Effect of Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro: A Preliminary Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Treatments and Cell Culture
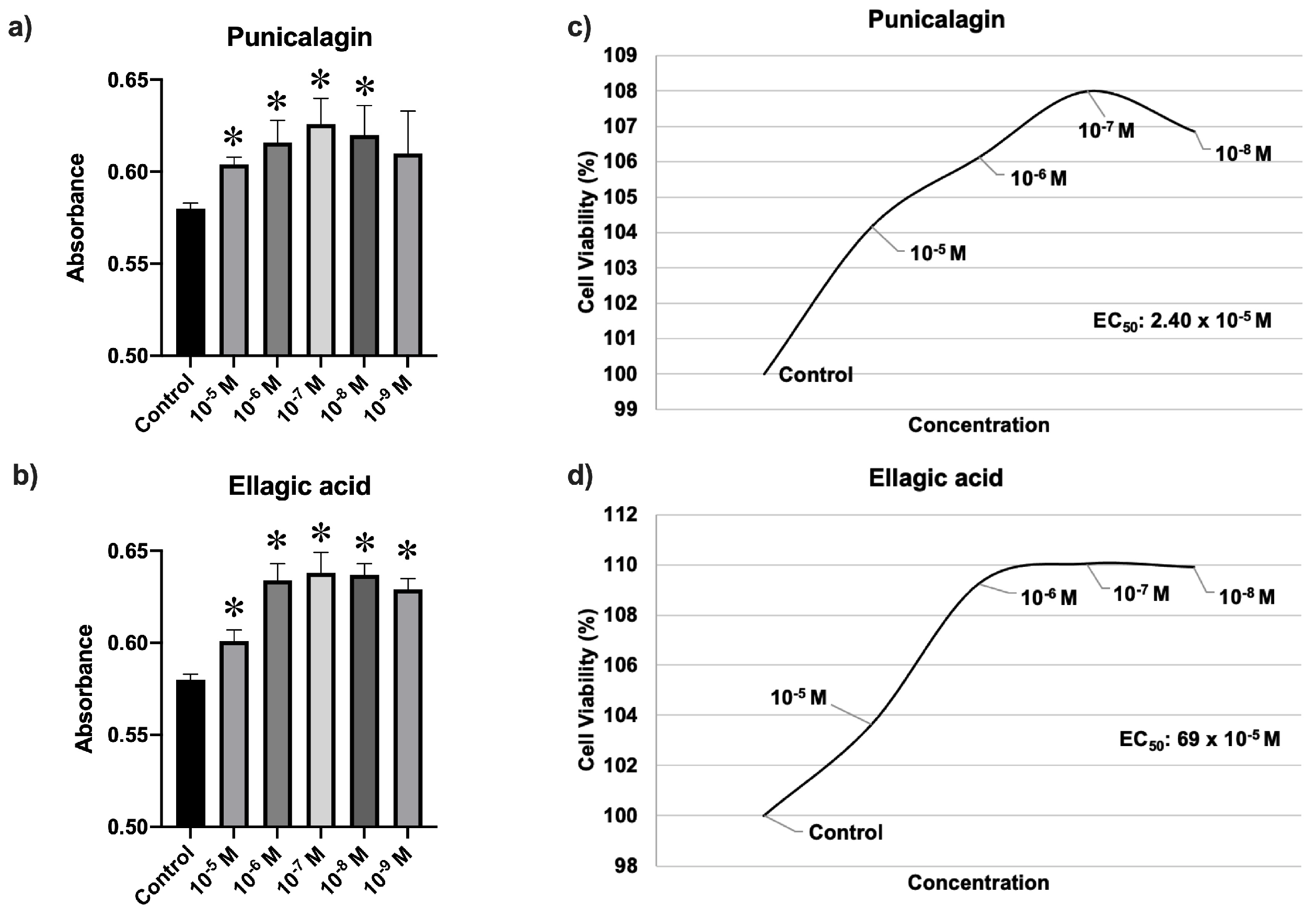
2.2. Cell Viability Assay
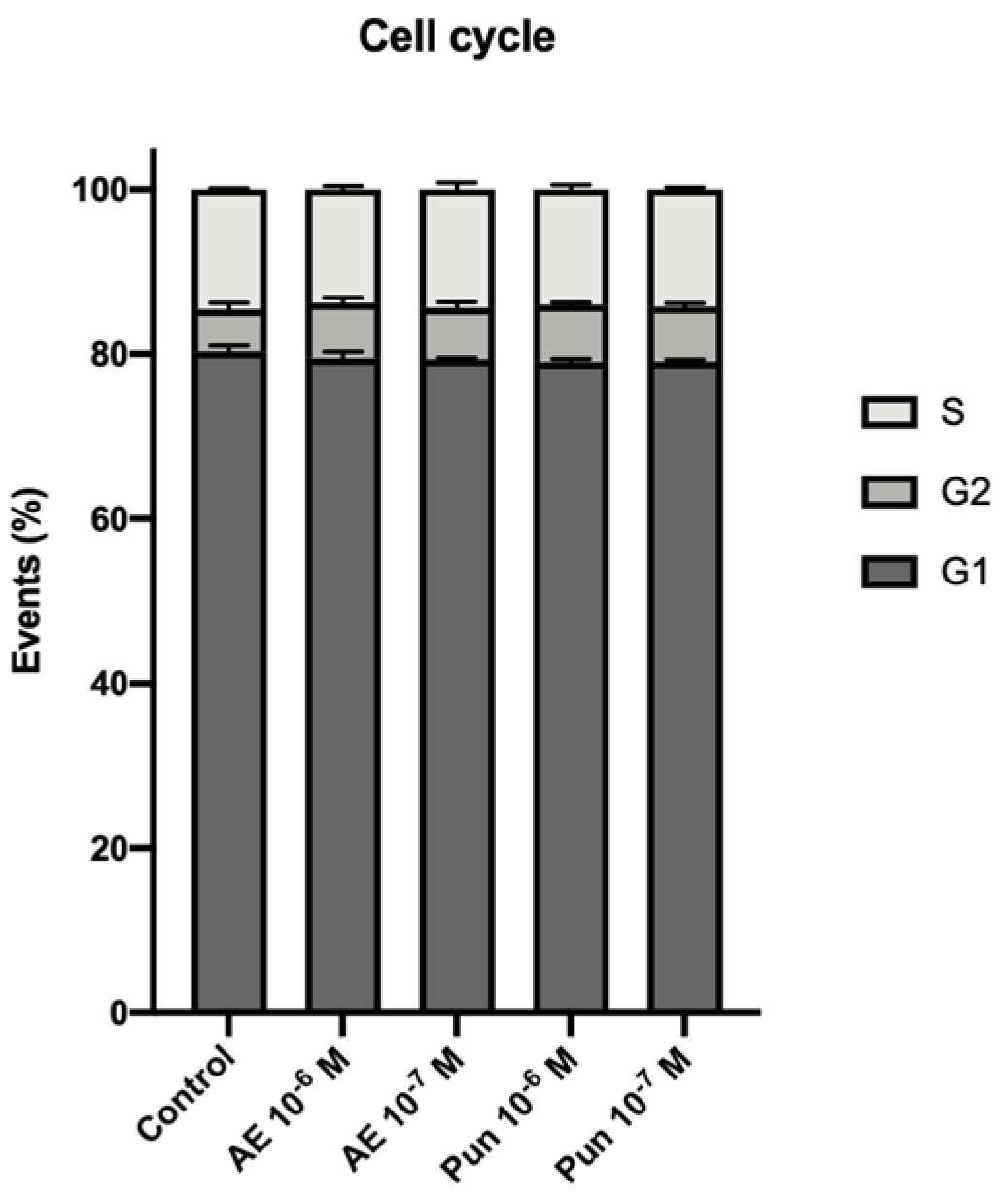
2.3. Cell Cycle
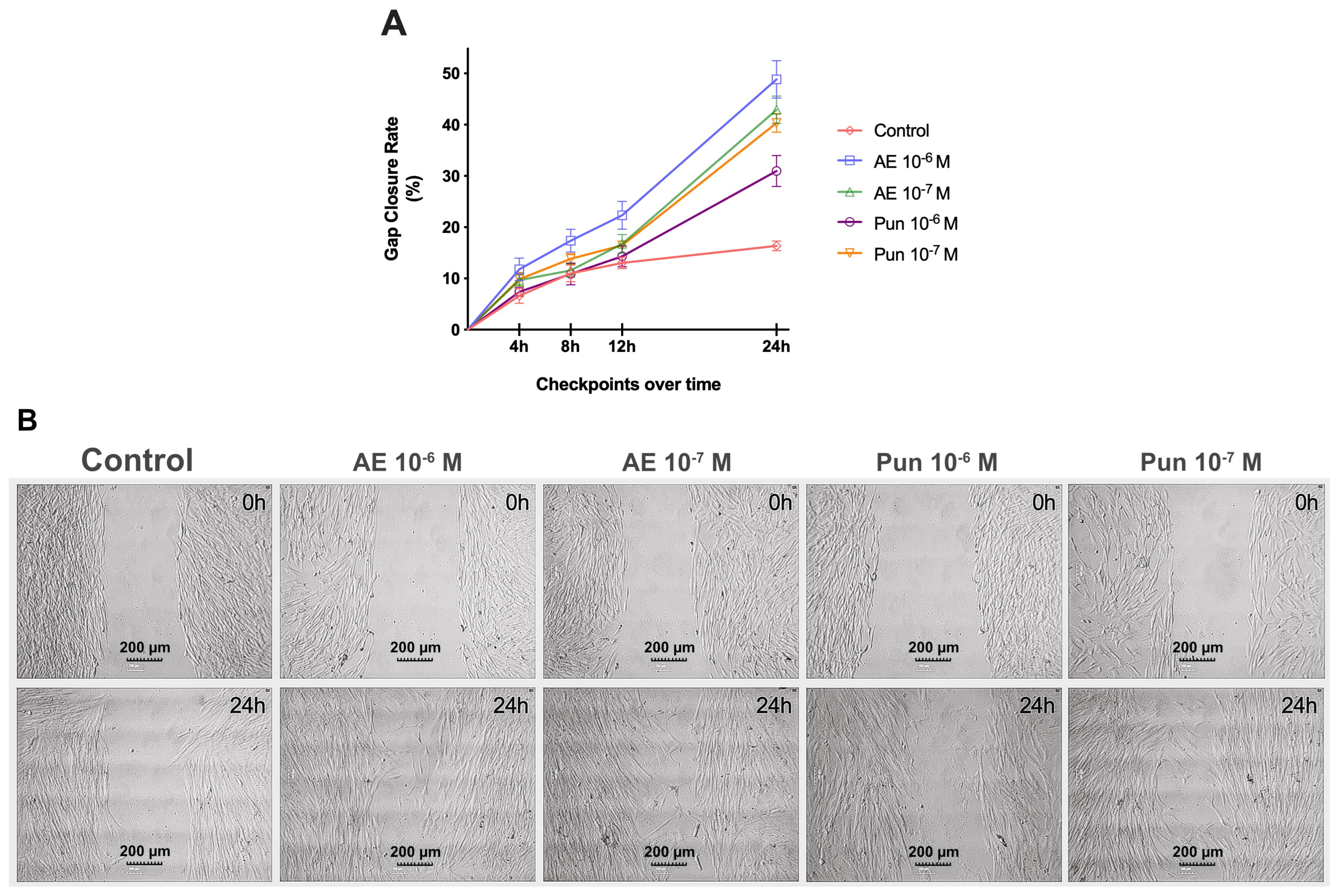
2.4. Migration Assay
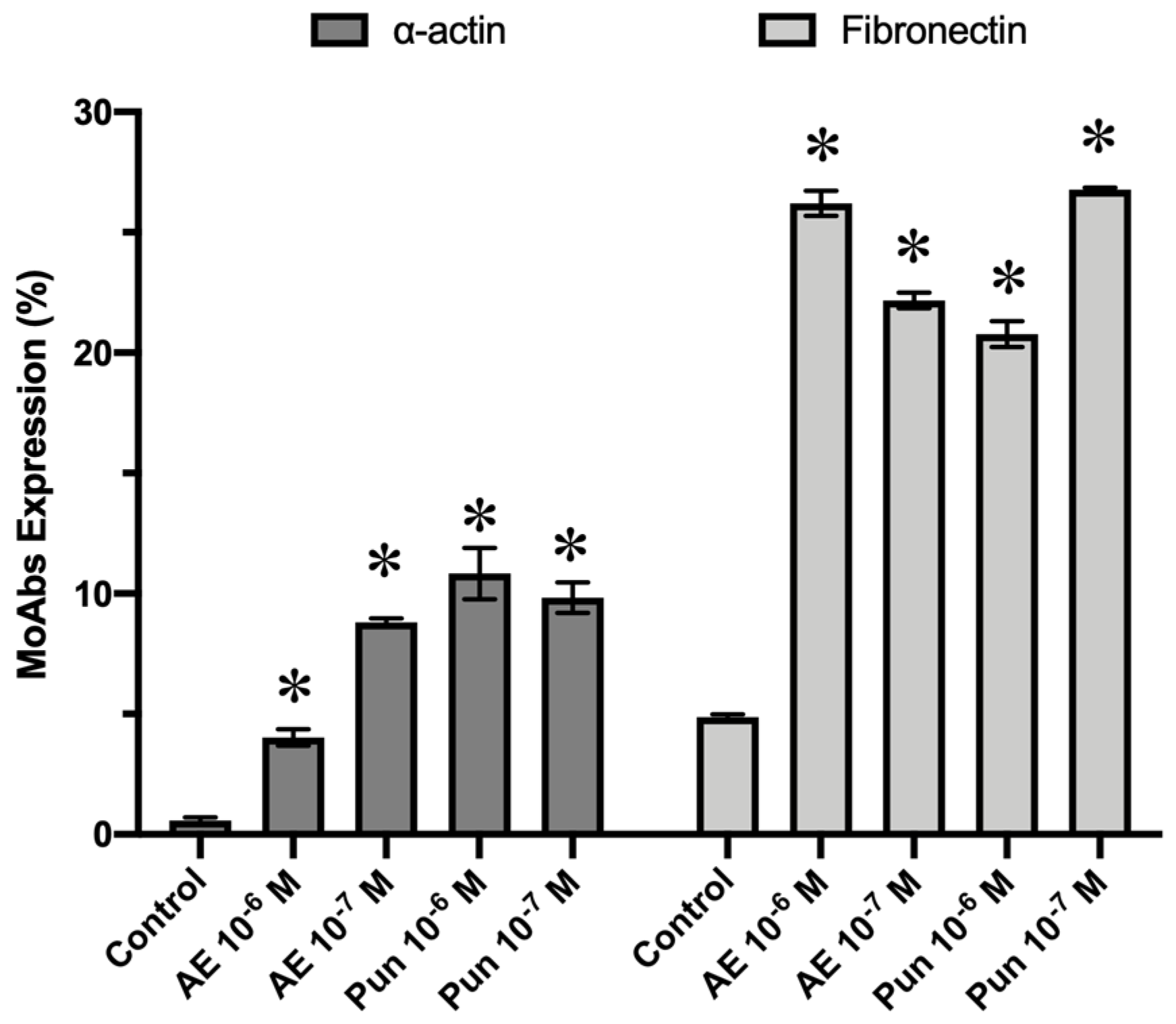
2.5. Antigenic Profile Study
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Immunocytochemistry
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability Assay
3.2. Cell Cycle
3.3. Migration Assay
3.4. Antigenic Profile
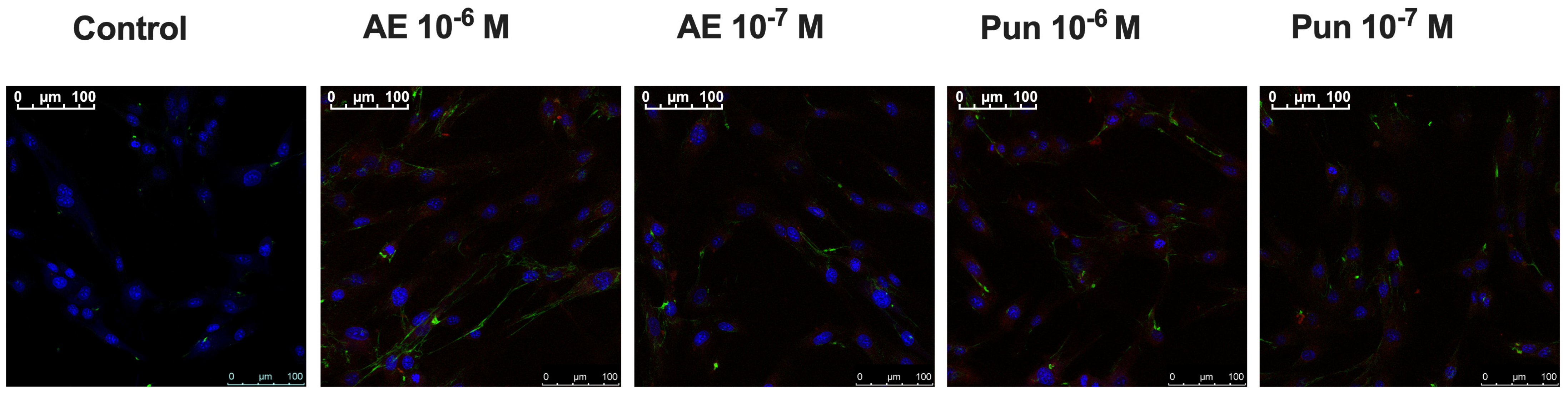
3.5. Immunocytochemistry
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russo, M.; Fanali, C.; Tripodo, G.; Dugo, P.; Muleo, R.; Dugo, L.; De Gara, L.; Mondello, L. Analysis of Phenolic Compounds in Different Parts of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Fruit by HPLC-PDA-ESI/MS and Evaluation of Their Antioxidant Activity: Application to Different Italian Varieties. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 3507–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Gouvinhas, I.; Rocha, J.; Barros, A.I.R.N.A. Phytochemical and Antioxidant Analysis of Medicinal and Food Plants towards Bioactive Food and Pharmaceutical Resources. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eghbali, S.; Askari, S.F.; Avan, R.; Sahebkar, A. Therapeutic Effects of Punica granatum (Pomegranate): An Updated Review of Clinical Trials. J. Nutr. Metab. 2021, 2021, 5297162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viuda-Martos, M.; Fernández-López, J.; Pérez-Álvarez, J.A. Pomegranate and Its Many Functional Components as Related to Human Health: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2010, 9, 635–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mphahlele, R.R.; Fawole, O.A.; Mokwena, L.M.; Opara, U.L. Effect of Extraction Method on Chemical, Volatile Composition and Antioxidant Properties of Pomegranate Juice. South Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 103, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandylis, P.; Kokkinomagoulos, E. Food Applications and Potential Health Benefits of Pomegranate and Its Derivatives. Foods 2020, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Ya’akov, I.; Tian, L.; Amir, R.; Holland, D. Primary Metabolites, Anthocyanins, and Hydrolyzable Tannins in the Pomegranate Fruit. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, H.; Hegazi, N.; El-Shamy, S.; Farag, M.A. Pomegranate Juice as a Functional Food: A Comprehensive Review of Its Polyphenols, Therapeutic Merits, and Recent Patents. Food Funct. 2020, 11, 5768–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorzadeh, E.; Heidary, Z.; Mohammadi, M.; Nadjarzadeh, A.; Ramezani-Jolfaie, N.; Salehi-Abargouei, A. Does Pomegranate Consumption Improve Oxidative Stress? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2022, 47, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebkar, A.; Ferri, C.; Giorgini, P.; Bo, S.; Nachtigal, P.; Grassi, D. Effects of Pomegranate Juice on Blood Pressure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vučić, V.; Grabež, M.; Trchounian, A.; Arsić, A. Composition and Potential Health Benefits of Pomegranate: A Review. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 25, 1817–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, E.; Sangiovanni, E.; Dell’agli, M. A Review on the Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Pomegranate in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 2013, 247145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.; Jahan, A.; Samrana, S.; Ali, A.; Ali, S.; Kabir, N.; Ali, A.; Ullah, R.; Mothana, R.A.; Murtaza, B.N.; et al. Hepatoprotective Potential of Pomegranate in Curbing the Incidence of Acute Liver Injury by Alleviating Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 694607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, V.; Estévez, M.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Morcuende, D.; Martín, I.; Delgado, J. Biodegradation of Punicalagin into Ellagic Acid by Selected Probiotic Bacteria: A Study of the Underlying Mechanisms by MS-Based Proteomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 16273–16285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selma, M.V.; Espín, J.C.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A. Interaction between Phenolics and Gut Microbiota: Role in Human Health. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 6485–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; González-Sarrías, A.; García-Villalba, R.; Núñez-Sánchez, M.A.; Selma, M.V.; García-Conesa, M.T.; Espín, J.C. Urolithins, the Rescue of “Old” Metabolites to Understand a “New” Concept: Metabotypes as a Nexus among Phenolic Metabolism, Microbiota Dysbiosis, and Host Health Status. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2017, 61, 1500901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Liu, C.; Tang, Q.; Li, D.; Wan, Y.; Li, J.-H.; Gao, X.-H.; Seeram, N.P.; Ma, H.; Chen, H.-D. Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Extract and Its Polyphenols Reduce the Formation of Methylglyoxal-DNA Adducts and Protect Human Keratinocytes against Methylglyoxal-Induced Oxidative Stress. J. Funct. Foods 2021, 83, 104564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Palencia, L.A.; Noratto, G.; Hingorani, L.; Talcott, S.T.; Mertens-Talcott, S.U. Protective Effects of Standardized Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Polyphenolic Extract in Ultraviolet-Irradiated Human Skin Fibroblasts. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8434–8441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atit, R.; Thulabandu, V.; Chen, D. Dermal Fibroblast in Cutaneous Development and Healing. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2018, 7, 10.1002/wdev.307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.F.; desJardins-Park, H.E.; Mascharak, S.; Borrelli, M.R.; Longaker, M.T. Understanding the Impact of Fibroblast Heterogeneity on Skin Fibrosis. Dis. Model. Mech. 2020, 13, dmm044164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorrentino, S.; Studt, J.-D.; Medalia, O.; Tanuj Sapra, K. Roll, Adhere, Spread and Contract: Structural Mechanics of Platelet Function. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 94, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furie, B.; Furie, B.C. Mechanisms of Thrombus Formation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, R.; Grinstein, S.; Canton, J. The Life Cycle of Phagosomes: Formation, Maturation, and Resolution. Immunol. Rev. 2016, 273, 156–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorch, S.K.; Kubes, P. An Emerging Role for Neutrophil Extracellular Traps in Noninfectious Disease. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound Repair and Regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, B. The Myofibroblast: Paradigm for a Mechanically Active Cell. J. Biomech. 2010, 43, 146–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caley, M.P.; Martins, V.L.C.; O’Toole, E.A. Metalloproteinases and Wound Healing. Adv. Wound Care 2015, 4, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, S.H. Biology of Fibroblasts and Myofibroblasts. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 334–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plikus, M.V.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Ito, M.; Li, Y.R.; Dedhia, P.H.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, M.; Gay, D.L.; Ramos, R.; Hsi, T.-C.; et al. Regeneration of Fat Cells from Myofibroblasts during Wound Healing. Science 2017, 355, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younesi, F.S.; Son, D.O.; Firmino, J.; Hinz, B. Myofibroblast Markers and Microscopy Detection Methods in Cell Culture and Histology. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2299, 17–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbott, H.E.; Mascharak, S.; Griffin, M.; Wan, D.C.; Longaker, M.T. Wound Healing, Fibroblast Heterogeneity, and Fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Acedo, A.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Ruiz, C.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; García-Martínez, O. The Benefits of Olive Oil for Skin Health: Study on the Effect of Hydroxytyrosol, Tyrosol, and Oleocanthal on Human Fibroblasts. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.-Y.; Choi, J.-S.; Kang, S.-W.; Lee, Y.-J.; Park, J.; Kang, Y.-H. Dietary Compound Ellagic Acid Alleviates Skin Wrinkle and Inflammation Induced by UV-B Irradiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, e182–e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celiksoy, V.; Moses, R.L.; Sloan, A.J.; Moseley, R.; Heard, C.M. Evaluation of the In Vitro Oral Wound Healing Effects of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Rind Extract and Punicalagin, in Combination with Zn (II). Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleck, A.; Cabral, P.F.G.; Vieira, F.F.M.; Pinheiro, D.A.; Pereira, C.R.; Santos, W.C.; Machado, T.B. Punica granatum L. Hydrogel for Wound Care Treatment: From Case Study to Phytomedicine Standardization. Molecules 2016, 21, 1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.; Kim, J.; Choi, Y.; Jin, S.; Kim, S.; Son, D.; Shin, M. Punicalagin-Loaded Alginate/Chitosan-Gallol Hydrogels for Efficient Wound Repair and Hemostasis. Polymers 2022, 14, 3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiswanto, B.S.; Miranti, A.; Sudjarwo, S.A.; Primarizky, H.; Yuniarti, W.M. Evaluation of Wound Healing Potential of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Whole Fruit Extract on Skin Burn Wound in Rats (Rattus norvegicus). J. Adv. Vet. Anim. Res. 2019, 6, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, J.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Kaewnopparat, N.; Nitiruangjaras, A.; Reanmongkol, W. Wound Healing Activities of Standardized Pomegranate Rind Extract and Its Major Antioxidant Ellagic Acid in Rat Dermal Wounds. J. Nat. Med. 2014, 68, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Peng, K.; Wang, Q.; Gu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Deng, F.; et al. Effect of Pomegranate Peel Polyphenol Gel on Cutaneous Wound Healing in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Chin. Med. J. 2013, 126, 1700–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Marcelino, S.; Mandim, F.; Taofiq, O.; Pires, T.C.S.P.; Finimundy, T.C.; Prieto, M.A.; Barros, L. Valorization of Punica granatum L. Leaves Extracts as a Source of Bioactive Molecules. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Guo, L.; Li, R.; Shao, J.; Lu, L.; Yang, P.; Zhao, A.; Liu, Y. Ellagic Acid-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex-Loaded Thiol-Ene Hydrogel with Antioxidant, Antibacterial, and Anti-Inflammatory Properties for Wound Healing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 4959–4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinz, B. Formation and Function of the Myofibroblast during Tissue Repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; de Luna-Bertos, E.; Manzano-Moreno, F.J.; Garcia-Martinez, O.; Ruiz, C. Human Fibroblast- Like Cultures in the Presence of Platelet- Rich Plasma as a Single Growth Factor Source: Clinical Implications. Adv. Ski. Wound Care 2014, 27, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; Illescas-Montes, R.; Costela-Ruiz, V.J.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; de Luna-Bertos, E.; García-Martínez, O.; Ruiz, C. Antimicrobial Properties of Olive Oil Phenolic Compounds and Their Regenerative Capacity towards Fibroblast Cells. J. Tissue Viability 2021, 30, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Huang, M.; Li, J.; Lai, F.; Lee, H.; Hsu, Y. Punicalagin Induces Apoptotic and Autophagic Cell Death in Human U87MG Glioma Cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, L.; Duan, Y.; Ma, F.; Lou, L. Punicalagin Inhibits the Viability, Migration, Invasion, and EMT by Regulating GOLPH3 in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. 2020, 40, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Ou, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Wu, B.; Huang, M. Inhibitory Effect of Punicalagin on Inflammatory and Angiogenic Activation of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 727920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, A.; Biltekin, B.; Ozevren, H. Antitumor Activity of Irinotecan with Ellagic Acid in C6 Glioma Cells. Rev. Assoc. Med. Bras. 2022, 68, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnasto-Rilla, M.; Järvenpää, J.; Huovinen, M.; Schroderus, A.-M.; Ihantola, E.-L.; Küblbeck, J.; Khadeer, M.; Moaddel, R.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M. Effects of Galloflavin and Ellagic Acid on Sirtuin 6 and Its Anti-Tumorigenic Activities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenSaad, L.A.; Kim, K.H.; Quah, C.C.; Kim, W.R.; Shahimi, M. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Ellagic Acid, Gallic Acid and Punicalagin A&B Isolated from Punica granatum. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čolić, M.; Mihajlović, D.; Bekić, M.; Marković, M.; Dragišić, B.; Tomić, S.; Miljuš, N.; Šavikin, K.; Škrbić, R. Immunomodulatory Activity of Punicalagin, Punicalin, and Ellagic Acid Differs from the Effect of Pomegranate Peel Extract. Molecules 2022, 27, 7871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, H.-A.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, H.-Y. Regulatory Effect of Ellagic Acid on Immune Function in Burned Rats. J. Burn. Care Res. 2023, 44, 982–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| mAb | Fluorochrome | Supplier |
|---|---|---|
| Control PE | PE | Caltag (Burlingame, CA, USA) |
| Control FITC | FITC | Caltag (Burlingame, CA, USA) |
| Anti-human Fibronectin-Fluorescein | FITC | R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA) |
| Anti-human α-Actin-PE | PE | R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Illescas-Montes, R.; Rueda-Fernández, M.; González-Acedo, A.; Melguizo-Rodríguez, L.; García-Recio, E.; Ramos-Torrecillas, J.; García-Martínez, O. Effect of Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro: A Preliminary Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Potential. Nutrients 2024, 16, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010023
Illescas-Montes R, Rueda-Fernández M, González-Acedo A, Melguizo-Rodríguez L, García-Recio E, Ramos-Torrecillas J, García-Martínez O. Effect of Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro: A Preliminary Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Potential. Nutrients. 2024; 16(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleIllescas-Montes, Rebeca, Manuel Rueda-Fernández, Anabel González-Acedo, Lucía Melguizo-Rodríguez, Enrique García-Recio, Javier Ramos-Torrecillas, and Olga García-Martínez. 2024. "Effect of Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro: A Preliminary Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Potential" Nutrients 16, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010023
APA StyleIllescas-Montes, R., Rueda-Fernández, M., González-Acedo, A., Melguizo-Rodríguez, L., García-Recio, E., Ramos-Torrecillas, J., & García-Martínez, O. (2024). Effect of Punicalagin and Ellagic Acid on Human Fibroblasts In Vitro: A Preliminary Evaluation of Their Therapeutic Potential. Nutrients, 16(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu16010023








