Paddy Rice Phenological Mapping throughout 30-Years Satellite Images in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
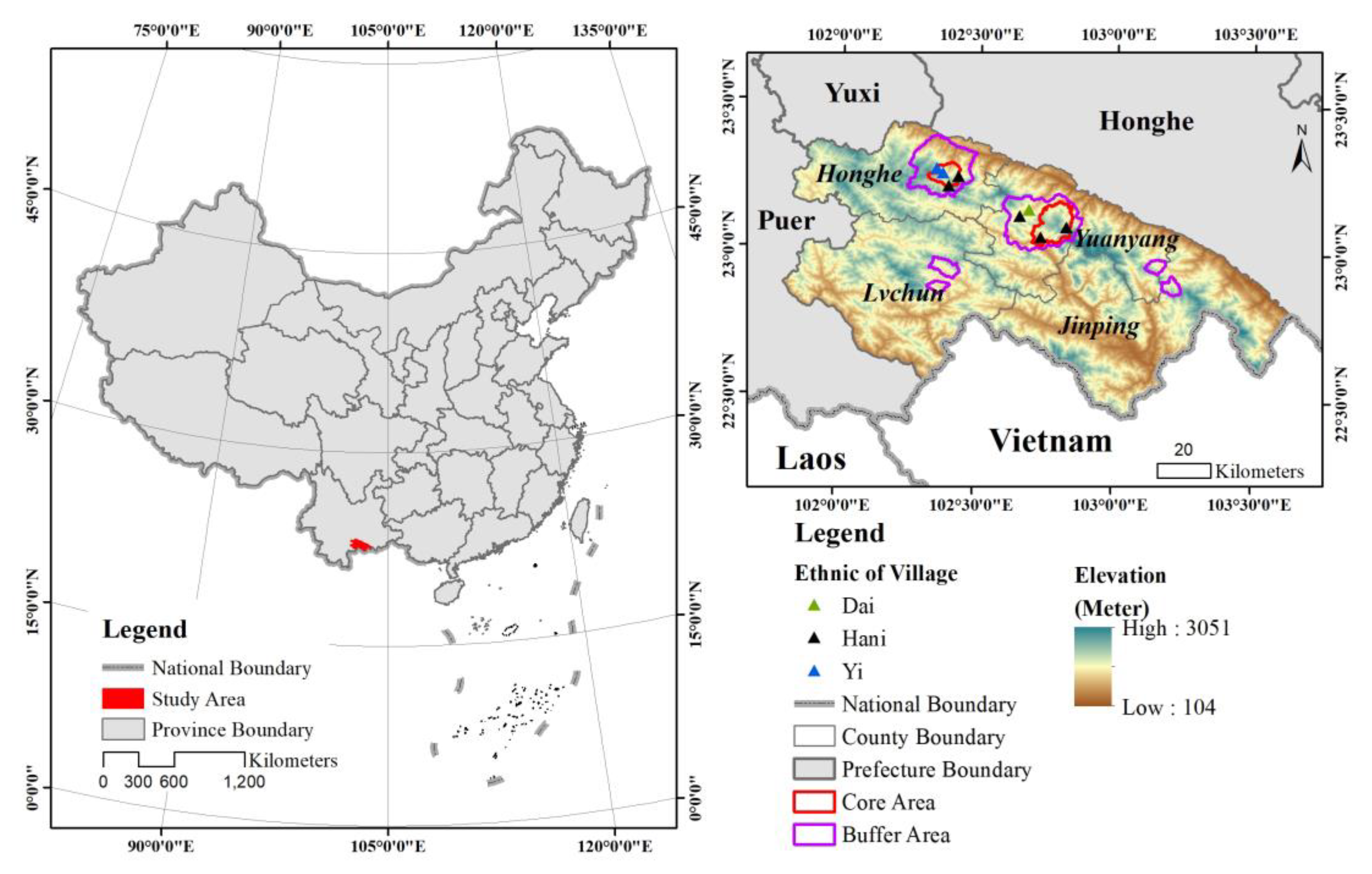
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Phenological Features of Paddy Rice in the HHRT
2.2.1. Traditional Ecological Knowledge Investigation
2.2.2. Traditional Paddy Rice Ecological Knowledge
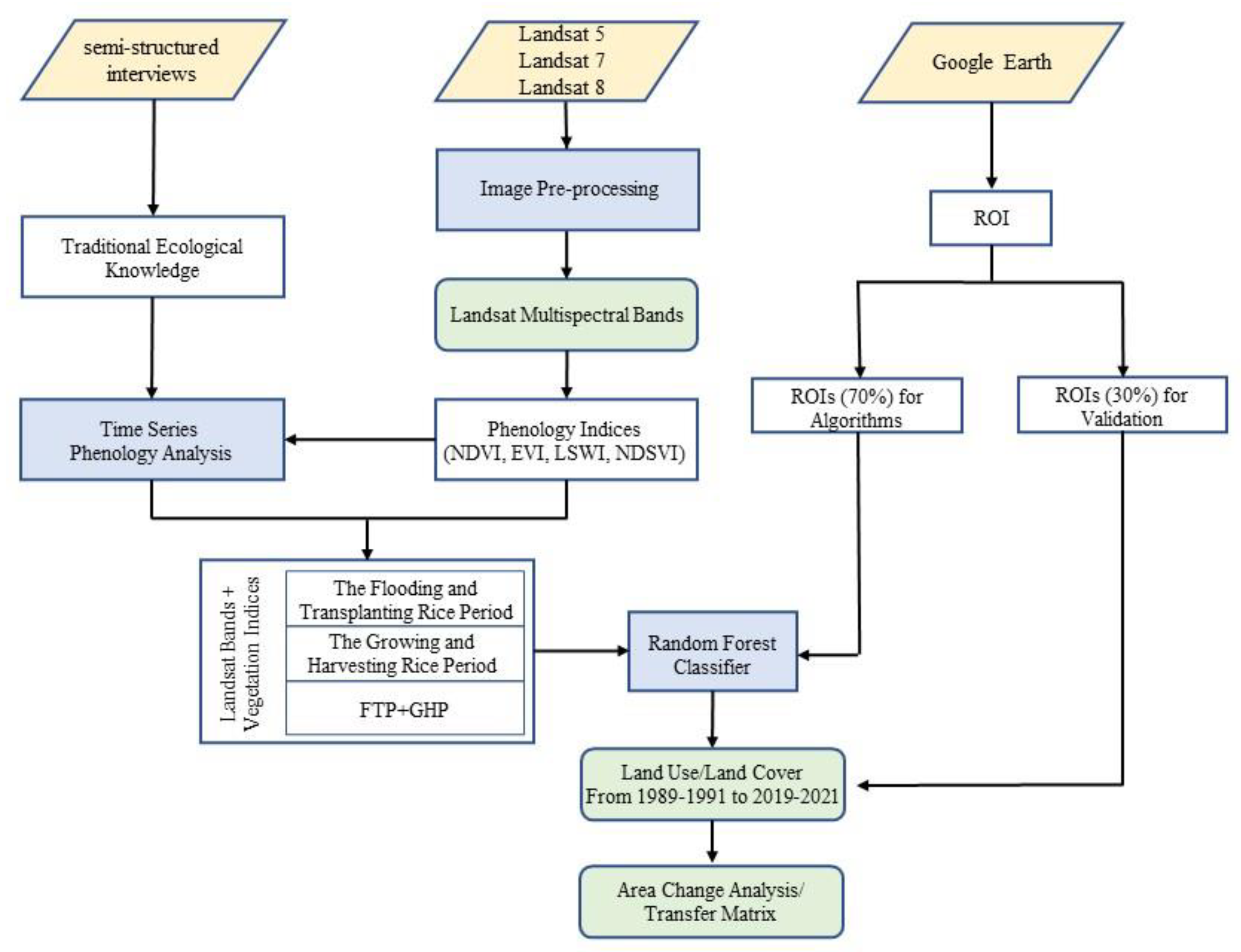
2.3. Landsat Data Pre-Processing
2.4. Ground Reference Data
2.5. Classification & Data Input
2.6. Validation
2.7. Area Changes and Driving Force Analysis
3. Results
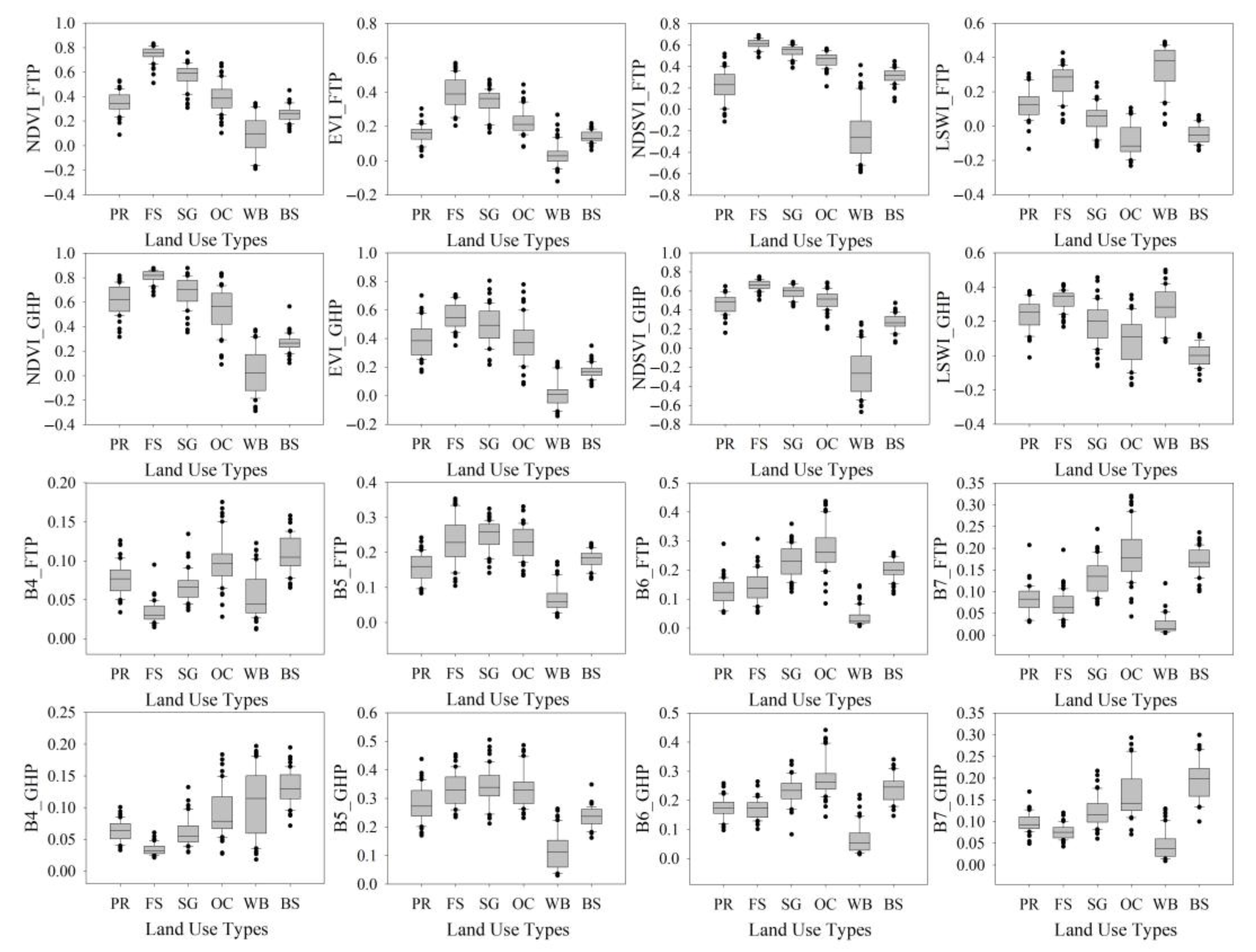
3.1. The Separability Analysis in Two Phenological Periods
3.2. Phenological Information Improved Mapping Accuracy
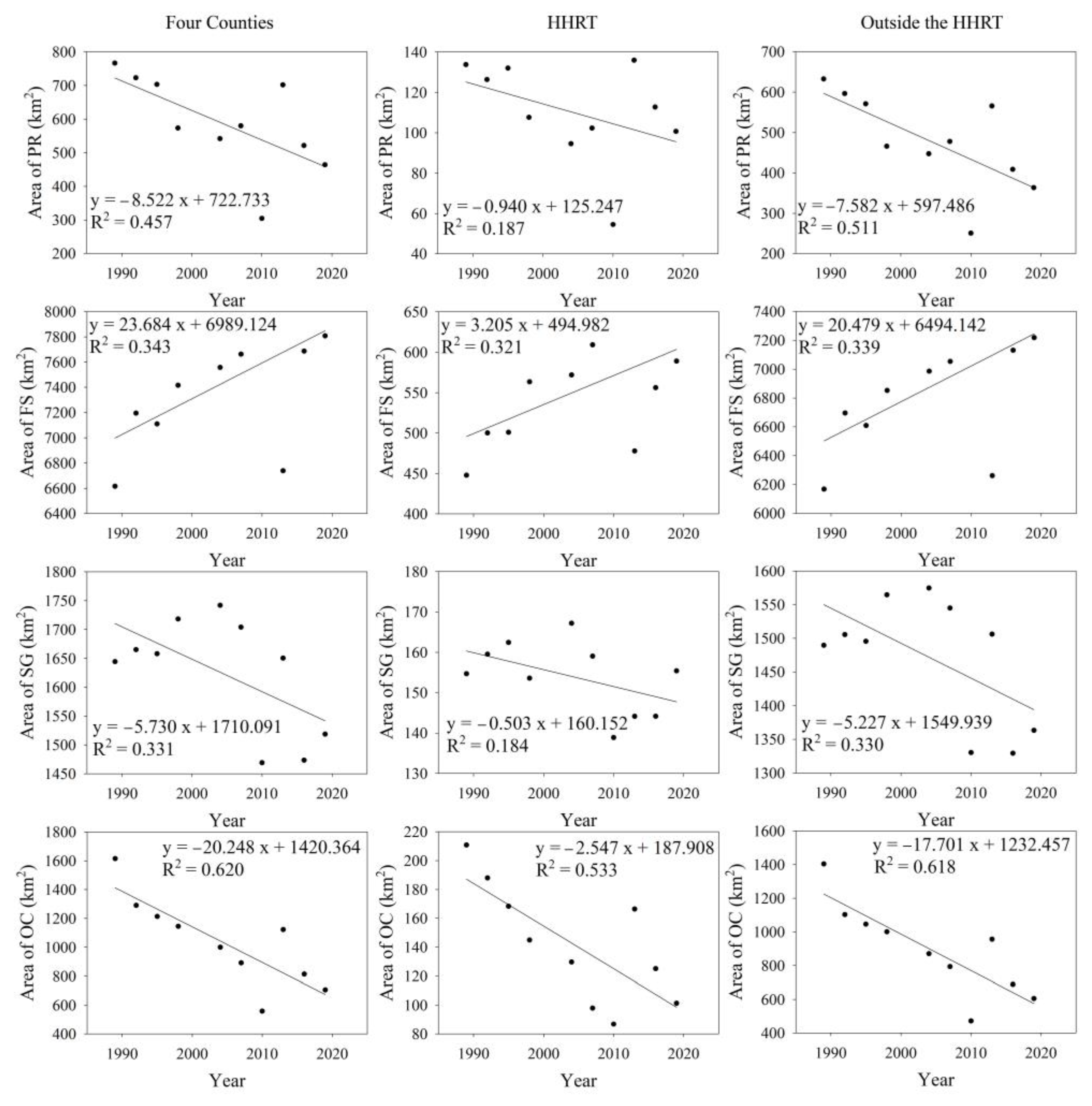
3.3. Paddy Rice Decreased from the 1990s to 2020s
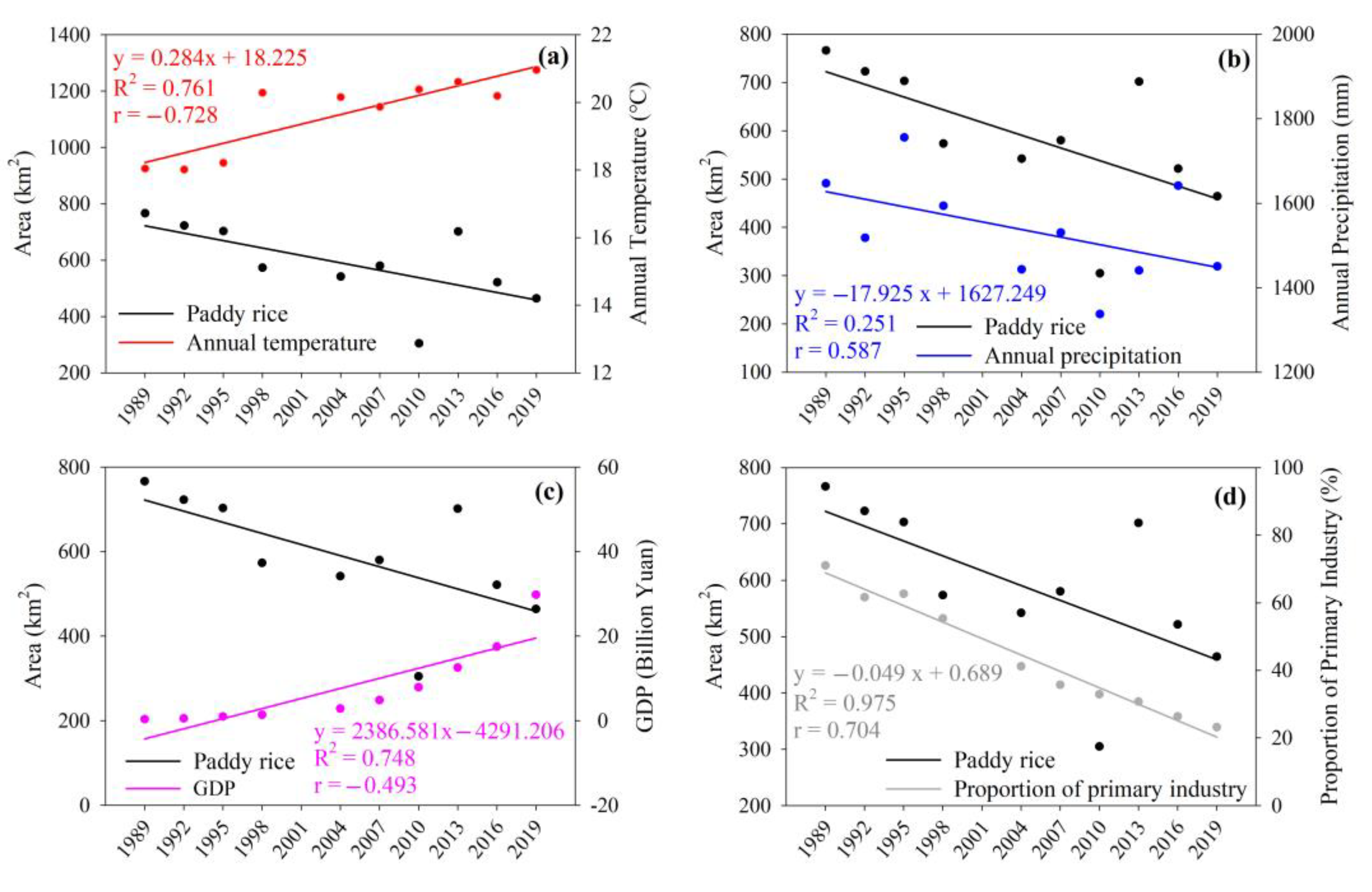
3.4. The Driving Factors of LULC
4. Discussion
4.1. Phenological Features Improve Paddy Rice Mapping
4.2. The Area Changes of Paddy Rice in the Hani Terraces
4.3. Applications
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuenzer, C.; Knauer, K. Remote Sensing of Rice Crop Areas—A Review. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2101–2139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elphick, C.S. Functional Equivalency between Rice Fields and Seminatural Wetland Habitats. Conserv. Biol. 2000, 14, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X. Evolution of regional to global paddy rice mapping methods: A review. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 119, 214–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, L.; Fujita, G.; Kito, K.; Miyashita, T. Historical mapping of rice fields in Japan using phenology and temporally aggregated Landsat images in Google Earth Engine. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 191, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, S.A.; Kaduk, J.; Tansey, K.; Balzter, H.; Lawal, U.M. Detecting phenological changes in plant functional types over West African savannah dominated landscape. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2021, 42, 567–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Gong, W.; Zhu, B.; Huang, X. Wavelength selection and spectral discrimination for paddy rice, with laboratory measurements of hyperspectral leaf reflectance. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2011, 66, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toan, T.L.; Ribbes, F.; Li-Fang, W.; Floury, N.; Kung-Hau, D.; Jin Au, K.; Fujita, M.; Kurosu, T. Rice crop mapping and monitoring using ERS-1 data based on experiment and modeling results. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Liu, J.; Zhuang, D.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in southern China using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 480–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Boles, S.; Frolking, S.; Li, C.; Babu, J.Y.; Salas, W.; Moore, B. Mapping paddy rice agriculture in South and Southeast Asia using multi-temporal MODIS images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 95–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Kou, W.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, G.; Li, L.; Jin, C.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Biradar, C.; et al. Tracking the dynamics of paddy rice planting area in 1986–2010 through time series Landsat images and phenology-based algorithms. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 160, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontgis, C.; Schneider, A.; Ozdogan, M. Mapping rice paddy extent and intensification in the Vietnamese Mekong River Delta with dense time stacks of Landsat data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xin, L.; Li, X.; Tan, M.; Wang, R. Decreasing Rice Cropping Intensity in Southern China from 1990 to 2015. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.M. Using the Landsat archive to map crop cover history across the United States. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 232, 111286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Huang, X. The 30m annual land cover dataset and its dynamics in China from 1990 to 2019. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 3907–3925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulla-Menashe, D.; Gray, J.M.; Abercrombie, S.P.; Friedl, M.A. Hierarchical mapping of annual global land cover 2001 to present: The MODIS Collection 6 Land Cover product. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 222, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelick, N.; Hancher, M.; Dixon, M.; Ilyushchenko, S.; Thau, D.; Moore, R. Google Earth Engine: Planetary-scale geospatial analysis for everyone. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 202, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Roder, G.; Jiao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Z.; Tarolli, P. Farmers’ landslide risk perceptions and willingness for restoration and conservation of world heritage site of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces, China. Landslides 2020, 17, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, L.; Takeuchi, K.; Okuro, T.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L. Indigenous ecological knowledge and natural resource management in the cultural landscape of China’s Hani Terraces. Ecol. Res. 2012, 27, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.-C.; Wang, D.; Guo, L. Application of Traditional Knowledge of Hani People in Biodiversity Conservation. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.H.; Iankova, K.; Zhang, Y.; McDonald, T.; Qi, X. The role of self-gentrification in sustainable tourism: Indigenous entrepreneurship at Honghe Hani Rice Terraces World Heritage Site, China. J. Sustain. Tour. 2016, 24, 1262–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNESCO. Cultural Landscape of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces; UNESCO: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, H.; Jiao, Y.; Liang, L. Strengthening the socio-ecological resilience of forest-dependent communities: The case of the Hani Rice Terraces in Yunnan, China. Forest Policy Econ. 2012, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xu, G.; Shen, N.; Nie, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Valuation of Ecosystem Services for the Sustainable Development of Hani Terraces: A Rice-Fish-Duck Integrated Farming Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Qian, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, A. Why are the Longji Terraces in Southwest China maintained well? A conservation mechanism for agricultural landscapes based on agricultural multi-functions developed by multi-stakeholders. Land Use Pol. 2019, 85, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, G.; Yu, L.; Chen, M. Agroecosystem composition and landscape ecological risk evolution of rice terraces in the southern mountains, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, A. Economics of underproduction: A polycentric approach for a depopulated commons in Japan. Ecol. Econ. 2020, 171, 106597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasushi, M.; Masaya, S.; Eisei, M.; Kumiko, T. When do rice terraces become rice terraces? Paddy Water Environ. 2019, 17, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnáez, J.; Lana-Renault, N.; Lasanta, T.; Ruiz-Flaño, P.; Castroviejo, J. Effects of farming terraces on hydrological and geomorphological processes. A review. Catena 2015, 128, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, R.C.; Matchoc, O.R.O.; Bahatan, R.G.; Pena, F.A.D. Farmers’ knowledge, attitudes and practices of rice crop and pest management at Ifugao Rice Terraces, Philippines. Int. J. Pest Manag. 2000, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Liu, M.; Lun, F.; Yuan, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Min, Q. An Analysis on Crops Choice and Its Driving Factors in Agricultural Heritage Systems—A Case of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces System. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Min, Q.; Zhang, C.; He, L.; Zhang, S.; Yang, L.; Tian, M.; Xiong, Y. Traditional culture as an important power for maintaining agricultural landscapes in cultural heritage sites: A case study of the Hani terraces. J. Cult. Herit. 2017, 25, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Min, Q. How to balance the relationship between conservation of Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (IAHS) and socio-economic development? A theoretical framework of sustainable industrial integration development. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 204, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallio, H.; Pietilä, A.-M.; Johnson, M.; Kangasniemi, M. Systematic methodological review: Developing a framework for a qualitative semi-structured interview guide. J. Adv. Nurs. 2016, 72, 2954–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-Q.; Mammides, C.; Corlett, R.T. Reasons for the Survival of Tropical Forest Fragments in Xishuangbanna, Southwest China. Forests 2020, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Adaptation Mechanism on Climate Change of Traditional Agriculture Management in Hani Rice Terraces. Ph.D. Thesis, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q. geemap: A Python package for interactive mapping with Google Earth Engine. J. Open Source Softw. 2020, 5, 2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulder, M.A.; White, J.C.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Belward, A.S.; Cohen, W.B.; Fosnight, E.A.; Shaw, J.; Masek, J.G.; Roy, D.P. The global Landsat archive: Status, consolidation, and direction. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 185, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Xin, F.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Doughty, R.B.; Moore, B. Fingerprint of rice paddies in spatial–temporal dynamics of atmospheric methane concentration in monsoon Asia. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Marsett, R.; Heilman, P.; Bieden-bender, S.; Moran, S.; Goodrich, D.; Weltz, M. RANGES improves satellite-based information and land cover assessments in southwest United States. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2002, 83, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defries, R.S.; Townshend, J.R.G. NDVI-derived land cover classifications at a global scale. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3567–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, I.L.; Ching, N.P.; Benning, V.M.; D’Aguanno, J.A. Review Article A review of multi-channel indices of class separability. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 331–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, R.; Ehlers, M. Comparison of two feature selection methods for the separability analysis of intertidal sediments with spectrometric datasets in the German Wadden Sea. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2016, 52, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Y. Unsupervised Segmentation Evaluation Using Area-Weighted Variance and Jeffries-Matusita Distance for Remote Sensing Images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhai, D.-L. Integrating Phenological and Geographical Information with Artificial Intelligence Algorithm to Map Rubber Plantations in Xishuangbanna. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blickensdörfer, L.; Schwieder, M.; Pflugmacher, D.; Nendel, C.; Erasmi, S.; Hostert, P. Mapping of crop types and crop sequences with combined time series of Sentinel-1, Sentinel-2 and Landsat 8 data for Germany. Remote Sens. Environ. 2022, 269, 112831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Galiano, V.F.; Ghimire, B.; Rogan, J.; Chica-Olmo, M.; Rigol-Sanchez, J.P. An assessment of the effectiveness of a random forest classifier for land-cover classification. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 67, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Xiao, X.; Biradar, C.M.; Dong, J.; Qin, Y.; Menarguez, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, C.; Wang, J.; et al. Spatiotemporal patterns of paddy rice croplands in China and India from 2000 to 2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, G.; Menarguez, M.A.; Choi, C.Y.; Qin, Y.; Luo, P.; Zhang, Y.; Moore, B. Northward expansion of paddy rice in northeastern Asia during 2000–2014. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 3754–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridhikitti, A.; Overcamp, T.J. Estimation of Southeast Asian rice paddy areas with different ecosystems from moderate-resolution satellite imagery. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.-Z.; Uchida, S.; Liang, Y.; Hirano, A.; Sun, B. Discriminating different landuse types by using multitemporal NDXI in a rice planting area. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 585–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordelas, G.A.; Manakos, I.; Aragonés, D.; Díaz-Delgado, R.; Bustamante, J. Fast and Automatic Data-Driven Thresholding for Inundation Mapping with Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Kumar, A.; Lal, K. Kharif crop characterization using combination of SAR and MSI Optical Sentinel Satellite datasets. J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2019, 128, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, F.; Wang, Q.; Li, W.; Li, X. Water Bodies’ Mapping from Sentinel-2 Imagery with Modified Normalized Difference Water Index at 10-m Spatial Resolution Produced by Sharpening the SWIR Band. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, M. A Novel Technique for Segmentation of High Resolution Remote Sensing Images Based on Neural Networks. Neural Process. Lett. 2020, 52, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulz, C.; Holtgrave, A.-K.; Kleinschmit, B. Large-scale winter catch crop monitoring with Sentinel-2 time series and machine learning–An alternative to on-site controls? Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 186, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, F.; Xiao, X.; Dong, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, X.; Zou, Z.; Ma, J.; Du, G.; et al. Large increases of paddy rice area, gross primary production, and grain production in Northeast China during 2000–2017. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 711, 135183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, X.; Kuang, W.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, R.; Yan, C.; Yu, D.; Wu, S.; et al. Spatial patterns and driving forces of land use change in China during the early 21st century. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghose, B. Food security and food self-sufficiency in China: From past to 2050. Food Energy Secur. 2014, 3, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, L.; Liu, L.; Min, Q. Labor productivity of small-scale agriculture and its influence on agricultural landscape conservation in mountainous areas in China: A case study of rice farming in Hani terraced region. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39795–39806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ciais, P.; Li, L.; Ruget, F.; Vuichard, N.; Viovy, N.; Zhou, F.; Chang, J.; Wu, X.; Zhao, H.; et al. Management outweighs climate change on affecting length of rice growing period for early rice and single rice in China during 1991–2012. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2017, 233, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Tuo, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, D. Spatial and Temporal Evolution Characteristics of Drought in Yunnan Province from 1969 to 2018 Based on SPI/SPEI. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Nichol, J.E.; Qamer, F.M.; Xu, J. Characterization of Drought Development through Remote Sensing: A Case Study in Central Yunnan, China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4998–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.E.; Abbas, S. Integration of remote sensing datasets for local scale assessment and prediction of drought. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 503–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
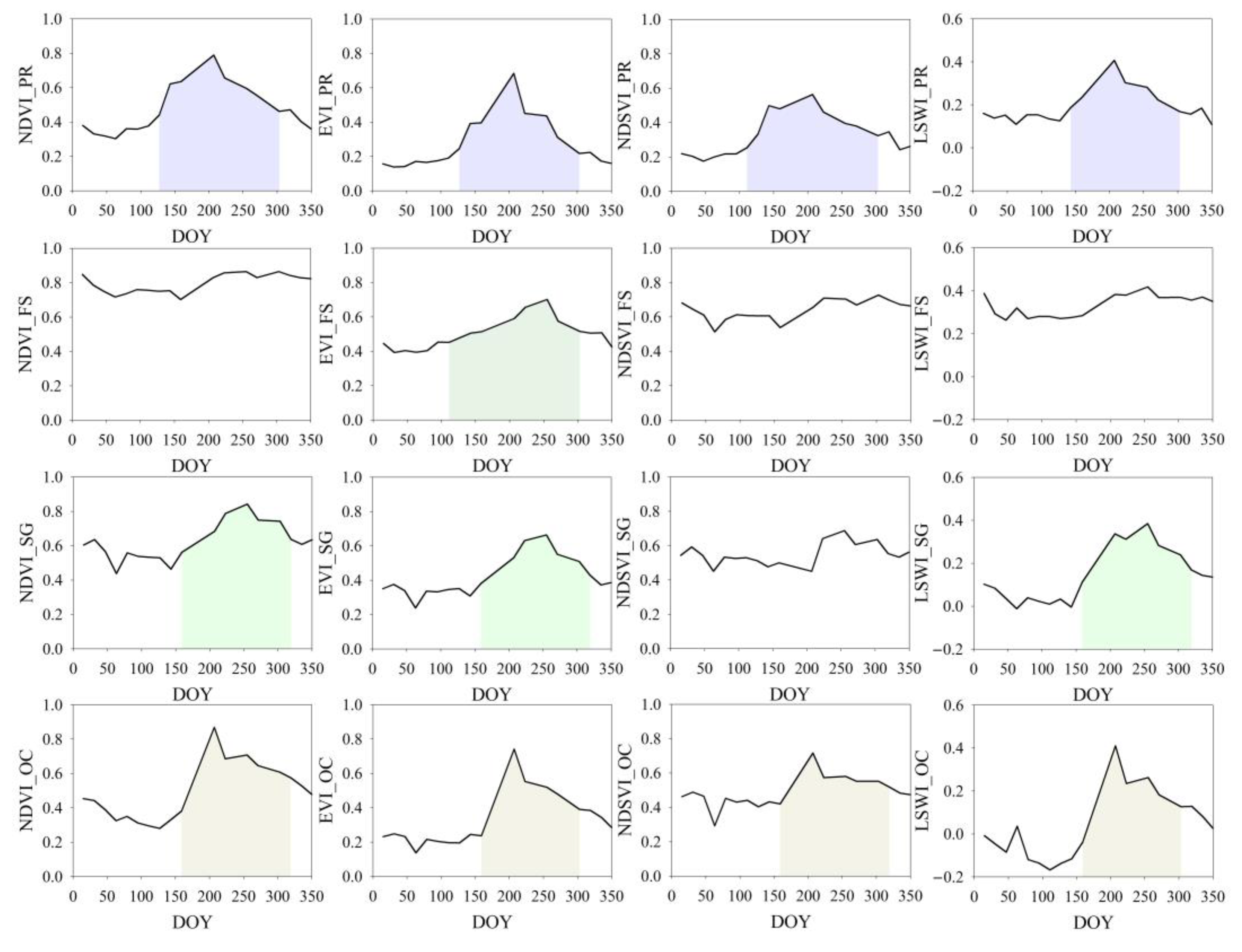


| Month of Lunar Calendar | Meaning of Hani Nationality | Farming Activities | Vegetation Indices Changes of Paddy Rice |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | The month of creatures awakening | Nursery rice seedlings | NDVI lower than 0.4; EVI, NDSVI, and LSWI lower than 0.2 |
| February | The season for transplanting seedlings | Transplant seedlings and hoeing in terraces | |
| March | |||
| April | The season of leisure | hoeing, hunting, repair farm tools | NDVI from 0.4 increased to 0.8; EVI, NDSVI, and LSWI from 0.2 increased to 0.7, 0.55, and 0.4, respectively. |
| May | |||
| June | The harvest preparation month | hoeing, repair farm tools, prepare for the harvest | |
| July | The month of rice growing | Autumn harvest, fallow | NDVI decreased to lower than 0.4; EVI, NDSVI, and LSWI decreased to lower than 0.2. |
| August | The month of rice maturation | ||
| September | The alternate month of the new year and the last year | Harvest late rice, fallow | |
| October | The first month of new year | Fallow, plough the paddy lands, repair ridges and farm tools | NDVI lower than 0.4; EVI, NDSVI, and LSWI lower than 0.2 |
| November | The month of creature hibernation | ||
| December | The month of seed germination |
| FTP | GHP | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indices or Bands | PR vs. FS | PR vs. SG | PR vs. OC | PR vs. WB | PR vs. BS | PR vs. FS | PR vs. SG | PR vs. OC | PR vs. WB | PR vs. BS |
| NDVI | 1.934 | 1.034 | 0.094 | 0.710 | 0.338 | 1.029 | 0.068 | 0.148 | 1.700 | 1.607 |
| EVI | 1.444 | 1.379 | 0.368 | 0.751 | 0.117 | 0.547 | 0.158 | 0.026 | 1.509 | 1.148 |
| NDSVI | 1.707 | 1.445 | 0.994 | 0.991 | 0.338 | 1.188 | 0.516 | 0.030 | 1.755 | 0.850 |
| LSWI | 0.458 | 0.193 | 0.842 | 0.833 | 1.092 | 0.398 | 0.111 | 0.504 | 0.088 | 1.465 |
| B4 | 1.118 | 0.062 | 0.339 | 0.237 | 0.462 | 1.038 | 0.057 | 0.650 | 0.793 | 1.394 |
| B5 | 0.531 | 0.952 | 0.618 | 0.968 | 0.186 | 0.175 | 0.209 | 0.155 | 1.136 | 0.325 |
| B6 | 0.035 | 0.856 | 1.059 | 1.006 | 0.749 | 0.007 | 0.428 | 0.803 | 1.070 | 0.594 |
| B7 | 0.037 | 0.527 | 0.979 | 0.814 | 1.247 | 0.304 | 0.269 | 0.798 | 0.764 | 1.305 |
| 1989–1991 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land Use Types | Paddy Rice | Forests | Shrubs or Grasslands | Other Croplands | Water Bodies | Buildings | ||
| 2019–2021 | Four counties | Paddy rice | 260.243 | 124.580 | 16.231 | 41.091 | 5.538 | 14.199 |
| Forests | 282.653 | 5629.271 | 1033.406 | 685.266 | 1.672 | 16.710 | ||
| Shrubs or Grasslands | 102.447 | 438.720 | 421.858 | 529.110 | 0.764 | 18.378 | ||
| Other Croplands | 90.305 | 137.487 | 135.016 | 326.121 | 1.158 | 13.950 | ||
| Water Bodies | 8.045 | 8.346 | 0.926 | 3.036 | 13.283 | 4.629 | ||
| Buildings | 16.243 | 16.889 | 11.022 | 23.117 | 1.485 | 17.310 | ||
| HHRT | Paddy rice | 68.315 | 17.112 | 2.508 | 9.658 | 0.562 | 2.225 | |
| Forests | 31.323 | 367.917 | 91.377 | 77.892 | 0.166 | 1.392 | ||
| Shrubs or GrasslandsOther Croplands | 14.261 | 31.550 | 40.941 | 66.429 | 0.032 | 1.540 | ||
| 17.277 | 13.469 | 16.272 | 52.263 | 0.054 | 1.639 | |||
| Water Bodies | 0.693 | 0.234 | 0.062 | 0.173 | 0.207 | 0.184 | ||
| Buildings | 1.550 | 2.443 | 2.339 | 4.134 | 0.027 | 2.843 | ||
| Out ofHHRT | Paddy rice | 191.935 | 107.459 | 13.722 | 31.425 | 4.976 | 11.962 | |
| Forests | 251.326 | 5261.489 | 942.090 | 607.408 | 1.506 | 15.317 | ||
| Shrubs or Grasslands | 88.190 | 407.126 | 380.884 | 462.603 | 0.732 | 16.830 | ||
| Other Croplands | 73.027 | 124.008 | 118.721 | 273.767 | 1.105 | 12.308 | ||
| Water Bodies | 7.352 | 8.111 | 0.864 | 2.863 | 13.078 | 4.444 | ||
| Buildings | 14.690 | 14.443 | 8.682 | 18.974 | 1.456 | 14.457 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhai, D.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Zhao, G. Paddy Rice Phenological Mapping throughout 30-Years Satellite Images in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092398
Yang J, Xu J, Zhou Y, Zhai D, Chen H, Li Q, Zhao G. Paddy Rice Phenological Mapping throughout 30-Years Satellite Images in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(9):2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092398
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jianbo, Jianchu Xu, Ying Zhou, Deli Zhai, Huafang Chen, Qian Li, and Gaojuan Zhao. 2023. "Paddy Rice Phenological Mapping throughout 30-Years Satellite Images in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces" Remote Sensing 15, no. 9: 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092398
APA StyleYang, J., Xu, J., Zhou, Y., Zhai, D., Chen, H., Li, Q., & Zhao, G. (2023). Paddy Rice Phenological Mapping throughout 30-Years Satellite Images in the Honghe Hani Rice Terraces. Remote Sensing, 15(9), 2398. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15092398






