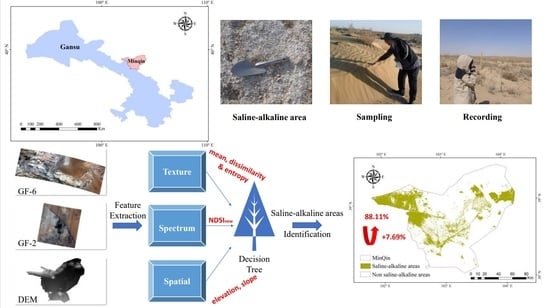
A High-Precision Remote Sensing Identification Method on Saline-Alkaline Areas Using Multi-Sources Data
Abstract
1. Introduction
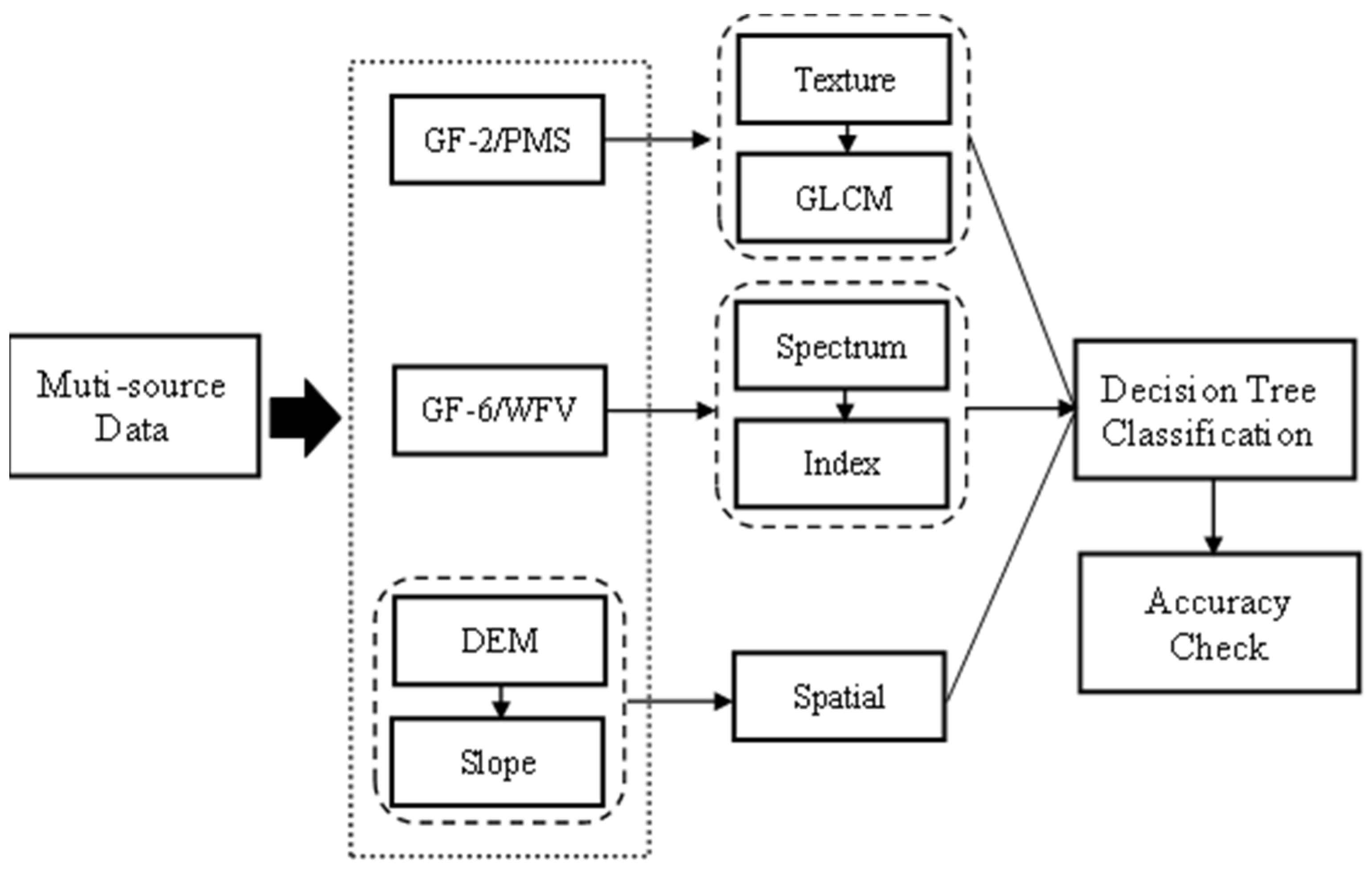
2. Methodology and Experimental Application
2.1. Methodology
2.1.1. Identification Method of Saline-Alkaline Area
2.1.2. Accuracy Evaluation Method
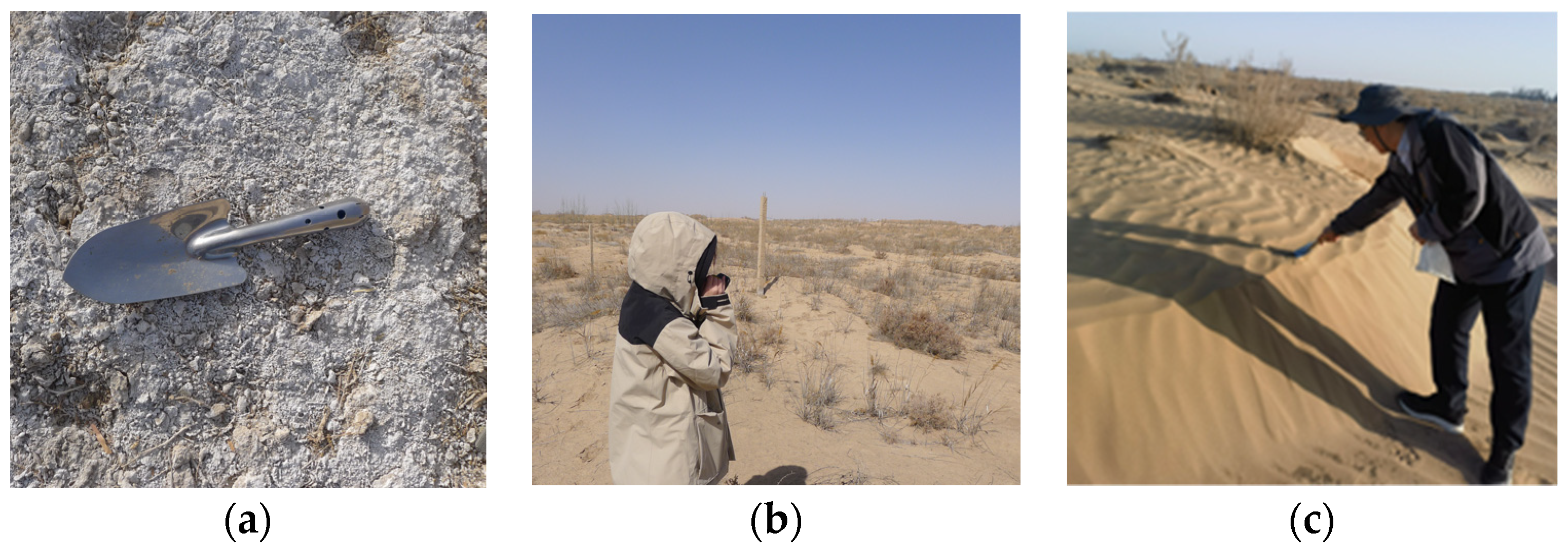
2.2. Experimental Application
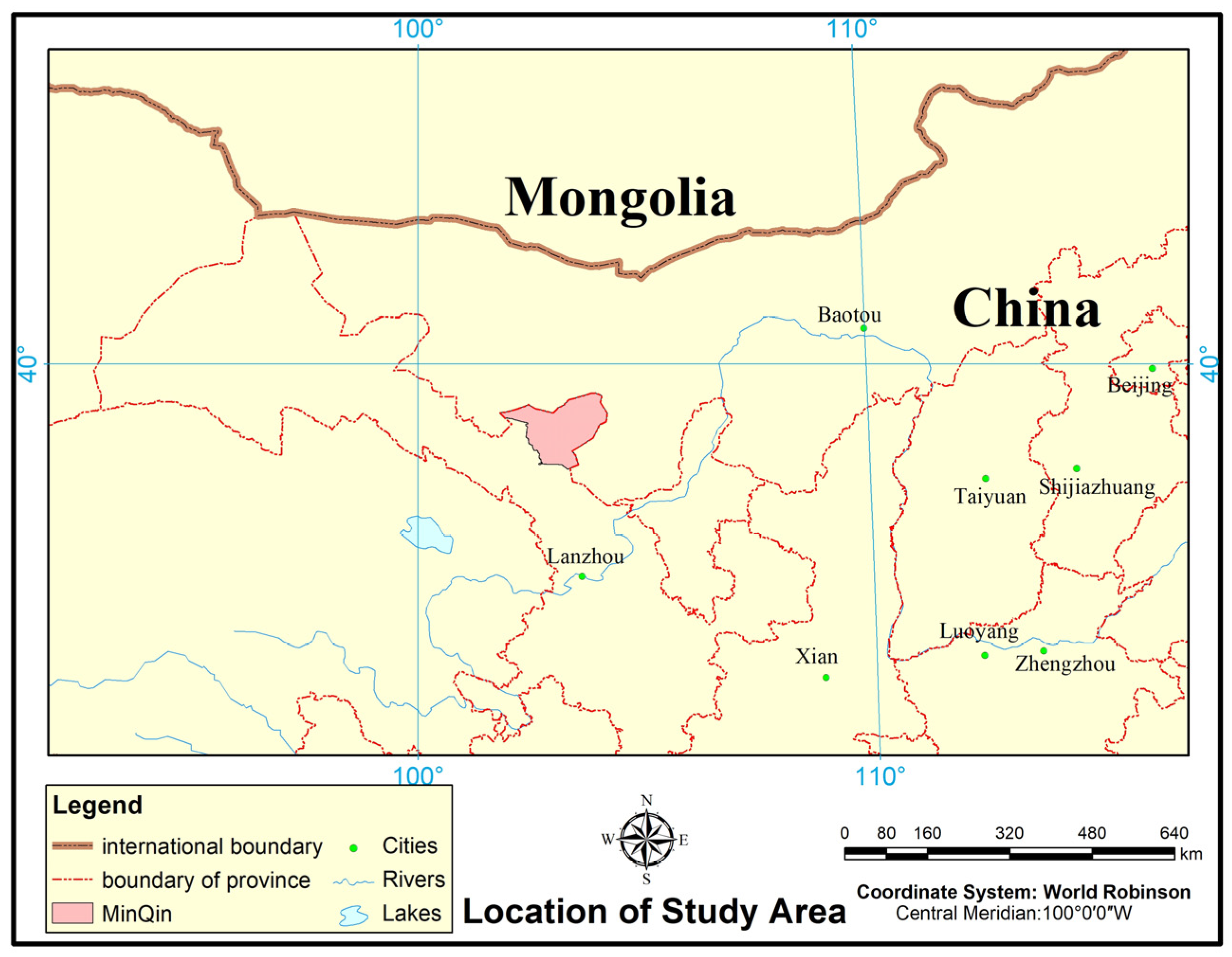
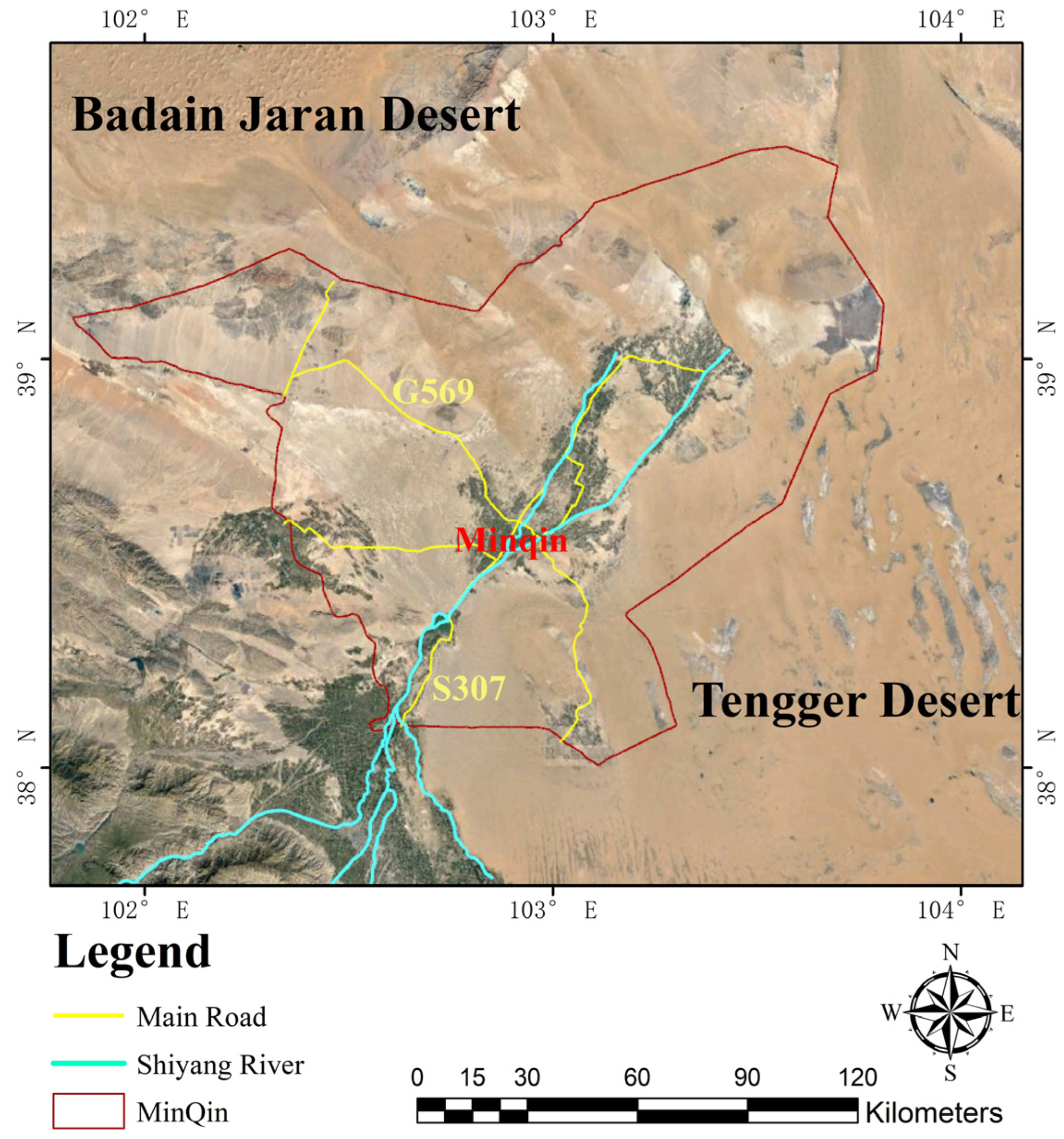
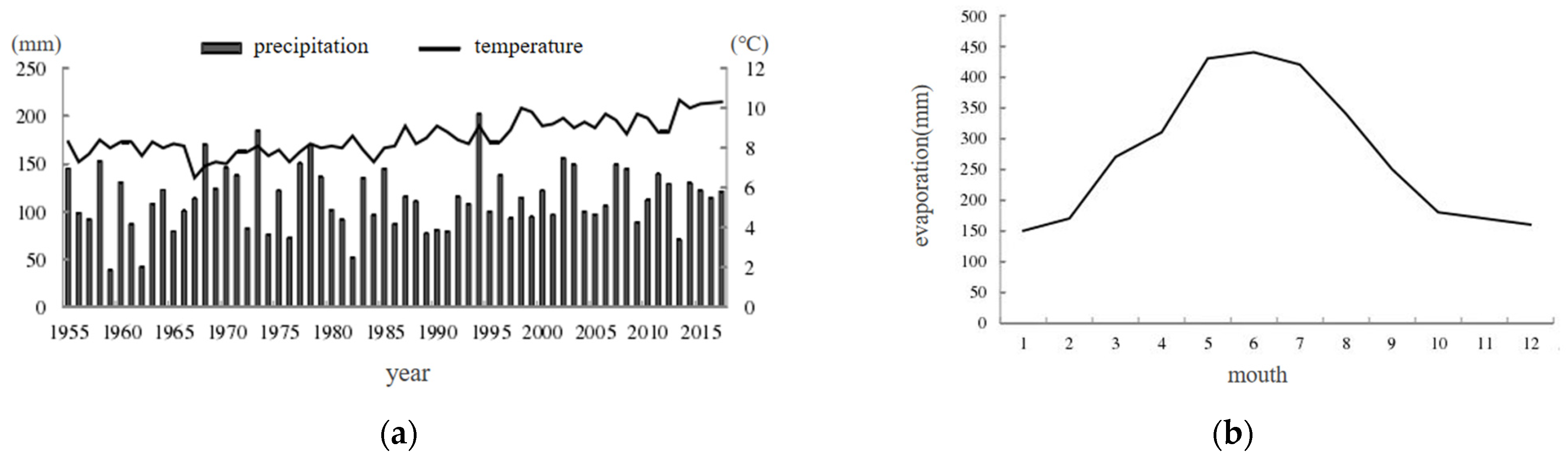
2.2.1. Study Area
2.2.2. Data
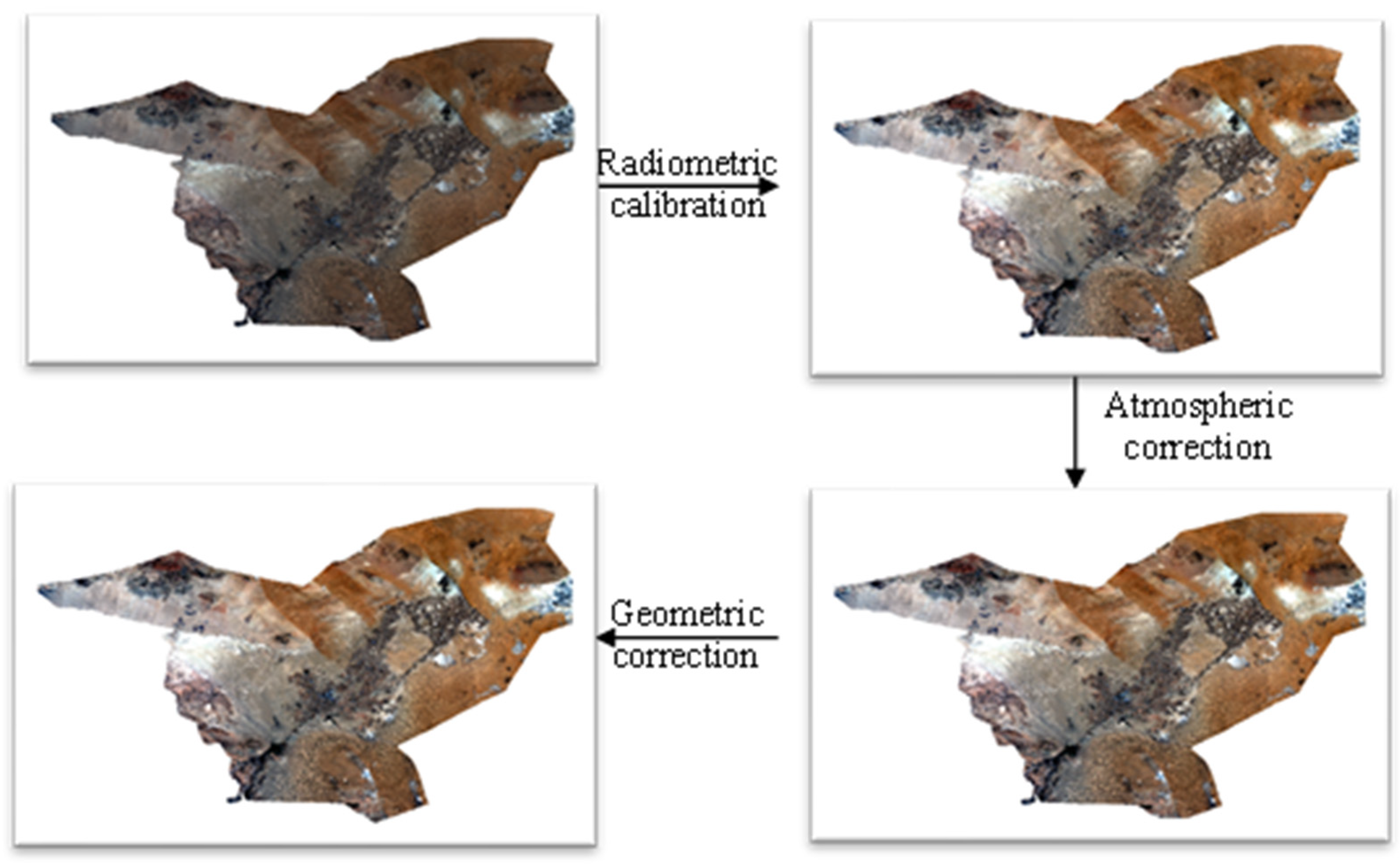
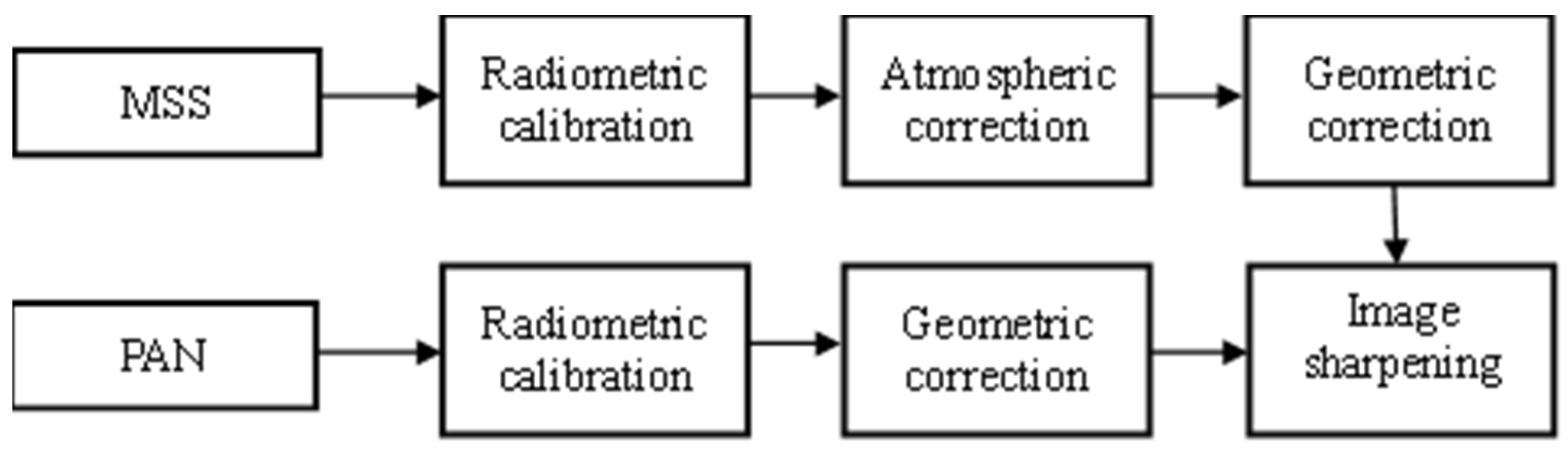
2.2.3. Feature Extraction
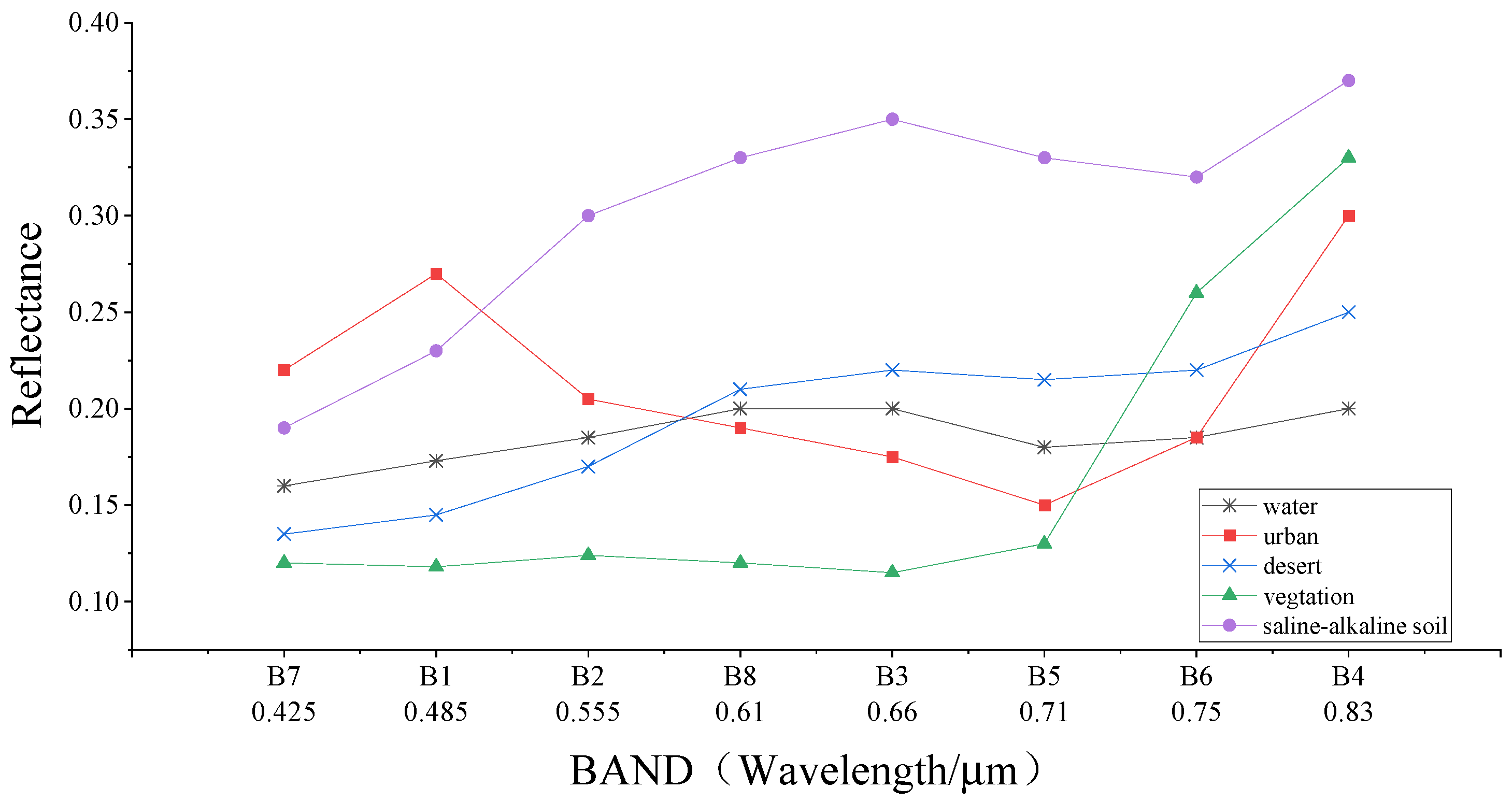
- Spectral features
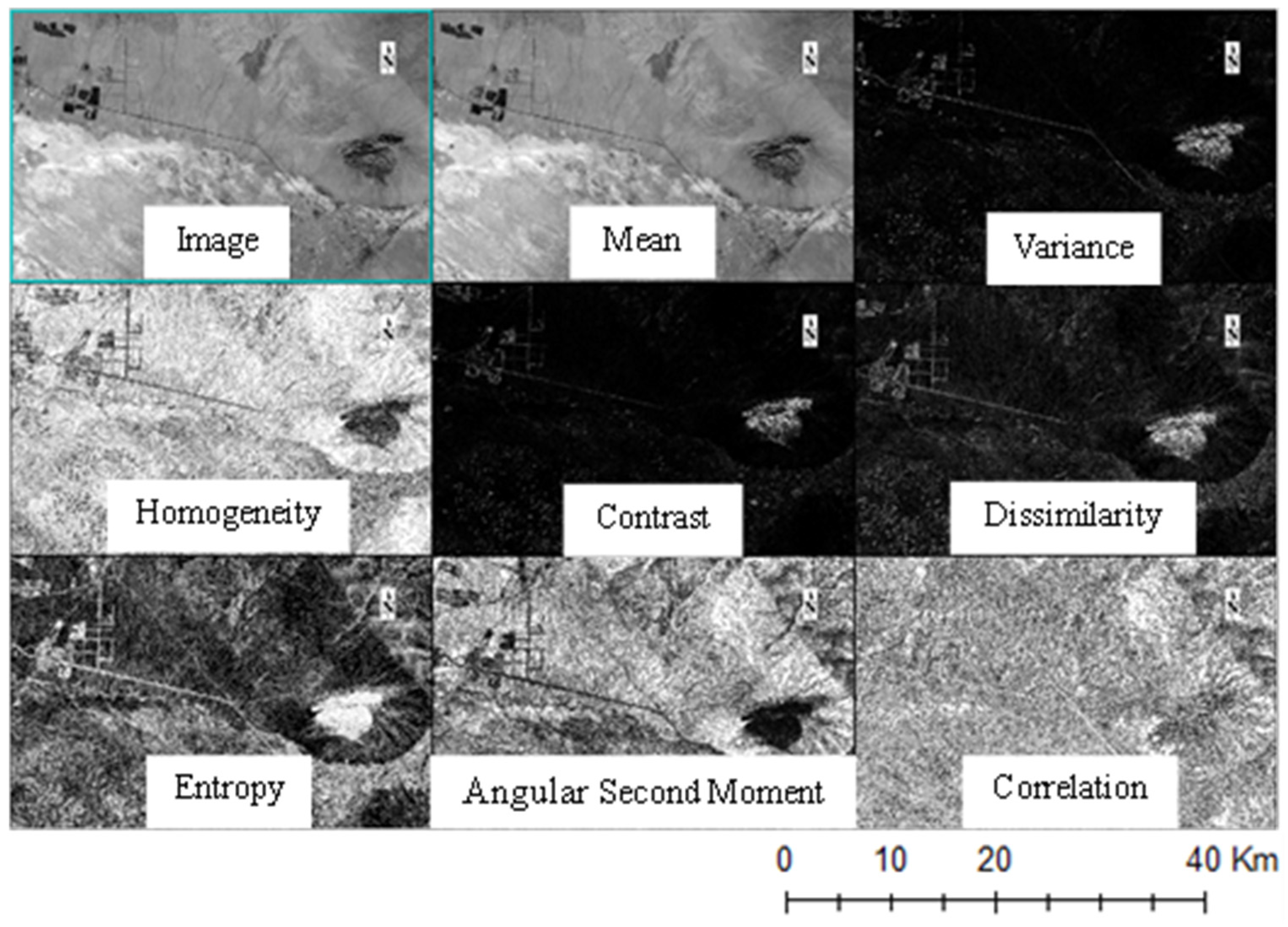
- Texture features
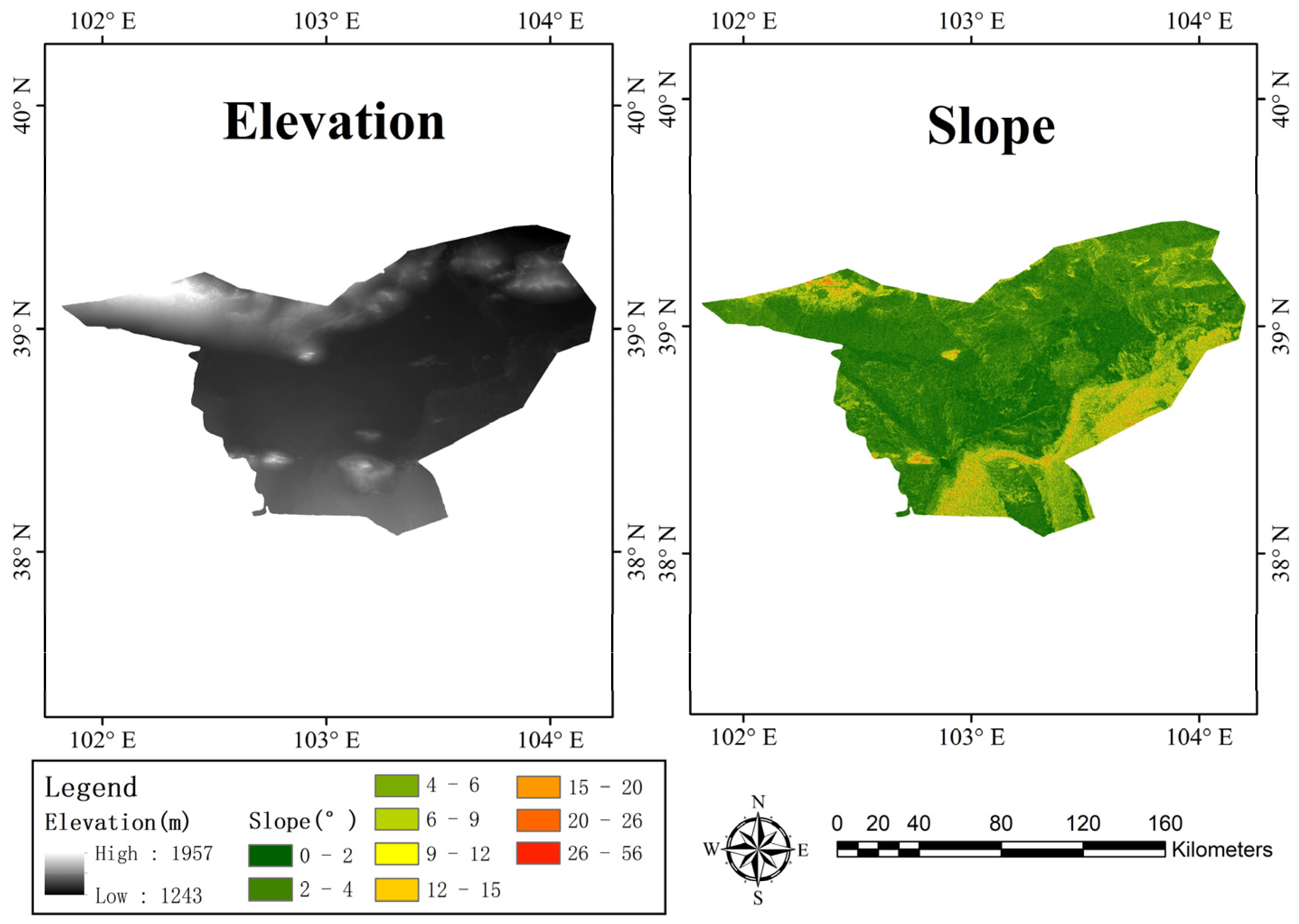
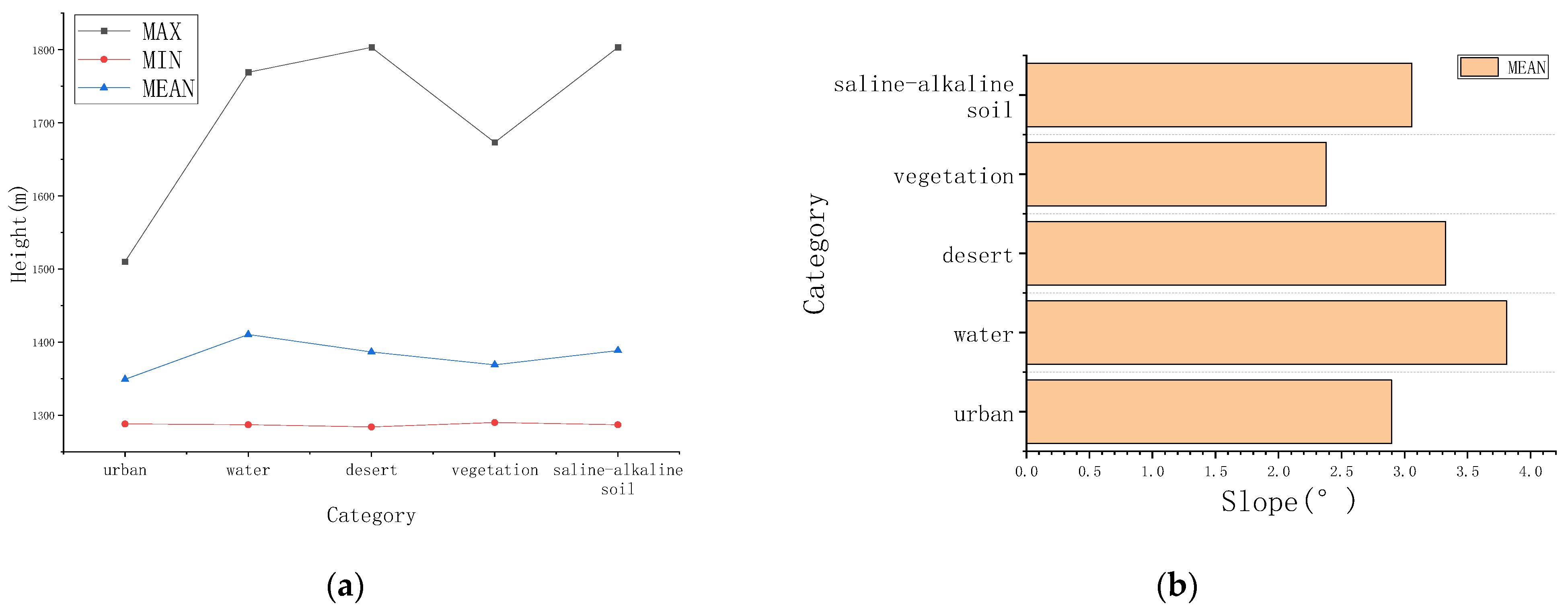
- Elevation features
3. Results and Discussion
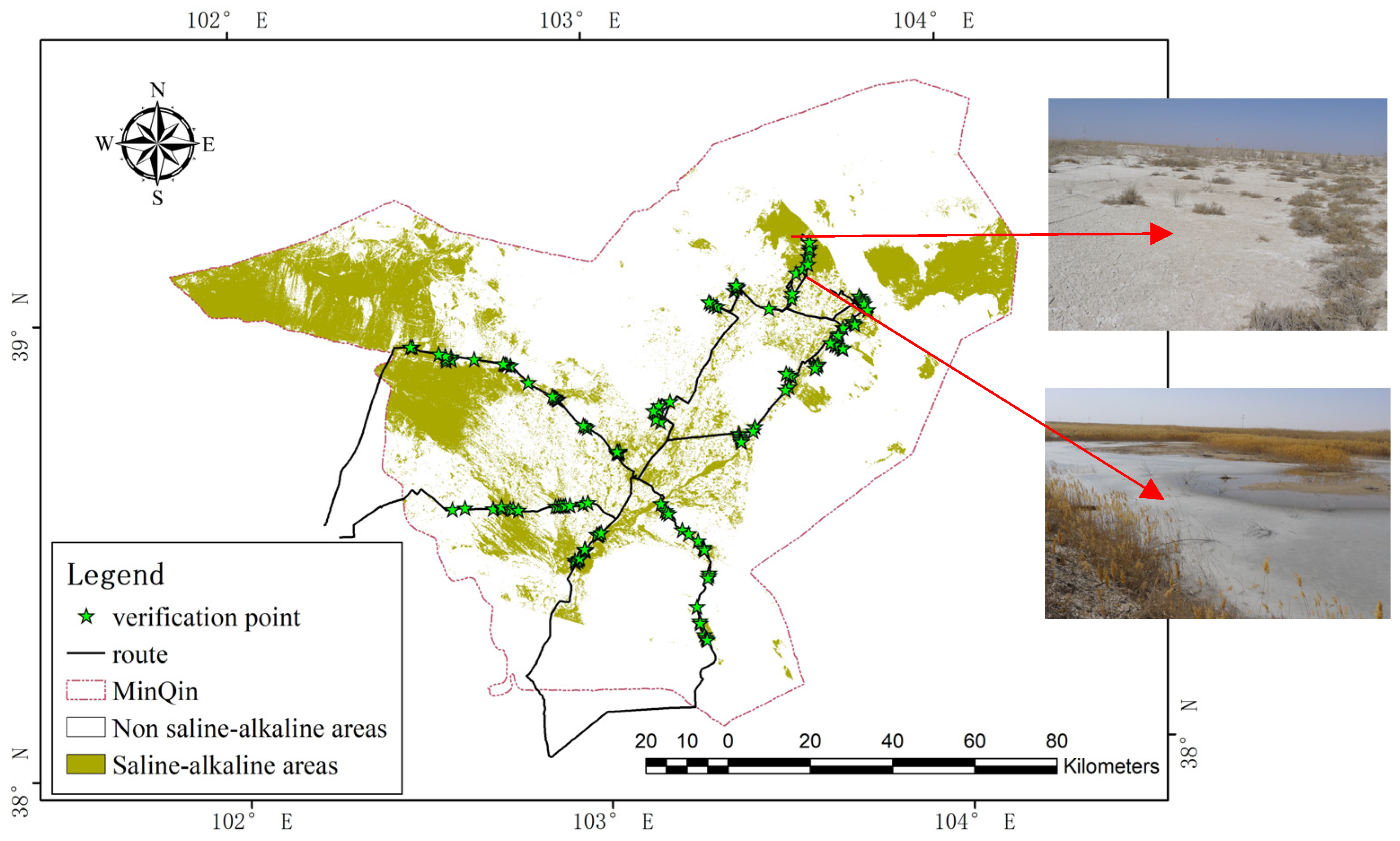
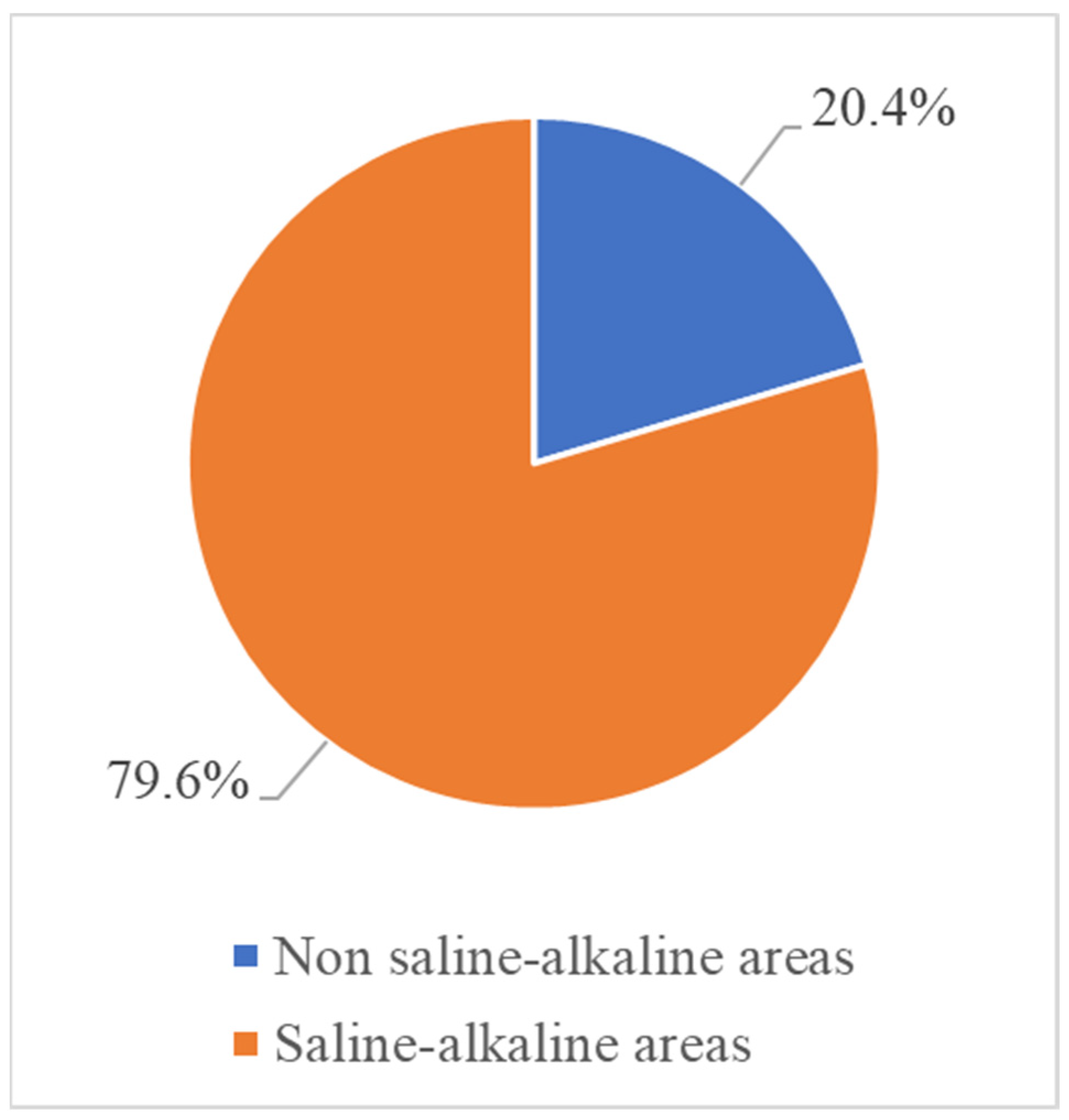
3.1. Classification and Verification
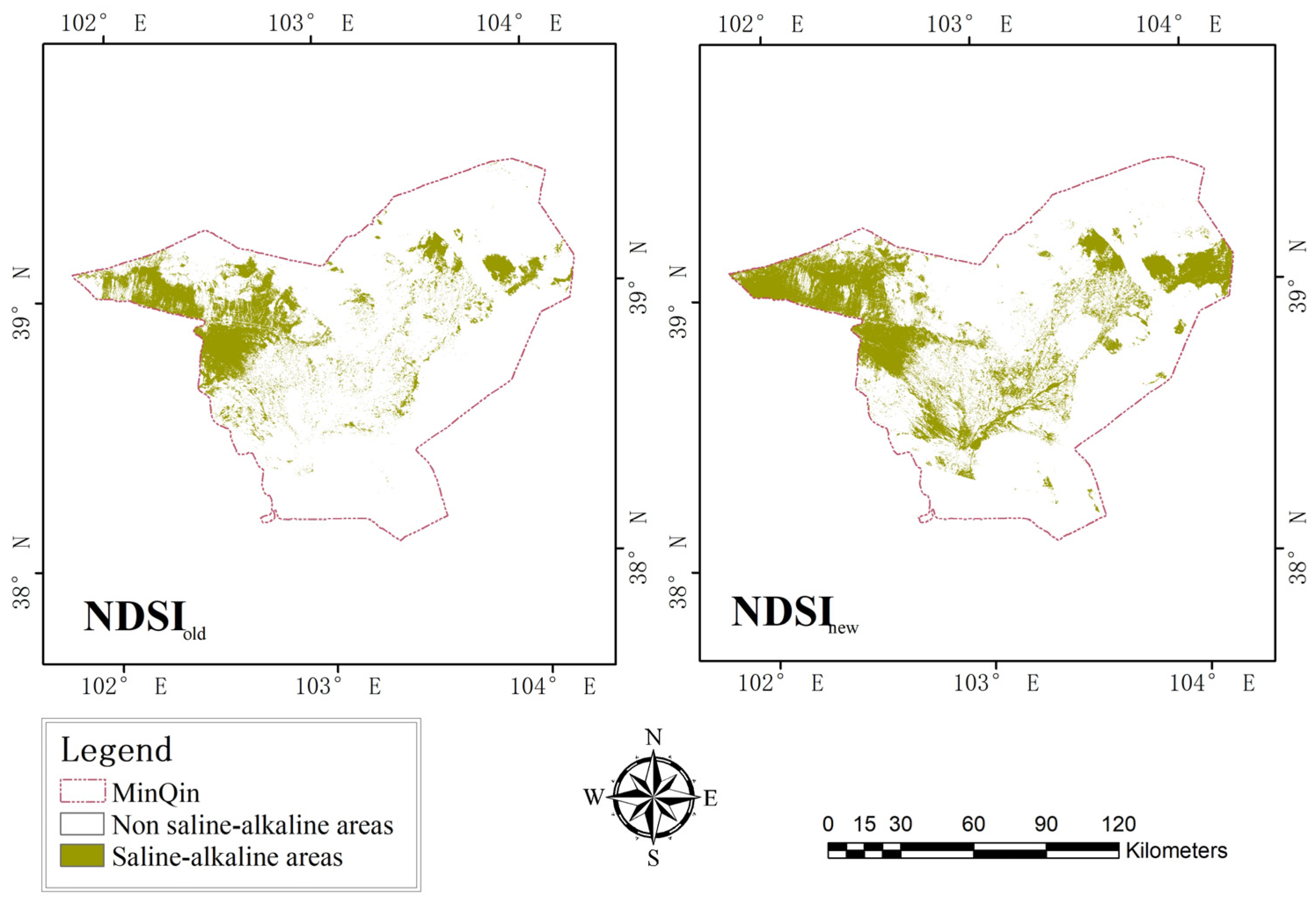
3.2. Comparison of the Results of Different Indices
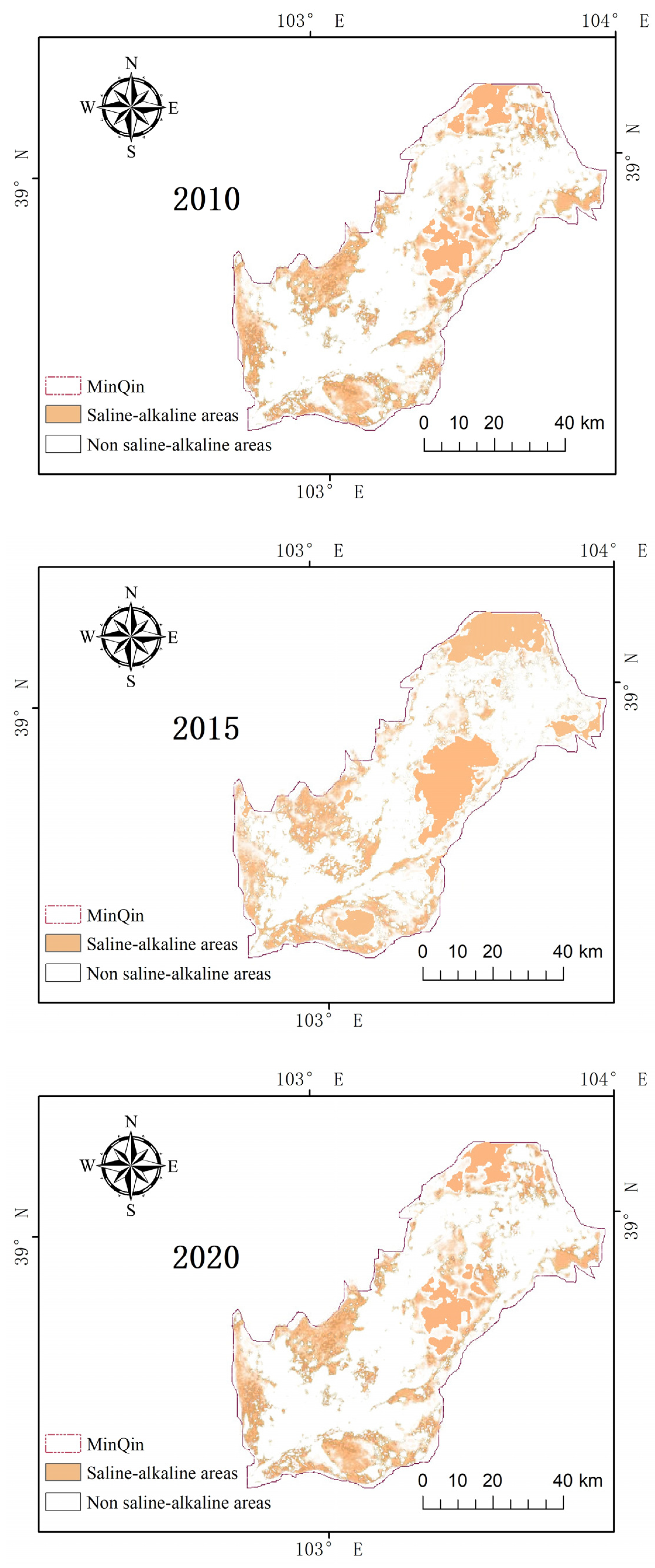
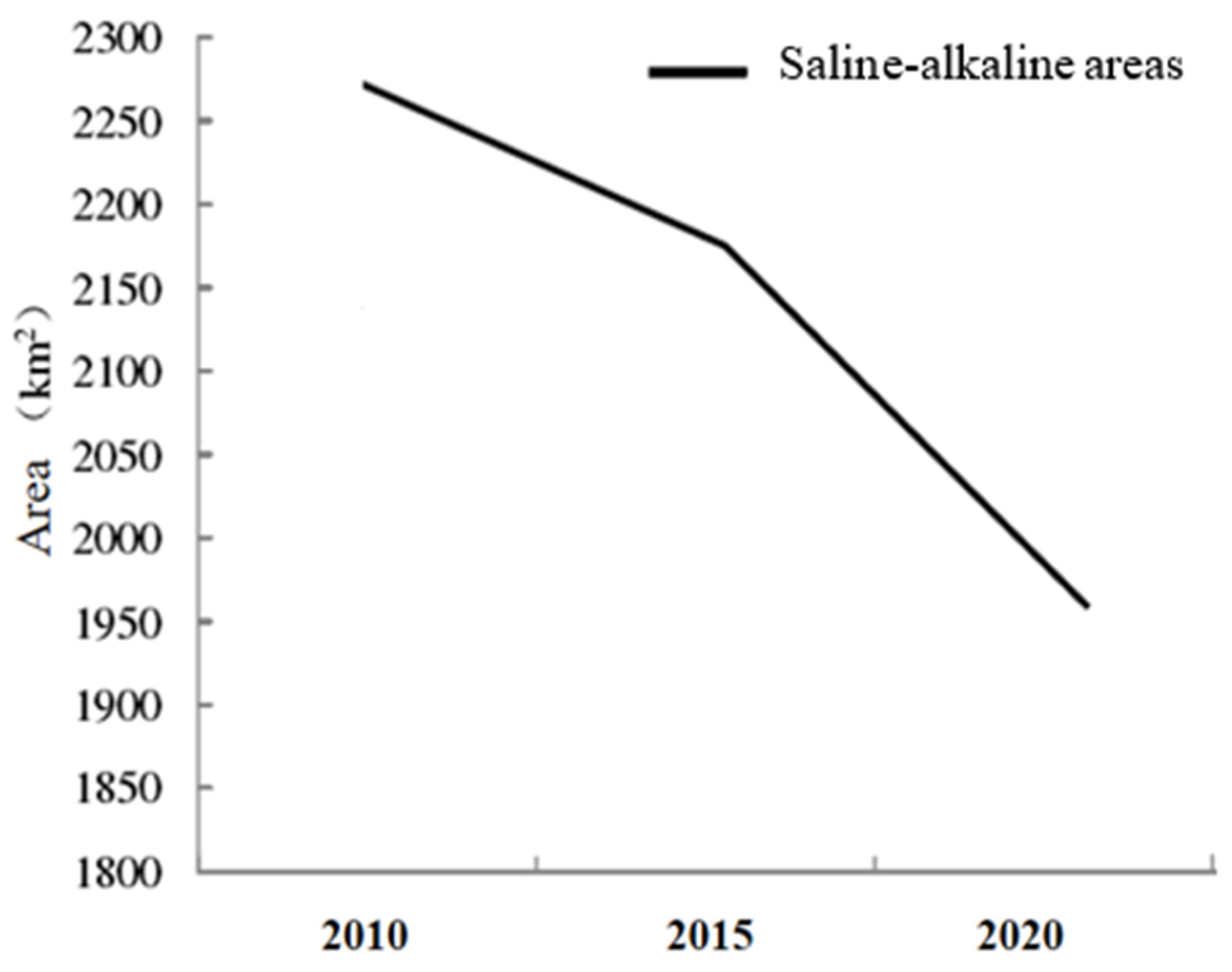
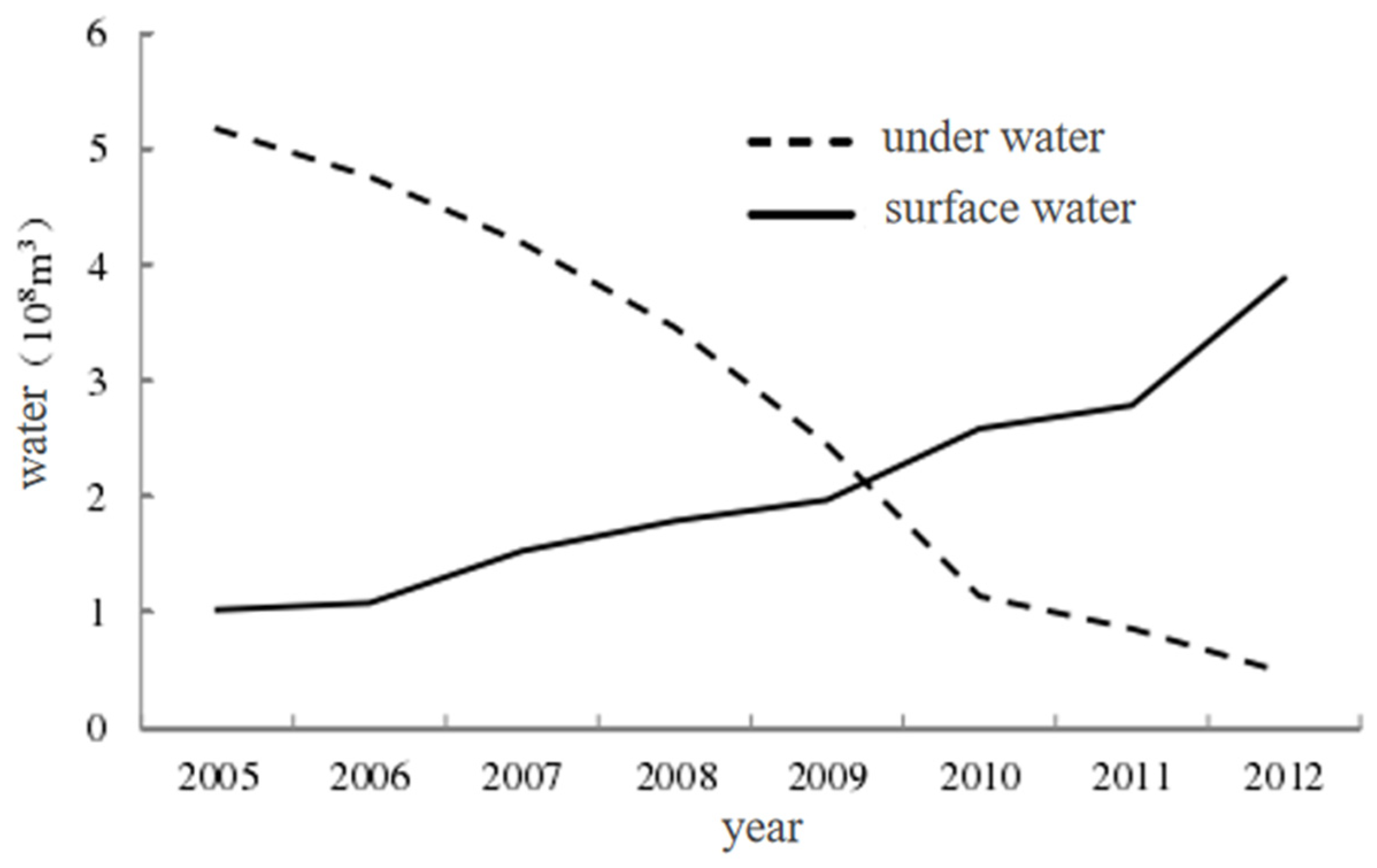
3.3. Analysis of Saline-Alkaline Area Change
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dennis, L.C. Climate change impacts on soil salinity in agricultural areas. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2020, 72, 842–862. [Google Scholar]
- Ivushkin, K.; Bartholomeus, H.; Bregt, A.K.; Pulatov, A.; Franceschini, M.H.D.; Kramer, H.; Loo, E.N.V.; Roman, V.J.; Finkers, R. UAV based soil salinity assessment of cropland. Geoderma 2018, 338, 501–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Jia, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Abd El Hamid, H.T. Remote Sensing Inversion for Simulation of Soil Salinization Based on Hyperspectral Data and Ground Analysis in Yinchuan, China. Nat. Resour. Res. 2021, 30, 4641–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bani, A.; Daghari, I.; Hatira, A.; Chaabane, A.; Daghari, H. Sustainable management of a cropping system under salt stress conditions (Korba, Cap-Bon, Tunisia). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 46469–46476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoud, A.; Koike, K. Arid land salinization detected by remotely-sensed landcover changes: A case study in the Siwa region, NW Egypt. J. Arid Environ. 2006, 66, 151–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arruda, G.P.D.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Chagas, C.D.S.; Fiorio, P.R.; Souza, A.; Fongaro, C.T. Digital soil mapping using reference area and artificial neural networks. Sci. Agric. 2015, 73, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Ma, L.; Jiang, P.; Li, B.; Huang, F.; Wu, H. Digital soil mapping to enable classification of salt-affected soils in desert agro-ecological zones. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 1944–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Biswas, A.; Jiang, Q.; Zhao, R.; Hu, J.; Hu, B.; Shi, Z. Estimating soil salinity from remote sensing and terrain data in southern Xinjiang Province, China. Geoderma 2019, 337, 1309–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidike, A.; Zhao, S.; Wen, Y. Estimating soil salinity in Pingluo County of China using QuickBird data and soil reflectance spectra. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 26, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Tang, Y.; Xing, X.; Liu, Z.; Xing, L. Formation and Evolution of Soil Salinization in Shouguang City Based on PMS and OLI/TM Sensors. Water 2019, 11, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathizad, H.; Ardakani, M.A.H.; Sodaiezadeh, H.; Kerry, R.; Taghizadeh-Mehrjardi, R. Investigation of the spatial and temporal variation of soil salinity using random forests in the central desert of Iran. Geoderma 2020, 365, 114233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, X.; Zhong, T.; Chen, Z. Review on Sustainable Utilization of Salt-affected Land. Acta Geol. Sin. 2011, 66, 673–684. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, K.; Jia, L.; Dou, L.; Nie, A. Effect of drip irrigation on the rapid growth and soil improvement of saline alkali ponies in coastal saline lands. China Rural Water Conserv. Hydropower 2021, 12, 209–215. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Shen, G. Study on the spatial distribution characteristics of soil salinity in mudflats in the Yangtze River Delta. Soil Crops 2022, 11, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy, S.; Shanmugam, R.S. Multispectral and Microwave Remote Sensing Models to Survey Soil Moisture and Salinity. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1412–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Categorical, F. A comparison between crisp and fuzzy class boundary modelling for mapping salt-affected soils using Landsat TM data and a classification based on anion ratios. Ecol. Model. 2003, 168, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, V.L.; Bruin, S.D.; Schaepman, M.E.; Mayr, T.R. The use of remote sensing in soil and terrain mapping: A review. Geoderma 2011, 162, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Hou, X.Y. Changes in normalized vegetation index (NDVI) in coastal areas of China from 1982–2014 and its effect on response of extreme climate. Geogr. Stud. 2019, 38, 807–821. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, R.S.; Rao, B.R.M. The selection of the best possible Landsat TM band combination for delineating salt-affected soils. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1992, 13, 2051–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farifteh, J.; Farshad, A.; George, R.J. Assessing salt-affected soils using remote sensing, solute modelling, and geophysics. Geoderma 2006, 130, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouaziz, M.; Matschullat, J.; Gloaguen, R. Improved remote sensing detection of soil salinity from a semi-arid climate in northeast Brazil. Comptes Rendus Geosci. 2011, 343, 795–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Wan, L.; Sun, X. Remote sensing retrieval of saline and alkaline land based on reflectance spectroscopy and RV-MELM in Zhenlai County. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 139, 106909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wan, L.; Xiao, D.; Le, B. Remote sensing inversion of saline and alkaline land based on reflectance spectroscopy and D-TELM algorithm in Wuyuan areas. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2020, 109, 103367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Wen, Y. Study on vegetation and soil salinity response in Qingtu Lake area. Agric. Res. Arid Areas 2020, 38, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Ashilenje, D.S.; Amombo, E.; Hirich, A.; Kouisni, L.; Devkota, K.P.; El Mouttaqi, A.; Nilahyane, A. Crop Species Mechanisms and Ecosystem Services for Sustainable Forage Cropping Systems in Salt-Affected Arid Regions. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.R.; Kajal, S.S.; Patel, V.R.; Patel, V.J.; Khristi, S.M. Impact of salt stress on nutrient uptake and growth of cowpea. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 22, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehaan, R.L.; Taylor, G.R. Field-derived spectra of salinized soils and vegetation as indicators of irrigation induced soil salinization. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ding, J.; Wu, M. Remote sensing monitoring models of soil salinization based on NDVI-SI feature space. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2010, 26, 168–173. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, G.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y. Soil salinization in the oasis areas of downstream inland rivers—Case Study: Minqin oasis. Quat. Int. 2020, 537, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.Y.; Ding, J.L. Soil salinization information extraction method based on gf-1 image. Arid Land Geogr. 2016, 39, 171–181. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, J.; Yue, C. Research on decision tree classification method based on spectral features—A case study of northeastern Kunming city. J. Northwest For. Acad. 2010, 25, 222–226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X. Overview of performance metrics of classification learning algorithms. Comput. Sci. 2021, 48, 209–219. [Google Scholar]
- Barranco, C.I.; Carrillo, G.R.M. Techniques to Deal with Off-Diagonal Elements in Confusion Matrices. Mathematics 2021, 9, 3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.Q.; Zhang, F.H.; Yang, S.W. Historical change and evolution of sandy land in Minqin County (during 1991–2015). Mapp. Spat. Geogr. Inf. 2018, 41, 106–109. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Hao, R. Analysis of dynamic changes of vegetation cover in Minqin Oasis from 2013-2015 based on GF-1 remote sensing images. J. Southwest For. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2017, 37, 163–170. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Lv, S.; Dong, Z.; Fan, G.; Chen, L. Temporal and spatial variation characteristics of precipitation around Badain Jardan Desert. J. Desert Res. 2015, 35, 94–105. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Jie, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wei, J. Analysis of spatial and temporal changes of oasis in Minqin County from 1986–2015. Arid Zone Res. 2017, 34, 1410–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, T.; Tsunekawa, A.; Masunaga, T.; Wang,, T. Analysis of the Spatial Variation of Soil Salinity and Its Causal Factors in China’s Minqin Oasis. Math. Probl. Eng. 2017, 2017, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Li, C.; Feng, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Ravinesh, C.D. Direct and indirect impacts of ionic components of saline water on irrigated soil chemical and microbial processes. Catena 2019, 172, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Jim, Y.; Tao, B.; Xu, K. Effects of spatial resolution and texture features on multispectral remote sensing classification. J. Geoinf. Sci. 2018, 20, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, H.; Vidyarthi, A.; Chitre, A.V.; Wanjale, K.H.; Anusha, M.; Majrashi, A.; Hinga, S.K. Local Binary Patterns Based on Neighbor Center Difference Image for Color Texture Classification with Machine Learning Techniques. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ren, T.; Dong, P. Research on climate change trend prediction technology in Minqin County. Gansu Sci. Technol. Vert. 2017, 46, 29–31+22. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X. The impact of land use change on social resilience of rural communities in arid zones: The case of Minqin Oasis. Resour. Sci. 2021, 43, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Gansu Water Resources and hydropower Survey and Design Institute. Key Governance Planning of Shiyang River Basin. 2007. Available online: http://www.ndrc.gov.cn/fggz/fzzlgh/gjjzxgh/200806/P020191104623858217901.pdf (accessed on 27 December 2022).
- Yao, A.; Che, T.; Jiang, L.; Feng, Y. Remote sensing classification of desertification in minqin county of gansu area unused study. J. Res. For. Sci. 2014, 27, 195–200. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, C. Status and dynamics of land desertification in Minqin County, Gansu Province. J. Desert Res. 2014, 34, 970–974. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, J.; Shan, L.; Sun, X.; Zhao, X.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, S.; Zeng, X. Minqin county even the analysis of characteristics of the ancient city of national nature reserve of land desertification. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2019, 54, 99–107. [Google Scholar]


| Classified Data | Truth Data | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | Class 2 | … | Class n | Total | |
| Class 1 | X11 | X12 | X1n | Cd1 = | |
| Class 2 | X21 | X22 | X2n | Cd2 = | |
| … | |||||
| Class n | Xn1 | Xn2 | Xnn | Cdn = | |
| Total | Td1 = | Td2 = | Tdn = | All = | |
| Data | Date | Spatial Resolution | Parameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| GF-6/WFV | 2022.6.13 | 16 m | Spectra |
| GF-2/PMS | 2022.7.13 | 1 m(PAN)/4 m(MSS) | Texture |
| SRTM_DEM | 30 m | Elevation | |
| Slope | |||
| Vector boundary | 2020 | Zone |
| Atmospheric Model | Aerosol Model | Aerosol Retrieval | Initial Visibility | Spectral Response Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mid-Latitude Summer | Rural | None | 40 km | gf6_wfv.sli |
| Band | Wavelength/μm | Name | Spatial Resolution/m | Scan Width/km |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B01 | 0.45~0.52 | Blue | 16 | 800 |
| B02 | 0.52~0.59 | Green | ||
| B03 | 0.63~0.69 | Red | ||
| B04 | 0.77~0.89 | NIR | ||
| B05 | 0.69~0.73 | Red edge1 | ||
| B06 | 0.73~0.77 | Red edge2 | ||
| B07 | 0.40~0.45 | Violet | ||
| B08 | 0.59~0.63 | Yellow |
| Classified Data | Checked Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Saline-Alkaline Area | Saline-Alkaline Area | Total | UA | |
| Non-saline-alkaline area | 64 | 4 | 68 | 94.12% |
| Saline-alkaline area | 13 | 62 | 75 | 82.67% |
| Total | 77 | 66 | 143 | |
| PA | 83.12% | 93.94% | ||
| OA | 88.11% | |||
| Kappa | 0.76 | |||
| Date | Satellite | Sensor | Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2010.7.25 | Landsat 8 | OIL | 131/33 |
| 2015.7.22 | |||
| 2020.8.2 |
| Order Number | Contents | Date | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Classification of unused land | 2016 | Yao, A. et al., 2014 [45] |
| 2 | Dynamic monitoring of land desertification | 2004–2009 | Chen, X. et al., 2014 [46] |
| 3 | Analysis of land desertification characteristics | 2012–2013 | Ma, J. et al., 2019 [47] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Wang, Q.; Chang, D.; Xu, W.; Yuan, B. A High-Precision Remote Sensing Identification Method on Saline-Alkaline Areas Using Multi-Sources Data. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102556
Yang J, Wang Q, Chang D, Xu W, Yuan B. A High-Precision Remote Sensing Identification Method on Saline-Alkaline Areas Using Multi-Sources Data. Remote Sensing. 2023; 15(10):2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102556
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jingyi, Qinjun Wang, Dingkun Chang, Wentao Xu, and Boqi Yuan. 2023. "A High-Precision Remote Sensing Identification Method on Saline-Alkaline Areas Using Multi-Sources Data" Remote Sensing 15, no. 10: 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102556
APA StyleYang, J., Wang, Q., Chang, D., Xu, W., & Yuan, B. (2023). A High-Precision Remote Sensing Identification Method on Saline-Alkaline Areas Using Multi-Sources Data. Remote Sensing, 15(10), 2556. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs15102556