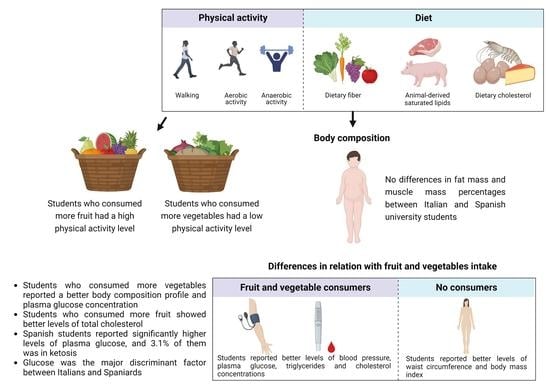
Body Composition and Metabolic Status of Italian and Spanish University Students: Relationship with Fruit and Vegetable Consumption
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Recruitment, and Data Collection
2.2. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet
2.3. Physical Activity
2.4. Anthropometric, Body Composition and Blood Pressure Measurements
2.5. Capillary Blood Sampling
2.6. Food Consumption Analysis
2.7. Statistics
3. Results
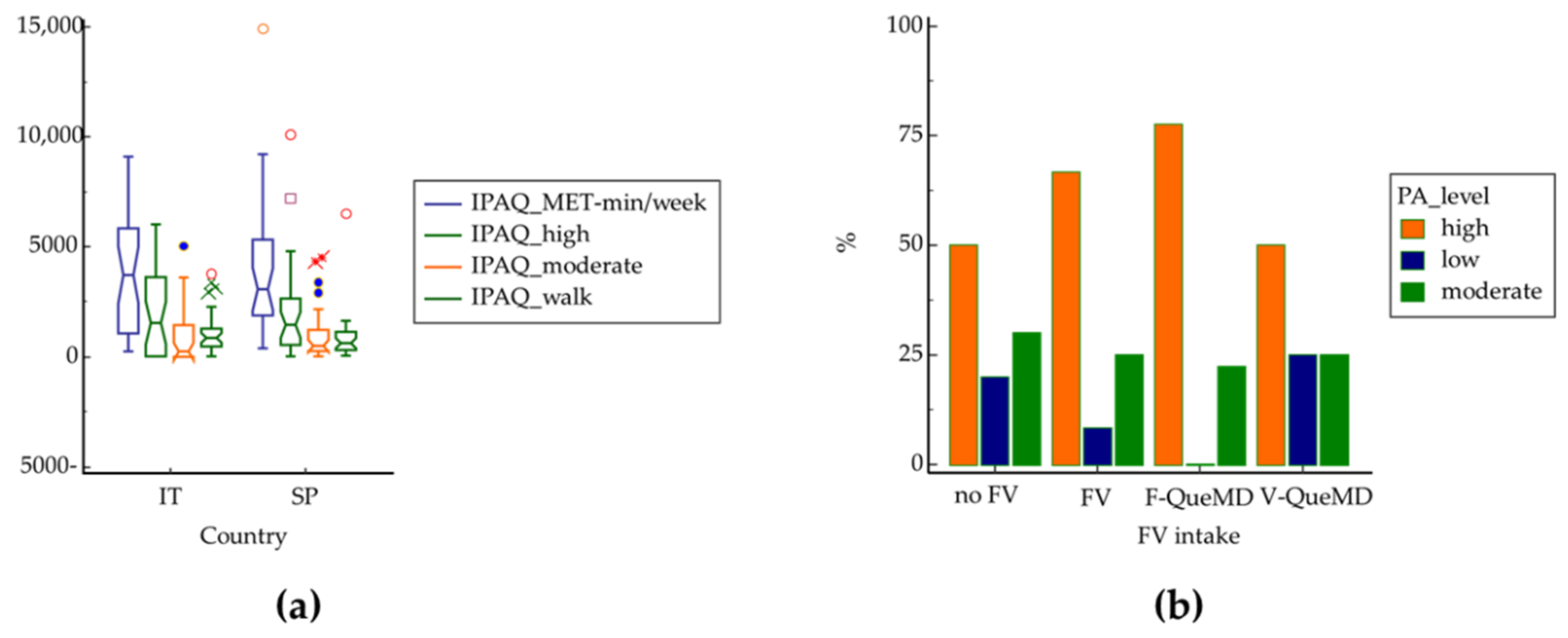
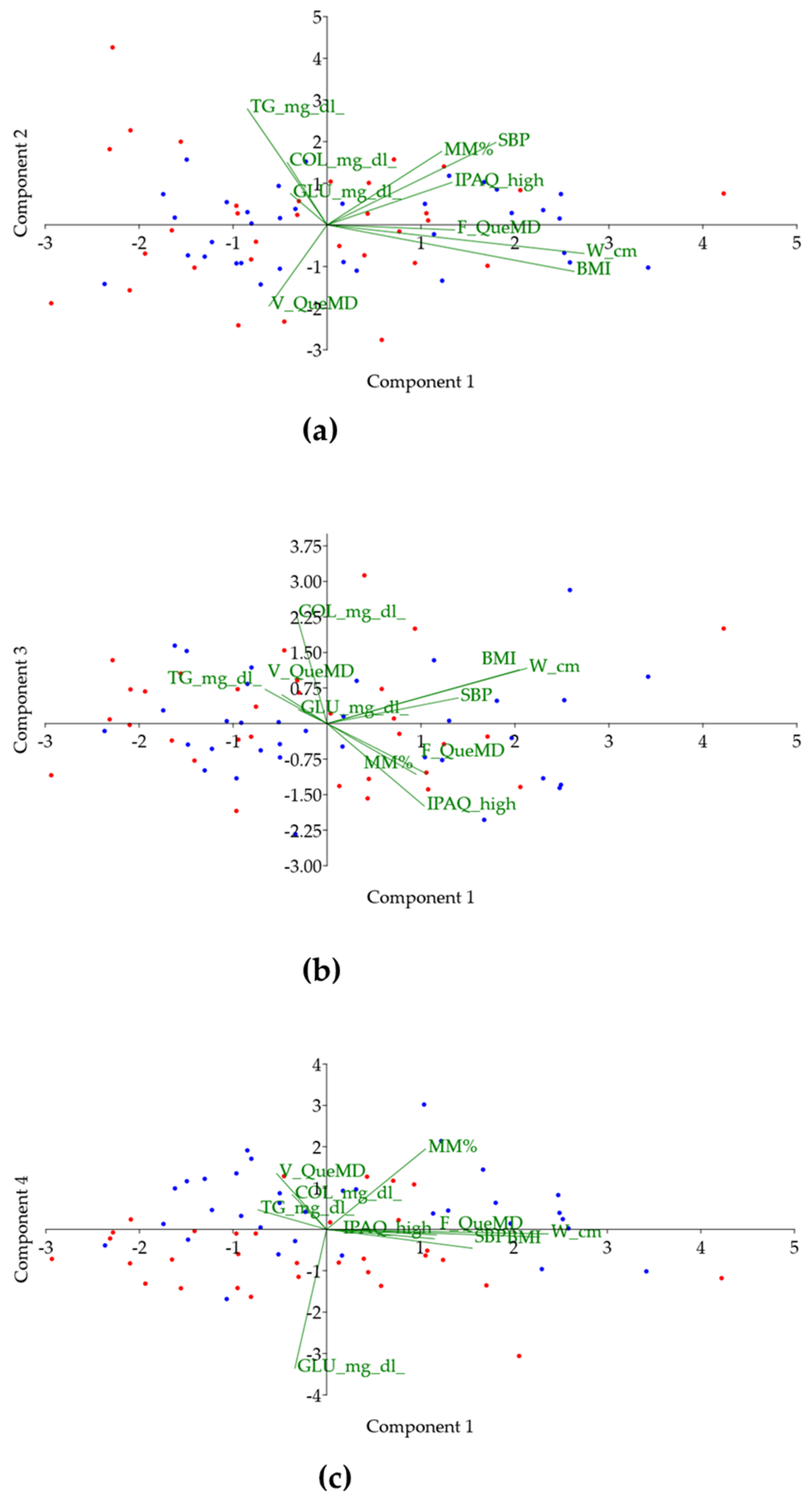
3.1. Differences between Italians and Spaniards
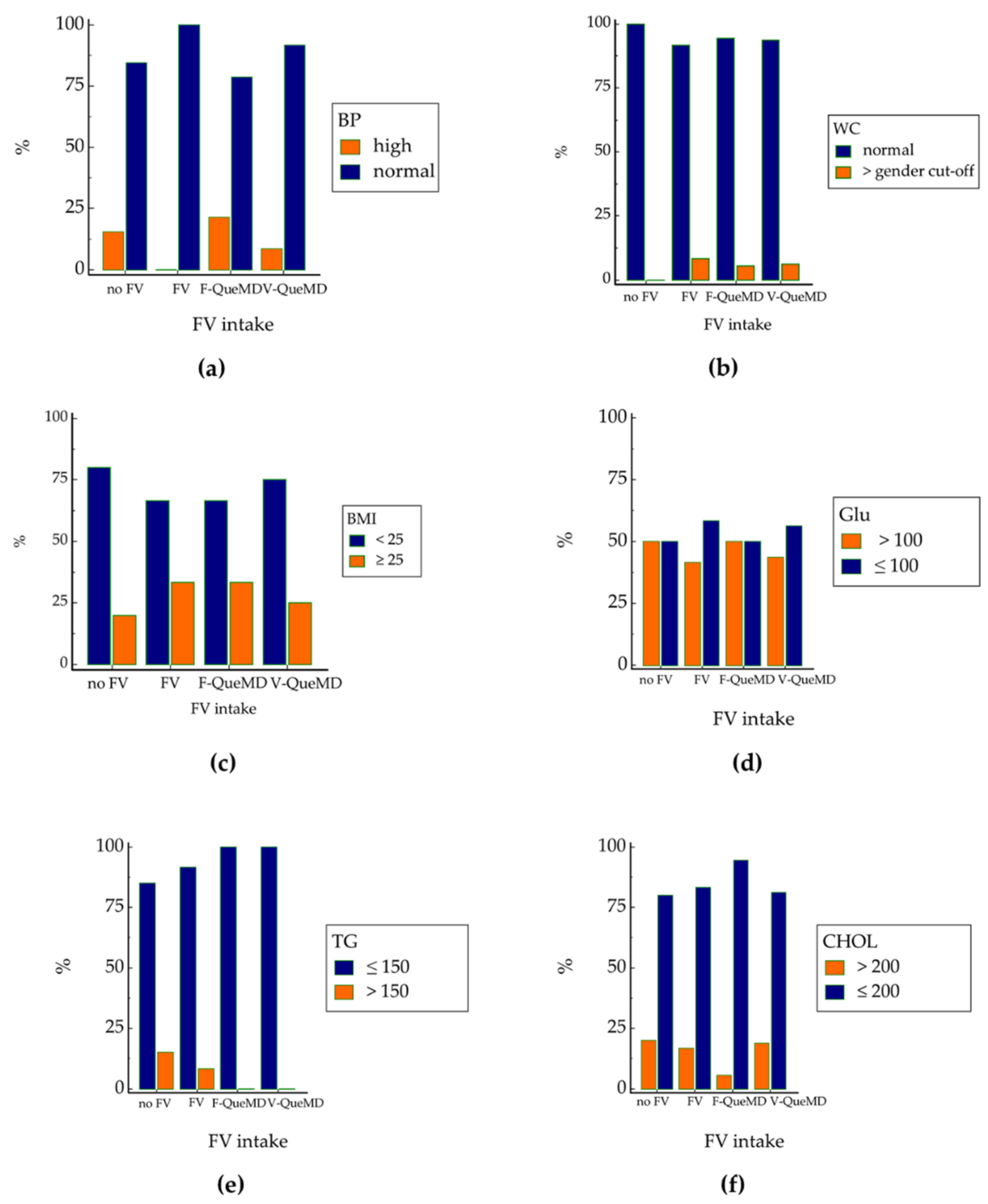
3.2. Fruit and Vegetable Intakes and Metabolic Risk Factors Prevalence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Finicelli, M.; Squillaro, T.; Di Cristo, F.; Di Salle, A.; Melone, M.A.B.; Galderisi, U.; Peluso, G. Metabolic Syndrome, Mediterranean Diet, and Polyphenols: Evidence and Perspectives. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 5807–5826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiva-Blanch, G.; Badimon, L. Effects of Polyphenol Intake on Metabolic Syndrome: Current Evidences from Human Trials. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 5812401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vogli, R.; Kouvonen, A.; Gimeno, D. The Influence of Market Deregulation on Fast Food Consumption and Body Mass Index: A Cross-National Time Series Analysis. Bull. World Health Organ. 2014, 92, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Body Mass Index; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, T.; Purohit, G.; Nair, S.P.; Patel, B.; Rawal, Y.; Shah, R.M. Assessment of Obesity, Overweight and Its Association with the Fast Food Consumption in Medical Students. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2014, 8, CC05–CC07. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, P.; Cameron, D.; Epton, T.; Webb, T.L.; Harris, P.R.; Millings, A.; Sheeran, P. A Randomized Controlled Trial of a Brief Online Intervention to Reduce Alcohol Consumption in New University Students: Combining Self-Affirmation, Theory of Planned Behaviour Messages, and Implementation Intentions. Br. J. Health Psychol. 2018, 23, 108–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiraki, M.; Grammatikopoulou, M.G.; Stylianou, C.; Tsigga, M. Nutrition Transition and Health Status of Cretan Women: Evidence from Two Generations. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosso, G.; Marventano, S.; Yang, J.; Micek, A.; Pajak, A.; Scalfi, L.; Galvano, F.; Kales, S.N. A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis on Evidence of Mediterranean Diet and Cardiovascular Disease: Are Individual Components Equal? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 3218–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belahsen, R. Nutrition Transition and Food Sustainability. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2014, 73, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengpid, S.; Peltzer, K. Prevalence and Correlates of Multiple Behavioural Risk Factors of Non-Communicable Diseases among University Students from 24 Countries. J. Public Health 2021, 43, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracale, R.; Vaccaro, C.M.; Coletta, V.; Cricelli, C.; Gamaleri, F.C.; Parazzini, F.; Carruba, M. Nutrition Behaviour and Compliance with the Mediterranean Diet Pyramid Recommendations: An Italian Survey-Based Study. Eat. Weight. Disord. 2020, 25, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Blanco, C.; Rodríguez-Almagro, J.; Onieva-Zafra, M.D.; Parra-Fernández, M.L.; Prado-Laguna, M.D.C.; Hernández-Martínez, A. Physical Activity and Sedentary Lifestyle in University Students: Changes during Confinement Due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, E6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Tong, X.; Yu, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Cui, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, N.; et al. Obesity and Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults: A Cross-Sectional Study in Shanghai, China. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruano, C.; Lucumi, E.; Albán, J.; Arteaga, S.; Fors, M. Obesity and Cardio-Metabolic Risk Factors in Ecuadorian University Students. First Report, 2014–2015. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2018, 12, 917–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukács, A.; Horváth, E.; Máté, Z.; Szabó, A.; Virág, K.; Papp, M.; Sándor, J.; Ádány, R.; Paulik, E. Abdominal Obesity Increases Metabolic Risk Factors in Non-Obese Adults: A Hungarian Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Public Health 2019, 19, 1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, E.; Tabares, M.; Baile, J.I.; Salazar, J.G.; Zepeda, A.P. Eating Behaviors Associated with Weight Gain among University Students Worldwide and Treatment Interventions: A Systematic Review. J. Am. Coll. Health 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, P.; Peluso, I.; Villaño Valencia, D. Alcohol Consumption by Italian and Spanish University Students in Relation to Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet and to the Food Neophobia: A Pilot Study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Sang, S.; McClements, D.J.; Chen, L.; Long, J.; Jiao, A.; Jin, Z.; Qiu, C. Polyphenols as Plant-Based Nutraceuticals: Health Effects, Encapsulation, Nano-Delivery, and Application. Foods 2022, 11, 2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, R.M.; Mohan, V. Changing Definitions of Metabolic Syndrome. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, E.; Monaghan, M.; Sreenivasan, S. Pathophysiology of the Metabolic Syndrome. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarup, S.; Goyal, A.; Grigorova, Y.; Zeltser, R. Metabolic Syndrome; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-González, M.A.; García-Arellano, A.; Toledo, E.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Corella, D.; Covas, M.I.; Schröder, H.; Arós, F.; Gómez-Gracia, E.; et al. A 14-Item Mediterranean Diet Assessment Tool and Obesity Indexes among High-Risk Subjects: The PREDIMED Trial. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Milias, G.A.; Pitsavos, C.; Stefanadis, C. MedDietScore: A Computer Program That Evaluates the Adherence to the Mediterranean Dietary Pattern and Its Relation to Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2006, 83, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagiotakos, D.B.; Pitsavos, C.; Chrysohoou, C.; Stefanadis, C.; Toutouzas, P. Risk Stratification of Coronary Heart Disease in Greece: Final Results from the CARDIO2000 Epidemiological Study. Prev. Med. 2002, 35, 548–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnagnarella, P.; Dragà, D.; Misotti, A.M.; Sieri, S.; Spaggiari, L.; Cassano, E.; Baldini, F.; Soldati, L.; Maisonneuve, P. Validation of a Short Questionnaire to Record Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet: An Italian Experience. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2018, 28, 1140–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach-Faig, A.; Berry, E.M.; Lairon, D.; Reguant, J.; Trichopoulou, A.; Dernini, S.; Medina, F.X.; Battino, M.; Belahsen, R.; Miranda, G.; et al. Mediterranean Diet Pyramid Today. Science and Cultural Updates. Public Health Nutr. 2011, 14, 2274–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Questionario Sull’attività Fisica Quotidiana (IPAQ). 2. Available online: http://www.societaitalianadiendocrinologia.it/public/pdf/questionario_ipaq.pdf (accessed on 10 October 2021).
- Lohman, T.G.; Roche, A.F.; Martorell, R. Anthropometric Standardization Reference Manual; Human Kinetics Books: Champaign, IL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Dossier Scientifico Delle Linee Guida per Una Sana Alimentazione (Edizione 2018). Available online: https://www.crea.gov.it/en/web/alimenti-e-nutrizione/-/dossier-scientifico-linee-guida-per-una-sana-alimentazione-2018 (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Duren, D.L.; Sherwood, R.J.; Czerwinski, S.A.; Lee, M.; Choh, A.C.; Siervogel, R.M.; Cameron Chumlea, W. Body Composition Methods: Comparisons and Interpretation. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2008, 2, 1139–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siri, W.E. The Gross Composition of the Body. Adv. Biol. Med. Phys. 1956, 4, 239–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biohcemical Systems International s.r.l. MultiCare in User’s Manual In-Vitro Diagnostic Aid for Self Testing. 2013. Available online: https://www.gimaitaly.com/DocumentiGIMA/Manuali/EN/M23967EN.pdf (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Roche Diabetes Care GmbH ACCU-CHEK Softclix AST Cap Alternate Site Testing (AST) Cap for Obtaining Blood from a Non-Fingertip Testing Site 2017. Available online: https://www.rochediabetescaremea.com/fr/node/7281 (accessed on 27 September 2021).
- Biochemical Systems International s.r.l. Reagent Strips for the Determination of Glucose Concentration in Whole Blood. 2011. Available online: http://www.gimaitaly.com (accessed on 28 July 2021).
- Gima 23972 CHOLESTEROL STRIPS—for Code 23965/66/67 Owner’s Manual | Manualzz. Available online: https://manualzz.com/doc/61344621/gima-23972-cholesterol-strips---for-code-23965-66-67-owne (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- Strisce Reattive per la Determinazione Della Concentrazione dei Trigliceridi. Available online: https://www.gimaitaly.com/DocumentiGIMA/Manuali/IT/M23973IT.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Menarini Diagnostics s.r.l. GlucoMen Aero 2K User Manual. 2019. Available online: https://www.glucomen.co.uk (accessed on 28 September 2021).
- Atlante Fotografico delle Porzioni degli Alimenti per Adulti. Available online: https://www.scottibassani.it/atlante-fotografico-delle-porzioni-degli-alimenti/ (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- AlimentiNUTrizione—Ricerca per Alimento. Available online: https://www.alimentinutrizione.it/tabelle-nutrizionali/ricerca-per-alimento (accessed on 16 July 2022).
- LIPIDI. Available online: https://sinu.it/2019/07/09/lipidi/ (accessed on 27 July 2022).
- Poscia, A.; Teleman, A.A.; Azzolini, E.; de Waure, C.; Maged, D.; Virdis, A.; Ricciardi, W.; Di Pietro, M.L. Eating Episode Frequency and Fruit and Vegetable Consumption among Italian University Students. Ann. Dell’istituto Super. Sanità 2017, 53, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias López, M.T.; Cuesta Santa Teresa, E.; Sáez Crespo, A. Comparative study of habits in students before and during the university in northwest area of Madrid. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 31, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Socarrás, V.; Aguilar Martínez, A. Food habits and health-related behaviors in a university population. Nutr. Hosp. 2014, 31, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazzeri, G.; Pammolli, A.; Azzolini, E.; Simi, R.; Meoni, V.; de Wet, D.R.; Giacchi, M.V. Association between Fruits and Vegetables Intake and Frequency of Breakfast and Snacks Consumption: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutr. J. 2013, 12, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Moncada, R.; Navarro, A.; Martí, A.; Fernández-Sáez, J.; Blanes, M. Do the Spanish University Students Follow Mediterranean Dietary Patterns? Nutr. Hosp. 2012, 27, 1952–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledo-Varela, M.T.; de Luis Román, D.A.; González-Sagrado, M.; Izaola Jauregui, O.; Conde Vicente, R.; Aller de la Fuente, R. Características Nutricionales y Estilo de Vida En Universitarios. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 814–818. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nyanchoka, M.A.; van Stuijvenberg, M.E.; Tambe, A.B.; Zuma, M.K.; Mbhenyane, X.G. Fruit and Vegetable Consumption Patterns and Risk of Chronic Diseases of Lifestyle among University Students in Kenya. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, V.; Vizdiklar, C.; Akici, A.; Akman, M.; Gogas Yavuz, D.; Altikardes, Z.A.; Kucukguzel, S.G.; Topcu, M.; Aysevinc, B.; Fak, A.S. Evaluation of Health-Related Knowledge, Attitudes, and Behaviors of Undergraduate Students by Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Prim. Health Care Res. Dev. 2021, 22, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guedes, D.P.; Silva, A.L.D.S. Exercise and Fruit/Vegetable Intake, and Their Associations with Body Weight Status in University Students. Nutr. Hosp. 2021, 38, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Gunn, P.; Gibson, S. Waist-to-Height Ratio Is a Better Screening Tool than Waist Circumference and BMI for Adult Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwell, M.; Hsieh, S.D. Six Reasons Why the Waist-to-Height Ratio Is a Rapid and Effective Global Indicator for Health Risks of Obesity and How Its Use Could Simplify the International Public Health Message on Obesity. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2005, 56, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, G.; Zanaboni, A.M.; Gaito, S.; Sirtori, C.R. Waist-to-Height Ratio Is a Highly Sensitive Index for the Metabolic Syndrome in a Mediterranean Population. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2009, 7, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgoon, M.J.; Al-Zahrani, M.H.; Alkhattabi, N.A.; Alzahrani, N.A. The Correlation between Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Young Female University Students in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2019, 13, 2399–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, O.; Shahraki, M.; Shahraki, T. Obesity Indices in Relation to Lipid Abnormalities among Medical University Students in Zahedan, South-East of Iran. Int. J. Prev. Med. 2019, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ogawa, S.; Tayama, J.; Sagara, I.; Takeoka, A.; Bernick, P.; Kawano, T.; Abiru, N.; Hayashida, M.; Shirabe, S. Intra-Abdominal Fat Accumulation Is an Important Predictor of Metabolic Syndrome in Young Adults. Medicine 2020, 99, e22202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haq, I.U.; Mariyam, Z.; Zeb, F.; Jiang, P.; Wu, X.; Shah, J.; Xu, C.; Zhou, M.; Feng, Q.; Li, M. Identification of Body Composition, Dietary Patterns and Its Associated Factors in Medical University Students in China. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2020, 59, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimers, C.D.; Knapp, G.; Reimers, A.K. Does Physical Activity Increase Life Expectancy? A Review of the Literature. J. Aging Res. 2012, 2012, 243958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, A.; Dallongeville, J.; Haas, B.; Ruidavets, J.B.; Amouyel, P.; Ferrières, J.; Simon, C.; Arveiler, D. Sedentary Behaviour, Physical Activity and Dietary Patterns Are Independently Associated with the Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Metab. 2012, 38, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra Majem, L.; Ortiz Andrellucchi, A.; Serra Majem, L.; Ortiz Andrellucchi, A. La Dieta Mediterránea Como Ejemplo de Una Alimentación y Nutrición Sostenibles: Enfoque Multidisciplinar. Nutr. Hosp. 2018, 35, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tárraga López, P.J.; Tárraga Marcos, A.; Panisello, J.M.; Herencia Carbayo, J.A.; Tárraga Marcos, M.L.; López-Gil, J.F. Physical Activity and Its Association with Mediterranean Diet Patterns among Spanish University Students. Nutr. Hosp. 2022, 39, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Duais, M.A.; Al-Awthan, Y.S. Prevalence of Dyslipidemia among Students of a Yemeni University. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2019, 14, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ru, D.; Xue, B.; Wen, S.; Zhou, H. Serum Iron Levels Are Negatively Correlated with Serum Triglycerides Levels in Female University Students. Ann. Palliat. Med. 2020, 9, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez Ramírez, A.A.; Peláez, J.L.; Bermúdez, I.M.; Gordon Botero, J.Y. Prevalence of Hyperlipidemia and Its Associated Factors in University Students in Colombia. Heliyon 2020, 6, e05417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, A.; Yokoyama, T.; Mizukami, T.; Matsui, T.; Shiraishi, K.; Kimura, M.; Matsushita, S.; Higuchi, S.; Maruyama, K. Alcoholic Ketosis: Prevalence, Determinants, and Ketohepatitis in Japanese Alcoholic Men. Alcohol Alcohol. 2014, 49, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, C.; Kocher, S.; Neeser, K.; Joshi, S.R. Prevention of Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Self-Monitoring of Ketone Bodies: An Overview. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2009, 25, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, L.A.; Gallo, T.F.; Young, S.L.; Fotheringham, A.K.; Barclay, J.L.; Walker, J.L.; Moritz, K.M.; Akison, L.K. Adherence to Dietary and Physical Activity Guidelines in Australian Undergraduate Biomedical Students and Associations with Body Composition and Metabolic Health: A Cross-Sectional Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiba, S.; Shiba, A. Association between Non-Obesity and Health State among Young Japanese Male University Students. J. Phys. Ther. Sci. 2020, 32, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Li, Y.; Bhupathiraju, S.N.; Rosner, B.A.; Sun, Q.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Rimm, E.B.; Manson, J.E.; Willett, W.C.; Stampfer, M.J.; et al. Fruit and Vegetable Intake and Mortality: Results From 2 Prospective Cohort Studies of US Men and Women and a Meta-Analysis of 26 Cohort Studies. Circulation 2021, 143, 1642–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Physical Activity. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity (accessed on 28 July 2022).
| Variable | IT (n = 34) | SP (n = 32) | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) * | 25.9 ± 3.6 | 24.0 ± 3.7 | 0.0382 |
| GenderMales (%) | 44.1 | 43.8 | >0.999 |
| Smokers (%) | 17.7 | 12.5 | 0.1030 |
| Height (m) | 1.69 ± 0.09 | 1.71 ± 0.09 | 0.3940 |
| Weight (kg) | 62.2 (54.4–81.6) | 67.0 (57.1–76.4) | 0.9416 |
| WC (cm) | 72.4 (67.0–85.5) | 74.5 (67.7–82.0) | 0.9365 |
| HC (cm) | 95.0 (90.6–100.0) | 96.1 (91.8–101.2) | 0.5988 |
| WHR | 0.77 (0.73–0.84) | 0.78 (0.74–0.83) | 0.8656 |
| WHtR | 0.43 (0.41–0.49) | 0.44 (0.41–0.46) | 0.5844 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.1 (20.9–26.3) | 22.7 (21.0–25.3) | 0.9011 |
| Overweight (%) | 23.5 | 21.9 | |
| Obese (%) | 5.9 | 3.1 | |
| % FM | |||
| Plicometry | 25.1 ± 15.5 | 20.7 ± 6.7 | 0.1600 |
| BIA | 26.5 ± 7.5 | 24.2 ± 9.3 | 0.2674 |
| % MM | 30.2 (28.8–37.9) | 29.5 (22.1–36.7) | 0.0815 |
| BP (mmHg) | |||
| Systolic | 120.0 (110.0–120.0) | 115.5 (105.5–120.0) | 0.1730 |
| Diastolic | 75.0 (66.5–80.0) | 70.0 (58.8–79.3) | 0.0960 |
| Variable | IT | SP | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| MED-55 | 34.1 ± 3.8 | 33.4 ± 7.4 | 0.6183 |
| MDS-14 | 6.0 (5.0–8.0) | 7.0 (6.0–9.0) | 0.1384 |
| QueMD | 13.2 ± 3.5 | 13.8 ± 3.2 | 0.4694 |
| aMED | 4.0 (3.0–5.0) | 3.0 (2.3–4.0) | 0.7759 |
| Protein % energy | 12.5 (10.0–15.5) | 13.5 (11.8–17.3) | 0.3277 |
| Lipids % energy** | 33.0 (29.0–37.8) | 50.5 (44.8–65.0) | 0.0011 |
| Carbohydrates % energy** | 49.7 ± 9.9 | 33.5 ± 12.4 | 0.0031 |
| Fiber (g) | 16.0 ± 5.8 | 20.7 ± 5.6 | 0.1217 |
| Energy (Kcal) * | 2156 (1828–2614) | 3118 (2695–3333) | 0.0240 |
| Variable | IT | SP | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glu (mg/dL) **** | 91.0 (81.8–98.3) | 104.0 (99.0–110.8) | <0.0001 |
| Hypoglycemia (%) | - | - | |
| >100 mg/dL (%) | 20.6 | 50 | |
| Diabetes (%) | - | - | |
| TC (mg/dL) | 155.5 (138.3–175.5) | 158.5 (130.0–189.5) | 0.9770 |
| >200 mg/dL (%) | 11.8 | 18.8 | |
| TG (mg/dL) | 78.0 (63.3–92.0) | 73.0 (51.3–101.0) | 0.4607 |
| >150 mg/dL (%) | 2.9 | 9.4 | |
| Ket (mmol/L) | 0.2 (0.1–0.2) | 0.2 (0.2–0.2) | 0.0740 |
| Ketosis (%) | - | 3.1 | |
| Ketoacidosis (%) | - | - |
| F-QueMD | V-QueMD | |
|---|---|---|
| BMI | 0.244 (0.048) | |
| WHR | 0.251 (0.042) | |
| IPAQ MET-min/week | 0.257 (0.037) | |
| MDS-14 | 0.359 (0.003) | |
| QueMD | 0.483 (<0.001) | |
| aMED | 0.639 (<0.001) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aiello, P.; Peluso, I.; Di Giacomo, S.; Di Sotto, A.; Villaño Valencia, D. Body Composition and Metabolic Status of Italian and Spanish University Students: Relationship with Fruit and Vegetable Consumption. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163296
Aiello P, Peluso I, Di Giacomo S, Di Sotto A, Villaño Valencia D. Body Composition and Metabolic Status of Italian and Spanish University Students: Relationship with Fruit and Vegetable Consumption. Nutrients. 2022; 14(16):3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163296
Chicago/Turabian StyleAiello, Paola, Ilaria Peluso, Silvia Di Giacomo, Antonella Di Sotto, and Débora Villaño Valencia. 2022. "Body Composition and Metabolic Status of Italian and Spanish University Students: Relationship with Fruit and Vegetable Consumption" Nutrients 14, no. 16: 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163296
APA StyleAiello, P., Peluso, I., Di Giacomo, S., Di Sotto, A., & Villaño Valencia, D. (2022). Body Composition and Metabolic Status of Italian and Spanish University Students: Relationship with Fruit and Vegetable Consumption. Nutrients, 14(16), 3296. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14163296