B Vitamins, Glucoronolactone and the Immune System: Bioavailability, Doses and Efficiency
Abstract
1. Introduction
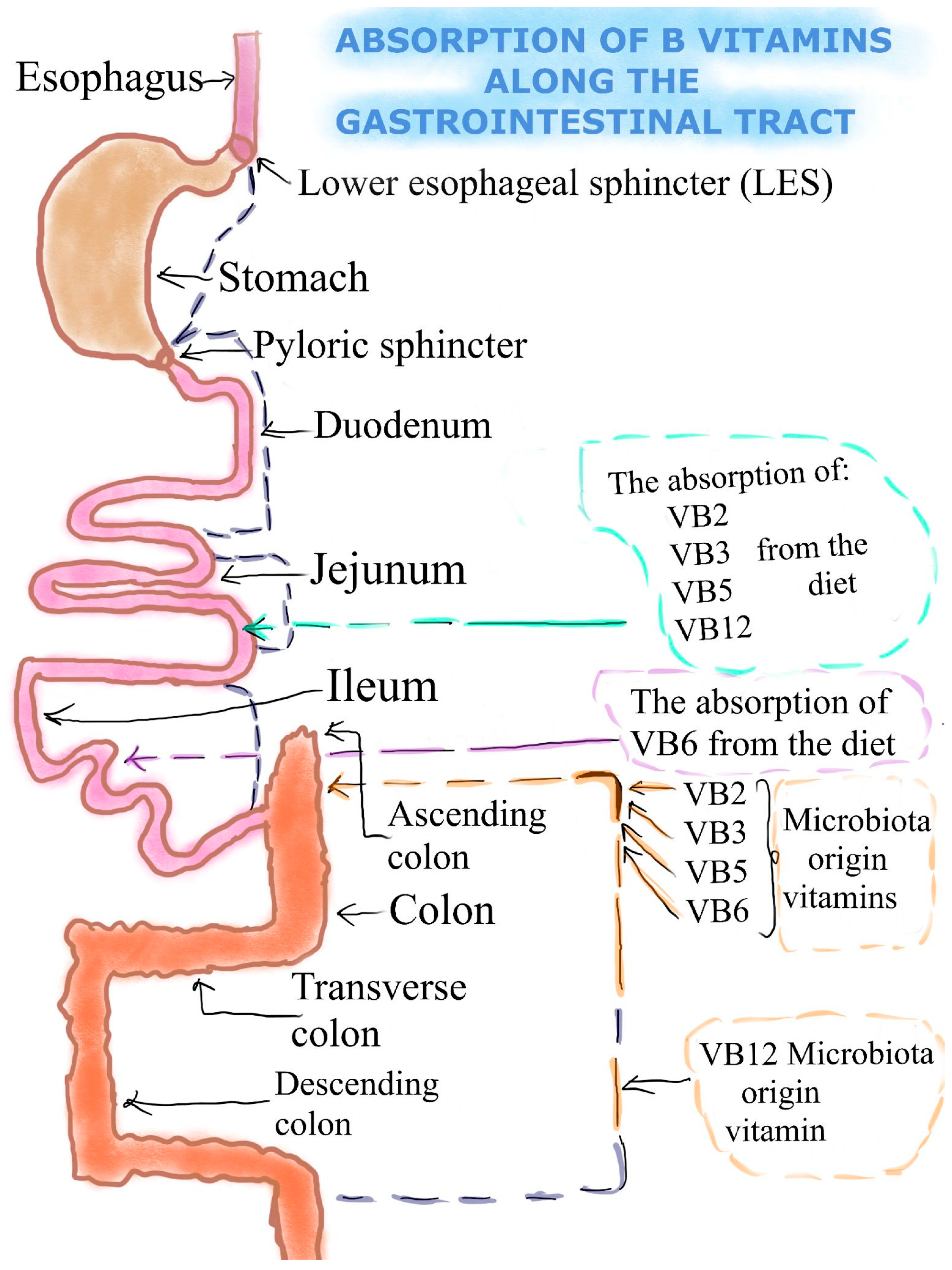
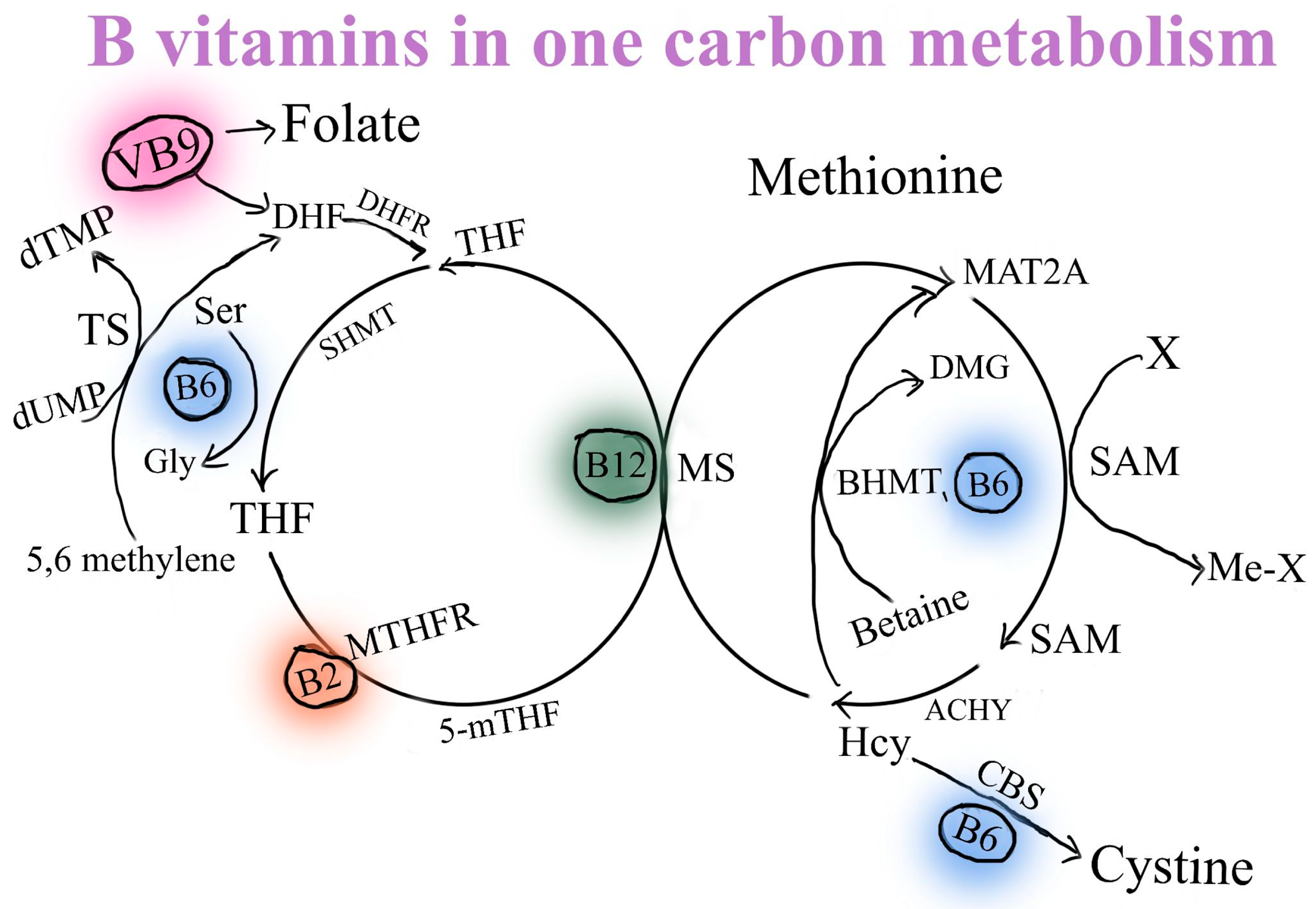
2. The Absorption of Selected B Vitamins (B2, B3, B5, B6, B12) and Glucuronolactone
3. The Riboflavin/Vitamin B2 (RF/VB2) Dose, Efficiency and Bioavailability
4. The Effects of Niacin/VB3 Bioavailability, Dose and Efficiency
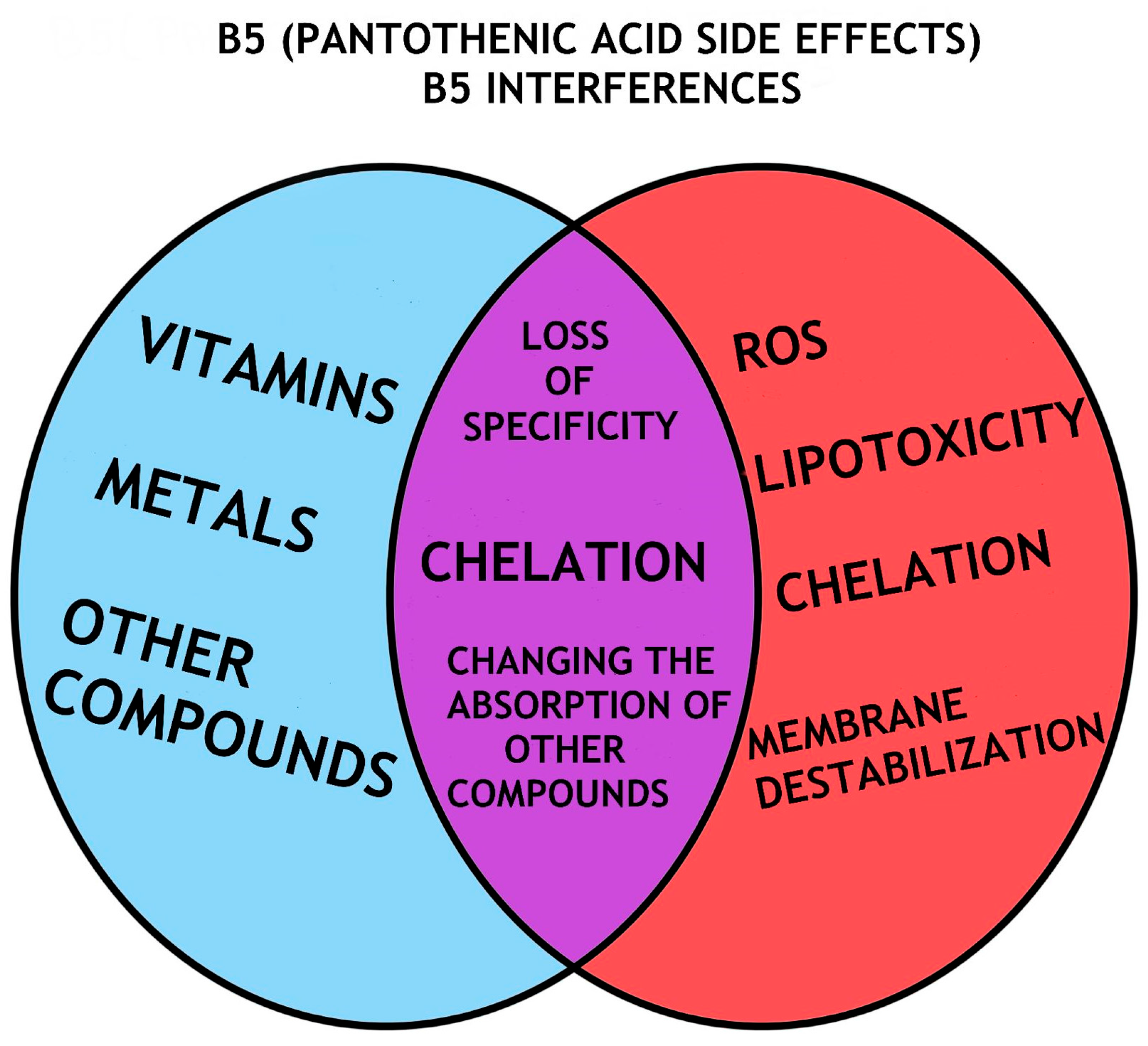
5. Pantothenic Acid/VB5 Bioavailability, Dose and Efficiency
6. The Effects of Pyridoxine/VB6 Bioavailability, Dose and Efficiency
7. The Cobalamin/VB12 Bioavailability, Dose and Efficiency
8. The Glucuronolactone Bioavailability, Dose and Efficiency
9. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alsunni, A.A. Energy Drink Consumption: Beneficial and Adverse Health Effects. Int. J. Health Sci. 2015, 9, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soós, R.; Gyebrovszki, Á.; Tóth, Á.; Jeges, S.; Wilhelm, M. Effects of Caffeine and Caffeinated Beverages in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults: Short Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, E.R.; Plass, J.L.; Hayward, E.O.; Homer, B.D. Emotional design in multimedia learning. J. Educ. Psychol. 2012, 104, 485–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Hellín, J.; Varillas-Delgado, D. Energy drinks and sports performance, cardiovascular risk, and genetic associations; future prospects. Nutrients 2021, 13, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subaiea, G.M.; Altebainawi, A.F.; Alshammari, T.M. Energy drinks and population health: Consumption pattern and adverse effects among Saudi population. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curran, C.P.; Marczinski, C.A. Taurine, caffeine, and energy drinks: Reviewing the risks to the adolescent brain. Birth Defects Res. 2017, 109, 1640–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamishehkar, H.; Ranjdoost, F.; Asgharian, P.; Mahmoodpoor, A.; Sanaie, S. Vitamins, are they safe? Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 6, 467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitra, S.; Paul, S.; Roy, S.; Sutradhar, H.; Bin Emran, T.; Nainu, F.; Khandaker, M.U.; Almalki, M.; Wilairatana, P.; Mubarak, M.S. Exploring the Immune-Boosting Functions of Vitamins and Minerals as Nutritional Food Bioactive Compounds: A Comprehensive Review. Molecules 2022, 27, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, H.M.; Mohammed, Z.M. Intestinal absorption of water-soluble vitamins: An update. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 22, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyina, R.; Dodoala, S. Evaluation of the Neurobehavioural Toxic Effects of Taurine, Glucuronolactone, and Gluconolactone Used in Energy Drinks in Young Rats. Turk. J. Pharm Sci. 2020, 17, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.O. B Vitamins and the Brain: Mechanisms, Dose and Efficacy—A Review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes and its Panel on Folate, Other B Vitamins, and Choline. Dietary Reference Intakes for Thiamin, Riboflavin, Niacin, Vitamin B6, Folate, Vitamin B12, Pantothenic Acid, Biotin, and Choline; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Aparicio-Ugarriza, R.; Olza, J.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Gil, Á.; Ortega, R.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; Varela-Moreiras, G.; González-Gross, M. Dietary Intake and Food Sources of Niacin, Riboflavin, Thiamin and Vitamin B₆ in a Representative Sample of the Spanish Population. The Anthropometry, Intake, and Energy Balance in Spain (ANIBES) Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrubša, M.; Siatka, T.; Nejmanová, I.; Vopršalová, M.; Kujovská Krčmová, L.; Matoušová, K.; Javorská, L.; Macáková, K.; Mercolini, L.; Remião, F.; et al. Biological Properties of Vitamins of the B-Complex, Part 1: Vitamins B1, B2, B3, and B5. Nutrients 2022, 14, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, M.; Jaqua, E.; Nguyen, V.; Clay, J. B Vitamins: Functions and Uses in Medicine. Perm J. 2022, 26, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, L.H.; Miller, J.W.; de Groot, L.; Rosenberg, I.H.; Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H.; Raiten, D.J. Biomarkers of Nutrition for Development (BOND): Vitamin B-12 Review. J. Nutr. 2018, 148 (Suppl. S4), 1995S–2027S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavriša, Ž.; Hristov, H.; Hribar, M.; Žmitek, K.; Kušar, A.; Koroušić Seljak, B.; Gregorič, M.; Blaznik, U.; Gregorič, N.; Zaletel, K.; et al. Dietary Intake and Status of Vitamin B12 in Slovenian Population. Nutrients 2022, 14, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.T.; Zempleni, J. Riboflavin. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 973–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagim, A.R.; Harty, P.S.; Barakat, A.R.; Erickson, J.L.; Carvalho, V.; Khurelbaatar, C.; Camic, C.L.; Kerksick, C.M. Prevalence and Amounts of Common Ingredients Found in Energy Drinks and Shots. Nutrients 2022, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibe, M.N.; Kellar, J.Z. Niacin toxicity. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Rumberger, J.A.; Napolitano, J.; Azumano, I.; Kamiya, T.; Evans, M. Pantethine, a derivative of vitamin B(5) used as a nutritional supplement, favorably alters low-density lipoprotein cholesterol metabolism in low- to moderate-cardiovascular risk North American subjects: A triple-blinded placebo and diet-controlled investigation. Nutr. Res. 2011, 31, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRae, M.P. Treatment of hyperlipoproteinemia with pantethine: A review and analysis of efficacy and tolerability. Nutr. Res. 2005, 25, 319–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.; Rucker, R. Pantothenic Acid. In Present Knowledge in Nutrition; Wiley-Blackwell: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tynes, M.; Hepprich, M.; Timper, K. Regular intake of energy drinks and multivitamin supplements is associated with elevated plasma vitamin B6 levels in post-bariatric patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Gutierrez, J.; Díaz-Cortés, S.; Montoya-Giraldo, M.A.; Zuluaga, A.F. Toxicity induced by multiple high doses of vitamin B12 during pernicious anemia treatment: A case report. Clin. Toxicol. 2020, 58, 129–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, F.; Romano, D.; Villa, R.; Clark, J. Production of fine chemicals by (bio) transformation of agro-food by-products and wastes. In Comprehensive Biotechnology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnoff, N. L-ascorbic acid biosynthesis. Vitam. Horm. 2001, 61, 241–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, K.; Tomar, S.K.; Singh, A.K.; Mandal, S.; Arora, S. Riboflavin and health: A review of recent human research. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 22, 3650–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, H.M. Intestinal absorption of water-soluble vitamins in health and disease. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yonezawa, A.; Inui, K. Novel riboflavin transporter family RFVT/SLC52: Identification, nomenclature, functional characterization and genetic diseases of RFVT/SLC52. Mol. Aspects Med. 2013, 34, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrong, O.; Edmonds, C.J.; Chadwick, V.S. The Large Intestine: Its Role in Mammalian Nutrition and Homeostasis; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Powers, H.J. Riboflavin (vitamin B-2) and health. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1352–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coates, P.M.; Betz, J.M.; Blackman, M.R.; Cragg, G.M.; Levine, M.; Moss, J.; White, J.D. (Eds.) Encyclopedia of Dietary Supplements; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; National Institute of Health: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bechgaard, H.; Jespersen, S. GI absorption of niacin in humans. J. Pharm Sci. 1977, 66, 871–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazzaniga, F.; Stebbins, R.; Chang, S.Z.; McPeek, M.A.; Brenner, C. Microbial NAD metabolism: Lessons from comparative genomics. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2009, 73, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnúsdóttir, S.; Ravcheev, D.; de Crécy-Lagard, V.; Thiele, I. Systematic genome assessment of B-vitamin biosynthesis suggests co-operation among gut microbes. Front. Genet. 2015, 20, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deguchi, Y.; Morishita, T.; Mutai, M. Comparative studies on synthesis of water-soluble vitamins among human species of bifidobacteria. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1985, 49, 13–19. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, J.S.; Subramanian, V.S.; Kapadia, R.; Kashyap, M.L.; Said, H.M. Mammalian colonocytes possess a carrier-mediated mechanism for uptake of vitamin B3 (niacin): Studies utilizing human and mouse colonic preparations. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G207–G213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Kong, D.; Wang, Q.; Wu, W.; Tang, Y.; Bai, T.; Guo, L.; Wei, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, Y.; et al. Niacin ameliorates ulcerative colitis via prostaglandin D2-mediated D prostanoid receptor 1 activation. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.C.; Caballero, B.; Cousins, R.J.; Tucker, K.L. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease; Jones & Bartlett Learning: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Ross, A.C.; Caballero, B.; Cousins, R.J.; Katherine, L.; Thomas, T.; Ziegler, R. Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 17th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health Adis (ESP); Bloomberg School of Public Health: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee, N.S.; Kumar, C.K.; Ortiz, A.; Rubin, S.A.; Said, H.M. Molecular mechanism of the intestinal biotin transport process. Am. J. Physiol. 1999, 277, C605–C613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shils, M.E.; Olson, J.A.; Shike, M. Modern nutrition in health and disease. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 8th ed.; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, M.; Chrubasik, S. Topical herbal therapies for treating osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 31, CD010538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshii, K.; Hosomi, K.; Sawane, K.; Kunisawa, J. Metabolism of Dietary and Microbial Vitamin B Family in the Regulation of Host Immunity. Front. Nutr. 2019, 17, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooney, S.; Leuendorf, J.E.; Hendrickson, C.; Hellmann, H. Vitamin B6: A long known compound of surprising complexity. Molecules 2009, 14, 329–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uebanso, T.; Shimohata, T.; Mawatari, K.; Takahashi, A. Functional roles of B-vitamins in the gut and gut microbiome. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2020, 64, 2000426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guéant, J.L.; Guéant-Rodriguez, R.M.; Alpers, D.H. Vitamin B12 absorption and malabsorption. Vitam. Horm. 2022, 119, 241–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadros, E.V. Advances in the understanding of cobalamin assimilation and metabolism. Br. J. Haematol. 2010, 148, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, S.; Jayatilleke, E.; Meyers, S.; Colman, N.; Herzlich, B.; Herbert, V. The ileum is the major site of absorption of vitamin B12 analogues. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1989, 84, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hewitt, J.E.; Gordon, M.M.; Taggart, R.T.; Mohandas, T.K. Alpers DH. Human gastric intrinsic factor: Characterization of cDNA and genomic clones and localization to human chromosome 11. Genomics 1991, 10, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Żółtaszek, R.; Hanausek, M.; Kiliańska, Z.; Walaszek, Z. Biologiczna rola kwasu D-glukarowego i jego pochodnych; potencjalne zastosowanie w medycynie. Postępy Hig. I Med. Doświadczalnej 2008, 62, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Ayyadurai, V.A.S.; Deonikar, P.; Fields, C. Mechanistic Understanding of D-Glucaric Acid to Support Liver Detoxification Essential to Muscle Health Using a Computational Systems Biology Approach. Nutrients 2023, 15, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dym, O.; Eisenberg, D. Sequence-structure analysis of FAD-containing proteins. Protein Sci. 2001, 10, 1712–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buehler, B.A. Vitamin B2: Riboflavin. J. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2011, 16, 88–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwannasom, N.; Kao, I.; Pruß, A.; Georgieva, R.; Bäumler, H. Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lienhart, W.D.; Gudipati, V.; Macheroux, P. The human flavoproteome. Arch Biochem. Biophys. 2013, 15, 150–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyosawa, T.; Suzuki, M.; Kodama, K.; Araki, S. Effects of intravenous infusion of highly purified vitamin B2 on lipopolysaccharide-induced shock and bacterial infection in mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 492, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toyosawa, T.; Suzuki, M.; Kodama, K.; Araki, S. Potentiation by amino acid of the therapeutic effect of highly purified vitamin B2 in mice with lipopolysaccharide-induced shock. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 493, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, N.O.; Imam, F.; Nadeem, A.; Al-Harbi, M.M.; Korashy, H.M.; Sayed-Ahmed, M.M.; Hafez, M.M.; Al-Shabanah, O.A.; Nagi, M.N.; Bahashwan, S. Riboflavin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in rats. Toxicol. Mech. Methods. 2015, 25, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, M.; Wiegmann, K.; Schramm, S.; Gluschko, A.; Herb, M.; Utermöhlen, O.; Krönke, M. Riboflavin (vitamin B2) deficiency impairs NADPH oxidase 2 (Nox2) priming and defense against Listeria monocytogenes. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, D.; Shishido, S.M.; Queiroz, K.C.; Oliveira, D.N.; Faria, A.L.; Catharino, R.R.; Spek, C.A.; Ferreira, C.V. Irradiated riboflavin diminishes the aggressiveness of melanoma in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Goding Sauer, A.; Fedewa, S.A.; Butterly, L.F.; Anderson, J.C.; Cercek, A.; Smith, R.A.; Jemal, A. Colorectal cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 145–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Huangfu, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, P.; Shen, L.; Zhou, Y. High serum riboflavin is associated with the risk of sporadic colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 2023, 83, 102342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cincović, M.; Hristovska, T.; Belić, B. Niacin, Metabolic Stress and Insulin Resistance in Dairy Cows. In B Group Vitamins-Current Uses and Perspectives; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Sidawy, A.P.; Perler, B.A. Rutherford’s Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy; E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, M.C.; Evans, D.A.; Bienias, J.L.; Scherr, P.A.; Tangney, C.C.; Hebert, L.E.; Bennett, D.A.; Wilson, R.S.; Aggarwal, N. Dietary niacin and the risk of incident Alzheimer’s disease and of cognitive decline. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 8, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robin, S.; Buchanan, R.; Poole, R. Energy drinks and adolescents–A hepatic health hazard? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durham, S.H.; Covington, E.W.; Clemmons, K.J. Hepatotoxicity upon using niacin to pass a drug test: A case report. J. Am. Pharm. Assoc. 2018, 58, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heemskerk, M.M.; van den Berg, S.A.; Pronk, A.C.; van Klinken, J.B.; Boon, M.R.; Havekes, L.M.; Rensen, P.C.; van Dijk, K.W.; van Harmelen, V. Long-term niacin treatment induces insulin resistance and adrenergic responsiveness in adipocytes by adaptive downregulation of phosphodiesterase 3B. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E808–E813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nitto, T.; Onodera, K. The linkage between coenzyme a metabolism and inflammation: Roles of pantetheinase. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 123, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Hu, S.; Du, X.; Wen, Q.; Zhong, X.P.; Zhou, X.; Zhou, C.; Xiong, W.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Vitamin B5 reduces bacterial growth via regulating innate immunity and adaptive immunity in mice infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtczak, L.; Slyshenkov, V.S. Protection by pantothenic acid against apoptosis and cell damage by oxygen free radicals-the role of glutathione. Biofactors 2003, 17, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slyshenkov, V.S.; Dymkowska, D.; Wojtczak, L. Pantothenic acid and pantothenol increase biosynthesis of glutathione by boosting cell energetics. FEBS Lett. 2004, 569, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, M.; Rumberger, J.A.; Azumano, I.; Napolitano, J.J.; Citrolo, D.; Kamiya, T. Pantethine, a derivative of vitamin B5, favorably alters total, LDL and non-HDL cholesterol in low to moderate cardiovascular risk subjects eligible for statin therapy: A triple-blinded placebo and diet-controlled investigation. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2014, 10, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourgin, M.; Kepp, O.; Kroemer, G. Immunostimulatory effects of vitamin B5 improve anticancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 2022, 11, 2031500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noda, S.; Umezaki, H.; Yamamoto, K.; Araki, T.; Murakami, T.; Ishii, N. Reye-like syndrome following treatment with the pantothenic acid antagonist, calcium hopantenate. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1988, 51, 582–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erdmann, J.; Wiciński, M.; Wódkiewicz, E.; Nowaczewska, M.; Słupski, M.; Otto, S.W.; Kubiak, K.; Huk-Wieliczuk, E.; Malinowski, B. Effects of energy drink consumption on physical performance and potential danger of inordinate usage. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazot, C.; Steiber, A.L.; Kopple, J.D. Vitamin metabolism and requirements in chronic kidney disease and kidney failure. In Nutritional Management of Renal Disease; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Williams & Wilkins: Baltimore, MD, USA, 2022; pp. 413–465. [Google Scholar]
- Fenech, M.; Baghurst, P.; Luderer, W.; Turner, J.; Record, S.; Ceppi, M.; Bonassi, S. Low intake of calcium, folate, nicotinic acid, vitamin E, retinol, β-carotene and high intake of pantothenic acid, biotin and riboflavin are significantly associated with increased genome instability—Results from a dietary intake and micronucleus index survey in South Australia. Carcinogenesis 2005, 26, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havaux, M.; Ksas, B.; Szewczyk, A.; Rumeau, D.; Franck, F.; Caffarri, S.; Triantaphylidès, C. Vitamin B6 deficient plants display increased sensitivity to high light and photo-oxidative stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2009, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.H.; Ma, J.; Smith-Warner, S.A.; Lee, J.E.; Giovannucci, E. Vitamin B6 and colorectal cancer: Current evidence and future directions. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2013, 19, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.S.; Picciano, M.F.; Jacques, P.F.; Selhub, J. Plasma pyridoxal 5′-phosphate in the US population: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2003–2004. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 87, 1446–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaumburg, H.; Kaplan, J.; Windebank, A.; Vick, N.; Rasmus, S.; Pleasure, D.; Brown, M.J. Sensory neuropathy from pyridoxine abuse: A new megavitamin syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1983, 309, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, K.; Zeris, S.; Kothari, M.J. Elevated B6 levels and peripheral neuropathies. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 48, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Driskell, J.A. Vitamin B-6 requirements of humans. Nutr. Res. 1994, 14, 293–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, T.D.; Sowa, G.A. Abnormal vitamin B6 and response to supplementation with pyridoxal 5-phosphate (P5P) in patients with neuropathic pain: A case series. PM&R 2013, 9, S216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mocellin, S.; Briarava, M.; Pilati, P. Vitamin B6 and cancer risk: A field synopsis and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamai, Y.; Wada, K.; Tsuji, M.; Nakamura, K.; Sahashi, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Yamamoto, K.; Ando, K.; Nagata, C. Dietary intake of vitamin B12 and folic acid is associated with lower blood pressure in Japanese preschool children. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 1215–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.D.; Refsum, H. Vitamin B-12 and cognition in the elderly. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 707S–711S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, H.N.; Wang, R.; Jin, A.; Koh, W.P.; Yuan, J.M. The association between dietary vitamin B12 and lung cancer risk: Findings from a prospective cohort study. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. Off. J. Eur. Cancer Prev. Organ. (ECP) 2021, 30, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, V.; Chabrun, F.; Lacout, C.; Ghali, A.; Capitain, O.; Patsouris, A.; Lavigne, C.; Urbanski, G. Persistent elevation of plasma vitamin B12 is strongly associated with solid cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żółtaszek, R.; Hanausek, M.; Kiliańska, Z.M.; Walaszek, Z. The biological role of D-glucaric acid and its derivatives: Potential use in medicine. Adv. Hyg. Exp. Med. 2008, 62, 451–462. [Google Scholar]
- Petit, A.; Karila, L.; Lejoyeux, M. Abuse of energy drinks: Does it pose a risk? Presse Medicale 2015, 44, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhong, F.Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, X.P. Efficacy of Jian’ganle (健肝乐) versus Hugan Pian (护肝片), glucuronolactone and reduced glutathione in prevention of antituberculosis drug-induced liver injury. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. [Med. Sci.] 2014, 34, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, F.; Charrondiere, U.R.; Dusemund, B.; Galtier, P.; Gilbert, J.; Gott, D.M.; Grilli, S.; Guertler, R.; Kass, G.E.N.; Koenig, J.; et al. The use of taurine and D-glucurono-γ-lactone as constituents of the so-called “energy” drinks. EFSA J. 2009, 935, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLellan, T.M.; Lieberman, H.R. Do energy drinks contain active components other than caffeine? Nutr. Rev. 2012, 70, 730–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevrioukova, I.F. Apoptosis-inducing factor: Structure, function, and redox regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2011, 14, 2545–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, D.A.; Gannon, S.A.; Thorpe, C. Oxidative protein folding: From thiol-disulfide exchange reactions to the redox poise of the endoplasmic reticulum. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hino, S.; Sakamoto, A.; Nagaoka, K.; Anan, K.; Wang, Y.; Mimasu, S.; Umehara, T.; Yokoyama, S.; Kosai, K.; Nakao, M. FAD-dependent lysine-specific demethylase-1 regulates cellular energy expenditure. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moat, S.J.; Ashfield-Watt, P.A.; Powers, H.J.; Newcombe, R.G.; McDowell, I.F. Effect of riboflavin status on the homocysteine-lowering effect of folate in relation to the MTHFR (C677T) genotype. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramaniam, S.; Christodoulou, J.; Rahman, S. Disorders of riboflavin metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivlin, R. Riboflavin; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; Plenus Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Giulivi, C.; Zhang, Y.F.; Omanska-Klusek, A.; Ross-Inta, C.; Wong, S.; Hertz-Picciotto, I.; Tassone, F.; Pessah, I.N. Mitochondrial dysfunction in autism. JAMA 2010, 304, 2389–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, N.S.; Hansen, T.P. Riboflavin deficiency is associated with selective preservation of critical flavoenzyme-dependent metabolic pathways. Biofactors 1992, 3, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mestdagh, F.; De Meulenaer, B.; De Clippeleer, J.; Devlieghere, F.; Huyghebaert, A. Protective influence of several packaging materials on light oxidation of milk. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, T.K.; Vishnuvajjala, B.R.; Witiak, D.T.; Gerald, M.C. Antagonism of amphetamine stereotyped behavior by diastereoisomeric dihydrodibenzothiepin neuroleptics. Experientia 1977, 33, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, F.; Chen, Y.; He, J.Z.; Long, L.; Chen, Y.; Luo, H.J.; Xu, Y.W.; Pang, X.X.; Yang, Q.; Wang, J.J.; et al. Dietary riboflavin deficiency promotes N-nitrosomethylbenzylamine-induced esophageal tumorigenesis in rats by inducing chronic inflammation. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 2469–2481. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, F.B. The global implications of diabetes and cancer. Lancet 2014, 383, 1947–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katona, B.W.; Weiss, J.M. Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 368–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, N.; Ren, J.; Feng, X.; Lyu, Z.; Wei, L.; Li, X.; Guo, L.; Zheng, Z.; Zou, S.; et al. Participation and yield of a population-based colorectal cancer screening programme in China. Gut 2019, 68, 1450–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarda, J. Niacin (Vitamin B3): Helping Food Turn into Energy. Nutradex 2021, 6. Available online: https://www.nutrastar.com/niacin-b3-in-multivitamins-supplements/ (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Gibson, R.S. Principles of Nutritional Assessment; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chuck, R. Technology development in nicotinate production. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2005, 280, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawy, A.A. Pellagra and alcoholism: A biochemical perspective. Alcohol Alcohol. 2014, 49, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spasiano, D.; Marotta, R.; Di Somma, I.; Mancini, G. Production of pyridinecarboxy aldehydes, nicotinic and isonicotinic and picolinic acids by TiO2-sacrificial photocatalysis at ambient conditions and in aqueous solution through artificial solar radiation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 163, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldie, C.; Taylor, A.J.; Nguyen, P.; McCoy, C.; Zhao, X.Q.; Preiss, D. Niacin therapy and the risk of new-onset diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Heart 2016, 102, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Ficca, M.; Kirkland, J.B. Niacin. Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 556–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florentin, M.; Liberopoulos, E.N.; Kei, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Elisaf, M.S. Pleiotropic effects of nicotinic acid: Beyond high density lipoprotein cholesterol elevation. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 9, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mularski, R.A.; Grazer, R.E.; Santoni, L.; Strother, J.S.; Bizovi, K.E. Treatment advice on the internet leads to a life-threatening adverse reaction: Hypotension associated with Niacin overdose. Clin. Toxicol. 2006, 44, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Morgan, B. Encyclopedia of Toxicology, 3rd ed.; Philip Wexler US National Library of Medicine: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, L.A. Nicotinic acid: The broad-spectrum lipid drug. A 50th Anniv. Rev. J. Intern. Med. 2005, 258, 94–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, G.R.; Nelson, A.G. Niacin supplementation impairs exercise performance. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2021, 93, 385–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringseis, R.; Gessner, D.K.; Beer, A.M.; Albrecht, Y.; Wen, G.; Most, E.; Krüger, K.; Eder, K. Nicotinic acid improves endurance performance of mice subjected to treadmill exercise. Metabolites 2020, 10, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gille, A.; Bodor, E.T.; Ahmed, K.; Offermanns, S. Nicotinic acid: Pharmacological effects and mechanisms of action. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2008, 48, 79–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, J.N. The plasma free fatty acid rebound induced by nicotinic acid. J. Lipid Res. 1967, 8, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringseis, R.; Rosenbaum, S.; Gessner, D.K.; Herges, L.; Kubens, J.F.; Mooren, F.C.; Krüger, K.; Eder, K. Supplementing obese Zucker rats with niacin induces the transition of glycolytic to oxidative skeletal muscle fibers. J. Nutr. 2013, 143, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou Mrad, J.; Yakubu, F.; Lin, D.; Peters, J.C.; Atkinson, J.B.; Hill, J.O. Skeletal muscle composition in dietary obesity-susceptible and dietary obesity-resistant rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 1992, 262, R684–R688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanner, C.J.; Barakat, H.A.; Dohm, G.L.; Pories, W.J.; MacDonald, K.G.; Cunningham, P.R.; Swanson, M.S.; Houmard, J.A. Muscle fiber type is associated with obesity and weight loss. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E1191–E1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pette, D. Training effects on the contractile apparatus. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1998, 162, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunbar, R.L.; Gelfand, J.M. Seeing red: Flushing out instigators of niacin-associated skin toxicity. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 2651–2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamanna, V.S.; Ganji, S.H.; Kashyap, M.L. The mechanism and mitigation of niacin-induced flushing. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 63, 1369–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antagonists, T.N.F. LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury; National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, B.; Lin, P.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Yin, D.; Zeng, J.; Liao, B.; Kang, Z. Niacin exacerbates β cell lipotoxicity in diet-induced obesity mice through upregulation of GPR109A and PPARγ2: Inhibition by incretin drugs. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1057905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirkland, J.B. Niacin and carcinogenesis. Nutr. Cancer. 2003, 46, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschi, S.; Bidoli, E.; Barón, A.E.; La Vecchia, C. Maize and risk of cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx, and esophagus in northeastern Italy. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1407–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrubsole, M.J.; Shu, X.O.; Li, H.L.; Cai, H.; Yang, G.; Gao, Y.T.; Gao, J.; Zheng, W. Dietary B vitamin and methionine intakes and breast cancer risk among Chinese women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 173, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfait, P.; Moren, A.; Dillon, J.C.; Brodel, A.; Begkoyian, G.; Etchegorry, M.G.; Malenga, G.; Hakewill, P. An outbreak of pellagra related to changes in dietary niacin among Mozambican refugees in Malawi. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1993, 22, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavente, C.A.; Jacobson, M.K.; Jacobson, E.L. NAD in skin: Therapeutic approaches for niacin. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, W. Nicotinic acid/niacinamide and the skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2004, 3, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surjana, D.; Halliday, G.M.; Damian, D.L. Nicotinamide enhances repair of ultraviolet radiation-induced DNA damage in human keratinocytes and ex vivo skin. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 1144–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Xu, W.; Guan, C.; Zhou, M.; Hong, W.; Fu, L.; Liu, D.; Xu, A. Niacin protects against UVB radiation-induced apoptosis in cultured human skin keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Chen, W.C.; Thornton, M.J.; Qin, K.; Rosenfield, R. Sexual hormones in human skin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, M.S.; Grant-Kels, J.M. Hormones, nevi, and melanoma: An approach to the patient. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2007, 57, 919–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koomen, E.R.; Joosse, A.; Herings, R.M.; Casparie, M.K.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Nijsten, T. Estrogens, oral contraceptives and hormonal replacement therapy increase the incidence of cutaneous melanoma: A population-based case–control study. Ann. Oncol. 2009, 20, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begley, T.P.; Kinsland, C.; Strauss, E. The biosynthesis of coenzyme A in bacteria. Vitam. Horm. 2001, 61, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanvictores, T.; Chauhan, S. Vitamin B5 (pantothenic acid). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Dezfouli, M.A.; Jaberi, E.; Alavi, A.; Rezvani, M.; Shahidi, G.; Elahi, E.; Rohani, M. Pantothenate kinase 2 mutation with eye-of-the-tiger sign on magnetic resonance imaging in three siblings. Iran. J. Neurol. 2012, 11, 155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurian, M.A.; Hayflick, S.J. Pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration (PKAN) and PLA2G6-associated neurodegeneration (PLAN): Review of two major neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA) phenotypes. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2013, 110, 49–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawla, J.; Kvarnberg, D. Hydrosoluble vitamins. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 120, 891–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, A.; Savka, M.A.; Hudson, A.O. The synthesis and role of β-alanine in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Ahn, S.Y.; Lee, H.A.; Won, K.S.; Chang, H.W.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, H.W. Dietary intake of pantothenic acid is associated with cerebral amyloid burden in patients with cognitive impairment. Food Nutr. Res. 2018, 62, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rucker, R.B.; Zempleni, J.; Suttie, J.W.; McCormick, D.B. Handbook of Vitamins, 4th ed.; Chapter 9; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitfield, J.; Harris, R.C.; Broad, E.M.; Patterson, A.K.; Ross, M.L.R.; Shaw, G.; Spriet, L.L.; Burke, L.M. Chronic pantothenic acid supplementation does not affect muscle coenzyme A content or cycling performance. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 46, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aronson, J.K. Meyler’s side effects of drugs: The international encyclopedia of adverse drug reactions and interactions. In Newnes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Tan, M.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, S.; Yang, J.; Xie, H.; Chen, P.; et al. Study on the correlation between B vitamins and breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, N.; He, Q.; Guo, Z.; Liu, L.; Song, Y.; Chen, P.; Wei, Y.; Xu, Q.; et al. Association between plasma Vitamin B5 levels and all-cause mortality: A nested case-control study. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2022, 24, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berruyer, C.; Martin, F.M.; Castellano, R.; Macone, A.; Malergue, F.; Garrido-Urbani, S.; Millet, V.; Imbert, J.; Duprè, S.; Pitari, G.; et al. Vanin-1−/− mice exhibit a glutathione-mediated tissue resistance to oxidative stress. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 7214–7224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouyet, L.; Roisin-Bouffay, C.; Clément, A.; Millet, V.; Garcia, S.; Chasson, L.; Issaly, N.; Rostan, A.; Hofman, P.; Naquet, P.; et al. Epithelial vanin-1 controls inflammation-driven carcinogenesis in the colitis-associated colon cancer model. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2010, 16, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapsokefalou, M.; Roe, M.; Turrini, A.; Costa, H.S.; Martinez-Victoria, E.; Marletta, L.; Berry, R.; Finglas, P. Food Composition at Present: New Challenges. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, M.T.; Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, N.; Huang, S.J.; Yu, H.; Zhao, X.J.; Huang, C.Y.; Liu, Z.Y. A comprehensive toxicity evaluation in rats after long-term oral Gelsemium elegans exposure. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 137, 111284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhury, S.R.; Singh, S.K.; Roy, S.; Sengupta, D.N. An insight into the sequential, structural and phylogenetic properties of banana 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase 1 and study of its interaction with pyridoxal-5′-phosphate and aminoethoxyvinylglycine. J. Biosci. 2010, 35, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, H.M. Recent advances in carrier-mediated intestinal absorption of water-soluble vitamins. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2004, 66, 419–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keles, M.; Al, B.; Gumustekin, K.; Demircan, B.; Ozbey, I.; Akyuz, M.; Yilmaz, A.; Demir, E.; Uyanik, A.; Ziypak, T.; et al. Antioxidative status and lipid peroxidation in kidney tissue of rats fed with vitamin B6-deficient diet. Ren. Fail. 2010, 32, 618–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Fang, Y.Z.; Yang, S.; Lupton, J.R.; Turner, N.D. Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mascolo, E.; Vernì, F. Vitamin B6 and diabetes: Relationship and molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalton, K.; Dalton, M.J.T. Characteristics of pyridoxine overdose neuropathy syndrome. Acta Neurol. Scand. 1987, 76, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.T. 6-Fluoropyridoxol. 2006 May 9 [updated 2008 Mar 25]. In Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database (MICAD) [Internet]; National Center for Biotechnology Information: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Rios-Avila, L.; Coats, B.; Ralat, M.; Chi, Y.Y.; Midttun, Ø.; Ueland, P.M.; Stacpoole, P.W. Gregory Pyridoxine supplementation does not alter in vivo kinetics of one-carbon metabolism but modifies patterns of one-carbon and tryptophan metabolites in vitamin B-6–insufficient oral contraceptive users. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 616–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, A.; Lumeng, L.; Aronoff, G.R.; Li, T.K. Relationship between body store of vitamin B6 and plasma pyridoxal-P clearance: Metabolic balance studies in humans. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1985, 106, 491–497. [Google Scholar]
- Schneider, M.; Nössler, C. Die Bedeutung der Ernährung im Kindes-und Jugendalter. Nie Wieder 2015, 63, 163. [Google Scholar]
- Vrolijk, M.F.; Opperhuizen, A.; Jansen, E.H.J.M.; Hageman, G.J.; Bast, A.; Haenen, G. The vitamin B6 paradox: Supplementation with high concentrations of pyridoxine leads to decreased vitamin B6 function. Toxicol. Vitr. 2017, 44, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morra, M.; Philipszoon, H.D.; D’Andrea, G.; Cananzi, A.R.; L’Erario, R.; Milone, F.F. Sensory and motor neuropathy caused by excessive ingestion of vitamin B6: A case report. Funct. Neurol. 1993, 8, 429–432. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Albin, R.; Albers, J.W.; Greenberg, H.S.; Townsend, J.B.; Lynn, R.B.; Burke, J.M.; Alessi, A.G. Acute sensory neuropathy-neuronopathy from pyridoxine overdose. Neurology 1987, 37, 1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, C.; D’Cruz, D. Pyridoxine toxicity courtesy of your local health food store. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 1666–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, M.P.; Plecko, B.; Mills, P.B.; Clayton, P.T. Disorders affecting vitamin B6 metabolism. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 2019, 42, 629–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, W.P.; Shu, X.O.; Xiang, Y.B.; Li, H.; Zheng, W.; Lan, Q.; Visvanathan, K.; Bolton, J.H.; Ueland, P.M.; Midttun, Ø.; et al. Circulating folate, vitamin B6, and methionine in relation to lung cancer risk in the Lung Cancer Cohort Consortium (LC3). JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, T.J.; Woodson, K.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Virtamo, J.; Selhub, J.; Barrett, M.J.; Albanes, D. Association of the B-vitamins pyridoxal 5′-phosphate (B6), B12, and folate with lung cancer risk in older men. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 153, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulvik, A.; Midttun, Ø.; Pedersen, E.R.; Eussen, S.J.; Nygård, O.; Ueland, P.M. Evidence for increased catabolism of vitamin B-6 during systemic inflammation. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 100, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueland, P.M.; McCann, A.; Midttun, Ø.; Ulvik, A. Inflammation, vitamin B6 and related pathways. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 53, 10–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Ueland, P.M.; Midttun, Ø.; Vollset, S.E.; Tell, G.S.; Theofylaktopoulou, D.; Travis, R.C.; Boutron-Ruault, M.C.; Fournier, A.; Severi, G.; et al. Results from the European prospective investigation into cancer and nutrition link vitamin B6 catabolism and lung cancer risk. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, H.; Ueland, P.M.; Midttun, Ø.; Tell, G.S.; Fanidi, A.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Prentice, R.; et al. Vitamin B6 catabolism and lung cancer risk: Results from the Lung Cancer Cohort Consortium (LC3). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, H.; Ueland, P.M.; Eussen, S.J.; Tell, G.S.; Vollset, S.E.; Nygård, O.; Midttun, Ø.; Meyer, K.; Ulvik, A. Markers of vitamin B6 status and metabolism as predictors of incident cancer: The H ordaland H ealth S tudy. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, 2932–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolk, B.J.; Ganetsky, M.; Babu, K.M. Toxicity of energy drinks. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2012, 24, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, Z.; Stroiński, A. Comprehensive B12: Chemistry, Biochemistry, Nutrition, Ecology, Medicine; Walter de Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Heldt, D.; Lawrence, A.D.; Lindenmeyer, M.; Deery, E.; Heathcote, P.; Rigby, S.E.; Warren, M.J. Aerobic synthesis of vitamin B12: Ring contraction and cobalt chelation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2005, 33, 815–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.J.; Warren, M.J. The anaerobic biosynthesis of vitamin B12. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, K. Mucosal adsorption and absorption of vitamin B12 in the intestine of the rat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1962, 111, 320–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, F.; Yabuta, Y.; Bito, T.; Teng, F. Vitamin B12-containing plant food sources for vegetarians. Nutrients 2014, 6, 1861–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruvada, P.; Stover, P.J.; Mason, J.B.; Bailey, R.L.; Davis, C.D.; Field, M.S.; Finnell, R.H.; Garza, C.; Green, R.; Gueant, J.L.; et al. Knowledge gaps in understanding the metabolic and clinical effects of excess folates/folic acid: A summary, and perspectives, from an NIH workshop. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2020, 112, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doets, E.L.; In’t Veld, P.H.; Szczecińska, A.; Dhonukshe-Rutten, R.A.; Cavelaars, A.E.; van’t Veer, P.; Brzozowska, A.; de Groot, L.C. Systematic review on daily vitamin B12 losses and bioavailability for deriving recommendations on vitamin B12 intake with the factorial approach. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2013, 62, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, L.H. Bioavailability of vitamin B12. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2010, 80, 330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogiatzoglou, A.; Smith, A.D.; Nurk, E.; Berstad, P.; Drevon, C.A.; Ueland, P.M.; Vollset, S.E.; Tell, G.S.; Refsum, H. Dietary sources of vitamin B-12 and their association with plasma vitamin B-12 concentrations in the general population: The Hordaland Homocysteine Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2009, 89, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tucker, K.L.; Rich, S.; Rosenberg, I.; Jacques, P.; Dallal, G.; Wilson, P.W.; Selhub, J. Plasma vitamin B-12 concentrations relate to intake source in the Framingham Offspring study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morkbak, A.L.; Poulsen, S.S.; Nexo, E. Haptocorrin in humans. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2007, 45, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Yamazaki, Y.; Yamada, H. Fate of cobalamins in humans following oral and intramuscular administration of cyanocobalamin, hydroxocobalamin, adenosyl-cobalamin and methylcobalamin. Vitamins 1981, 55, 155–161. [Google Scholar]
- Hurlock, L.; Lee, M. Potential health problems with the use of energy drinks. West Indian Med. J. 2012, 61, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vivekanandarajah, A.; Ni, S.; Waked, A. Acute hepatitis in a woman following excessive ingestion of an energy drink: A case report. J. Med. Case Rep. 2011, 5, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasavada, A.; Sanghavi, D. Cyanocobalamin. In Europepmc.Org; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, R. Is vitamin B12 deficiency a risk factor for cardiovascular disease in vegetarians? Am. J. Prev. Med. 2015, 48, e11–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Tracking of blood pressure from childhood to adulthood: A systematic review and meta–regression analysis. Circulation 2008, 117, 3171–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonke, D.; Nickel, B. Improvement of fine motoric movement control by elevated dosages of vitamin B1, B6, and B12 in target shooting. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 1989, 30, 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Harb, J.N.; Taylor, Z.A.; Khullar, V.; Sattari, M. Rare cause of acute hepatitis: A common energy drink. Case Rep. 2016, 2016, bcr2016216612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baylin, S.B. DNA methylation and gene silencing in cancer. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2 (Suppl. S1), S4–S11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, A.C.; Maddocks, O.D. One-carbon metabolism in cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1499–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.I. Folate and DNA methylation: A mechanistic link between folate deficiency and colorectal cancer? Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2004, 13, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ham, M.S.; Lee, J.K.; Kim, K.C. S-adenosyl methionine specifically protects the anticancer effect of 5-FU via DNMTs expression in human A549 lung cancer cells. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebbing, M.; Bønaa, K.H.; Nygård, O.; Arnesen, E.; Ueland, P.M.; Nordrehaug, J.E.; Rasmussen, K.; Njølstad, I.; Refsum, H.; Nilsen, D.W.; et al. Cancer incidence and mortality after treatment with folic acid and vitamin B12. JAMA 2009, 302, 2119–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brasky, T.M.; White, E.; Chen, C.L. Long-term, supplemental, one-carbon metabolism–related vitamin B use in relation to lung cancer risk in the Vitamins and Lifestyle (VITAL) Cohort. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanidi, A.; Carreras-Torres, R.; Larose, T.L.; Yuan, J.M.; Stevens, V.L.; Weinstein, S.J.; Albanes, D.; Prentice, R.; Pettinger, M.; Cai, Q.; et al. Is high vitamin B12 status a cause of lung cancer? Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassett, J.K.; Hodge, A.M.; English, D.R.; Baglietto, L.; Hopper, J.L.; Giles, G.G.; Severi, G. Dietary intake of B vitamins and methionine and risk of lung cancer. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 66, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.; Relton, C.; Ueland, P.M.; Vollset, S.E.; Midttun, Ø.; Nygård, O.; Slimani, N.; Boffetta, P.; Jenab, M.; Clavel-Chapelon, F.; et al. Serum B vitamin levels and risk of lung cancer. JAMA 2010, 303, 2377–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takata, Y.; Shu, X.O.; Buchowski, M.S.; Munro, H.M.; Wen, W.; Steinwandel, M.D.; Hargreaves, M.K.; Blot, W.J.; Cai, Q. Food intake of folate, folic acid and other B vitamins with lung cancer risk in a low-income population in the Southeastern United States. Eur. J. Nutr. 2020, 59, 671–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, J.F.; Nexo, E. Cobalamin related parameters and disease patterns in patients with increased serum cobalamin levels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serraj, K.; Mecili, M.; Housni, I.; Andrès, E. Hypervitaminémie B12: Physiopathologie et intérêt en pratique clinique. La Presse Médicale 2011, 40, 1120–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arendt, J.F.H.; Farkas, D.K.; Pedersen, L.; Nexo, E.; Sørensen, H.T. Elevated plasma vitamin B12 levels and cancer prognosis: A population-based cohort study. Cancer Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatami, M.; Vahid, F.; Esmaeil Akbari, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Ameri, F.; Eini-Zeinab, H.; Jamshidi-Naeini, Y.; Hossein Davoodi, S. The vitamins involved in one-carbon metabolisms are associated with reduced risk of breast cancer in overall and subtypes. Int. J. Vitam. Nutr. Res. 2019, 90, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, A.; Marakis, G.; Lampen, A.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I. Risk assessment of energy drinks with focus on cardiovascular parameters and energy drink consumption in Europe. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 130, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio, C.; Cámara, M.; Giner, R.M.; González-Muñoz, M.J.; López-García, E.; Morales, F.J.; Moreno-Arribas, M.V.; Portillo, M.P.; Bethencourt, E. Caffeine, D-glucuronolactone and Taurine Content in Energy Drinks: Exposure and Risk Assessment. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armendáriz, C.R.; Hurtado, M.M.C.; Pons, R.M.G.; Muñoz, M.J.G.; García, E.L.; Navas, F.J.M.; Moreno, V.; Baquedano, M.P.P. del Comité Científico de la Agencia Española de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (AESAN) sobre los riesgos asociados al consumo de bebidas energéticas. Rev. Com. Científico AESAN 2021, 33, 151–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamay, A. Neurotransmitter and Brain Modulating Oral Delivery System for Enhancement of Cognitive Functions and Energy. U.S. Patent Application No. 15/896,789, 23 August 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen-Khac, E.; Thevenot, T.; Piquet, M.A.; Benferhat, S.; Goria, O.; Chatelain, D.; Tramier, B.; Dewaele, F.; Ghrib, S.; Rudler, M.; et al. Glucocorticoids plus N-acetylcysteine in severe alcoholic hepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cui, H.; Niu, H.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Sun, J.; Wei, Q.; Dong, J.; Liu, L.; Xian, C.J. Hydrocortisone suppresses early paraneoplastic inflammation and angiogenesis to attenuate early hepatocellular carcinoma progression in rats. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 9481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Compounds | Recommended Daily Dose for Adult Women | Recommended Daily Dose for Adult Men | Recommended Daily Dose for Pregnant Women | Recommended Daily Dose for Teenagers Girls | Recommended Daily Dose for Teenagers Boys |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) [12] | 1.1 mg | 1.3 mg | 1.4 mg | 1.0 mg | 1.3 mg |
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) [13] | 14 mg | 16 mg | 18 mg | 14 mg | 16 mg |
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) [14] | 5 mg | 5 mg | 6 mg | 5 mg | 5 mg |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) [15] | 1–1.7 mg | 1–1.7 mg | 1.9 mg | 1.2 mg | 1.3 mg |
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) [16,17] | 2.4 mcg | 2.4 mcg | 2.6 mcg | 2.4 mcg | 2.4 mcg |
| Compounds | Efficiency in the Immune System | Negative Impacts of High Doses |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) | ||
| Vitamin B3 (Niacin) |
|
|
| Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid) |
| |
| Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) | ||
| Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) | ||
| Glucuronolactone |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Munteanu, C.; Schwartz, B. B Vitamins, Glucoronolactone and the Immune System: Bioavailability, Doses and Efficiency. Nutrients 2024, 16, 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010024
Munteanu C, Schwartz B. B Vitamins, Glucoronolactone and the Immune System: Bioavailability, Doses and Efficiency. Nutrients. 2024; 16(1):24. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010024
Chicago/Turabian StyleMunteanu, Camelia, and Betty Schwartz. 2024. "B Vitamins, Glucoronolactone and the Immune System: Bioavailability, Doses and Efficiency" Nutrients 16, no. 1: 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010024
APA StyleMunteanu, C., & Schwartz, B. (2024). B Vitamins, Glucoronolactone and the Immune System: Bioavailability, Doses and Efficiency. Nutrients, 16(1), 24. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010024






