Abstract
The orbit maneuver detection is crucial in Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) precise orbit determination, which is necessary for adjusting data processing strategies. The frequency of orbit maneuvers for the BeiDou Navigation System is significantly higher than that of other navigation systems, especially for geosynchronous orbit (GEO) and inclined geosynchronous orbit (IGSO) satellites. We propose a novel real-time and postprocessing method for detecting orbit maneuvers for BeiDou satellites based on the orbit differences between the epoch-updated orbit estimated using square root information (SRIF) and the predicted orbit according to the precise orbit estimated during non-maneuver period, as well as the orbital state difference during maneuver and non-maneuver periods. This method has significant advantages over using observation residuals and it is not affected by observation outliers, thus improving the accuracy and timeliness of orbit maneuver detection. We demonstrated that 32 orbit maneuver events of BeiDou satellites were successfully detected in 2022, of which 1 was for medium Earth orbit (MEO), 7 were for IGSO with an average detected maneuvering time of 7–8 min, and 24 were for GEO satellites with an average detected time of 4–5 min. Moreover, our method can be easily integrated into current real-time filter-based precise orbit determination (POD) processing without any extra task line, which simplifies the overall data processing. The data used in this method can be accessed easily, including GNSS observation data, broadcast ephemeris, and other open-source information files.
1. Introduction
Satellites are influenced by the non-spherical gravity of the earth as well as other perturbations, such as solar radiation pressure (SRP) and the gravitational effects of celestial bodies such as the Sun, Moon, and other objects in space [1]. Over time, satellite orbits may deviate from their intended values, necessitating the implementation of orbit maneuvers by propulsion devices to maintain an optimal satellite orbit constellation. This procedure is commonly referred to as orbit maneuvers [2,3]. The frequency of orbit maneuvers is primarily determined by the characteristics of the orbits, particularly their rotation periods [4]. GEO and IGSO satellites have a greater frequency of orbit maneuvers in comparison to MEO satellites due to the resonance effect induced by the earth’s rotation [5]. The BeiDou Satellite Navigation System (BDS) is comprised of GEO, IGSO, and MEO satellites, resulting in a much higher frequency of orbit maneuvers in comparison to other satellite navigation systems [3,6,7].
Orbit maneuvers can cause the orbit of a maneuvering satellite to be insufficiently described by a single orbit arc, leading to the loss of real-time and post-processing precise products from the product providers, such as the Analysis Centers of International GNSS Service (IGS) and International GNSS Monitoring & Assessment System (iGMAS). Due to the loss of precise GNSS service products, the continuity, reliability, and integrity of GNSS services can be decreased. This is particularly serious in complex environments such as canyons and urban areas, where adding one more satellite observation can greatly enhance the positioning performance of precise point positioning (PPP). The accurate detection of orbit maneuvers in time is critical in adjusting precise orbit determination strategies. Without it, the GNSS observations may be falsely excluded as outliers due to the system errors of maneuvering satellites, which could potentially crush the whole estimator. Due to the orbit maneuver information being undisclosed by BDS officials, research on satellite orbit maneuver detection is necessary.
In the past, great efforts were made towards the orbit maneuver detection of GNSS satellites. Orbit maneuvers can be detected and analyzed by using the orbital elements from broadcast ephemeris [3,7,8]. Qin and Huang et al., used the OMC (observation minus computation) and SPP (single point positioning) results according to broadcast ephemeris and pseudo-range observation data to detect orbit maneuver time [9,10,11]. Qiao and Song et al. detected the start and end times of orbit maneuvers based on triple-differenced observations [5,12]. Tu and Zhang detected the orbital maneuvers of the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BDS) using carrier phase observations and broadcast ephemeris data [13]. Du et al. utilized orbital monitoring data obtained from the China Area Positioning System (CAPS) to detect the orbital maneuvers of GEO satellites [14]. Ye et al. detected the orbit maneuvers of BeiDou satellites using the orbit difference of post-processed precise orbit products, before and after the maneuvering [15]. The above efforts can be summarized into two types: based on the orbital elements and the observation residuals.
The first type utilizes the precise orbit or orbit parameter data before and after the maneuver to accurately determine the orbit maneuvering satellite, but it cannot accurately detect the orbit maneuver time because the broadcast ephemeris is only updated once every 1–2 h and becomes invalid for 6–8 h after the orbit maneuver. The second method is based on the pseudo-range or carrier phase observations, but it has certain limitations due to the lack of an accurate orbit of the maneuvering satellite and the influence of observation outliers.
The current research mainly focuses on using GNSS phase and pseudo-range observations to detect satellite orbit maneuvers. Our and other scholars’ previous studies also used GNSS observations to detect orbit maneuvers and determine the time of the maneuver. However, the inconsistency between the observation and the geometry distance between the satellite and station has certain limitations in orbit maneuver detection. Orbit maneuvers will cause OMC anomalies in multiple measurement stations, but there are also other situations that can cause this phenomenon, such as satellite clock anomalies. In addition, the first 6–7 h of a satellite orbit after the start of the orbit maneuver cannot be obtained, the satellite status is marked as unhealthy in the broadcast ephemeris, and the orbit elements are in an invalid state, which also adds difficulty to the detection of orbit maneuvers because of the error geometry distance between satellites and stations. As is well known, the acceleration caused by the orbit maneuver thrust directly changes the satellite orbit state. If the orbit of the maneuvering satellite can be calculated and compared with the orbit before and after the maneuver, the start and end time of the orbit maneuver can be analyzed. The most direct and effective method for detecting orbit maneuvers is to analyze the orbit estimates of the maneuvering satellite, which avoids relying on the invalid broadcast ephemeris and eliminates the potential interference caused by observation errors in detecting orbit maneuvers. However, the main challenge is the presence of system errors induced by the maneuvering thrust, which makes it difficult to estimate the precise orbit of maneuvering satellites by using conventional mechanical models.
In this study, we propose a novel method to detect the maneuvering start and end-time for GNSS orbit maneuvering satellites, which is applicable for both post-processing and real time cases. We adopt the SRIF for real-time POD estimation and maneuver detection, in which the effect caused by the orbit maneuver, that is, the abrupt change in orbit accelerations and the corresponding changes in orbit velocities and positions, can be properly adjusted via the covariance of the state constraint equations. The orbit difference with the predicted orbit before and after orbit maneuvering can accurately detect the start and end time of the orbit maneuvers. The proposed method can only detect the start time of the maneuver as it relies on the precise orbit of the maneuvering satellite one day after the end of the maneuvering. However, the real-time detection of the end of the orbit maneuver can also be achieved by utilizing the instability of the satellite orbit during the maneuver period.
In this paper, we analyze the data from BeiDou satellites in 2022 and prove that the method can accurately detect the start and end times of orbit maneuvers. In the next section, the methodology of SRIF is introduced briefly and the description is focused on orbit maneuver detection. Then, the experiment results from one year (2022) are analyzed, followed by conclusions and discussions in the last section.
2. Mathematical Model
The orbits of maneuvering satellites will be altered because of the orbit maneuvering thrust, which cannot be expressed using the same set of orbital parameters. This problem could be solved completely if the orbit maneuvering thrust can be obtained or estimated, but it is difficult to be realized in real-time. Considering the advantages of SRIF, where the orbit could be estimated epoch-wisely, the orbit information is transferred to the next epoch through the state constraint equation. The systematic errors caused by orbit maneuvering thrust are thus absorbed by adjusting the prior covariance of the state constraint equation, and the processes are as follows.
2.1. Epoch-Updated Orbit Estimation
The square root information filter is a parameter estimation method that is based on the standardization and Householder matrix transformations [16,17,18]. It provides an efficient and computationally stable approach to estimate the parameters. Unlike traditional methods, the SRIF operates directly on the square root of the information matrix, which avoids the need for matrix inversions and reduces computational complexity. By utilizing the square root factorization, the SRIF offers improved numerical stability and accuracy, making it well suited for applications in sensor fusion, navigation, and control systems. A brief explanation of the SRIF principle is provided in this section.
where is the estimated parameters; is the design matrix; is the observation error; and is the vector including observations and initial values. It is noted that Equation (1) contains the observation equation and the state constraint equation of the estimated parameters. Additionally, it needs to be normalized . To minimize the mean square observation,
By applying the Householder orthogonal transformation and the minimum variance criterion for observation error [19], the latter can be derived as
where is the orthogonal transformation matrix; is the information matrix, which is also an upper triangular matrix; and is the vector of the observation residual, respectively. Combining with Equation (2), it is obvious that can be derived as
SRIF has been successfully applied to precise orbit determination and clock estimation in GNSS satellites [20,21,22,23], which includes orbit integration, parameter state updates, observation updates, quality control, and parameter solutions. The Runge–Kutta integration method was employed in this study [24,25], and the detailed method of quality can be found in reference [20]. Due to the unknown duration of orbital maneuvers, weakly constrained parameter states could be employed at all times to absorb system errors caused by orbit maneuver thrust. The weakly constrained state solution estimates the orbit that is not highly precise, but the solution is sufficient to fulfill the requirements for maneuver detection. The state constraint equation for the position and velocity of the satellite can be shown,
where denotes the initial position and velocity of satellites in the celestial reference system (CRS), with the subscript denoting the epoch symbol and the superscript denoting the corresponding time of the estimated parameters. The time of the estimated parameters at the current epoch is represented by , while the corresponding time of the next epoch is represented by , for example (); denotes the correction values of the parameters to be estimated; is the state transfer matrix; and is the process noise. Additionally, the prior variance is shown,
where is the prior variance of the state constraint equation; is the standard deviation of the estimated parameters; and the empirical values in our study are about 1d-5 km and 1d-6 km/s for position and velocity, respectively, which ensures that the system errors caused by orbit maneuvering thrust can be absorbed, thus preventing the observation values from being eliminated. As a result, the correct position and velocity of the maneuvering satellite can be determined.
2.2. Orbit Maneuver Detection
First, there is a concept that needs to be redefined, and the schematic diagram of orbit maneuver is shown in Figure 1.
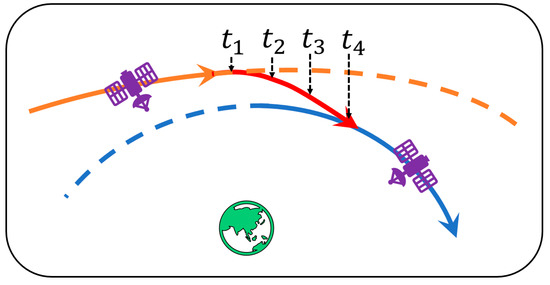
Figure 1.
The schematic diagram orbit maneuver. is the actual start time of orbit maneuver, which means the time when satellite propulsion device is active; is the start time of when the satellite deviates from the original orbit; is actual end time of orbit maneuver, which means the time when satellite propulsion device stops; is the time when the satellite returns to a stable state after the maneuver.
The “start time” and “end time” of satellite maneuvers mentioned in GNSS data processing are not the actual time when the satellite propulsion device activates or stops. When the satellite propulsion device is activated, the observation of the satellite will not be changed significantly and instantaneously. Orbit maneuvers change the satellite track with a certain angle with respect to the original orbit. Then, the satellite will deviate from the original orbit quickly. The “start time” of the orbit maneuver in GNSS data processing is the time when the satellite deviates from the original orbit after orbit maneuvering. In addition, the actual end time of the maneuver is when the satellite propulsion device no longer applies external forces to the satellite. However, external forces will act on the satellite for a short time, which will take some time for the satellite to return to a stable state. The “end time” of the orbit maneuver in GNSS data processing is the time when the satellites return to the stable state. We were unable to obtain the active and stop times of the satellite propulsion device. Instead, we can only compare and analyze the orbit of the maneuvering satellite before and after the orbital maneuver to determine the time when the satellite deviated from its original orbit and when it returned to a stable state. Therefore, the “start time” and “end time” of the satellite orbit maneuver mentioned in this paper refer to the time when the satellite deviates from the original orbit and the time when the satellite returns to a stable state after the maneuver, respectively.
The SRIF method can accurately estimate the correct orbit of a maneuvering satellite during both maneuver and non-maneuver periods. High-precision orbital parameters can be obtained by fitting the precise orbit from the day before the maneuver. The correct orbit prior to the maneuver can then be obtained through orbit integration using the high-precision orbital parameters. Similarly, by using the precise orbit from one day after the orbit maneuver, the correct orbit after the completion of the maneuver can also be obtained. The schematic diagram is shown below (Figure 2).
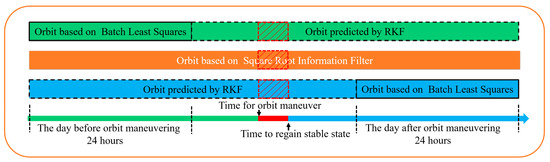
Figure 2.
The schematic diagram of the required orbit for orbit maneuver detection. The green rectangle with a solid border represents the high-precision orbit one day before orbit maneuvering, while the green rectangle with a dashed border represents the orbit predicted by orbital integration. The blue rectangle with a solid border represents the high-precision orbit one day after the orbit maneuvering, while the blue rectangle with a dashed border represents the orbit predicted through reverse orbital integration. The orange rectangle represents the satellite orbit estimated by using the SRIF method.
The difference between the orbit estimated by the SRIF method and the forward predicted orbit can be used to detect the start time of the orbit maneuver in real time. Similarly, the end time of the orbit maneuver can be detected by using the difference between the orbit estimated using the SRIF method and the orbit predicted by reverse integration, which is the time when the satellite returns to a stable state.
This method cannot achieve the real-time detection of the end time of the orbit maneuver, as it relies on the precise orbit obtained one day after the end of the maneuver. Therefore, we utilized the unstable state of a satellite during the maneuvering period to achieve real-time detection for the end time of maneuvering. This method’s schematic diagram is shown in the following Figure 3.
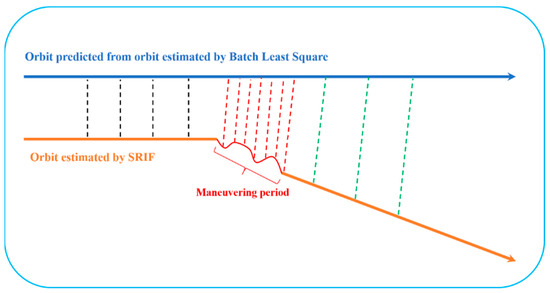
Figure 3.
The schematic diagram for maneuvering end time detection in real-time.
In Figure 3, the blue line represents the orbit arc before orbit maneuvering; the orange line represents the satellite orbit estimated using the SRIF method; and the red line represents the orbit during orbit maneuvering period. They can all be obtained in real time. The black dashed line, red dashed line, and green dashed line represent the orbit difference before the orbit maneuvering, during the maneuvering period, and after maneuvering, respectively.
As is well known, satellites remain in a stable state during non-maneuver periods. Therefore, the orbit differences do not undergo jumps during non-maneuver periods. The difference between the two orbits before orbit maneuvering is small, and the epoch difference of the orbit difference tends to be zero. After the end of the orbit maneuver, the orbit difference gradually increases, but the difference between the epochs of the orbit difference tends to stabilize and absolute values become positive. During the orbit maneuver adjustment period, the epoch-to-epoch difference in the orbit difference shows irregular jumps. Based on this characteristic, the real-time detection of the end time of orbit maneuvers can be achieved. The orbit can be estimated in real time based on the SRIF algorithm and each epoch only costs 3 s. As long as epoch-wise orbits are obtained, we can then determine whether maneuvering happens immediately. This approach is necessary for the processing of maneuvered satellites in real-time processing as mis-detecting will cause filter divergence.
3. Data Processing and Validation
In this section, first, a brief introduction is provided on the data and estimation strategy used for orbit determination based on the SRIF method and the corresponding orbit accuracy. Second, a detailed analysis of the results of the orbital maneuver detection is presented; the velocity change of satellites has been estimated and compared to indicate that the proposed method in this paper can accurately detect the start and end times of orbit maneuvers in post-processing and real time. Finally, the start and end times of maneuvering satellites for BDS satellites in 2022 are given.
3.1. Network and Processing Strategy
The data from a network of 103 globally distributed multi-GNSS (MGEX) [26] stations in 2022 were utilized for orbit estimation validation, with all stations capable of tracking BDS signals. The distribution of stations is illustrated in Figure 4.
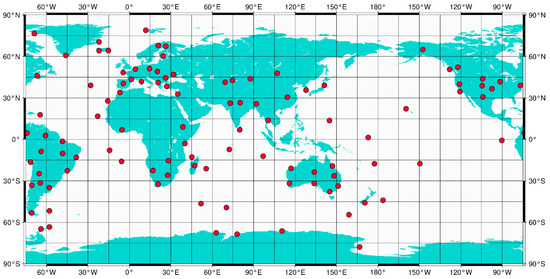
Figure 4.
Distribution of stations for precise orbit determination for BDS on 325th day of 2022. The red points denote the position of stations.
The validation process involves using the upgraded PANDA software package [27], which includes a real-time orbit estimation procedure on a Linux server. The data processing strategy for orbit estimation is detailed in Table 1.

Table 1.
Modeling and parameterization strategy for orbit determination.
3.2. Experimental Results and Verification
In order to verify the accuracy of the orbit estimated with the SRIF method with the corresponding estimation strategy, we compared it with the GBM precise orbit product from GFZ, and the orbit accuracy is shown in Figure 5.
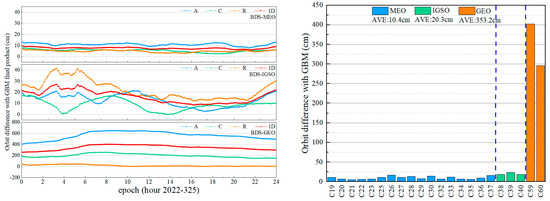
Figure 5.
Orbit accuracy time series and statistical results. The left-hand side shows the time series of orbit accuracy, with the top, middle, and bottom sections corresponding to BeiDou MEO, IGSO, and GEO satellites, respectively. The blue points denote the orbit difference in along-track direction, green points denote the orbit difference in cross-track direction, and orange points denote orbit difference in radial direction; red points denote the 1D-RMS. The right-hand side displays the orbit accuracy statistical results, with the orbit accuracy of MEO, IGSO, and GEO satellites represented by blue, green, and orange bars, respectively.
It is evident from the results that, using the estimation strategy in this study, the accuracy of BeiDou MEO satellites is significantly better than IGSO and GEO satellites. The average one-dimensional accuracy of MEO satellites is 10.4 cm, while that of IGSO and GEO is 20.3 cm and 353.2 cm, respectively. After an orbit maneuver, the adjusted orbit will quickly diverge from its previous orbit [5]. So, the accuracy of the estimated orbit is sufficient for orbit maneuver detection, and this study does not discuss how to improve orbit accuracy with the SRIF estimation method.
The results of orbit maneuver detection for GEO, IGSO, and MEO satellites are presented in this section. In Figure 6, the orbit maneuver detection results of C59 on 215th day of 2022 are taken as an example.
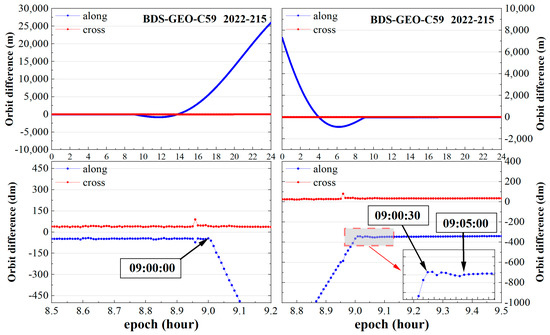
Figure 6.
The orbit maneuver detection for C59 satellite on 215th day of 2022 (upper) and the zoom-in plots (lower). The vertical axis denotes the orbit difference between the SRIF-method-estimated orbit and the predicted orbit according to the orbit parameters estimated using batch least squares, measured in dm units. On the left-hand side are the orbit differences between the estimated orbit and the forward-predicted orbit using the precise orbit from previous day, which could be used for detecting the orbit maneuvering start time. On the right-hand side are the orbit differences between the estimated orbit and the backward-predicted orbit using the precise orbit from following day, which could be used for detecting the orbit maneuvering end time. The red dots represent the orbit differences in along-track direction of the C59 satellite, while the blue dots represent the orbit difference in cross-track direction. Orbit maneuvers can be divided into coplanar and non-coplanar maneuvers. Coplanar maneuvers can be reflected in orbit differences in along-track direction, while non-coplanar maneuvers can be reflected in orbit difference in cross-track direction. In addition, considering the strong coupling relationship between the orbit in radial direction and the clock offset, the orbit differences in radial direction are not used in this study.
First, analyzing the left-hand side of Figure 6, it can be clearly seen that before 09:00:00, the orbit differences in along-track and cross-track directions were stable and had good agreement with the orbit precision in the non-maneuver period (also see Figure 4). This is due to the gradual degradation in the precision of the predicted orbit as the prediction time increased. Applying thrust to a satellite for orbit maneuvering will change its state, causing its orbit to rapidly deviate from predicted orbit. As a consequence, there was a rapid increase in the differences between the actual orbit and the predicted orbit. It was easy to detect that the C59 satellite had an orbit maneuver at 09:00:00 on the 215th day of 2022. Due to the possibility of employing coplanar or non-coplanar orbit maneuvering, or both, an increase in the orbit difference in any direction can be regarded as an occurrence of orbit maneuvering.
Orbit maneuvers can involve coplanar or non-coplanar adjustments, or both, leading to changes in the orbit in different directions [5]. Therefore, a significant increase in the orbit differences in any direction can be considered an indication of orbit maneuvering. Due to the 30 s data processing interval used in this experiment, the maneuver detection results only can be accurate to 30 s.
Second, it is evident from the right-hand side of Figure 6 that before 09:00:00, the orbit differences rapidly increased due to the inconsistency between the orbit estimated using the SRIF and the reverse-predicted orbit after orbit maneuvering. The orbit differences began to show a stable trend, but minor variations still persisted from 09:00:30 to 09:05:00 due to the continuation of maneuvering thrust on the satellite. The satellite remained unstable during this time and had not yet achieved a stable state. After the orbit maneuvering thrust applied to the satellite completely disappeared, the satellite returned to a stable state. Based on this characteristic, it was easy to detect that the C59 satellite returned to a stable state at 09:05:00. Therefore, the end time of the orbit maneuvering for the C59 satellite was 09:05:00 on the 215th day of 2022.
To demonstrate the applicability of this orbit maneuver detection method to IGSO and MEO satellites, the analysis results are presented in Figure 7 and Figure 8.
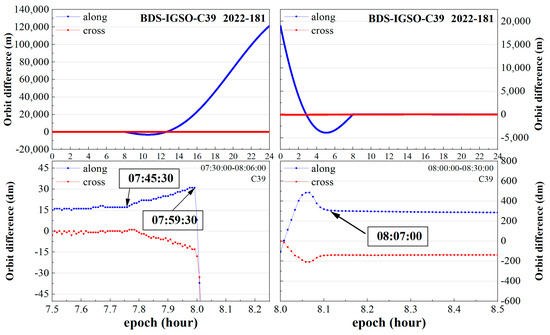
Figure 7.
The orbit maneuver detection for C39 satellite on 181st day of 2022. This is the same as Figure 6, but for a different satellite in a different day.
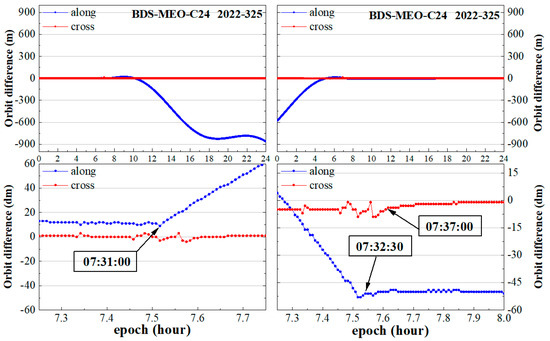
Figure 8.
The orbit maneuver detection for C24 satellite on 325th day of 2022. This is the same as Figure 6, but for a different satellite in a different day.
From Figure 7, it can be clearly seen that before 07:45:30, the orbit differences in the along-track and cross-track directions were nonzero, but they remained in a linear and stable state for a brief period. From 07:45:30 to 07:59:30, the orbit differences gradually exhibited a small upward trend. Due to the relatively small magnitude of the orbit differences, we cannot assert with certainty that they were a result of orbit maneuvers. Because different orbital types may require different adjustments for orbit maneuvering, we speculate that this phenomenon may be due to satellite attitude adjustments made in preparation for such maneuvers. However, since we have been unable to obtain official information, this remains an unconfirmed speculation. It was easy to detect that the C39 satellite had an orbit maneuver at 07:45:30 on the 181st day of 2022. Second, it is evident from the right-hand side of Figure 7 that, before 08:07:00, the orbit differences rapidly decreased due to the inconsistency between the orbit estimated using the SRIF and the reverse-predicted orbit after orbital maneuvering. After the orbit maneuvering thrust applied to a satellite completely disappears, the satellite will be in a stable state. Based on this characteristic, it was easy to detect that the C39 satellite had returned to a stable state at 08:07:00. Therefore, the end time of the orbit maneuvering for the C39 satellite was 08:07:00 on the 181st day of 2022.
From Figure 8, it can be clearly seen that before 07:31:00, the orbit differences in the along-track and cross-track directions remained in a linear and stable state for a brief period. From 07:31:00, there was no significant change in the cross-track component of the orbit differences, but the along-track component exhibited a rapid increase. It was easy to detect that the C24 satellite had an orbit maneuver at 07:31:00 on the 325th day of 2022. Second, as shown on the right-hand side of Figure 8, prior to 07:31:00, the orbit difference in the along-track direction was rapidly decreasing. From 07:32:30, it reached a stable state. However, the orbit difference in the cross-track direction fluctuated between 07:32:30 and 07:37:00, and only after that did it tend towards a stable state. Therefore, it can be concluded that the time for the C24 satellite to return to a stable state was 07:37:00 on the 325th day of 2022, which can be regarded as the end time of the orbit maneuvering.
In addition, we conducted an experimental verification of the real-time detection method for the end time of the maneuver proposed in this paper. The experimental results, shown in Figure 9, correspond to the time series of Equation (4).
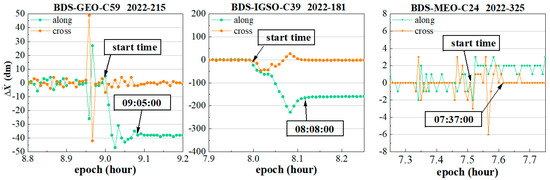
Figure 9.
Real-time detection of the end time for orbit maneuvers. On the left-hand side is the maneuver detection for the GEO satellite C59, in the middle is the detection for the IGSO satellite C39, and on the right-hand side is the detection for the MEO satellite C24. The horizontal axis represents time in hours, and the vertical axis represents the difference between the epochs of the orbit difference, along-track difference is represented by green dots, and the cross-track difference is represented by orange dots.
From the left-hand side in Figure 9, it can be clearly seen that before the orbit maneuvering start time, the values in along-track and cross-track directions were in a stable state, and randomly distributed around zero, there was a large jump due to gross errors. However, this jump did not affect the detection results of the start time of orbit maneuvering. The start time of orbit maneuvers can be detected in real time using the previous method, and it has been marked.
During the orbit maneuvering, the values had a significant jump in both the along-track and cross-track directions, particularly along-track, due to the thrust exerted on the satellite. Once the satellite returned to stability, the values began to stabilize, enabling us to detect the end time of orbit maneuvering for the C59 satellite as 09:05:00. Similarly, based on the results in the middle and on the right-hand side, we can detect the end time of the orbit maneuvers for the C39 and C24 satellites as 09:08:00 and 07:37:00, respectively. Compared to the post-detection results of the above orbit maneuver end times, there was only a one-minute delay for the C39 satellite, which can be seen as negligible compared to the hours-long delay in the broadcast ephemeris.
As the official publication of orbit maneuver information for the BeiDou satellites is not publicly available, we estimated the velocity pulses of the satellites using batch least squares to verify the accuracy of the detection results in this study. To avoid the effect of the position and velocity in the radial direction, which have a strong correlation with the clock offset, on the estimated velocity pulses, we only estimated the velocity pulses pseudo-random parameters in the along and cross directions. The results for MEO/IGSO and GEO satellites are shown in Figure 10 and Figure 11.
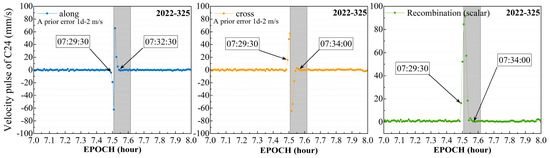
Figure 10.
The velocity pulse estimated for C24 satellite on 325th day of 2022. The estimation results of velocity pulses of the C24 satellite in along and cross directions are shown from left to right, with the combined value on the right part, represented by blue, orange, and cyan dots. The horizontal axis denotes the time axis on the 325th day of 2022, and the shaded area represents the detection results of orbit maneuver period in this study.
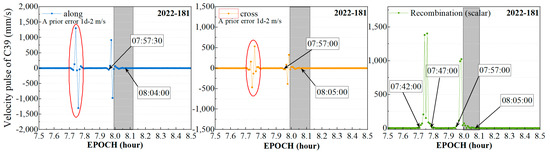
Figure 11.
The velocity pulse estimated for C38 satellite on 187th day of 2022.
The results clearly indicate that the values of the velocity pulses in the along-track and cross-track directions of the satellite remained stable at below 3 mm during the non-maneuver period. These values began to gradually increase at 07:29:30, reaching a maximum value of approximately 60 mm/s at 07:30:30, and returned to a stable state at 07:34:00. In this study, the detection period was from 07:30:30 to 07:37:00. Upon comparison, it was found that the start time differed by 1 min, and the end time differed by 3 min. The verification results for IGSO satellite are presented below.
It is worth noting that the velocity pulses of the C39 satellite experienced jumps in two time periods. The first occurred between 07:42:00 and 07:55:00, and combined with the relatively small changes in the orbit differences shown in Figure 7, this further confirms our previous speculation that the satellite may need to adjust its attitude for the orbit maneuver. However, such an adjustment in attitude would not be reflected significantly in the orbital position, resulting in relatively small changes in orbit differences. The second jump occurred between 07:57:00 and 08:05:00. Our detection results of orbit maneuver for C39 are from 07:59:30 to 08:07:00. When compared, it was found that the start time differed by 2.5 min and the end time differed by 3 min. The verification results for the GEO satellite are presented in Figure 12.
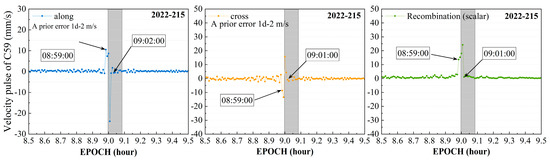
Figure 12.
The velocity pulse estimated for C59 satellite on 215th day of 2022.
The results clearly indicate that the values of the velocity pulses in the along-track and cross-track directions of the satellite remained stable at below 3 mm during the non-maneuver period. These values began to gradually increase at 08:59:00, reaching a maximum value of approximately 25 mm/s at 09:00:00, and returned to a stable state at 09:01:00. In this study, the detection period was from 09:00:00 to 09:05:00. Upon comparison, it was found that the start time differed by 1 min, and the end time differed by 4 min.
The reasons for this difference between detection using the orbit difference and velocity pulse are mainly due to three factors. Firstly, there were errors in the predicted orbit and SRIF-estimated orbit. Secondly, the acceleration of the orbit maneuver thrust was not immediately reflected in the GNSS distance observations, resulting in a 1–2 min delay in the start time of the detection. Thirdly, during the satellite orbit maneuver period, the initial orbit used in the SRIF estimation method was based on the predicted orbits from the previous epoch, and the low accuracy of the initial orbit during the satellite orbit maneuver period and the convergence process caused a three-minute delay in the end time compared to the velocity pulse results. Compared with the broadcast ephemeris delay time of 6–7 h, a delay of several minutes will not affect the adjustment of processing strategies for real-time and post-processed orbit determination. Additionally, these results show that the orbit maneuver period can also be detected by estimating the satellite velocity pulses, but it is impractical to estimate the velocity pulses for all epochs without knowing the approximate time period of the orbit maneuver.
In addition, the start and end times of orbit maneuvering can be accurately detected in real time and post-processing using the method proposed in this paper. Subsequently, all the maneuver detection results of the BeiDou satellites in 2022 are presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
The detected orbit maneuvers of BeiDou satellites in 2022.
There were 32 instances of orbit maneuvers of BeiDou satellites detected successfully in 2022. The results indicate that the orbit maneuvering frequency of GEO satellites is higher than others, occurring approximately once a month, with an average maneuvering time of around 4–5 min. The IGSO satellites have the second-highest maneuvering frequency, occurring approximately every 4–6 months, with an average maneuvering time of around 7–8 min. Only one MEO satellite, C24, was detected to be adjusted by orbit maneuvering in 2022. It should be noted that we have not discussed the occurrence of multiple maneuvers on the same day or consecutive days, as this is a rare event for BeiDou satellites and cannot be reliably validated. We will further investigate it in the future.
4. Conclusions and Discussion
This study proposes a real-time and post-processing detection method for orbit maneuvering of BeiDou satellites. Based on the SRIF estimation method, the correct orbit of the maneuvering satellite can be correctly estimated and compared with the forward- and backward-predicted orbits according to the precise orbit before and after the maneuver. This method can accurately detect the start and end time of the orbit maneuvers, and can also achieve maneuvering start time detection in real time. In addition, we propose a real-time detection method for the end time of orbit maneuvering, based on the state difference during maneuver and non-maneuver periods. By analyzing the epoch-to-epoch variation in orbit differences, the end time of orbit maneuvers can be detected in real time.
Our experimental analysis validates the correctness of the proposed method. There were 32 instances of orbit maneuvers of BeiDou satellites detected successfully in 2022. The maneuvering frequency of BeiDou GEO satellites is once a month, with an average maneuvering time of 4–5 min, while the frequency of IGSO satellites is 4–6 months, with an average maneuvering time of 7–8 min. This method is applicable to satellites of all orbit types of GNSS, including GEO, IGSO, and MEO satellites.
Moreover, the method is easily implemented for all common users and data used can be accessed easily, including GNSS observation data, broadcast ephemeris, and other open-source information files. The results of orbit maneuver detection are crucial in precise orbit determination in real-time and post-processing. They provide critical information for adjusting precise orbit determination strategies, further improving the continuity and reliability of precise service products of the BDS, thereby further enhancing the PNT service performance of the BeiDou Navigation System.
This method also has some limitations. As our proposed approach requires precise orbit products from the day before and after the orbit maneuver, the detection of a satellite with continuous two-day maneuver adjustments will fail. On the other hand, it is also limited by the accuracy of the estimated orbit, resulting in a delay of several minutes in the detection results. The orbit constraints also need further investigation. When the constraint is too tight, the system error caused by the orbit maneuver acceleration cannot be fully absorbed. Conversely, the loose constraints make the orbit accuracy poor. In addition, the situation of multiple maneuvers may occur in the same day, and the real-time method performs worse than the post-processing method. These questions need to be addressed in future studies.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.Q. and Q.Z.; methodology, Z.Q. and G.H.; software, Z.Q. and L.T.; validation, Z.Q., L.T. and J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.Q. and Q.Z.; writing—review and editing, J.W., G.H. and X.W.; supervision, Q.Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, CHD (300102260707), Chinese Scholarship Council studentship (ref. 202006560033), Programs of the National Natural Science Foundation of China (42127802), and the Key R&D Program of Shaanxi Province (2022ZDLSF07-12).
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank GFZ for the computer equipment and iGMAS, MGEX, and IGS for data support.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Steigenberger, P.; Hugentobler, U.; Hauschild, A.; Montenbruck, O. Orbit and clock analysis of Compass GEO and IGSO satellites. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.D.; Wang, R.L.; Wang, J. A simple and valid analysis method for orbit anomaly detection. Adv. Space Res. 2012, 49, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.W.; Huang, G.W.; Zhang, Q.; Le, W.; Xie, S.C.; She, H.N.; Lai, W.; Wang, X.L. The analysis and detection of orbit maneuvers for the BeiDou satellites based on orbital elements. Acta Geod. Geophys. 2021, 56, 501–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dach, R.; Brockmann, E.; Schaer, S.; Beutler, G.; Meindl, M.; Prange, L.; Bock, H.; Jaggi, A.; Ostini, L. GNSS processing at CODE: Status report. J. Geod. 2009, 83, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Chen, W. Beidou satellite maneuver thrust force estimation for precise orbit determination. Gps Solut. 2018, 22, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.W.; Huang, G.W.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.Y.; Xie, S.C.; Cao, Y.; Wang, X.L. Precise Orbit Determination for BeiDou GEO/IGSO Satellites during Orbit Maneuvering with Pseudo-Stochastic Pulses. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.W.; Wang, L.; Huang, G.W.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, X.Y.; Xie, S.C.; She, H.N.; Yue, F.; Wang, X.L. Prediction of BeiDou Satellite Orbit Maneuvers to Improve the Reliability of Real-Time Navigation Products. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.H.; Tu, R.; Zhang, R.; Han, J.Q.; Zhang, P.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Hong, J.; Lu, X.C. An orbit maneuver detection method based on orbital elements for BeiDou GEO and IGSO satellites. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 3644–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Fan, L.; Wang, X. A Real-Time Robust Method to Detect BeiDou GEO/IGSO Orbital Maneuvers. Sensors 2017, 17, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Wang, X. An Optimized Method to Detect BDS Satellites’ Orbit Maneuvering and Anomalies in Real-Time. Sensors 2018, 18, 726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Huang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L.; Yan, X.; Kang, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, S. A Method to Determine BeiDou GEO/IGSO Orbital Maneuver Time Periods. Sensors 2019, 19, 2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.W.; Li, C.L.; Dai, X.L.; Lou, Y.D.; Xu, Y. BDS near real-time maneuver detection based on triple-differenced phase observations. Adv. Space Res. 2022, 69, 3032–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, R.; Zhang, R.; Fan, L.; Han, J.; Zhang, P.; Lu, X. Real-Time Detection of Orbital Maneuvers Using Epoch-Differenced Carrier Phase Observations and Broadcast Ephemeris Data: A Case Study of the BDS Dataset. Sensors 2020, 20, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, R.; Liu, L.; Guo, R. Station-keeping Maneuver Monitoring and Moving-window Ground Track Fitting of GEO Satellites. Acta Geod. Cartogr. Sin. 2014, 43, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Yuan, Y.; Tan, B.; Ou, J. A Robust Method to Detect BeiDou Navigation Satellite System Orbit Maneuvering/Anomalies and Its Applications to Precise Orbit Determination. Sensors 2017, 17, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierman, G.J. Factorization Methods for Discrete Sequential Estimation; Dover Publications, Inc.: Mineola, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 128. [Google Scholar]
- Bierman, G.J. Sequential square root filtering and smoothing of discrete linear systems. Automatica 1974, 10, 147–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierman, G.J. The treatment of bias in the square-root information filter/smoother. J. Optim. Theory Appl. 1975, 16, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Householder, A.S. Unitary Triangularization of a Nonsymmetric Matrix. J. ACM 1958, 5, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, X.; Jiang, X.; Li, P.; Wang, J.; Ge, M.; Schuh, H. A square root information filter for multi-GNSS real-time precise clock estimation. Satell. Navig. 2021, 2, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Lou, Y.D.; Dai, Z.Q.; Qing, Y.; Li, M.; Shi, C. Real-time precise orbit determination for BDS satellites using the square root information filter. Gps Solut. 2019, 23, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.L.; Gong, X.P.; Li, C.L.; Qing, Y.; Gu, S.F.; Lou, Y.D. Real-time precise orbit and clock estimation of multi-GNSS satellites with undifferenced ambiguity resolution. J. Geod. 2022, 96, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, B.B.; Hugentobler, U.; Chen, J.P.; Selmke, I.; Wang, J.X. Prediction versus real-time orbit determination for GNSS satellites. Gps Solut. 2019, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairer, E. A Runge-Kutta Method of Order 10. IMA J. Appl. Math. 1978, 21, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Gill, E. Satellite Orbits, Models, Methods and Applications. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2000, 55, B27–B28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenbruck, O.; Steigenberger, P.; Prange, L.; Deng, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Perosanz, F.; Romero, I.; Noll, C.; Stürze, A.; Weber, G.; et al. The Multi-GNSS Experiment (MGEX) of the International GNSS Service (IGS)–Achievements, prospects and challenges. Adv. Space Res. 2017, 59, 1671–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing-nan, L.; Mao-rong, G. PANDA software and its preliminary result of positioning and orbit determination. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2003, 8, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, R.; Dach, R.; Collilieux, X.; Jäggi, A.; Schmitz, M.; Dilssner, F. Absolute IGS antenna phase center model igs08.atx: Status and potential improvements. J. Geod. 2015, 90, 343–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wu, S.C.; Hajj, G.A.; Bertiger, W.I.; Lichten, S.M. Effects of antenna orientation on GPS carrier phase. In Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Astrodynamics Conference, Durango, CO, USA, 19–22 August 1992; pp. 1647–1660. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, J.; Niell, A.; Tregoning, P.; Schuh, H. Global Mapping Function (GMF): A new empirical mapping function based on numerical weather model data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, 25546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzum, B.; Petit, G. The IERS Conventions (2010): Reference systems and new models. Proc. Int. Astron. Union 2015, 10, 227–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlis, N.K.; Holmes, S.A.; Kenyon, S.C.; Factor, J.K. The development and evaluation of the Earth Gravitational Model 2008 (EGM2008). J Geophys. Res.-Sol. Ea 2012, 117, 8916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyard, F.; Lefevre, F.; Letellier, T.; Francis, O. Modelling the global ocean tides: Modern insights from FES2004. Ocean. Dyn. 2006, 56, 394–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, D.; Meindl, M.; Beutler, G.; Dach, R.; Schaer, S.; Lutz, S.; Prange, L.; Sosnica, K.; Mervart, L.; Jaggi, A. CODE’s new solar radiation pressure model for GNSS orbit determination. J. Geod. 2015, 89, 775–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Q.L.; Ge, M.R. Improving the Orbits of the BDS-2 IGSO and MEO Satellites with Compensating Thermal Radiation Pressure Parameters. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).