Natura 2000 Grassland Habitats Mapping Based on Spectro-Temporal Dimension of Sentinel-2 Images with Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
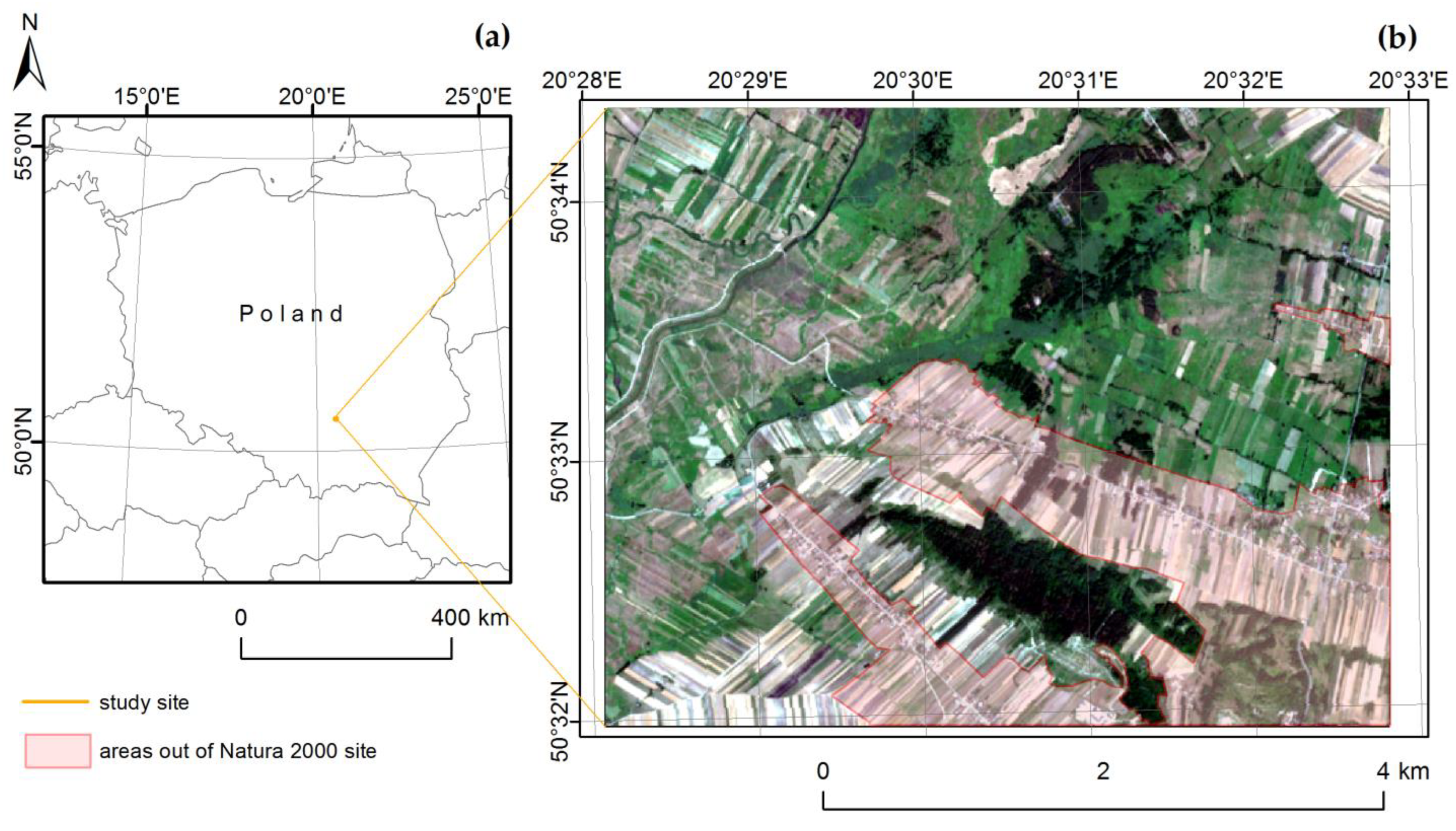
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Ground Truth Data
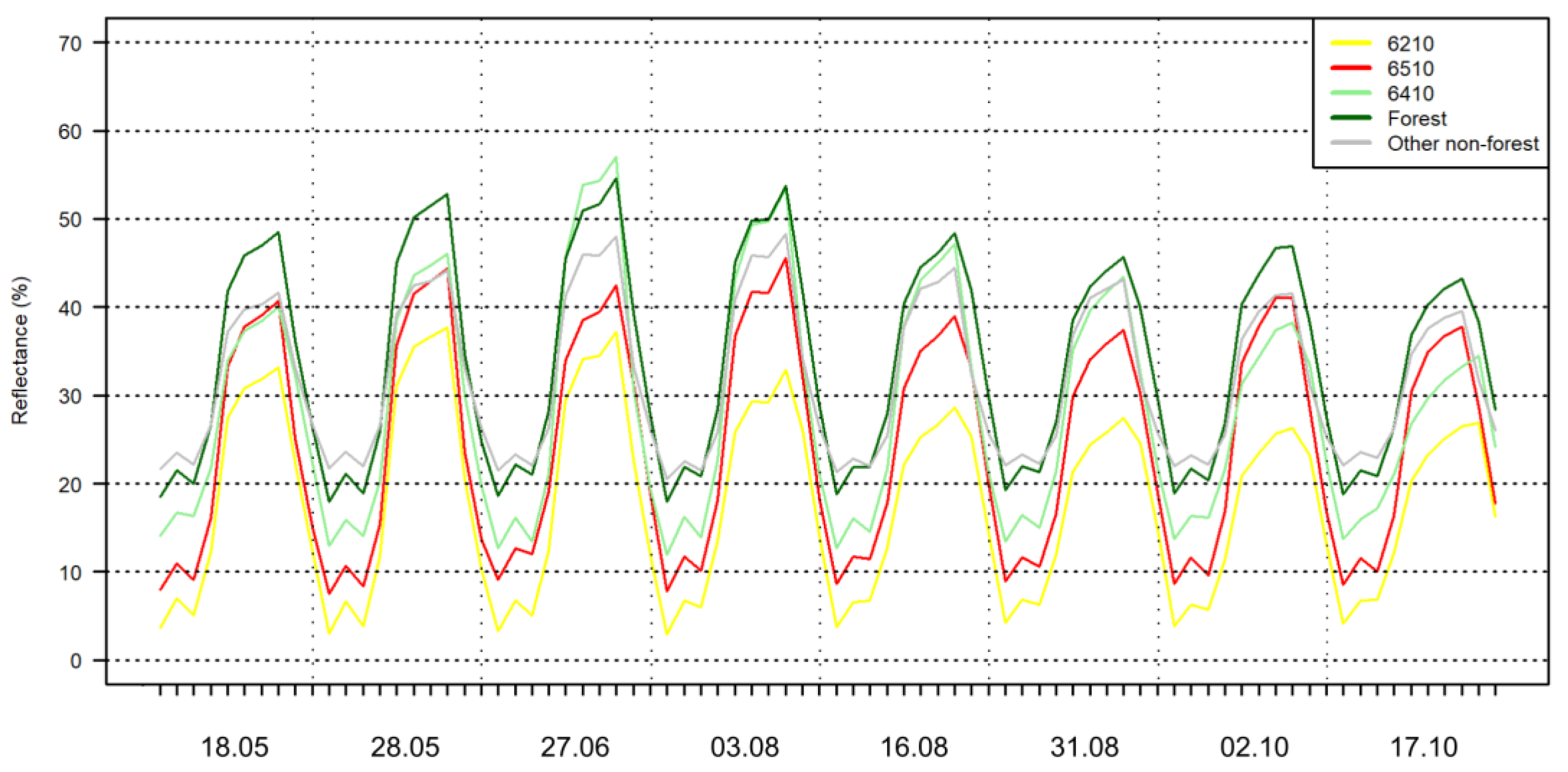
2.3. Sentinel-2 Images
2.4. Classification and Accuracy Assessment
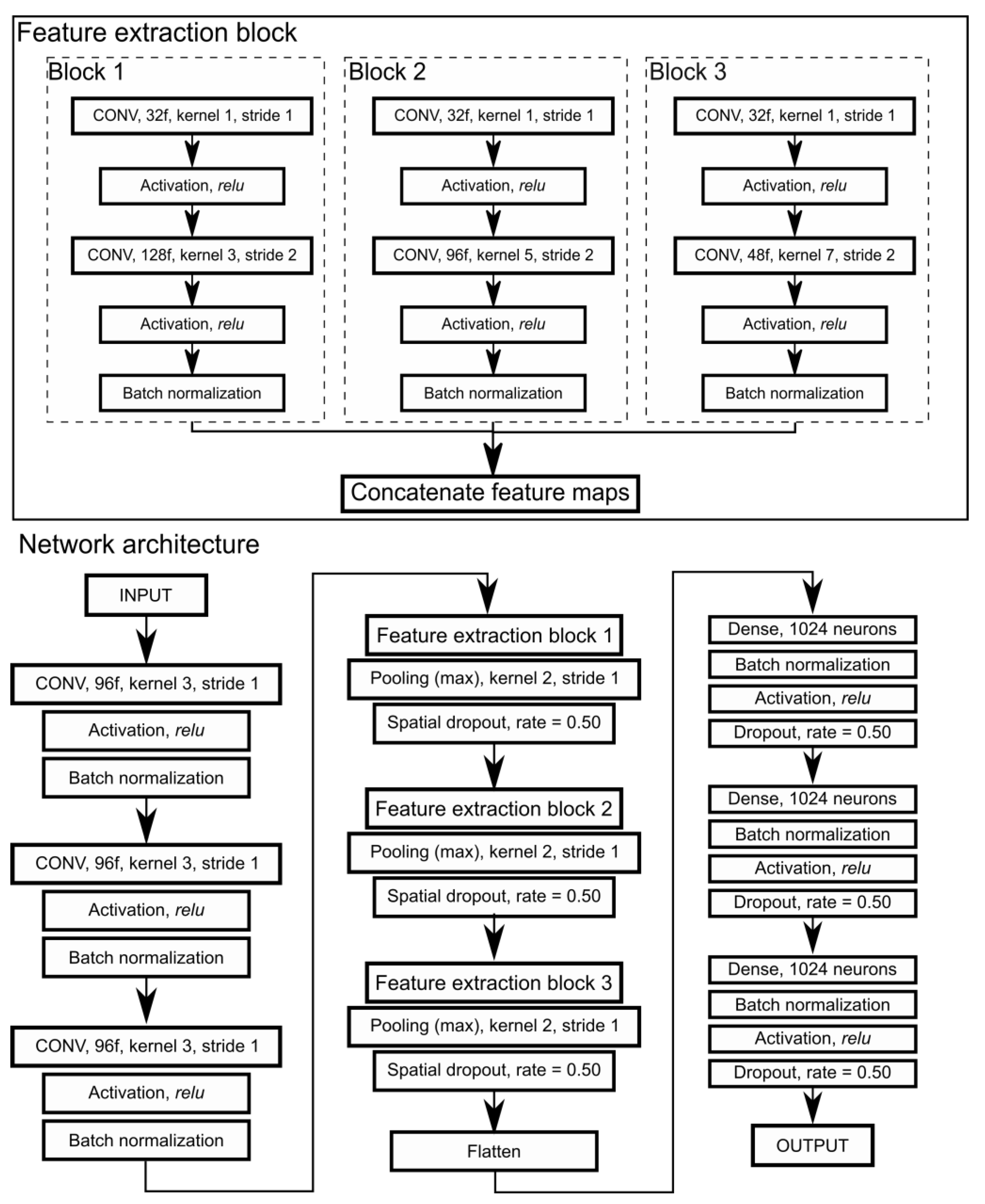
2.4.1. CNNs
2.4.2. RF
2.4.3. SVM
3. Results
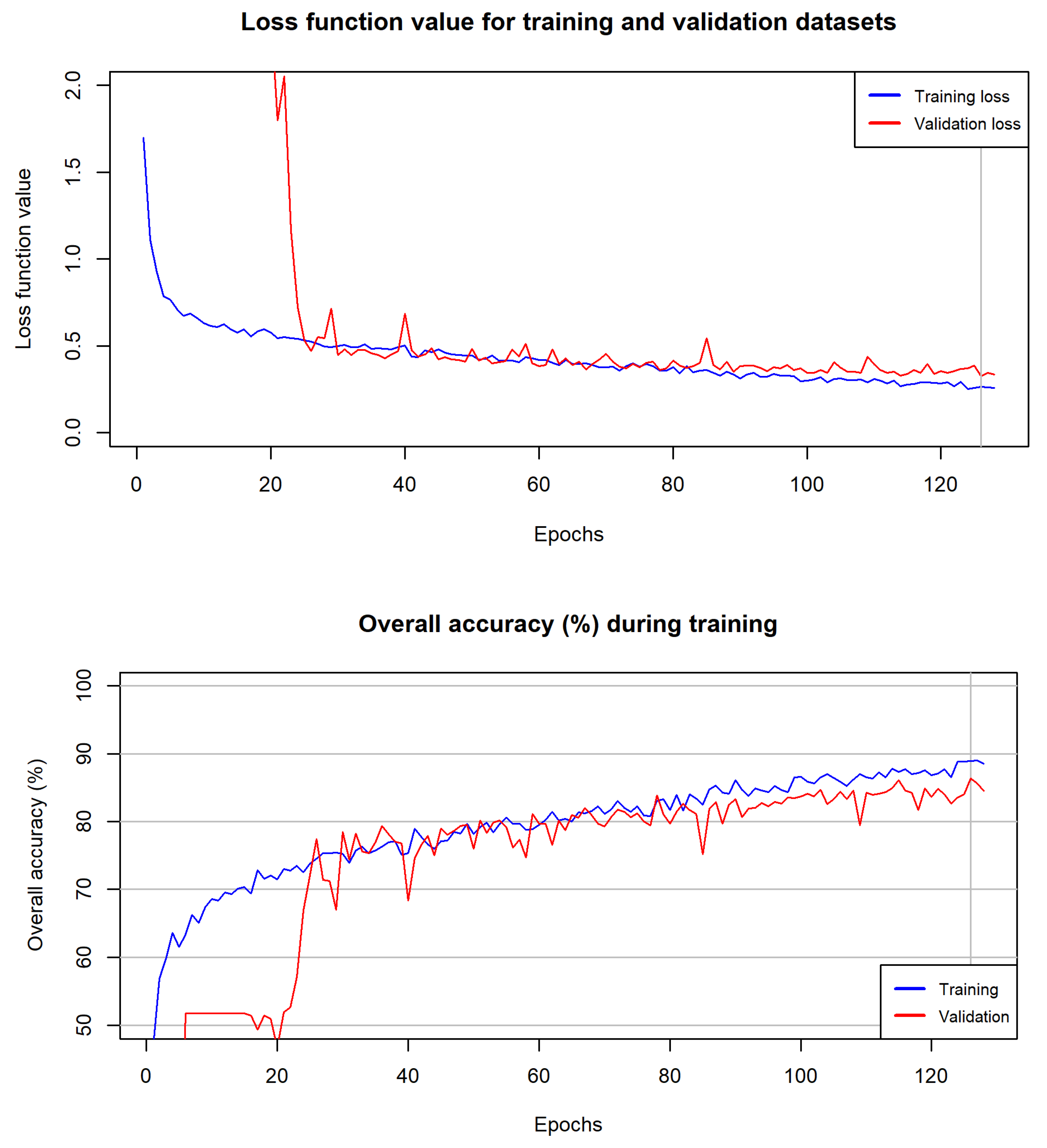
3.1. Selected Parameters for Classifiers
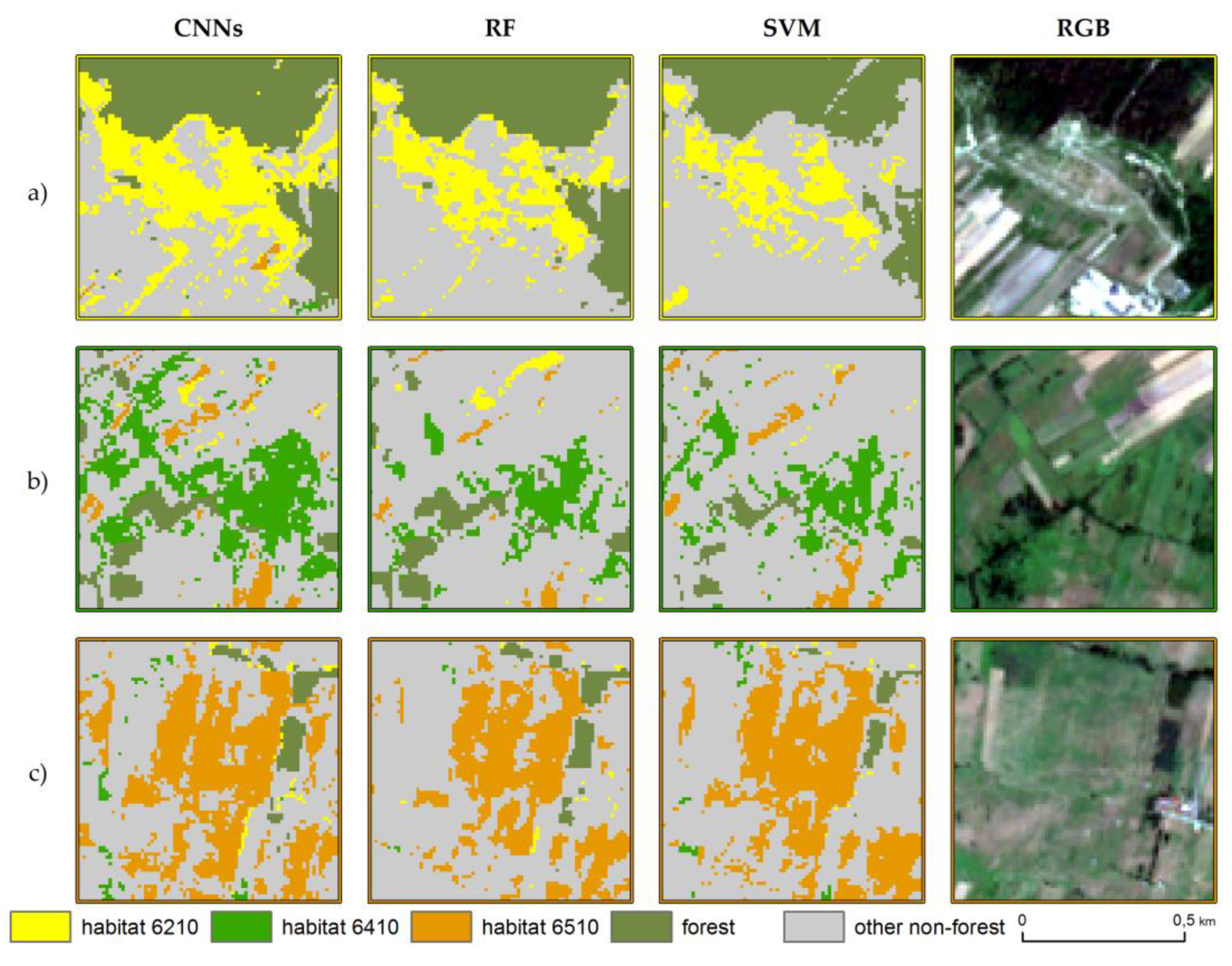
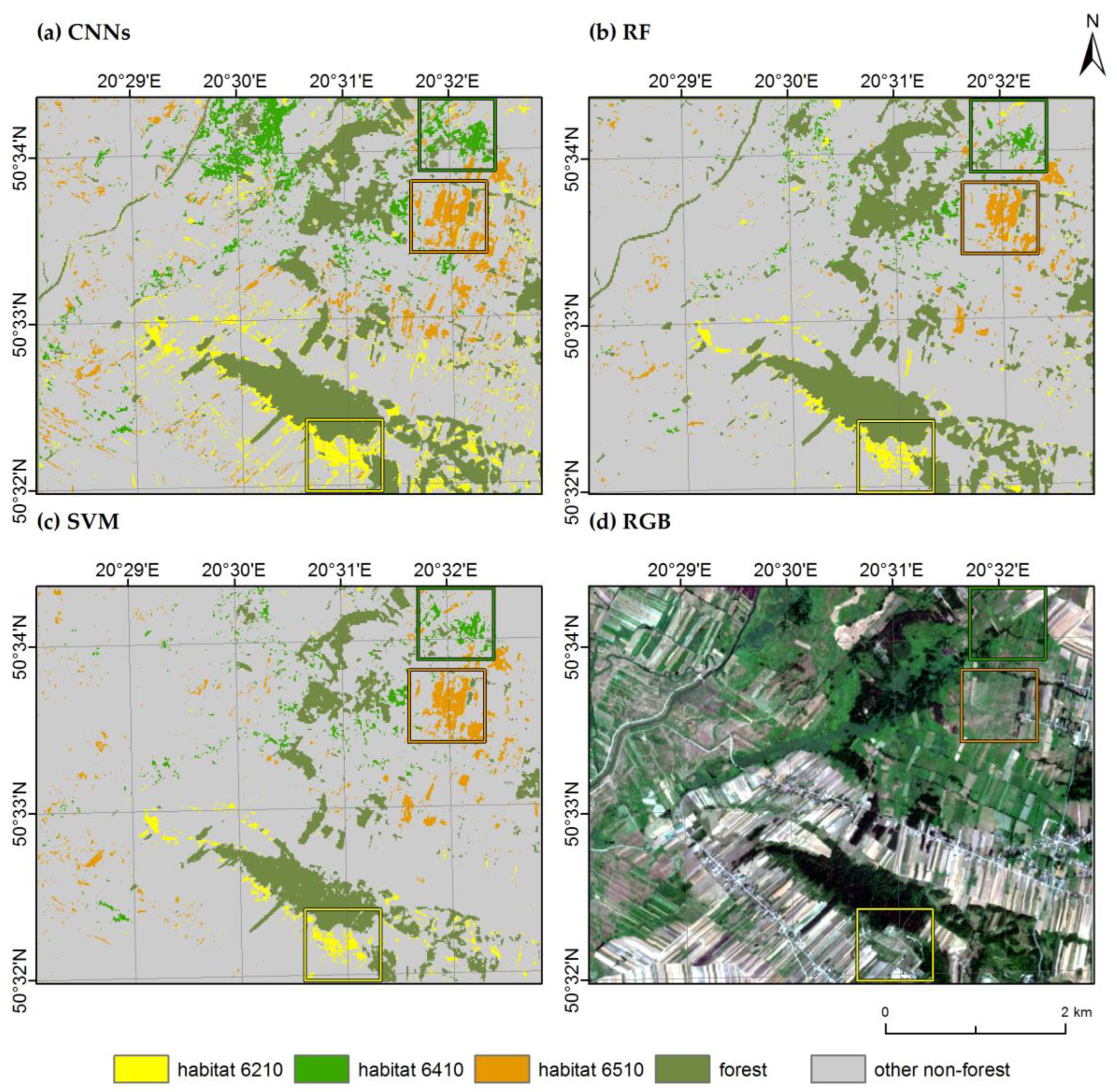
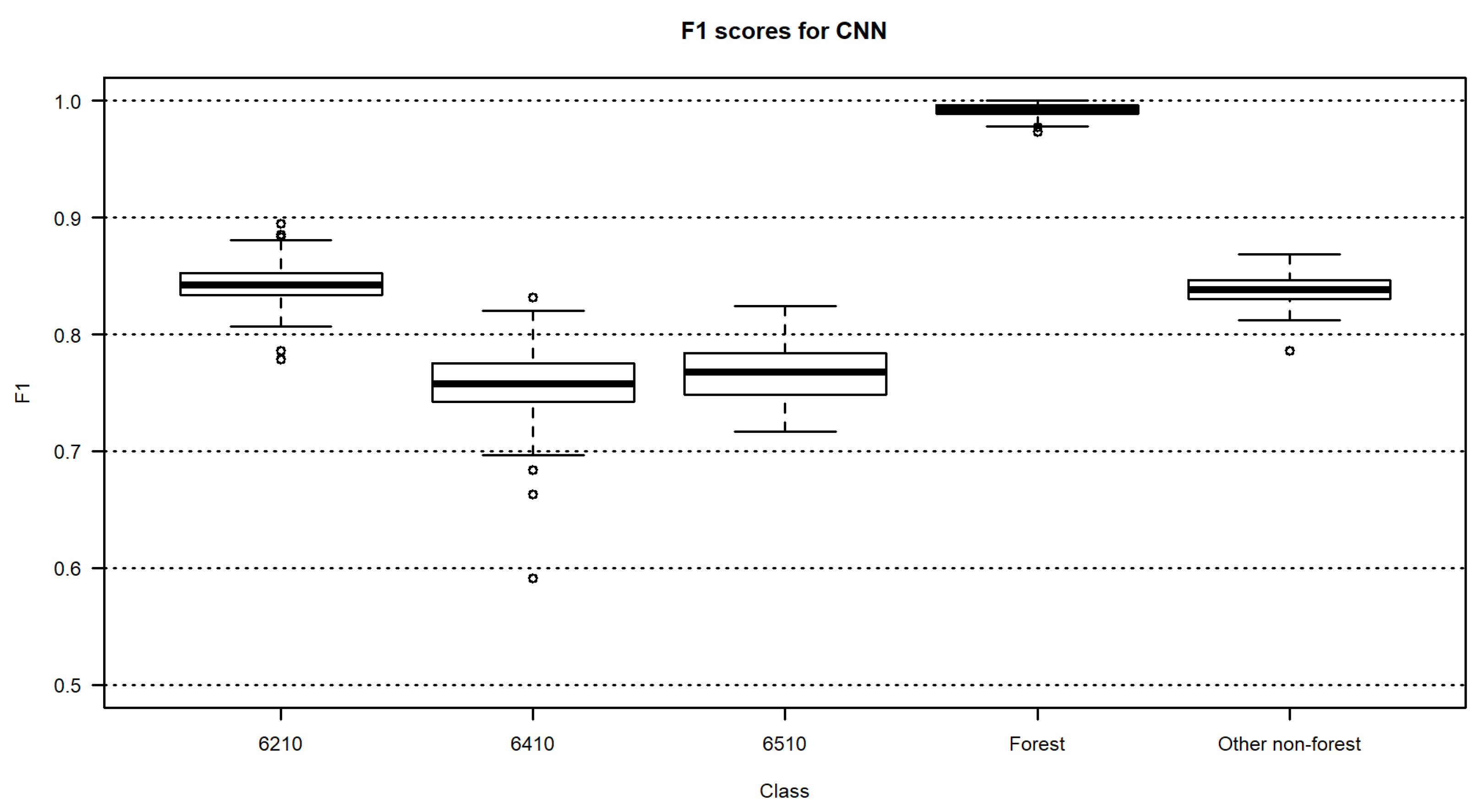
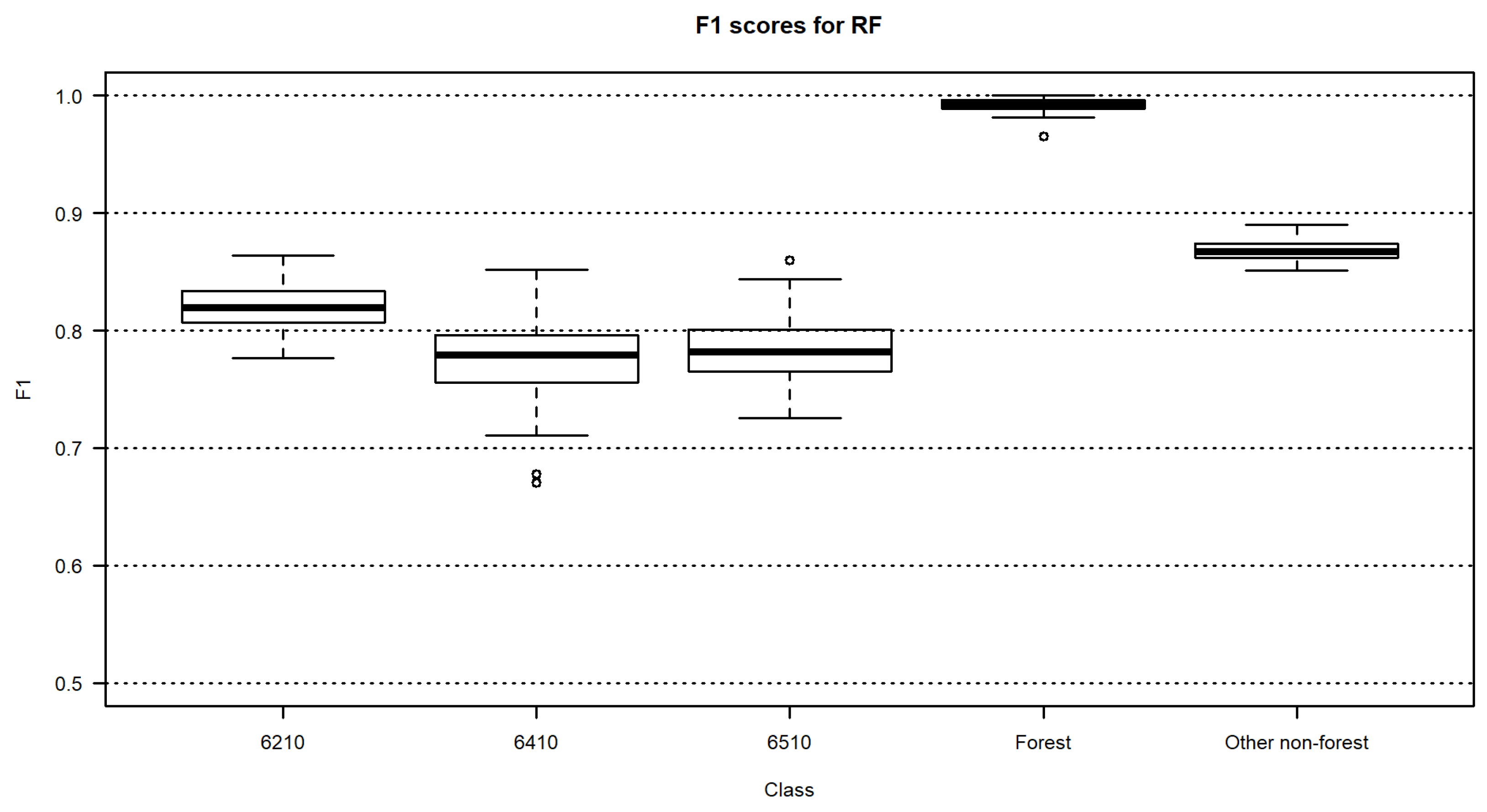
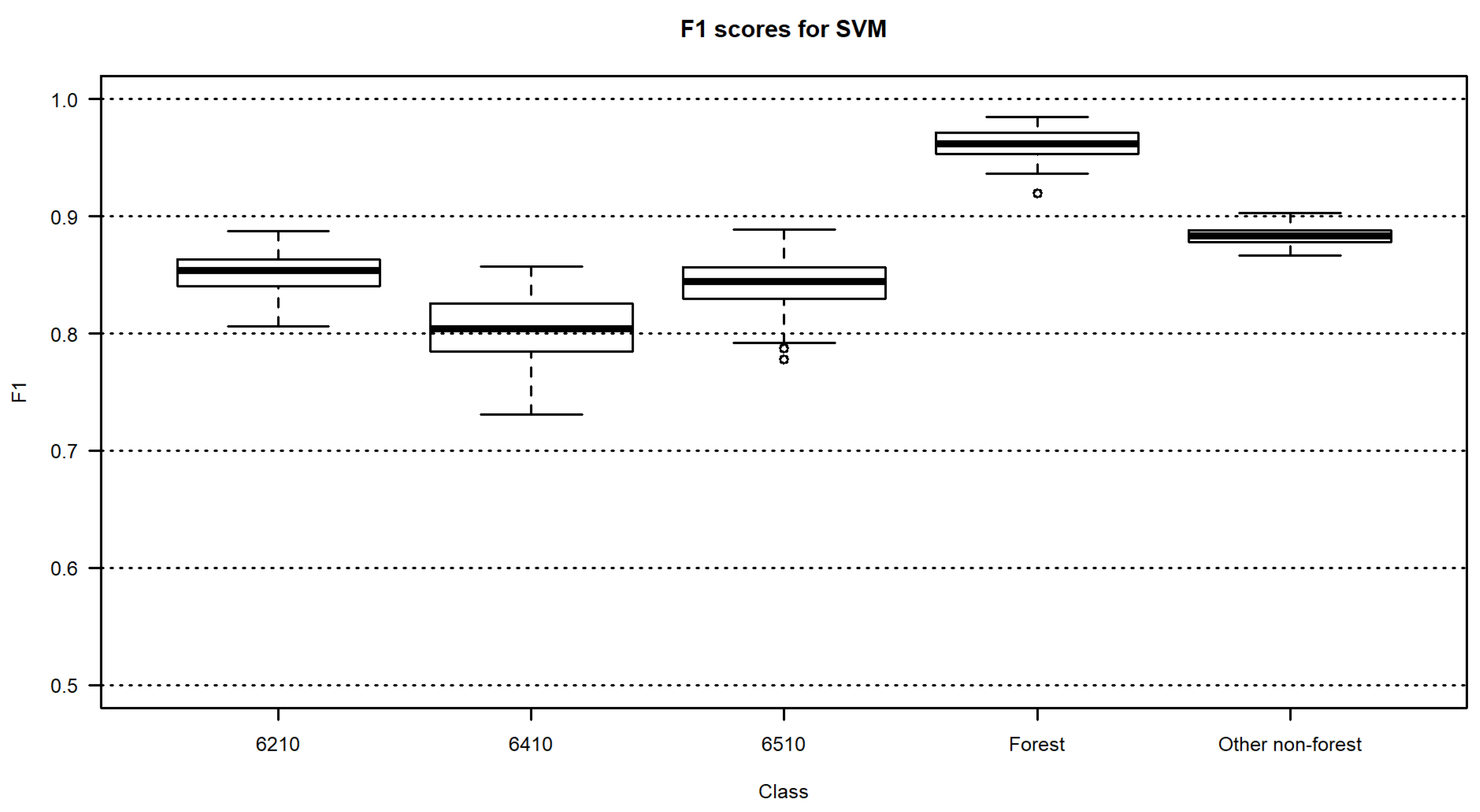
3.2. Habitat Maps and Accuracies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- European Comission Council. European Comission Council Directive 92/43/EEC of 21 May 1992 on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora (OJ L 206 22.07.1992 p. 7). Doc. Eur. Community Environ. Law 2010, 206, 568–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habel, J.C.; Dengler, J.; Janišová, M.; Török, P.; Wellstein, C.; Wiezik, M. European grassland ecosystems: Threatened hotspots of biodiversity. Biodivers. Conserv. 2013, 22, 2131–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, O.; Millán, V.E.G.; Klink, A.; Pakzad, K. Using information layers for mapping grassland habitat distribution at local to regional scales. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 37, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, C.; Schmidt, T.; Conrad, C.; Kleinschmit, B.; Förster, M. Grassland habitat mapping by intra-annual time series analysis -Comparison of RapidEye and TerraSAR-X satellite data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2015, 34, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilhauer, H.; Thonfeld, F.; Faude, U.; He, K.S.; Rocchini, D.; Schmidtlein, S. Assessing floristic composition with multispectral sensors-A comparison based: On monotemporal and multiseasonal field spectra. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2012, 21, 218–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Große-Stoltenberg, A.; Hellmann, C.; Werner, C.; Oldeland, J.; Thiele, J. Evaluation of continuous VNIR-SWIR spectra versus narrowband hyperspectral indices to discriminate the invasive Acacia longifolia within a mediterranean dune ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska-Ochtyra, A.; Gryguc, K.; Ochtyra, A.; Kopeć, D.; Jarocińska, A.; Sławik, Ł. Multitemporal Hyperspectral Data Fusion with Topographic Indices—Improving Classification of Natura 2000 Grassland Habitats. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Carabaza, S.; Boydell, O.; O’Connell, J. Habitat classification using convolutional neural networks and multitemporal multispectral aerial imagery. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2021, 15, 042406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarchi, L.; Kania, A.; Ciezkowski, W.; Piórkowski, H.; Oświecimska-Piasko, Z.; Chormański, J. Recursive feature elimination and random forest classification of natura 2000 grasslands in lowland river valleys of poland based on airborne hyperspectral and LiDAR data fusion. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarocińska, A.; Kopeć, D.; Kycko, M.; Piórkowski, H.; Błońska, A. Hyperspectral vs. Multispectral data: Comparison of the spectral differentiation capabilities of Natura 2000 non-forest habitats. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2022, 184, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenzel, S.; Feilhauer, H.; Mack, B.; Metz, A.; Schmidtlein, S. Remote sensing of scattered natura 2000 habitats using a one-class classifier. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 33, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilhauer, H.; Dahlke, C.; Doktor, D.; Lausch, A.; Schmidtlein, S.; Schulz, G.; Stenzel, S. Mapping the local variability of Natura 2000 habitats with remote sensing. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2014, 17, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenske, K.; Feilhauer, H.; Förster, M.; Stellmes, M.; Waske, B. Hierarchical classification with subsequent aggregation of heathland habitats using an intra-annual RapidEye time-series. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 87, 102036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sittaro, F.; Hutengs, C.; Semella, S.; Vohland, M. A Machine Learning Framework for the Classification of Natura 2000 Habitat Types at Large Spatial Scales Using MODIS Surface Reflectance Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabska, E.; Hostert, P.; Pflugmacher, D.; Ostapowicz, K. Forest stand species mapping using the sentinel-2 time series. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hościło, A.; Lewandowska, A. Mapping Forest Type and Tree Species on a Regional Scale Using Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, S.; Mancini, A.; Quattrini, G.; Casavecchia, S. Mapping mediterranean forest plant associations and habitats with functional principal component analysis using Landsat 8 NDVI time series. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praticò, S.; Solano, F.; Di Fazio, S.; Modica, G. Machine learning classification of mediterranean forest habitats in google earth engine based on seasonal sentinel-2 time-series and input image composition optimisation. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immitzer, M.; Neuwirth, M.; Böck, S.; Brenner, H.; Vuolo, F.; Atzberger, C. Optimal Input Features for Tree Species Classification in Central Europe Based on Multi-Temporal Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapinel, S.; Mony, C.; Lecoq, L.; Clément, B.; Thomas, A.; Hubert-Moy, L. Evaluation of Sentinel-2 time-series for mapping floodplain grassland plant communities. Remote Sens. Environ. 2019, 223, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakulinśka, M.; Marcinkowska-Ochtyra, A. Multi-temporal sentinel-2 data in classification of mountain vegetation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Dez, M.; Robin, M.; Launeau, P. Contribution of Sentinel-2 satellite images for habitat mapping of the Natura 2000 site ‘Estuaire de la Loire’ (France). Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 24, 100637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesaresi, S.; Mancini, A.; Quattrini, G.; Casavecchia, S. Functional Analysis for Habitat Mapping in a Special Area of Conservation Using Sentinel-2 Time-Series Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, C.; Forte, L.; Blonda, P.; Vicario, S.; Tomaselli, V.; Beierkuhnlein, C.; Adamo, M. Intra-annual sentinel-2 time-series supporting grassland habitat discrimination. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazzini, P.; Proia, G.D.F.; Adamo, M.; Blonda, P.; Petracchini, F.; Forte, L.; Tarantino, C. Sentinel-2 remote sensed image classification with patchwise trained convnets for grassland habitat discrimination. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests LEO. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osińska-Skotak, K.; Radecka, A.; Piórkowski, H.; Michalska-Hejduk, D.; Kopeć, D.; Tokarska-Guzik, B.; Ostrowski, W.; Kania, A.; Niedzielko, J. Mapping Succession in Non-Forest Habitats by Means of Remote Sensing: Is the Data Acquisition Time Critical for Species Discrimination? Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sławik, Ł.; Niedzielko, J.; Kania, A.; Piórkowski, H.; Kopeć, D. Multiple flights or single flight instrument fusion of hyperspectral and ALS data? A comparison of their performance for vegetation mapping. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burai, P.; Deák, B.; Valkó, O.; Tomor, T. Classification of herbaceous vegetation using airborne hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2046–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabat-Tomala, A.; Raczko, E.; Zagajewski, B. Comparison of Support Vector Machine and Random Forest Algorithms for Invasive and Expansive Species Classification Using Airborne Hyperspectral Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zagajewski, B.; Kluczek, M.; Raczko, E.; Njegovec, A.; Dabija, A.; Kycko, M. Comparison of random forest, support vector machines, and neural networks for post-disaster forest species mapping of the krkonoše/karkonosze transboundary biosphere reserve. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheykhmousa, M.; Mahdianpari, M.; Ghanbari, H.; Mohammadimanesh, F.; Ghamisi, P.; Homayouni, S. Support Vector Machine Versus Random Forest for Remote Sensing Image Classification: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2020, 13, 6308–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabija, A.; Kluczek, M.; Zagajewski, B.; Raczko, E.; Kycko, M.; Al-Sulttani, A.H.; Tardà, A.; Pineda, L.; Corbera, J. Comparison of support vector machines and random forests for corine land cover mapping. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vapnik, V.N. An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1999, 10, 988–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeCun, Y.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In Advances in neural information. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krówczyńska, M.; Raczko, E.; Staniszewska, N.; Wilk, E. Asbestos-cement roofing identification using remote sensing and convolutional neural networks (CNNs). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, Q.; Wu, G.; Xu, Y.; Shibasaki, R.; Shao, X. Village building identification based on Ensemble Convolutional Neural Networks. Sensors 2017, 17, 2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GDOŚ. Available online: https://www.gov.pl/web/gdos/dostep-do-danych-geoprzestrzennych (accessed on 14 January 2023).
- Main-Knorn, M.; Pflug, B.; Louis, J.; Debaecker, V.; Müller-Wilm, U.; Gascon, F. Sen2Cor for Sentinel-2. Proc. SPIE 2017, 10427, 1042704. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 18 November 2022).
- Hijmans, R.J.; van Etten, J. raster: Geographic Analysis and Modeling with Raster Data. R Packag. Version 2.5-2. 2015. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=raster (accessed on 20 November 2022).
- Bivand, R.; Keitt, T.; Rowlingson, B. Package ‘rgdal’—Bindings for the “Geospatial” Data Abstraction Library; 2019. Available online: http://www.tinyurl.com/h8w8n29 (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Kuhn, M. Contributions from Jed Wing, Steve Weston, Andre Williams, Chris Keefer, Allan Engelhardt, Tony Cooper, Zachary Mayer, Brenton Kenkel, the R Core Team, Michael Benesty, Reynald Lescarbeau, Andrew Ziem, Luca Scrucca, Yuan Tang, Can Candan, and T. H. caret: Classification and Regression Training. R Packag. Version 6.0-79. 2018. Available online: https://www.machinelearningplus.com/machine-learning/caret-package/ (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Weston, S. Getting Started with doSMP and Foreach. R Packag. Version. 2011; pp. 2–7. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/doMC/vignettes/gettingstartedMC.pdf (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Raczko, E.; Zagajewski, B. Tree species classification of the UNESCO man and the biosphere Karkonoski National Park (Poland) using artificial neural networks and APEX hyperspectral images. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.; Fassnacht, F.E.; Joshi, P.K.; Kochb, B. A framework for mapping tree species combining hyperspectral and LiDAR data: Role of selected classifiers and sensor across three spatial scales. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rijsbergen, C.J. Information Retrieval, 2nd ed.; Butterworths: London, UK, 1979; Volume 208, pp. 374–375. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G. A review of assessing the accuracy of classifications of remotely sensed data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1991, 37, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abadi, M.; Barham, P.; Chen, J.; Chen, Z.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; Ghemawat, S.; Irving, G.; Isard, M.; et al. TensorFlow: A system for large-scale machine learning. In Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, OSDI 2016, Savannah, GA, USA, 2–4 November 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Allaire, J.; Chollet, F. keras: R Interface to “Keras.” Version 2.4.0. 2021. Available online: https://rdrr.io/cran/keras/ (accessed on 10 January 2023).
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and Regression by randomForest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, D.; Dimitriadou, E.; Hornik, K.; Weingessel, A.; Leisch, F.; Chang, C.-C.; Lin, C.-C. Misc Functions of the Department of Statistics, Probability Theory Group (Formerly: E1071); TU Wien: Vienna, Austria, 2019; ISBN 0805331700. [Google Scholar]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăgu, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska-Ochtyra, A.; Zagajewski, B.; Raczko, E.; Ochtyra, A.; Jarocińska, A. Classification of high-mountain vegetation communities within a diverse Giant Mountains ecosystem using airborne APEX hyperspectral imagery. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasiak, N.; Dejoux, J.F.; Monteil, C.; Sheeren, D. Spatial dependence between training and test sets: Another pitfall of classification accuracy assessment in remote sensing. Mach. Learn. 2022, 111, 2715–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Niculescu, S. Mapping and monitoring of land cover/land use (LCLU) changes in the crozon peninsula (Brittany, France) from 2007 to 2018 by machine learning algorithms (support vector machine, random forest, and convolutional neural network) and by post-classification comparison (PCC). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sothe, C.; De Almeida, C.M.; Schimalski, M.B.; La Rosa, L.E.C.; Castro, J.D.B.; Feitosa, R.Q.; Dalponte, M.; Lima, C.L.; Liesenberg, V.; Miyoshi, G.T.; et al. Comparative performance of convolutional neural network, weighted and conventional support vector machine and random forest for classifying tree species using hyperspectral and photogrammetric data. GIScience Remote Sens. 2020, 57, 369–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wang, L.; Lin, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, B. Mapping plastic greenhouses with two-temporal sentinel-2 images and 1d-cnn deep learning. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalponte, M.; Ørka, H.O.; Gobakken, T.; Gianelle, D.; Næsset, E. Tree species classification in boreal forests with hyperspectral data. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 2632–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raab, C.; Stroh, H.G.; Tonn, B.; Meißner, M.; Rohwer, N.; Balkenhol, N.; Isselstein, J. Mapping semi-natural grassland communities using multi-temporal RapidEye remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 5638–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, J.; Roberts, D.A.; Halligan, K.; Menz, G. Hierarchical Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis (MESMA) of yperspectral imagery for urban environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 1712–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Class | No. of Polygons | No. of Pixels |
|---|---|---|
| habitats: | ||
| 6210 | 264 | 548 |
| 6410 | 172 | 290 |
| 6510 | 207 | 438 |
| background: | ||
| forest | 203 | 365 |
| other non-forest | 771 | 1757 |
| sum | 1617 | 3398 |
| Date | Satellite | Processing Level |
|---|---|---|
| 18 May 2017 | S2A | 2A |
| 28 May 2017 | S2A | 2A |
| 27 June 2017 | S2A | 2A |
| 3 August 2017 | S2A | 2A |
| 16 August 2017 | S2A | 2A |
| 31 August 2017 | S2B | 1C |
| 02 October 2017 | S2A | 2A |
| 17 October 2017 | S2B | 1C |
| Class | Training Dataset | Validation Dataset |
|---|---|---|
| habitats: | ||
| 6210 | 347 | 201 |
| 6410 | 184 | 106 |
| 6510 | 277 | 161 |
| background: | ||
| forest | 231 | 134 |
| other non-forest | 1111 | 646 |
| sum | 2150 | 1248 |
| Algorithm | Habitat | Background | OA (%) | OA 95% Conf. Interval (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6210 | 6410 | 6510 | Forest | Non-Forest | |||
| CNNs | 0.84 | 0.76 | 0.77 | 0.99 | 0.84 | 84.0 | 83.7–84.2 |
| RF | 0.82 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.99 | 0.87 | 85.5 | 85.2–85.7 |
| SVM | 0.85 | 0.80 | 0.84 | 0.96 | 0.88 | 87.5 | 87.3–87.7 |
| Habitat | Hyperspectral [7] | Multispectral [This Study] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Term | Three Terms/Three Terms with Topographic Indices | Eight Terms | |
| 6210 | 0.74/0.80/0.78 | 0.84/0.85 | 0.85 |
| 6410 | 0.69/0.75/0.75 | 0.82/0.83 | 0.80 |
| 6510 | 0.52/0.60/0.61 | 0.70/0.69 | 0.84 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marcinkowska-Ochtyra, A.; Ochtyra, A.; Raczko, E.; Kopeć, D. Natura 2000 Grassland Habitats Mapping Based on Spectro-Temporal Dimension of Sentinel-2 Images with Machine Learning. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051388
Marcinkowska-Ochtyra A, Ochtyra A, Raczko E, Kopeć D. Natura 2000 Grassland Habitats Mapping Based on Spectro-Temporal Dimension of Sentinel-2 Images with Machine Learning. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(5):1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051388
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarcinkowska-Ochtyra, Adriana, Adrian Ochtyra, Edwin Raczko, and Dominik Kopeć. 2023. "Natura 2000 Grassland Habitats Mapping Based on Spectro-Temporal Dimension of Sentinel-2 Images with Machine Learning" Remote Sensing 15, no. 5: 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051388
APA StyleMarcinkowska-Ochtyra, A., Ochtyra, A., Raczko, E., & Kopeć, D. (2023). Natura 2000 Grassland Habitats Mapping Based on Spectro-Temporal Dimension of Sentinel-2 Images with Machine Learning. Remote Sensing, 15(5), 1388. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15051388









