The Relationship between Body Composition and a Gluten Free Diet in Children with Celiac Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
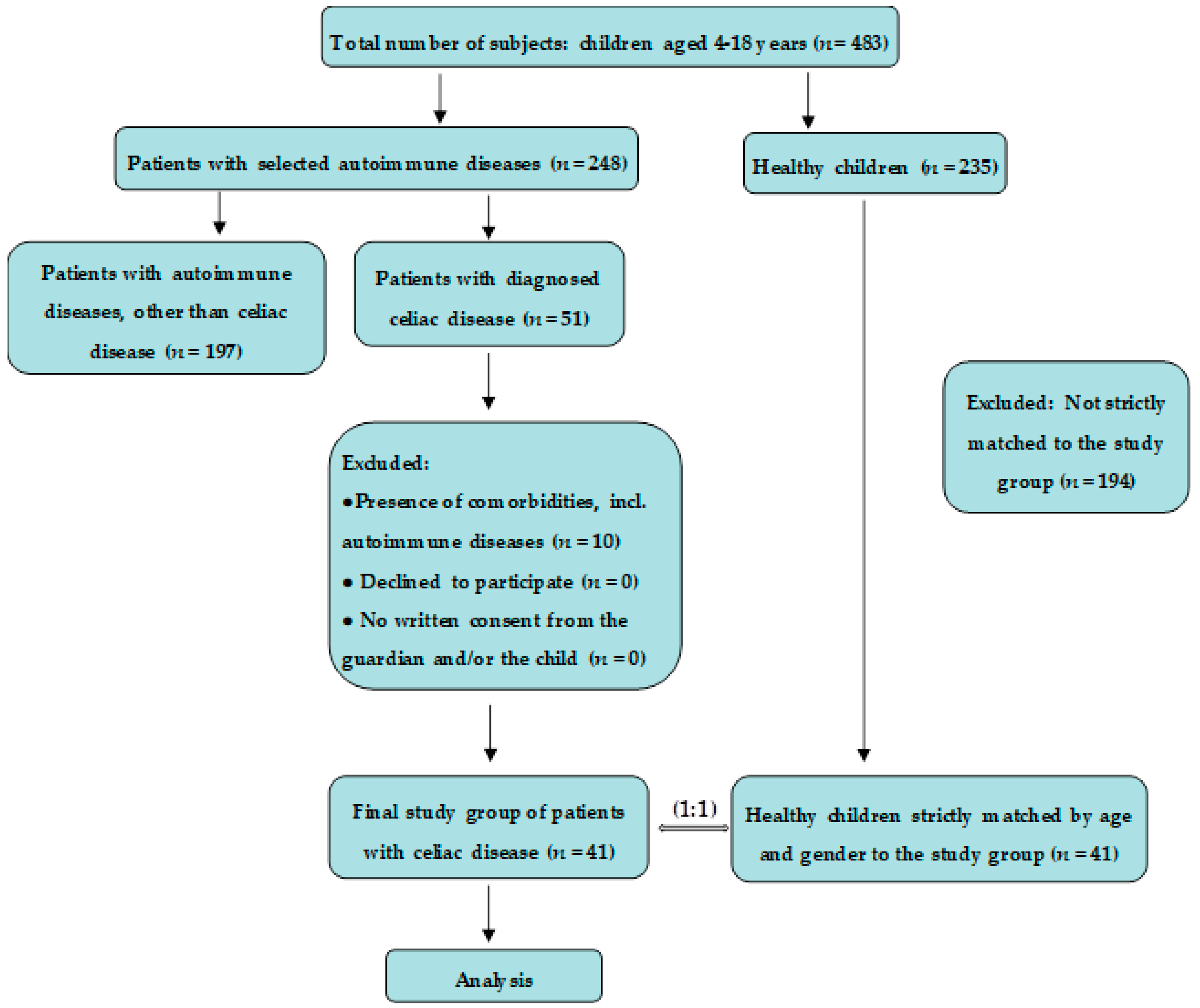
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Assessments
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Husby, S.; Koletzko, S.; Korponay-Szabó, I.R.; Mearin, M.L.; Phillips, A.; Shamir, R.; Troncone, R.; Giersiepen, K.; Branski, D.; Catassi, C.; et al. European society for pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition guidelines for the diagnosis of coeliac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2012, 54, 136–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivarsson, A.; Myléus, A.; Norström, F.; van der Pals, M.; Rosén, A.; Högberg, L.; Danielsson, L.; Halvarsson, B.; Hammarroth, S.; Hernell, O.; et al. Prev–alence of childhood celiac disease and changes in infant feeding. Pediatrics 2013, 131, e687–e694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almazán, M.V.; Ortega, E.; Moreno Torres, R.; Tovar, M.; Romero, J.; López-Casado, M.Á.; Jáimez, L.; Jiménez-Jáimez, J.; Ballesteros, A.; Caballero-Villarraso, J.; et al. Diagnostic screening for subclinical celiac disease using a rapid test in children aged 2–4. Pediatr. Res. 2015, 78, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bascuñán, K.A.; Roncoroni, L.; Branchi, F.; Doneda, L.; Scricciolo, A.; Ferretti, F.; Araya, M.; Elli, L. The 5 Ws of a gluten challenge for gluten-related disorders. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustalahti, K.; Catassi, C.; Reunanen, A.; Fabiani, E.; Heier, M.; McMillan, S.; Murray, L.; Metzger, M.H.; Gasparin, M.; Bravi, E.; et al. The prevalence of celiac disease in Europe: Results of a centralized, international mass screening project. Ann. Med. 2010, 42, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obtułowicz, K.; Waga, J.; Dyga, W. Gluten-mechanisms of intolerance, symptoms and treatment possibilities of IgE-related allergy for gluten in the light of actual clinical and immunological studies. Przegl. Lek. 2015, 72, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fasano, A.; Catassi, C. Clinical practice. Celiac disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2419–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parzanese, I.; Qehajaj, D.; Patrinicola, F.; Aralica, M.; Chiriva-Internati, M.; Stifter, S.; Elli, L.; Grizzi, F. Celiac disease: From pathophysiology to treatment. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2017, 8, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulido, O.; Zarkadas, M.; Dubois, S.; Macisaac, K.; Cantin, I.; La Vieille, S.; Godefroy, S.; Rashid, M. Clinical features and symptom recovery on a gluten-free diet in Canadian adults with celiac disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 27, 449–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzaben, A.S.; Turner, J.; Shirton, L.; Samuel, T.M.; Persad, R.; Mager, D. Assessing nutritional quality and adherence to the gluten-free diet in children and adolescents with celiac disease. Can. J. Diet. Pract. Res. 2015, 76, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurikka, P.; Salmi, T.; Collin, P.; Huhtala, H.; Mäki, M.; Kaukinen, K.; Kurppa, K. Gastrointestinal symptoms in celiac disease patients on a long-term gluten-free diet. Nutrients 2016, 8, E429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shepherd, S.J.; Gibson, P.R. Nutritional inadequacies of the gluten-free diet in both recently-diagnosed and long-term patients with coeliac disease. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2013, 26, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brambilla, P.; Picca, M.; Dilillo, D.; Meneghin, F.; Cravidi, C.; Tischer, M.C.; Vivaldo, T.; Bedogni, G.; Zuccotti, G.V. Changes of body mass index in celiac children on a gluten-free diet. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 23, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anania, C.; Pacifico, L.; Olivero, F.; Perla, F.M.; Chiesa, C. Cardiometabolic risk factors in children with celiac disease on a gluten-free diet. World J. Clin. Pediatr. 2017, 6, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiountsioura, M.; Wong, J.E.; Upton, J.; McIntyre, K.; Dimakou, D.; Buchanan, E.; Cardigan, T.; Flynn, D.; Bishop, J.; Russell, R.K.; et al. Detailed assessment of nutritional status and eating patterns in children with gastrointestinal diseases attending an outpatients clinic and contemporary healthy controls. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 68, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newnham, E.D.; Shepherd, S.J.; Strauss, B.J.; Hosking, P.; Gibson, P.R. Adherence to the gluten-free diet can achieve the therapeutic goals in almost all patients with coeliac disease: A 5-year longitudinal study from diagnosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, M.C.; Pitzalis, G.; Ferri, M.; Nenna, R.; Thanasi, E.; Andreoli, A.; De Lorenzo, A.; Bonamico, M. Body composition in coeliac disease adolescents on a gluten-free diet: A longitudinal study. Acta Diabetol. 2003, 40, S171–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barera, G.; Mora, S.; Brambilla, P.; Ricotti, A.; Menni, L.; Beccio, S.; Bianchi, C. Body composition in children with celiac disease and the effects of a gluten-free diet: A prospective case-control study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 71–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lorenzo, A.; Di Campli, C.; Andreoli, A.; Sasso, G.F.; Bonamico, M.; Gasbarrini, A. Assessment of body composition by bioelectrical impedance in adolescent patients with celiac disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1999, 94, 2951–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Morgan, S.L. Celiac disease and metabolic bone disease. J. Clin. Densitom. 2013, 16, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Więch, P.; Dąbrowski, M.; Bazaliński, D.; Sałacińska, I.; Korczowski, B.; Binkowska-Bury, M. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle as an indicator of malnutrition in hospitalized children with diagnosed inflammatory bowel diseases—A case control study. Nutrients 2018, 10, 499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bardella, M.T.; Molteni, N.; Prampolini, L.; Giunta, A.M.; Baldassarri, A.R.; Morganti, D.; Bianchi, P.A. Need for follow up in coeliac disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 1994, 70, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troncone, R.; Mayer, M.; Spagnuolo, F.; Maiuri, L.; Greco, L. Endomysial antibodies as unreliable markers for slight dietary transgressions in adolescents with celiac disease. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 1995, 21, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberhuber, G.; Granditsch, G.; Vogelsang, H. The histopathology of coeliac disease: Time for a standardized report scheme for pathologists. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1999, 11, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanovski, S.Z.; Hubbard, V.S.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Lukaski, H.C. Bioelectrical impedance analysis in body composition measurement: National institutes of health technology assessment conference statement. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1996, 64, 524S–532S. [Google Scholar]
- Kyle, U.G.; Bosaeus, I.; de Lorenzo, A.D.; Deurenberg, P.; Elia, M.; Manuel Gómez, J.; Heitmann, B.L.; Kent-Smith, L.; Melchior, J.C.; Pirlich, M.; et al. Bioelectrical impedance analysis—Part II: Utilization in clinical practice. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 23, 1430–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushner, R.F. Bioelectrical impedance analysis: A review of principles and applications. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1992, 11, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barone, M.; Della, V.N.; Rosania, R.; Facciorusso, A.; Trotta, A.; Cantatore, F.P.; Falco, S.; Pignatiello, S.; Viggiani, M.T.; Amoruso, A.; et al. A comparison of the nutritional status between adult celiac patients on a long-term, strictly gluten-free diet and healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 70, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capristo, E.; Addolorato, G.; Mingrone, G.; De Gaetano, A.; Greco, A.V.; Tataranni, P.A.; Gasbarrini, G. Changes in body composition, substrate oxidation, and resting metabolic rate in adult celiac disease patients after a 1-y gluten-free diet treatment. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazina, S.; Bratanic, N.; Campa, A.S.; Blagus, R.; Orel, R. Bone mineral density and importance of strict gluten-free diet in children and adolescents with celiac disease. Bone 2010, 47, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abenavoli, L.; Delibasic, M.; Peta, V.; Turkulov, V.; De Lorenzo, A.; Medić-Stojanoska, M. Nutritional profile of adult patients with celiac disease. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 4285–4292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forchielli, M.L.; Fernicola, P.; Diani, L.; Scrivo, B.; Salfi, N.C.; Pessina, A.C.; Lima, M.; Conti, V.; Pession, A. Gluten-free diet and lipid profile in children with celiac disease: Comparison with general population standards. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 61, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sue, A.; Dehlsen, K.; Ooi, C.Y. Paediatric patients with coeliac disease on a gluten-free diet: Nutritional adequacy and macro- and micronutrient imbalances. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2018, 22, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessahraoui, M.; Bouziane, N.K.; Boudraa, G.; Touhami, M. Growth and puberty in the coeliac disease of the child. Pediatr. Res. 2011, 70, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Yonamine, G.H.; Fernandes Satiro, C.A. Rate and determinants of non-adherence to a gluten-free diet and nutritional status assessment in children and adolescents with celiac disease in a tertiary Brazilian referral center: A cross-sectional and retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickey, W.; Kearney, N. Overweight in celiac disease: Prevalence, clinical characteristics, and effect of a gluten-free diet. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 101, 2356–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nenna, R.; Mosca, A.; Mennini, M.; Papa, R.E.; Petrarca, L.; Mercurio, R.; Montuori, M.; Piedimonte, A.; Bavastrelli, M.; De Lucia, I.C.; et al. Coeliac disease screening among a large cohort of overweight/obese children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, N.R.; Aguilar, K.; Hassid, B.G.; Cheng, J.; Defelice, A.R.; Kazlow, P.; Bhagat, G.; Green, P.H. Celiac disease in normal-weight and overweight children: Clinical features and growth outcomes following a gluten-free diet. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2011, 53, 528–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddh, L.; Sengar, G.S.; Nagraj, N.; Shyam, R.; Garg, P. Body mass index in celiac disease and effect of a gluten-free diet on body mass index. Int. J. Adv. Med. 2016, 3, 813–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radlović, N.; Mladenović, M.; Leković, Z.; Zivanović, D.; Brdar, R.; Radlović, V.; Ristić, D.; Pavlović, M.; Stojsić, Z.; Vuletić, B.; et al. Effect of gluten-free diet on the growth and nutritional status of children with coeliac disease. Srp. Arh. Celok. Lek. 2009, 137, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glissen Brown, J.R.; Singh, P. Coeliac disease. Paediatr. Int. Child. Health. 2018, 13, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, J.C.; Kumar, P.; Dutta, A.K.; Basu, S.; Kumar, A. Assessmentof dietary compliance to gluten free diet and psychosocialproblems in Indian children with celiac disease. Indian J. Pediatr. 2010, 77, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roma, E.; Roubani, A.; Kolia, E.; Panayiotou, J.; Zellos, A.; Syriopoulou, V.P. Dietarycompliance and life style of children with coeliac disease. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2010, 23, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.J.; Walker-Smith, J.; Milla, P.; Harris, G.; Colyer, J.; Halliday, R. Theteenage coeliac: Follow up study of 102 patients. Arch. Dis. Child. 1988, 63, 916–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, L.E.; Bannerman, E.; Gillett, P.M. Coeliac disease and the gluten-free diet: A review of the burdens; factors associated with adherence and impact on health-related quality of life, with specific focus on adolescence. J. Hum. Nutr. Diet. 2016, 29, 593–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Celiac Disease (N = 41) | Control (N = 41) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age, years | 10.81 | 3.96 | 10.63 | 4.01 | 0.989 |
| Gender, n | 1.000 | ||||
| Male | 21 | n/a | 21 | n/a | |
| Female | 20 | n/a | 20 | n/a | |
| Weight, kg | 33.59 | 13.79 | 39.70 | 15.25 | 0.046 * |
| Height, cm | 137.62 | 21.68 | 144.20 | 19.63 | 0.167 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 16.94 | 2.65 | 18.29 | 3.49 | 0.089 |
| Parameter | Celiac Disease (N = 41) | Control (N = 41) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| FM, kg | 6.66 | 4.19 | 9.47 | 5.15 | 0.007 * |
| FFM, kg | 26.15 | 10.72 | 30.24 | 11.57 | 0.098 |
| MM, kg | 17.17 | 7.45 | 19.55 | 8.10 | 0.168 |
| TBW, L | 22.71 | 10.96 | 23.73 | 8.72 | 0.312 |
| ECW, L | 9.33 | 3.47 | 10.28 | 3.73 | 0.246 |
| ICW, L | 12.35 | 4.86 | 13.55 | 5.16 | 0.170 |
| BCM, kg | 13.89 | 6.11 | 15.85 | 6.64 | 0.164 |
| FM% | 19.32 | 7.36 | 23.34 | 7.36 | 0.015 * |
| FFM% | 80.68 | 7.36 | 76.66 | 7.36 | 0.015 * |
| MM% | 50.72 | 5.98 | 48.94 | 5.62 | 0.168 |
| TBW% | 65.22 | 8.94 | 60.47 | 7.66 | 0.012 * |
| ECW% | 43.86 | 5.18 | 43.82 | 3.59 | 0.981 |
| ICW% | 56.14 | 5.18 | 56.18 | 3.59 | 0.981 |
| BCM% | 50.66 | 3.96 | 51.62 | 3.73 | 0.373 |
| BCMI | 6.91 | 1.28 | 7.22 | 1.50 | 0.322 |
| PA | 5.45 | 0.67 | 5.63 | 0.69 | 0.241 |
| Parameter | Compliant to GFD (N = 26) | Non-Compliant to GFD (N = 15) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age, years | 11.00 | 4.10 | 10.47 | 3.82 | 0.683 |
| Gender, n | 0.239 | ||||
| Male | 11 | n/a | 10 | n/a | |
| Female | 15 | n/a | 5 | n/a | |
| Disease duration, months | 74.23 | 58.10 | 26.07 | 40.93 | 0.002 * |
| Marsh scale | 0.584 | ||||
| IIIA | 4 | n/a | 3 | n/a | |
| IIIB | 9 | n/a | 7 | n/a | |
| IIIC | 13 | n/a | 5 | n/a | |
| Weight, kg | 35.67 | 14.07 | 29.99 | 12.96 | 0.208 |
| Height, cm | 141.02 | 21.73 | 131.73 | 21.00 | 0.190 |
| BMI | 17.22 | 2.55 | 16.45 | 2.84 | 0.272 |
| FM | 7.48 | 4.24 | 5.24 | 3.82 | 0.064 |
| FFM | 28.19 | 11.01 | 22.62 | 9.53 | 0.110 |
| MM | 17.95 | 7.63 | 15.83 | 7.17 | 0.388 |
| TBW | 22.49 | 8.00 | 23.08 | 15.12 | 0.675 |
| ECW | 9.65 | 3.56 | 8.76 | 3.35 | 0.434 |
| ICW | 12.91 | 4.67 | 11.37 | 5.18 | 0.457 |
| BCM | 14.52 | 6.26 | 12.79 | 5.89 | 0.390 |
| FM% | 20.81 | 6.60 | 16.73 | 8.10 | 0.087 |
| FFM% | 79.19 | 6.60 | 83.27 | 8.10 | 0.087 |
| MM% | 49.88 | 5.60 | 52.17 | 6.52 | 0.241 |
| TBW% | 63.89 | 8.69 | 67.52 | 9.19 | 0.214 |
| ECW% | 43.27 | 4.15 | 44.88 | 6.64 | 0.345 |
| ICW% | 56.73 | 4.15 | 55.12 | 6.64 | 0.345 |
| BCM% | 50.80 | 3.18 | 50.41 | 5.17 | 0.745 |
| BCMI | 6.91 | 1.16 | 6.90 | 1.50 | 0.978 |
| PA | 5.47 | 0.58 | 5.43 | 0.83 | 0.862 |
| Parameter | Baseline (N = 22) | Follow-Up (N = 22) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Age, years | 10.05 | 4.08 | 11.41 | 4.08 | <0.001 * |
| Disease duration, months | 63.68 | 67.61 | 80.86 | 68.14 | <0.001 * |
| Weight, kg | 32.40 | 15.68 | 36.01 | 14.08 | <0.001 * |
| Height, cm | 134.50 | 24.62 | 142.14 | 23.14 | <0.001 * |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 16.81 | 2.76 | 17.07 | 2.09 | 0.046 * |
| FM, kg | 7.20 | 4.62 | 7.42 | 3.75 | 0.101 |
| FFM, kg | 25.20 | 12.17 | 28.59 | 11.91 | 0.001 * |
| MM, kg | 16.05 | 8.45 | 18.33 | 8.24 | <0.001 * |
| TBW, L | 20.16 | 9.25 | 22.81 | 9.02 | <0.001 * |
| ECW, L | 8.63 | 3.89 | 9.83 | 3.95 | 0.003 * |
| ICW, L | 11.63 | 5.61 | 12.98 | 5.28 | <0.001 * |
| BCM, kg | 12.99 | 6.93 | 14.85 | 6.74 | <0.001 * |
| FM% | 22.05 | 6.50 | 21.17 | 6.94 | 0.972 |
| FFM% | 77.95 | 6.50 | 78.83 | 6.94 | 0.972 |
| MM% | 48.78 | 5.76 | 49.96 | 5.76 | 0.167 |
| TBW% | 62.66 | 8.50 | 63.39 | 9.00 | 0.455 |
| ECW% | 43.79 | 5.03 | 43.56 | 4.40 | 0.788 |
| ICW% | 56.21 | 5.03 | 56.44 | 4.40 | 0.788 |
| BCM% | 50.40 | 3.58 | 51.13 | 3.19 | 0.102 |
| BCMI | 6.60 | 1.26 | 6.88 | 1.12 | 0.005 * |
| PA | 5.40 | 0.64 | 5.54 | 0.61 | 0.121 |
| Parameter | Compliant to GFD (N = 17) | Non-Compliant to GFD (N = 5) | p Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | ||
| Weight increase, kg | 4.16 | 6.65 | 1.74 | 0.40 | 0.034 * |
| Height increase, cm | 8.12 | 5.47 | 6.00 | 3.37 | 0.426 |
| BMI increase, kg/m2 | 0.47 | 2.13 | -0.44 | 0.78 | 0.021 * |
| FM increase, kg | 0.47 | 3.66 | -0.64 | 2.06 | 0.078 |
| FFM increase, kg | 3.69 | 4.90 | 2.38 | 2.39 | 0.308 |
| MM increase, kg | 2.51 | 3.26 | 1.48 | 1.86 | 0.182 |
| TBW increase, L | 2.45 | 3.21 | 3.34 | 3.47 | 0.597 |
| ECW increase, L | 1.37 | 2.04 | 0.64 | 0.60 | 0.209 |
| ICW increase, L | 0.96 | 1.45 | 2.70 | 2.92 | 0.610 |
| BCM increase, kg | 2.05 | 2.64 | 1.22 | 1.57 | 0.240 |
| BCMI increase | 0.31 | 0.72 | 0.20 | 0.53 | 0.289 |
| PA increase | 0.14 | 0.41 | 0.12 | 0.40 | 0.919 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Więch, P.; Chmiel, Z.; Bazaliński, D.; Sałacińska, I.; Bartosiewicz, A.; Mazur, A.; Korczowski, B.; Binkowska-Bury, M.; Dąbrowski, M. The Relationship between Body Composition and a Gluten Free Diet in Children with Celiac Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111817
Więch P, Chmiel Z, Bazaliński D, Sałacińska I, Bartosiewicz A, Mazur A, Korczowski B, Binkowska-Bury M, Dąbrowski M. The Relationship between Body Composition and a Gluten Free Diet in Children with Celiac Disease. Nutrients. 2018; 10(11):1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111817
Chicago/Turabian StyleWięch, Paweł, Zdzisława Chmiel, Dariusz Bazaliński, Izabela Sałacińska, Anna Bartosiewicz, Artur Mazur, Bartosz Korczowski, Monika Binkowska-Bury, and Mariusz Dąbrowski. 2018. "The Relationship between Body Composition and a Gluten Free Diet in Children with Celiac Disease" Nutrients 10, no. 11: 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111817
APA StyleWięch, P., Chmiel, Z., Bazaliński, D., Sałacińska, I., Bartosiewicz, A., Mazur, A., Korczowski, B., Binkowska-Bury, M., & Dąbrowski, M. (2018). The Relationship between Body Composition and a Gluten Free Diet in Children with Celiac Disease. Nutrients, 10(11), 1817. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10111817







