Effect of the Fermented Soy Q-CAN® Product on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidation in Adults with Cardiovascular Risk, and Canonical Correlations between the Inflammation Biomarkers and Blood Lipids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Study Dietary Supplements
2.3. Laboratory Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Characteristics
3.2. Effect of Fermented Soy Supplementation on Inflammation and Oxidation Markers
3.3. Stratification of Inflammatory and Oxidative Markers by Sex and Baseline BMI
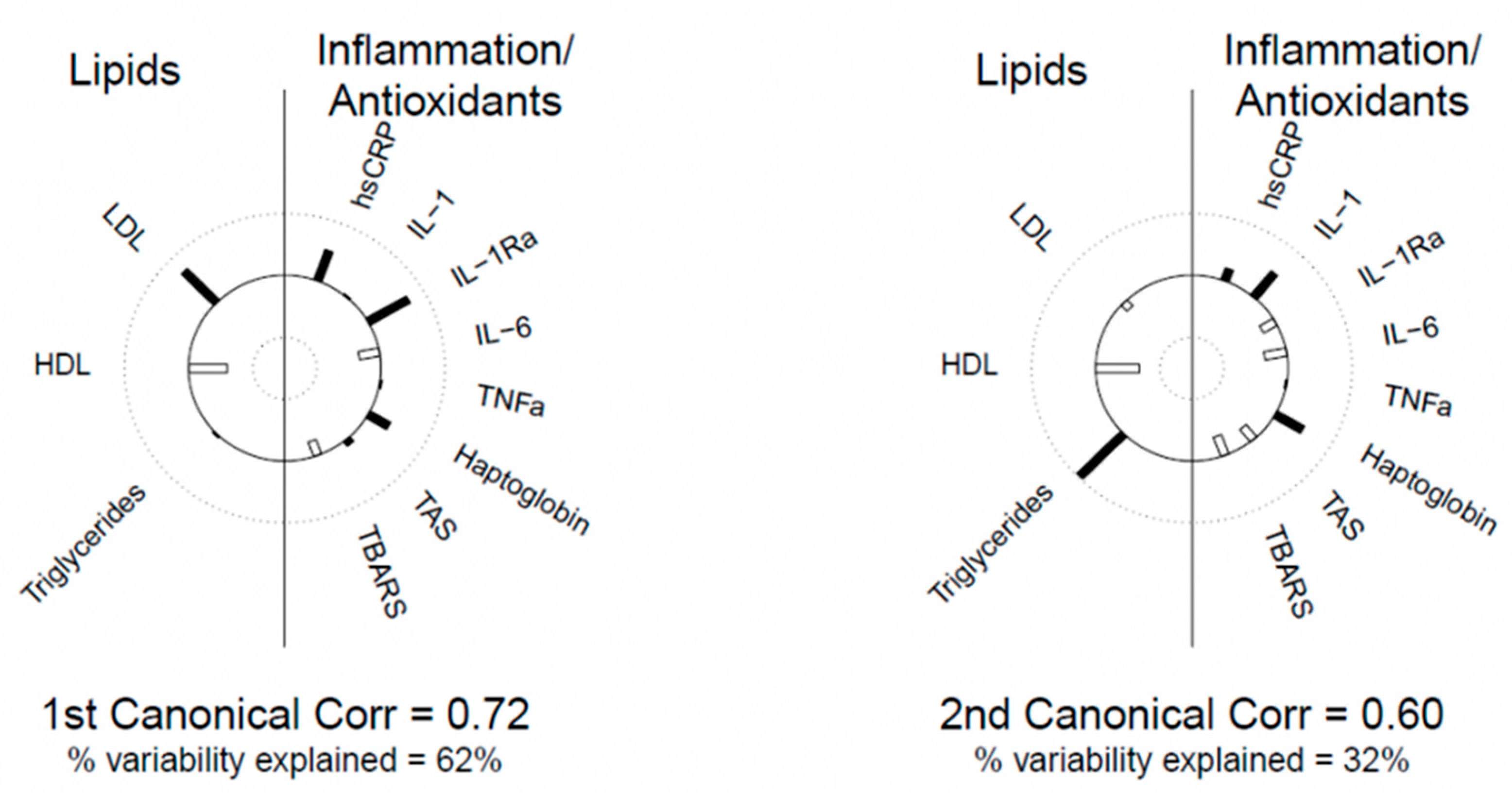
3.4. Canonical Correlation Analysis between Blood Lipids and Inflammation
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bennett, J.M.; Reeves, G.; Billman, G.E.; Sturmberg, J.P. Inflammation-Nature’s Way to Efficiently Respond to All Types of Challenges: Implications for Understanding and Managing “the Epidemic” of Chronic Diseases. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Shi, Y.; Kong, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S. Dietary Inflammatory Index and Its Association with the Prevalence of Coronary Heart Disease among 45,306 US Adults. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragagnolo, F.S.; Álvarez-Rivera, G.; Breitkreitz, M.C.; Ibáñez, E.; Cifuentes, A.; Funari, C.S. Metabolite Profiling of Soy By-Products: A Comprehensive Approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 7321–7341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenstein, A.H.; Jalbert, S.M.; Adlercreutz, H.; Goldin, B.R.; Rasmussen, H.; Schaefer, E.J.; Ausman, L.M. Lipoprotein response to diets high in soy or animal protein with and without isoflavones in moderately hypercholesterolemic subjects. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2002, 22, 1852–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tikkanen, M.J.; Adlercreutz, H. Dietary soy-derived isoflavone phytoestrogens. Could they have a role in coronary heart disease prevention? Biochem. Pharmacol. 2000, 60, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valsecchi, A.E.; Franchi, S.; Panerai, A.E.; Rossi, A.; Sacerdote, P.; Colleoni, M. The soy isoflavone genistein reverses oxidative and inflammatory state, neuropathic pain, neurotrophic and vasculature deficits in diabetes mouse model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 650, 694–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdrengh, M.; Jonsson, I.M.; Holmdahl, R.; Tarkowski, A. Genistein as an anti-inflammatory agent. Inflamm. Res. 2003, 52, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradkar, P.N.; Blum, P.S.; Berhow, M.A.; Baumann, H.; Kuo, S.M. Dietary isoflavones suppress endotoxin-induced inflammatory reaction in liver and intestine. Cancer Lett. 2004, 215, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, T.H.; Wu, W.M.; Hung, C.F.; Wu, W.B.; Chen, B.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of isoflavone powder produced from soybean cake. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 11068–11079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.H.; Shu, X.O.; Chow, W.H.; Xiang, Y.B.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.L.; Cai, Q.; Ji, B.T.; Cai, H.; Rothman, N.; et al. Soy food intake and circulating levels of inflammatory markers in Chinese women. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2012, 112, 996–1004.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicastro, H.L.; Mondul, A.M.; Rohrmann, S.; Platz, E.A. Associations between urinary soy isoflavonoids and two inflammatory markers in adults in the United States in 2005–2008. Cancer Causes Control CCC 2013, 24, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cao, S.; Nagamani, M.; Anderson, K.E.; Grady, J.J.; Lu, L.J. Decreased circulating levels of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in postmenopausal women during consumption of soy-containing isoflavones. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 3956–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christie, D.R.; Grant, J.; Darnell, B.E.; Chapman, V.R.; Gastaldelli, A.; Sites, C.K. Metabolic effects of soy supplementation in postmenopausal Caucasian and African American women: A randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 153.e1–153.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangano, K.M.; Hutchins-Wiese, H.L.; Kenny, A.M.; Walsh, S.J.; Abourizk, R.H.; Bruno, R.S.; Lipcius, R.; Fall, P.; Kleppinger, A.; Kenyon-Pesce, L.; et al. Soy proteins and isoflavones reduce interleukin-6 but not serum lipids in older women: A randomized controlled trial. Nutr. Res. 2013, 33, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadbakht, L.; Atabak, S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Soy protein intake, cardiorenal indices, and C-reactive protein in type 2 diabetes with nephropathy: A longitudinal randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebon, J.; Riesco, E.; Tessier, D.; Dionne, I.J. Additive effects of isoflavones and exercise training on inflammatory cytokines and body composition in overweight and obese postmenopausal women: A randomized controlled trial. Menopause 2014, 21, 869–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, M.; Vahedi, H.; Poustchi, H.; Hekmatdoost, A. Soy isoflavones and cholecalciferol reduce inflammation, and gut permeability, without any effect on antioxidant capacity in irritable bowel syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2019, 34, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanat, S.; Eftekhari, M.H.; Fararouei, M.; Bagheri Lankarani, K.; Massoumi, S.J. Genistein supplementation improves insulin resistance and inflammatory state in non-alcoholic fatty liver patients: A randomized, controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 37, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesinski, G.B.; Reville, P.K.; Mace, T.A.; Young, G.S.; Ahn-Jarvis, J.; Thomas-Ahner, J.; Vodovotz, Y.; Ameen, Z.; Grainger, E.; Riedl, K.; et al. Consumption of soy isoflavone enriched bread in men with prostate cancer is associated with reduced proinflammatory cytokines and immunosuppressive cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2015, 8, 1036–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadadur, M.; Stanczyk, F.Z.; Tseng, C.C.; Kim, L.; Wu, A.H. The Effect of Reduced Dietary Fat and Soy Supplementation on Circulating Adipocytokines in Postmenopausal Women: A Randomized Controlled 2-Month Trial. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beavers, K.M.; Serra, M.C.; Beavers, D.P.; Cooke, M.B.; Willoughby, D.S. Soymilk supplementation does not alter plasma markers of inflammation and oxidative stress in postmenopausal women. Nutr. Res. 2009, 29, 616–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greany, K.A.; Nettleton, J.A.; Wangen, K.E.; Thomas, W.; Kurzer, M.S. Consumption of isoflavone-rich soy protein does not alter homocysteine or markers of inflammation in postmenopausal women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A.; Lang, N.; Peleg, A.; Vigder, F.; Israeli, P.; Gumanovsky, M.; Lupovitz, S.; Elgazi, A.; Ben-Ami, M. Effects of oral soy protein on markers of inflammation in postmenopausal women with mild hypercholesterolemia. Am. Heart J. 2003, 145, e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.A.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Chiavaroli, L.; Viguiliouk, E.; Li, S.S.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Vuksan, V.; Sievenpiper, J.L. Cumulative Meta-Analysis of the Soy Effect Over Time. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan-Borchers, T.A.; Park, J.S.; Chew, B.P.; McGuire, M.K.; Fournier, L.R.; Beerman, K.A. Soy isoflavones modulate immune function in healthy postmenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2006, 83, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverri, E.J.; LaSalle, C.D.; Franke, A.A.; Steinberg, F.M. Soy provides modest benefits on endothelial function without affecting inflammatory biomarkers in adults at cardiometabolic risk. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, D.; Sarkar, S.; Borsingh Wann, S.; Kalita, J.; Manna, P. Current perspectives on the anti-inflammatory potential of fermented soy foods. Food Res. Int. 2022, 152, 110922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- do Prado, F.G.; Pagnoncelli, M.G.B.; de Melo Pereira, G.V.; Karp, S.G.; Soccol, C.R. Fermented Soy Products and Their Potential Health Benefits: A Review. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.M.; Haddad, E.H.; Kaur, A.; Sirirat, R.; Kim, A.Y.; Oda, K.; Rajaram, S.; Sabaté, J. A Non-Probiotic Fermented Soy Product Reduces Total and LDL Cholesterol: A Randomized Controlled Crossover Trial. Nutrients 2021, 13, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugam, S.; Dioletis, E.; Paiva, R.; Fields, M.R.; Weiss, T.R.; Secor, E.R.; Ali, A. Fermented Soy Beverage Q-CAN Plus Consumption Improves Serum Cholesterol and Cytokines. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 560–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asbaghi, O.; Yaghubi, E.; Nazarian, B.; Kelishadi, M.R.; Khadem, H.; Moodi, V.; Naeini, F.; Ghaedi, E. The effects of soy supplementation on inflammatory biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cytokine 2020, 136, 155282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumah, J.; Gonzalez de Mejia, E. Impact of soybean bioactive compounds as response to diet-induced chronic inflammation: A systematic review. Food Res. Int. 2022, 162, 111928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meier, C.A.; Bobbioni, E.; Gabay, C.; Assimacopoulos-Jeannet, F.; Golay, A.; Dayer, J.M. IL-1 receptor antagonist serum levels are increased in human obesity: A possible link to the resistance to leptin? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 1184–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luotola, K. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist (IL-1Ra) Levels and Management of Metabolic Disorders. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicklin, M.J.; Hughes, D.E.; Barton, J.L.; Ure, J.M.; Duff, G.W. Arterial inflammation in mice lacking the interleukin 1 receptor antagonist gene. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 191, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uusitupa, M.; Hermansen, K.; Savolainen, M.J.; Schwab, U.; Kolehmainen, M.; Brader, L.; Mortensen, L.S.; Cloetens, L.; Johansson-Persson, A.; Onning, G.; et al. Effects of an isocaloric healthy Nordic diet on insulin sensitivity, lipid profile and inflammation markers in metabolic syndrome—A randomized study (SYSDIET). J. Intern. Med. 2013, 274, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, D.J.; Kendall, C.W.; Connelly, P.W.; Jackson, C.J.; Parker, T.; Faulkner, D.; Vidgen, E. Effects of high- and low-isoflavone (phytoestrogen) soy foods on inflammatory biomarkers and proinflammatory cytokines in middle-aged men and women. Metab. Clin. Exp. 2002, 51, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezazadegan, M.; Mirjalili, F.; Clark, C.C.T.; Rouhani, M.H. The effect of soya consumption on inflammatory biomarkers: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 125, 780–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, M.; Ghasemi, A.; Baradaran, H.R.; Mollanoroozy, E.; Gholami, A. Beneficial effect of soy isoflavones and soy isoflavones plus soy protein on serum concentration of C-reactive protein among postmenopausal women: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2021, 59, 102715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajerska, J.; Łagowska, K.; Mori, M.; Reguła, J.; Skoczek-Rubińska, A.; Toda, T.; Mizuno, N.; Yamori, Y. A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials of the Effects of Soy Intake on Inflammatory Markers in Postmenopausal Women. J. Nutr. 2022, 152, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Mollanoroozy, E.; Reza Baradaran, H.; Hariri, M. The efficacy of soy isoflavones combined with soy protein on serum concentration of interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-α among post-menopausal women? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2022, 49, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, G. The Antioxidant Role of Soy and Soy Foods in Human Health. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, S. The biochemistry, chemistry and physiology of the isoflavones in soybeans and their food products. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2010, 8, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer, D.J.; Vinchi, F.; Ingoglia, G.; Tolosano, E.; Buehler, P.W. Haptoglobin, hemopexin, and related defense pathways-basic science, clinical perspectives, and drug development. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKellar, M.; Vigerust, D.J. Role of Haptoglobin in Health and Disease: A Focus on Diabetes. Clin. Diabetes Publ. Am. Diabetes Assoc. 2016, 34, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- di Masi, A.; De Simone, G.; Ciaccio, C.; D’Orso, S.; Coletta, M.; Ascenzi, P. Haptoglobin: From hemoglobin scavenging to human health. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 73, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Due, A.; Toubro, S.; Stender, S.; Skov, A.R.; Astrup, A. The effect of diets high in protein or carbohydrate on inflammatory markers in overweight subjects. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2005, 7, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melamed-Frank, M.; Lache, O.; Enav, B.I.; Szafranek, T.; Levy, N.S.; Ricklis, R.M.; Levy, A.P. Structure-function analysis of the antioxidant properties of haptoglobin. Blood 2001, 98, 3693–3698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarlin, B.K.; Venable, A.S.; Henning, A.L.; Prado, E.A.; Best Sampson, J.N.; Vingren, J.L.; Hill, D.W. Natural cocoa consumption: Potential to reduce atherogenic factors? J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrati, M.; Razza, C.; Biasini, C.; Di Nunzio, C.; Vancini, A.; Dall’Asta, M.; Lovotti, G.; Trevisi, E.; Rossi, F.; Cavanna, L. Mediterranean Diet Affects Blood Circulating Lipid-Soluble Micronutrients and Inflammatory Biomarkers in a Cohort of Breast Cancer Survivors: Results from the SETA Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichanthiran, K.; Ma, Z.F.; Zhang, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, C.W.; Muhammad, S.; Aglago, E.K.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Pan, B. Phytochemical Profile of Brown Rice and Its Nutrigenomic Implications. Antioxidants 2018, 7, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation during the life cycle of the atherosclerotic plaque. Cardiovasc. Res. 2021, 117, 2525–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henein, M.Y.; Vancheri, S.; Longo, G.; Vancheri, F. The Role of Inflammation in Cardiovascular Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danesh, J. Smoldering Arteries? Low-grade Inflammation and Coronary Heart Disease. JAMA 1999, 282, 2169–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laessig, R.E.; Duckett, E.J. Canonical correlation analysis: Potential for environmental health planning. Am. J. Public Health 1979, 69, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galié, S.; García-Gavilán, J.; Papandreou, C.; Camacho-Barcía, L.; Arcelin, P.; Palau-Galindo, A.; Rabassa, A.; Bulló, M. Effects of Mediterranean Diet on plasma metabolites and their relationship with insulin resistance and gut microbiota composition in a crossover randomized clinical trial. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 3798–3806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Tai, P.; Kou, F.; Jia, W.; Han, K.; Liu, M.; He, Y. Canonical Correlation Analysis on the Association between Sleep Quality and Nutritional Status Among Centenarians in Hainan. Front. Public Health 2020, 8, 585207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Loscalzo, J.; Ridker, P.M.; Farkouh, M.E.; Hsue, P.Y.; Fuster, V.; Hasan, A.A.; Amar, S. Inflammation, Immunity, and Infection in Atherothrombosis: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, B.M.; MacFadyen, J.G.; Thuren, T.; Libby, P.; Glynn, R.J.; Ridker, P.M. Inhibition of Interleukin-1β and Reduction in Atherothrombotic Cardiovascular Events in the CANTOS Trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1660–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, M.S.; Yu, O.K.; Cha, Y.S.; Park, T.S. Korean traditional Chungkookjang improves body composition, lipid profiles and atherogenic indices in overweight/obese subjects: A double-blind, randomized, crossover, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 1116–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.H.; Green-Johnson, J.M.; Buckley, N.D.; Lin, Q.Y. Bioactivity of soy-based fermented foods: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 223–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayachandran, M.; Xu, B. An insight into the health benefits of fermented soy products. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 362–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.; Takayanagi, T.; Harada, K.; Sawada, S.; Ishikawa, F. Bioavailability of isoflavones after ingestion of soy beverages in healthy adults. J. Nutr. 2006, 136, 2291–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Champagne, C.P.; Tompkins, T.A.; Buckley, N.D.; Green-Johnson, J.M. Effect of fermentation by pure and mixed cultures of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus helveticus on isoflavone and B-vitamin content of a fermented soy beverage. Food Microbiol. 2010, 27, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, C.; Gleddie, S.; Xiao, C.W. Soybean Bioactive Peptides and Their Functional Properties. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Nakamoto, M.; Shuto, E.; Hata, A.; Aki, N.; Shikama, Y.; Bando, Y.; Ichihara, T.; Minamigawa, T.; Kuwamura, Y.; et al. Associations between intake of dietary fermented soy food and concentrations of inflammatory markers: A cross-sectional study in Japanese workers. J. Med. Investig. 2018, 65, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura, H.; Katsuura-Kamano, S.; Nakamoto, M.; Yamaguchi, M.; Fujioka, M.; Iwasaki, Y.; Arisawa, K. Inverse association between soy food consumption, especially fermented soy products intake and soy isoflavone, and arterial stiffness in Japanese men. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariri, M.; Salehi, R.; Feizi, A.; Mirlohi, M.; Ghiasvand, R.; Habibi, N. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial on probiotic soy milk and soy milk: Effects on epigenetics and oxidative stress in patients with type II diabetes. Genes Nutr. 2015, 10, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Feng, Z. Fermented soybean foods: A review of their functional components, mechanism of action and factors influencing their health benefits. Food Res. Int. 2022, 158, 111575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Du, B.; Xu, B. A systematic, comparative study on the beneficial health components and antioxidant activities of commercially fermented soy products marketed in China. Food Chem. 2015, 174, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, J.N.; Kucuk, O.; Djuric, Z.; Sarkar, F.H. Soy isoflavone supplementation in healthy men prevents NF-kappa B activation by TNF-alpha in blood lymphocytes. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2001, 30, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Y.; Zhou, J. The protective activity of natural flavonoids against osteoarthritis by targeting NF-κB signaling pathway. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1117489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.S.; Yang, W.S.; Kim, C.H. Beneficial Effects of Soybean-Derived Bioactive Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Chen, J.; Su, C.; Zha, L. Advances in the Bioactivities of Phytochemical Saponins in the Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioletis, E.; Paiva, R.S.; Kaffe, E.; Secor, E.R.; Weiss, T.R.; Fields, M.R.; Ouyang, X.; Ali, A. The fermented soy beverage Q-CAN® plus induces beneficial changes in the oral and intestinal microbiome. BMC Nutr. 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, C.H.; Oh, J.; Lim, J.S.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.S. Fermented Soy Products: Beneficial Potential in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Foods 2021, 10, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, T.T.; Trang, T.T.; Hai, T.T. Effectiveness of germinated brown rice on metabolic syndrome: A randomized control trial in Vietnam. AIMS Public Health 2020, 7, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sequence 1 Fermented Soy → Control | Sequence 2 Control → Fermented Soy | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | ||
| Age, y | 50.3 (12.3) | 52.5 (14.8) | 0.68 1 |
| Sex | |||
| Female, n (%) | 8 (66.7) | 13 (86.7) | |
| Male, n (%) | 4 (33.3) | 2 (13.3) | 0.36 2 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 32.3 (9.0) | 32.2 (5.9) | 0.98 1 |
| LDL-C, mmol/L | 3.03 (0.68) | 3.07 (1.17 | 0.93 1 |
| HDL-C, mmol/L | 1.36 (0.31) | 1.41 (0.30) | 0.71 1 |
| Triglycerides, mmol/L | 1.35 (0.56) | 1.51 (0.36) | 0.53 3 |
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | ||
| High-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), mg/L | 5.45 (1.10, 9.85) | 3.90 (2.05, 7.15) | 0.999 3 |
| Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), pg/mL | 0.07 (0.02, 0.11) | 0.08 (0.03, 0.12 | 0.598 3 |
| Interleukin-1-receptor agonist (IL-1Ra), pg/mL | 771 (565, 832) | 340 (309, 482) | 0.143 3 |
| Interleukin-6 (IL-6), pg/mL | 2.92 (0.56, 5.04) | 0.50 (0.20, 2.44) | 0.162 3 |
| Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), pg/mL | 1.33 (0.63, 1.77) | 1.15 (0.55, 1.99) | 0.815 3 |
| Haptoglobin, pg/mL | 88.1 (57.1, 110.5) | 108.1 (88.1, 129.5) | 0.356 3 |
| Total antioxidant status (TAS), mmol Trolox eq/L | 1.75 (1.61, 1.92) | 1.83 (1.68, 2.05) | 0.500 3 |
| Thiobarbituric reactive substances (TBARS), μM | 0.58 (0.54, 0.64) | 0.55 (0.43, 0.62) | 0.298 3 |
| Fermented Soy Supplement | Control Supplement | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variables 3 | Baseline | End of Study | Ratio (End/Baseline) | Within p Value 1 | Baseline | End of Study | Ratio (End/Baseline) | Within p Value 1 | Between p Value 2 |
| Mean (95% CI) | Mean (95% CI) | ||||||||
| hsCRP, mg/L | 4.07 (2.11, 7.86) | 5.02 (2.62, 9.62) | 1.23 (0.98, 1.54) | 0.068 | 3.54 (1.83, 6.86) | 3.76 (1.96, 7.21) | 1.06 (0.85, 1.33) | 0.606 | 0.346 |
| IL-1β, pg/mL | 0.05 (0.04, 0.08) | 0.07 (0.05, 0.10) | 1.30 (0.68, 2.49) | 0.278 | 0.06 (0.04, 0.09) | 0.08 (0.05, 0.12) | 1.27 (0.66, 2.41) | 0.336 | 0.929 |
| IL-1Ra, pg/mL | 475 (301, 749) | 533 (338, 839) | 1.12 (1.03, 1.22) | 0.011 | 411 (261, 647) | 397 (252, 625) | 0.97 (0.88, 1.06) | 0.450 | 0.022 |
| IL-6, pg/mL | 1.49 (0.68, 3.25) | 3.32 (1.52, 7.28) | 2.23 (1.25, 3.97) | 0.007 | 1.86 (0.86, 4.04) | 1.88 (0.87, 4.08) | 1.01 (0.58, 1.78) | 0.971 | 0.052 |
| TNF-α, pg/mL | 0.89 (0.69, 1.15) | 0.77 (0.59, 1.00) | 0.86 (0.64, 1.15) | 0.175 | 0.96 (0.74, 1.24) | 0.83 (0.63, 1.08) | 0.86 (0.64, 1.16) | 0.194 | 0.968 |
| Haptoglobinpg/mL | 88.6 (54.9, 143.2) | 98.2 (60.8, 158.6) | 1.11 (0.89, 1.37) | 0.339 | 86.3 (53.6, 140.6) | 101.4 (62.6, 164.2) | 1.17 (0.93, 1.46) | 0.168 | 0.731 |
| TAS, mmol Trolox eq/L | 1.93 (1.80, 2.08) | 2.06 (1.92, 1.22) | 1.07 (1.01, 1.13) | 0.028 | 1.88 (1.75, 2.02) | 1.93 (1.80, 2.08) | 1.03 (0.97, 1.09) | 0.348 | 0.370 |
| TBARS, μM | 0.60 (0.51, 0.70) | 0.58 (0.50, 0.68) | 0.97 (0.87, 1.08) | 0.570 | 0.60 (0.51, 0.70) | 0.66 (0.56, 0.77) | 1.10 (0.99, 1.23) | 0.083 | 0.1041 |
| Fermented Soy Supplement | Control Supplement | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | End of Study | Within p Value 1 | Baseline | End of Study | Within p Value 1 | Between p Value 2 | ||
| Mean (95% CI) | Mean (95% CI) | |||||||
| Stratification by Sex | ||||||||
| TNF-α, pg/mL | Female | 0.89 (0.66, 1.19) | 0.73 (0.54, 0.99) | 0.021 | 0.89 (0.66, 1.19) | 0.88 (0.65, 1.20) | 0.950 | 0.104 |
| Male | 1.30 (0.93, 1.81) | 1.32 (0.63, 2.78) | 0.965 | 2.05 (1.47, 2.85) | 1.04 (0.49, 2.17) | 0.143 | 0.271 | |
| TAS status, mmol Trolox eq/L | Female | 1.91 (1.78, 2.06) | 1.98 (1.85, 2.13) | 0.232 | 1.81 (1.69, 1.94) | 1.89 (1.76,2.02) | 0.185 | 0.911 |
| Male | 1.91 (1.64, 2.25) | 2.31 (1.97, 2.71) | 0.032 | 2.08 (1.78, 2.44) | 2.01 (1.72, 2.36) | 0.658 | 0.063 | |
| Stratification by BMI | ||||||||
| Haptoglobin, pg/mL | BMI < 30 | 71.1 (30, 165) | 73 (31, 169) | 0.879 | 58 (25, 136) | 93 (40, 218) | 0.006 | 0.046 |
| BMI ≥ 30 | 100 (76, 130) | 121 (92, 158 | 0.121 | 123 (93, 161) | 99 (76, 129) | 0.090 | 0.026 | |
| LDL-C | HDL-C | Triglycerides | |
|---|---|---|---|
| hs-CRP | 0.292 | −0.281 | 0.145 |
| IL-1β | −0.148 | −0.285 | 0.250 |
| IL-1Ra | 0.326 | −0.257 | −0.150 |
| IL-6 | −0.195 | 0.246 | −0.231 |
| TNF-α | −0.006 | −0.017 | −0.022 |
| Haptoglobin | 0.224 | −0.311 | 0.316 |
| TAS | 0.154 | 0.114 | −0.117 |
| TBARS | −0.085 | 0.254 | −0.193 |
| Canonical Variate 1 | Canonical Variate 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| Blood lipids | ||
| LDL-C | 0.715 | −0.133 |
| HDL-C | −0.605 | −0.674 |
| Triglycerides | 0.030 | 0.971 |
| Inflammation–oxidation markers | ||
| hs-CRP | 0.518 | −0.206 |
| IL-1 | 0.022 | 0.503 |
| IL-1Ra | 0.726 | −0.277 |
| IL-6 | −0.324 | −0.353 |
| TNF-α | 0.029 | −0.025 |
| Haptoglobin | 0.369 | 0.488 |
| TAS | 0.096 | −0.257 |
| TBARS | −0.251 | −0.335 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jung, S.M.; Kaur, A.; Amen, R.I.; Oda, K.; Rajaram, S.; Sabatè, J.; Haddad, E.H. Effect of the Fermented Soy Q-CAN® Product on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidation in Adults with Cardiovascular Risk, and Canonical Correlations between the Inflammation Biomarkers and Blood Lipids. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143195
Jung SM, Kaur A, Amen RI, Oda K, Rajaram S, Sabatè J, Haddad EH. Effect of the Fermented Soy Q-CAN® Product on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidation in Adults with Cardiovascular Risk, and Canonical Correlations between the Inflammation Biomarkers and Blood Lipids. Nutrients. 2023; 15(14):3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143195
Chicago/Turabian StyleJung, Sarah M., Amandeep Kaur, Rita I. Amen, Keiji Oda, Sujatha Rajaram, Joan Sabatè, and Ella H. Haddad. 2023. "Effect of the Fermented Soy Q-CAN® Product on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidation in Adults with Cardiovascular Risk, and Canonical Correlations between the Inflammation Biomarkers and Blood Lipids" Nutrients 15, no. 14: 3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143195
APA StyleJung, S. M., Kaur, A., Amen, R. I., Oda, K., Rajaram, S., Sabatè, J., & Haddad, E. H. (2023). Effect of the Fermented Soy Q-CAN® Product on Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidation in Adults with Cardiovascular Risk, and Canonical Correlations between the Inflammation Biomarkers and Blood Lipids. Nutrients, 15(14), 3195. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15143195







