Decadal and Heterogeneous Deformation of Breakwater Dams and Reclaimed Lands in Xuwei Port Revealed by Radar Interferometry Measurements
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. InSAR Data Processing
3. Results
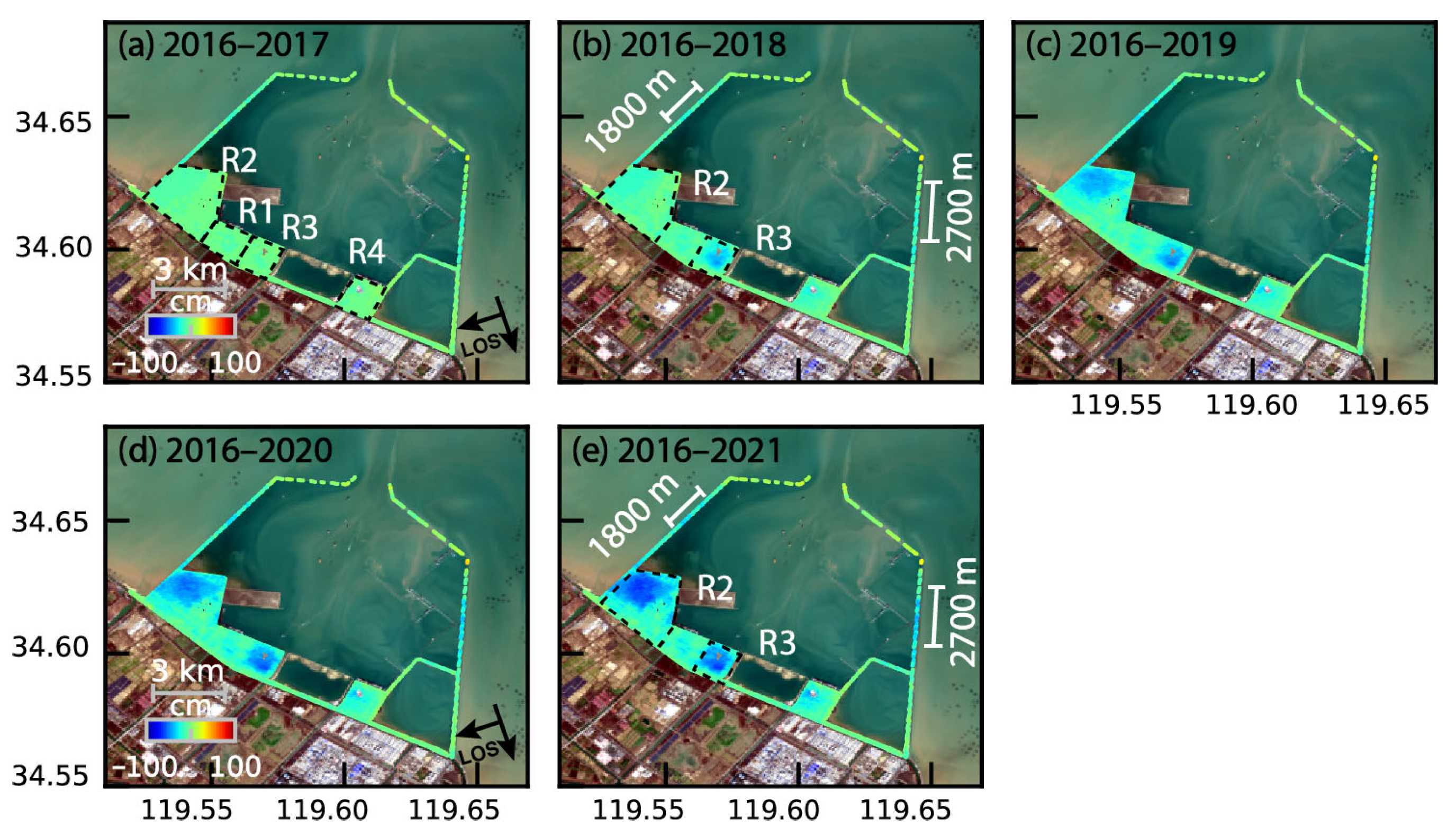
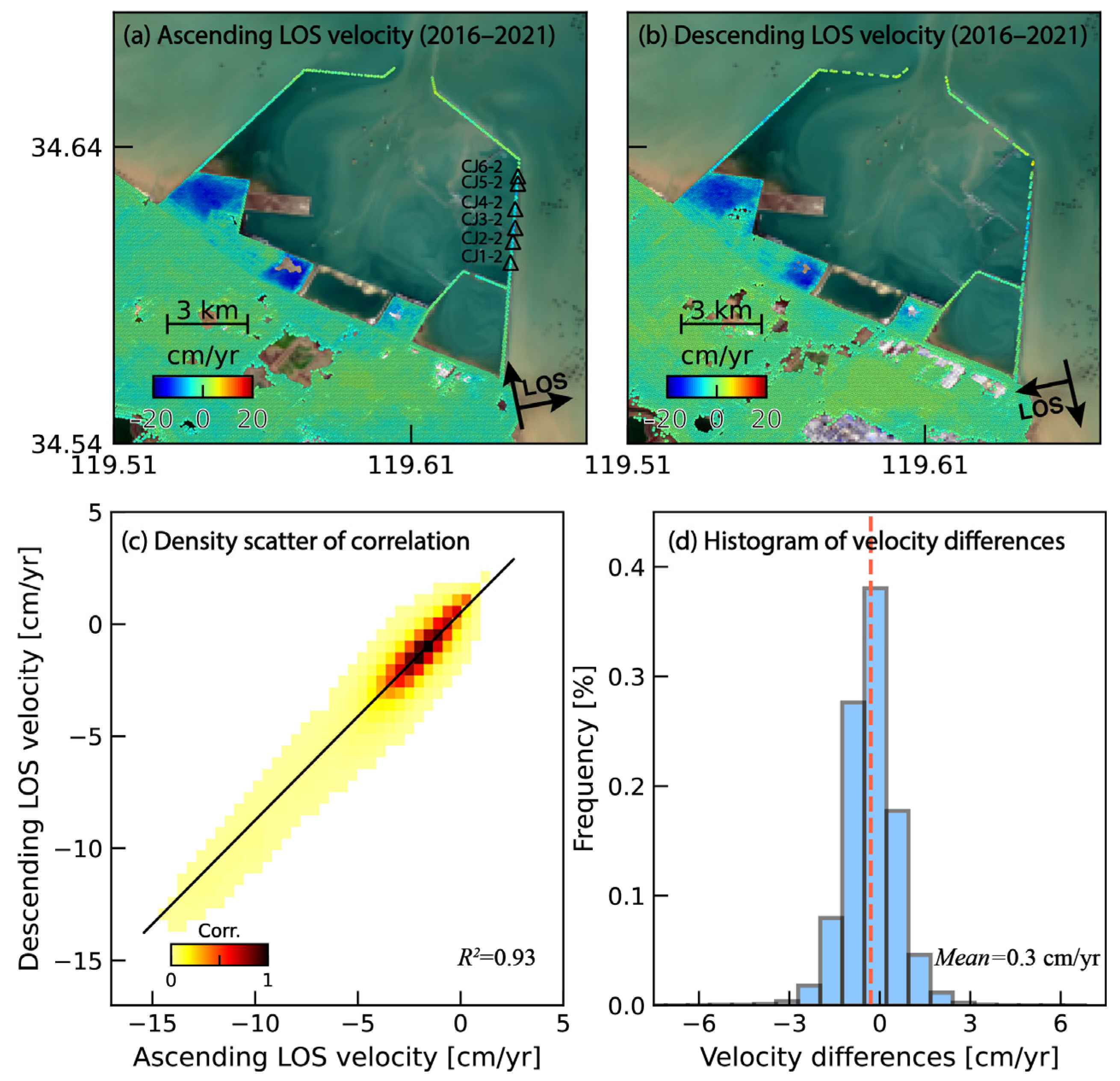
3.1. InSAR Deformation and Validation
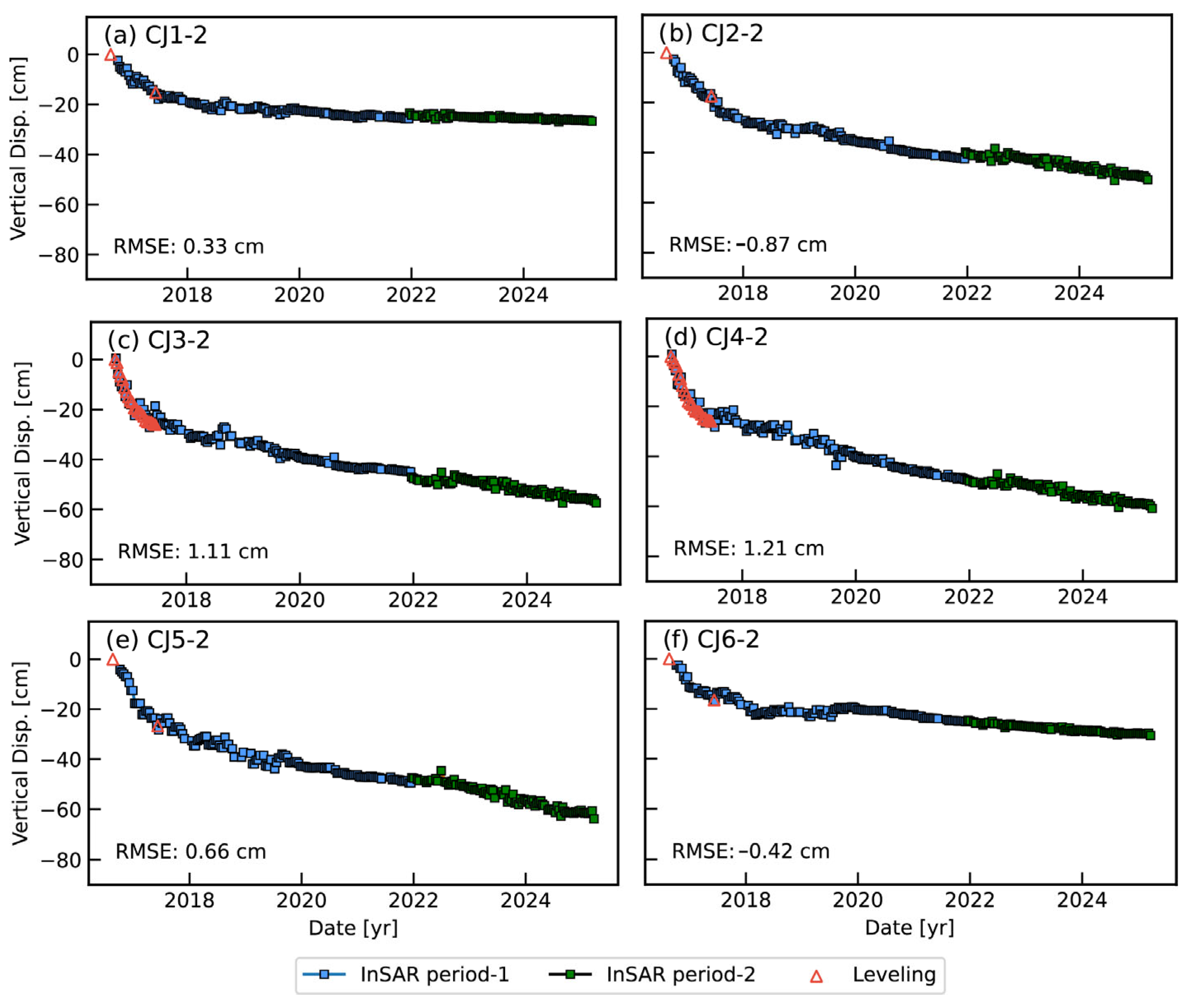
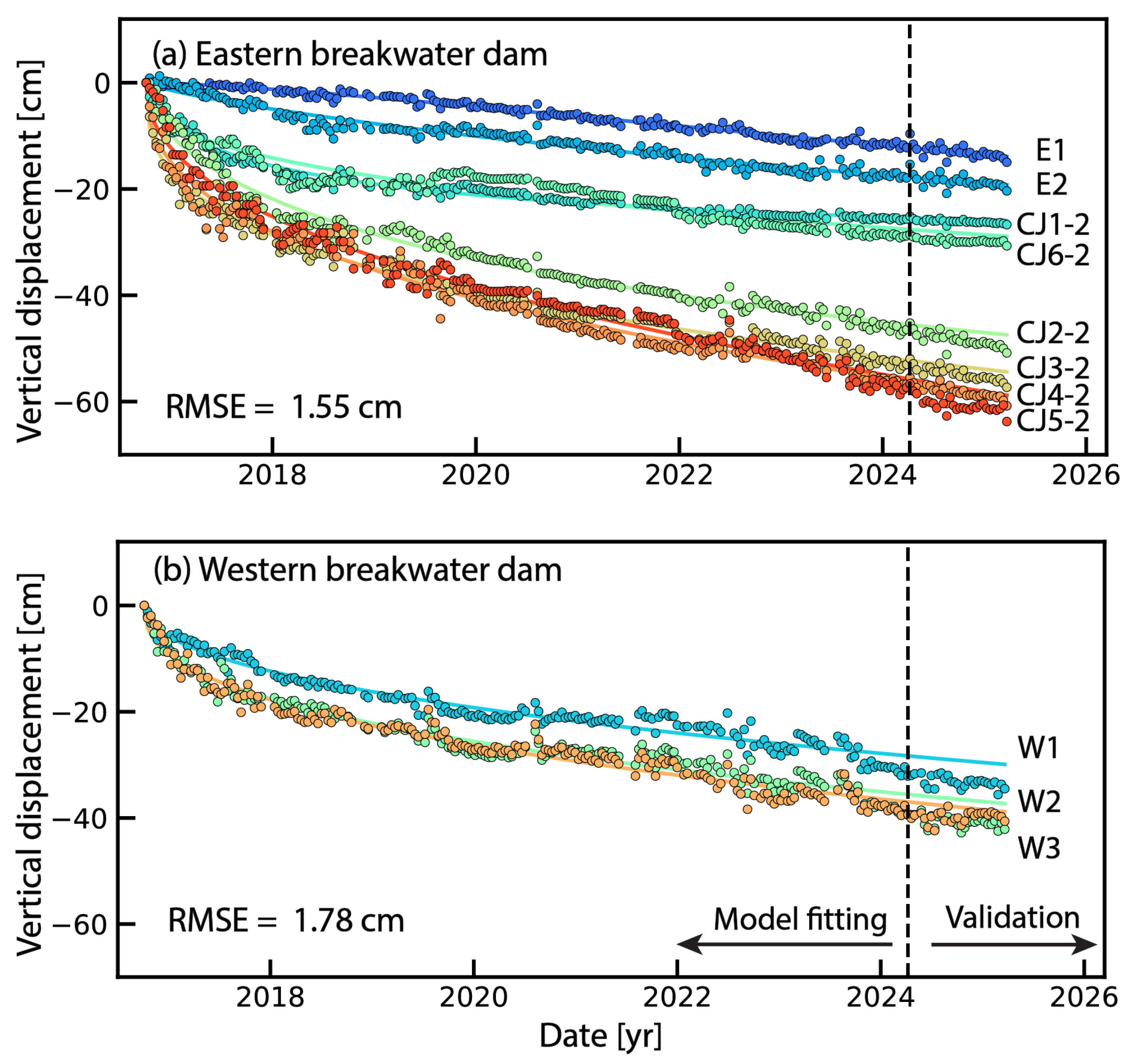
3.2. Time-Series Deformation on Breakwater Dams
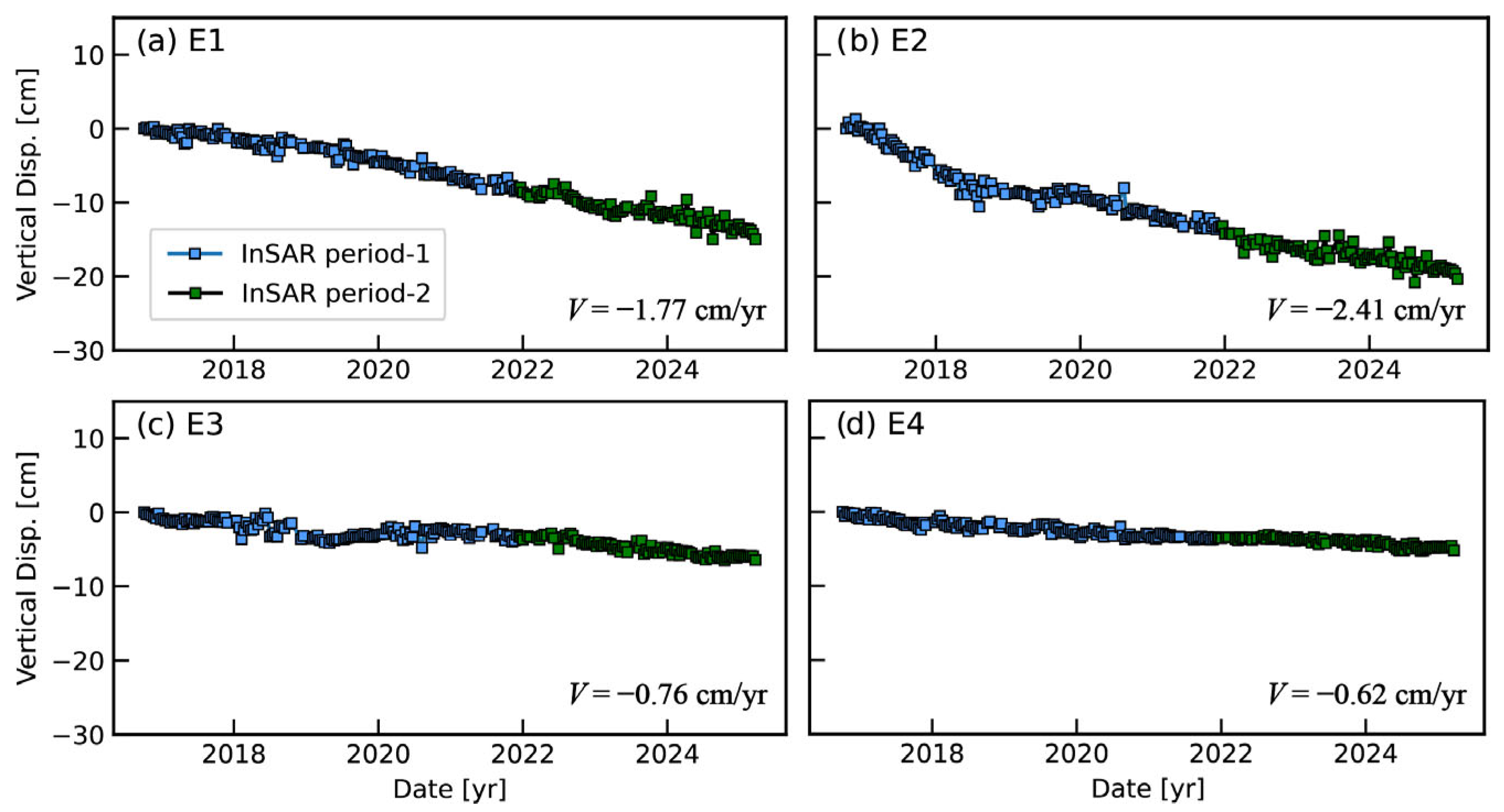
3.2.1. Eastern Breakwater Dam
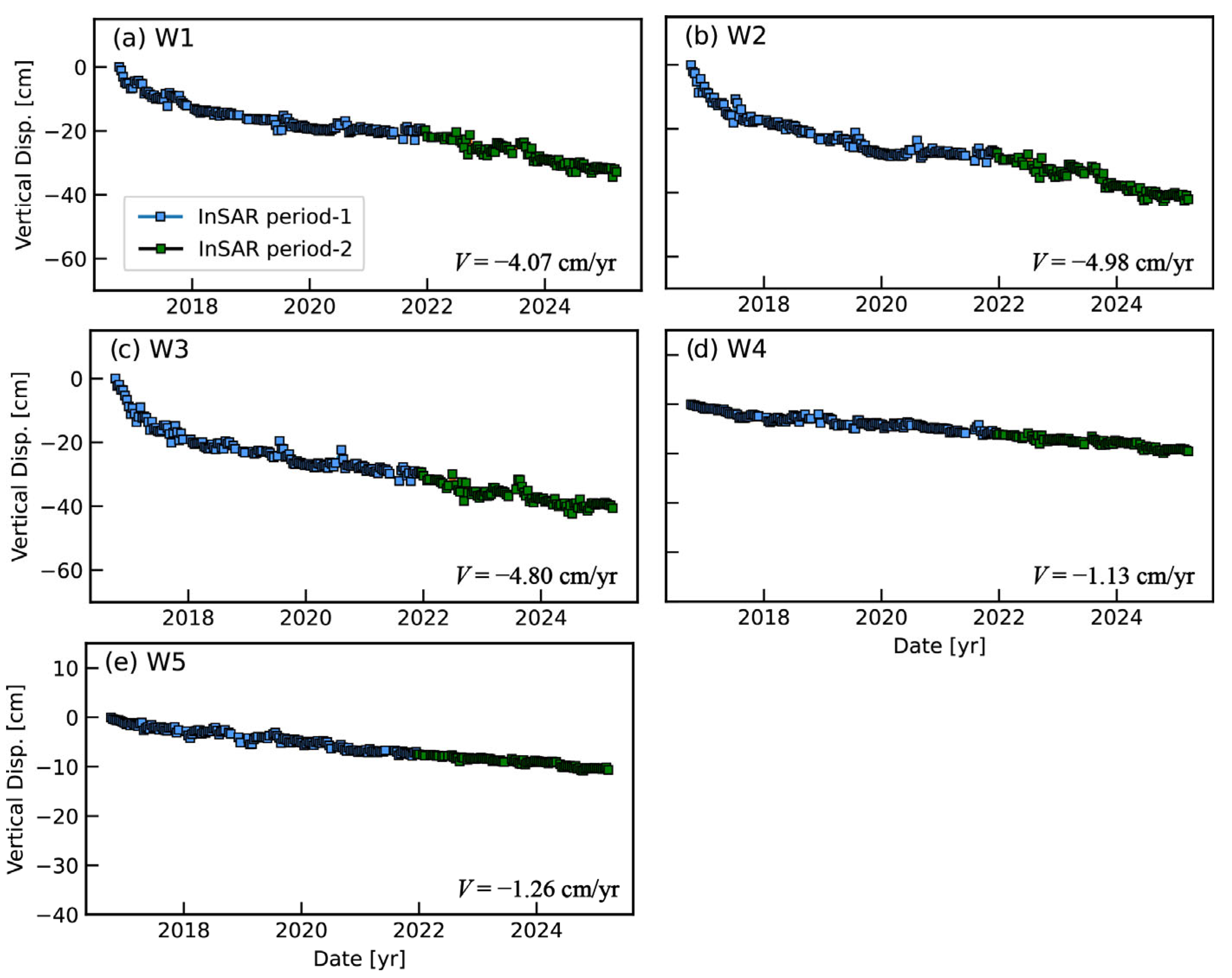
3.2.2. Western Breakwater Dam
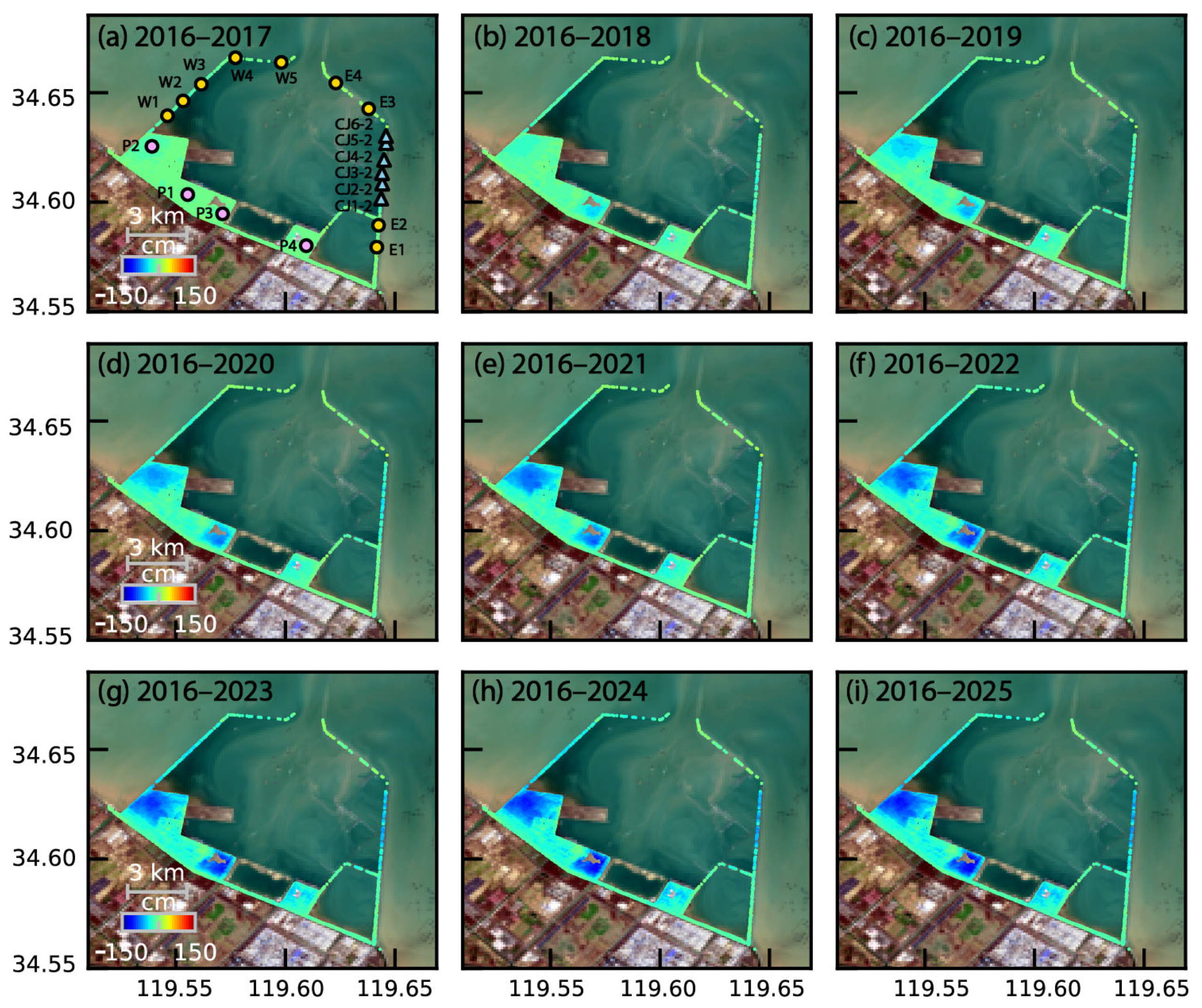
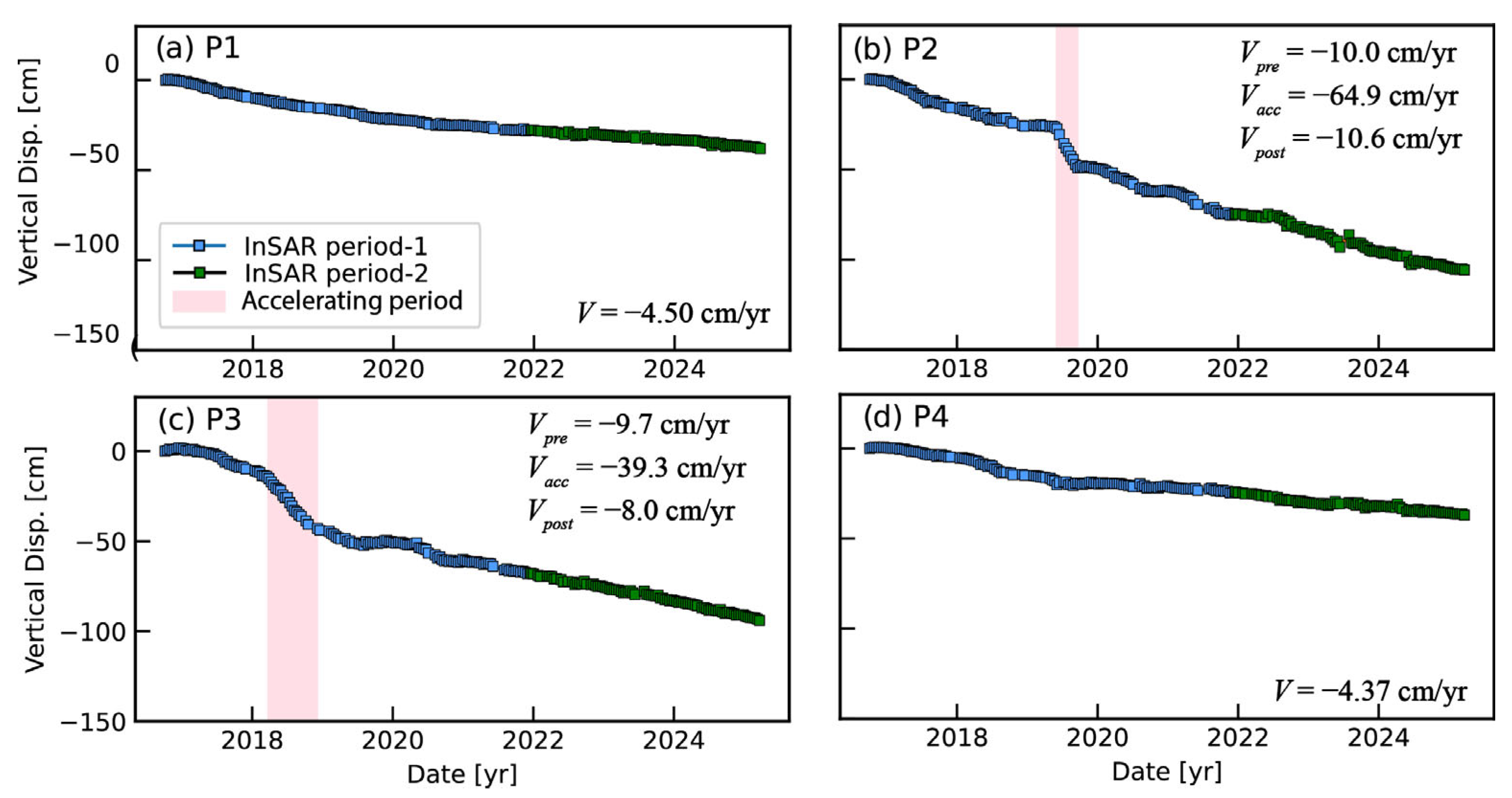
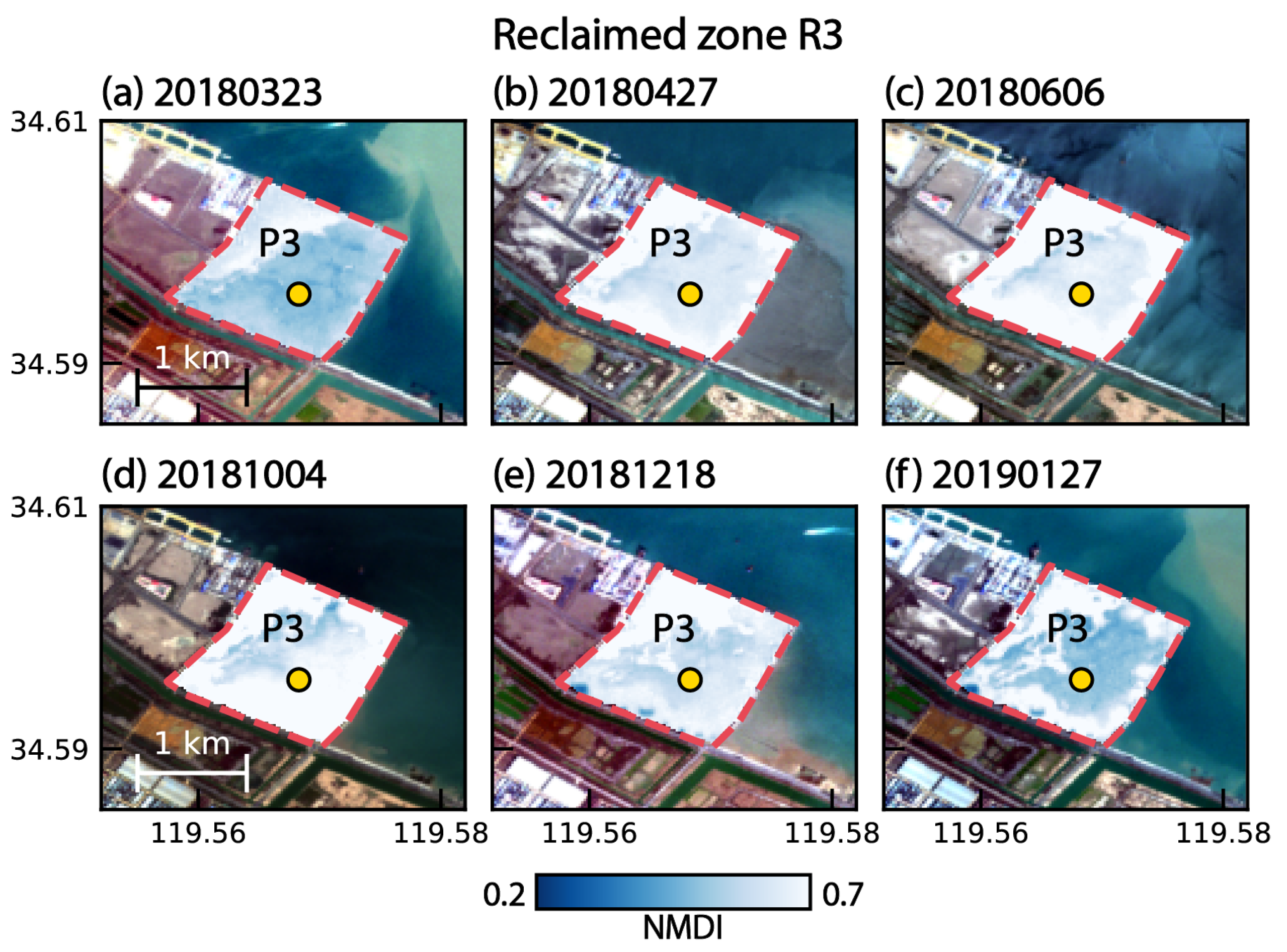
3.3. Time-Series Deformation on Reclamation Lands
4. Discussion
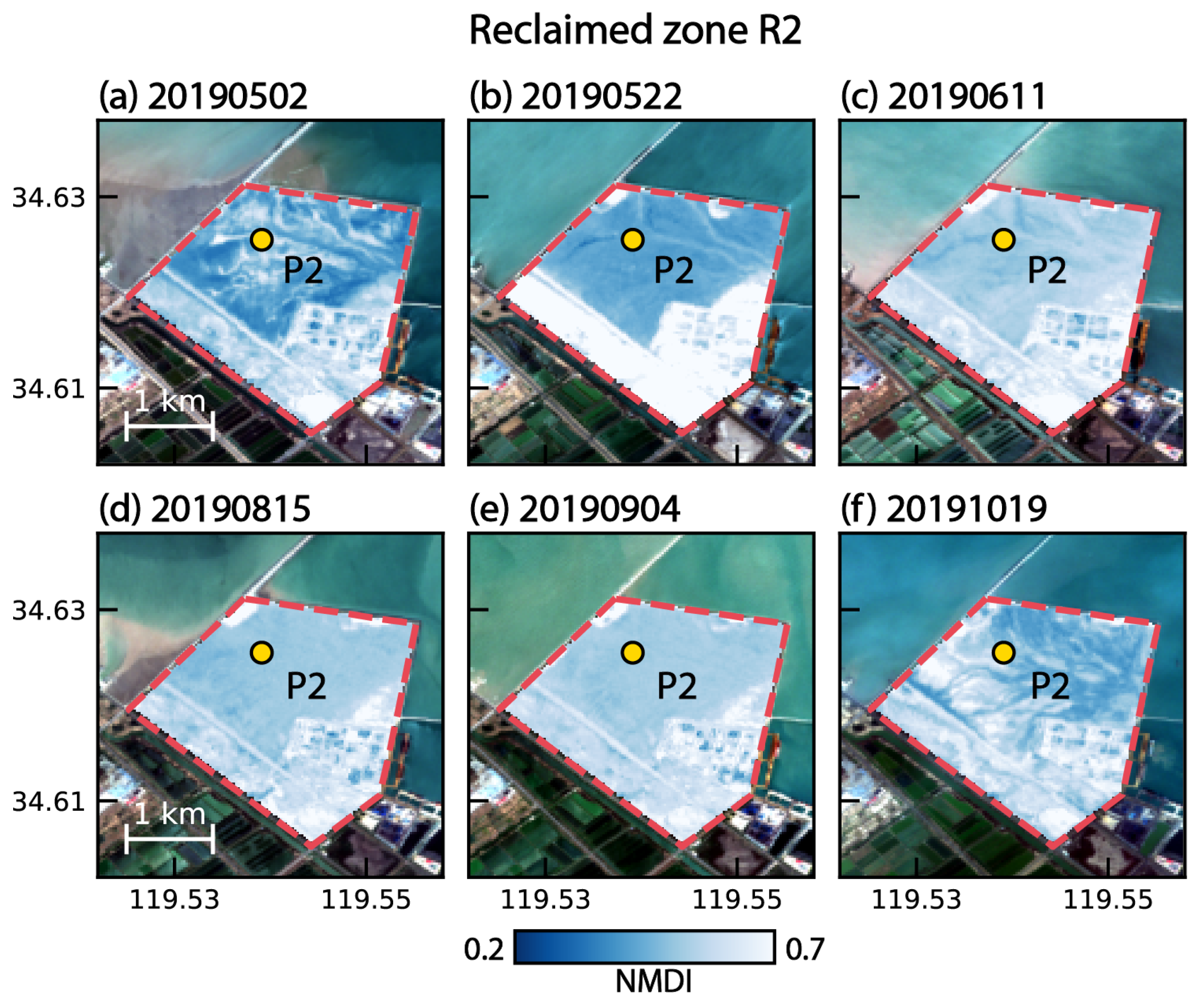
4.1. The Mechanism of Dam Deformation
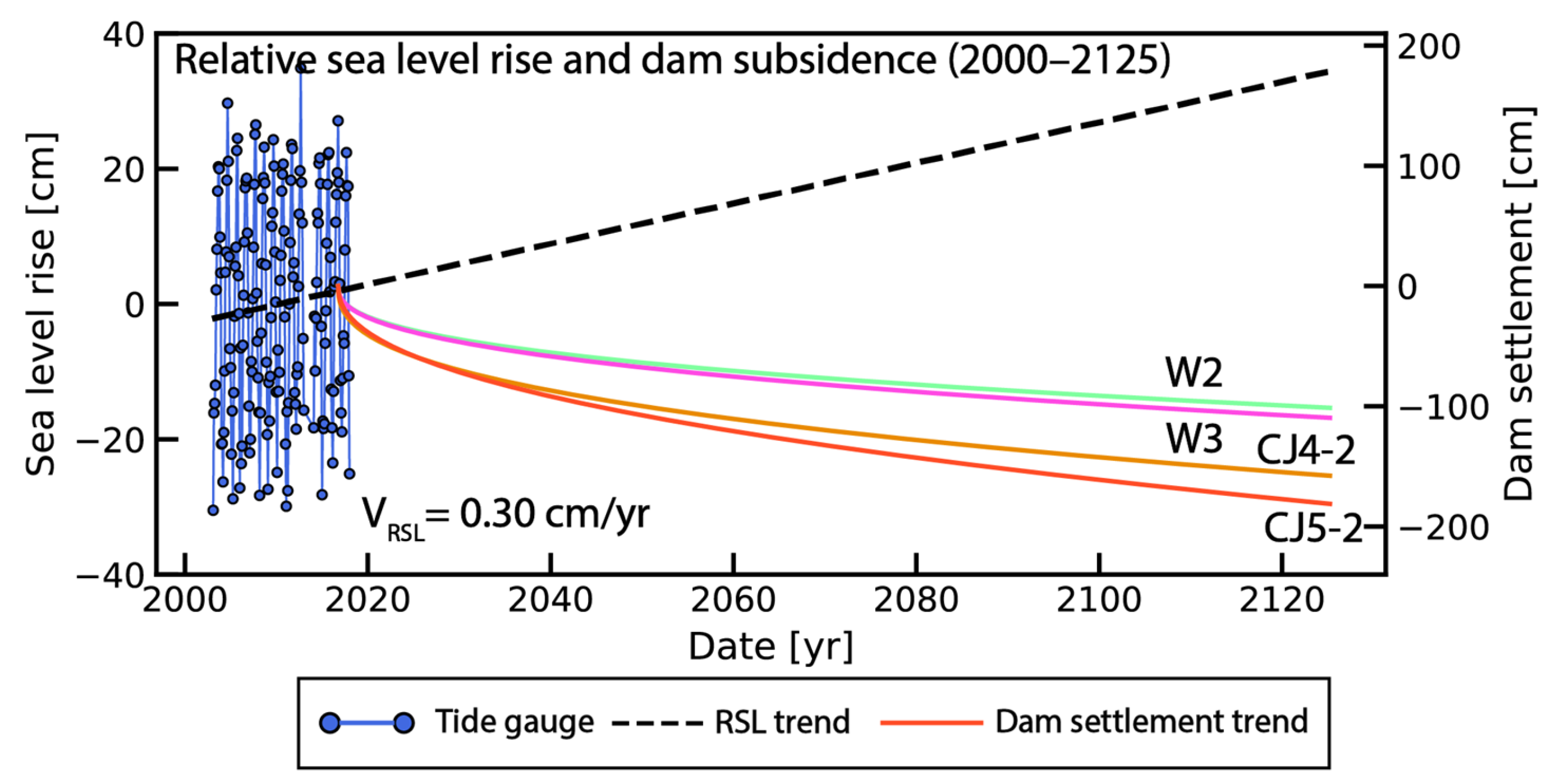
4.2. The Implications of Port Subsidence and Sea Level Rise
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Monioudi, I.Ν.; Asariotis, R.; Becker, A.; Bhat, C.; Dowding-Gooden, D.; Esteban, M.; Feyen, L.; Mentaschi, L.; Nikolaou, A.; Nurse, L.; et al. Climate Change Impacts on Critical International Transportation Assets of Caribbean Small Island Developing States (SIDS): The Case of Jamaica and Saint Lucia. Reg. Environ. Change 2018, 18, 2211–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, M.; Takagi, H.; Nicholls, R.J.; Fatma, D.; Pratama, M.B.; Kurobe, S.; Yi, X.; Ikeda, I.; Mikami, T.; Valenzuela, P.; et al. Adapting Ports to Sea-Level Rise: Empirical Lessons Based on Land Subsidence in Indonesia and Japan. Marit. Policy Manag. 2020, 47, 937–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mega, V.P. Conscious Coastal Cities: Sustainability, Blue Green Growth, and The Politics of Imagination; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; ISBN 978-3-319-20217-4. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Shi, G.; Wu, S.; Ding, X.; Zhao, C.; Wong, M.S.; Lu, Z. Unveiling Multimodal Consolidation Process of the Newly Reclaimed HKIA 3rd Runway from Satellite SAR Interferometry, ICA Analytics and Terzaghi Consolidation Theory. Remote Sens. Environ. 2025, 318, 114561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wu, S.; Shi, G.; Ding, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z. Mapping Ground Deformation in the Northern Yangtze River Estuary Using Improved MT-InSAR Based on ICA and Non-Stationary Analysis. Geo-Spat. Inf. Sci. 2025, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz Zanjani, F.; Amelung, F.; Piter, A.; Sobhan, K.; Tavakkoliestahbanati, A.; Eberli, G.P.; Haghighi, M.H.; Motagh, M.; Milillo, P.; Mirzaee, S.; et al. InSAR Observations of Construction-Induced Coastal Subsidence on Miami’s Barrier Islands, Florida. Earth Space Sci. 2024, 11, e2024EA003852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Wang, C.; An, B. AdpPL: An Adaptive Phase Linking-Based Distributed Scatterer Interferometry with Emphasis on Interferometric Pair Selection Optimization and Adaptive Regularization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín-Antón, M.; Negro, V.; del Campo, J.M.; López-Gutiérrez, J.S.; Esteban, M.D. Review of Coastal Land Reclamation Situation in the World. J. Coast. Res. 2016, 75, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadali, L.; Motagh, M.; Haghshenas Haghighi, M. Characterizing Post-Construction Settlement of the Masjed-Soleyman Embankment Dam, Southwest Iran, Using TerraSAR-X SpotLight Radar Imagery. Eng. Struct. 2017, 143, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, W.; Li, Z. Review of the SBAS InSAR Time-Series Algorithms, Applications, and Challenges. Geod. Geodyn. 2022, 13, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Wang, C.; Liao, M.; Lu, Z.; Dong, J.; Dai, K. Research Progress of Phase Linking Method in Time-Series InSAR. Geomat. Inf. Sci. Wuhan Univ. 2025, 50, 1483–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aswathi, J.; Binoj Kumar, R.B.; Oommen, T.; Bouali, E.H.; Sajinkumar, K.S. InSAR as a Tool for Monitoring Hydropower Projects: A Review. Energy Geosci. 2022, 3, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xu, W.; Aoki, Y. Extracting a Decadal Deformation on Xiaolangdi Upstream Dam Slope Using Seasonally Inundated Distributed Scatterers InSAR (SIDS-InSAR). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2025, 138, 104462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchamalo-Sacristán, M.; Ruiz-Armenteros, A.M.; Lamas-Fernández, F.; González-Rodrigo, B.; Martínez-Marín, R.; Delgado-Blasco, J.M.; Bakon, M.; Lazecky, M.; Perissin, D.; Papco, J.; et al. MT-InSAR and Dam Modeling for the Comprehensive Monitoring of an Earth-Fill Dam: The Case of the Benínar Dam (Almería, Spain). Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, M.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, W.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, B.; Li, G.; Wang, Y. Soil and Rockfill Dams Safety Assessment for Henan Province: Monitoring, Analysis and Prediction. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanssen, R.F.; van Leijen, F.J. Monitoring Water Defense Structures Using Radar Interferometry. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Radar Conference, Rome, Italy, 26–30 May 2008; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pros, F.; Gonzalez-Lopez, S.; Martinez-Benjamin, J.J.; Palau, V.; Duro, J. Breakwater Settlement Monitoring with InSAR Data. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Quebec City, QC, Canada, 16 July 2014; pp. 414–417. [Google Scholar]
- Wasowski, J.; Bovenga, F.; Nutricato, R.; Nitti, D.O.; Chiaradia, M.T. High Resolution Satellite Multi-Temporal Interferometry for Monitoring Infrastructure Instability Hazards. Innov. Infrastruct. Solut. 2017, 2, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Yuan, S.; Wu, Z.; He, X. Measuring Dam Deformation of Long-Distance Water Transfer Using Multi-Temporal Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry: A Case Study in South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.Q.; Huang, Q.H.; He, N.; He, B.; Wang, Z.C.; Wang, Y.A. Displacement Monitoring of Upper Atbara Dam Based on Time Series InSAR. Surv. Rev. 2020, 52, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, B.; Cai, X.; Yan, B.; Li, G.; Li, W.; Zhao, C.; Yang, L.; Zheng, S.; Cui, L. Coastal Reclamation Embankment Deformation: Dynamic Monitoring and Future Trend Prediction Using Multi-Temporal InSAR Technology in Funing Bay, China. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Xu, W.; Ding, X.; Bürgmann, R.; Giri, S.; Liu, X. A Multi-Platform, Open-Source, and Quantitative Remote Sensing Framework for Dam-Related Hazard Investigation: Insights into the 2020 Sardoba Dam Collapse. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 111, 102849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, R.; Jiang, M.; Li, Z.; He, X. New Insights into the 2020 Sardoba Dam Failure in Uzbekistan from Earth Observation. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2022, 107, 102705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Li, P.; Li, Z.; Ding, D.; Qiao, L.; Xu, J.; Li, G.; Wang, H. Coastal Dam Inundation Assessment for the Yellow River Delta: Measurements, Analysis and Scenario. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Q.; He, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Monitoring time-series settlements of breakwaters based on PSI. Chin. J. Geotech. Eng. 2019, 41, 761–768. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Pan, J. Research on breakwater settlement in Lianyungang by InSAR. Geospat. Inf. 2021, 19, 55–59. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F. Analysis of water and sand characteristics along Lianyungang coastal and Xuwei port area. China Water Transp. 2024, 12, 79–80. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y. Research on Uneven Settlement Law and Its Influence on Crack Propagation of Utility Tunnel of Coastal Soft Foundation. Master Thesis, Henan Polytechnic University, Jiaozuo, China, 2022. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Qi, X.; Ding, D. Breakwater project of Xuwei District in Lianyungang Port. China Harb. Eng. 2016, 36, 1–5. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Song, J. Formwork design and construction for standard barrel type breakwater Foundation in xuwei port. Constr. Technol. 2015, 44, 93–95. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, P.A.; Gurrola, E.; Sacco, G.F.; Zebker, H. The InSAR Scientific Computing Environment; IEEE: Nuremberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A New Algorithm for Processing Interferometric Data-Stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, H.; De Zan, F.; Bamler, R. Efficient Phase Estimation for Interferogram Stacks. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2018, 56, 4109–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Phase Unwrapping for Large SAR Interferograms: Statistical Segmentation and Generalized Network Models. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 1709–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.-P.; Guillaso, S.; Peltzer, G.; Dailu, R.; Sun, J.; Shen, Z.-K.; Xu, X. Shallow Creep on the Haiyuan Fault (Gansu, China) Revealed by SAR Interferometry: Creep on Haiyuan Fault. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2012, 117, B06401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. DEM Error Correction in InSAR Time Series. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4249–4259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzaghi, K.; Peck, R.B.; Mesri, G. Soil Mechanics in Engineering Practice, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1996; ISBN 978-0-471-08658-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Qu, J.J. NMDI: A Normalized Multi-band Drought Index for Monitoring Soil and Vegetation Moisture with Satellite Remote Sensing. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 2007GL031021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, C.; Wang, B.; Liu, X.; Chen, H. Land Subsidence Monitoring and Dynamic Prediction of Reclaimed Islands with Multi-Temporal InSAR Techniques in Xiamen and Zhangzhou Cities, China. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedd, P.; Charles, C.J.A.; Holton, I.R.; Robertshaw, A.C. The Effect of Reservoir Drawdown and Long-Term Consolidation on the Deformation of Old Embankment Dams. Géotechnique 1997, 47, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Li, S. Concrete Dam Deformation Prediction Model for Health Monitoring Based on Extreme Learning Machine. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2017, 24, e1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Yang, J.; Chang, M. A Deep Learning Model for Concrete Dam Deformation Prediction Based on RS-LSTM. J. Sens. 2019, 2019, 4581672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Zhang, H.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tang, Q. Absolute Sea Level Changes Along the Coast of China from Tide Gauges, GNSS, and Satellite Altimetry. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2022, 127, e2022JC018994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-S.; Wang, H.; Xiang, W.-X.; Wang, A.-M.; Xu, W.-Q.; Jiang, Y.-X.; Wu, X.-H.; Quan, M.-Y. Sea-Level Change in Coastal Areas of China: Status in 2021. Adv. Clim. Change Res. 2024, 15, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Xu, S.; Yin, K. Spatial Inhomogeneity Analyses of Extreme Sea Levels along Lianyungang Coast Based on Numerical Simulation and Monte Carlo Model. Reg. Stud. Mar. Sci. 2024, 79, 103856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
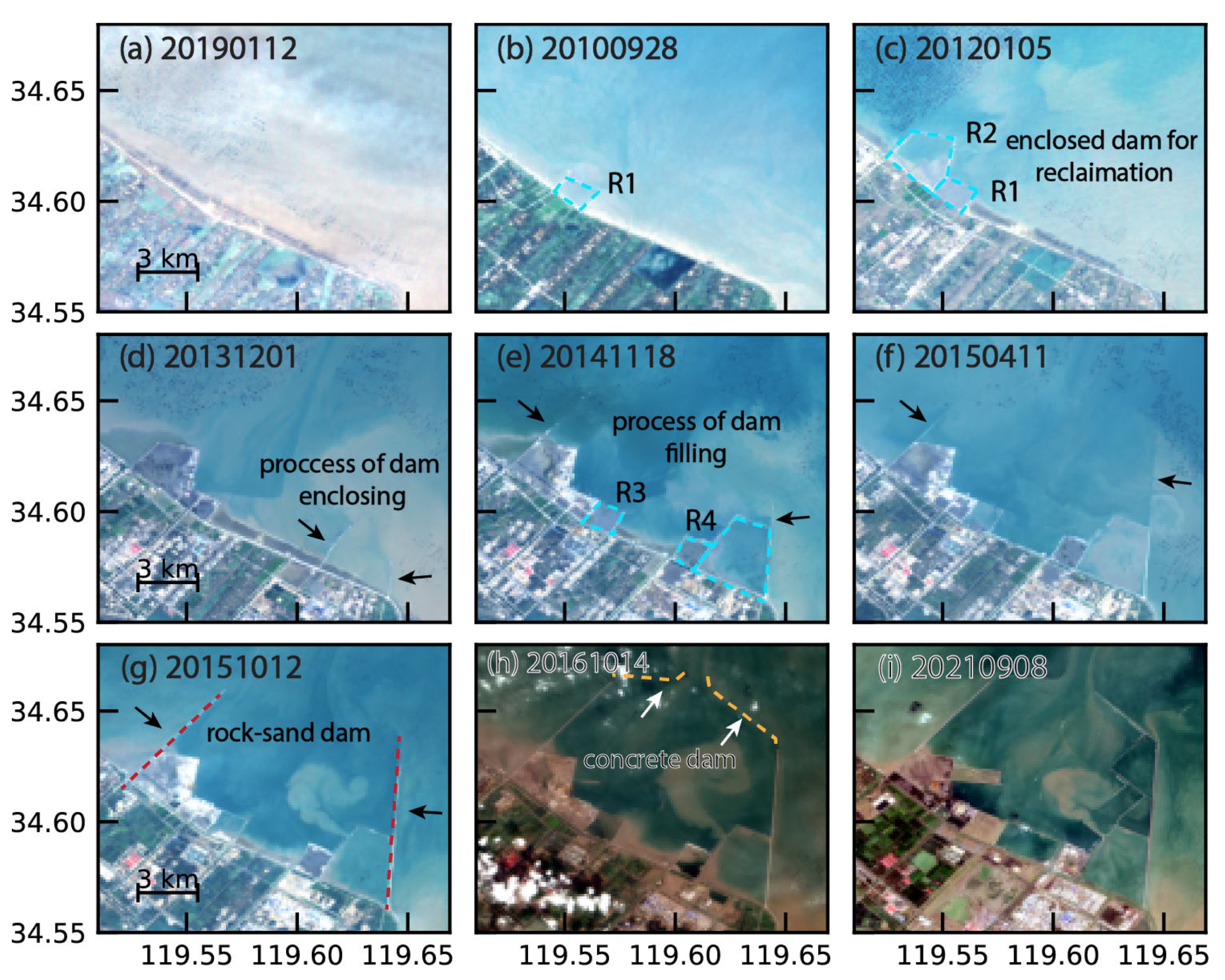
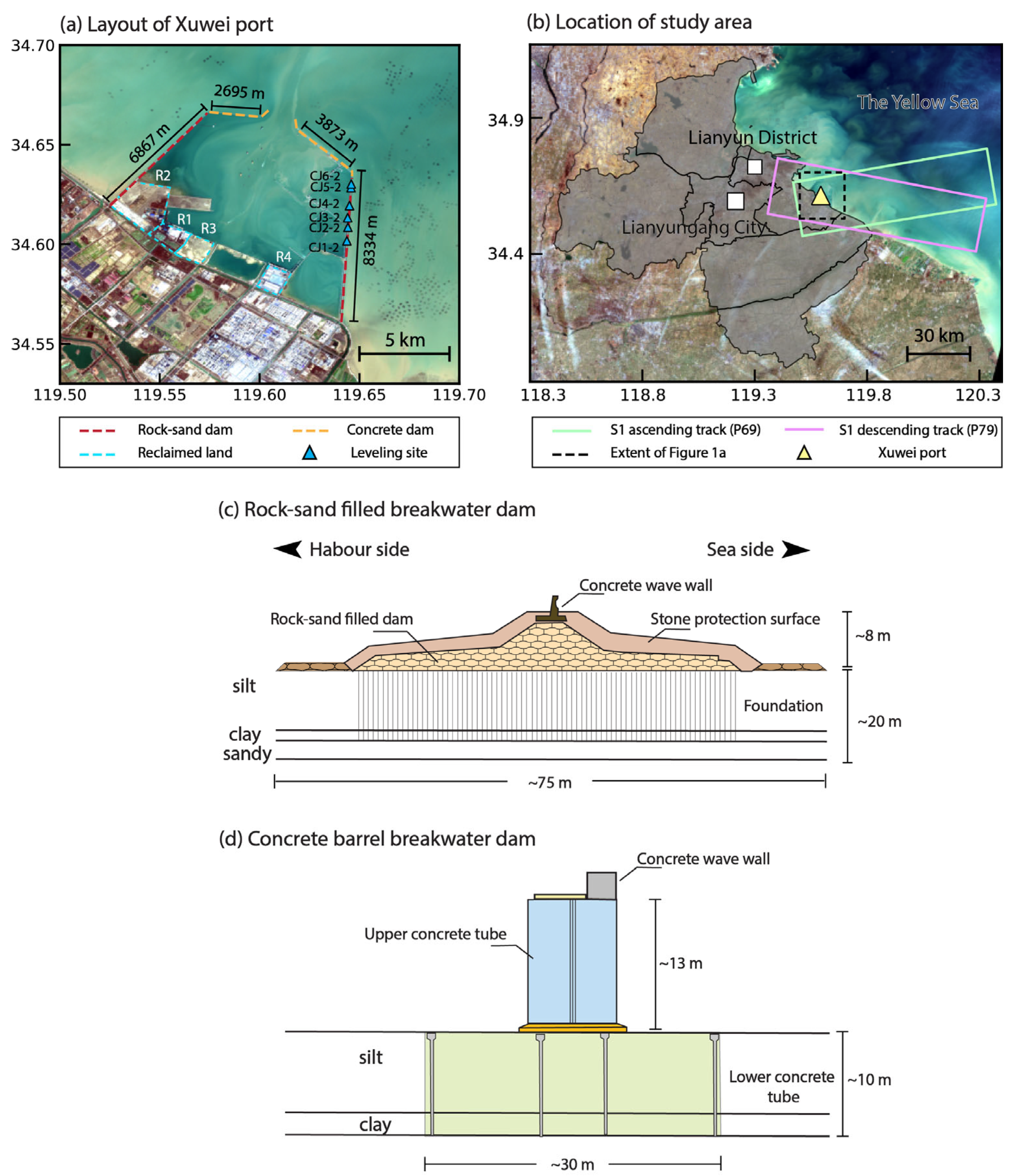

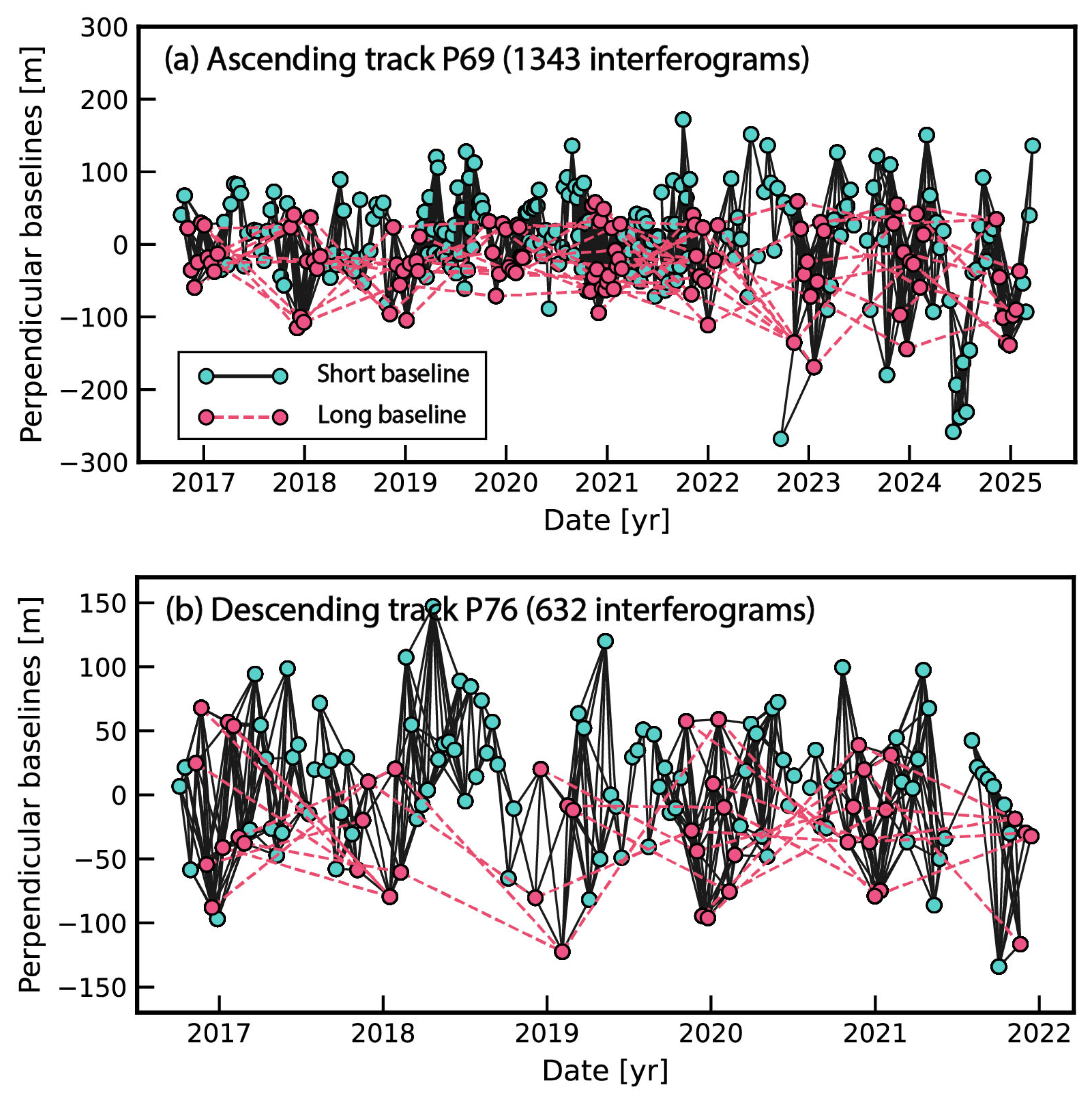
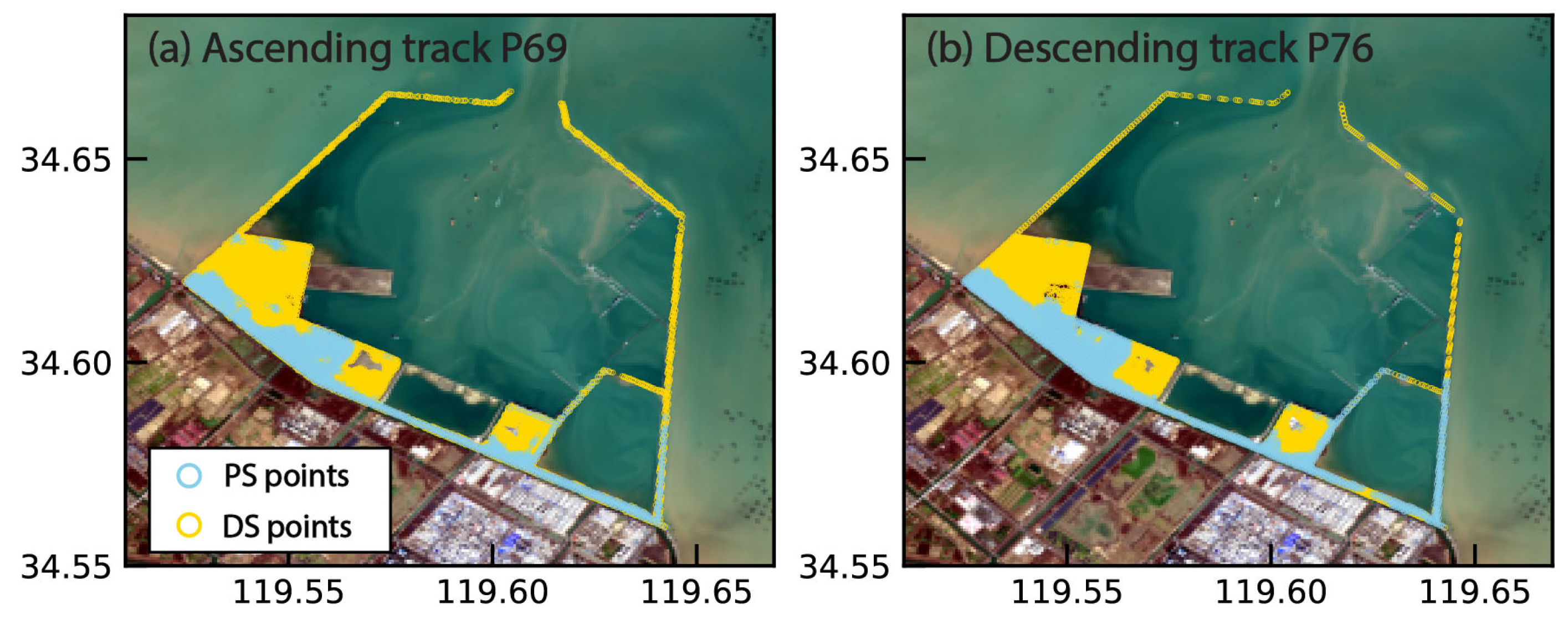
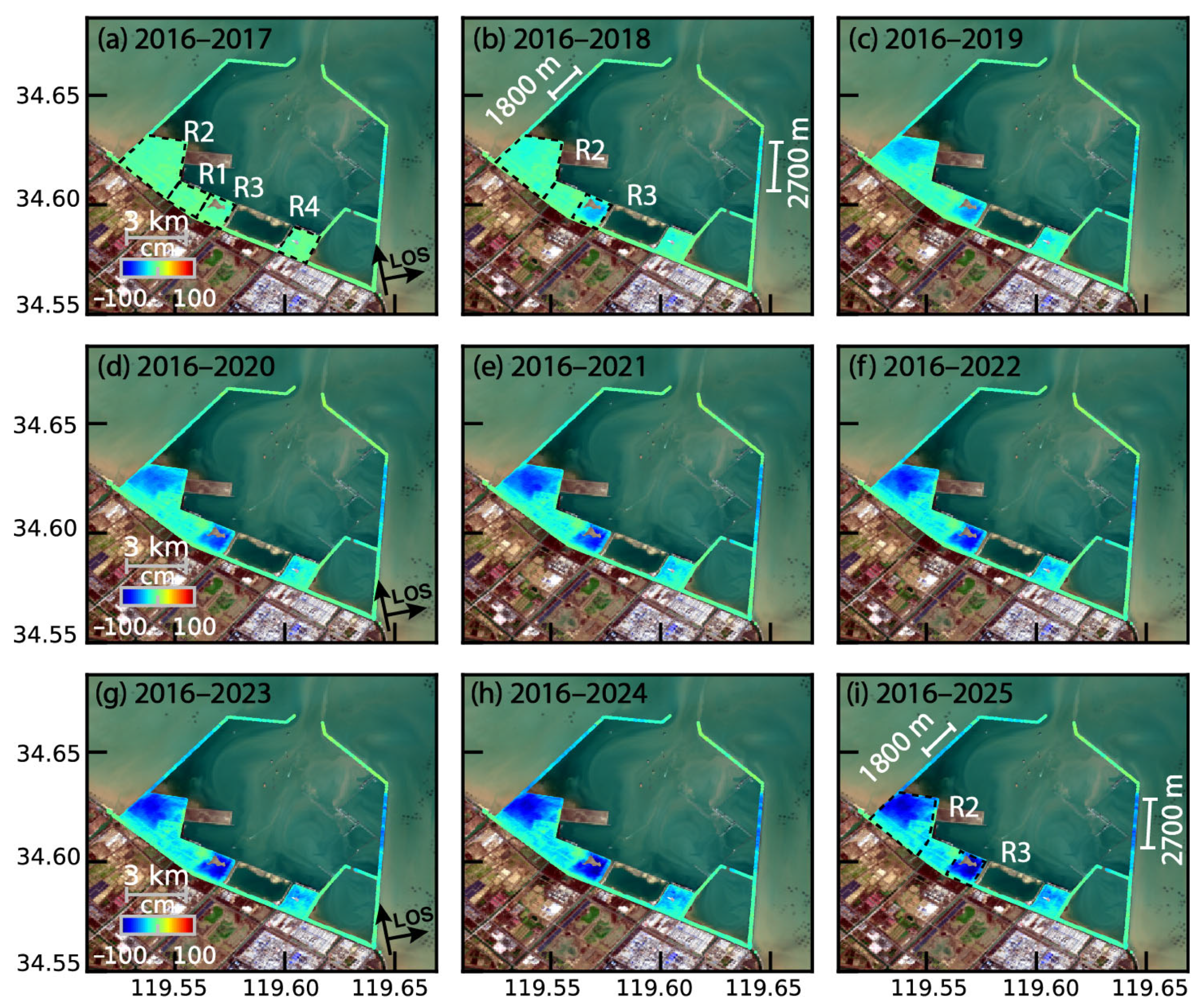
| Satellite | Flight Direction | Orbit Path | IW No. | Burst No. | Period | Scene No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sentinel-1 | Ascending | 69 | 3 | 3 | 29 September 2016–22 March 2025 | 307 |
| Descending | 76 | 1 | 2 | 5 October 2016–14 December 2021 | 140 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, S.; Ali, E.; Xu, W. Decadal and Heterogeneous Deformation of Breakwater Dams and Reclaimed Lands in Xuwei Port Revealed by Radar Interferometry Measurements. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162778
Xie L, Liu J, Wang X, Wu S, Ali E, Xu W. Decadal and Heterogeneous Deformation of Breakwater Dams and Reclaimed Lands in Xuwei Port Revealed by Radar Interferometry Measurements. Remote Sensing. 2025; 17(16):2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162778
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Lei, Jinheng Liu, Xiang Wang, Songbo Wu, Eslam Ali, and Wenbin Xu. 2025. "Decadal and Heterogeneous Deformation of Breakwater Dams and Reclaimed Lands in Xuwei Port Revealed by Radar Interferometry Measurements" Remote Sensing 17, no. 16: 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162778
APA StyleXie, L., Liu, J., Wang, X., Wu, S., Ali, E., & Xu, W. (2025). Decadal and Heterogeneous Deformation of Breakwater Dams and Reclaimed Lands in Xuwei Port Revealed by Radar Interferometry Measurements. Remote Sensing, 17(16), 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs17162778









