Generation of Linear Traveling Waves in Piezoelectric Plates in Air and Liquid
Abstract
1. Introduction
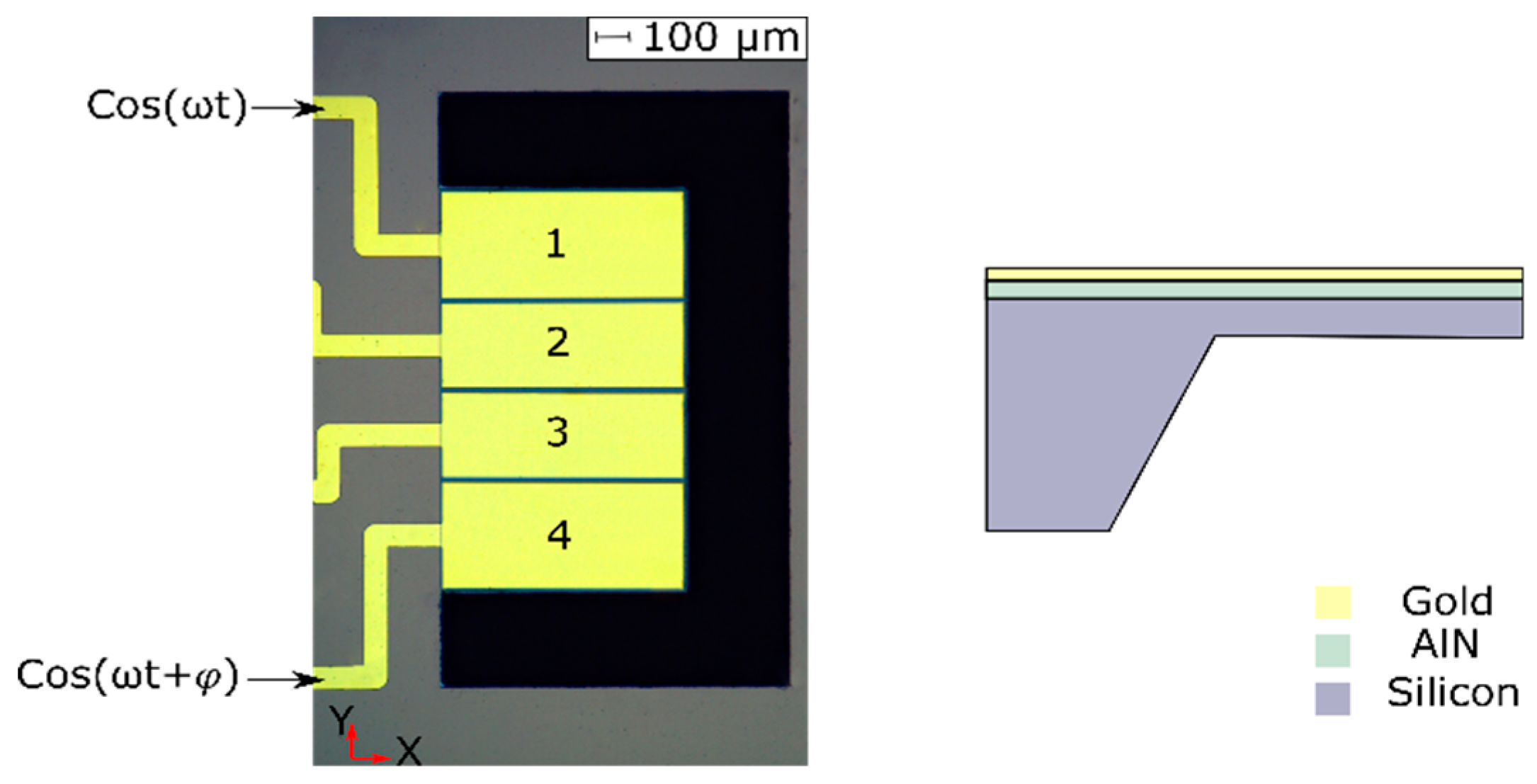
2. Materials and Methods
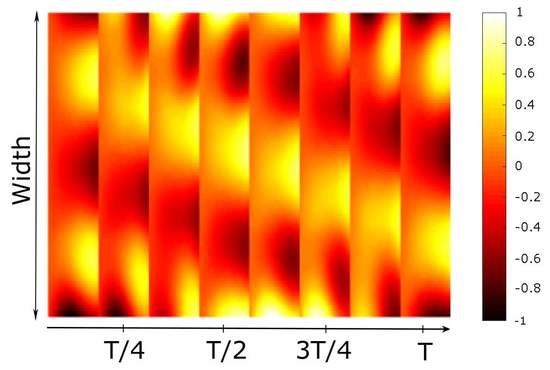
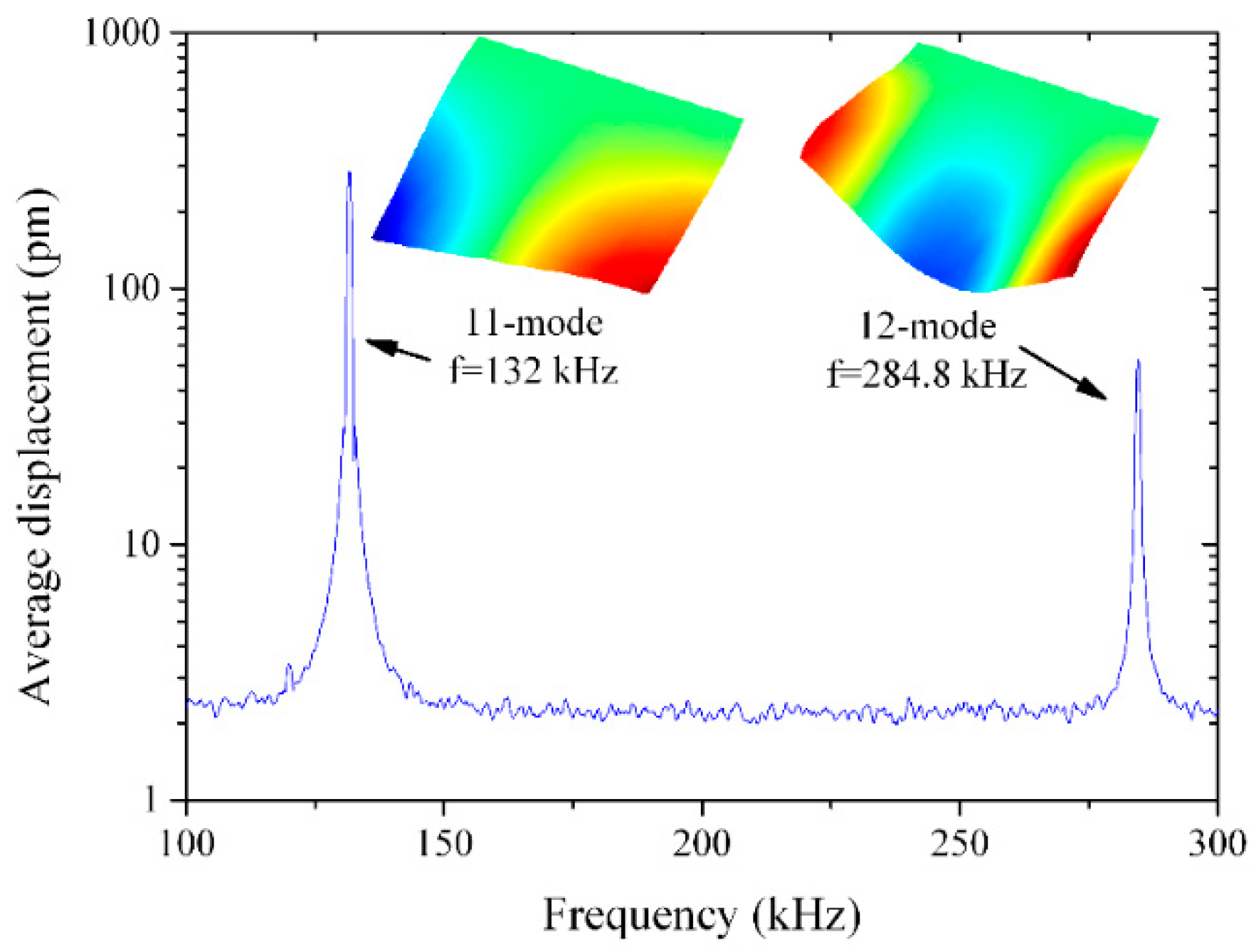
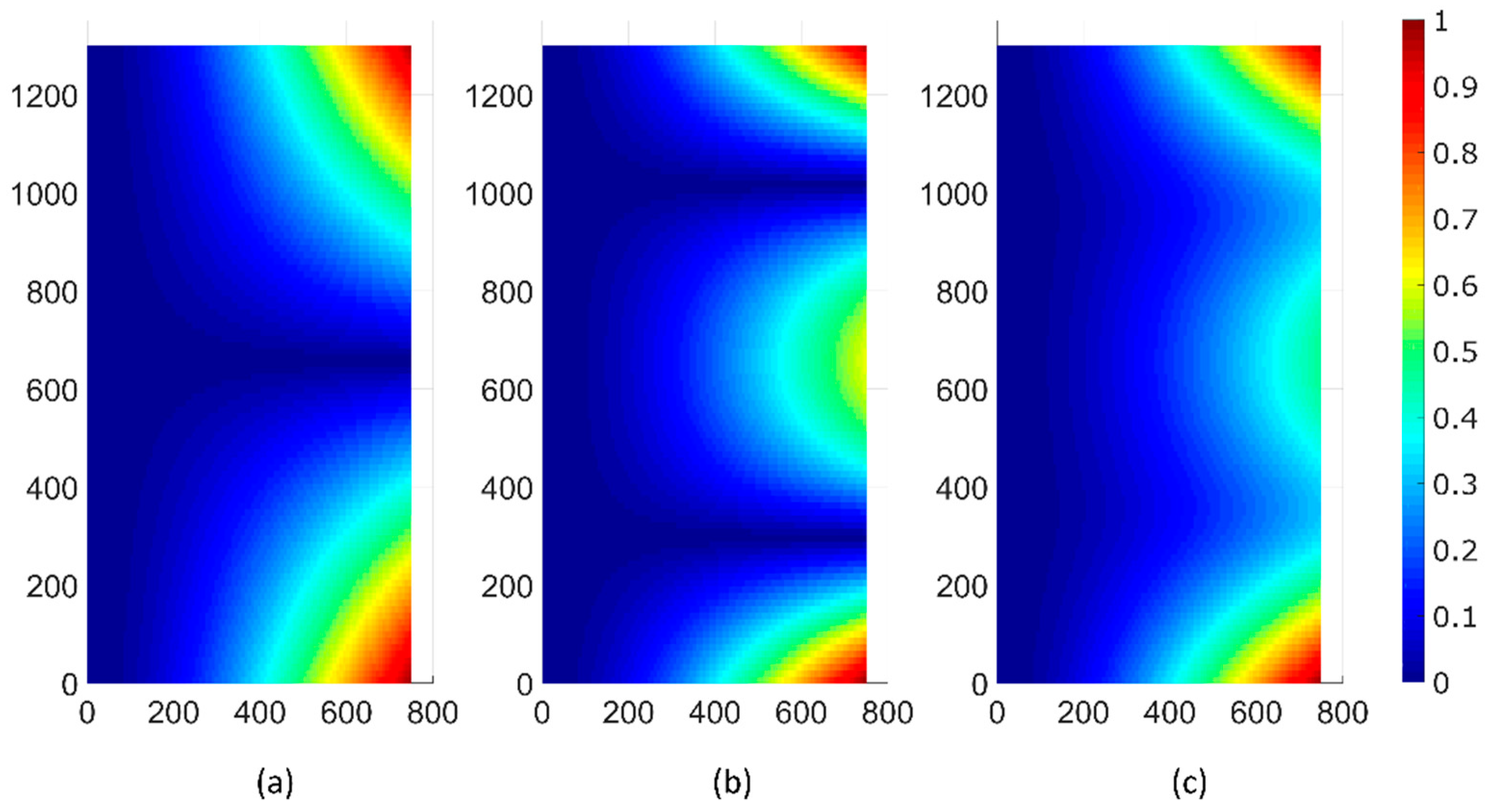
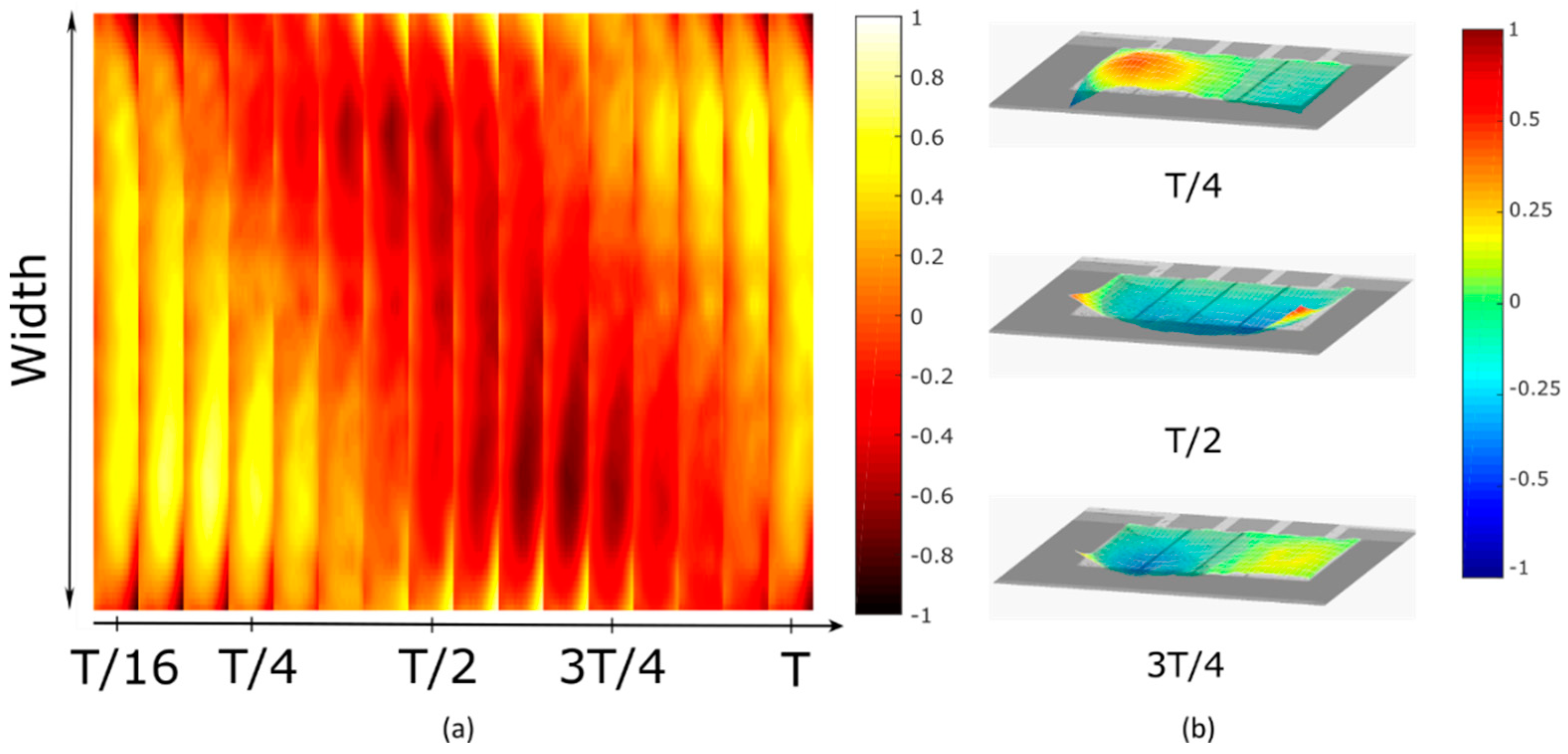
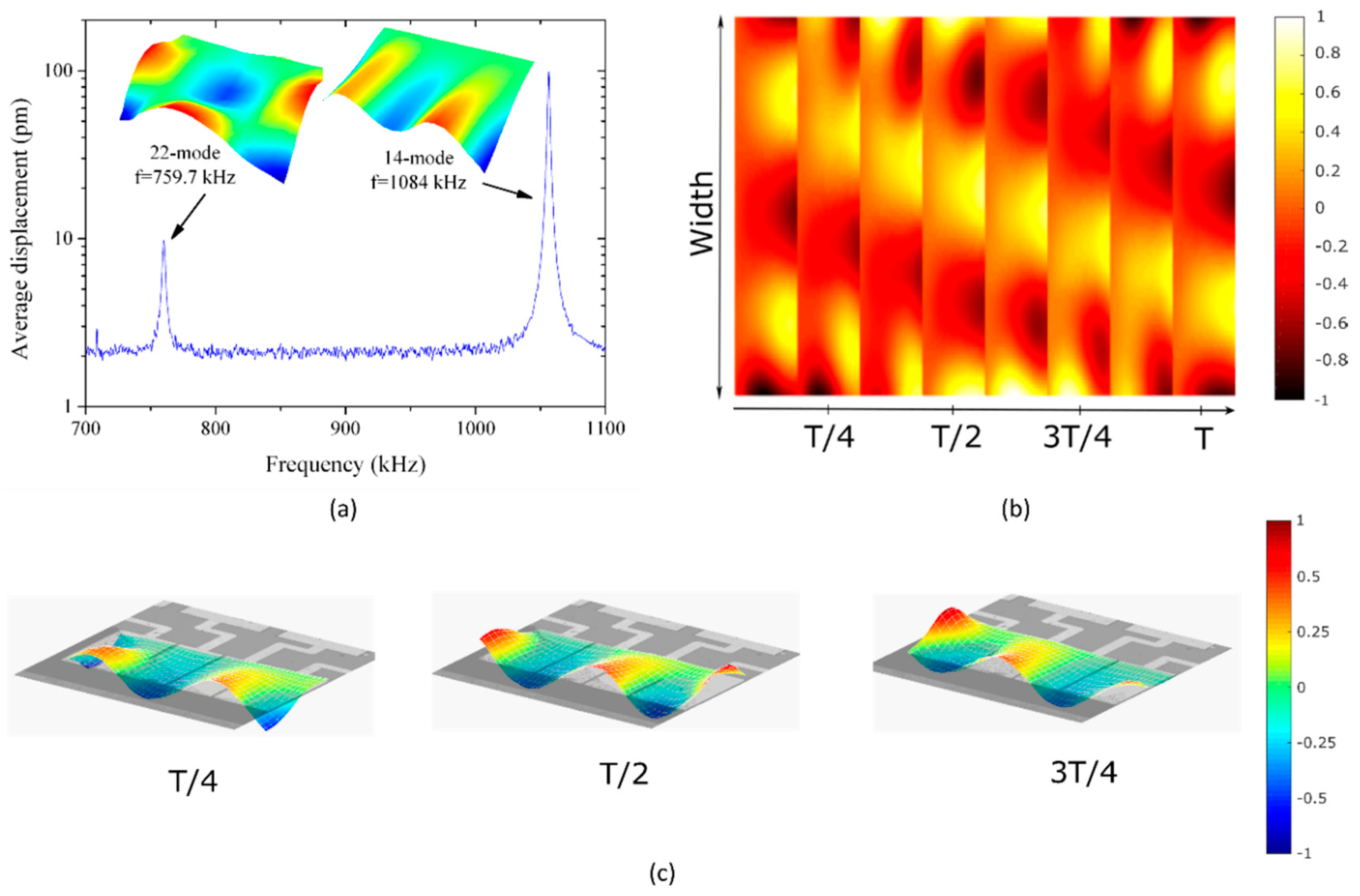
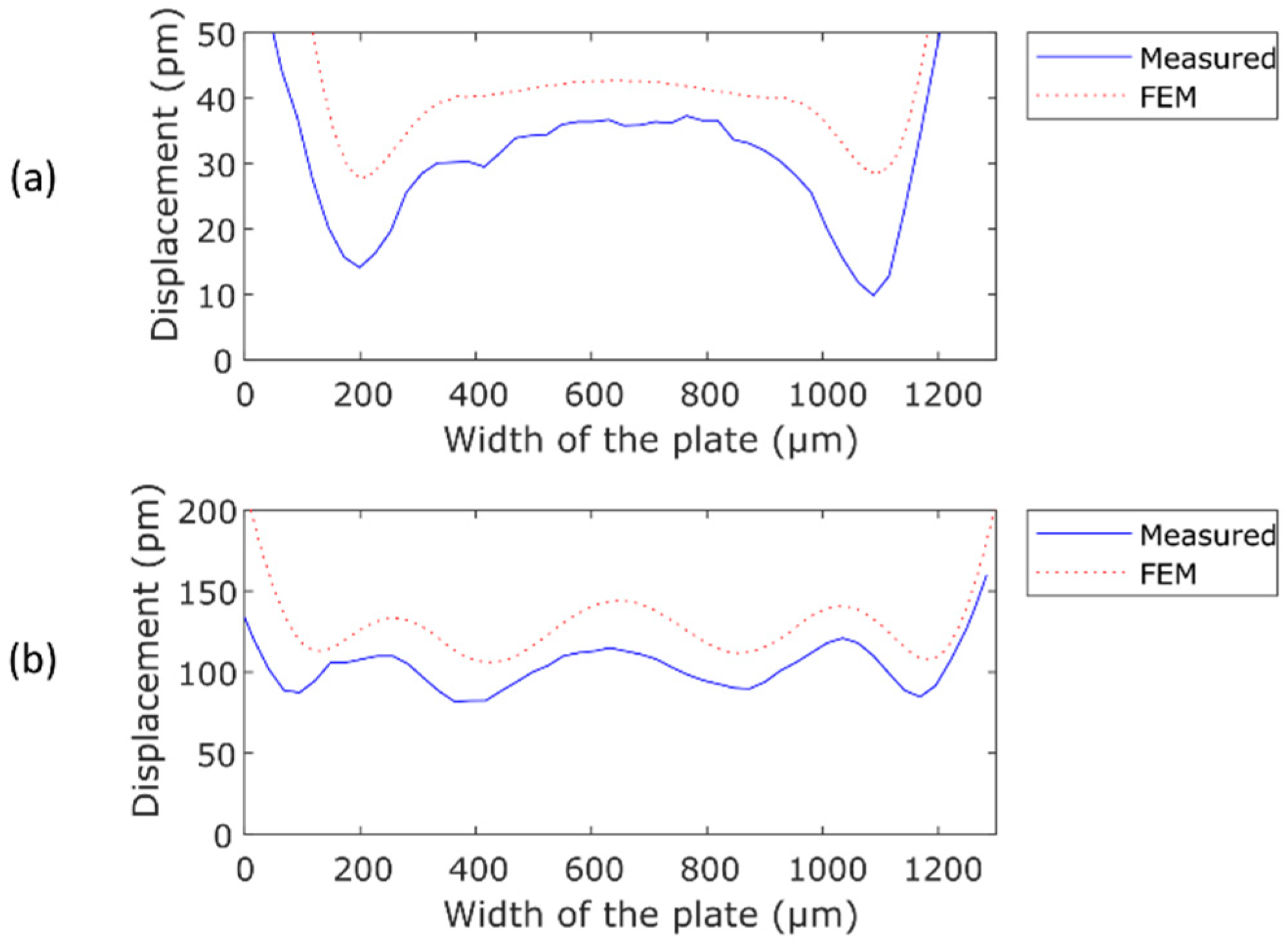
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bogue, R. Recent developments in MEMS sensors: A review of applications, markets and technologies. Sens. Rev. 2013, 33, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, E.W.H. Microrobots for Micrometer-Size Objects in Aqueous Media: Potential Tools for Single-Cell Manipulation. Science 2000, 288, 2335–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palagi, S.; Fischer, P. Bioinspired microrobots. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, H.; Bernard, Y.; Razek, A. Locomotion principles for piezoelectric miniature robots. In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 14–16 June 2010; pp. 1015–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Calisti, M.; Picardi, G.; Laschi, C. Fundamentals of soft robot locomotion. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G. Analysis of the swimming of microscopic organisms. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. A Math. Phys. Sci. 1951, 209, 447–461. [Google Scholar]
- Hagedorn, P.; Wallaschek, J. Travelling wave ultrasonic motors, Part I: Working principle and mathematical modelling of the stator. J. Sound Vib. 1992, 155, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Chenm, J.; Dong, S. A square-plate ultrasonic linear motor operating in two orthogonal first bending modes. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2013, 60, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomikawa, Y.; Takano, T.; Umeda, H. Thin Rotary and Linear Ultrasonic Motors Using a Double-Mode Piezoelectric Vibrator of the First Longitudinal and Second Bending Modes. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 31, 3073–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Li, X.; Dong, S. A high-temperature piezoelectric linear actuator operating in two orthogonal first bending modes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 052902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.L.; Rudy, R.Q.; Polcawich, R.G.; DeVoe, D.L. Integrated thin-film piezoelectric traveling wave ultrasonic motors. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2012, 188, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehez, B.; Vloebergh, C.; Labrique, F. Study and optimization of traveling wave generation in finite-length beams. Math. Comput. Simul. 2010, 81, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, H.; Bernard, Y.; Razek, A. A traveling wave piezoelectric beam robot. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014, 23, 025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malladi, V.V.S.; Albakri, M.; Tarazaga, P.A. An experimental and theoretical study of two-dimensional traveling waves in plates. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, H.; Bernard, Y.; Razek, A. 2-D Traveling Wave Driven Piezoelectric Plate Robot for Planar Motion. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2018, 23, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfakiotakis, M.; Lane, D.M.; Davies, J.B.C. Review of fish swimming modes for aquatic locomotion. IEEE J. Ocean. Eng. 1999, 24, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopman, V.; Porfiri, M. Design, Modeling, and Characterization of a Miniature Robotic Fish for Research and Education in Biomimetics and Bioinspiration. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2013, 18, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Wei, Q.; Tan, M.; Yu, J. A Bio-Inspired Robot With Undulatory Fins and Its Control Methods. IEEE/ASME Trans. Mechatron. 2017, 22, 206–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, K.H.; Willy, A. Biomimetic Motion Planning of an Undulating Robotic Fish Fin. J. Vib. Control 2006, 12, 1337–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ababneh, A.; Al-Omari, A.N.; Dagamseh, A.M.K.; Qiu, H.C.; Feili, D.; Ruiz-Díez, V.; Manzaneque, T.; Hernando, J.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L.; Bittner, A.; et al. Electrical characterization of micromachined AlN resonators at various back pressures. Microsyst. Technol. 2014, 20, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Díez, V.; Hernando-García, J.; Toledo, J.; Manzaneque, T.; Kucera, M.; Pfusterschmied, G.; Schmid, U.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L. Modelling and characterization of the roof tile-shaped modes of AlN-based cantilever resonators in liquid media. J. Micromechan. Microeng. 2016, 26, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leissa, A.W. Vibration of Plates; Scientific and Technical Information Division, National Aeronautics and Space Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1969.
- Malladi, V.V.N.S. Continual Traveling waves in Finite Structures: Theory, Simulations, and Experiments. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University, Blacksburg, VA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Rojas, J.L.; Hernando, J.; Donoso, A.; Bellido, J.C.; Manzaneque, T.; Ababneh, A.; Seidel, H.; Schmid, U. Modal optimization and filtering in piezoelectric microplate resonators. J. Micromechan. Microeng. 2010, 20, 055027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, R.; Tokushima, A.; Kawasaki, O.; Ise, Y.; Yoneno, H. Piezoelectric Ultrasonic Motor. In Proceedings of the IEEE 1987 Ultrasonics Symposium, New York, NY, USA, 14–16 October 1987; pp. 747–756. [Google Scholar]
- Minikes, A.; Gabay, R.; Bucher, I.; Feldman, M. On the sensing and tuning of progressive structural vibration waves. IEEE Trans. Ultrason. Ferroelectr. Freq. Control 2005, 52, 1565–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghenna, S.; Giraud, F.; Giraud-Audine, C.; Amberg, M.; Lemaire-Semail, B. Modelling and control of a travelling wave in a finite beam, using multi-modal approach and vector control method. In Proceedings of the 2015 Joint Conference of the IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium & the European Frequency and Time Forum, Denver, CO, USA, 12–16 April 2015; pp. 509–514. [Google Scholar]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Molina, A.; Ruiz-Díez, V.; Hernando-García, J.; Ababneh, A.; Seidel, H.; Sánchez-Rojas, J.L. Generation of Linear Traveling Waves in Piezoelectric Plates in Air and Liquid. Micromachines 2019, 10, 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050283
Díaz-Molina A, Ruiz-Díez V, Hernando-García J, Ababneh A, Seidel H, Sánchez-Rojas JL. Generation of Linear Traveling Waves in Piezoelectric Plates in Air and Liquid. Micromachines. 2019; 10(5):283. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050283
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Molina, Alex, Víctor Ruiz-Díez, Jorge Hernando-García, Abdallah Ababneh, Helmut Seidel, and José Luis Sánchez-Rojas. 2019. "Generation of Linear Traveling Waves in Piezoelectric Plates in Air and Liquid" Micromachines 10, no. 5: 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050283
APA StyleDíaz-Molina, A., Ruiz-Díez, V., Hernando-García, J., Ababneh, A., Seidel, H., & Sánchez-Rojas, J. L. (2019). Generation of Linear Traveling Waves in Piezoelectric Plates in Air and Liquid. Micromachines, 10(5), 283. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10050283