Dietary Intake, Nutritional Adequacy and Food Sources of Total Fat and Fatty Acids, and Relationships with Personal and Family Factors in Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years: Results of the EsNuPI Study †
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Sample
2.2. Dietary Data Collection
2.3. Sociodemographic and Anthropometric Data
2.4. Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior Habits
2.5. Evaluation of Plausible, Under-, and Over-Reporting (Misreporting)
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Subjects’ Characteristics
3.2. Dietary Lipid Profile and Distribution
3.3. Major Fatty Acid Profile and Distribution
3.4. Adequacy of Lipid Profile According to European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Recommendations
3.5. Adequacy of Lipid Profile to the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (UN-FAO) Recommendations
3.6. Individual Usual Intake of Total Fat and Main Fatty Acids and Family and Personal Factors
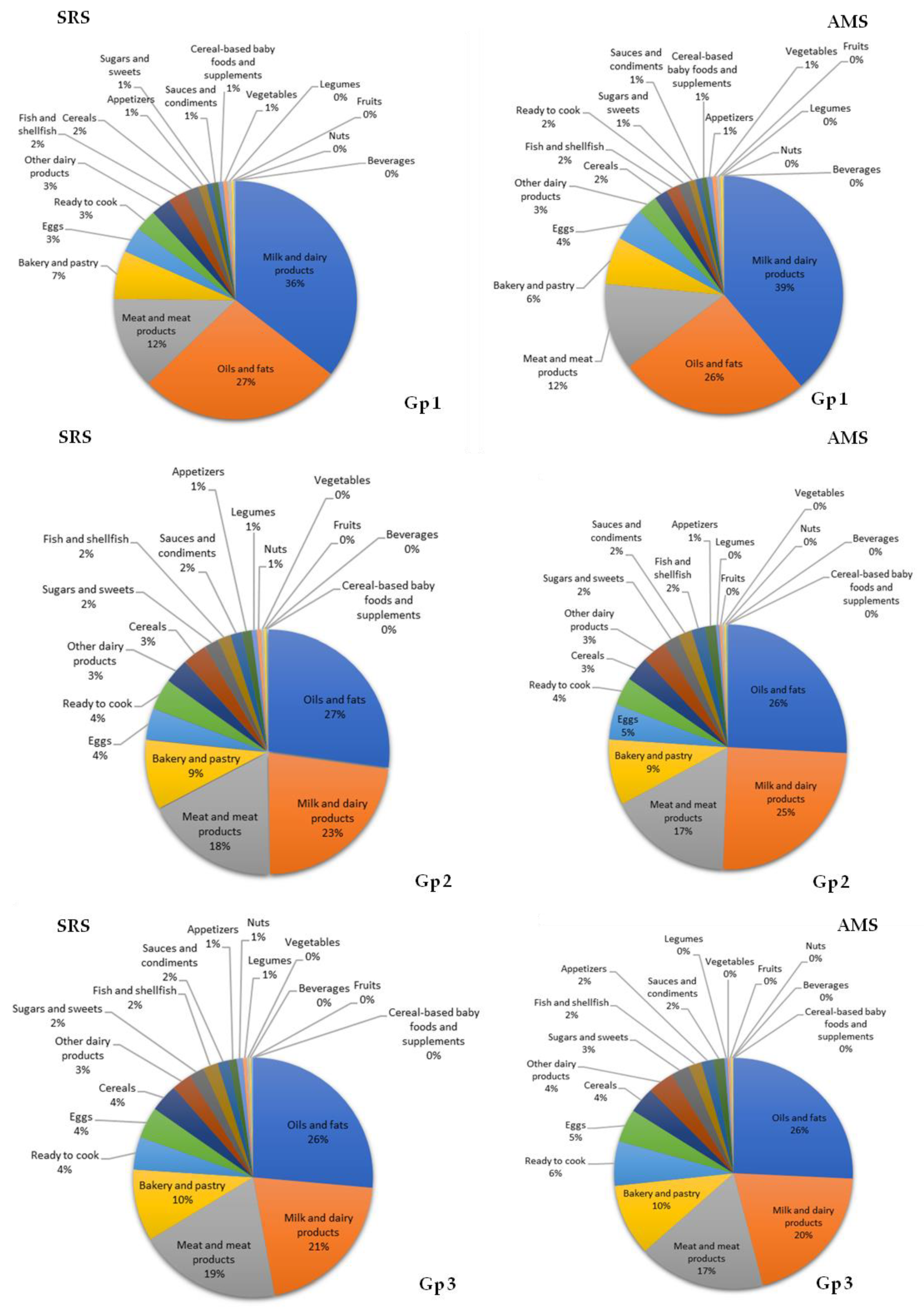
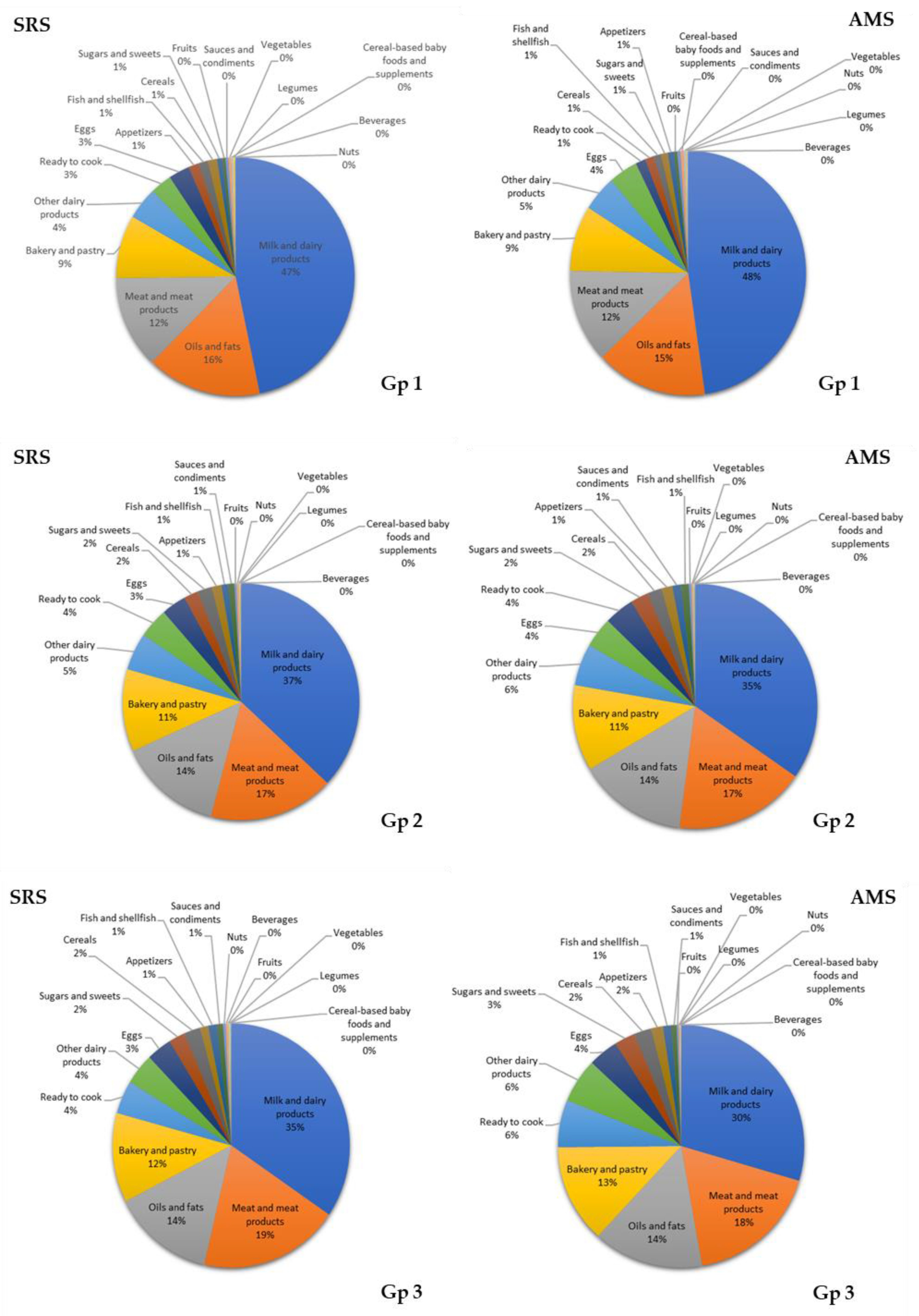
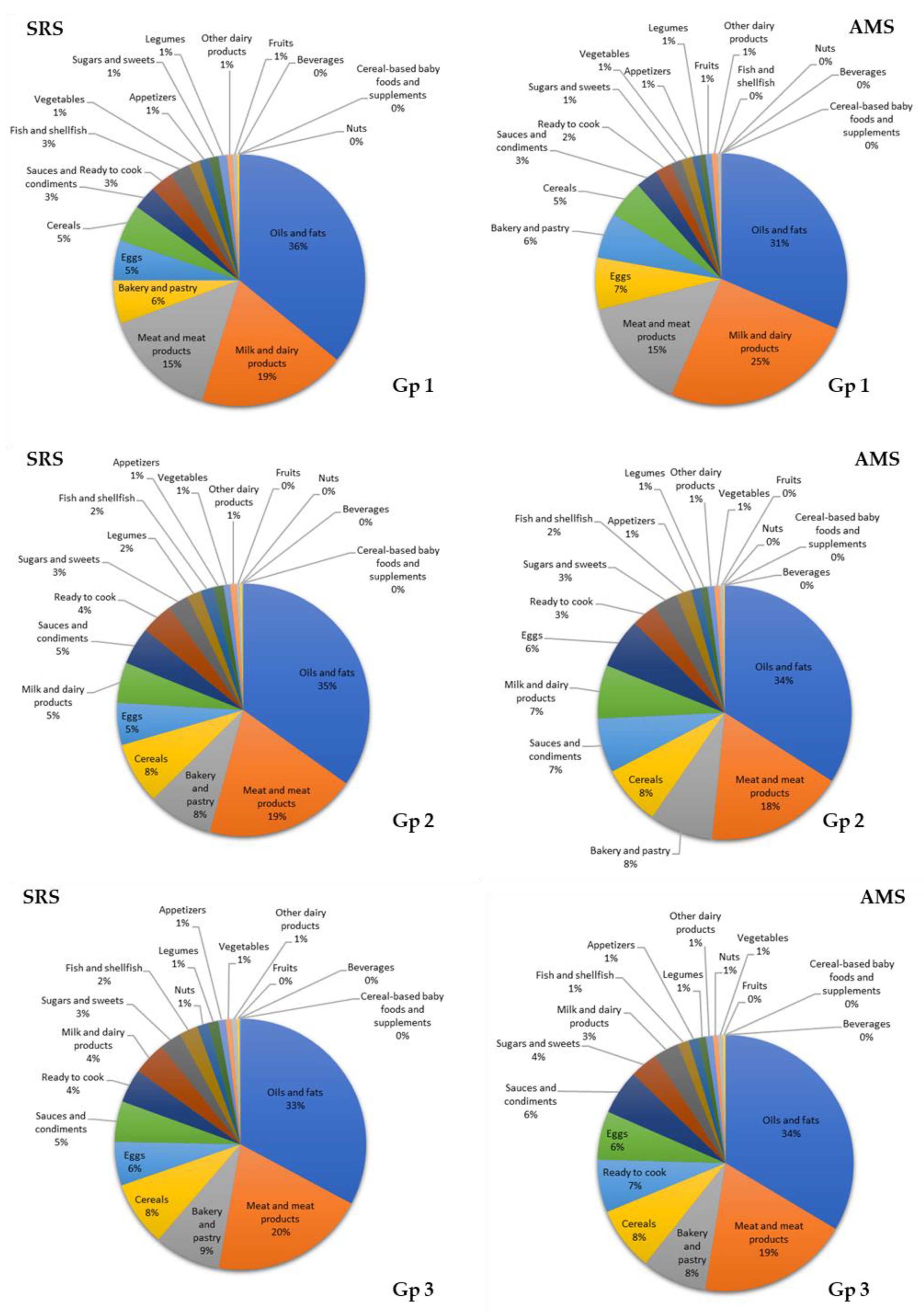
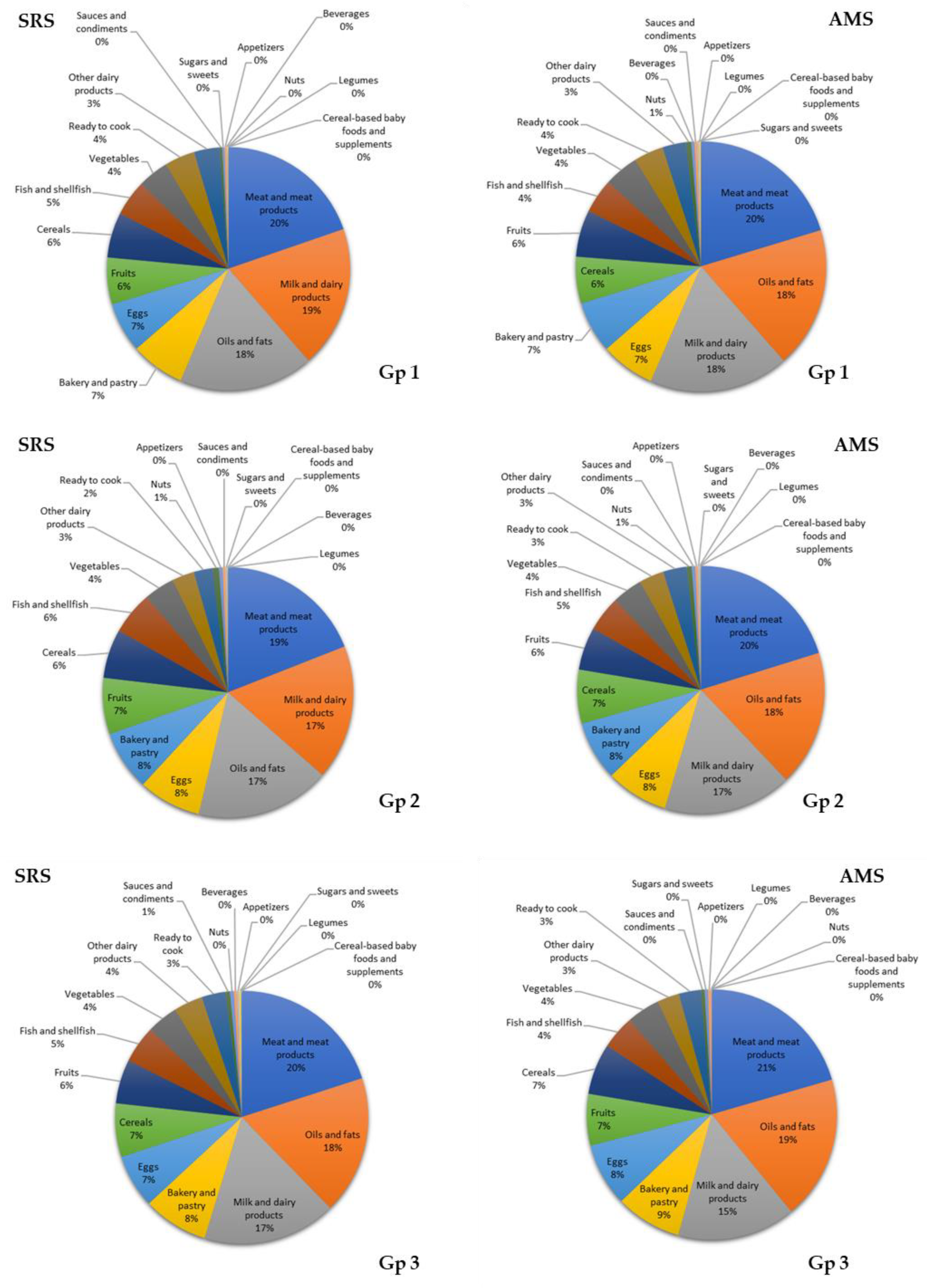
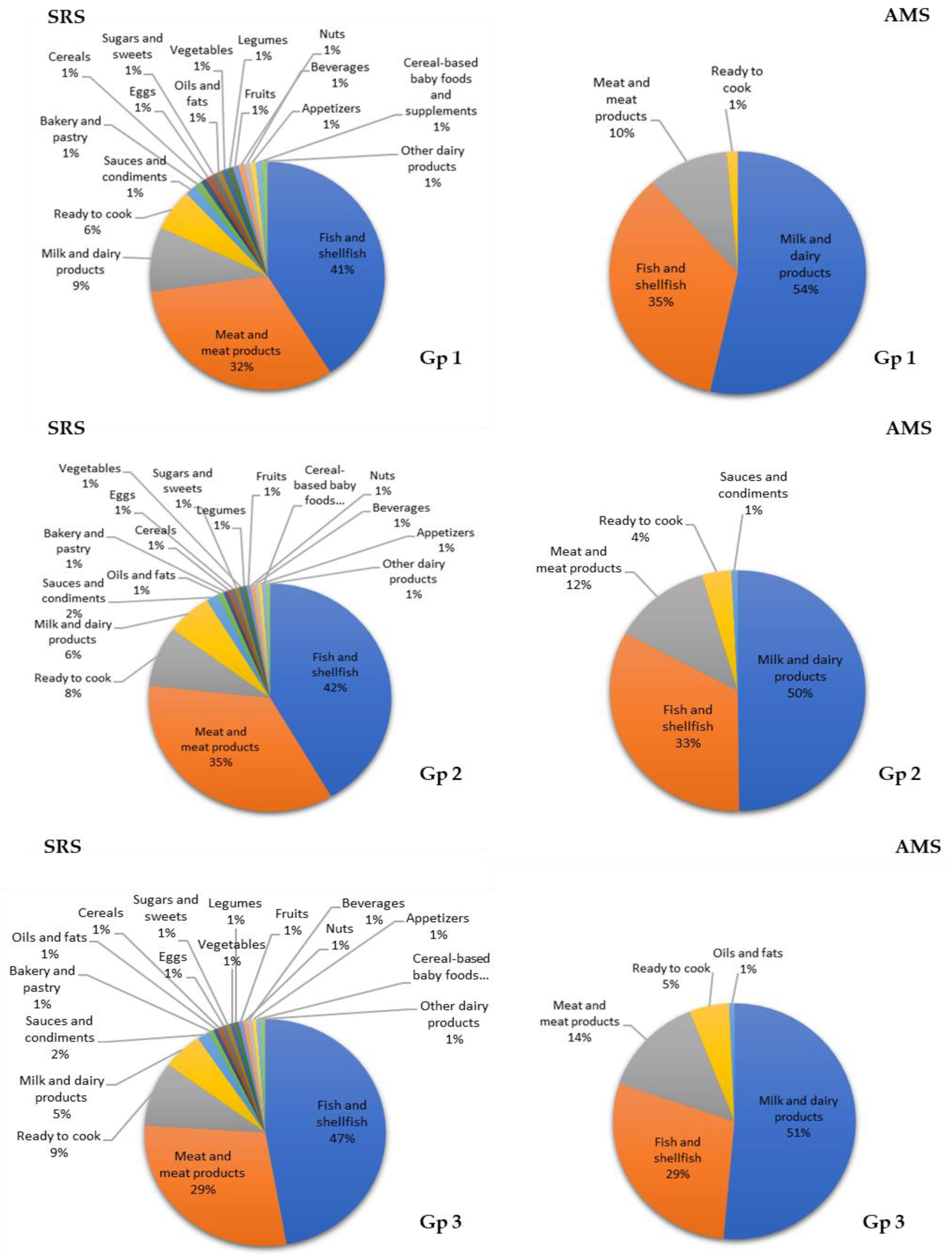
3.7. Contribution of Food Groups to Total Lipid and Main Fatty Acid Intake
4. Discussion
4.1. Lipid Profile and Adequacy
4.2. Contributions of Food Groups to Fat and Major Fatty Acid Consumption
4.3. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Pérez-Rodrigo, C. Determinants of Childhood Obesity: ANIBES Study. Nutr. Hosp. 2016, 33, 339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, L.; Ayoub, J.; Jawaldeh, A. Review of the Nutrition Situation in the Eastern Mediterranean Region. East Mediterr. Health J. 2018, 24, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foreman, K.J.; Marquez, N.; Dolgert, A.; Fukutaki, K.; Fullman, N. Forecasting life expectancy, years of life lost, and all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 250 causes of death: Reference and alternative scenarios for 2016–40 for 195 countries and territories. Lancet 2018, 392, 2052–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Sobaler, A.M.; Aparicio, A.; Rubio, J.; Marcos, V.; Sanchidrián, R.; Santos, S.; Pérez-Farinós, N.; Dal-Re, M.Á.; Villar-Villalba, C.; Yusta-Boyo, M.J.; et al. Adequacy of usual macronutrient intake and macronutrient distribution in children and adolescents in Spain: A National Dietary Survey on the Child and Adolescent Population, ENALIA 2013–2014. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.; Lopez, A. Measuring the Global Burden of Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 448–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tognon, G.; Hebestreit, A.; Lanfer, A.; Moreno, L.A.; Pala, V.; Siani, A.; Tornaritis, M.; De Henauw, S.; Veidebaum, T.; Molnár, D.; et al. Mediterranean diet, overweight and body composition in children from eight European countries: Cros-sectional and prospective results from the IDEFICS study. NMCD 2014, 63, 2960–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, E.; Ávila, J.M.; Valero, T.; del Pozo, S.; Rodríguez, P.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Gil, Á.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; et al. Energy Intake, Profile, and Dietary Sources in the Spanish Population: Findings of the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2015, 7, 4739–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guglielmo, D.; Welsh, J.A. Consumption of sugars, saturated fat, and sodium among US children from infancy through preschool age, NHANES 2009–2014. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 868–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sereni, S.; Fasano, E.; Piccioni, E.; Cittadini, A.; Calviello, G. Dietary n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and the Paradox of Their Health Benefits and Potential Harmful Effects. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2011, 4, 2093–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksen, C.; Almaas, A.N.; Westerberg, A.E.; Drevon, C.; Olversen, P.; Nakstad, B. Growth, metabolic markers, and cognition in 8-year old children born prematurely, follow-up of a randomized controlled trial with essential fatty acids. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2016, 9, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumbe, T.; Comstock, S.; Harris, W.; Kinabo, J.; Pontifex, M.; Frenton, J. Whole-blood fatty acids are associated with executive function in Tanzanian children aged 4–6 years: A cross-sectional study. Br. J. Nutr. 2016, 9, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. Fundación Iberoamericana de Nutrición. Grasas y Acidos Grasos en Nutrición Humana. Consulta de Expertos; FAO: Ginebra, Suiza, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ros, E.; López-Miranda, J.; Picó, C.; Rubio, M.Á.; Babio, N.; Sala-Vila, A.; Pérez-Jiménez, F.; Escrich, E.; Bulló, M.; Solanas, M.; et al. Consenso sobre las grasas y aceites en la alimentación de la población española adulta; postura de la Federación Española de Sociedades de Alimentación, Nutrición y Dietética (FESNAD). Nutr. Hosp. 2015, 32, 435–477. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mazzocchi, A.; D’Oria, V.; De Cosmi, V.; Bettocchi, S.; Milani, G.P.; Silano, M.; Agostoni, C. The Role of Lipids in Human Milk and Infant Formulae. Nutrients 2018, 10, 567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadley, K.; Ryan, A.S.; Forsyth, S.; Gautier, S.; Salem, N. The Essentialy of Arachidonic acid in Infant Development. Nutrients 2016, 8, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, S.E.; Colombo, J. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Arachidonic Acid Nutrition in Early Development. Adv. Pediatr. 2016, 63, 453–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billingsley, H.; Carbone, S.; Lavie, C.J. Dietary Fats and Chronic Noncommunicable Diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parletta, N.; Cooper, P.; Gent, D.N.; Petkov, J.; Odea, K. Effects of fish oil supplementation on learning and behaviour of children from Australian Indigenous remote community schools: A randomised controlled trial. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2013, 89, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo-Reyes, V.; Pérez-García, M.; Loya-Méndez, Y.; Puente, A.E. Clinical significance of neuropsychological improvement after supplementation with omega-3 in 8-12 years old malnourished Mexican children: A randomized, double-blind, placebo and treatment clinical trial. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2014, 35, 861–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, F.; Dutta, R.; Reynolds, L.; Sergeant, S.; Mathias, R.A.; Seeds, M. Precision Nutrition and Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: A Case for Personalized Supplementation Approaches for the Prevention and Management of Human Diseases. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chianese, R.; Coccurello, R.; Viggiano, A.; Scafuro, M.; Fiore, M.; Coppola, G.; Operto, F.F.; Fasano, S.; Layé, S.; Pierantoni, R.; et al. Impact of Dietary Fats on Brain Functions. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2018, 16, 1059–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. The WHO Child Growth Standards. 2006. Available online: https://www.who.int/childgrowth/en/ (accessed on 13 March 2020).
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Panel on Dietetic Products Nutrition, and Allergies (NDA). Scientific Opinion on Dietary Reference Values for fats, including saturated fatty acids, polyunsaturated fatty acids, monounsaturated fatty acids, trans fatty acids, and cholesterol. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 1461. [Google Scholar]
- Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes; The National Academies Press: Washington, WA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Gil-Campos, M.; Serra, J.D. Importancia del ácido docosahexaenoico (DHA): Funciones y recomendaciones para su ingesta en la infancia. An. Pediatr. 2010, 73, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Dietary Reference Values for the European Union 2019. Available online: https://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/topics/topic/dietary-reference-values (accessed on 1 March 2020).
- Dalmau, J.; Peña, L.; Morais, A.; Martínez, V.; Varea, V.; Martínez, M.; Soler, B. Análisis cuantitativo de la ingesta de nutrientes en niños menores de 3 años. An. Pediatr. 2015, 82, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laroche, H.H.; Hofer, T.P.; Davis, M.M. Adult fat intake associated with the presence of children in households: Findings from NHANES III. J. Am. Board. Fam. Med. 2007, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, R.M.; Jiménez, A.I.; Perea, J.M.; Cuadrado, E.; Aparicio, A.; López-Sobaler, A.M. Nutritional Value of Dairy Products and Recommended Daily Consumption. Nutr. Hosp. 2019, 36, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Bertram, H.C.; Bonjour, J.P.; De Groot, L.C.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Feeney, E.L.; Garg, M.L.; Givens, I.; Kok, F.J.; Krauss, R.M.; et al. WHO draft guidelines on dietary saturated and trans fatty acids: Time for a new approach? BMJ 2019, 366, l4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller-Rouassant, S.; Flores-Quijano, M.E. Young Children, Toddlers and School Age Children. Gac. Med. Mex. 2016, 1, 22–28. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Astrup, A.; Lovegrove, J.A.; Gijsbers, L.; Givens, D.I.; Soedamah-Muthu, S. Milk and Dairy Consumption and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases and All-Cause Mortality: Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 32, 269–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Bradley, B.H.; Brenna, T.; Delplanque, B.; Ferry, M.; Torres-Gonzalez, M. Regular-Fat Dairy and Human Health: A Synopsis of Symposia Presented in Europe and North America (2014–2015). Nutrients 2016, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Te Morenga, L.; Montez, J.M. Health effects of saturated and trans-fatty acid intake in children and adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovács, E.; Siani, A.; Konstabel, K.; Hadjigeorgiou, C.; De Bourdeaudhuij, I.; Eiben, G.; Lissner, L.; Gwozdz, W.; Reisch, L.; Pala, V.; et al. Adherence to the obesity-related lifestyle intervention targets in the IDEFICS study. Int. J. Obes. 2014, 38, S144–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madrigal, C.; Soto-Méndez, M.J.; Hernández-Ruiz, A.; Ruiz, E.; Valero, T.; Ávila, J.M.; Lara-Villoslada, F.; Leis, R.; de Martínez Victoria, E.; Moreno, J.M.; et al. Dietary and Lifestyle Patterns in the Spanish Pediatric Population (One to <10 Years Old): Design, Protocol, and Methodology of the EsNuPI Study. Nutrients 2019, 11, 3050. [Google Scholar]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Guidance of the EU Menu methodology. EFSA J. 2014, 12, 3944.
- Moreiras, O.; Carbajal, A.; Cabrera, L. Ingestas Diarias Recomendadas de Energía y Nutrientes para la Población Española. In Tablas de Composición de Alimentos, 19th ed.; Ediciones Pirámide (Grupo Anaya, SA): Madrid, Spain, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-López, M.D.; de Martínez Victoria, E.; Gil, A. Guía Fotográfica de Porciones de Alimentos Consumidos en España; Fundación Iberoamericana de Nutrición: Granada, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ocké, M.; De Boer, E.; Brants, H.; Van der Laan, J.; Niekerk, M.; Van Rossum, C.; Temme, L.; Freisling, H.; Nicolas, G.; Casagrande, C.; et al. Pancake—Pilot study for the Assessment of Nutrient intake and food Consumption Among Kids in Europe. EFSA J. 2012, 9, 339E. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fundación Española de la Nutrición (FEN) Software VD-FEN 2.1 Programa de Valoración Dietética de la FEN; Fundación Española de la Nutrición (FEN): Madrid, Spain, 2013.
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Kott, P.S.; Guenther, P.M. Mean proportion and population proportion: Two answers to the same question? J. Am. Diet. Assoc. 1989, 89, 671–676. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, D.M.; Santisteban, S.; Paredes, E.; Flórez, M.; Bueno, D.A. Confiabilidad de un cuestionario para medir actividad física y comportamientos sedentarios en niños desde preescolar a cuarto grado de primaria. Biomedica 2015, 35, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA). Example of a Protocol for Identification of Misreporting (Under- and Overreporting of Energy Intake) Based on the PILOT-PANEU Project. Available online: http://www.efsa.europa.eu/sites/default/files/efsa_rep/blobserver_assets/3944A-8-2-1.pdf (accessed on 1 November 2019).
- Goldberg, G.R.; Black, A.E.; Jebb, S.A.; Cole, T.J.; Murgatroyd, P.R.; Coward, W.A.; Prentice, A.M. Critical evaluation of energy intake data using fundamental principles of energy physiology: 1. Derivation of cutoff limits to identify under-recording. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 45, 569–581. [Google Scholar]
- Black, A.E. Critical evaluation of energy intake using the Goldberg cut-off for energy intake: Basal metabolic rate. A practical guide to its calculation, use and limitations. Int. J. Obes. 2000, 24, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal, C.; Soto-Méndez, M.J.; Hernández-Ruiz, Á.; Valero, T.; Ávila, J.M.; Ruiz, E.; Lara Villoslada, F.; Leis, R.; Martínez de Victoria, E.; Moreno, J.M.; et al. Energy Intake, Macronutrient Profile and Food Sources of Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years—Results from the EsNuPI Study †. Nutrients 2020, 12, 893. [Google Scholar]
- Souverein, O.W.; Dekkers, A.L.; Geelen, A.; Haubrock, J.; de Vries, J.H. Comparing four methods to estimate usual intake distributions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 65, s92–s101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuadrado-Soto, E.; López-Sobaler, A.M.; Jiménez-Ortega, A.I.; Aparicio, A.; Bermejo, L.M.; Hernández-Ruiz, Á.; Lara Villoslada, F.; Leis, R.; Martínez de Victoria, E.; Moreno, J.M.; et al. Usual Dietary Intake, Nutritional Adequacy and Food Sources of Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium and Vitamin D of Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years. Findings from the EsNuPI Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1787. [Google Scholar]
- Samaniego-Vaesken, M.D.; Partearroyo, T.; Ruiz, E.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Gil, Á.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; Varela-Moreiras, G. The Influence of Place of Residence, Gender and Age Influence on Food Group Choices in the Spanish Population: Findings from the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, Y.J.; Shim, J.E.; Song, S.J. Dietary intake of fat and fatty acids by 1–5-year-old children in Korea: A cross-sectional study based on data from the sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2018, 12, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keim, S.; Branum, A.M. Dietary intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids and fish among US children 12–60 months of age. Matern. Child Nutr. 2015, 11, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, A.; Milne, T.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, R.; Grant, C.; Wall, C.R. Evaluation of the Effect of a Growing up Milk Lite vs. Cow’s Milk on Diet Quality and Dietary Intakes in Early Childhood: The Growing up Milk Lite (GUMLi) Randomised Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, E.; Wall, R.; Fitzgerald, G.F.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Health Implications of High Dietary Omega-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. J. Nutr. Metab. 2012, 2012, 539426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guesnet, P.; Tressou, J.; Buaud, B.; Simon, N.; Pasteau, S. Inadequate Daily Intakes of n-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFA) in the General French Population of Children (3–10 Years) and Adolescents (11–17 Years): The INCA2 Survey. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drouin, G.; Rioux, V.; Legrand, P. The n-3 docosapentaenoic acid (DPA): A new player in the n-3 long chain polyunsaturated fatty acid family. Biochimie 2019, 159, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahidi, F.; Ambigaipalan, P. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids and Their Health Benefits. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 25, 345–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calder, P.C.; Dangour, A.D.; Diekman, C.; Eilander, A.; Koletzko, B.; Meijer, G.W.; Mozaffarian, D.; Niinikoski, H.; Osendarp, S.J.; Pietinen, P.; et al. Essential fats for future health. Proceedings of the 9th Unilever Nutrition Symposium, 26-27 May 2010. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, S1–S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.J.; Butt, C.M.; Mohajeri, M.H. Docosahexaenoic Acid and Cognition throughout the Lifespan. Nutrients 2016, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzocchi, A.; Agostoni, C. Long-Chain ω-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Do Genetic Steps Match Metabolic Needs? Curr. Dev. Nutr. 2019, 149, 1690–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioen, I.; Van Lieshout, L.; Eilander, A.; Fleith, M.; Lohner, S. Systematic Review on N-3 and N-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Intake in European Countries in Light of the Current Recommendations-Focus on Specific Population Groups. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2017, 70, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, K.W.; Cheatha, C.L. Omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid intake of children and older adults in the U.S.: Dietary intake in comparison to current dietary recommendations and the Healthy Eating Index. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.; Hein, N.; Hanson, C.; Smith, L.M.; Anderson-Berry, A. Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake by Age, Gender, and Pregnancy Status in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2003–2014. Nutrients 2019, 11, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisolfi, J.; Fantino, M.; Turck, D.; Potier de Courcy, G.; Vidailhet, M. Nutrient Intakes of Children Aged 1–2 Years as a Function of Milk Consumption, Cows’ Milk or Growing-Up Milk. Public Health Nutr. 2013, 16, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoça, M.A.; Coelho, A.; Borgo, L.A.; de Rodrigues Alencar, E. Lipid profile of different infant formulas for infants. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177812. [Google Scholar]
- Hojsak, I.; Bronsky, J.; Campoy, C.; Domellöf, M.; Embleton, N.; Fidler, M.; Hulst, J.; Indrio, F.; Lapillonne, A.; ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition; et al. Young Child Formula: A Position Paper by the ESPGHAN Committee on Nutrition. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2018, 66, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouraqui, J.P.; Turck, D.; Tavoularis, G. The Role of Young Child Formula in Ensuring a Balanced Diet in Young Children (1–3 Years Old). Nutrients 2019, 11, 2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieux, F.; Brouzes, C.; Maillot, M.; Briend, A.; Hankard, R.; Lluch, A.; Darmon, N. Role of Young Child Formulae and Supplements to Ensure Nutritional Adequacy in U.K. Young Children. Nutrients 2016, 8, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eussen, S.; Pean, J.; Olivier, L.; Delaere, F.; Lluch, A. Theoretical Impact of Replacing Whole Cow’s Milk by Young-Child Formula on Nutrient Intakes of UK Young Children: Results of a Simulation Study. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 67, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vyncke, K.E.; Libuda, L.; De Vriendt, T.; Moreno, L.A.; Van Winckel, M.; Manios, Y.; Gottrand, F.; Molnar, D.; Vanaelst, B.; Sjöström, M.; et al. Dietary Fatty Acid Intake, Its Food Sources and Determinants in European Adolescents: The HELENA (Healthy Lifestyle in Europe by Nutrition in Adolescence) Study. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 108, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, E.; Ávila, J.M.; Valero, T.; Del Pozo, S.; Rodriguez, P.; Aranceta-Bartrina, J.; Gil, Á.; González-Gross, M.; Ortega, R.M.; Serra-Majem, L.; et al. Macronutrient Distribution and Dietary Sources in the Spanish Population: Findings from the ANIBES Study. Nutrients 2016, 8, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neil, C.; Nicklas, T.; Fulgoni, V. Food Sources of Energy and Nutrients of Public Health Concern and Nutrients to Limit with a Focus on Milk and other Dairy Foods in Children 2 to 18 Years of Age: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2011–2014. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duchen, K.; Faresjö, A.O.; Klingberg, S.; Faresjö, T.; Ludvigsson, J. Fatty fish intake in mothers during pregnancy and in their children in relation to the development of obesity and overweight in childhood: The prospective ABIS study. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2020, 6, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnayake, W.M.; Galli, C. Fat and fatty acid terminology, methods of analysis and fat digestion and metabolism: A background review paper. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2009, 55, 8–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Mozaffarian, D.; Kromhout, D.; Bertoni, A.G.; Sibley, C.T.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr.; Nettleton, J.A. Dietary intake of saturated fat by food source and incident cardiovascular disease: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran-Ressler, R.R.; Bae, S.; Lawrence, P.; Wang, D.H.; Brenna, J.T. Branched-chain fatty acid content of foods and estimated intake in the USA. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harcombe, Z. US dietary guidelines: Is saturated fat a nutrient of concern? Br. J. Sports Med. 2019, 53, 1393–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, D.; Tallman, D.A.; Khosla, P. The health effects of saturated fats e the role of whole foods and dietary patterns. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 151–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurotani, K.; Sato, M.; Yasuda, K.; Kashima, K.; Tanaka, S.; Hayashi, T.; Shirouchi, B.; Akter, S.; Kashino, I.; Hayabuchi, H.; et al. Even- and odd chain saturated fatty acids in serum phospholipids are differentially associated with adipokines. PLoS ONE. 2017, 12, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrup, A.; Magkos, F.; Bier, D.M.; Brenna, J.T.; de Oliveira Otto, M.C.; Hill, J.O.; King, J.C.; Mente, A.; Ordovas, J.M.; Volek, J.S.; et al. Saturated Fats and Health: A Reassessment and Proposal for Food-based Recommendations: JACC State-of -the-Art Review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micha, R.; Mozaffarian, D. Saturated fat and cardiometabolic risk factors, coronary heart disease, stroke, and diabetes: A fresh look at the evidence. Lipids 2010, 45, 893–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Tsai, M.Y.; Sun, Q.; Hinkle, S.N.; Rawal, S.; Mendola, P.; Ferrara, A.; Albert, P.S.; Zhang, C. A prospective and longitudinal study of plasma phospholipid saturated fatty acid profile in relation to cardiometabolic biomarkers and the risk of gestational diabetes. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 107, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mente, A.; Dehghan, M.; Rangarajan, S.; McQueen, M.; Dagenais, G.; Wielgosz, A.; Lear, S.; Li, W.; Chen, H.; Yi, S.; et al. Association of dietary nutrients with blood lipids and blood pressure in 18 countries: A cross-sectional analysis from the PURE study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017, 5, 774–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjepong, M.; Yakah, W.; Harris, W.S.; Colecraft, E.; Marquis, G.S.; Fenton, J.I. Association of Whole Blood Fatty Acids and Growth in Southern Ghanaian Children 2–6 Years of Age. Nutrients 2018, 10, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, E.L.; Richard, C.; Hoffmanc, D.R. DHA and ARA addition to infant formula: Current status and future research directions. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 2018, 128, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seves, S.M.; Verkaik-Kloosterman, J.; Biesbroek, S.; Temme, E. Are more environmentally sustainable diets with less meat and dairy nutritionally adequate? Public Health Nutr. 2017, 20, 2050–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| EsNuPI Study Population | Whole Population | Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 1448 | n = 707 | n = 741 | ||
| Sex | Boys | 728 | 357 | 371 |
| Girls | 720 | 350 | 370 | |
| Age (years) | Group 1 1 to <3 | 456 | 162 | 294 |
| Group 2 3 to <6 | 506 | 244 | 262 | |
| Group 3 6 to <10 | 486 | 301 | 185 | |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | |||||||||||||||||
| (g) | Total n = 707 | 1 to <3 years n = 162 | 3 to <6 years n = 244 | 6 to <10 years n = 301 | p | ||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | ||
| Total Fat | 61.31 | 20.39 | 59.77 | 24.86 | 49.60 | 16.84 | 47.34 a | 22.89 | 60.83 | 17.89 | 60.34 b | 20.73 | 68.00 | 21.16 | 64.77 c | 27.29 | <0.001 |
| SFAs | 22.24 | 8.47 | 21.23 | 10.75 | 17.58 | 7.81 | 16.88 a | 8.53 | 22.43 | 7.20 | 22.18 b | 9.44 | 24.59 | 8.77 | 23.45 b | 10.60 | <0.001 |
| MUFAs | 25.38 | 9.53 | 25.13 | 11.38 | 19.19 | 8.75 | 19.25 a | 11.56 | 25.56 | 8.21 | 25.29 b | 10.33 | 28.57 | 9.33 | 27.62 c | 11.83 | <0.001 |
| PUFAs | 7.79 | 3.96 | 7.16 | 4.56 | 5.66 | 3.79 | 5.15 a | 4.16 | 7.72 | 3.41 | 7.16 b | 3.83 | 8.99 | 3.99 | 8.17 c | 4.21 | <0.001 |
| n-3 | 0.65 | 0.33 | 0.59 | 0.35 | 0.53 | 0.28 | 0.49 a | 0.30 | 0.63 | 0.27 | 0.59 b | 0.33 | 0.73 | 0.37 | 0.66 c | 0.37 | <0.001 |
| n-6 | 6.56 | 3.58 | 5.91 | 3.99 | 5.09 | 3.28 | 4.51 a | 3.51 | 6.44 | 3.25 | 5.91 b | 3.77 | 7.44 | 3.73 | 6.75 c | 4.01 | <0.001 |
| n-6:n-3 | 11.47 | 7.38 | 10.14 | 6.09 | 11.94 | 11.24 | 9.25 a | 6.36 | 11.14 | 5.31 | 10.13 a,b | 5.95 | 11.48 | 6.16 | 10.50 b | 5.81 | <0.001 |
| Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |||||||||||||||||
| (g) | Total n = 741 | 1 to <3 years n = 294 | 3 to <6 years n = 262 | 6 to <10 years n = 185 | p | ||||||||||||
| Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | ||
| Total Fat | 56.64 | 19.42 | 54.94 * | 27.42 | 45.98 | 15.47 | 43.20 a,* | 20.71 | 61.22 | 18.64 | 61.12 b | 26.85 | 67.09 | 17.90 | 64.90 c | 24.44 | <0.001 |
| SFAs | 19.28 | 7.47 | 18.46 * | 10.48 | 15.18 | 5.73 | 14.90 a,* | 7.91 | 21.08 | 7.05 | 20.88 b,* | 10.57 | 23.25 | 7.34 | 22.00 c | 9.75 | <0.001 |
| MUFAs | 23.88 | 9.30 | 23.56 * | 12.14 | 18.67 | 8.14 | 18.38 a | 11.12 | 26.18 | 8.46 | 25.40 b | 12.10 | 28.88 | 8.08 | 28.00 c | 11.26 | <0.001 |
| PUFAs | 7.23 | 3.61 | 6.60 * | 4.36 | 5.17 | 2.70 | 4.90 a | 3.57 | 8.20 | 3.53 | 7.50 b | 4.67 | 9.10 | 3.37 | 8.51 c | 4.38 | <0.001 |
| n-3 | 0.70 | 0.33 | 0.64 * | 0.34 | 0.61 | 0.29 | 0.58 a,* | 0.29 | 0.72 | 0.32 | 0.68 b,* | 0.36 | 0.79 | 0.37 | 0.71 b,* | 0.37 | <0.001 |
| n-6 | 5.89 | 3.12 | 5.21 * | 3.82 | 4.54 | 2.39 | 4.20 a | 2.75 | 6.55 | 3.31 | 5.62 b | 4.08 | 7.12 | 3.08 | 6.53 c | 3.99 | <0.001 |
| n-6:n-3 | 9.13 | 4.87 | 8.38 * | 5.29 | 8.11 | 5.36 | 7.33 a,* | 4.54 | 9.82 | 4.49 | 9.21 b,* | 5.33 | 9.76 | 4.27 | 8.91 b,* | 4.75 | <0.001 |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total n = 707 | 1–<3 years n = 162 | 3–<6 years n = 244 | 6–<10 years n = 301 | p | Total n = 741 | 1–<3 years n = 294 | 3–<6 years n = 262 | 6–<10 years n = 185 | p | |
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |||
| Total Fat | 36.2 | 36.1 | 36.1 | 36.6 | 0.56 | 35.8 | 34.8 a,* | 36.3 b | 37.0 b | <0.001 |
| SFAs | 13.1 | 12.5 | 13.4 | 13.0 | 0.101 | 12.1 * | 11.3 a,* | 12.3 b,* | 12.7 b | <0.001 |
| MUFAs | 14.9 | 13.9 a | 15.1 b | 15.2 b | <0.001 | 15.2 | 13.9 a | 15.4 b | 15.9 b | <0.001 |
| PUFAs | 4.2 | 3.5 a | 4.3 b | 4.5 b | <0.001 | 4.3 | 3.6 a | 4.7 b,* | 4.8 b,* | <0.001 |
| n-3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.71 | 0.4 * | 0.4 a,* | 0.4 b,* | 0.4 a,b,* | 0.030 |
| n-6 | 3.5 | 3.4 a | 3.5 a,b | 3.6 b | 0.016 | 3.5 | 3.3 a | 3.6 b | 3.7 b | <0.001 |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | p | Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | p | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total n = 707 | 1–<3 Years n = 162 | 3–<6 Years n = 244 | 6–<10 Years n = 301 | Total N = 741 | 1–<3 Years N = 294 | 3–<6 Years n = 262 | 6–<10 Years n = 185 | |||
| % | % | % | % | % | % | % | % | |||
| Total Fat | 36.9 | 36.7 | 36.8 | 37.4 | 0.44 | 36.5 * | 35.2 a,* | 36.8 b | 37.6 b | <0.001 |
| SFAs | 13.3 | 13.1 | 13.5 | 13.3 | 0.27 | 12.2 * | 11.4 a,* | 12.5 b,* | 13.0 b,* | <0.001 |
| MUFAs | 15.4 | 14.5 a | 15.5 b | 15.8 b | <0.001 | 15.6 | 14.3 a | 15.9 b,* | 16.3 b,* | <0.001 |
| PUFAs | 4.2 | 3.9 a | 4.2 b | 4.2 b | 0.001 | 4.1 * | 3.9 a | 4.3 b | 4.2 c | <0.001 |
| n-3 | 0.4 | 0.4 a | 0.4 a | 0.4 b | 0.001 | 0.5 * | 0.5 a,* | 0.5 b,* | 0.4 b,* | 0.004 |
| n-6 | 3.8 | 3.6 a | 3.9 b | 3.9 b | 0.001 | 3.7 * | 3.4 a,* | 3.9 b | 3.7 c,* | <0.001 |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total n = 687 | Total n = 726 | |||||||
| (g) | Mean | β | CI (95%) | p | Mean | β | CI (95%) | p |
| Total Fat | 61.1 | 56.8 | ||||||
| Nielsen area | −0.84 | −1.25–(−0.418) | <0.001 | −0.84 | −1.25–(−0.418) | <0.001 | ||
| Family income | 0.95 | −0.032–1.94 | 0.058 | 0.95 | −0.032–1.94 | 0.058 | ||
| Highest level of education achieved by one of the parents | −1.73 | −3.20–(−0.25) | 0.022 | −1.73 | −3.20–(−0.25) | 0.022 | ||
| SFAs | 22.1 | 19.3 | ||||||
| Nielsen area | −0.22 | −0.384–(−0.049) | 0.011 | −0.22 | −0.384–(−0.049) | 0.011 | ||
| Family income | 0.15 | −0.25–0.54 | 0.47 | 0.15 | −0.25–0.54 | 0.47 | ||
| Highest level of education achieved by one of the parents | −0.74 | −1.33–(−0.15) | 0.014 | −0.74 | −1.33–(−0.15) | 0.014 | ||
| PUFAs | 7.78 | 7.27 | ||||||
| Nielsen area | −0.17 | −0.25–(−0.10) | <0.001 | −0.17 | −0.25–(−0.10) | <0.001 | ||
| Family income | 0.10 | −0.084–(0.29) | 0.28 | 0.10 | −0.084–(0.29) | 0.28 | ||
| Highest level of education achieved by one of the parents | −0.40 | −0.68–(−0.12) | 0.005 | −0.40 | −0.68–(−0.12) | 0.005 | ||
| n-3 | 0.647 | 0.695 | ||||||
| Nielsen area | 0.001 | −0.006–0.008 | 0.82 | 0.001 | −0.006–0.008 | 0.82 | ||
| Family income | 0.013 | −0.003–0.030 | 0.109 | 0.013 | −0.003–0.030 | 0.109 | ||
| Highest level of education achieved by one of the parents | 0.009 | −0.015–0.034 | 0.451 | 0.009 | −0.015–0.034 | 0.451 | ||
| n-6 | 6.54 | 5.93 | ||||||
| Nielsen area | −0.152 | −0.222–(−0.082) | <0.001 | −0.152 | −0.222–(−0.082) | <0.001 | ||
| Family income | 0.115 | −0.050–0.281 | 0.172 | 0.115 | −0.050–0.281 | 0.172 | ||
| Highest level of education achieved by one of the parents | −0.387 | −0.635–(−0.138) | 0.002 | −0.387 | −0.635–(−0.138) | 0.002 | ||
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total n = 707 | 1 to <3 Years n = 162 | 3 to <6 Years n = 244 | 6 to <10 Years n = 301 | ||||||||||||||
| Fatty acids (g) | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | p |
| Myristic acid 14:0 | 1.72 | 0.84 | 1.63 | 1.07 | 1.47 | 0.80 | 1.43 a | 1.02 | 1.73 | 0.77 | 1.61 b | 1.10 | 1.85 | 0.88 | 1.76 b | 1.03 | <0.001 |
| Palmitic acid 16:0 | 10.82 | 4.44 | 10.45 | 6.03 | 8.13 | 4.03 | 7.48 a | 4.52 | 10.96 | 3.74 | 10.66 b | 5.09 | 12.15 | 4.54 | 11.67 c | 6.02 | <0.001 |
| Stearic acid 18:0 | 4.17 | 1.95 | 3.96 | 2.26 | 3.05 | 1.60 | 2.89 | 2.04 | 4.23 | 1.65 | 4.14 | 2.01 | 4.72 | 2.10 | 4.33 | 2.42 | <0.001 |
| Palmitoleic acid 16:1 n-7 | 1.05 | 0.46 | 1.01 | 0.58 | 0.85 | 0.43 | 0.82 a | 0.49 | 1.05 | 0.39 | 1.03 b | 0.47 | 1.16 | 0.49 | 1.07 b | 0.63 | <0.001 |
| Oleic acid 18:1 n-9 | 22.26 | 8.69 | 21.73 | 10.98 | 16.84 | 8.17 | 16.55 a | 11.19 | 22.51 | 7.72 | 22.29 b | 9.81 | 24.97 | 8.39 | 23.83 c | 10.97 | <0.001 |
| Linoleic acid 18:2 n-6 | 6.48 | 3.57 | 5.85 | 3.94 | 5.03 | 3.28 | 4.45 a | 3.44 | 6.36 | 3.24 | 5.85 b | 3.77 | 7.36 | 3.72 | 6.68 c | 3.99 | <0.001 |
| α-Linolenic acid 18:3 n-3 | 0.46 | 0.19 | 0.44 | 0.21 | 0.36 | 0.15 | 0.35 a | 0.20 | 0.45 | 0.16 | 0.43 b | 0.16 | 0.51 | 0.21 | 0.49 c | 0.23 | <0.001 |
| Arachidonic acid 20:4 n-6 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 a | 0.05 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.07 b | 0.07 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.07 b | 0.06 | <0.001 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid 20:5 n-3 | 0.06 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.01 | 0.10 | 0.121 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid 22:5 n-3 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.03 | 0.02 a | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.04 b | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 b | 0.04 | <0.001 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid 22:6 n-3 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.12 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.02 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.16 | 0.02 | 0.15 | 0.144 |
| Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total n = 741 | 1 to <3 Years n = 294 | 3 to <6 Years n = 262 | 6 to <10 Years n = 185 | ||||||||||||||
| Fatty acids (g) | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | Mean | SD | Median | IQR | p |
| Myristic acid 14:0 | 1.12 | 0.71 | 1.02 * | 0.98 | 0.86 | 0.64 | 0.70 a,* | 0.76 | 1.22 | 0.63 | 1.12 b,* | 0.93 | 1.38 | 0.77 | 1.29 b,* | 1.12 | <0.001 |
| Palmitic acid 16:0 | 8.29 | 4.05 | 7.85 * | 5.28 | 6.16 | 3.67 | 5.52 a,* | 4.32 | 9.27 | 3.62 | 8.99 b,* | 4.99 | 10.28 | 3.67 | 9.64 c,* | 5.19 | <0.001 |
| Stearic acid 18:0 | 3.18 | 1.73 | 2.95 | 2.27 | 2.21 | 1.29 | 2.00 a,* | 1.27 | 3.63 | 1.66 | 3.52 b,* | 2.28 | 4.09 | 1.67 | 3.76 c,* | 2.05 | <0.001 |
| Palmitoleic acid 16:1 n-7 | 0.84 | 0.49 | 0.76 | 0.52 | 0.71 | 0.53 | 0.61 a,* | 0.46 | 0.92 | 0.42 | 0.84 b,* | 0.51 | 0.96 | 0.44 | 0.88 b,* | 0.47 | <0.001 |
| Oleic acid 18:1 n-9 | 18.60 | 8.30 | 17.74 * | 11.15 | 14.33 | 7.66 | 13.67 a,* | 9.23 | 20.39 | 7.27 | 19.62 b,* | 10.29 | 22.85 | 7.54 | 22.64 c,* | 10.77 | <0.001 |
| Linoleic acid 18:2 n-6 | 5.83 | 3.11 | 5.15 * | 3.82 | 4.48 | 2.38 | 4.15 a | 2.75 | 6.48 | 3.30 | 5.56 b | 4.07 | 7.05 | 3.06 | 6.42 c | 3.96 | <0.001 |
| α-Linolenic acid 18:3 n-3 | 0.44 | 0.20 | 0.42 * | 0.20 | 0.40 | 0.17 | 0.38 a,* | 0.20 | 0.45 | 0.19 | 0.42 b | 0.23 | 0.48 | 0.18 | 0.45 b,* | 0.19 | <0.001 |
| Arachidonic acid 20:4 n-6 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 * | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.04 a | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.05 b,* | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.05 | 0.06 b,* | 0.07 | <0.001 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid 20:5 n-3 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.06 * | 0.13 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.01 a | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.07 b,* | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.11 c,* | 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid 22:5 n-3 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 * | 0.04 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.02 a | 0.03 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 0.03 b,* | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.04 c | 0.04 | <0.001 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid 22:6 n-3 | 0.13 | 0.16 | 0.09 * | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.10 * | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.09 * | 0.15 | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.08 * | 0.12 | 0.903 |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | 1 to <3 Years | 3 to <6 Years | 6 to <10 Years | ||||||||||||||
| n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | p | |
| Total Fat | 707 | 13.7 | 41.7 | 44.6 | 162 | 42.0 | 35.8 a | 22.2 | 244 | 11.9 | 50.8 b | 37.3 | 301 | 0.0 | 37.5 a | 62.5 | <0.001 |
| Linoleic acid | 707 | 57.4 | 26.4 | 16.1 | 162 | 66.7 | 25.3 | 8.0 | 244 | 56.6 | 27.5 | 16.0 | 301 | 53.2 | 26.2 | 20.6 | NS |
| α-Linolenic acid | 707 | 99.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 162 | 98.8 | 1.2 | 0.0 | 244 | 99.6 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 301 | 98.7 | 1.3 | 0.0 | NS |
| EPA+DHA | 707 | 73.4 | 2.4 | 24.2 | 162 | 73.5 | 1.9 | 24.7 | 244 | 75.0 | 2.0 | 23.0 | 301 | 72.1 | 3.0 | 24.9 | NS |
| Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | 1 to <3 Years | 3 to <6 Years | 6 to <10 Years | ||||||||||||||
| n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | p | |
| Total Fat | 741 | 27.9 * | 37.1 * | 35.0 * | 294 | 56.5 * | 35.0 a | 8.5 * | 262 | 15.6 | 45.0 b | 39.3 | 185 | 0.0 | 29.2 a | 70.8 | <0.001 |
| Linoleic acid | 741 | 64.6 * | 24.4 * | 10.9 * | 294 | 77.9 * | 13.9 a,* | 8.2 | 262 | 53.8 | 32.4 b | 13.7 | 185 | 58.9 | 29.7 b | 11.4 * | <0.001 |
| α-Linolenic acid | 741 | 96.6 * | 2.4 * | 0.9 * | 294 | 93.2 * | 4.8 a | 2.0 | 262 | 99.2 | 0.4 b | 0.4 | 185 | 98.4 | 1.6 a,b | 0.0 | <0.001 |
| EPA+DHA | 741 | 59.2 * | 2.6 * | 38.2 * | 294 | 56.1 * | 4.4 | 39.5 * | 262 | 63.4 * | 1.1 | 35.5 * | 185 | 58.4 * | 1.6 | 40.0 * | NS |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | 1 to <3 Years | 3 to <6 Years | 6 to <10 Years | ||||||||||||||
| n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | p | |
| Total Fat | 707 | 4.0 | 38.2 | 57.9 | 162 | 16.0 | 30.9 a | 53.1 | 244 | 0.8 | 43.9 b | 55.3 | 301 | 0.0 | 37.5 a,b | 62.5 | <0.001 |
| SFAs ‡ | 629 | 0.6 | 1.1 | 98.3 | 84 | 2.4 | 3.6 | 94.0 | 244 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 98.8 | 301 | 0.3 | 0.7 | 99.0 | NS |
| PUFAs | 707 | 88.8 | 11.2 | 0.0 | 162 | 51.9 | 48.1 a | 0.0 | 244 | 100.0 | 0.0 b | 0.0 | 301 | 99.7 | 0.3 b | 0.0 | <0.001 |
| EPA+DHA | 707 | 67.8 | 5.0 | 27.3 | 162 | 66.7 | 4.9 | 28.4 | 244 | 66.0 | 4.5 | 29.5 | 301 | 69.8 | 5.3 | 24.9 | NS |
| Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |||||||||||||||||
| Total | 1 to <3 Years | 3 to <6 Years | 6 to <10 Years | ||||||||||||||
| n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | n | % BR | % MR | % AR£ | p | |
| Total Fat | 741 | 11.6 * | 35.6 * | 52.8 * | 294 | 29.3 * | 33.7 a,b | 37.1 * | 262 | 0.0 | 42.4 b | 57.6 | 185 | 0.0 | 29.2 a | 70.8 | <0.001 |
| SFAs ‡ | 582 | 0.5 | 2.7 | 96.7 | 135 | 2.2 | 7.4 a | 90.4 | 262 | 0.0 | 1.5 b | 98.5 | 185 | 0.0 | 1.1 b | 98.9 | <0.001 |
| PUFAs | 741 | 78.5 * | 21.5 * | 0.0 * | 294 | 45.9 | 54.1 a | 0.0 | 262 | 100 | 0.0 b | 0.0 | 185 | 100 | 0.0 b | 0.0 | <0.001 |
| EPA+DHA | 741 | 46.0 * | 12.0 * | 42.0 * | 294 | 47.3 * | 13.3 * | 39.5 * | 262 | 42.4 * | 11.5 * | 46.2 * | 185 | 49.2 * | 10.8 * | 40.0 * | NS |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Fat (g/Day) (≥P50) † | SFAs (g/Day) (≥P50) † | MUFAs (g/Day) (≥P50) † | ||||||||
| Factor | Subcategories | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p |
| Sex | Boys | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| Girls | 1.183 | 0.845–1.656 | 0.328 | 1.046 | 0.753–1.454 | 0.787 | 1.424 | 1.017–1.994 | 0.039 * | |
| Age | 1 to <3 years | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 3 to <6 years | 0.089 | 0.054–0.146 | <0.001 * | 0.150 | 0.095–0.237 | <0.001 * | 0.081 | 0.049–0.135 | <0.001 * | |
| 6 to <10 years | 0.416 | 0.290–0.597 | <0.001 * | 0.580 | 0.406–0.830 | 0.003 * | 0.414 | 0.288–0.596 | <0.001 * | |
| Number of feeding bottles or glasses of milk per day | Less than 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 2 or more | 0.894 | 0.626–1.277 | 0.539 | 0.758 | 0.535–1.074 | 0.119 | 1.032 | 0.721–1.477 | 0.864 | |
| Physical activity level (PAL) | ≥P50 by sex and age | 0.756 | 0.371–1.540 | 0.441 | 0.917 | 0.460–1.831 | 0.807 | 0.889 | 0.434–1.821 | 0.748 |
| Size of municipality (n) | 50,000–300,000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| >300,000 | 0.809 | 0.577–1.132 | 0.216 | 0.790 | 0.570–1.095 | 0.156 | 1.063 | 0.757–1.491 | 0.725 | |
| Family income (€) | ≤1500 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 1501–2000 | 1.095 | 0.660–1.817 | 0.724 | 1.196 | 0.735–1.946 | 0.470 | 1.071 | 0.645–1.780 | 0.790 | |
| ≥2000 | 1.258 | 0.748–2.115 | 0.397 | 0.983 | 0.594–1.627 | 0.948 | 1.134 | 0.674–1.909 | 0.635 | |
| Not known/no answer | 1.251 | 0.801–1.954 | 0.325 | 1.280 | 0.830–1.973 | 0.264 | 1.151 | 0.736–1.799 | 0.537 | |
| Highest level of education achieved by one parent | ≤10 years of education | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Secondary education | 1.074 | 0.676–1.705 | 0.763 | 1.621 | 1.037–2.535 | 0.034 * | 0.813 | 0.512–1.292 | 0.381 | |
| University studies | 0.911 | 0.621–1.337 | 0.633 | 1.050 | 0.726–1.517 | 0.796 | 0.814 | 0.554–1.196 | 0.294 | |
| Anthropometry | z-height for age | 1.085 | 0.979–1.202 | 0.121 | 1.067 | 0.967–1.178 | 0.197 | 1.064 | 0.960–1.180 | 0.236 |
| z-BMI for age | 1.076 | 0.973–1.191 | 0.152 | 1.063 | 0.963–1.172 | 0.225 | 1.029 | 0.931–1.137 | 0.581 | |
| Spanish Reference Cohort (SRS) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUFAs (g/Day) (≥P50) † | n-3 (g/Day) (≥P50) † | n-6 (g/Day) (≥P50) † | n-6:n-3 (g/Day) (≥P50) † | ||||||||||
| Factor | Subcategories | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p |
| Sex | Boys | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Girls | 1.386 | 0.984–1.951 | 0.062 | 1.043 | 0.758–1.435 | 0.797 | 1.144 | 0.832–1.571 | 0.408 | 1.194 | 0.876–1.627 | 0.262 | |
| Age | 1 to <3 years | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 3 to <6 years | 0.087 | 0.052–0.145 | <0.001 * | 0.323 | 0.213–0.489 | <0.001 * | 0.293 | 0.191–0.449 | <0.001 * | 0.601 | 0.403–0.896 | 0.013 * | |
| 6 to <10 years | 0.443 | 0.306–0.642 | <0.001 * | 0.659 | 0.462–0.939 | 0.021 * | 0.697 | 0.488–0.996 | 0.048 * | 0.794 | 0.560–1.125 | 0.195 | |
| Number of feeding bottles or glasses of milk per day | Less than 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 2 or more | 1.283 | 0.896–1.837 | 0.173 | 0.898 | 0.641–1.260 | 0.535 | 1.087 | 0.773–1.528 | 0.632 | 1.299 | 0.933–1.808 | 0.122 | |
| Physical activity level (PAL) | ≥P50 by sex and age | 0.459 | 0.224–0.942 | 0.034 * | 0.789 | 0.415–1.500 | 0.470 | 0.795 | 0.413–1.530 | 0.492 | 1.464 | 0.782–2.740 | 0.233 |
| Size of municipality (n) | 50,000–300,000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| >300,000 | 0.719 | 0.512–1.009 | 0.057 | 0.817 | 0.597–1.120 | 0.210 | 0.745 | 0.543–1.023 | 0.069 | 0.869 | 0.637–1.184 | 0.374 | |
| Family income (€) | ≤1500 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| 1501–2000 | 0.979 | 0.588–1.628 | 0.934 | 0.775 | 0.483–1.243 | 0.290 | 1.253 | 0.778–2.020 | 0.353 | 1.119 | 0.703–1.780 | 0.636 | |
| ≥2000 | 1.168 | 0.693–1.969 | 0.559 | 0.755 | 0.464–1.229 | 0.258 | 1.271 | 0.779–2.074 | 0.337 | 1.356 | 0.840–2.187 | 0.212 | |
| Not known/no answer | 1.077 | 0.688–1.684 | 0.746 | 0.882 | 0.581–1.341 | 0.558 | 1.093 | 0.717–1.666 | 0.679 | 1.134 | 0.751–1.712 | 0.549 | |
| Highest level of education achieved by one parent | ≤10 years of education | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Secondary education | 1.310 | 0.822–2.087 | 0.256 | 0.951 | 0.619–1.462 | 0.818 | 1.583 | 1.026–2.441 | 0.038 * | 1.353 | 0.887–2.065 | 0.160 | |
| University studies | 0.801 | 0.545–1.178 | 0.260 | 0.838 | 0.585–1.201 | 0.335 | 1.116 | 0.778–1.600 | 0.552 | 1.118 | 0.785–1.593 | 0.536 | |
| Anthropometry | z-height for age | 1.094 | 0.986–1.214 | 0.091 | 0.966 | 0.876–1.065 | 0.484 | 1.085 | 0.986–1.194 | 0.096 | 1.043 | 0.947–1.149 | 0.395 |
| z-BMI for age | 1.007 | 0.909–1.114 | 0.898 | 1.115 | 1.011–1.229 | 0.029 * | 1.025 | 0.933–1.127 | 0.604 | 0.946 | 0.863–1.037 | 0.237 | |
| Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Fat (g/Day) (≥P50) † | SFAs (g/Day) (≥P50) † | MUFAs (g/Day) (≥P50) † | ||||||||
| Factor | Subcategories | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p |
| Sex | Boys | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Girls | 0.796 | 0.541–1.172 | 0.247 | 0.905 | 0.622–1.317 | 0.602 | 0.812 | 0.559–1.181 | 0.276 | |
| Age | 1 to <3 years | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 3 to <6 years | 0.011 | 0.005–0.021 | <0.001 * | 0.021 | 0.012–0.037 | <0.001 * | 0.018 | 0.010–0.033 | <0.001 * | |
| 6 to <10 years | 0.104 | 0.055–0.197 | <0.001 * | 0.199 | 0.116–0.341 | <0.001 * | 0.149 | 0.084–0.264 | <0.001 * | |
| Number of feeding bottles or glasses of milk per day | Less than 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| 2 or more | 1.232 | 0.784–1.936 | 0.365 | 1.146 | 0.734–1.790 | 0.549 | 1.162 | 0.746–1.810 | 0.508 | |
| Physical activity level (PAL) | ≥P50 by sex and age | 0.704 | 0.319-1.551 | 0.384 | 0.651 | 0.303–1.399 | 0.271 | 0.754 | 0.349–1.628 | 0.472 |
| Size of municipality (n) | 50,000–300,000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| >300,000 | 1.198 | 0.802–1.789 | 0.377 | 0.788 | 0.542–1.147 | 0.214 | 1.264 | 0.862–1.855 | 0.230 | |
| Family income (€) | ≤1500 | 1 | 1 | |||||||
| 1501–2000 | 0.659 | 0.381–1.142 | 0.137 | 0.825 | 0.480–1.417 | 0.485 | 0.751 | 0.442–1.278 | 0.292 | |
| ≥2000 | 0.487 | 0.271–0.873 | 0.016 * | 0.622 | 0.354–1.093 | 0.099 | 0.523 | 0.297–0.920 | 0.025 * | |
| Not known/no answer | 0.763 | 0.467–1.246 | 0.280 | 0.810 | 0.500-1.312 | 0.392 | 0.807 | 0.502–1.298 | 0.377 | |
| Highest level of education achieved by one parent | ≤10 years of education | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||
| Secondary education | 1.390 | 0.771–2.506 | 0.273 | 1.524 | 0.863–2.691 | 0.146 | 1.332 | 0.756–2.348 | 0.321 | |
| University studies | 1.236 | 0.806–1.894 | 0.331 | 1.159 | 0.766–1.752 | 0.485 | 1.273 | 0.842–1.925 | 0.252 | |
| Anthropometry | z- height for age | 1.079 | 0.966–1.205 | 0.179 | 1.098 | 0.987–1.223 | 0.086 | 1.102 | 0.990–1.226 | 0.075 |
| z- BMI for age | 1.016 | 0.895–1.152 | 0.810 | 1.071 | 0.950–1.208 | 0.259 | 1.028 | 0.910–1.161 | 0.662 | |
| Adapted Milk Consumers Cohort (AMS) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PUFAs (g/Day) (≥P50) † | n-3 (g/Day) (≥P50) † | n-6 (g/Day) (≥P50) † | n-6:n-3 (g/Day) (≥P50) † | ||||||||||
| Factor | Subcategories | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p | OR | CI | p |
| Sex | Boys | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Girls | 1.023 | 0.684–1.530 | 0.912 | 0.918 | 0.679–1.242 | 0.581 | 0.975 | 0.714–1.331 | 0.872 | 1.041 | 0.770–1.406 | 0.796 | |
| Age | 1 to <3 years | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 3 to <6 years | 0.009 | 0.004–0.018 | <0.001 * | 0.365 | 0.247–0.540 | <0.001 * | 0.186 | 0.124–0.280 | <0.001 * | 0.432 | 0.295–0.632 | <0.001 * | |
| 6 to <10 years | 0.098 | 0.049–0.196 | <0.001 * | 0.697 | 0.469–1.034 | 0.073 | 0.530 | 0.353–0.795 | 0.002 * | 1.008 | 0.685–1.483 | 0.968 | |
| Number of feeding bottles or glasses of milk per day | Less than 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 2 or more | 1.552 | 0.974–2.474 | 0.065 | 1.113 | 0.777–1.595 | 0.559 | 0.962 | 0.662–1.398 | 0.839 | 0.930 | 0.650–1.331 | 0.692 | |
| Physical activity level (PAL) | ≥P50 by sex and age | 1.037 | 0.448–2.400 | 0.932 | 0.882 | 0.480–1.621 | 0.687 | 1.007 | 0.533–1.905 | 0.982 | 1.106 | 0.601–2.039 | 0.745 |
| Size of municipality (n) | 50,000–300,000 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| >300,000 | 1.117 | 0.738–1.692 | 0.600 | 0.985 | 0.719–1.347 | 0.922 | 1.185 | 0.863–1.627 | 0.295 | 0.991 | 0.725–1.354 | 0.955 | |
| Family income (€) | ≤1500 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| 1501–2000 | 1.348 | 0.760–2.390 | 0.306 | 0.639 | 0.407–1.003 | 0.051 | 0.710 | 0.455–1.107 | 0.131 | 1.077 | 0.687–1.688 | 0.747 | |
| ≥2000 | 1.593 | 0.323–1.087 | 0.091 | 0.567 | 0.358–0.898 | 0.016 * | 0.696 | 0.436–1.110 | 0.128 | 0.770 | 0.489–1.215 | 0.262 | |
| Not known/no answer | 0.732 | 0.439–1.218 | 0.230 | 0.940 | 0.636–1.387 | 0.754 | 0.673 | 0.450–1.006 | 0.053 | 0.821 | 0.557–1.209 | 0.318 | |
| Highest level of education achieved by one parent | ≤10 years of education | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||||||||
| Secondary education | 1.416 | 0.768–2.610 | 0.266 | 0.870 | 0.552–1.371 | 0.547 | 1.412 | 0.883–2.256 | 0.149 | 1.562 | 1.021–2.390 | 0.040 * | |
| University studies | 1.233 | 0.791–1.922 | 0.355 | 1.327 | 0.948–1.857 | 0.099 | 1.213 | 0.858–1.715 | 0.274 | 1.066 | 0.767–1.483 | 0.703 | |
| Anthropometry | z-height for age | 1.185 | 1.052–1.335 | 0.005 * | 1.019 | 0.937–1.109 | 0.657 | 1.017 | 0.932–1.109 | 0.712 | 1.031 | 0.949–1.121 | 0.467 |
| z-BMI for age | 1.089 | 0.955–1.243 | 0.204 | 0.989 | 0.898–1.089 | 0.819 | 0.998 | 0.904–1.102 | 0.967 | 0.985 | 0.895–1.084 | 0.756 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Madrigal, C.; Soto-Méndez, M.J.; Leis, R.; Hernández-Ruiz, Á.; Valero, T.; Lara Villoslada, F.; Martínez de Victoria, E.; Moreno, J.M.; Ortega, R.M.; Ruiz-López, M.D.; et al. Dietary Intake, Nutritional Adequacy and Food Sources of Total Fat and Fatty Acids, and Relationships with Personal and Family Factors in Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years: Results of the EsNuPI Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082467
Madrigal C, Soto-Méndez MJ, Leis R, Hernández-Ruiz Á, Valero T, Lara Villoslada F, Martínez de Victoria E, Moreno JM, Ortega RM, Ruiz-López MD, et al. Dietary Intake, Nutritional Adequacy and Food Sources of Total Fat and Fatty Acids, and Relationships with Personal and Family Factors in Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years: Results of the EsNuPI Study. Nutrients. 2020; 12(8):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082467
Chicago/Turabian StyleMadrigal, Casandra, María José Soto-Méndez, Rosaura Leis, Ángela Hernández-Ruiz, Teresa Valero, Federico Lara Villoslada, Emilio Martínez de Victoria, José Manuel Moreno, Rosa M. Ortega, María Dolores Ruiz-López, and et al. 2020. "Dietary Intake, Nutritional Adequacy and Food Sources of Total Fat and Fatty Acids, and Relationships with Personal and Family Factors in Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years: Results of the EsNuPI Study" Nutrients 12, no. 8: 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082467
APA StyleMadrigal, C., Soto-Méndez, M. J., Leis, R., Hernández-Ruiz, Á., Valero, T., Lara Villoslada, F., Martínez de Victoria, E., Moreno, J. M., Ortega, R. M., Ruiz-López, M. D., Varela-Moreiras, G., & Gil, Á. (2020). Dietary Intake, Nutritional Adequacy and Food Sources of Total Fat and Fatty Acids, and Relationships with Personal and Family Factors in Spanish Children Aged One to <10 Years: Results of the EsNuPI Study. Nutrients, 12(8), 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12082467











