Constructing Ecological Networks and Analyzing Impact Factors in Multi-Scenario Simulation Under Climate Change
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
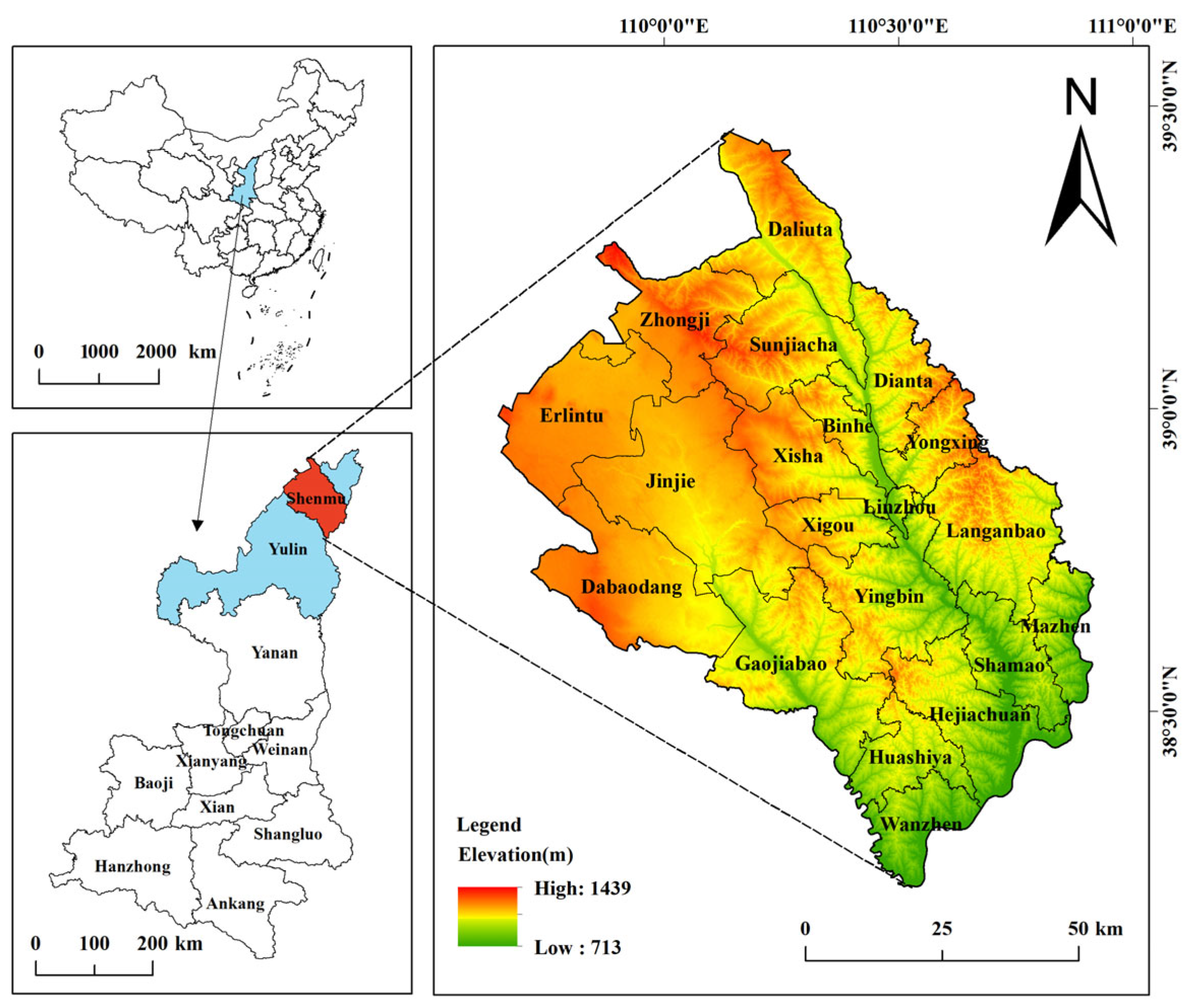
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Materials and Methods
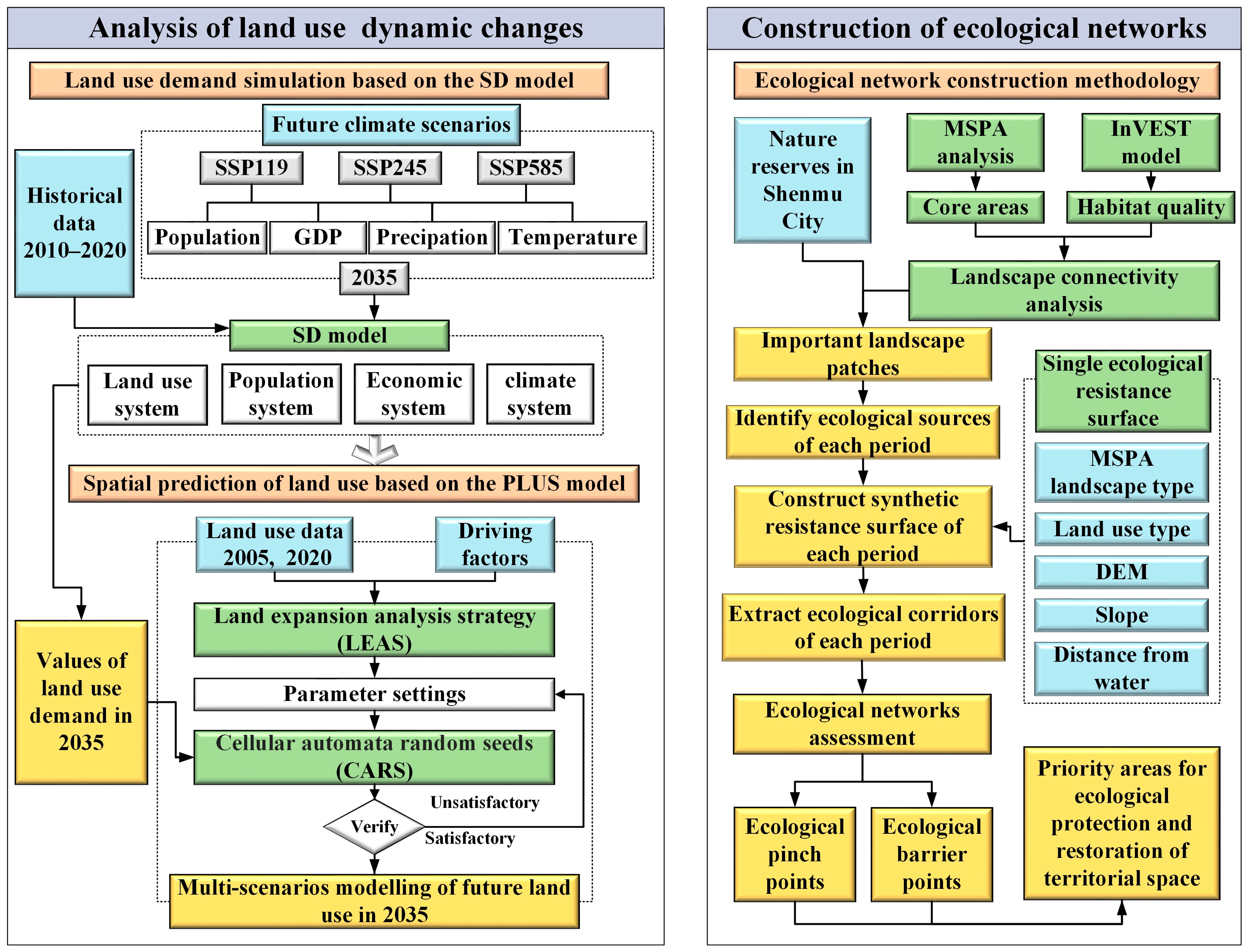
3.1. Multi-Scenario Simulation of Land Use Under Climate Change
3.1.1. SSPs-RCPs Scenario Settings
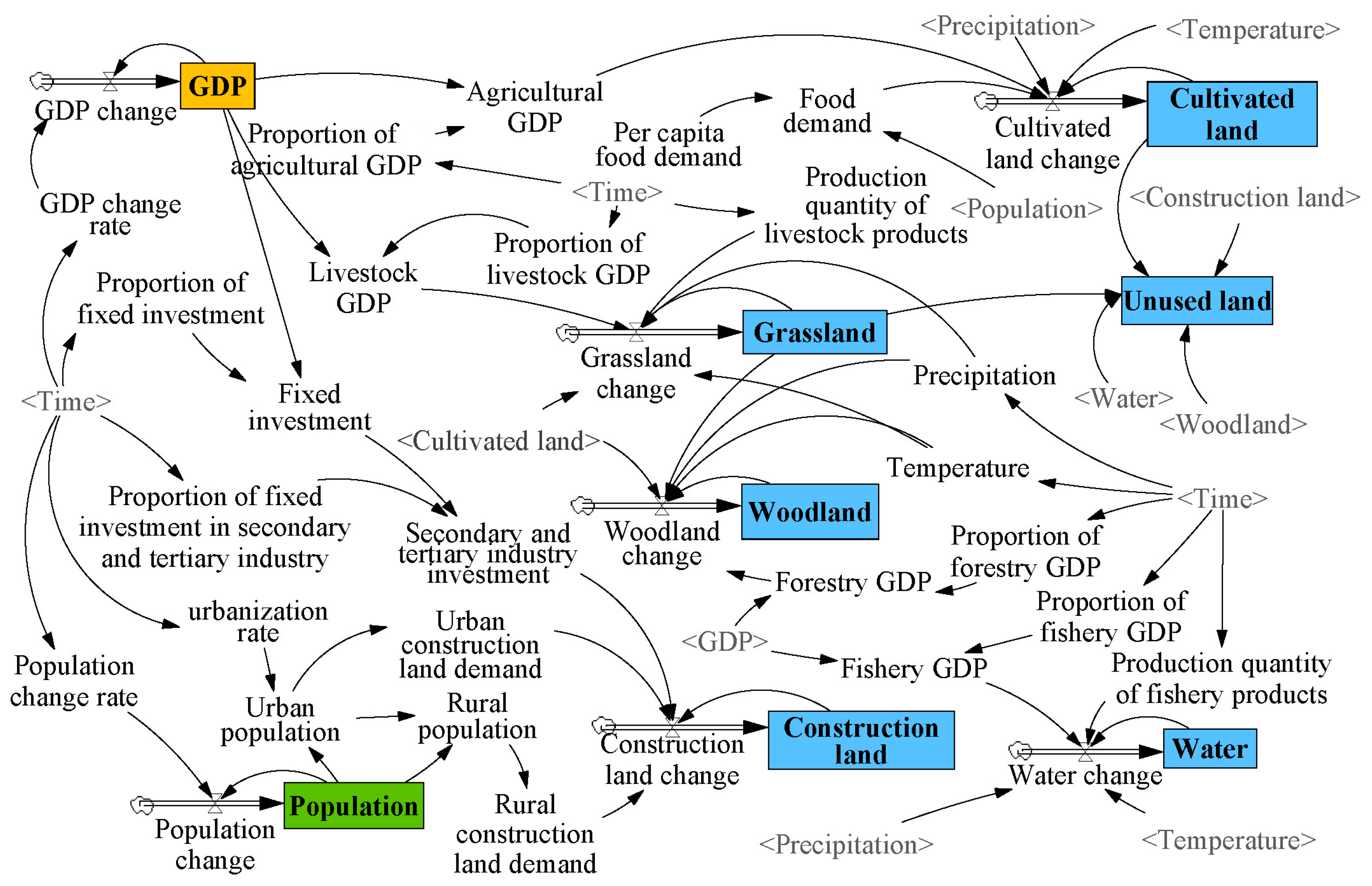
3.1.2. SD Model Construction
3.1.3. PLUS Model Simulation
3.2. Methods of Constructing and Assessing Ecological Networks
3.2.1. Identification of Ecological Sources
3.2.2. Construction of Ecological Resistance Surfaces
3.2.3. Extraction of Ecological Corridors
3.2.4. Assessment of Ecological Networks
3.3. Identification of Ecological Restoration Priority Areas
3.3.1. Identification of Ecological Pinch Points
3.3.2. Identification of Ecological Barrier Points
3.4. GeoDetector
4. Results
4.1. Spatiotemporal Dynamic Change Characteristics in Land Use
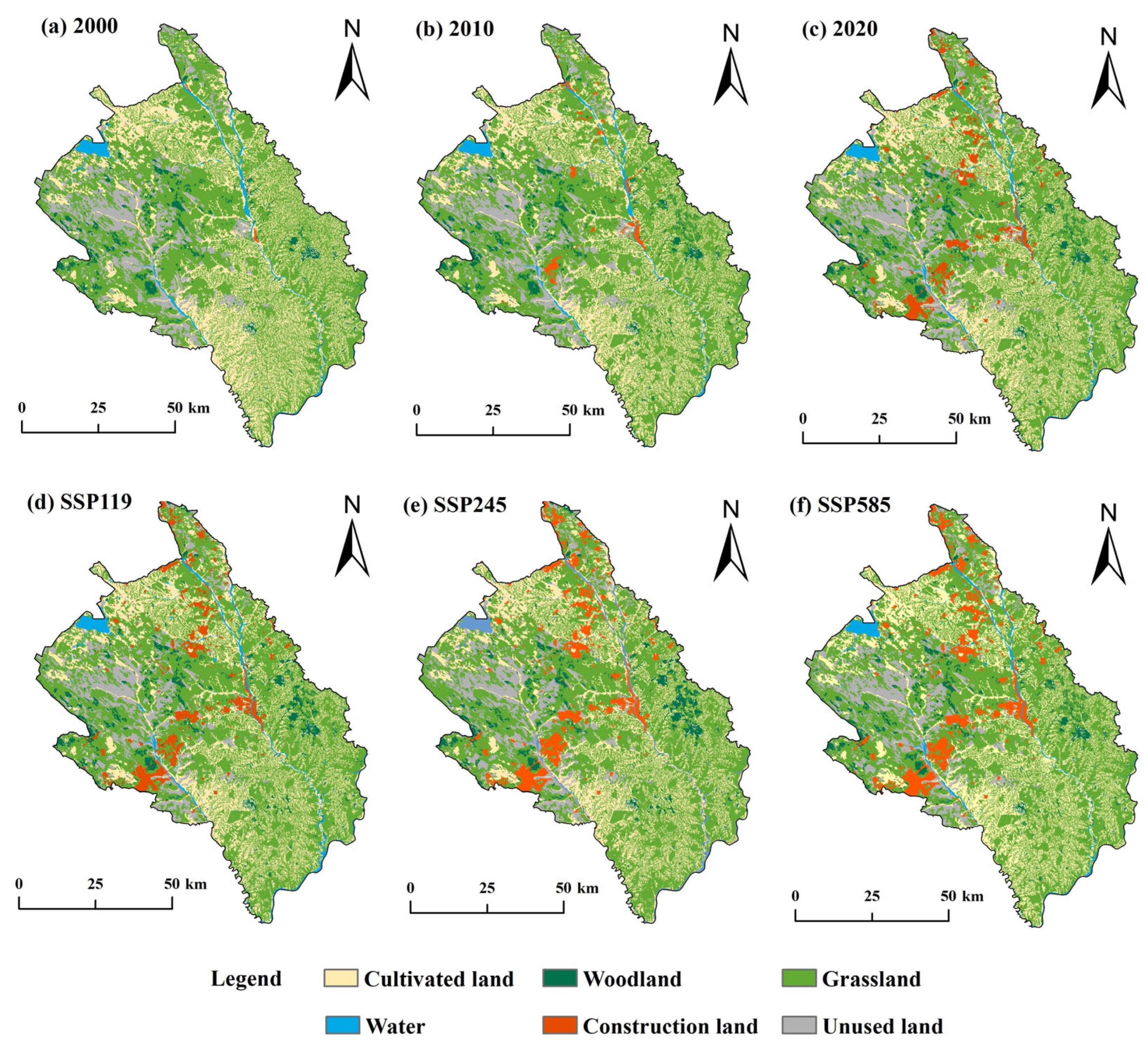
4.1.1. “Historical–Present” Land Use Changes
4.1.2. Future Land Use Changes Under Climate Change Multi-Scenarios
4.2. Spatiotemporal Dynamic Change Characteristics in Ecological Networks
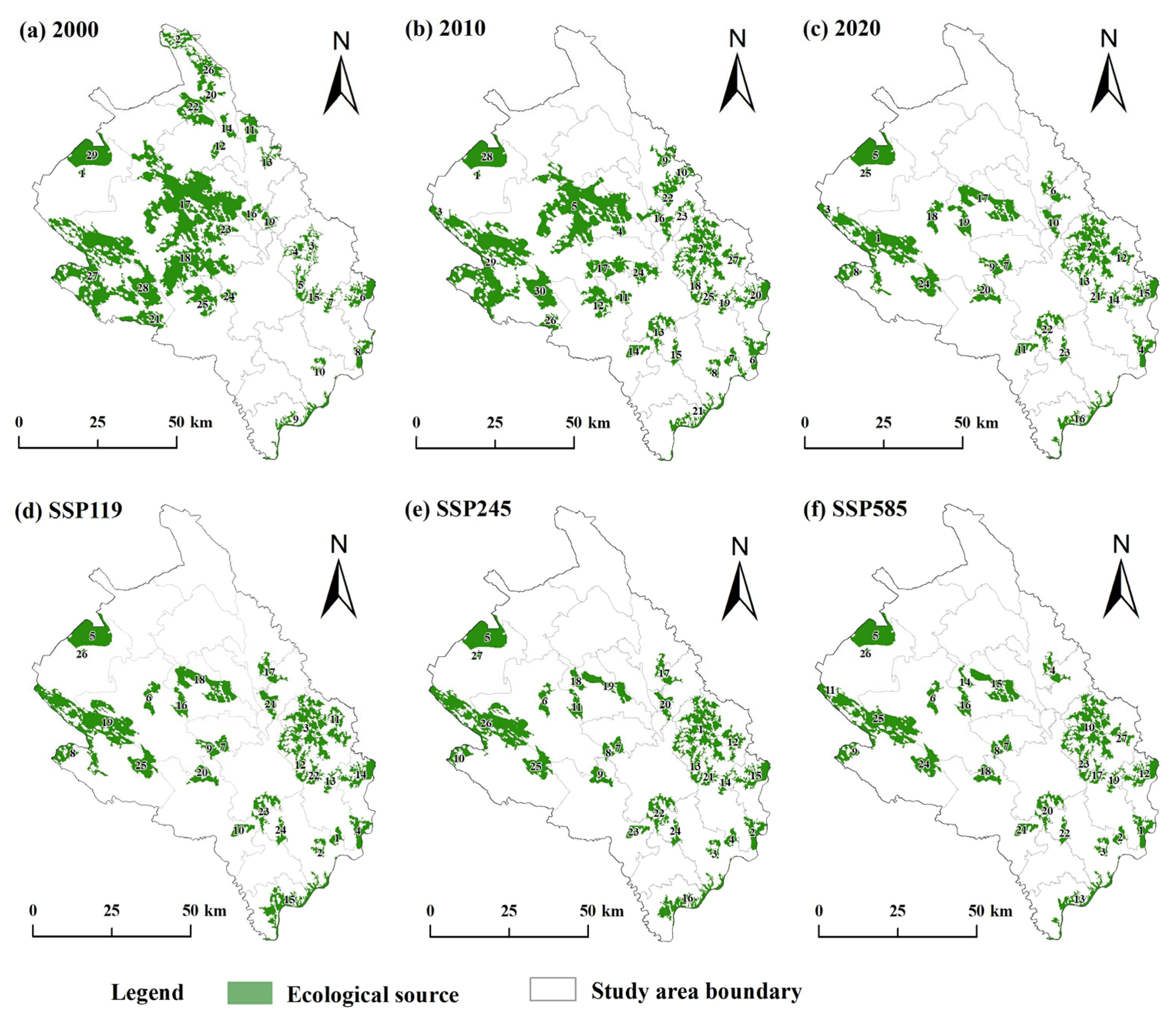
4.2.1. Dynamic Changes in Ecological Sources
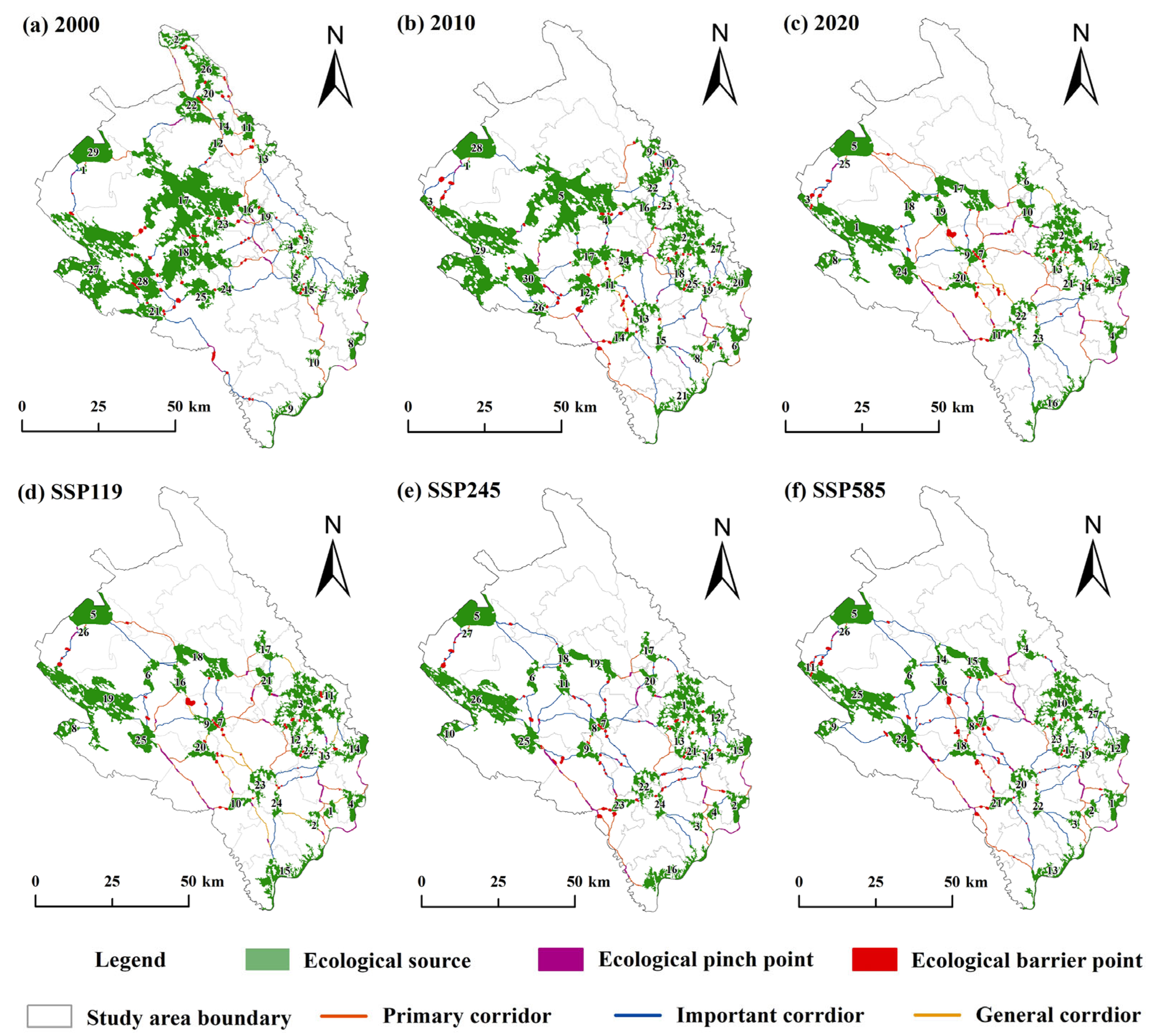
4.2.2. Dynamic Changes in Ecological Corridors
4.2.3. Assessment Results of Ecological Networks
4.3. Analysis of Dynamic Changes in Ecological Nodes
4.3.1. Ecological Pinch Points Change Analysis
4.3.2. Ecological Barrier Points Change Analysis
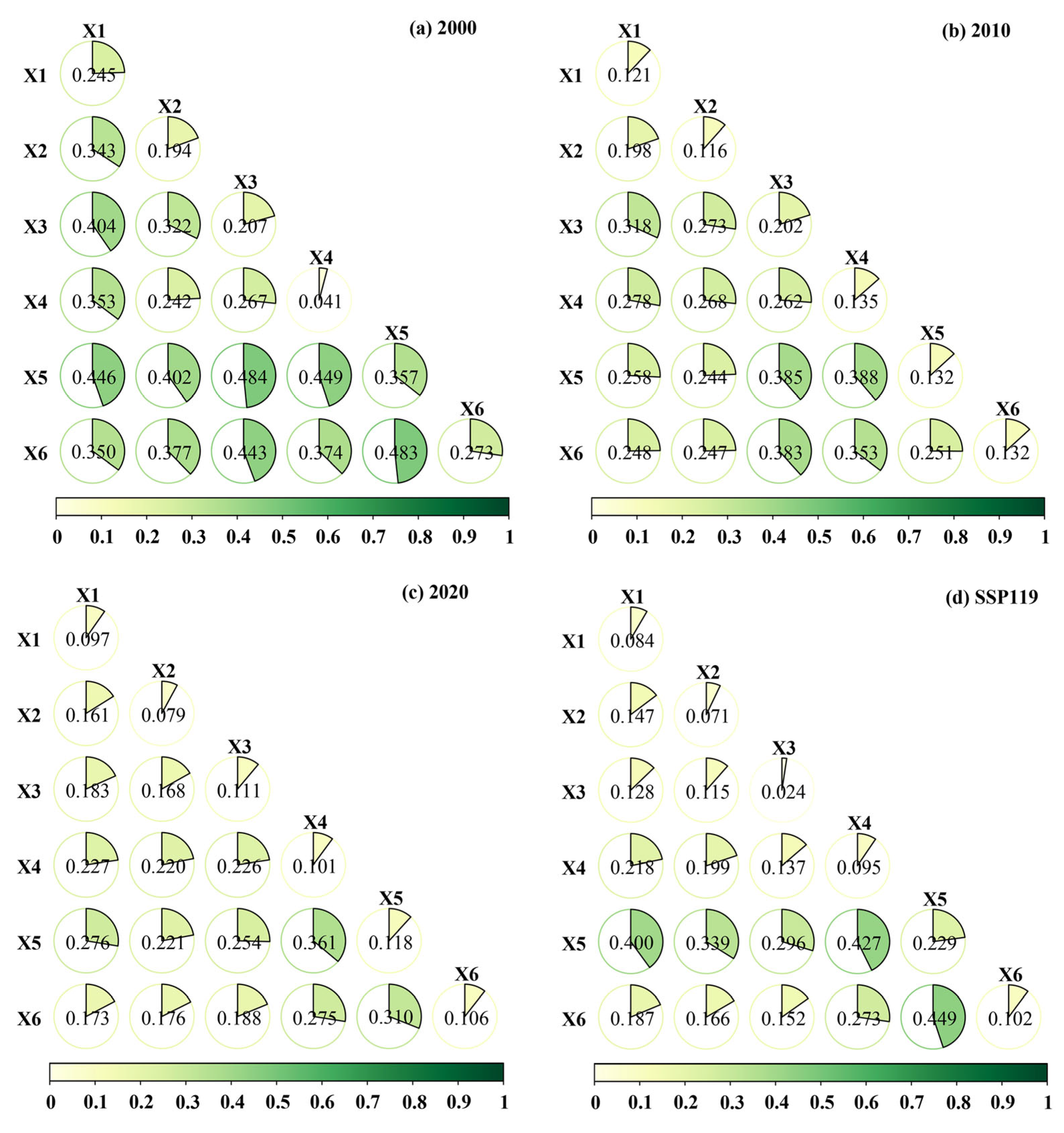
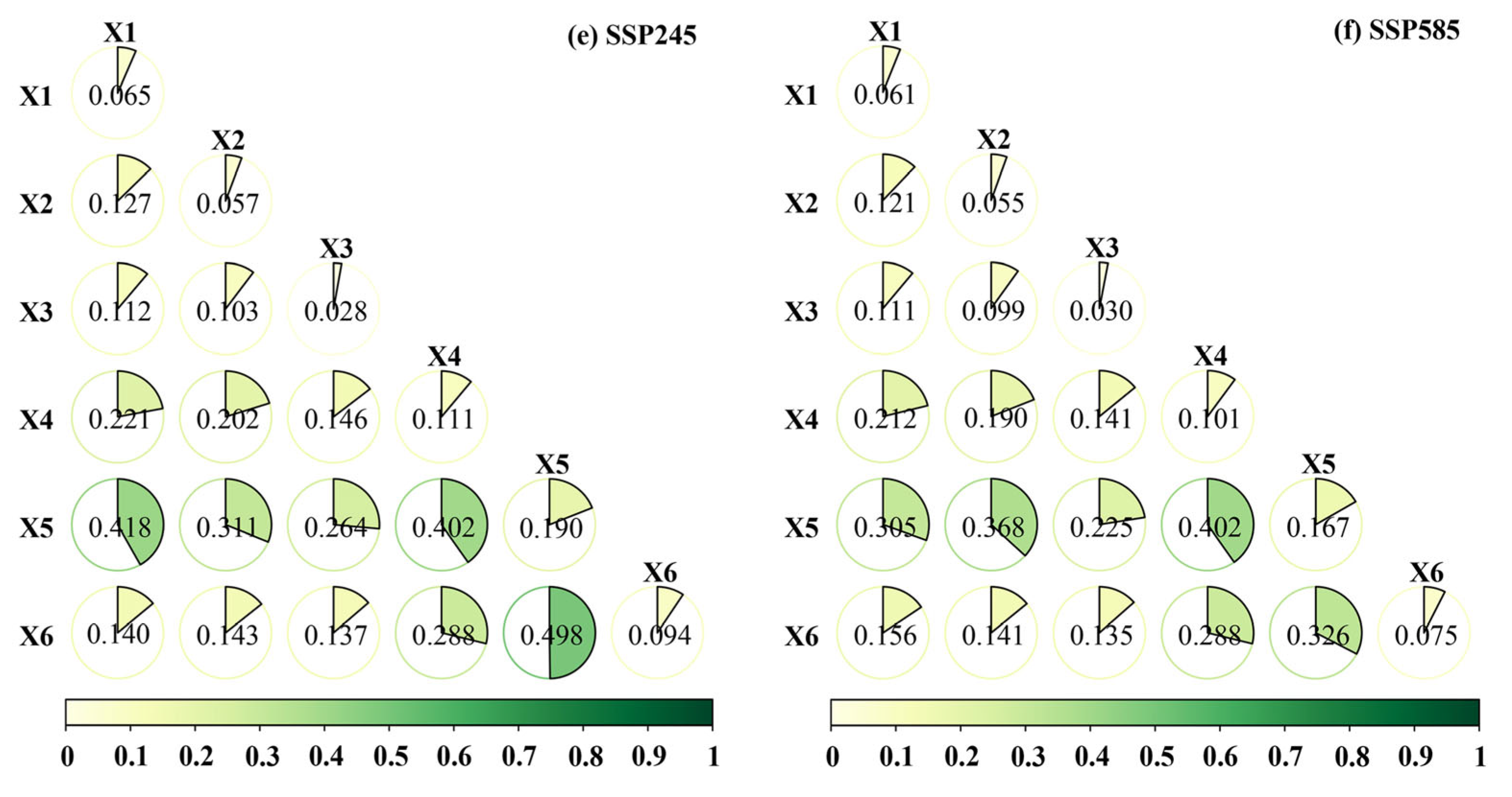
4.4. GeoDetector Analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Framework of Ecological Network Analysis in Multi-Scenarios Under Climate Change
5.2. Suggestions and Strategies for Future Ecological Restoration
5.3. Driving Factors Influencing the Ecological Networks
5.4. Deficiency and Prospects
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MSPA | Morphological spatial pattern analysis |
| SSPs | Shared Socioeconomic Pathways |
| RCPs | Representative Concentration Pathways |
| SD | System dynamics |
| DEM | Digital Elevation Model |
| PLUS | Patch-generating Land Use Simulation |
References
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Scholes, R.; Arneth, A.; Barnes, D.; Burrows, M.T.; Diamond, S.; Duarte, C.M.; Kiessling, W.; Leadley, P.; Managi, S. Overcoming the coupled climate and biodiversity crises and their societal impacts. Science 2023, 380, eabl4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, X.; Liu, X. Analysis of spatial-temporal patterns and driving mechanisms of land desertification in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 909, 168429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Ma, X.; Feng, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhu, M.; Niu, J.; Liu, G.; Shi, L. Patterns and controls of ecosystem service values under different land-use change scenarios in a mining-dominated basin of northern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 151, 110321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, M.K.; Hemp, A.; Appelhans, T.; Becker, J.N.; Behler, C.; Classen, A.; Detsch, F.; Ensslin, A.; Ferger, S.W.; Frederiksen, S.B. Climate–land-use interactions shape tropical mountain biodiversity and ecosystem functions. Nature 2019, 568, 88–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Lin, L.; Feng, X.; Wang, X.; Kong, D.; Lin, K.; Yang, J. Construction of ecological security pattern and quantitative diagnosis of ecological problems in Shenmu City. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosma, M.; Laita, A.; Duflot, R. No net loss of connectivity: Conserving habitat networks in the context of urban expansion. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2023, 239, 104847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yan, W.; Li, Z.; Wende, W.; Xiao, S. A framework for integrating ecosystem service provision and connectivity in ecological spatial networks: A case study of the Shanghai metropolitan area. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Xiong, J.; Wen, L.; Weng, A.; Lin, Y.; Li, B. Predicting the ecosystem service values and constructing ecological security patterns in future changing land use patterns. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Xia, Y.; Ji, Y.; Lai, W.; Li, J.; Yin, Y.; Qi, J.; Chang, Y.; Sun, H. Balancing Urban Expansion and Ecological Connectivity through Ecological Network Optimization—A Case Study of ChangSha County. Land 2023, 12, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-X.; Chiou, S.-C.; Li, W.-Y. Landscape Pattern and Ecological Network Structure in Urban Green Space Planning: A Case Study of Fuzhou City. Land 2021, 10, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Li, Z.; Guo, H.; Chen, H.; Luo, P. Urban green space planning based on remote sensing and geographic information systems. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 4213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Dickson, B.G.; Keitt, T.H.; Shah, V.B. Using circuit theory to model connectivity in ecology, evolution, and conservation. Ecology 2008, 89, 2712–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Kang, B.; Li, M.; Du, Z.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Identification of priority areas for territorial ecological conservation and restoration based on ecological networks: A case study of Tianjin City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; Li, X.; Ma, H.; Du, X.; Huang, J.; Su, W.; Yu, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, H.; Yin, D. Evaluation of the policy-driven ecological network in the Three-North Shelterbelt region of China. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 218, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. Cost-benefit analysis of ecological restoration based on land use scenario simulation and ecosystem service on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2022, 34, e02006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnell, N.W.; Lowe, J.A.; Bernie, D.; Nicholls, R.J.; Brown, S.; Challinor, A.J.; Osborn, T.J. The global and regional impacts of climate change under representative concentration pathway forcings and shared socioeconomic pathway socioeconomic scenarios. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 084046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyring, V.; Bony, S.; Meehl, G.A.; Senior, C.A.; Stevens, B.; Stouffer, R.J.; Taylor, K.E. Overview of the Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 6 (CMIP6) experimental design and organization. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1937–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Dong, Z.; Shi, R.; Sun, G.; Guo, Y.; Peng, Z.; Deng, M.; Chen, K. Urban Multi-Scenario Land Use Optimization Simulation Considering Local Climate Zones. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Tang, B.-s.; Yeung, S.; Hu, Y.; Cheung, G. A system dynamics model for the sustainable land use planning and development. Habitat Int. 2009, 33, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, X.; Sun, Y.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.; Li, K. Land use and habitat quality change in the Yellow River Basin: A perspective with different CMIP6-based scenarios and multiple scales. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 345, 118729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Guan, Q.; Clarke, K.C.; Liu, S.; Wang, B.; Yao, Y. Understanding the drivers of sustainable land expansion using a patch-generating land use simulation (PLUS) model: A case study in Wuhan, China. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2021, 85, 101569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Li, X.; Xu, X.; Ou, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Pei, F. A future land use simulation model (FLUS) for simulating multiple land use scenarios by coupling human and natural effects. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 168, 94–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Gong, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Liang, X. Ecological network assessment in dynamic landscapes: Multi-scenario simulation and conservation priority analysis. Land Use Policy 2024, 139, 107059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Wu, W.; Tian, S.; Wang, J. A multi-scale analysis framework of different methods used in establishing ecological networks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2022, 228, 104579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, C.D. Geodetector: Principle and prospective. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2017, 72, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Halik, Ü.; Shi, L.; Welp, M. Ecological risk assessment and multi-scenario dynamic prediction of the arid oasis cities in northwest China from 1990 to 2030. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 3099–3115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, D.; Yoshida, T.; Yamagata, Y. Gridded GDP projections compatible with the five SSPs (shared socioeconomic pathways). Front. Built Environ. 2021, 7, 760306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Meng, X.; Long, Y. Projecting 1 km-grid population distributions from 2020 to 2100 globally under shared socioeconomic pathways. Sci. Data 2022, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Wang, J.; Cai, W.; Wang, C.; Wang, K. Provincial and gridded population projection for China under shared socioeconomic pathways from 2010 to 2100. Sci. Data 2020, 7, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, X.; Tang, Q.; Li, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D. Can reservoir regulation mitigate future climate change induced hydrological extremes in the Lancang-Mekong River Basin? Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 785, 147322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yue, D.; Zhao, Y. Streamflow Variation under Climate Conditions Based on a Soil and Water Assessment Tool Model: A Case Study of the Bailong River Basin. Sustainability 2024, 16, 3901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanns, T.; Helming, K.; Schmidt, K.; König, H.J.; Faust, H. Stakeholder Strategies for Sustainability Impact Assessment of Land Use Scenarios: Analytical Framework and Identifying Land Use Claims. Land 2015, 4, 778–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, L.; Bai, W.; He, Z.; Luo, F.; Wang, Z. Prediction of ecological security patterns based on urban expansion: A case study of Chengdu. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Peihao, S.; Xijun, H.; Cunyou, C.; Baojing, W.; Siwen, Z. Coupled effects of land use and climate change on water supply in SSP–RCP scenarios: A case study of the Ganjiang river Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110745. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, C.; Xu, Y. Ecological connectivity analysis of typical coastal areas in China: The case of Zhangzhou City, Fujian Province. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Du, F.; Zuo, L.; Jiang, Y. Integrating ecosystem services and rocky desertification into identification of karst ecological security pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 2020, 36, 2113–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, R.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Wood, S.; Guerry, A.; Tallis, H.; Ricketts, T.; Nelson, E.; Ennaanay, D.; Wolny, S.; Olwero, N.; et al. InVEST User’s Guide; The Natural Capital Project, Stanford University: Stanford, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Y.; Jia, L.; YANG, L.A.; Li, Y.; Dong, Q. Spatio-temporal Evolution and Prediction Analysis of Habitat Quality in Yulin City Coupled with InVEST-PLUS Model. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Hall, S.A.; Beier, P.; Theobald, D.M. Where to restore ecological connectivity? Detecting barriers and quantifying restoration benefits. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saura, S.; Torné, J. Conefor Sensinode 2.2: A software package for quantifying the importance of habitat patches for landscape connectivity. Environ. Model. Softw. 2009, 24, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, P.D.; Fahrig, L.; Henein, K.; Merriam, G. Connectivity is a vital element of landscape structure. Oikos 1993, 68, 571–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Wang, S.; Rong, W. Construction of ecological network in Suzhou based on the PLUS and MSPA models. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhang, H.-O.; Liu, K.; Wu, Q. Construction of an ecological resistance surface model and its application in urban expansion simulations. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, B.H.; Shah, V.; Edelman, A. Circuitscape: Modeling landscape connectivity to promote conservation and human health. Nat. Conserv. 2016, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, E.A. Landscape structure indices for assessing urban ecological networks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2002, 58, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohlmann, M.; Miele, V.; Dray, S.; Chalmandrier, L.; O’connor, L.; Thuiller, W. Diversity indices for ecological networks: A unifying framework using Hill numbers. Ecol. Lett. 2019, 22, 737–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yi, S. An integrated approach to constructing ecological security patterns and identifying ecological restoration and protection areas: A case study of Jingmen, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, B.G.; Albano, C.M.; Gray, M.E.; Mcclure, M.L.; Schumaker, N.H. Circuit-theory applications to connectivity science and conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2018, 33, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, G.; Li, T.; Ren, S.; Chen, B.; Feng, K.; Li, W.; Zhao, X.; Qin, P.; Zhao, J. Importance of ecosystem services and ecological security patterns on Hainan Island, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1323673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Liu, S.; Sun, Y.; Shi, F.; Beazley, R. Construction and optimization of an ecological network based on morphological spatial pattern analysis and circuit theory. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2059–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Bai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Z. Habitat Quality Effect and Driving Mechanism of Land Use Transitions: A Case Study of Henan Water Source Area of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project. Land 2021, 10, 796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; O’Connor, P.J.; Zhang, L.; Yan, J. Landscape Ecological Risk Assessment under Multiple Indicators. Land 2021, 10, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Feng, Z.; Zhao, H.; Wu, K. Identification of ecosystem service bundles and driving factors in Beijing and its surrounding areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 134687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, S.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Chen, Y. Spatial-temporal evolution and motivation of ecological vulnerability based on RSEI and GEE in the Jianghan Plain from 2000 to 2020. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1191532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Jia, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, S. Spatio-temporal dynamics and influencing factors of ecological security network elements in Yichang, Hubei Province. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 6154–6169. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Siyu, L.; Shuai, B. Identification and optimization of ecological corridors in Shenmu City based on landscape ecological security. Arid Zone Res. 2021, 38, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Jing, X.B.; Zhang, X.L.; Han, B.; Li, H.B.; Zhou, Y.K. Comparison and Evaluation of the Ecological Network Construction Method Based on Principles of Landscape Ecology. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2023, 43, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wei, X.; Hong, Z. Multi-scenario Simulation of LUCC and Spatio-temporal Evolution and Prediction of Habitat Quality in Nanchang City. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2023, 54, 170–180. [Google Scholar]
- Nunez, S.; Alkemade, R.; Kok, K.; Leemans, R. Potential biodiversity change in Central Asian grasslands: Scenarios for the impact of climate and land-use change. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, D.; Pan, J. Ecological network identification and connectivity robustness evaluation in the Yellow River Basin under a multi-scenario simulation. Ecol. Model. 2023, 482, 110384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, M.; Lu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Ma, W. Evaluation of ecological city and analysis of obstacle factors under the background of high-quality development: Taking cities in the Yellow River Basin as examples. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 118, 106771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Das, A.; Pereira, P. Impact of urbanization induced land use and land cover change on ecological space quality-mapping and assessment in Delhi (India). Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Liu, Y.; An, R.; Luo, X.; Liu, S.; Zhang, B. Optimization of ecological network function and structure by coupling spatial operators and biomimetic intelligent algorithm. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 142794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Fang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, S.; He, S.; Qi, W.; Bao, C.; Ma, H.; Fan, Y. Global impacts of future urban expansion on terrestrial vertebrate diversity. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Tian, Y.; Qian, J.; Gao, Y.; Hong, Y.; Liu, Y. The impact of different road grades on ecological networks in a mega-city Wuhan City, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Data Type | Date | Year | Data Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Land use | Land use data | 2000–2020 | http://www.resdc.cn |
| Natural factors | DEM | 2020 | http://www.gscloud.cn |
| Slope | 2020 | Extracted from DEM | |
| NDVI | 2020 | https://doi.org/10.12199/nesdc.ecodb.rs.2021.012 | |
| Soil type | 2020 | https://www.resdc.cn | |
| Precipitation | 2000–2020 | http://www.geodata.cn/ https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-11-1931-2019 | |
| Temperature | 2000–2020 | ||
| Socioeconomic factors | Nighttime light data | 2020 | http://nnu.geodata.cn/ |
| GDP | 2000–2020 | http://www.resdc.cn | |
| Population | 2000–2020 | https://www.worldpop.org/ | |
| POI | 2020 | https://www.openhistoricalmap.org | |
| Roads | 2020 | https://www.openhistoricalmap.org | |
| Nature reserve vector data | Shenmu City Natural Resources Bureau | ||
| Statistical Yearbooks of Yulin City | 2010–2020 | Yulin City Statistics Bureau | |
| Statistical Yearbooks of Shenmu City | 2010–2020 | Shenmu City Statistics Bureau | |
| Overall planning of land space in Shenmu City (2021–2035 year) | Government disclosure |
| SSPs-RCPs Scenarios | 2020–2030 | 2030–2035 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSP119 | SSP245 | SSP585 | SSP119 | SSP245 | SSP585 | |
| Rate of GDP change (%) | 8.62 | 6.46 | 10.60 | 4.62 | 2.49 | 5.86 |
| Rate of population change (%) | −0.28 | −0.16 | −0.23 | −0.50 | −0.35 | −0.45 |
| Rate of change in urbanization rate (%) | 0.76 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.54 | 0.46 | 0.54 |
| Stress Factor | Maximum Impact Distance | Weight | Decay Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated land | 4 | 0.6 | Linear |
| Construction land | 8 | 1 | Exponential |
| Unused land | 3 | 0.3 | Linear |
| Land Use Type | Habitat Suitability | Sensitivity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cultivated Land | Construction Land | Unused Land | ||
| Cultivated land | 0.45 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.35 |
| Woodland | 1 | 0.65 | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| Grassland | 0.8 | 0.55 | 0.65 | 0.6 |
| Water | 0.85 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| Construction land | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Unused land | 0.15 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.1 |
| Category | MSPA Landscape Type | Land Use Type | DEM (m) | Slope (°) | Distance from Water (m) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grade | Value | Grade | Value | Grade | Value | Grade | Value | Grade | Value | |
| Subclass | Core | 1 | Woodland | 1 | <750 | 1 | <5 | 1 | <500 | 1 |
| Bridge | 10 | Water | 10 | 750–950 | 30 | 5~15 | 30 | 500–1000 | 30 | |
| Loop, Branch | 30 | Grassland | 20 | 950–1150 | 50 | 15~20 | 50 | 1000–1500 | 50 | |
| Islet, Edge | 50 | Cultivated land | 50 | 1150–1350 | 70 | 20~30 | 70 | 1500–2000 | 70 | |
| Perforation | 70 | Unused land | 70 | >1350 | 90 | >30 | 90 | >2000 | 90 | |
| Background | 90 | Construction land | 100 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |
| Weights | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.16 | 0.13 | 0.08 | |||||
| Years/ Scenarios | Ecological Source | Source Area (km2) | Ecological Corridor | Corridor Length (km) | α Index | β Index | γ Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 29 | 1523.93 | 63 | 568.82 | 0.66 | 2.17 | 0.78 |
| 2010 | 30 | 1403.92 | 71 | 616.47 | 0.76 | 2.37 | 0.85 |
| 2020 | 25 | 910.11 | 56 | 609.44 | 0.71 | 2.24 | 0.81 |
| SSP119 | 26 | 1005.11 | 59 | 584.92 | 0.72 | 2.27 | 0.82 |
| SSP245 | 27 | 927.88 | 60 | 671.86 | 0.69 | 2.22 | 0.80 |
| SSP585 | 27 | 878.25 | 62 | 705.39 | 0.73 | 2.30 | 0.83 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, H.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J.; Chen, H. Constructing Ecological Networks and Analyzing Impact Factors in Multi-Scenario Simulation Under Climate Change. Land 2025, 14, 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051120
Bai H, Zhang Y, Huang J, Chen H. Constructing Ecological Networks and Analyzing Impact Factors in Multi-Scenario Simulation Under Climate Change. Land. 2025; 14(5):1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051120
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Hua, Yaoyun Zhang, Jiazhuo Huang, and Haopeng Chen. 2025. "Constructing Ecological Networks and Analyzing Impact Factors in Multi-Scenario Simulation Under Climate Change" Land 14, no. 5: 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051120
APA StyleBai, H., Zhang, Y., Huang, J., & Chen, H. (2025). Constructing Ecological Networks and Analyzing Impact Factors in Multi-Scenario Simulation Under Climate Change. Land, 14(5), 1120. https://doi.org/10.3390/land14051120







