, fewer studies have examined and identified the factors involved in these school shooting incidents. Although Newman et al. (2004) highlighted that firearms access was a critical factor for comprehending school shootings, later empirical research has identified other factors associated with these incidents. Fridel (2019) found that expenditures per student, neighborhood disadvantage, and school community crime rates increased the likelihood of school shootings. Kalesan et al. (2017) found that states with background checks for firearm purchases, higher mental health and K-12 expenditures, and densely populated urban areas were associated with fewer school shooting incidents. Holland et al. (2019) found that personal and gang disputes were the most common motives for school shootings, and these incidents resulted in fewer causalities.
Although school shootings are rare, some evidence suggests that near-fatal incidents are fairly common (Anderson et al. 2001; Holland et al. 2019; Kaufman et al. 2012; Pah et al. 2017). Further, school shootings occur more often in high schools (Freilich et al. 2022; Gammell et al. 2021; Livingston et al. 2019). Freilich et al. (2022) identified that most school shooting incidents were intentional, non-fatal, and an average of 24 shootings occur annually. From the extant literature, the characteristics of school shootings share many similarities with factors associated with blue-collar crime (Freilich et al. 2022). The research on perpetrators of schools has provided some clarity on characteristics; however, empirical investigation into the topic is severely lacking and overemphasizes one school shooting type.
Although a disproportionate amount of empirical investigation concentrates on comprehending and explaining perpetrators of rampage school shootings, some investigation has been conducted on perpetrators of general school shootings. The extant literature has found that perpetrators are disproportionately male and are racial/ethnic minorities (Anderson et al. 2001; Holland et al. 2019; Kalesan et al. 2017; Kaufman et al. 2012; Shultz et al. 2013); however, rampage school shooters are disproportionately White (Muschert 2007; Newman et al. 2004; Rocque 2012). Several studies have found school shooting perpetrators have antisocial histories or prior arrest and the role of psychological issues remain unclear and may vary between single- versus multi-victim incidents (Anderson et al. 2001; Arluke and Madfis 2014; Bender et al. 2001; Gerard et al. 2016; Gaughan et al. 2001; Holland et al. 2019; Ioannou et al. 2015; McGee and DeBernardo 1999; Muschert 2007; Rajan and Lane 2018; Rocque 2012; Vossekuil et al. 2004; Weisbrot 2008; Wike and Fraser 2009). Further, adverse childhood experiences (ACEs), gang affiliation, poor school attachment, home firearm access, personal and social losses, adverse interactions, and poor home environment have been cited as potential factors that identify school shooting perpetrators (Abel et al. 2022; Anderson et al. 2001; Bonanno and Levenson 2014; Freilich et al. 2020; Gerard et al. 2016; Holland et al. 2019; Kimmel and Mahler 2003; Langman 2020; Muschert 2007; Newman et al. 2004; Rajan and Lane 2018; Rocque 2012; Sommer et al. 2014; Turanovic and Siennick 2020; Vossekuil et al. 2004). Although these findings are promising, the extant literature remains inconclusive on developing a valid and helpful profile for potential school shooters (Vossekuil et al. 2004).
3. The Current Study
In the context of the empirical literature, general school shootings have received scant empirical attention. Most empirical scrutiny has concentrated on comprehending the rarest type of school shooting (i.e., rampage school shootings). Although school shootings research is burgeoning, empirical evidence is inconclusive on factors related to perpetration, incident occurrence, and characteristics (Freilich et al. 2022). Everytown for Gun Safety (n.d.) reports that 91% of school shooters are connected with the institution where the incident occurs. Considering this, it is probable that most perpetrators are familiar with the institution’s security measures and can take advantage of previous relationships to gain access to perpetrate shootings. Further, coupled with the knowledge that the scant literature has investigated the perpetrators relationship with the severity of school shooting incidents, the current study aims to address this gap in the extant literature. Therefore, the current study attempts to explore the characteristics of school shootings and examine the perpetrators relationship with the total number of victims.
4. Methods
Data
The current study uses the K-12 School Shooting database (K-12 SSDB), which is a database established by the Naval Postgraduate School’s Center for Homeland Defense and Security (CHDS) in 2018. The database is a comprehensive list of all the instances a firearm was brandished or fired on school property and school-related events throughout the United States from 1970 to the present (i.e., updates are made as new incidents occur), regardless of the number of victims, time period, day of the week, offender motivation, or location (e.g., school bus and sports field) (Fridel 2019; Reidman 2022). As previously stated, incidents involving the brandishing or firearm, the use of non-firearms (e.g., airsoft, pellet guns, the firing), off-campus events, and unverifiable events were excluded from the analysis (n = 487). The K-12 SSDB includes detailed information about each incident, a reliability score that quantifies the dependability of information, and verified primary source citations to allow for academic examination (Reidman 2022). The case information is from over twenty other school shooting databases and independently verified with information from peer-reviewed studies, government reports, newspaper articles, and other publicly available sources (Reidman 2022). On average, cases for the database had an average reliability score of 2.71 out of 5, indicating that most incidents were substantiated by mainstream media sources (Reidman 2022).
5. Dependent Variable
Total Number of Victims. The dependent variable for this study is the total number of victims reported in a school shooting event, which includes injuries and fatalities that were caused by the shooter(s). The study’s definition includes school shootings that ended in suicide, accidental, and officer-involved injury or fatality. The reason is to effectively capture all shooting incidents that targeted schools or occurred on campus grounds. Unclear incidents about the number of injured and dead were dropped from the dataset following a careful review.
6. Independent Variable
Shooter Relationship to institution. The variable affiliation was collapsed into three broad categories 0 = Unknown, 1 = Daily, 2 = Uncommon/Rare. Incidents in which the perpetrators relationship with the institution could not be verified were coded as 0. Incidents perpetrated by individuals that are expected to be on campus frequently (i.e., students, other staff, teacher, police officer/SRO, and parent) were coded as 1. Due to the parental involvement in the K-12 system and the fact many parents elect to drop off and pick up their children from school, we decided to consider including parents in Daily category. Finally, incidents perpetrated by individual(s) that are not expected to be on campus daily or invited to participate in an event (i.e., former student, student from rival school, relative, visiting student, non-student using athletic facilities, former teacher, no relation, gang member, and no relation) were coded as 2.
7. Control Variable
School level. The types of schools in the analysis are 1 = elementary, 2 = middle/junior high 3 = high school, and 4 = other educational institutions that do not conform to the standard grade levels within these schools (e.g., 6-12, K-12, 5-12, etc.). The U.S. Department of Education (2019) defines elementary schools as institutions serving grades kindergarten or 1st–5th. Middle schools are defined as institutions serving grades 6th–8th, while junior high schools consist of grades 7th–9th or 7th–8th (U.S. Department of Education 2019); considering the overlap, these institutions were collated. Finally, high schools are institutions serving grades 9th–12th or 10th–12th (U.S. Department of Education 2019). Incidents that occurred at institutions that did not conform to the grade levels in these institutions were used as the reference category (e.g., 8-12, K-12, 5-12, 6-12) in the analysis to examine the relationship in the most common school types nationwide.
During School Hours. A review of key phrases (e.g., lunch, hallway on the way to classroom, during class, at breakfast, and while in school) allowed for researchers to determine when the shooting occurred. Incidents that occurred during school hours were coded as 1 and incidents that occurred outside of these hours were coded as “0”.
Presence of multiple firearms. Events where multiple firearms were identified in the shooting were coded as 1; incidents in which a single firearm was identified were coded as 0. Situations where multiple firearms of the same type or a combination of different firearms were coded as 1, because these incidents involved multiple firearms present. Unverifiable incidents were removed from the analysis.
Presence of Multiple shooters. Incidents where a single shooter was present, were coded as 0, and situations where multiple shooters were present, were coded as 1. Unverifiable incidents were removed from the analysis.
Presence of Adult Shooters. Shooting incidents involving a perpetrator of at least 18 years of age were coded as an adult shooter, while shootings involving perpetrator(s) under 18 were coded as non-adult. Previous work has found that adult status was significantly associated with the total number of fatalities, injuries, and the total number of victims in school shootings; therefore, the current study controls for the influence of this variable (Gammell et al. 2021). Unverifiable incidents were removed from the analysis.
Firearm type. Since many firearm policies reduce firearm access, and firearm availability is typically mentioned following these tragic events, coupled with the literature associating firearm type with the total number of victims (Livingston et al. 2019; Silva and Greene-Colozzi 2020; Yelderman et al. 2019), it is imperative to control for firearm type. Firearm type was coded as 0 = Unknown, 1 = Handgun, 2 = Shotgun, 3 = Rifle, and a 4 = Combination of different firearms. Incidents where the firearm type could not be identified are the reference category and coded as “Unknown”. Firearm type was identified by reviewing sources for key phrases (e.g., a handgun was found at the scene; a pistol was found at the scene; the Rifle was recovered at the scene; a 0.38 caliber pistol was in the shooter’s hands; and the shooter was armed with shotgun, rifles, and pistols).
Pre-planned. The definition for pre-planned shootings are incidents in which the shooter planned to attack and kill individuals on school grounds. School shootings that were pre-planned were dichotomously coded, 0 = Not pre-planned and 1 = Pre-planned, and a manual review of sources clarified if the shooting was planned or not. A review of several sources indicates some degree of planning before the shooting.
8. Analytic Strategy
The dependent variable for the current study is a count variable (i.e., total number of victims); therefore a Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was carried out using the Statistical Packages for the Social Sciences (SPSS). The results of the analysis (KS = 11.67, M/SD = 1.55(3.09), p < 0.001), suggest that the dependent variable is overdispersed. A Vuong (1989) test was conducted to determine whether the negative binomial was a better fit for the dependent variable compared to a Poisson regression (Cohen et al. 2003; Vuong 1989) in Rv4.3. The results confirmed that a negative binomial regression was the most appropriate analytical approach for the data. The results of the Vuong test can be made available upon request.
9. Results
Each of the figures provides a breakdown of the number of shootings by school type for a variable of interest. Overall, most school shootings occurred at high schools and were the highest category for preplanned, shooter relationship, number of weapons, during school, presence of adult shooter, multiple shooters, and weapon type (see Table 1). Most school shooters that perpetrated shootings at high schools are categorized as individuals with the daily expectation of being on school grounds, n = 648 (71.1%) (e.g., students, parents, teachers, and staff), and the second highest category is junior high/middle school, n = 152 (16.7%). Shootings that involve individuals categorized with the uncommon/rare expectation to be on campus mostly occur at high schools, n = 269 (54.5%) (e.g., rival students, former students, and gang members), followed by elementary schools, n = 150 (30.4%). Finally, amongst shooters that cannot be identified, most still attacked high schools, n = 130 (73.9%), followed by incidents at elementary schools, n = 24 (13.6%) (see Figure 1).

Table 1.
Sample Descriptives.
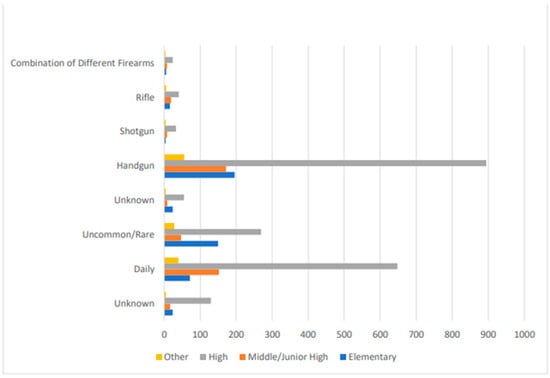
Figure 1.
Firearm type and perpetrator relationship by school type.
Figure 1 illustrates that school shootings involving handguns disproportionately occur at high schools, n = 894 (67.8%), followed by elementary, n = 196 (14.9%), junior high/middle, n = 172 (13.1%), and other, n = 56 (4.2%). School shootings involving shotguns mostly occur at high schools, n = 33 (67.3%), followed by junior high/middle, n = 8 (16.3%), and elementary and other, n = 4 (8.2%). School shootings involving rifles mostly occur at high schools, n = 41 (50%), followed by junior high/middle, n = 19 (23.2%), elementary, n = 16 (19.5%), and other, n = 6 (7.3%). School shootings involving a combination of different weapons mostly occur at high schools, n = 24 (58.5%), followed by junior high/middle, n = 8 (19.5%), elementary, n = 6 (14.6%), and other, n = 3 (7.3%). Figure 2 illustrates that school shootings involving multiple firearms mostly occurred at high schools, n = 70 (62.5%), followed by elementary, n = 21 (18.8%), junior high/middle, n = 15 (13.4%), and other, n = 6 (5.4%). Figure 2 illustrates that school shootings involving multiple shooters mostly occurred at high schools, n = 110 (68.8%), followed by elementary, n = 25 (15.6%), junior high/middle, n = 17 (10.6%), and other, n = 8 (5%). Figure 2 illustrates that school shootings involving adult shooters mostly occurred at high schools, n = 415 (59%), followed by elementary, n = 173 (24.6%), junior high/middle, n = 68 (9.7%), and other, n = 47 (6.7%). Figure 3 illustrates that school shootings that occurred during school hours mostly occurred at high schools, n = 687 (66.4%), followed by junior high/middle, n = 160 (15.5%), elementary, n = 132 (12.8%), and other, n = 55 (5.3%). Figure 3 illustrates that school shootings that were pre-planned mostly occurred at high schools, n = 72 (63.2%), followed by junior high/middle, n = 25 (21.9%), elementary, n = 10 (8.8%), and other, n = 7 (6.1%).
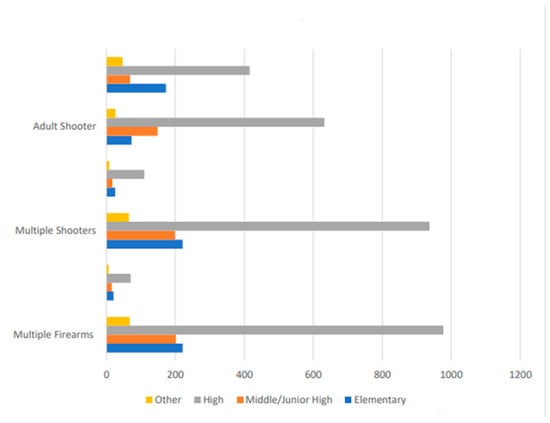
Figure 2.
School shootings involving multiple firearms, shooters, and adults by school type.
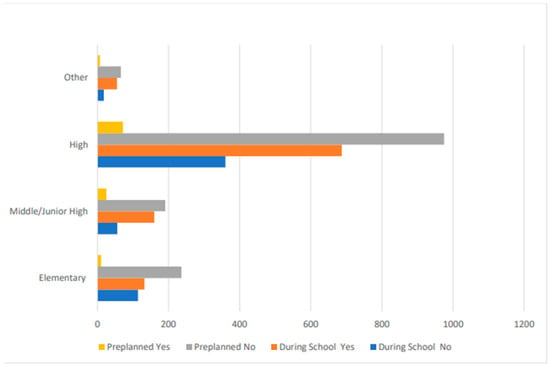
Figure 3.
School shootings that occurred during school and pre-planned by school type.
A negative binomial regression was conducted to determine the relationship between school type, during school hours, pre-planned, presence of an adult shooter, presence of multiple firearms, presence of multiple shooters, firearm type, and school relationship and the total number of victims (see Table 2). The result of the analysis shows school type, preplanned, presence of multiple firearms, presence of multiple shooters, and firearm type significantly predicted the total number of victims in a school shooting incident. Elementary school shootings were associated with a 41% increase in the log victim count (b = 0.35, p < 0.01) compared to school shootings at schools categorized as other. High school shootings were associated with a 28% increase in the log victim count (b = 0.25, p < 0.01) compared to school shootings at schools categorized as other. Planned school shootings were associated with a 115% increase in log victim count (b = 0.77, p < 0.001) compared to unplanned shootings. School shootings involving multiple firearms were associated with a 75% increase in log victim count (b = 0.56, p < 0.001) compared to school shootings involving a single firearm. School shootings involving multiple shooters were associated with a 29% increase in log victim count (b = 0.25, p < 0.01) compared to school shootings involving a single shooter. School shootings with a combination of different firearms were associated with a 17% increase in log victim count (b = 0.16, p < 0.001) compared to school shootings involving a firearm that could not be identified. School shootings with a rifle were associated with a 11% increase in log victim count (b = 0.11, p < 0.05) compared to school shootings involving a firearm that could not be identified.

Table 2.
Negative Binomial Regression Model Estimates.
10. Discussion
The current study’s goal is twofold: (1) to contribute to the descriptive understanding of school shooting characteristics; and (2) to address the gaps in the extant literature through examining the perpetrators relationship with the school on the total number of victims during a school shooting incident. A description of the school shootings shows that most occur in high schools, are perpetrated by individuals expected to be on campus, are youth shooters, involve both handguns and single shooters, occur during school hours, and are not preplanned. These findings are similar to studies attempting to describe school shooting characteristics (Freilich et al. 2022; Gammell et al. 2021; Livingston et al. 2019). Fridel (2019) suggests these incidents reflect community characteristics (e.g., homicide rates and violent crime rates) of the schools. Another probable explanation related to the descriptive findings is that many of these incidents may stem from interpersonal disputes, and these communities foster a street culture that promotes and supports violent solutions to conflict (Fridel 2019; Holland et al. 2019).
Results from the negative binomial regression model revealed that school shootings at elementary and high schools, preplanned, involved different firearms, rifles, multiple perpetrators, and multiple firearms were associated with a higher expected count of injuries and deaths. The findings suggest that the perpetrator’s relationship to the schools is not associated with the number of victims during a school shooting incident, although school shooting incidents were mostly perpetrated by individuals with a daily expectation to be on campus. The significant findings are consistent with previous studies on school and rampage school shooting incidents (Gammell et al. 2021; Livingston et al. 2019; Newman et al. 2004; Silva and Greene-Colozzi 2020; Yelderman et al. 2019). Considering that most school shooting incidents involve a single victim, the findings are likely associated with rampage school shootings, which, due to their indiscriminate nature, result in more injuries and casualties overall (Joseph et al. 2023; Madfis 2014, 2017). Perpetrators that plan school shootings develop extensive plans (e.g., attack locations, time/date of the attack, and order of attack) to exploit the weaknesses of their target and cause the most damage possible during these incidents (Gammell et al. 2021; Joseph et al. 2023; Madfis 2014, 2017; National Threat Assessment Center 2021).
11. Policy Implications
Several of the findings in the current study have policy-laden relevance that is somewhat congruent with routine activities theory. First, we find that a pre-planned shooting was the strongest predictor of casualties in our multivariate model. A pre-planned attack presumably represents a rational choice by the offender to inflict the maximum amount of harm (Schildkraut et al. 2022), and any policies focused on harm mitigation may be useful here. Mitigation strategies should be implemented that acknowledge the hedonistic calculus employed by offenders when determining when to perpetrate the act, making the potential act less attractive and enhancing the risk (Clarke 1995; Joseph et al. 2023; Schildkraut et al. 2022). We find that school shootings in elementary schools are associated with a significantly higher total victim count. Therefore, target-hardening and harm-reduction policies may be particularly relevant for elementary schools. A routine activities approach would postulate that the higher expected casualty count that is witnessed in elementary school shootings is largely a function of victim inertia (i.e., soft targets) that have limited capacity to defend themselves when under attack (Greenberg 2007; Hesterman 2015; Schildkraut et al. 2019). In particular, policies that target access control, location entry, increased security personnel (e.g., SRO’s), and exit screening are ostensibly more useful in areas with populations with challenges defending themselves; this is magnified considering elementary schools implemented the fewest target-hardening strategies (Martaindale et al. 2017; Schildkraut et al. 2019; U.S. Department of Education 2019). Further, target-hardening approaches should be implement with caution, considering the evidence regarding these strategies’ relationship with the school-to-prison pipeline (Dodson 2022; Fisher and Devlin 2020).
Recent scholarship in this area (e.g., Schildkraut et al. 2019; Schildkraut et al. 2022) cautions against difficult-to-implement policy implications primarily focusing on criminal motivation (e.g., mental health) or weapon availability. These authors posit that attempting to profile mass shooters as a threat assessment is unfruitful from an evidence-based perspective, as any such profile ostensibly overestimates the number of potential mass shooters. Madfis (2014, 2017) suggests implementing a restorative justice approach for school discipline to develop a supportive, trusting, and positive school environment, considering previous evidence has identified that punitive school environments foster distrust between stakeholders (i.e., staff and students) and may play a role in rampage school shooting incidents. Schools that implement a restorative justice approach for classroom discipline could improve the relationship between students and staff, which in turn make students more willing to provide information on peers that may display warning signs of perpetrating a school shooting incident to staff (e.g., suicide, rampage school shooting, escalation of dispute shooting) (Madfis 2014, 2017). Restorative practices promote a culture change within the school to an inclusionary environment that allows students, administrators, and teachers to openly communicate about issues and problems within the school without fear of punishment or retaliation (King and Bracy 2019). Although imperfect, this approach may serve as a viable alternative to the punitive approach, considering that most schools implement punitive approaches and the negative consequences that have been documented using these approaches in the extant literature (Aguado and Joseph 2023).
While not a focus in the current research, recent examinations of the correlates of rampage school shootings (e.g., Schildkraut et al. 2022) have identified the time dimension as a salient correlate of harm amplification. Not only are most of these events pre-planned, but most school shootings are disproportionately likely to occur during “disruptions” (e.g., arrival, lunch, and departure) in the school day. Hence, it is logical to deploy more security personnel to vulnerable areas (e.g., lunchrooms, libraries, and parking lots) when these events are most prone to occur (Schildkraut et al. 2022). Another potential policy suggestion is restricting firearms access, specifically, the ability to acquire multiple and diverse firearms and rifle types to reduce school shooting causalities. Rifles (5.1%), incidents involving multiple firearms (7.1%), and a combination of different weapons (2.6%) were a small percentage of incidents; however, each significantly accounted for more victims during a school shooting incident (Joseph et al. 2023; Silva and Greene-Colozzi 2020; Yelderman et al. 2019). Further, although contentious, the findings suggest restricting gun access, in general, would be an effective policy as a preventative measure to reduce the incidents occurring and the overall number of victims (Newman et al. 2004).
12. Limitations and Future Research
This research is somewhat limited to the available measures/indicators in the K-12 School Shootings Database, particularly regarding mental health indicators and weapon availability. Specifically, several relevant weapons-related items could not be properly operationalized with these data (e.g., if the weapon was purchased legally, an assault weapon was employed in the commission of the shooting, etc.). Moreover, although previous research (Schildkraut et al. 2022) correctly identifies the challenges/problems with trying to find a “one-size-fits-all” approach to the motivation behind school shootings, this area of research would unquestionably benefit from more specific indicators to capture mental health, including self-reported indicators of mental health, as well as official diagnoses and treatment/care (see Yelderman et al. 2019). Further, relevant variables of interest (i.e., number of students, school community characteristics, and spatial characteristics) are not present in the dataset for analysis. As indicated by Yelderman et al. (2019), there is likely an interaction in these episodes between weapon availability and mental illness, but the inability to properly operationalize construct in these data is a liability of the current research. While there is some merit for a proactive community-based approach in which potentially violent offenders are supervised by laypeople in the community, evidence for any such policy implementation, despite its considerable merit, cannot be borne out with these data.
Despite the limitations, the current study contributes to the understanding of school shooting causalities and incidents by providing a descriptive analysis of the incidents over the past 50 years and the importance of the perpetrator’s relationship to the school on the severity of the incident. Further, the current study improves on the limitations of Joseph et al. (2023)’s study by including incidents at non-traditional and less modern educational institutions (e.g., K-12, alternative schools and daycares). In closing, the current study provides valuable information that may be useful for social scientists, policy makers, and practitioners. Future research will benefit from databases that include spatial characteristics, community characteristics, school characteristics, and perpetrator features to allow for a more robust analysis of school shooting incidents.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.J.J. and C.W.P.; methodology, J.J.J.; software, J.J.J.; validation, J.J.J. and C.W.P.; formal analysis, J.J.J.; investigation, J.J.J.; resources, J.J.J.; data curation, J.J.J.; writing—original draft preparation, J.J.J. and C.W.P.; writing—review and editing, J.J.J. and C.W.P.; visualization, J.J.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
No external funding to report.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The current study did not require approval by IRB.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data used in this research were made publicly available by the Center for Homeland Defense and Security who own the data and can be found at https://www.chds.us/ssdb/, accessed on 30 May 2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abel, Meagan N., Steven Chermak, and Joshua D. Freilich. 2022. Pre-attack warning behaviors of twenty adolescent school shooters: A case study analysis. Crime and Delinquency 68: 786–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, N. Alexander, and Justin J. Joseph. 2023. The Carceral State of American Schools: The Impact of Symbolic Threat of Public School Policy. In Addressing Violence in the US Public School System. Edited by Jeffrey D. Herron, Sharon R. Sartin and Joseph Budd. Hershey: IGI Global, pp. 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, Mark, Joanne Kaufman, Thomas R. Simon, Lisa Barrios, Len Paulozzi, George Ryan, Rodney Hammond, William Modzeleski, Thomas Feucht, Lloyd Potter, and et al. 2001. School-associated violent deaths in the United States, 1994–1999. JAMA 286: 2695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arluke, Arnold, and Eric Madfis. 2014. Animal abuse as a warning sign of school massacres: A critique and refinement. Homicide Studies 18: 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, William N., Terresa H. Shubert, and Phillip J. McLaughlin. 2001. Invisible kids: Preventing school violence by identifying kids in trouble. Intervention in School and Clinic 37: 105–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonanno, Caitlin M., and Richard L. Levenson Jr. 2014. School Shooters: History, Current Theoretical and Empirical Findings, and Strategies for Prevention. Journal of Police Emergency Response 4: 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, Alexander L., Justin T. Pickett, Cheryl Lero Jonson, Francis T. Cullen, and Velmer S. Burton Jr. 2021. Public support for policies to reduce school shootings: A moral-altruistic model. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency 58: 269–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, Ronald V. 1995. Situational Crime Prevention. Crime and Justice 19: 91–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, Jacob, Patricia Cohen, Stephen G. West, and Leona S. Aiken. 2003. Applied Multiple Regression/Correlation Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences. Mahwah: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates. [Google Scholar]
- Dodson, Hannah. 2022. Abusing discretion: The battle for childhood in schools. Michigan Journal of Race and Law 27: 417–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everytown for Gun Safety. n.d. Stop Arming Teachers. Available online: https://www.everytown.org/solutions/arming-teachers/ (accessed on 29 May 2022).
- Fisher, Benjamin W., and Deanna N. Devlin. 2020. School crime and the patterns of roles of school resource officers: Evidence from a national longitudinal study. Crime and Delinquency 66: 1606–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, Joshua D., Steven M. Chermak, and Brent R. Klein. 2020. Investigating the applicability of Situational Crime Prevention to the public mass violence context. Criminology and Public Policy 19: 271–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freilich, Joshua D., Steven M. Chermak, Nadine M. Connell, Brent R. Klein, and Emily A. Greene-Colozzi. 2022. Using open-source data to better understand and respond to American school shootings: Introducing and exploring the American School Shooting Study (TASSS). Journal of School Violence 21: 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridel, Emma E. 2019. The Contextual Correlates of School Shootings. Justice Quarterly 38: 596–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gammell, Sarah P., Nadine M. Connell, and Michael G. Huskey. 2021. A Descriptive Analysis of the Characteristics of School Shootings Across Five Decades. American Journal of Criminal Justice 47: 818–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaughan, Edward, Jay D. Cerio, and Robert A. Myers. 2001. Lethal Violence in Schools. Alfred: Alfred University. [Google Scholar]
- Gerard, F. Jeane, K. C. Whitfield, L. E. Porter, and K. D. Browne. 2016. Offender and offence characteristics of school shooting incidents. Journal of Investigative Psychology and Offender Profiling 13: 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenberg, Sheldon F. 2007. Active shooters on college campuses: Conflicting advice, roles of the individual and first responder, and the need to maintain perspective. Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness 1: S57–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesterman, Jennifer. 2015. Soft Target-Hardening: Protecting People from Attack. Boca Raton: CRC Press. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, Kristin M., Jeffrey E. Hall, Jing Wang, Elizabeth M. Gaylor, Linda L. Johnson, Daniel Shelby, Thomas R. Simon, and School-Associated Violent Deaths Study Group. 2019. Characteristics of School-Associated Youth Homicides—United States, 1994–2018. MMWR. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report 68: 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou, Maria, Laura Hammond, and Olivia Simpson. 2015. A model for differentiating school shooters characteristics. Journal of Criminal Psychology 5: 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, Justin J., Christoper W. Purser, Elizabeth Elia, and Logan A. Yelderman. 2023. The Impact of Routine Activities on the Number of School Shooting Injuries and Fatalities. In Addressing Violence in the US Public School System. Edited by Jeffrey D. Herron, Sharon R. Sartin and Joseph Budd. Hershey: IGI Global, pp. 191–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalesan, Bindu, Kinan Lagast, Marcos Villarreal, Elizabeth Pino, Jeffrey Fagan, and Sandro Galea. 2017. School shootings during 2013–15 in the USA. Injury Prevention 23: 321–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Joanne M., Jeffrey E. Hall, and Michelle Zagura. 2012. Sex, race/ethnicity, and context in school-associated student homicides. Journal of Interpersonal Violence 27: 2373–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, Michael S., and Matthew Mahler. 2003. Adolescent masculinity, homophobia, and violence: Random school shootings, 1982–2001. American Behavioral Scientist 46: 1439–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, Sanna, and Nicole L. Bracy. 2019. School security in the post-Columbine era: Trends, consequences, and future directions. Journal of Contemporary Criminal Justice 35: 274–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langman, Peter. 2020. Desperate identities. Criminology & Public Policy 19: 61–84. [Google Scholar]
- Livingston, Melvin D., Matthew E. Rossheim, and Kelli Stidham Hall. 2019. A descriptive analysis of school and school shooter characteristics and the severity of school shootings in the United States, 1999–2018. Journal of Adolescent Health 64: 797–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madfis, Eric. 2014. The Risk of School Rampage: Assessing and Preventing Threats of School Violence. Berlin and Heidelberg: Springer. [Google Scholar]
- Madfis, Eric. 2017. In search of meaning: Are school rampage shootings random and senseless violence? The Journal of Psychology 151: 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martaindale, M. Hunter, William L. Sandel, and J. Pete Blair. 2017. Active-shooter events in the workplace: Findings and policy implications. Journal of Business Continuity & Emergency Planning 11: 6–20. [Google Scholar]
- McGee, James P., and Caren R. DeBernardo. 1999. The classroom avenger: A behavioral profile of school based shootings. The Forensic Examiner 8: 16–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mooney, Taylor, Lilia Luciano, and Justin Sherman. 2022. Texas Laws Allow Teachers to Carry Guns on School Grounds with Little Regulation. CBS Report. November 17. Available online: https://www.cbsnews.com/news/texas-teachers-guns-at-school/ (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Muschert, Glenn W. 2007. Research in school shootings. Sociology Compass 1: 60–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Threat Assessment Center. 2019. Protecting America’s Schools: A U.S. Secret Services Analysis of Targeted School Violence. February. Available online: https://www.secretservice.gov/sites/default/files/2020-04/Protecting_Americas_Schools.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- National Threat Assessment Center. 2021. Averting Targeted School Violence: A Secret Service Analysis of Plots against Schools. March. Available online: https://www.secretservice.gov/sites/default/files/reports/2021-03/USSS%20Averting%20Targeted%20School%20Violence.2021.03.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Newman, Katherine S., Cybelle Fox, David Harding, Jal Mehta, and Wendy Roth. 2004. Rampage: The Social Roots of School Shootings. New York: Basic Books. [Google Scholar]
- Pah, Adam R., Jim Hagan, Andrew-Logan Jennings, Aditya Jain, Kat Albrecht, Adam J. Hockenberry, and Luis A. Nunes Amaral. 2017. Economic insecurity and the rise in gun violence at US schools. Nature Human Behaviour 1: 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradice, David. 2017. An analysis of US school shooting data (1840–2015). Education 138: 135–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rajan, Sheetal, and Jon Lane. 2018. School shootings: Making the case for translational criminology. The Criminologist 43: 1–36. Available online: https://asc41.com/wp-content/uploads/ASC-Criminologist-2018-05.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Rajan, Sonali, Charles C. Branas, Dawn Myers, and Nina Agrawal. 2019. Youth exposure to violence involving a gun: Evidence for adverse childhood experience classification. Journal of Behavioral Medicine 42: 646–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeping, Paul M., Louis Klarevas, Sonali Rajan, Ali Rowhani-Rahbar, Justin Heinze, April M. Zeoli, Monika K. Goyal, Marc A. Zimmerman, and Charles C. Branas. 2022. State firearm laws, gun ownership, and K-12 school shootings: Implications for school safety. Journal of School Violence 21: 132–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riedman, David. 2022. K-12 School Shooting Database. Available online: https://k12ssdb.org/ (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Rocque, Michael. 2012. Exploring school rampage shootings: Research, theory, and policy. The Social Science Journal 49: 304–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocque, Michael, and Grant Duwe. 2018. Rampage shootings: An historical, empirical, and theoretical overview. Current Opinion in Psychology 19: 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, Joseph A., Charern Lee, George W. Burruss, and Matthew J. Giblin. 2018. College student perceptions of campus safety initiatives. Criminal Justice Policy Review 29: 319–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildkraut, Jaclyn, Brandon M. Naman, and Mark C. Stafford. 2019. Advancing responses to mass shootings using a routine activity approach. Crime Prevention and Community Safety 21: 346–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schildkraut, Jaclyn, H. Jaymi Elsass, Mark C. Stafford, and Jacob Sheingold. 2022. Understanding more than 50 years of mass public shootings as a function of routine activities. Homicide Studies. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shultz, James M., Glenn W. Muschert, Alison Dingwall, and Alyssa M. Cohen. 2013. The Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting as tipping point: “This Time Is Different”. Disaster Health 1: 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Jason R., and Emily Ann Greene-Colozzi. 2020. Mass Shootings and Routine Activities Theory: The Impact of Motivation, Target Suitability, and Capable Guardianship on Fatalities and Injuries. Available online: https://psycnet.apa.org/record/2020-72269-001 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Sommer, Friederike, Vincenz Leuschner, and Herbert Scheithauer. 2014. Bullying, romantic rejection, and conflicts with teachers: The crucial role of social dynamics in the development of school shootings–A systematic review. International Journal of Developmental Science 8: 3–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanford, Libby. 2022. 45 Percent of American Adults Support Armed Teachers in School, Poll Finds. Education Week. August 11. Available online: https://www.edweek.org/leadership/45-percent-of-american-adults-support-armed-teachers-in-schools-poll-finds/2022/08 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Turanovic, Jillian J., and Sonja E. Siennick. 2020. Causes and Consequences of School Violence; Research Report Prepared for the National Institute of Justice STOP School Violence Program Assessment: Review of the Causes and Consequences of School Violence; Washington, DC: National Institute of Justice, Office of Justice Programs, Department of Justice.
- U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. 2019. School Safety and Security Measures. Available online: https://nces.ed.gov/fastfacts/display.asp?id=334 (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Vossekuil, Bryan, Robert A. Fein, Marisa Reddy, Randy Borum, and William Modzeleski. 2004. The Final Report and Findings of the Safe School Initiative; Washington, DC: US Secret Service and Department of Education.
- Vuong, Quang H. 1989. Likelihood ratio tests for model selection and non-nested hypotheses. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society 57: 307–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbrot, Deborah M. 2008. Prelude to a school shooting? Assessing threatening behaviors in childhood and adolescence. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 47: 847–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wike, Traci L., and Mark W. Fraser. 2009. School shootings: Making sense of the senseless. Aggression and Violent Behavior 14: 162–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelderman, Logan A., Justin J. Joseph, Matthew P. West, and Erycha Butler. 2019. Mass shootings in the United States: Understanding the importance of mental health and firearm considerations. Psychology, Public Policy, and Law 25: 212–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).