Microsatellite Instability and MMR Genes Abnormalities in Canine Mammary Gland Tumors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Tumor Sample Collection
2.3. Tumor Histopathological Assessment
2.4. DNA Extraction and PCR Amplification
2.5. Microsatellite Instability (MSI)
2.6. Expression Profiling by RT-qPCR Assay
2.7. Detection of Exon Mutations of the cMSH2 Gene
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
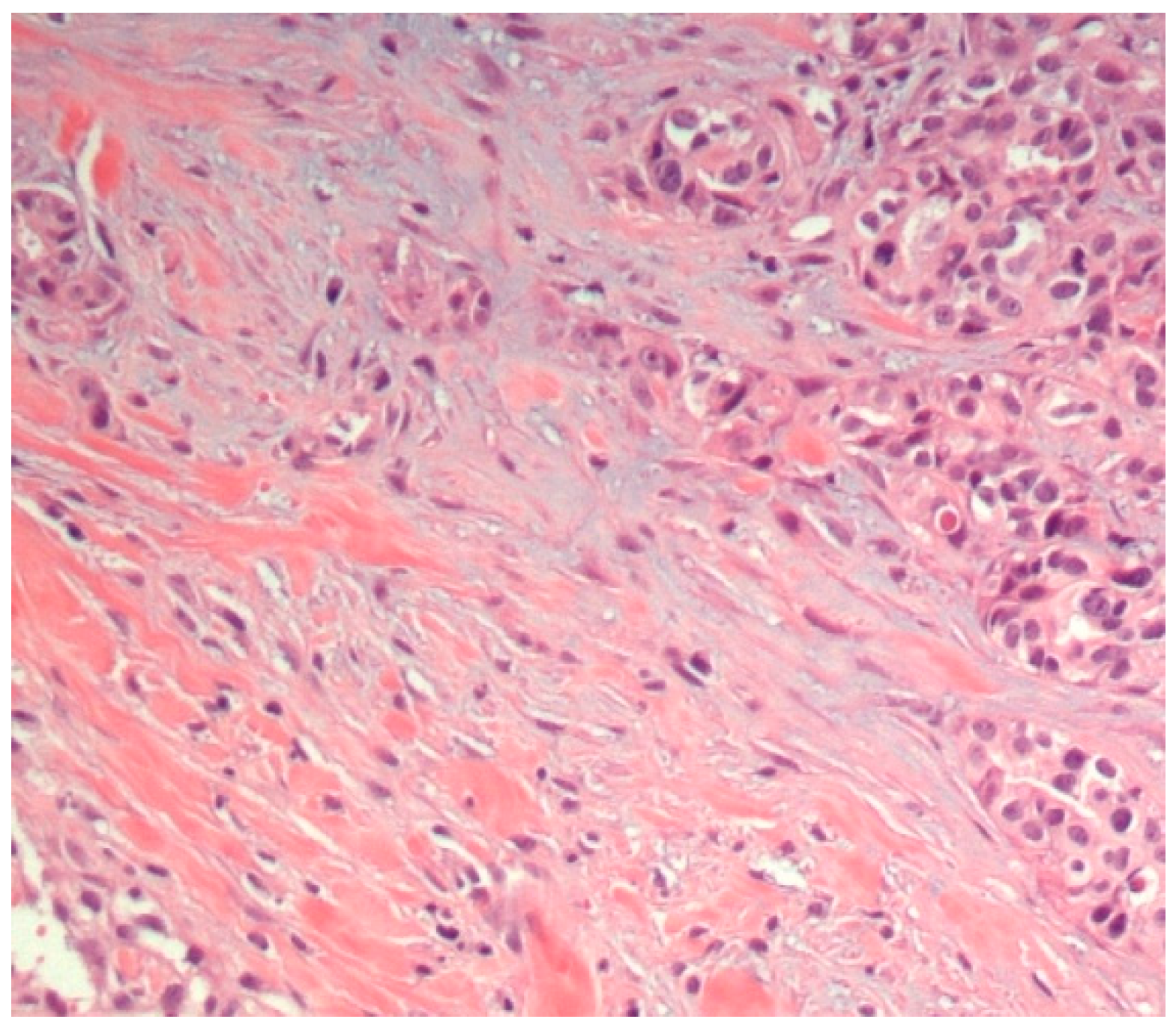
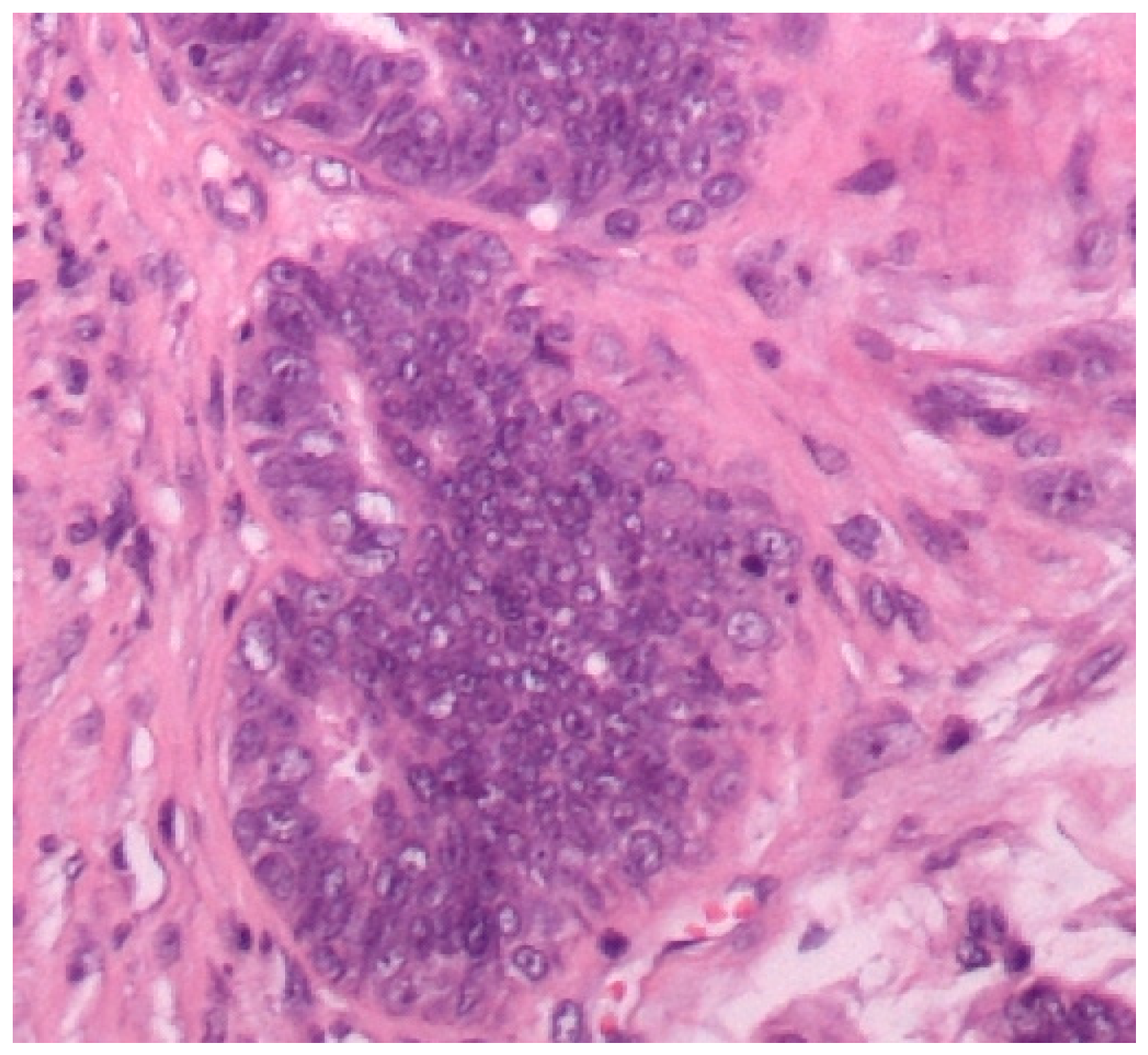
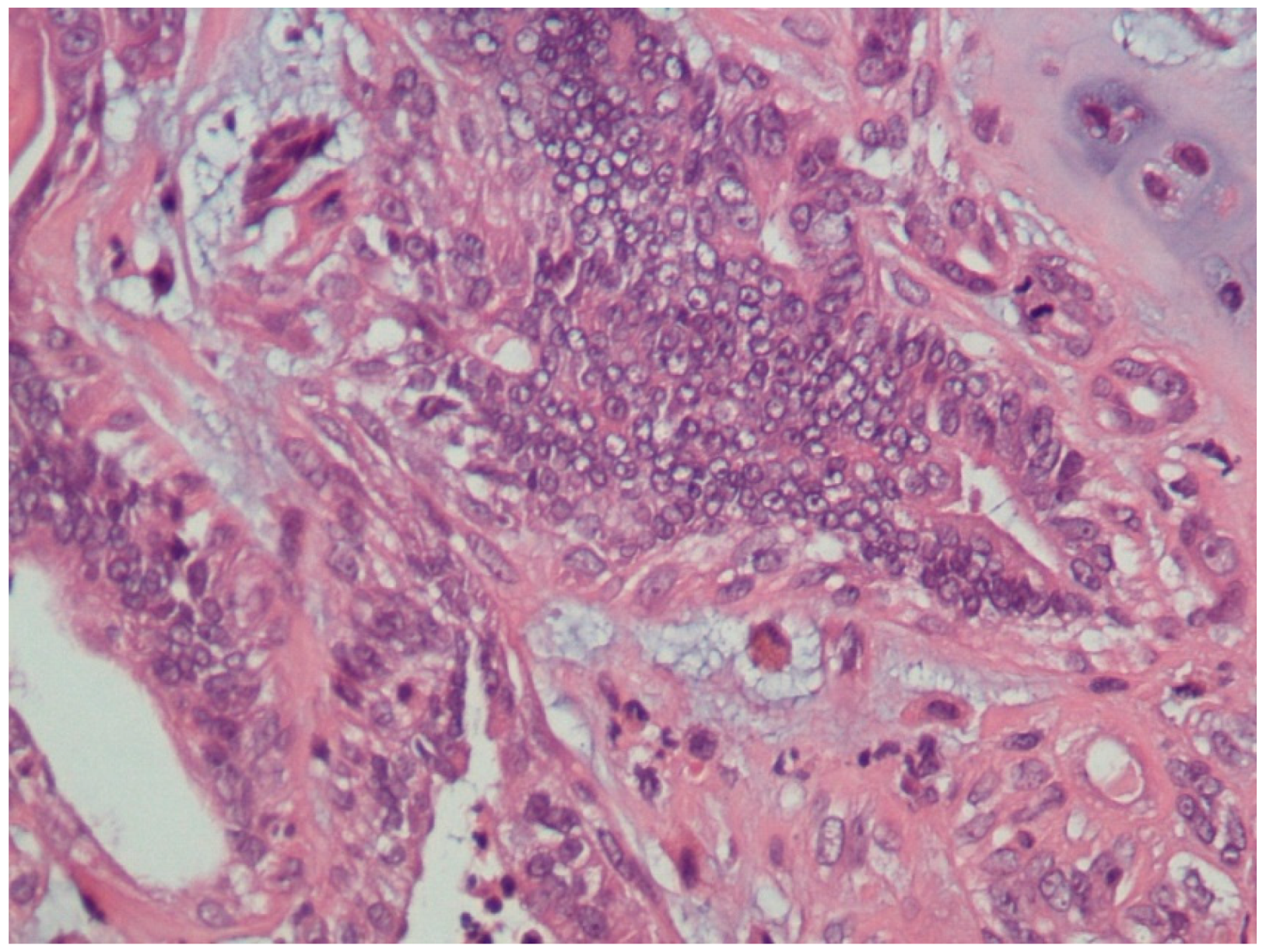
3.1. Histopathological Assessment
3.2. Microsatellite Instability (MSI) Screening
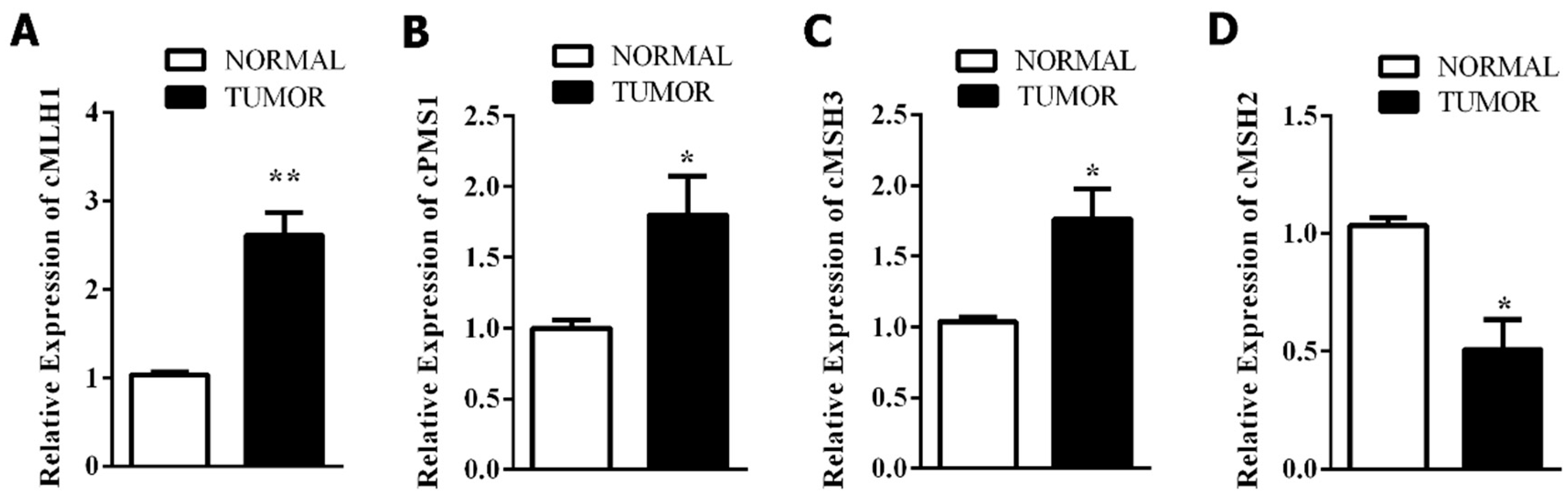
3.3. Mismatch Repair-Related Gene Expression
3.4. The Extent of Polymorphism in cMSH2 Gene
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HE | Hematoxylin and eosin |
| MMR | Mismatch repair |
| CMT | Gland tumor |
| CI | Chromosomal instability |
References
- Shen, Z. Genomic instability and cancer: An introduction. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thibodeau, S.N.; Bren, G.; Schaid, D. Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science 1993, 260, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, R.; Li, G.M.; Longley, M.J.; Fang, W.H.; Papadopoulos, N.; Jen, J.; de la Chapelle, A.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; Modrich, P. Hypermutability and mismatch repair deficiency in RER+ tumor cells. Cell 1993, 75, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klukowska, J.; Strabel, T.; Mackowski, M.; Switonski, M. Microsatellite polymorphism and genetic distances between the dog, red fox and arctic fox. J. Anim. Breed. Genet. 2003, 120, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkel, T.A.; Erie, D.A. DNA mismatch repair. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2005, 74, 681–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schofield, M.J.; Hsieh, P. DNA mismatch repair: Molecular mechanisms and biological function. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2003, 57, 579–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, J.; Silva, S.N.; Azevedo, A.P.; Teixeira, V.; Pina, J.E.; Rueff, J.; Gaspar, J.F. Association of common variants in mismatch repair genes and breast cancer susceptibility: A multigene study. Bmc Cancer 2009, 9, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niessen, R.C.; Berends, M.J.; Wu, Y.; Sijmons, R.H.; Hollema, H.; Ligtenberg, M.J.; de Walle, H.E.; de Vries, E.G.; Karrenbeld, A.; Buys, C.H. Identification of mismatch repair gene mutations in young patients with colorectal cancer and in patients with multiple tumours associated with hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer. Gut 2006, 55, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kane, M.F.; Loda, M.; Gaida, G.M.; Lipman, J.; Mishra, R.; Goldman, H.; Jessup, J.M.; Kolodner, R. Methylation of the hMLH1 promoter correlates with lack of expression of hMLH1 in sporadic colon tumors and mismatch repair-defective human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 808–811. [Google Scholar]
- Koopman, M.; Kortman, G.A.M.; Mekenkamp, L.; Ligtenberg, M.J.L.; Hoogerbrugge, N.; Antonini, N.F.; Punt, C.J.A.; Van, K.J.H.J.M. Deficient mismatch repair system in patients with sporadic advanced colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 100, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Poplawski, T.; Zadrozny, M.; Kolacinska, A.; Rykala, J.; Morawiec, Z.; Blasiak, J. Polymorphisms of the DNA mismatch repair gene HMSH2 in breast cancer occurence and progression. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2005, 94, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mik, M.; Dziki, L.; Malinowska, K.; Trzcinski, R.; Majsterek, I.; Dziki, A. Polymorphism of MSH2 Gly322Asp and MLH1 -93G>A in non-familial colon cancer—A case-controlled study. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2017, 13, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goldschmidt, M.; Pena, L.; Rasotto, R.; Zappulli, V. Classification and grading of canine mammary tumors. Vet. Pathol. 2011, 48, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litt, M.; Bestwick, M.; Winther, M.; Jakobs, P. Fifty-four new gene-based canine microsatellite markers. J. Hered. 2005, 96, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNiel, E.A.; Griffin, K.L.; Mellett, A.M.; Madrill, N.J.; Mickelson, J.R. Microsatellite instability in canine mammary gland tumors. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2007, 21, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouquand, S.; Priat, C.; Hitte, C.; Lachaume, P.; Andre, C.; Galibert, F. Identification and characterization of a set of 100 tri- and dinucleotide microsatellites in the canine genome. Anim Genet. 2000, 31, 266–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, K.; Yamamoto, H. Carcinogenesis and microsatellite instability: The interrelationship between genetics and epigenetics. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merlo, D.F.; Rossi, L.; Pellegrino, C.; Ceppi, M.; Cardellino, U.; Capurro, C.; Ratto, A.; Sambucco, P.L.; Sestito, V.; Tanara, G.; et al. Cancer incidence in pet dogs: Findings of the Animal Tumor Registry of Genoa, Italy. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2008, 22, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil Kumar, B.V.; Bhardwaj, R.; Mahajan, K.; Kashyap, N.; Kumar, A.; Verma, R. The overexpression of Hsp90B1 is associated with tumorigenesis of canine mammary glands. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 440, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Kumar, B.V.; Singh, S.; Verma, R. Development of recombinant matrix metalloproteinase-3 based sandwich ELISA for sero-diagnosis of canine mammary carcinomas. J. Immunoass. Immunochem. 2017, 38, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukola, A.; Eklin, K.; Laiho, P.; Salovaara, R.; Kristo, P.; Järvinen, H.; Mecklin, J.-P.; Launonen, V.; Aaltonen, L.A. Microsatellite marker analysis in screening for hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC). Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 4545–4549. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Iwase, H.; Ichihara, S.; Toyoshima, S.; Nakamura, T.; Yamashita, H.; Toyama, T.; Omoto, Y.; Karamatsu, S.; Mitsuyama, S.; et al. Loss of heterozygosity and microsatellite instability in ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast. Cancer Lett. 2000, 156, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halford, S.E.; Sawyer, E.J.; Lambros, M.B.; Gorman, P.; Macdonald, N.D.; Talbot, I.C.; Foulkes, W.D.; Gillett, C.E.; Barnes, D.M.; Akslen, L.A.; et al. MSI-low, a real phenomenon which varies in frequency among cancer types. J. Pathol. 2003, 201, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, C.J.; Roodi, N.; Verrier, C.S.; Parl, F.F. Microsatellite instability and loss of heterozygosity in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 1641–1644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Xu, G.; Lu, S. Overexpression of hMSH2 and hMLH1 protein in certain gastric cancers and their surrounding mucosae. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 19, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, T.; Chattopadhyay, P.; Mahapatra, A.K.; Sarkar, C.; Sinha, S. Increased hMSH2 protein expression in glioblastoma multiforme. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2004, 66, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castrilli, G.; Fabiano, A.; La Torre, G.; Marigo, L.; Piantelli, C.; Perfetti, G.; Ranelletti, F.O.; Piantelli, M. Expression of hMSH2 and hMLH1 proteins of the human DNA mismatch repair system in salivary gland tumors. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2002, 31, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, M.R.; Sun, M.; Roggero, E.; Sudilovsky, E.C.; Tuthill, R.J.; Wood, G.S.; Sudilovsky, O. Loss of heterozygosity, microsatellite instability, and mismatch repair protein alterations in the radial growth phase of cutaneous malignant melanomas. Mol. Carcinog. 2002, 34, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.; Villena-Heinsen, C.; Meyberg, R.; Woll-Hermann, A.; Reitnauer, K.; Schmidt, W.; Tilgen, W.; Reichrath, J. Immunohistochemical analysis of DNA ‘mismatch-repair’ enzyme human Mut-S-Homologon-2 in ovarian carcinomas. Histochem. J. 1999, 31, 717–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, F.S.; Hsieh, J.T.; Molberg, K.; Saboorian, M.H.; McConnell, J.D.; Sagalowsky, A.I. Expression of the human mismatch repair gene hMSH2: A potential marker for urothelial malignancy. Cancer 2000, 88, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, A.A.; Mandai, M.; Konishi, I.; Nanbu, K.; Tsuruta, Y.; Kusakari, T.; Kariya, M.; Kita, M.; Fujii, S. Cyclical change of hMSH2 protein expression in normal endometrium during the menstrual cycle and its overexpression in endometrial hyperplasia and sporadic endometrial carcinoma. Cancer 2002, 94, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.F.; Lawrence, M.S.; Demichelis, F.; Drier, Y.; Cibulskis, K.; Sivachenko, A.Y.; Sboner, A.; Esgueva, R.; Pflueger, D.; Sougnez, C.; et al. The genomic complexity of primary human prostate cancer. Nature 2011, 470, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lapointe, J.; Li, C.; Giacomini, C.P.; Salari, K.; Huang, S.; Wang, P.; Ferrari, M.; Hernandez-Boussard, T.; Brooks, J.D.; Pollack, J.R. Genomic profiling reveals alternative genetic pathways of prostate tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8504–8510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burger, M.; Denzinger, S.; Hammerschmied, C.G.; Tannapfel, A.; Obermann, E.C.; Wieland, W.F.; Hartmann, A.; Stoehr, R. Elevated microsatellite alterations at selected tetranucleotides (EMAST) and mismatch repair gene expression in prostate cancer. J. Mol. Med. (Berl. Ger. ) 2006, 84, 833–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahary, M.N.; Kaur, G.; Abu Hassan, M.R.; Singh, H.; Naik, V.R.; Ankathil, R. Germline mutation analysis of MLH1 and MSH2 in Malaysian Lynch syndrome patients. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2012, 18, 814–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyaki, M.; Konishi, M.; Tanaka, K.; Kikuchi-Yanoshita, R.; Muraoka, M.; Yasuno, M.; Igari, T.; Koike, M.; Chiba, M.; Mori, T. Germline mutation of MSH6 as the cause of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer. Nat. Genet. 1997, 17, 271–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
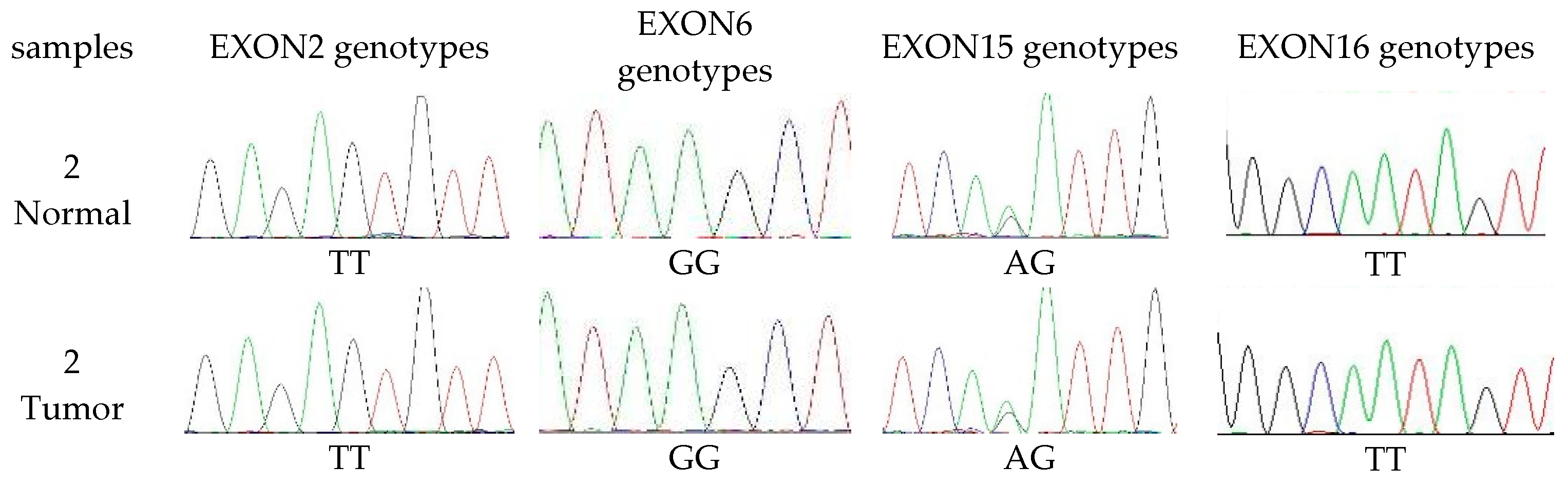
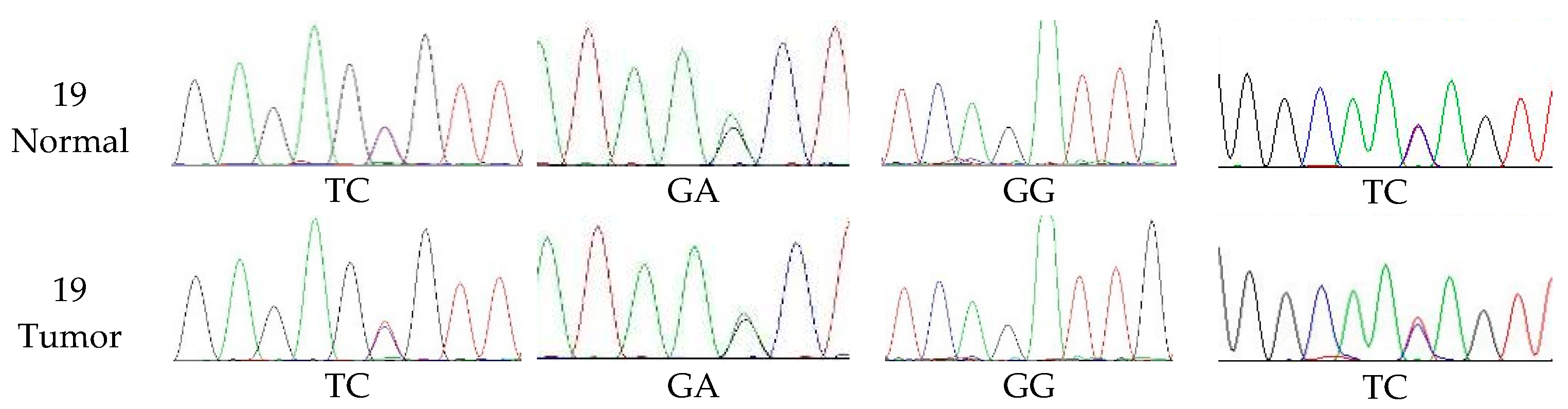
| CODE | Primer Forward 5′→3′ | Primer Reversed 5′→3′ | Expected Size bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| FLJ32685 | CTGCCTCAGCTGGGAAAATA | CACTACAGCTGGGATCAGCA | 433 |
| SCNA11 | GCAGTTTGGGGCTGCTAAA | AGAATGGAATCTTGCCCAGA | 267 |
| ABC9TETRA | GCATTAAGGAGGGCACTTGA | GACCCAGCCTTGAAAGAATG | 220 |
| SCNA10 | TCCAAGCATCCTCTTATCCA | CCACGTTGGTCTCCCTACTTA | 196 |
| ANGPT1 | GTTTTCCTGCTGTCCCAGTG | TTCCCTTTTGTGAATCCTGC | 414 |
| FLJ20511 | AAAGGCAGTCAACCAGTCC | CTGTGCAGTTTGCGGAGTAC | 403 |
| IGHE | CAAGACTGGCTCTGCTCTG | CCACTGAAAACAAGCCCATC | 140 |
| PPP1R9A | TAAAGATCCAAGTGGCGAGG | AACCACTCCCTTCACCACAG | 189 |
| MEPIA | GGTTCTGGGATCAAGTTCCA | CTGGTGGTTTCCTCTCCCTA | 345 |
| CDH4 | AAGTCAACAAGCTCCATCCC | AGGATTTTCCCCTAAGAGCTG | 142 |
| 9A5 | CATGCAGATGCCCCTAATCT | GGTGACAGGTGATTCTTGGA | 173 |
| No. | Name of GENE | Primer Sequence | Tm (C) | Amplicon Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | cMSH2 | F: CATTGGTGTCGTGGGTGTTA R: CAAAGTCCTAGCTTCCTCTGTATG | 62 | 96 |
| 2. | cMSH3 | F: CCTCGTGGCAAAGGGATATAA R: TTTCCGGGAGAACAGTGAAC | 62 | 100 |
| 3. | cMLH1 | F: GAGGGTCTGCCTATCTTCATTC R: GCACATTCTTTACTGAGGCTTTC | 62 | 92 |
| 4. | cPMS1 | F: CAGCAGTCGAGTAGTCAAGAAA R: GCATCCTCCAAACTGGTCTTA | 62 | 105 |
| 5. | GAPDH | F: GATGCTGGTGCTGAGTATGT R: CAGAAGGAGCAGAGATGATGAC | 62 | 112 |
| Primer | Sequence (5′–3′) | Size of Fragments Amplified (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| MSH2 exon1 F MSH2 exon1 R | GGACGCTCCGAAATGG GTCCACTCCCGCCCCT | 235 |
| MSH2 exon2 F MSH2 exon2 R | TGAGAGAAGAATGTAGGTTGGGG GCACACAATAGAATTCCCTCACA | 333 |
| MSH2 exon3 F MSH2 exon3 R | ATTGTGTATAAATCCAGCTGCCA CTTCATCCCTACCTTGATTCCCT | 421 |
| MSH2 exon4 F MSH2 exon4 R | TGGATTGGTTTGTTATGCTGTTGT TCACAAGCTTCGTCACAGTAAGA | 385 |
| MSH2 exon5 F MSH2 exon5 R | TGAAACAAGGTACCAGCATCTC TTACGCTTCTTAATTGTATTCTTCA | 443 |
| MSH2 exon6 F MSH2 exon6 R | TGGCACAGTAAGGTTTTCACTAA GATCAAGTGGCATAATCCTAGAGT | 269 |
| MSH2 exon7 F MSH2 exon7 R | TAATCCCAGTGCAATTTATTTCAGA CCCAACTTTATAAGGACAGCACA | 299 |
| MSH2 exon8 F MSH2 exon8 R | GAGACTTGCTGCGCTATTTGT TTCAAAAATACTTTGCTGCTGAAT | 276 |
| MSH2 exon9 F MSH2 exon9 R | ATTGTTATTTCCATCTTTACCCATC GAATTACTCAAACCACCAATGAG | 216 |
| MSH2exon10F MSH2exon10R | CTGTAGACATCTATGACCTTTTTCT GGAACATGCACATTTCATCCGAG | 277 |
| MSH2exon11F MSH2exon11R | GCTTATAGGACAGATGCTCTGGG TGCCTTGTAGCTCTTGGGTG | 832 |
| MSH2exon12F MSH2exon12R | TCAGTATTCCTGTGCACATTTTCT AAGCCCATAATTTAGGTGGGG | 323 |
| MSH2exon13F MSH2exon13R | TTTGGCAGTTAATGGTTCTGCTT CAGTCTGAGGGGACTGGGAAAT | 374 |
| MSH2exon14F MSH2exon14R | TGTCCCTTAACACATCTTTCCC CCAGTCACGCCCGAATTTAC | 399 |
| MSH2exon15F MSH2exon15R MSH2exon16F MSH2exon16R | GACAAGGTGAGGTGAACACG TCACACAGGAACAAATAACTCATC TGGTCAACTTAGGACTTTCTGTAA CCTTGGCTGCGACTTGTTTTT | 346 629 |
| Dog No. | Age of Dog | Breed | Tumor Histo-Type | Marker | Number of MSI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | Shish Tzu | Complex adenoma | CDH4 | 1/11 |
| 2 | 7 | Pomeranian | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Tubulopapillary carcinoma | ABC9TETRA, ANGPT1, PPP, MEPIA | 4/11 |
| 3 | 8 | Shish Tzu | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Solid carcinoma | 9A5, SCNA10 | 2/11 |
| 4 | 8 | Hybrid | Fibroadenoma | ANGPT1 | 1/11 |
| 5 | 9 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Complex carcinoma | 9A5, ABC9TETRA, FLJ20511, IGHE, FLJ32685 | 5/11 |
| 6 | 9 | Pomeranian | Adenoma | FLJ20511 | 1/11 |
| 7 | 9 | Hybrid | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-special types (Lipid-rich carcinoma) | SCNA10 | 1/11 |
| 8 | 10 | Shish Tzu | Complex adenoma | ABC9TETRA | 1/11 |
| 9 | 10 | Poodle | Malignant Mesenchymal neoplasms-osteosarcomas | ABC9TETRA, FLJ20511, SCNA10 | 3/11 |
| 10 | 10 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Tubulopapillary carcinoma | MEPIA, IGHE | 2/11 |
| 11 | 11 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Ductal carcinoma | PPP | 1/11 |
| 12 | 11 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Ductal carcinoma | FLJ32685 | 1/11 |
| 13 | 11 | Pomeranian | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Ductal carcinoma | ABC9TETRA, ANGPT1, SCNA10, SCNA11, MEPIA | 5/11 |
| 14 | 11 | Poodle | malignant mixed mammary tumor—carcinosarcoma | 9A5, FLJ32685, SCNA11, MEPIA | 4/11 |
| 15 | 11 | Pomeranian | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Complex carcinoma | ABC9TETRA, FLJ20511, FLJ32685, SCNA11 | 4/11 |
| 16 | 12 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Tubular carcinoma | SCNA11 | 1/11 |
| 17 | 12 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Ductal carcinoma | ANGPT1, IGHE, SCNA10, SCNA11, MEPIA, CDH4 | 6/11 |
| 18 | 12 | Hybrid | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Tubular carcinoma | 9A5, CDH4, PPP | 3/11 |
| 19 | 13 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Ductal carcinoma | 9A5, ABC9TETRA, FLJ20511, FLJ32685, SCNA11, PPP, MEPIA | 7/11 |
| 20 | 13 | Poodle | malignant mixed mammary tumor—carcinosarcoma | ABC9TETRA, 9A5 | 2/11 |
| 21 | 15 | Hybrid | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Tubulopapillary carcinoma | 9A5, FLJ20511, SCNA10, CDH4, MEPIA, | 5/11 |
| 22 | 15 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Ductal carcinoma | ABC9TETRA | 1/11 |
| 23 | 15 | Poodle | Malignant epithelial neoplasms-Ductal carcinoma | ABC9TETRA, FLJ20511, SCNA11, PPP, MEPIA | 5/11 |
| Markers | Tumor Cases | Frequency | Rate of Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABC9TETRA | 2, 5, 8, 9, 13, 15, 19, 20, 22, 23 | 10/23 | 43.4% |
| MEPIA | 2, 10, 13, 14, 17, 19, 21, 23 | 8/23 | 34.8% |
| 9A5 | 3, 5, 14, 18, 19, 20, 21 | 7/23 | 30.4% |
| SCNA 11 | 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 23 | 7/23 | 26.1% |
| FLJ20511 | 5, 6, 9, 15, 19, 21, 23 | 7/23 | 26.1% |
| SCNA10 | 3, 7, 9, 13, 17, 21 | 6/23 | 26.1% |
| FLJ32685 | 5, 12, 14, 15, 19 | 5/23 | 21.7% |
| PPP | 2, 11, 18, 19, 23 | 5/23 | 21.7% |
| ANGPT1 | 2, 4, 13, 17 | 4/23 | 17.4% |
| CDH4 | 1, 17, 18, 21 | 4/23 | 17.4% |
| IGHE | 5, 10, 17 | 3/23 | 13.0% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khand, F.M.; Yao, D.-W.; Hao, P.; Wu, X.-Q.; Kamboh, A.A.; Yang, D.-J. Microsatellite Instability and MMR Genes Abnormalities in Canine Mammary Gland Tumors. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020104
Khand FM, Yao D-W, Hao P, Wu X-Q, Kamboh AA, Yang D-J. Microsatellite Instability and MMR Genes Abnormalities in Canine Mammary Gland Tumors. Diagnostics. 2020; 10(2):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020104
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhand, Faiz Muhammad, Da-Wei Yao, Pan Hao, Xin-Qi Wu, Asghar Ali Kamboh, and De-Ji Yang. 2020. "Microsatellite Instability and MMR Genes Abnormalities in Canine Mammary Gland Tumors" Diagnostics 10, no. 2: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020104
APA StyleKhand, F. M., Yao, D.-W., Hao, P., Wu, X.-Q., Kamboh, A. A., & Yang, D.-J. (2020). Microsatellite Instability and MMR Genes Abnormalities in Canine Mammary Gland Tumors. Diagnostics, 10(2), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics10020104





