Temperature Modification of Ambient Ozone Association with Outpatient Visits for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data Collection and Analysis Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Population and Environmental Factor Characteristics
3.2. Association of O3 Exposure with ASCVD Outpatient Visits
3.3. Relationships Between Ambient Temperature and ASCVD Outpatient Visits
3.4. The Impact of Combined O3-Temperature on ASCVD Outpatient Visits
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roth, G.A.; Mensah, G.A.; Fuster, V. The Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks: A Compass for Global Action. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2980–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2021 Causes of Death Collaborators. Global burden of 288 causes of death and life expectancy decomposition in 204 countries and territories and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2024, 403, 2100–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risks 2023 Collaborators. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2023. JACC 2025, 86, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Buring, J.E.; Badimon, L.; Hansson, G.K.; Deanfield, J.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Tokgözoğlu, L.; Lewis, E.F. Atherosclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primer 2019, 5, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, G.A. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990–2019. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 2982–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, M.; Xue, W.; Herrmann, H.; Brasseur, G.P.; Wang, T.; Wang, Z. Evolution of Ozone Pollution in China: What Track Will It Follow? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, L.; Tang, M.; Gai, X.; Chen, M.; Ge, X. Temporal variations of six ambient criteria air pollutants from 2015 to 2018, their spatial distributions, health risks and relationships with socioeconomic factors during 2018 in China. Environ. Int. 2020, 137, 105556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, P.; Agathokleous, E.; Anenberg, S.C.; De Marco, A.; Paoletti, E.; Calatayud, V. Trends in urban air pollution over the last two decades: A global perspective. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, K.; Zhang, X. The rationale behind updates to ambient ozone guidelines and standards. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1273826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Wei, Y.; Fang, Z. Ozone Pollution: A Major Health Hazard Worldwide. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, J.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Meng, X.; Ji, J.S.; Gao, Y.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; et al. Hourly Air Pollutants and Acute Coronary Syndrome Onset in 1.29 Million Patients. Circulation 2022, 145, 1749–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Su, W.; Wang, H.; Li, N.; Song, Q.; Liang, Q.; Sun, C.; Liang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Song, E.J.; et al. Short-term exposure to ambient ozone and cardiovascular mortality in China: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 33, 958–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Wei, C.; Li, Y.; Deng, F.; Baccarelli, A.A.; et al. Ozone pollution and hospital admissions for cardiovascular events. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Y.; Wu, S. Impacts of Environmental Insults on Cardiovascular Aging. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2022, 9, 11–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.C.; Hayes, R.B.; Ahn, J.; Shao, Y.; Silverman, D.T.; Jones, R.R.; Garcia, C.; Bell, M.L.; Thurston, G.D. Long-Term Exposure to Ozone and Cause-Specific Mortality Risk in the United States. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2019, 200, 1022–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, R.; Liu, X.; Liang, J.; Lin, H.; Shen, P.; Zhang, J.; Lu, P.; Tang, X.; et al. Long-term exposure to ozone and cardiovascular mortality in a large Chinese cohort. Environ. Int. 2022, 165, 107280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, R.; Yin, P.; Meng, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, C.; Ji, J.S.; Qiu, Y.; Kan, H.; et al. Long-term exposure to ozone and cardiovascular mortality in China: A nationwide cohort study. Lancet Planet. Health 2022, 6, e496–e503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, M.C.; Jerrett, M.; Pope, C.A.; Krewski, D.; Gapstur, S.M.; Diver, W.R.; Beckerman, B.S.; Marshall, J.D.; Su, J.; Crouse, D.L.; et al. Long-Term Ozone Exposure and Mortality in a Large Prospective Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016, 193, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Zhao, B.; Wan, W.; Shi, S.; Xuan, C.; Yu, C.; Mao, W.; Yan, J. Long-term cardiometabolic effects of ambient ozone pollution in a large Chinese population. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 261, 115115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Meng, X.; Liu, C.; Niu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qi, J.; et al. Ambient Ozone Pollution and Daily Mortality: A Nationwide Study in 272 Chinese Cities. Environ. Health Perspect. 2017, 125, 117006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Niu, Y.; Liu, C.; Chen, R.; Cao, J.; Kan, H.; Cheng, Y. Short-term exposure to coarse particulate matter and outpatient visits for cardiopulmonary disease in a Chinese city. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 199, 110686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhou, M.; Ou, C.-Q.; Yin, P.; Li, M.; Tong, S.; Gasparrini, A.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; et al. Seasonal variations of temperature-related mortality burden from cardiovascular disease and myocardial infarction in China. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 224, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparrini, A.; Guo, Y.; Hashizume, M.; Kinney, P.L.; Petkova, E.P.; Lavigne, E.; Zanobetti, A.; Schwartz, J.D.; Tobias, A.; Leone, M.; et al. Temporal Variation in Heat-Mortality Associations: A Multicountry Study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Lu, X.; Cai, Z.; Brasseur, G.; Gao, M. Amplified Upward Trend of the Joint Occurrences of Heat and Ozone Extremes in China over 2013–20. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2022, 103, E1330–E1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wei, X.; Feng, X.; Ma, P.; Hu, W.; Xin, J.; Ni, C.; Wang, S.; Zheng, C. Temperature modulation of adverse consequences of ozone exposure on cardiovascular mortality: A study of multiple cities in China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 288, 119272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zheng, M.; Lv, J.; Shi, T.; Liu, P.; Wu, Y.; Feng, W.; He, W.; Guo, P. Interactions between ambient air pollutants and temperature on emergency department visits: Analysis of varying-coefficient model in Guangzhou, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, Z. Short-term exposure to various ambient air pollutants and emergency department visits for cause-stable ischemic heart disease: A time-series study in Shanghai, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 16989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khraishah, H.; Alahmad, B.; Ostergard, R.L.; AlAshqar, A.; Albaghdadi, M.; Vellanki, N.; Chowdhury, M.M.; Al-Kindi, S.G.; Zanobetti, A.; Gasparrini, A.; et al. Climate change and cardiovascular disease: Implications for global health. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 798–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Wang, W.; Shi, S.; Zhu, S.; Wang, P.; Chen, R.; Xiao, Q.; Xue, T.; Geng, G.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Evaluating the spatiotemporal ozone characteristics with high-resolution predictions in mainland China, 2013–2019. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 299, 118865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chen, G.; Liu, X.; Pan, M.; Kang, N.; Hou, X.; Liao, W.; Dong, X.; Yuchi, Y.; Mao, Z.; et al. Aging biomarkers: Potential mediators of association between long-term ozone exposure and risk of atherosclerosis. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 292, 512–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebi, K.L.; Capon, A.; Berry, P.; Broderick, C.; de Dear, R.; Havenith, G.; Honda, Y.; Kovats, R.S.; Ma, W.; Malik, A.; et al. Hot weather and heat extremes: Health risks. Lancet 2021, 398, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, I.H.; Oliveira, B.F.A.; Cortes, T.R.; Junger, W.L. The effect of ambient temperature on cardiovascular mortality in 27 Brazilian cities. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 691, 996–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yin, P.; Zhou, M.; Ou, C.-Q.; Guo, Y.; Gasparrini, A.; Liu, Y.; Yue, Y.; Gu, S.; Sang, S.; et al. Cardiovascular mortality risk attributable to ambient temperature in China. Heart Br. Card. Soc. 2015, 101, 1966–1972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunker, A.; Wildenhain, J.; Vandenbergh, A.; Henschke, N.; Rocklöv, J.; Hajat, S.; Sauerborn, R. Effects of Air Temperature on Climate-Sensitive Mortality and Morbidity Outcomes in the Elderly; a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Epidemiological Evidence. EBioMedicine 2016, 6, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Chen, C.; Xu, D.; Li, T. Effects of ambient temperature on myocardial infarction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 241, 1106–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodopoulou, S.; Samoli, E.; Chalbot, M.-C.G.; Kavouras, I.G. Air pollution and cardiovascular and respiratory emergency visits in Central Arkansas: A time-series analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 536, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analitis, A.; Michelozzi, P.; D’Ippoliti, D.; De’Donato, F.; Menne, B.; Matthies, F.; Atkinson, R.W.; Iñiguez, C.; Basagaña, X.; Schneider, A.; et al. Effects of heat waves on mortality: Effect modification and confounding by air pollutants. Epidemiol. Camb. Mass 2014, 25, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Cai, J.; Meng, X.; Kim, H.; Honda, Y.; Guo, Y.L.; Samoli, E.; Yang, X.; Kan, H. Ozone and daily mortality rate in 21 cities of East Asia: How does season modify the association? Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 180, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Woodward, A.; Hou, X.-Y.; Zhu, T.; Zhang, J.; Brown, H.; Yang, J.; Qin, R.; Gao, J.; Gu, S.; et al. Modification of the effects of air pollutants on mortality by temperature: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1556–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orru, H.; Ebi, K.L.; Forsberg, B. The Interplay of Climate Change and Air Pollution on Health. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2017, 4, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Stafoggia, M.; de’Donato, F.; Scortichini, M.; Zafeiratou, S.; Vazquez Fernandez, L.; Zhang, S.; Katsouyanni, K.; Samoli, E.; Rao, S.; et al. Heat-related cardiorespiratory mortality: Effect modification by air pollution across 482 cities from 24 countries. Environ. Int. 2023, 174, 107825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Sun, Q.; Du, P.; Tang, S.; Chen, C.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Shi, X. Modification Effects of Temperature on the Ozone-Mortality Relationship: A Nationwide Multicounty Study in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 2859–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Feng, X.; Hu, W.; Ma, P.; Xin, J.; Wang, S.; Zheng, C. Modification effects of ambient temperature on ozone-mortality relationships in Chengdu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 73011–73019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.E.; Prueitt, R.L.; Sax, S.N.; Pizzurro, D.M.; Lynch, H.N.; Zu, K.; Venditti, F.J. Ozone exposure and systemic biomarkers: Evaluation of evidence for adverse cardiovascular health impacts. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2015, 45, 412–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, P.; Gong, F.; Tan, Y.; Han, J.; Tian, L.; Yan, J.; Li, K.; Xi, Z.; Liu, X. Altered lipidomic profiles in lung and serum of rat after sub-chronic exposure to ozone. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
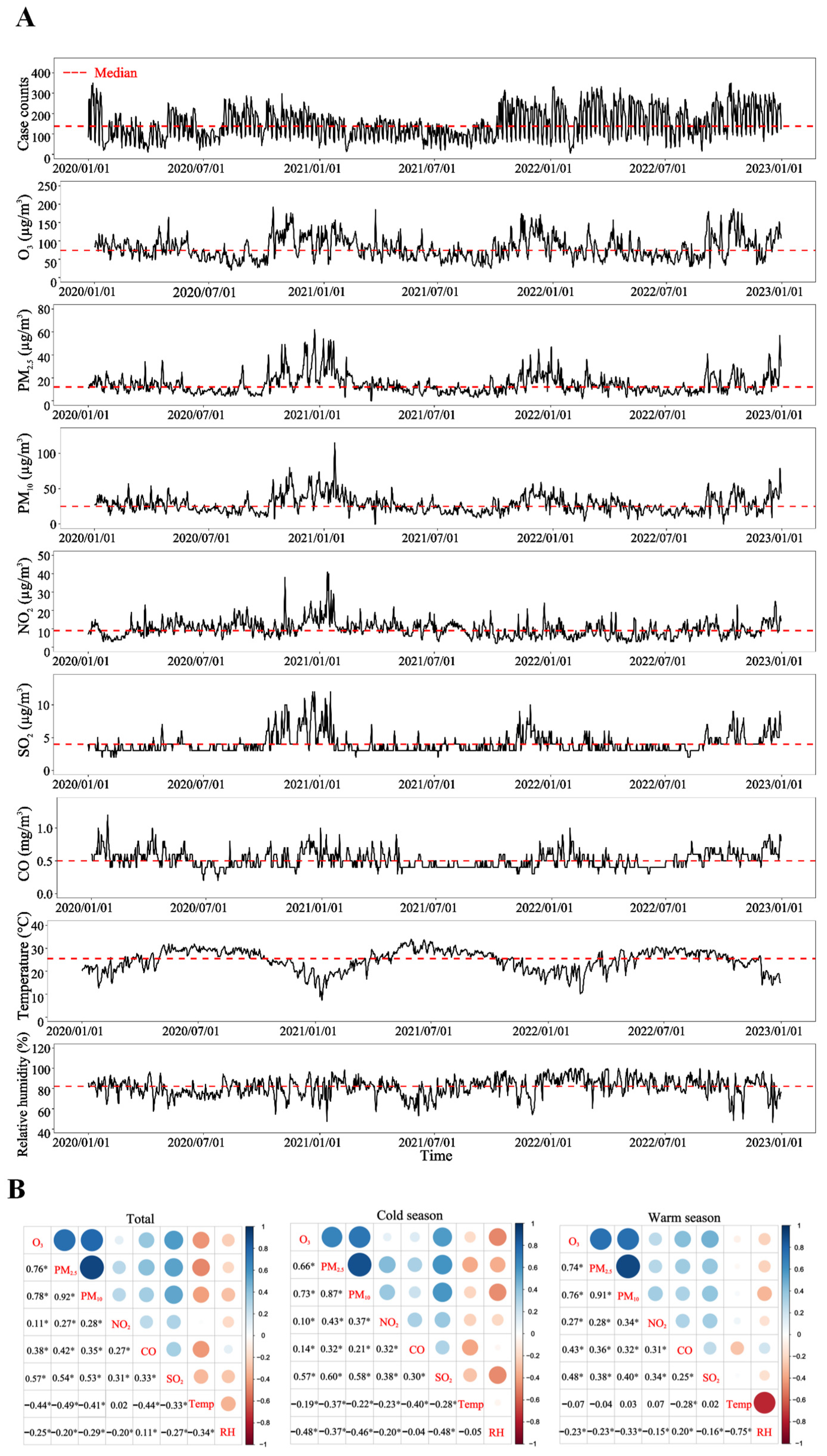
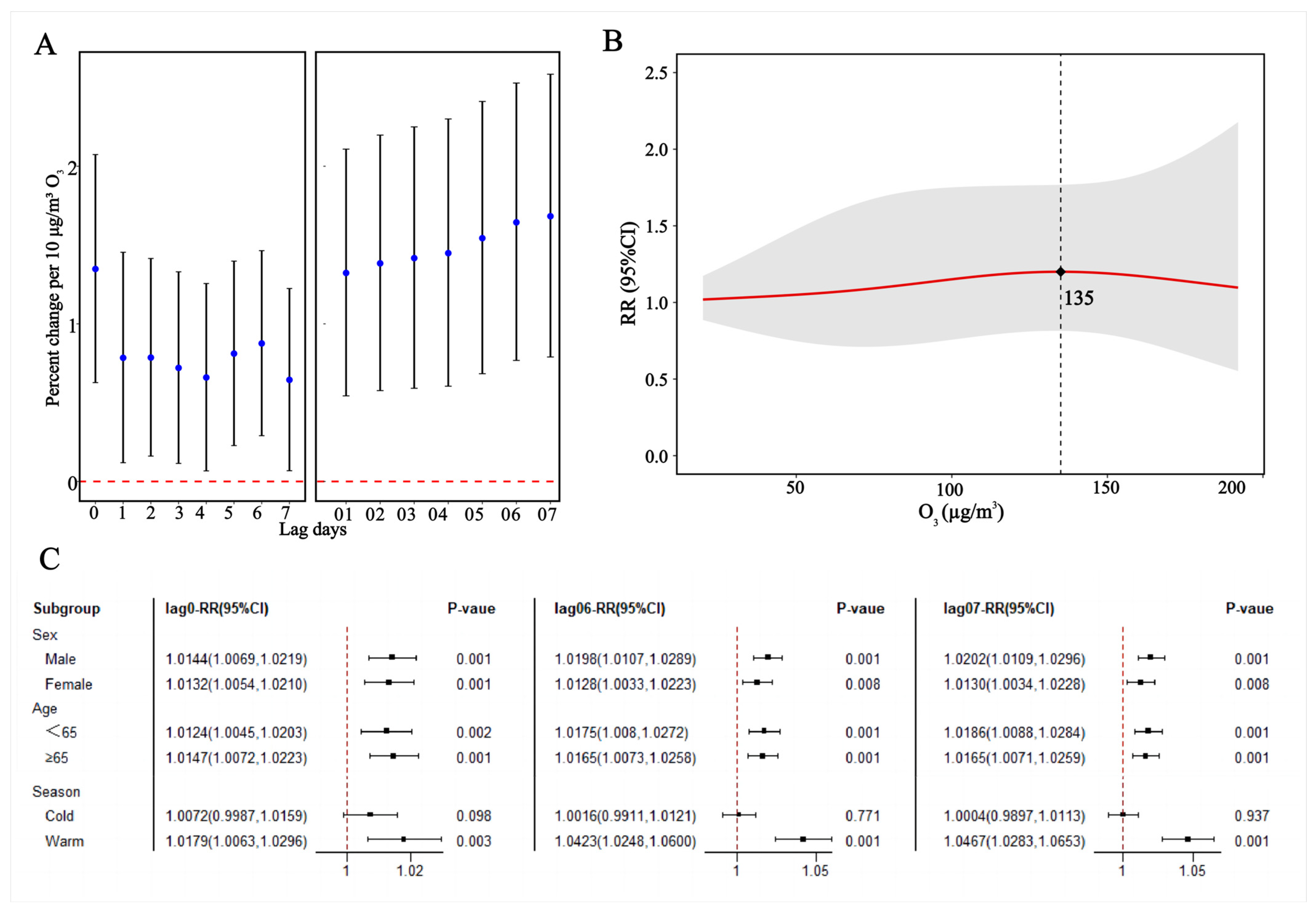
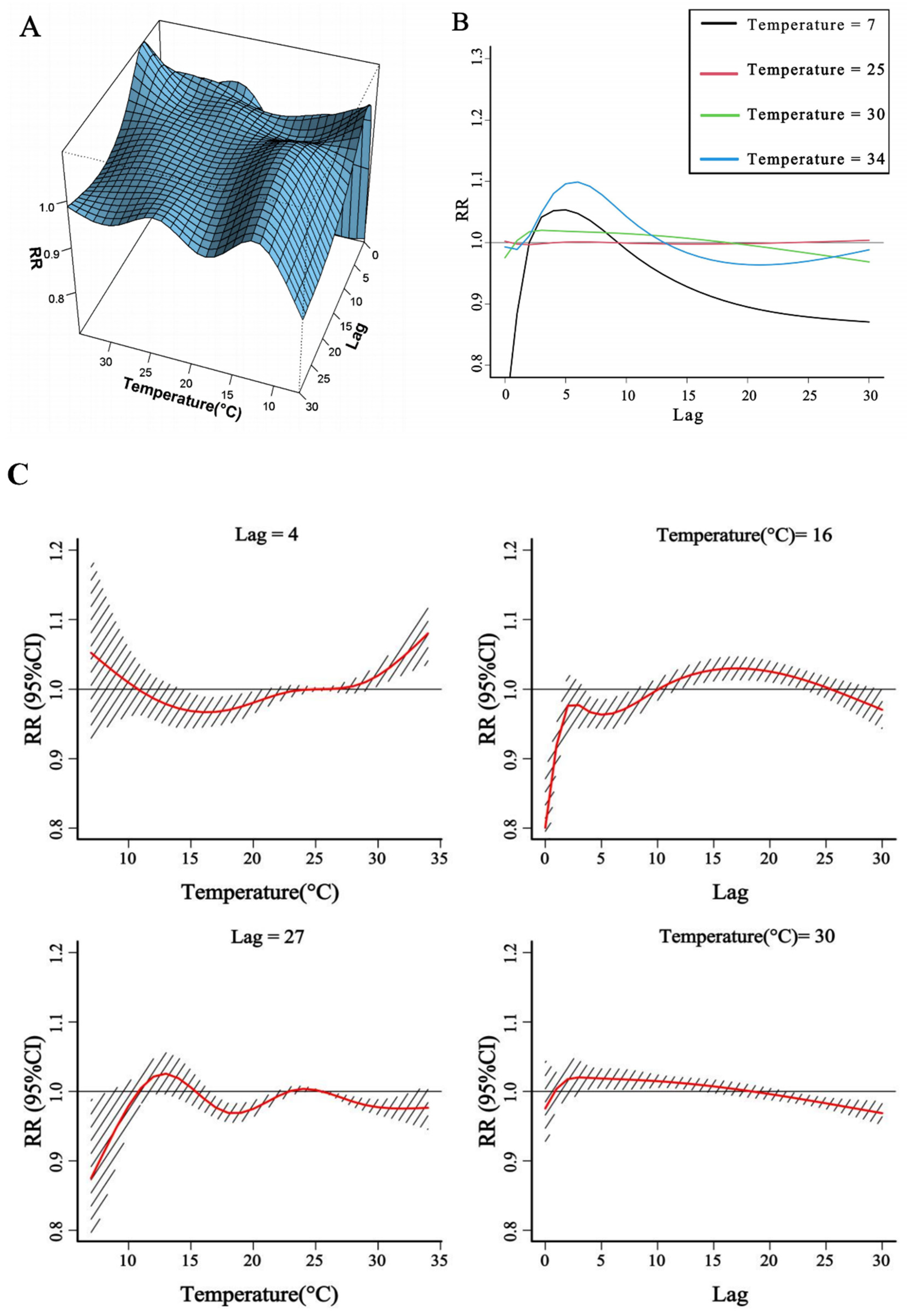
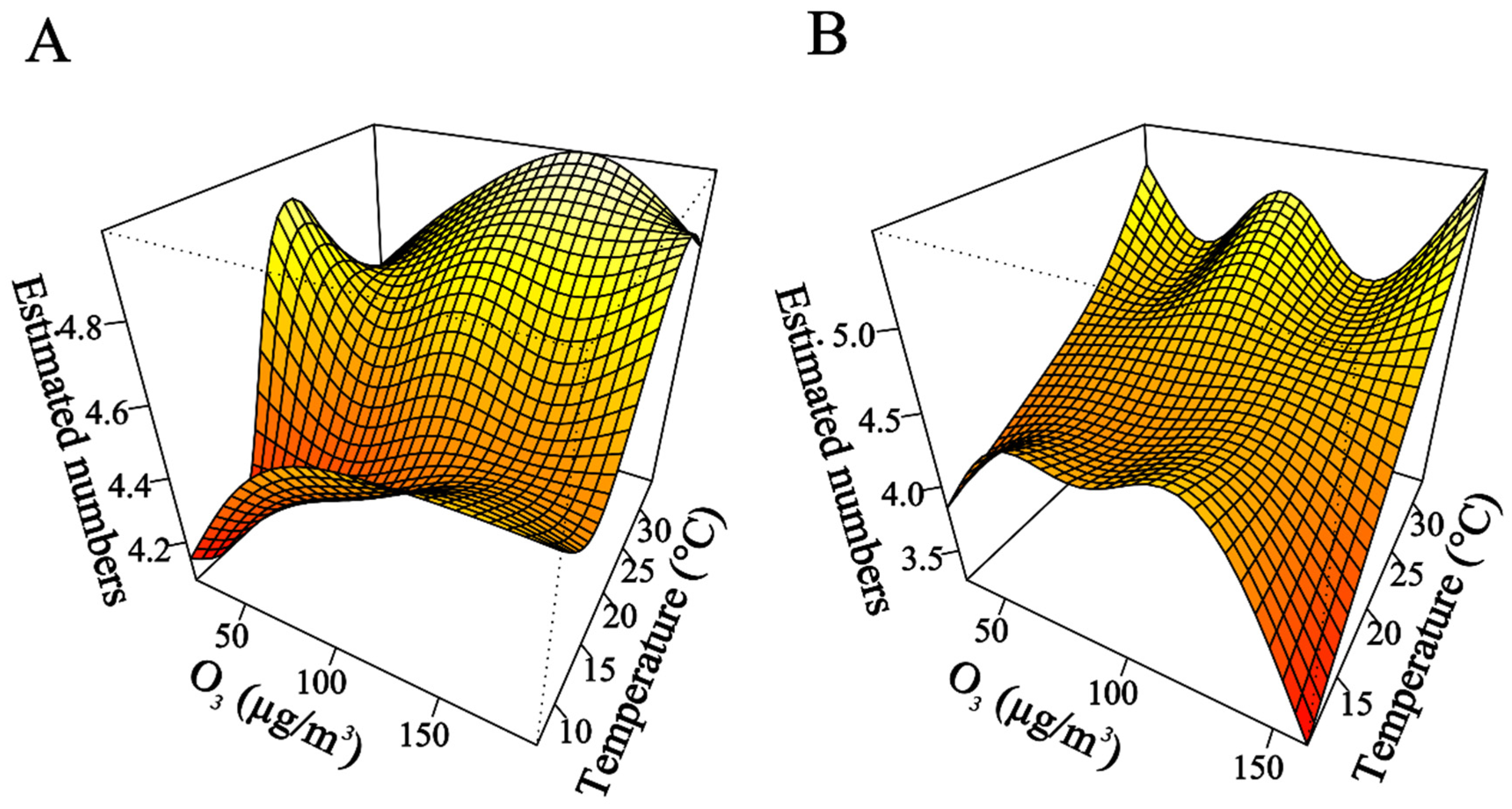
| Variables | Mean | SD | Min | Median | Max | IQR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Daily ASCVD Outpatient Visits | ||||||
| Total | 149 | 76 | 6 | 138 | 349 | 124 |
| Male | 88 | 47 | 3 | 79 | 229 | 77 |
| Female | 61 | 30 | 2 | 57 | 142 | 46 |
| <65 years | 56 | 30 | 3 | 52 | 139 | 50 |
| ≥65 years | 93 | 48 | 2 | 85 | 221 | 76 |
| Cold season | 161 | 82 | 6 | 155 | 349 | 138 |
| Warm season | 137 | 68 | 11 | 122 | 325 | 99 |
| O3(μg/m3) | ||||||
| Total | 80.0 | 31.3 | 20.0 | 74.0 | 192.0 | 40.3 |
| Cold season | 92.8 | 31.7 | 28.0 | 90.0 | 192.0 | 42.5 |
| Warm season | 67.3 | 25.2 | 20.0 | 63.0 | 180.0 | 30.0 |
| Temperature (℃) | ||||||
| Total | 24.7 | 4.6 | 7.4 | 25.5 | 34.0 | 7.0 |
| Cold season | 21.5 | 3.8 | 7.4 | 21.8 | 29.5 | 5.1 |
| Warm season | 28.0 | 2.6 | 15.3 | 28.4 | 34.0 | 2.6 |
| Relative humidity (%) | ||||||
| Total | 81.4 | 9.1 | 47 | 82.2 | 100 | 12 |
| Cold season | 82.4 | 9.8 | 47 | 84.1 | 100 | 12 |
| Warm season | 80.5 | 8.3 | 53 | 80.1 | 100 | 12 |
| Model | RR (95%CI) |
|---|---|
| O3 | 1.014 (1.007, 1.021) |
| O3 + PM2.5 | 1.014 (1.005, 1.022) |
| O3 + PM10 | 1.014 (1.005, 1.022) |
| O3 + NO2 | 1.012 (1.005, 1.019) |
| O3 + SO2 | 1.013 (1.005, 1.020) |
| O3 + CO | 1.011 (1.004, 1.019) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, F.; Yu, B.; Fu, L.; Li, W.; Song, J.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z. Temperature Modification of Ambient Ozone Association with Outpatient Visits for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121357
Wu F, Yu B, Fu L, Li W, Song J, Wu W, Li Y, Yan Z. Temperature Modification of Ambient Ozone Association with Outpatient Visits for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(12):1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121357
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Feifei, Benguo Yu, Liya Fu, Weixia Li, Jie Song, Weidong Wu, Yanbo Li, and Zhen Yan. 2025. "Temperature Modification of Ambient Ozone Association with Outpatient Visits for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases" Atmosphere 16, no. 12: 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121357
APA StyleWu, F., Yu, B., Fu, L., Li, W., Song, J., Wu, W., Li, Y., & Yan, Z. (2025). Temperature Modification of Ambient Ozone Association with Outpatient Visits for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases. Atmosphere, 16(12), 1357. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16121357






