MRI-Based Radiomics in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
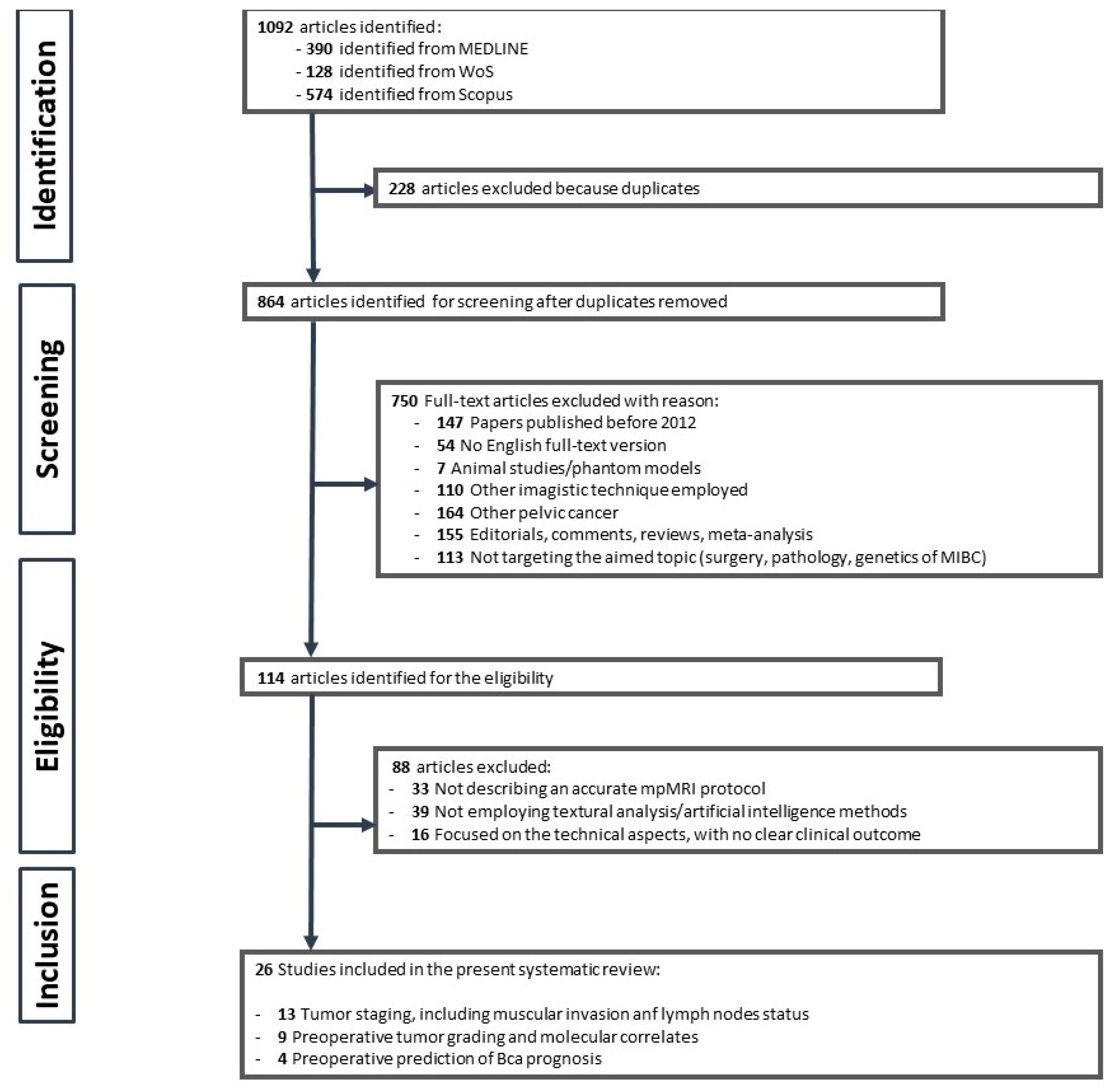
2.1. Literature Research and Study Selection
- evaluated BCa using an MRI-based radiomics approach.
- provided information related to tumor characterization (grading, staging, and muscular invasion status)
- provided information related to tumor prognosis (survival, recurrence rate, and response to neoadjuvant therapy)
- were written in English.
- studies based on other imaging modalities, such as ultrasound, CT, PET-CT
- publications designed as letters to the editor, editorial, conference abstract, review, systematic review, meta-analyses, or case reports.
- articles focusing on methodological aspects of radiomics and artificial intelligence, without well-established clinical application
- studies considering only semantic imaging features.
- topics out of the purpose of this review.
- studies with a sample size under 30.
2.2. Data Extraction
- general features, including the name of authors, country, publication year, and journal.
- study characteristics, including general aim, study design (prospective, retrospective), MRI technical data (e.g., type of scanner, field of strength, sequences used for radiomics analysis), sample size.
- Details of radiomics analysis, including software used for segmentation and feature extraction, segmentation method, imaging preprocessing, number and type of extracted features, feature selection methods/machine learning classifiers, number of selected radiomics features.
- performance or prognostic metrics of a radiomics model in terms of area under the curve (AUC) or concordance index (C-index).
2.3. Quality Assessement
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of Included Studies
3.2. Assessment of Study Quality
3.3. Prediction of BCa Grade and Molecular Correlates
3.4. Prediction of BCa Stage, including Muscle Invasion and N Stage
3.5. Prediction of BCa Prognosis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Padala, S.A.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology of Bladder Cancer. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Witjes, J.A.; Bruins, H.M.; Cathomas, R.; Compérat, E.M.; Cowan, N.C.; Gakis, G.; Hernández, V.; Espinós, E.L.; Lorch, A.; Neuzillet, Y.; et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Muscle-invasive and Metastatic Bladder Cancer: Summary of the 2020 guidelines. Eur. Urol. 2021, 79, 82–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Sankhwar, S.; Goel, A.; Kumar, M.; Purkait, B.; Aeron, R. Grading of complications of transurethral resection of bladder tumor using Clavien-Dindo classification system. Indian J. Urol. 2016, 32, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, S.W.E.; Veenboer, P.W.; Wessels, F.J.; Meijer, R.P. Diagnostic Accuracy of Multiparametric MRI for Local Staging of Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Urology 2020, 145, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panebianco, V.; Narumi, Y.; Altun, E.; Bochner, B.H.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Hafeez, S.; Huddart, R.; Kennish, S.; Lerner, S.; Montironi, R.; et al. Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Bladder Cancer: Development of VI-RADS (Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System). Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- da Silva, M.C.; Pecoraro, M.; Pisciotti, M.L.; Dehghanpour, A.; Forookhi, A.; Lucciola, S.; Bicchetti, M.; Messina, E.; Catalano, C.; Panebianco, V. The learning curve in bladder MRI using VI-RADS assessment score during an interactive dedicated training program. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 7494–7503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Rios-Velazquez, E.; Leijenaar, R.; Carvalho, S.; van Stiphout, R.G.; Granton, P.; Zegers, C.M.; Gillies, R.; Boellard, R.; Dekker, A.; et al. Radiomics: Extracting more information from medical images using advanced feature analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Timmeren, J.E.; Cester, D.; Tanadini-Lang, S.; Alkadhi, H.; Baessler, B. Radiomics in medical imaging-”how-to” guide and critical reflection. Insights Imaging 2020, 11, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramanzoli, P.; Castellani, D.; De Stefano, V.; Brocca, C.; Nedbal, C.; Chiacchio, G.; Galosi, A.B.; Da Silva, R.D.; Teoh, J.Y.; Tiong, H.Y.; et al. Radiomics vs radiologist in bladder and renal cancer. Results from a systematic review. Cent. Eur. J. Urol. 2023, 76, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, P.; Leijenaar, R.T.H.; Deist, T.M.; Peerlings, J.; de Jong, E.E.C.; van Timmeren, J.; Sanduleanu, S.; Larue, R.T.H.M.; Even, A.J.G.; Jochems, A.; et al. Radiomics: The bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 749–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whiting, P.F.; Rutjes, A.W.; Westwood, M.E.; Mallett, S.; Deeks, J.J.; Reitsma, J.B.; Leeflang, M.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Bossuyt, P.M.; QUADAS-2 Group. QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann. Intern. Med. 2011, 155, 529–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Meng, J.; Yang, Z.; Lu, H. Preoperative prediction of muscular invasiveness of bladder cancer with radiomic features on conventional MRI and its high-order derivative maps. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1896–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Tian, Q.; Li, B.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cui, G.; Lu, H. Radiomics assessment of bladder cancer grade using texture features from diffusion-weighted imaging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2017, 46, 1281–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tong, Y.; Udupa, J.K.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Venigalla, S.; Guzzo, T.J.; Mamtani, R.; Baumann, B.C.; Christodouleas, J.P.; Torigian, D.A. Radiomics-guided therapy for bladder cancer: Using an optimal biomarker approach to determine extent of bladder cancer invasion from t2-weighted magnetic resonance images. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 3, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z.; Shi, S.; Huang, M.; Yu, H.; Dong, W.; Huang, J.; Lin, T. Development and Validation of an MRI-Based Radiomics Signature for the Preoperative Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in Bladder Cancer. EBioMedicine 2018, 34, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Tian, Q.; Wang, H.; Cui, L.B.; Li, S.; Tang, X.; Li, B.; Dolz, J.; Ayed, I.B.; et al. Quantitative Identification of Nonmuscle-Invasive and Muscle-Invasive Bladder Carcinomas: A Multiparametric MRI Radiomics Analysis. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 49, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.S.; Tirumani, S.; van der Pol, C.B.; Alessandrino, F.; Sonpavde, G.P.; Silverman, S.G.; Shinagare, A.B. Use of Quantitative T2-Weighted and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient Texture Features of Bladder Cancer and Extravesical Fat for Local Tumor Staging After Transurethral Resection. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Hu, D.; Yao, H.; Chen, M.; Li, S.; Chen, H.; Luo, J.; Feng, Y.; Guo, Y. Radiomics analysis of multiparametric MRI for the preoperative evaluation of pathological grade in bladder cancer tumors. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 6182–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Yao, Q.; Liu, G.; Jin, D.; Chen, H.; Xu, J.; Li, Z.; Wu, G. Combining DWI radiomics features with transurethral resection promotes the differentiation between muscle-invasive bladder cancer and non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Du, P.; Zhang, F.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yuan, J.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; et al. A predictive nomogram for individualized recurrence stratification of bladder cancer using multiparametric MRI and clinical risk factors. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2019, 50, 1893–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Kong, J.; Wu, S.; Li, Y.; Cai, J.; Yu, H.; Xie, W.; Qin, H.; Wu, Z.; Huang, J.; et al. Development of a noninvasive tool to preoperatively evaluate the muscular invasiveness of bladder cancer using a radiomics approach. Cancer 2019, 125, 4388–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, L.; Du, P.; Li, S.; Tian, Q.; Ling, J.; Guo, Y.; et al. Elaboration of a multisequence MRI-based radiomics signature for the preoperative prediction of the muscle-invasive status of bladder cancer: A double-center study. Eur. Radiol. 2020, 30, 4816–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Song, M.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, S.; Sun, Q.; Zhai, G.; Liang, D.; Wu, G.; Li, Z.C. Radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of progression-free survival using diffusion-weighted imaging in patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 131, 109219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammouda, K.; Khalifa, F.; Soliman, A.; Ghazal, M.; El-Ghar, M.A.; Badawy, M.A.; Darwish, H.E.; Khelifi, A.; El-Baz, A. A multiparametric MRI-based CAD system for accurate diagnosis of bladder cancer staging. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2021, 90, 101911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Yoshida, S.; Tsuchiya, J.; Yamada, I.; Tanaka, H.; Yokoyama, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yoshimura, R.; Tateishi, U.; Fujii, Y. Usefulness of texture features of apparent diffusion coefficient maps in predicting chemoradiotherapy response in muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razik, A.; Das, C.J.; Sharma, R.; Malla, S.; Sharma, S.; Seth, A.; Srivastava, D.N. Utility of first order MRI-Texture analysis parameters in the prediction of histologic grade and muscle invasion in urinary bladder cancer: A preliminary study. Br. J. Radiol. 2021, 94, 20201114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, F.; Gu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Yao, X. Integrating multiparametric MRI radiomics features and the Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) for bladder cancer grading. Abdom. Radiol. 2021, 46, 4311–4323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, F.; Gu, Z.; Yan, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Yao, X. Combining Multiparametric MRI Radiomics Signature with the Vesical Imaging-Reporting and Data System (VI-RADS) Score to Preoperatively Differentiate Muscle Invasion of Bladder Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 619893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Gu, Z.; Xu, F.; Maskey, N.; He, Y.; Yan, Y.; Xu, T.; Liu, S.; Yao, X. Magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomics signature for preoperative prediction of Ki67 expression in bladder cancer. Cancer Imaging 2021, 21, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Q.; Meng, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y. Radiomics Nomogram Based on High-b-Value Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Distinguishing the Grade of Bladder Cancer. Life 2022, 12, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Dong, Q.; Li, Z.; Guo, Y.; Lu, H. The Additional Value of Tri-parametric MRI in Identifying Muscle-invasive Status in Bladder Cancer. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, W.; Wang, K.; Wu, J.; Qiu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, X. Integrating radiomics with the vesical imaging-reporting and data system to predict muscle invasion of bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2022, 41, 294.e1–294.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y. Development of a MRI-Based Radiomics Nomogram for Prediction of Response of Patients With Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 878499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Guo, Y.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Qiu, X.; Liu, S. CD8A as a Prognostic and Immunotherapy Predictive Biomarker Can Be Evaluated by MRI Radiomics Features in Bladder Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhe, X.; Chang, H.; Tang, M.; Lei, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X. An MRI-based radiomics nomogram in predicting histologic grade of non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1025972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Qiu, Z.; Cao, K.; Deng, L.; Zhang, W.; Xie, C.; Yang, S.; Yue, P.; Zhong, J.; Lyu, J.; et al. Predicting muscle invasion in bladder cancer based on MRI: A comparison of radiomics, and single-task and multi-task deep learning. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2023, 233, 107466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Zheng, Z.; He, Y.; Yao, X. Development of a Molecular-Subtype-Associated Immune Prognostic Signature That Can Be Recognized by MRI Radiomics Features in Bladder Cancer. Bioengineering 2023, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozikowski, M.; Suarez-Ibarrola, R.; Osiecki, R.; Bilski, K.; Gratzke, C.; Shariat, S.F.; Miernik, A.; Dobruch, J. Role of Radiomics in the Prediction of Muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Eur. Urol. Focus 2022, 8, 728–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Lan, X.; Deng, J.; Lei, Y.; Lin, F. The role of radiomics with machine learning in the prediction of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: A mini review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 990176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Chen, Y.; Yan, C.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, P.; Runa, A.; Liu, J. Study Progress of Radiomics with Machine Learning for Precision Medicine in Bladder Cancer Management. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Wang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Du, P.; Liu, Y.; Lu, H. Study Progress of Noninvasive Imaging and Radiomics for Decoding the Phenotypes and Recurrence Risk of Bladder Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 704039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglic, I.; Panebianco, V.; Vargas, H.A.; Bura, V.; Woo, S.; Pecoraro, M.; Cipollari, S.; Sala, E.; Barrett, T. MRI of Bladder Cancer: Local and Nodal Staging. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2020, 52, 649–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichtmann, B.D.; Harder, F.N.; Weiss, K.; Schönberg, S.O.; Attenberger, U.I.; Alkadhi, H.; Pinto Dos Santos, D.; Baeßler, B. Influence of Image Processing on Radiomic Features from Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Investig. Radiol. 2023, 58, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafiq-Ul-Hassan, M.; Zhang, G.G.; Latifi, K.; Ullah, G.; Hunt, D.C.; Balagurunathan, Y.; Abdalah, M.A.; Schabath, M.B.; Goldgof, D.G.; Mackin, D.; et al. Intrinsic dependencies of CT radiomic features on voxel size and number of gray levels. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Xu, P. Radiomics signature on dynamic contrast-enhanced MR images: A potential imaging biomarker for prediction of microvascular invasion in mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 6846–6855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, S.; Kim, C.H.; Park, H.G.; Prakash, D.; Madusanka, N.; Cho, N.H.; Choi, H.K. Multi-Features Classification of Prostate Carcinoma Observed in Histological Sections: Analysis of Wavelet-Based Texture and Colour Features. Cancers 2019, 11, 1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petresc, B.; Lebovici, A.; Caraiani, C.; Feier, D.S.; Graur, F.; Buruian, M.M. Pre-Treatment T2-WI Based Radiomics Features for Prediction of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Non-Response to Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy: A Preliminary Study. Cancers 2020, 12, 1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural Features for Image Classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man. Cybern. 1973, 6, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thibault, G.; Angulo, J.; Meyer, F. Advanced statistical matrices for texture characterization: Application to cell classification. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanzione, A.; Gambardella, M.; Cuocolo, R.; Ponsiglione, A.; Romeo, V.; Imbriaco, M. Prostate MRI radiomics: A systematic review and radiomic quality score assessment. Eur. J. Radiol. 2020, 129, 109095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Han, K. Methodologic Guide for Evaluating Clinical Performance and Effect of Artificial Intelligence Technology for Medical Diagnosis and Prediction. Radiology 2018, 286, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author (Year of Publication) | Journal | Study Design | No of Patients (Train vs. Test Cohort) | Surgical Technique | Reference Standard | Analyzed Outcome | MRI Sequence | Readers | Imaging Timing | Provided Protocol | Scanner |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xu et al. (2017) [12] | Abdominal Radiology | Retrospective | 68 | TURBT | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI | 2 | Prior to TURBT | yes | GE Discovery 750 3.0T |
| Zhang et al. (2017) [13] | Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Retrospective | 61 | NA | Pathological grade | Tumor grade | DWI and ADC | 2 | prior to treatment | yes | GE Discovery 750 3.0T |
| Tong et al. (2018) [14] | Advances in Radiation Oncology | Retrospective | 65 | RC | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI | 2 | Prior/after treatment | yes | 1.5 and 3.0T scanners |
| Wu et al. (2018) [15] | EBioMedicine | Retrospective | 103 (69:34) | RC | Pathological N stage | Lymph node status | T2WI | 2 | Preoperative | yes | Philips Intera Achieva 3.0T |
| Xu et al. (2019) [16] | Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Retrospective | 54 | NA | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI, DWI and ADC | 3 | Preoperative | yes | GE Discovery 750 3.0T |
| Lim et al. (2019) [17] | American Journal of Roentgenology | Retrospective | 36 | TURBT and RC | Pathological T stage | Tumor stage (muscle invasion and extravesical disease) | T2WI and ADC | 2 | Post TURBT, prior to RC | yes | 1.5 and 3.0T scanners |
| Wang et al. (2019) [18] | European Radiology | Retrospective | 100 (70:30) | TURBT or RC | Pathological grade | Tumor grade | T2WI, DWI and ADC | 2 | NA | yes | Siemens Magnetom Trio, 3.0T |
| Xu et al. (2020) [19] | European Radiology | Retrospective | 218 (131:87) | TURBT and RC | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | DWI and ADC | 2 | Prior to TURBT | yes | Philips Ingenia 3.0T MR |
| Xu et al. (2019) [20] | Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging | Retrospective | 71 (50:21) | TURBT or RC | NA | Recurrence Risk | T2WI, DWI, DCE | 2 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom 3.0T MR |
| Zheng et al. (2019) [21] | Cancer | Retrospective | 199 (130:69) | TURBT or RC | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI | 2 | Prior to treatment | yes | Philips Achieva 3.0T |
| Wang et al. (2020) [22] | European Radiology | Retrospective | 106 (64:42) | RC or PC or TURBT | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI, DWI and ADC | 3 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom 3.0T/GE Discovery 750 3.0T |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [23] | European Journal of Radiology | Retrospective | 210 (105:105) | TURBT or RC or CT or RT | NA | Progression-free Survival | DWI | 2 | NA | yes | Philips Ingenia 3.0T MR scanner |
| Hammouda et al. (2021) [24] | Computerized Medical Imaging and Graphics | Retrospective | 42 | NA | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI, DWI, ADC | NA | NA | yes | Philips Ingenia 3.0T |
| Kimura et al. (2022) [25] | EuropeanRadiology | Retrospective | 45 | PC or RC | Pathological T stage | Response to NCT | ADC | 2 | Prior to treatment | yes | Philips Intera Achieva 1.5T |
| Razik et al. (2021) [26] | The British Journal of Radiology | Retrospective | 40 | NA | Pathological grade | Muscle invasion + grade | T2WI, DWI and ADC | 2 | prior to treatment | yes | Philips Achieva 3.0T |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [27] | Abdominal Radiology | Retrospective | 294 | TURBT or RC | Pathological grade | Tumor grade | T2WI, DCE | 2 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom Verio 3.0T |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [28] | Frontiers in Oncology | Retrospective | 185 (129:56) | NA | Pathological T stage | MIBC | T2WI and DCE | 2 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom Verio 3.0T |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [29] | Cancer Imaging | Retrospective | 179 (125:54) | TURBT or RC | Immunohistochemistry | Ki-67 | T2WI and DCE | 2 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom Verio 3.0T |
| Feng et al. (2022) [30] | Life | Retrospective | 74 (58:16) | RC or PC or TURBT | Pathological grade | Tumor grade | ADC 1000, ADC 1700, ADC 3000 | 2 | prior to treatment | yes | GE Discovery 750 3.0T |
| Liu et al. (2023) [31] | Academic Radiology | Retrospective | 206 (165:41) | NA | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI, DWI, DCE | 3 | prior to treatment | yes | Siemens Magnetom Trio 3.0T |
| Wang et al. (2022) [32] | Urologic Oncology | Retrospective | 191 (121:70) | TURBT or RC | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | DWI | 2 | Preoperative | yes | GE Discovery 750 3.0T/United Imaging uMR790 3.0T |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [33] | Frontiers in Oncology | Retrospective | 70 | TURBT or RC or PC | Pathological T stage | Response to chemotherapy | T2, DWI, ADC | 2 | Prior to treatment | yes | GE Discovery 750 3.0T |
| Zheng et al. (2022) [34] | Cancers | Retrospective | 111 (77:34) | NA | Immunohistochemistry | CD8A | T2WI + DCE | 2 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom 3.0T MR |
| Li et al. (2023) [35] | Frontiers in Oncology | Retrospective | 169 (118:51) | NA | Pathological grade | Tumor grade | T2WI and ADC | 2 | prior to treatment | yes | Philips Ingenia and Ingenia X 3.0T MR |
| Li et al. (2023) [36] | Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine | Retrospective | 121 (93:28) | TURBT or RC or PC | Pathological T stage | Muscle invasion | T2WI | 1 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom Skyra 3.0T/United Imaging Healthcare 3.0T |
| Liu et al. (2023) [37] | Bioengineering | Retrospective | 111 (77:34) | NA | RNA sequencing | Immune Prognostic Signature | T2WI + DCE | 2 | Preoperative | yes | Siemens Magnetom 3.0T |
| Reference | 1. Image Protocol Quality | 2. Multiple Segmentations | 3. Phantom Study | 4. Imaging at Multiple Time Points | 5. Feature Reduction/Adjustment for Multiple Testing | 6. Multivariable Analysis with Non-Radiomics Features | 7. Biological Correlates | 8. Cut-Off Analysis | 9. Discrimination Statistics | 10. Calibration Statistics | 11. Prospective Study | 12. Validation | 13. Comparison to “Gold standard” | 14. Potential Clinical Utility | 15. Cost-Effectiveness Analysis | 16. Open Science and Data | Total | RQS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Score range | 0–2 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | −3–3 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–1 | 0–2 | 0–2 | 0–7 | −5–5 | 0–2 | 0–2 | 0–1 | 0–4 | −8–36 | 0–100% |
| Xu et al. (2017) [12] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 11% |
| Zhang et al. (2017) [13] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 14% |
| Tong et al. (2018) [14] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 33% |
| Wu et al. (2018) [15] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 47% |
| Xu et al. (2019) [16] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 6 | 17% |
| Lim et al. (2019) [17] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 8% |
| Wang et al. (2019) [18] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 33% |
| Xu et al. (2020) [19] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 33% |
| Xu et al. (2019) [20] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 17 | 47% |
| Zheng et al. (2019) [21] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 53% |
| Wang et al. (2020) [22] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 50% |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [23] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 39% |
| Hammouda et al. (2021) [24] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 33% |
| Kimura et al. (2022) [25] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 14% |
| Razik et al. (2021) [26] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 14% |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [27] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 44% |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [28] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 18 | 50% |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [29] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 14 | 39% |
| Feng et al. (2022) [30] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 11 | 31% |
| Liu et al. (2023) [31] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 33% |
| Wang et al. (2022) [32] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 36% |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [33] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | −5 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 19% |
| Zheng et al. (2022) [34] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 28% |
| Li et al. (2023) [35] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 19 | 53% |
| Li et al. (2023) [36] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 13 | 36% |
| Liu et al. (2023) [37] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 | 28% |
| Study | Risk of Bias | Applicability Concerns | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference standard | Flow & Timing | Patient Selection | Index Test | Reference standard | |
| Xu et al. (2017) [12] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zhang et al. (2017) [13] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Tong et al. (2018) [14] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Wu et al. (2018) [15] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Xu et al. (2019) [16] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Lim et al. (2019) [17] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Wang et al. (2019) [18] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Xu et al. (2020) [19] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Xu et al. (2019) [20] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zheng et al. (2019) [21] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Wang et al. (2020) [22] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [23] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Hammouda et al. (2021) [24] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Kimura et al. (2022) [25] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Razik et al. (2021) [26] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [27] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [28] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zheng et al. (2021) [29] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Feng et al. (2022) [30] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Liu et al. (2023) [31] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Wang et al. (2022) [32] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zhang et al. (2022) [33] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Zheng et al. (2022) [34] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Li et al. (2023) [35] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Li et al. (2023) [36] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
| Liu et al. (2023) [37] |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Boca, B.; Caraiani, C.; Telecan, T.; Pintican, R.; Lebovici, A.; Andras, I.; Crisan, N.; Pavel, A.; Diosan, L.; Balint, Z.; et al. MRI-Based Radiomics in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132300
Boca B, Caraiani C, Telecan T, Pintican R, Lebovici A, Andras I, Crisan N, Pavel A, Diosan L, Balint Z, et al. MRI-Based Radiomics in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment. Diagnostics. 2023; 13(13):2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132300
Chicago/Turabian StyleBoca, Bianca, Cosmin Caraiani, Teodora Telecan, Roxana Pintican, Andrei Lebovici, Iulia Andras, Nicolae Crisan, Alexandru Pavel, Laura Diosan, Zoltan Balint, and et al. 2023. "MRI-Based Radiomics in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment" Diagnostics 13, no. 13: 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132300
APA StyleBoca, B., Caraiani, C., Telecan, T., Pintican, R., Lebovici, A., Andras, I., Crisan, N., Pavel, A., Diosan, L., Balint, Z., Lupsor-Platon, M., & Buruian, M. M. (2023). MRI-Based Radiomics in Bladder Cancer: A Systematic Review and Radiomics Quality Score Assessment. Diagnostics, 13(13), 2300. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics13132300








