Abstract
Optical sensors have been widely reported to be useful tools to assess biomass, nutrition, and water status in several crops. However, the use of these sensors could be affected by the time of day and sky conditions. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of time of day and sky conditions (sunny versus overcast) on several vegetation indices (VI) calculated from two active sensors (the Crop Circle ACS-470 and Greenseeker RT100), two passive sensors (the hyperspectral bidirectional passive spectrometer and HandySpec Field sensor), and images taken from an unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). The experimental work was conducted in a wheat crop in south-west Germany, with eight nitrogen (N) application treatments. Optical sensor measurements were made throughout the vegetative growth period on different dates in 2019 at 9:00, 14:00, and 16:00 solar time to evaluate the effect of time of day, and on a sunny and overcast day only at 9:00 h to evaluate the influence of sky conditions on different vegetation indices. For most vegetation indices evaluated, there were significant differences between paired time measurements, regardless of the sensor and day of measurement. The smallest differences between measurement times were found between measurements at 14:00 and 16:00 h, and they were observed for the vehicle-carried and the handheld hyperspectral passive sensor being lower than 2% and 4%, respectively, for the indices NIR/Red edge ratio, Red edge inflection point (REIP), and the water index. Differences were lower than 5% for the vehicle-carried active sensors Crop Circle ACS-470 (indices NIR/Red edge and NIR/Red ratios, and NDVI) and Greenseeker RT100 (index NDVI). The most stable indices over measurement times were the NIR/Red edge ratio, water index, and REIP index, regardless of the sensor used. The most considerable differences between measurement times were found for the simple ratios NIR/Red and NIR/Green. For measurements made on a sunny and overcast day, the most stable were the indices NIR/Red edge ratio, water index, and REIP. In practical terms, these results confirm that passive and active sensors could be used to measure on-farm at any time of day from 9:00 to 16:00 h by choosing optimized indices.
1. Introduction
Optical sensors have been reported to be useful tools to assess plants’ biomass and health, e.g., nutritional status, water status, or disease incidence. The main advantage of sensors is that they can rapidly and non-destructively measure large representative areas, quickly generating results [1,2], which can be used for optimized management. Sensor-based management better accounts for the spatial and temporal variability of crop growth. It can be used, for example, for the variable application of N fertilizer in time, amount, and space, according to the crop N requirements [3,4], maximizing N use efficiency and reducing N losses to the environment [5,6,7].
Optical sensing has frequently been used to assess plant properties. However, measurements were done at different times of day and different days of the year, which may have influenced the sensed information. Environmental variables such as radiation intensity and solar elevation angle change during the day and across the season, influencing reflectance from plants and radiation received by sensors [5,8,9,10,11,12].
Within optical sensors, there are different types according to the principle of measurement. Reflectance sensors are optical multispectral or hyperspectral sensors that measure the reflectance properties by measuring the absorption and reflection of different radiation wavelengths from the crop canopy [13,14,15,16]. Reflectance sensors can be either passive or active, depending on the light source used [6,17]. Passive sensors depend on sunlight as the source of light, whereas active sensors have their own light source providing radiation regardless of sunlight [17]. Most canopy reflectance sensors are proximal sensors that are positioned relatively close to the crop canopy, either handheld or vehicle-mounted [6,17]. Multispectral reflectance sensors can also be mounted on light aircraft and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) [18,19]. UAVs have recently become popular tools widely used in a variety of monitoring applications, including precision agriculture and crop phenotyping, because of their high-spatial-resolution, flexibility in use, and measurement time [20,21].
From canopy reflectance measurements, multiple vegetation indices can be calculated to assess the crop N status, water stress, or other crop characteristics needed for optimized crop management [16]. Vegetation indices are mathematical expressions where reflectance data of 2–3 wavelengths are combined [8]. Their use has been prevalent because these indices are more sensitive to vegetation characteristics than individual wavelengths [22].
Measurements of passive reflectance sensors are influenced by time of day [10,12,17,23] and solar elevation angle [24], whereas active sensors are expected not to be influenced by irradiation conditions [25,26]. However, there is experimental evidence of slight effects of daytime on active canopy reflectance sensors; these differences generally depend on the vegetation indices considered [27,28]. Vegetation indices based on UAV imagery have shown the same capability to quantify crop responses as ground-based sensors. However, it is necessary to consider the angular variation in reflectance [29] and ambient light fluctuations [30].
Interestingly enough, such effects have so far received very little attention in proximal sensing, either using ground versus aerial, handheld versus tractor-mounted sensors, or active versus passive sensors, and the impact of time of day and sky conditions needs to be addressed more intensively.
Therefore, the present study evaluated the effect of daytime and sky conditions (sunny versus overcast) on different vegetation indices calculated from active and passive sensors and images taken from a UAV. This research was conducted with winter wheat grown at eight different nitrogen (N) application levels. Measurements were conducted on sunny days at three different dates within the growing season, each at three different times (9:00, 14:00, 16:00 h), to investigate the influence on various indices, and also on two succeeding days characterized by overcast and sunny conditions at 9:00 h. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study comparatively evaluating the influence of daytime and sky conditions on handheld or tractor-mounted sensing using active and passive sensors and multispectral UAV sensing.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
The experimental work was carried out at the Dürnast research station of the Technical University of Munich, in south-west Germany (8.406 N, 11.692 E, 470 m altitude). The fields used were mostly homogeneous Cambisol of silty clay loam texture. The average annual precipitation in this area is approximately 820 mm, and the annual mean temperature is 7.8 °C. Winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L., cultivar Rumor) was used as the experimental crop.
The experimental design was a randomized block design with four repetitions and eight N levels; the N treatments were: 0, 60, 120, 180, 240, 300, 360, and 420 kg N ha−1 applied in three doses on 26 March 2019 (Zadoks scale 23–26), 30 April 2019 (Zadoks scale 32), and 6 June 2019 (Zadoks scale 59) as calcium ammonium nitrate. Increased fertilizer rates of 300, 360, and 420 kg N ha−1 were chosen to evaluate whether excessively fertilized plants’ nutritional status could also be determined by spectral reflectance sensing. The nitrogen levels were varied to create a range in the nitrogen nutritional status and test the suitability of sensors to detect these differences. Since the soil nutrient status of all other nutrients was optimal, no further application was required.
The field experiment was organized as a 4 × 8 plot design, totaling 32 plots, each measuring 10 m × 1.5 m. The distance between plots in the driving direction was 1 m, and the plant row spacing was 14 cm. Sowing was done on 10 October 2018, at a rate of 250 kernels per square meter. Plants were harvested on 5 August 2019, with a plot combine harvester.
2.2. Spectral Reflectance Measurements
Spectral reflectance measurements were conducted throughout the vegetative growth period on four dates in 2019. Two measurement dates were at the flag leaf stage, and those measurements were conducted on 7 May, at overcast conditions at 9:00 h, and entirely sunny conditions at 14:00 and 16:00 h, and on the next day on 8 May, at completely sunny conditions at 9:00 h. The third and fourth measurement dates were on June 3 and 27 at the anthesis stage and ripening stages, respectively, and measurements were conducted at completely sunny conditions at 9:00, 14:00, and 16:00 h. Measurement conditions, including the sum of incoming solar radiation per hour, minutes of sunshine duration per hour, and air temperature at 2 m height, are indicated in Table 1. Measurements were made between 9:00 and 16:00 solar time to cover a frequent working period and avoid low solar elevation angles. Spectral reflectance measurements were made at the center of the plots avoiding 0.5 m at the beginning and the end of each plot to remove edge effects.

Table 1.
Meteorological measurement conditions: sum of incoming solar radiation per hour, minutes of sunshine duration per hour, and air temperature at 2 m height.
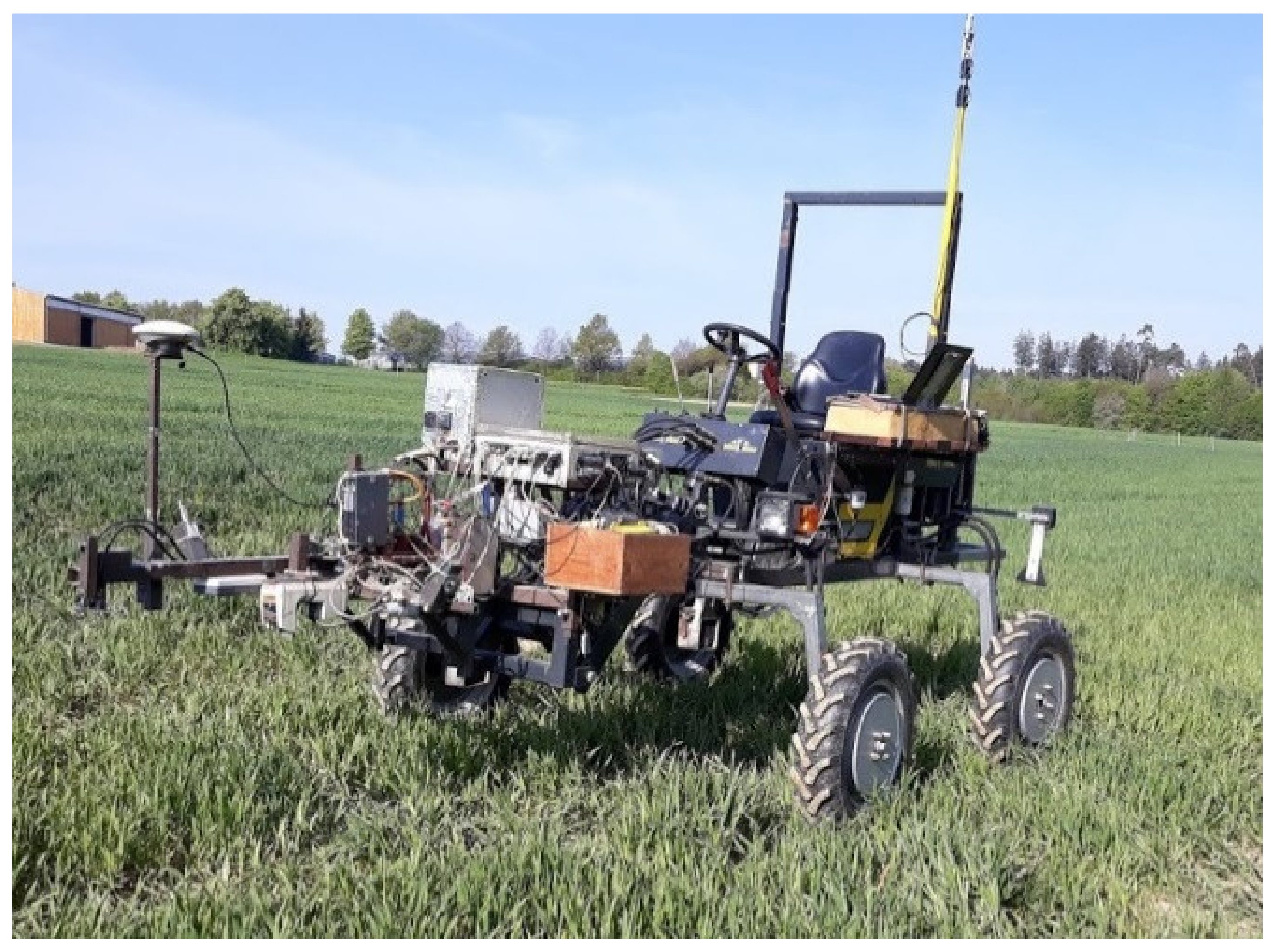
Different passive and active sensors were used to make the spectral reflectance measurements (Table 2), and various spectral indices were calculated based on previous work to indicate biomass and nitrogen status [6,17,19,26] allowing a comparison among sensors (Table 3). The Crop Circle ACS470, the Greenseeker TR100, and the hyperspectral bidirectional passive spectrometer were mounted on a custom-made vehicle called the PhenoTrac4 platform [31] (Figure 1). The sensor-target distance was set to 80 cm. This vehicle allows measurements above the canopy without touching it at a speed of 6 km h−1 and was set to be 2 km h−1 in this trial; the ground clearance was 0.90 m. Measurements with the HandySpec Field were made at walking speed (approx. at 2 km h−1).

Table 2.
Spectral reflectance sensor information.

Table 3.
Vegetation indices and their formulas calculated in the present work.

Figure 1.
PhenoTrac4 platform used to make measurements at 2 km h−1 (Chair of Plant Nutrition, Technical University of Munich).
For aerial-based multispectral sensing, the wing aircraft senseFly (“eBee,” SenseFly, Cheseaux Lausanne, Switzerland), equipped with a multispectral and sunshine sensor (Sequoia camera) (Parrot, Paris, France), was used for flying in an east–west direction capturing high-resolution aerial images [20]. The multispectral sensor Parrot Sequoia is comprised of an RGB camera and four spectral cameras for the spectral bandwidths of 530–570, 640–680, 730–740, and 770–810 nm. The focal length is 3.98 mm, the image size is 1280 × 960 pixels and the field of view is horizontally 61.9°, vertically 48.5°, and diagonally 73.7°. Additionally, this camera has a fully integrated sunshine sensor, which records the ambient light’s intensity performing a radiometric calibration to ensure the measurements’ coherence at any light conditions. The camera was equipped with a built-in RTK-capable GNSS antenna to construct a georeferenced reflectance map. Flights were conducted at 50 m above ground level resulting in ground sampling distances of about 5 cm/pixel. Mission planning was done with eMotion 3 for the Sequoia camera. All flights were planned for 80% overlap along flight corridors and subsequently carried out to the terrestrial sensor measurements. For segmenting the spectral information, each treatment plot was divided into 10 subplot polygons of 90 cm in length and having a width of 30 cm in the center of the plot. The GeoTIFFs with the spectral orthomosaics from Pix4D were combined with the subplot polygons and shapefile for all flights. The means from each subplot were generated using the zonal-statistics function in ArcGIS. The average ground sampling distance (GSD) was 6.5 cm, varying between 5.9 and 6.9 cm depending on the flight. Overlap was over 5 images for every pixel. WGS84 was used as the image coordinate system. Noise filtering and sharp surface smoothing were used as DSM filters. Camera radiometric calibration was done with the reflectance target for the camera, for the sun irradiance, and the sun angle, the latter only in clear sky conditions. The four spectral bands’ information was used to calculate the vegetation indices (NIR/Green, NIR/Red, Red/Red edge, NIR/Red edge ratios, NDVI, and GNDVI). The images captured with the camera were processed with the software Pix4D Mapper Pro (Pix4D S.A., Lausanne, Switzerland).
The buffer zones of the UAV were matched as closely as possible to the ground-based sensors. The length of the polygons for the ground-based sensors was set comparably to 90 cm, whereas the half-width signal maximum was set at 31 cm for the hyperspectral sensors and 47 cm and 36 cm for the Greenseeker and Crop Circle, respectively. Sensors were positioned at 80 cm above the crop canopy. About ten measurements were combined for the ground-based passive sensors to obtain the subplot means recorded and processed using proprietary software and ArcGis, whereas a much higher frequency of measurements was obtained for the active sensors and averaged as well per meter.
2.3. Data Analysis
Differences between time measurements for each vegetation index and sensor were evaluated with paired t-tests between paired time measurements (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h). SPSS 11 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for this statistical analysis. T-tests were also performed to compare measurements conducted on a sunny day versus measurements made on an overcast day. The Bonferroni correction was applied for multiple comparisons. The significance level used was 0.05, for multiple comparison after Bonferroni correction the significance level used was 0.016 (significance level/number of comparisons; 0.05/3).
Linear regressions were calculated between paired time measurements (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) for each vegetation index from the three measurement dates. The slope of linear regression was compared to the 1:1 line. Regression analysis was done with the software CurveExpert Professional®2.2.0 software (Daniel G. Hyams, MS, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of Time of Day Effects
For most of the vegetation indices evaluated, there were significant differences (p < 0.016, after Bonferroni correction) between paired time measurements (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h), regardless of sensor and day of measurement (Table 4, Table 5, Table 6 and Table 7). The smallest differences between measurement times were found between measurements at 14:00 and 16:00 h. The largest difference was found on May 7 between 9:00 h and the other two measurement times (14:00 and 16:00 h), regardless of the index and sensor considered.

Table 4.
Mean values of each vegetation index for paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) measured with two vehicle-carried active sensors, Crop Circle ACS-470 and Greenseeker RT100, on each date of measurement. Green shading indicates non-significant differences between paired measurement times using t-Tests; all other pairs were statistically different (p < 0.016, after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons). Backgroung color is necessary, since it allows to differentiate the two different sensors.

Table 5.
Mean values of each vegetation index for paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) were measured with a UAV on each measurement date. Green shading indicates non-significant differences between paired measurement times using t-Tests; all other pairs were statistically different (p < 0.016, after Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons).

Table 6.
Mean values of each vegetation index for paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) measured with the vehicle-carried hyperspectral bidirectional passive spectrometer on each date of measurement. Green shading indicates non-significant differences between paired measurement times using t-Tests; all other pairs were statistically different (p < 0.016, corrected by Bonferroni for multiple comparisons).

Table 7.
Mean values of each vegetation index for paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) measured with the handheld hyperspectral bidirectional HandySpec Field sensor on each date of measurement. Green shading indicates non-significant differences between paired measurement times using t-Tests; all other pairs were statistically different (p < 0.016, corrected by Bonferroni for multiple comparisons).
For the indices, NIR/Red edge, NIR/Red ratio, and NDVI measured with the vehicle-carried active sensor Crop Circle ACS-470 the differences between measurement times were lower than 5% (Table 4). The most considerable differences between measurement times were found for the Red edge/Red ratio, mainly on 7 May and 3 June. Compared with measurements made at 9:00 h, the Red edge/Red ratio index was around 10% lower at 14:00 and 16:00 h.
For the vegetation indices measured with the vehicle-carried Greenseeker RT100 sensor, the smallest differences between measurement times were found for the NDVI index, being lower than 5% (Table 4). The largest differences were found for the NIR/Red ratio, compared with measurements made at 9:00 h; this ratio was around 25% larger at 16:00 h on 3 June.
For indices calculated from unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) images, the smallest differences between measurement times were observed for the two normalized vegetation indices (i.e., NDVI and GNDVI); on average, for these indices, the difference between the three measurement dates was lower than 5% (Table 5). The largest difference between measurement times was observed for the NIR/Red ratio, followed by the NIR/Green ratio, and Red edge/Red ratio, mainly between 9:00 and 14:00 h on June 3 and 27. On June 3, compared with 9:00 h, the NIR/Red ratio was 35% lower at 14:00 h, the Red edge/Red was 29% lower, and the NIR/Green was 17% lower at the same time. The NIR/Red edge ratio had an intermediate performance between normalized vegetation indices and the other ratios, compared with 9:00 h, this ratio was 10% lower at 14:00 h on June 3, whereas the differences between the three measurement times were lower than 5% on June 27.
Considering the vehicle-carried hyperspectral bidirectional passive spectrometer measurements, the smallest differences between measurement times were found for the NIR/Red edge ratio, water index, and REIP index, the differences between measurement times were lower than 2% in the three measurement days (Table 6). The largest differences between measurement times were found for the NIR/Red ratio followed by the NIR/Green ratio on 7 May, followed by 3 June, mainly between 9:00 h and the other hours. For the NIR/Red ratio, the difference between 9:00 and 14:00 h on 7 May was 31.2%; on 3 June, this difference was 10.8% lower at 14:00 h; on 27 June, it was just 2.6% lower. For the NIR/Green ratio, the difference between 9:00 and 14:00 h was 12.4% on May 7; for the other two dates, the difference was lower than 2%. The differences between measurement times on June 27 were negligible regardless of the index considered.
As for the handheld hyperspectral bidirectional HandySpec Field sensor measurements, the smallest differences between measurement times were found for the NIR/Red edge ratio, water index, and REIP index, the differences between measurement times were lower than 4% regardless of measurement date (Table 7). For the normalized vegetation indices (i.e., NDVI and GNDVI), the difference between 9:00 and 14:00 h on May 7 was around 6% lower at 14:00 h; for the rest of the comparisons between hours, this difference was lower than 3%. The largest differences between measurement times were found for the NIR/Red, Red edge/Red, and NIR/Green ratios on May 7, mainly between 9:00 h and the other hours. For the NIR/Red ratio, the difference between 9:00 and 14:00 h on May 7 was 41.2% lower at 14:00 h; on the other dates, this difference was lower than 5%. For the Red edge/Red ratio, the difference between 9:00 and 14:00 h was 39% lower at 14:00 h on May 7; for the other dates, the difference was lower than 15%. For the NIR/Green ratio, the difference between 9:00 and 14:00 h was 19.5% lower at 14:00 h; for the other days, the difference was lower than 10%.
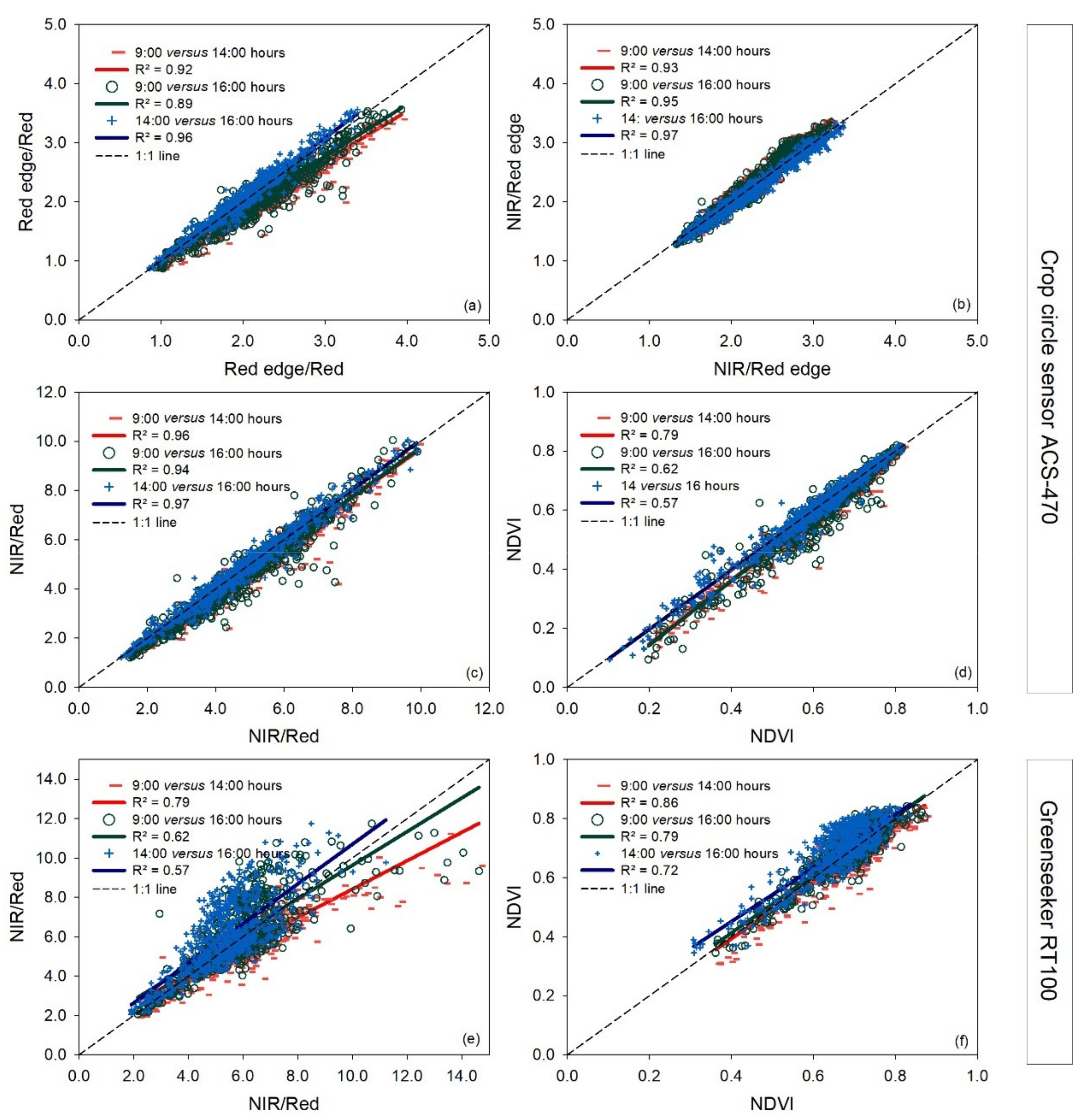
Comparing the indices measured with the vehicle-carried Crop Circle ACS-470 sensor at different measurement times, for the indices NIR/Red edge and NIR/Red ratios, and NDVI, no deviation was seen in the different paired times analyzed (Figure 2b–d). Values were lower for the Red edge/Red ratio at 9:00 than at 14:00 and 16:00 h (Figure 2a).
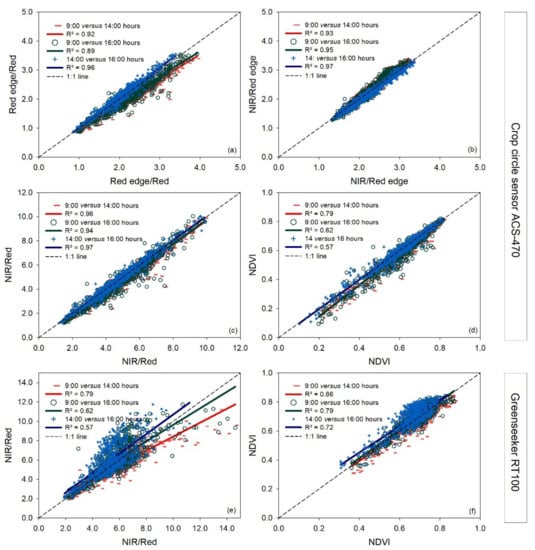
Figure 2.
Linear regressions between paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) for each vegetation index measured with two vehicle-carried active sensors, Crop Circle ACS-470 and Greenseeker RT100, for the three measurement dates together. Panels (a–d) show indices calculated with the Crop Circle ACS-470 sensor, and the other panels (e,f) show indices calculated with the Greenseeker RT100 sensor. R2: coefficient of determination. The dashed line represents the 1:1 line. In the pairwise comparison, the earlier time is indicated on the x-axis and the later time on the y-axis.
As for the vehicle-carried Greenseeker RT100 sensor, an apparent disagreement from the 1.1 line was observed for the NIR/Red ratio at 9:00 h relative to at 14:00 h, but not for the NDVI index at any measurement time (Figure 2e,f).
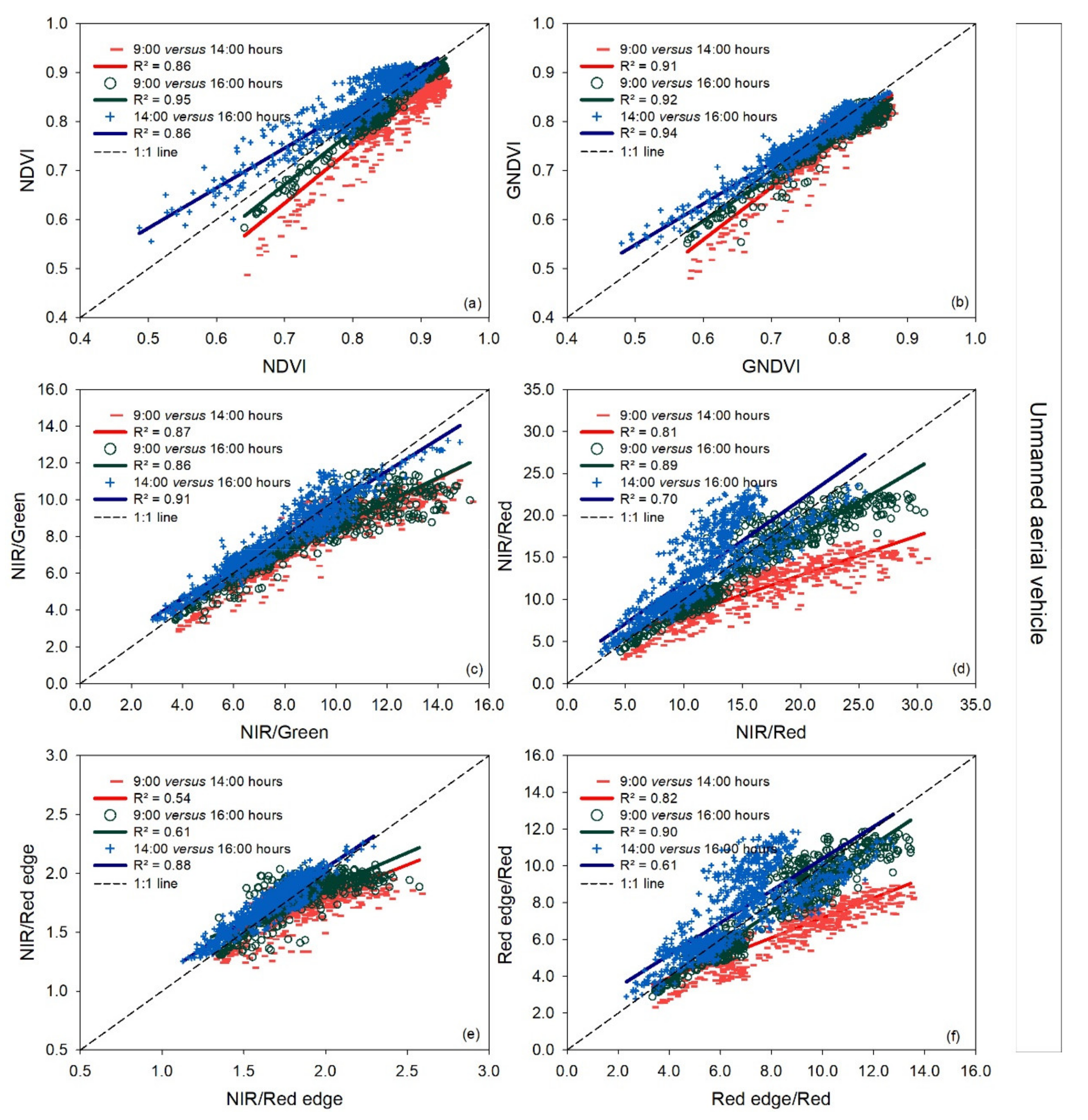
Compared to the 1:1 line, the vegetation indices NIR/Green, NIR/Red, and NIR/Green calculated from the UAV tended to disagree at 14:00 and 16:00 h compared to 9:00 h at high index values (Figure 3). However, a slight deviation was also observed for the NDVI and GNDVI at low index values at 14:00 h compared to 16:00 h.
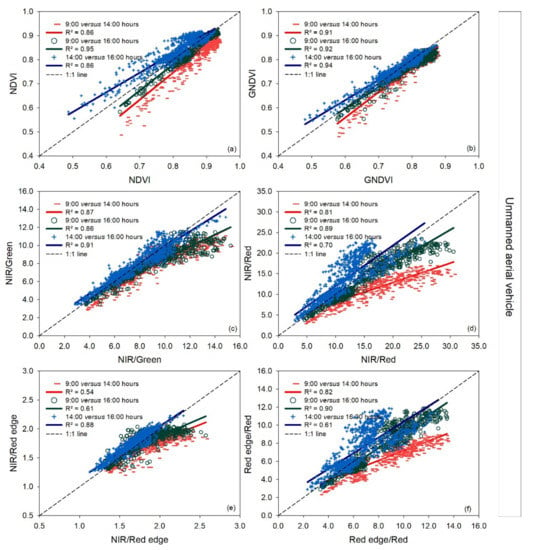
Figure 3.
Linear regressions between paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) for each vegetation index measured with a UAV for the three measurement dates together. R2: coefficient of determination. The dashed line represents the 1:1 line. In the pairwise comparison, the earlier time is indicated on the x-axis and the later time on the y-axis (a–f).
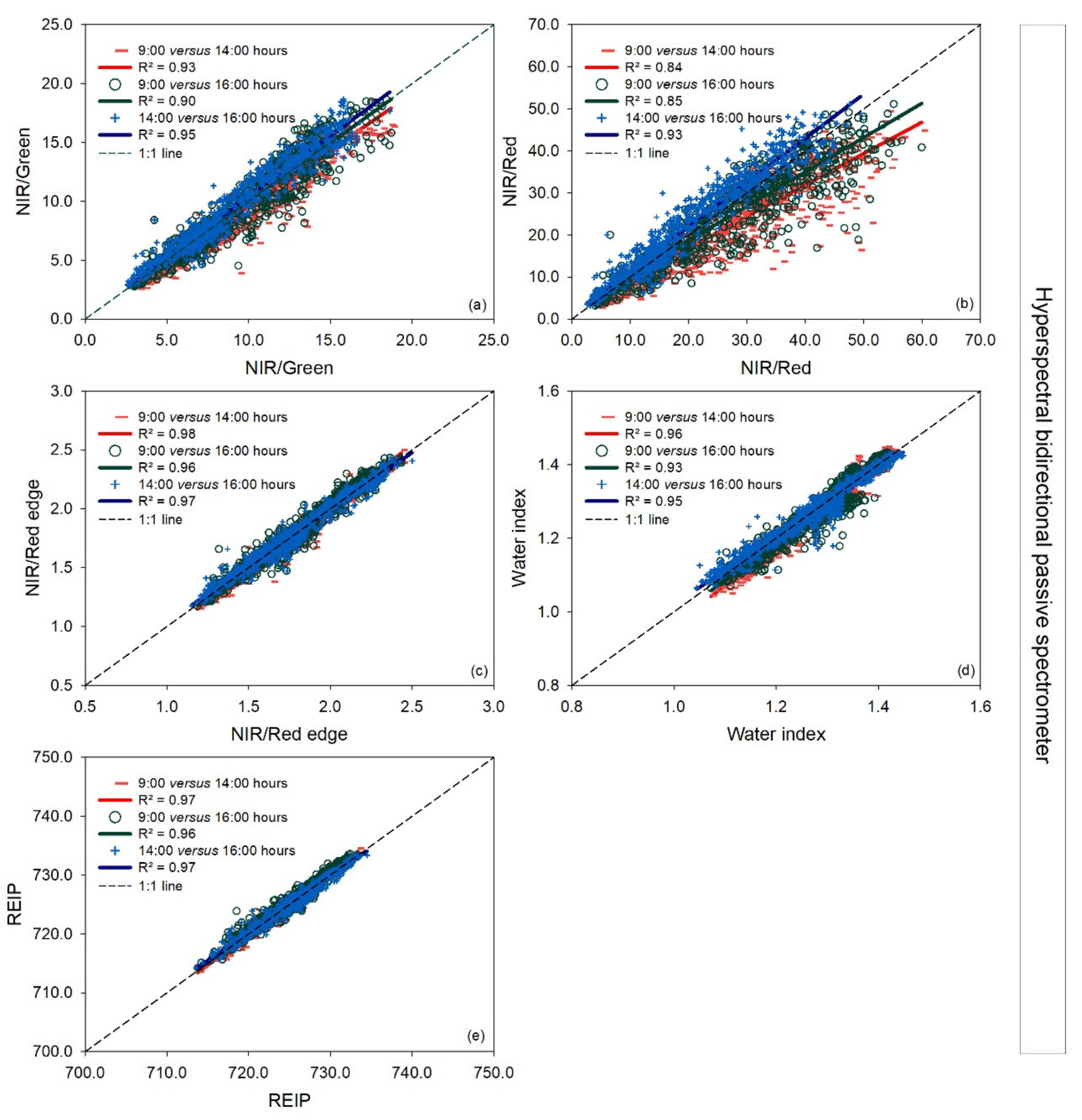
For the vegetation indices NIR/Green, NIR/Red edge, and REIP, and the water index measured with the vehicle-carried hyperspectral bidirectional passive spectrometer, there was no deviation between different paired time measurements observed (Figure 4a–e), in contrast to the NIR/Red ratio, where an underestimation was observed for measurements made at 14:00 and 16:00 h compared to 9:00 h, mainly at values higher than 25.
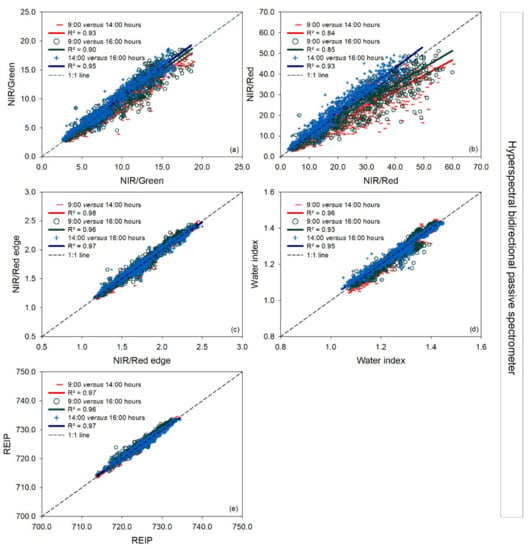
Figure 4.
Linear regressions between paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) for each vegetation index measured with a vehicle-carried hyperspectral bidirectional spectrometer for the three measurement dates together. R2: coefficient of determination. The dashed line represents the 1:1 line. In the pairwise comparison, the earlier time is indicated on the x-axis and the later time on the y-axis (a–e).
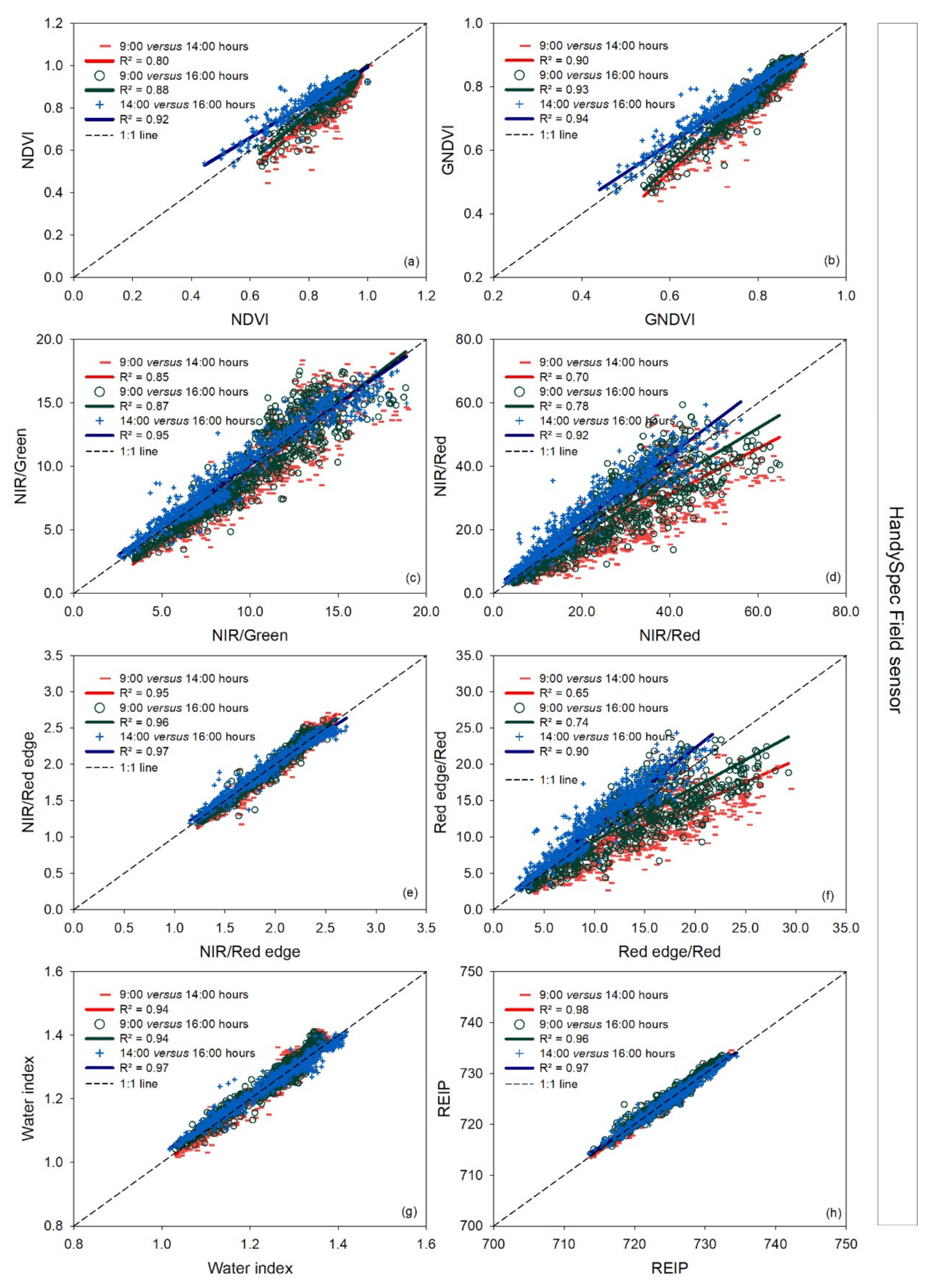
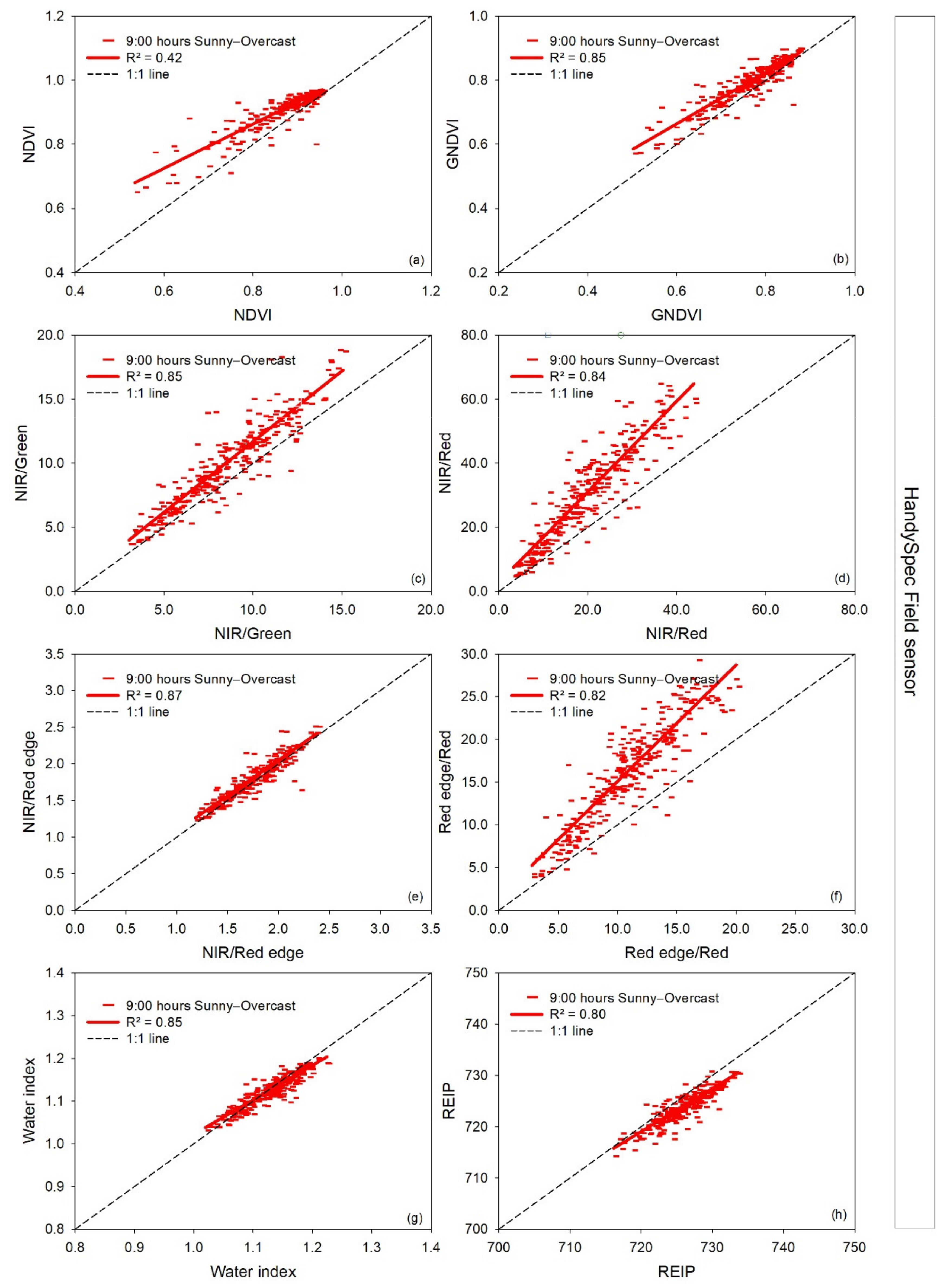
Of the vegetation indices measured with the handheld hyperspectral bidirectional HandySpec Field sensor, there was no deviation observed for the NIR/Green, NIR/Red edge ratios, and the water index REIP. The NDVI and GNDVI index was lower at 14:00 and 16:00 h relative to at 9:00 h at values below 0.70. The NIR/Red ratio showed an apparent deviation at 16:00 h compared to 9:00 h at values higher than 25 (Figure 5d).
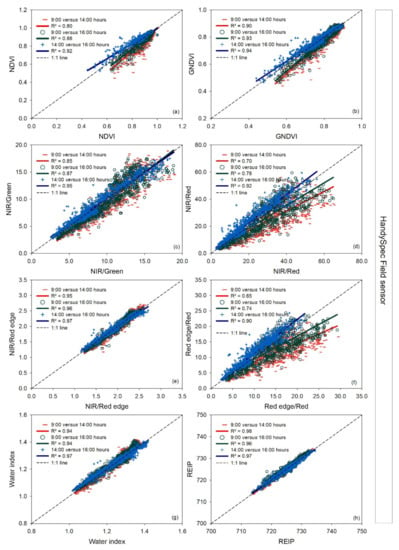
Figure 5.
Linear regressions between paired measurement times (9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) for each vegetation index measured with the handheld hyperspectral bidirectional HandySpec Field sensor for the three measurement dates together. R2: coefficient of determination. The dashed line represents the 1:1 line. In the pairwise comparison, the earlier time is indicated on the x-axis and the later time on the y-axis (a–h).
3.2. Evaluation of Sky Conditions Effects
For the indices assessed, there were significant differences between sky conditions (i.e., sunny versus overcast; p < 0.05) (Table 8), except for the NIR/Red edge ratio measured with the Crop Circle ACS-470 and the NDVI measured with the Greenseeker RT100 sensor.

Table 8.
Mean values of each vegetation index for paired measurement dates at 9:00 h on a sunny (08-05-2019) and overcast (07-05-2019) day measured with the vehicle-carried Crop Circle ACS 470, Greenseeker RT100, hyperspectral spectrometer, and the handheld hyperspectral HandySpec Field sensor in a wheat crop. Green shading indicates non-significant differences between paired measurement dates using t-Tests (p < 0.05); all other pairs were statistically different.
Analyzing the indices’ performance measured with the bidirectional passive hyperspectral sensors (i.e., vehicle-carried spectrometer and HandySpec Field sensor), the differences between sky conditions were slightly more significant with the HandySpec Field sensor than with the vehicle-carried spectrometer. For the NDVI, GNDVI, NIR/Red edge, water index, and REIP, the differences between sky conditions were lower than 5%, regardless of the passive sensor used. The largest differences for both sensors were found for the NIR/Red ratio, followed by the NIR/Green ratio. On average, the NIR/Red ratio was 34.6% (HandySpec Field sensor) and 29.3% (bidirectional spectrometer) higher on an overcast day compared to a sunny day. For the NIR/Green ratio, the differences were 14.3% (HandySpec Field sensor) and 12.4% (bidirectional spectrometer) higher on an overcast day compared to a sunny day.
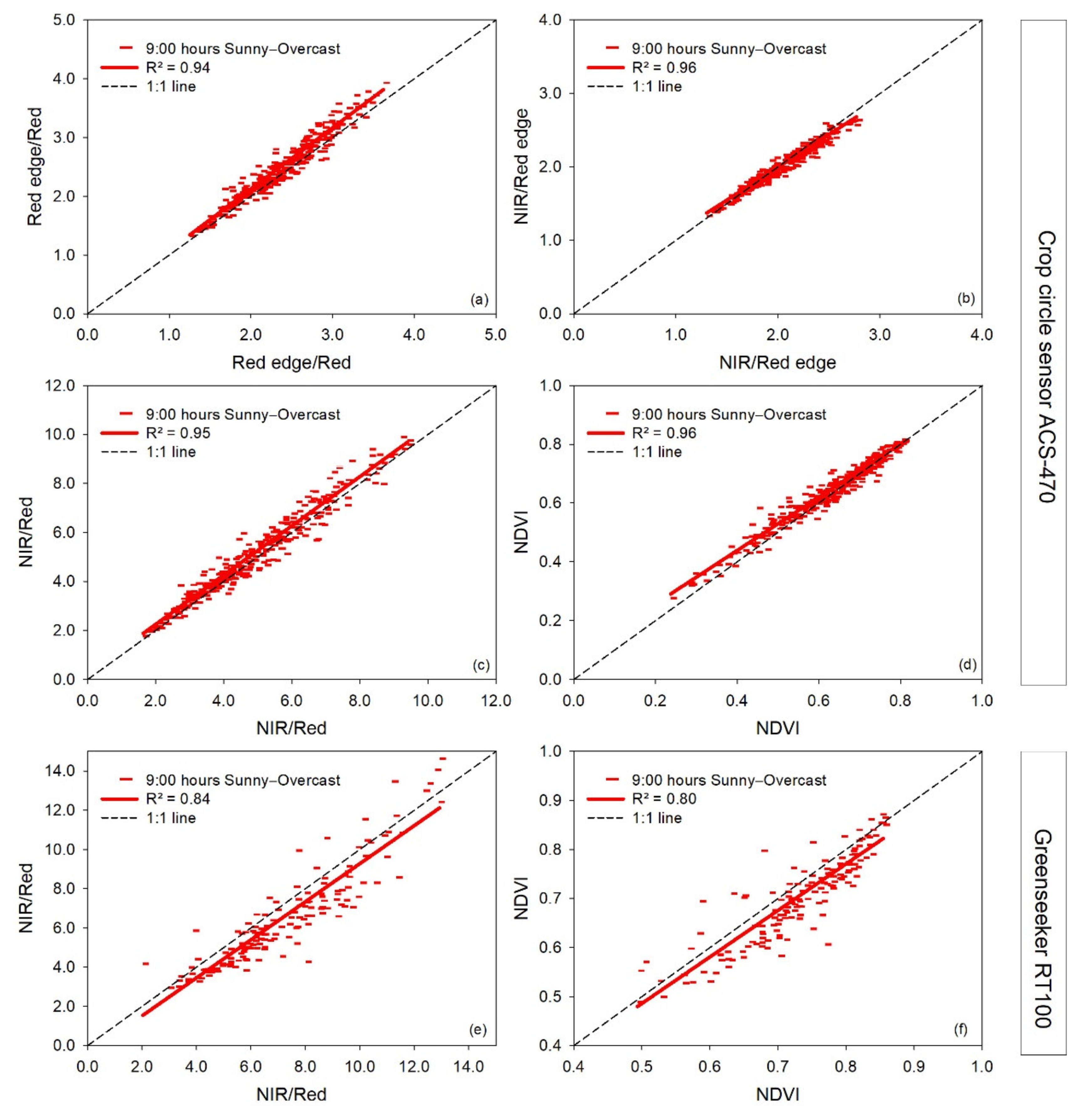
A relatively close agreement was observed on a sunny and an overcast day for the vegetation indices NIR/Red edge, NIR/Red, and NDVI measured with the active sensor Crop Circle ACS 470 (Figure 6b–d). In contrast, some deviation was observed for the Red edge/Red ratio measured with the same sensor at higher index values (Figure 6a), and similarly for the NDVI and NIR/Red measured with the Greenseeker RT100; however, at lower index values (Figure 6e,f).
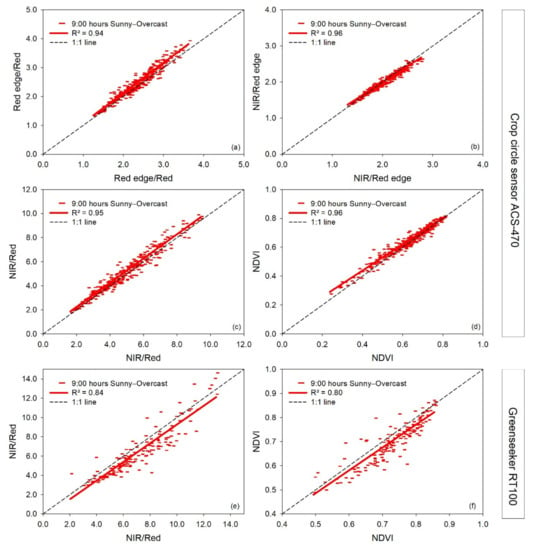
Figure 6.
Linear regressions between paired measurement times at 9:00 h in a sunny (independent variable) (08-05-2019) and overcast (dependent variable) (07-05-2019) day for each vegetation index measured with two active vehicle-carried sensors, Crop Circle ACS-470 and Greenseeker RT100. R2: coefficient of determination. The dashed line represents the 1:1 line. In the pairwise comparison, the sunny day’s information is indicated on the x-axis and for the overcast day on the y-axis (a–f).
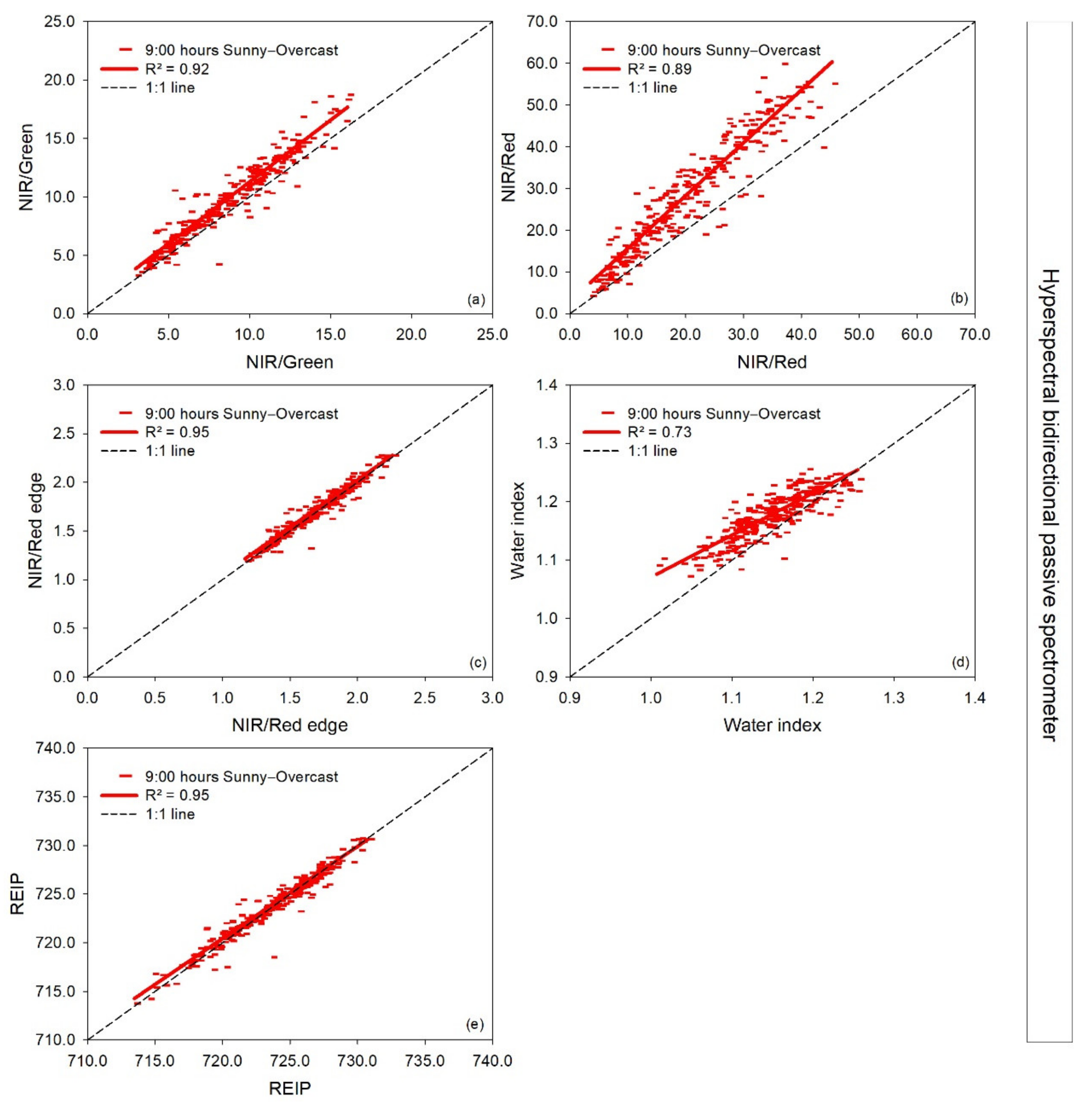
For the vegetation indices measured with the passive hyperspectral bidirectional sensors, measurements on an overcast day compared to a sunny day showed a particularly close agreement for the NIR/Red edge and REIP for the vehicle-carried spectrometer and less for the handheld HandySpec Field sensor (Figure 7 and Figure 8). Compared to the 1:1 line, the vegetation indices NIR/Red and NIR/Green calculated from the vehicle-carried hyperspectral sensor disagreed at high index values, and some bias was observed for the water index. For the handheld HandySpec Field sensor, the NDVI only weakly agreed on the overcast and sunny day, and the indices NIR/Green, Red edge/Red, and NIR/Red deviated from linearity at higher index values.
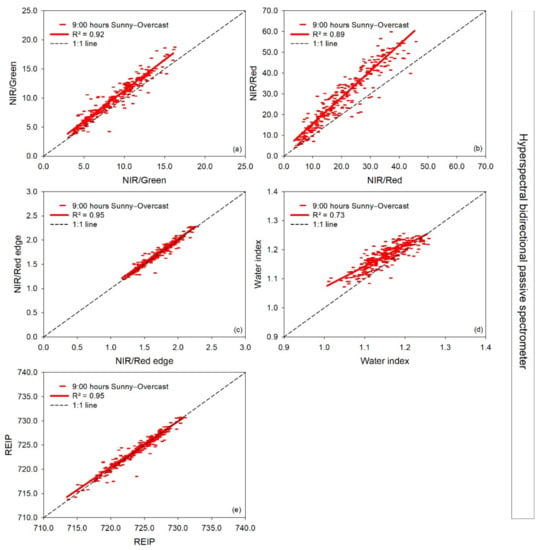
Figure 7.
Linear regressions between paired measurement times at 9:00 h in a sunny (independent variable) (08-05-2019) and overcast (dependent variable) (07-05-2019) day of each vegetation index measured with the vehicle-carried hyperspectral bidirectional spectrometer. R2: coefficient of determination. The dashed line represents the 1:1 line. In the pairwise comparison, the sunny day’s information is indicated on the x-axis and for the overcast day on the y-axis (a–e).
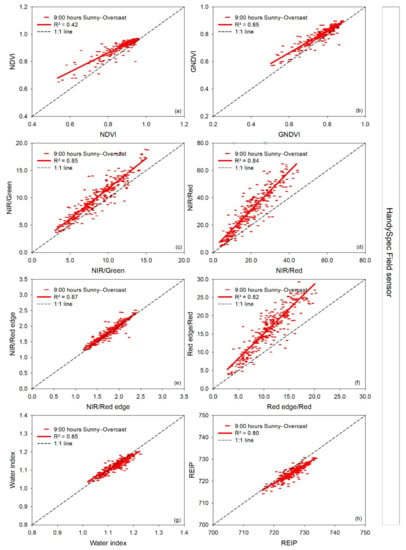
Figure 8.
Linear regressions between paired measurement times at 9:00 h in a sunny (independent variable) (08-05-2019) and overcast (dependent variable) (07-05-2019) day of each vegetation index measured with the handheld hyperspectral bidirectional HandySpec Field sensor. R2: coefficient of determination. The dashed line represents the 1:1 line. In the pairwise comparison, the sunny day’s information is indicated on the x-axis and for the overcast day on the y-axis (a–h).
4. Discussion
4.1. General Effects of Time of Day
This study showed significant differences between paired time measurements (i.e., 9:00 versus 14:00 h, 9:00 versus 16:00 h, and 14:00 versus 16:00 h) for most vegetation indices evaluated, regardless of optical sensors used. In most cases, these differences can be considered of little practical implication since they were less than 10% of the values measured for most of the vegetation indices evaluated and even less than 2–5% for optimized indices of the individual sensors.
The smallest differences between measurement times were observed for the vehicle-carried and the handheld hyperspectral bidirectional HandySpec Field sensor, lower than 2% and 4%, respectively, for the indices NIR/Red edge ratio, REIP, and the water index. Differences were lower than 5% for the vehicle-carried active sensors Crop Circle ACS-470 (indices NIR/Red edge and NIR/Red ratios, and NDVI) and Greenseeker RT100 (index NDVI). A wider spread of the reflectance values was evident for the Greenseeker than for the Crop Circle and even larger for the UAV.
The most considerable differences between paired time measurements were found in the first two measurement days, which corresponded with the flag leaf and anthesis stages, mainly for simple ratio vegetation indices such as NIR/Red and NIR/Green, regardless of the sensors considered. The differences found in these measurement days could be due to the effects of background soil since the plant size at those stages was smaller, and the background soil accounted for a significant part of the background reflectance signal. In addition, the background signal can significantly affect reflectance measurements in row-arranged crops due to the shadowing effect of crop rows under a specific solar angle [9,10], which depends on the local time at a given latitude and date [11]. Li et al. (2020) [10] suggested that an appropriate time for spectral measurements could minimize the soil effect since the soil background is almost shaded at 9:00 and 15:00 h but sunlit at 12:00 h for a north–south oriented crop canopy. These findings could explain the most significant differences between paired time measurements at the beginning of the current study’s crop growth period.
It has been demonstrated that the incident solar angle and other ambient factors such as the temperature could affect the performance of reflectance sensors [10,25,26]. Kipp et al. (2014) [26] found that the device temperature affects the active sensors’ reflectance output values, reflected in the different calculated vegetation indices. The application of these sensors in precision farming could be affected by normal air temperature variation throughout the day and subsequent sensor temperature variation. A regression equation using temperature, solar radiation, and solar time explained 45 to 50% of the variability for the Greenseeker and could potentially be used to correct values during field use [12]. However, temperature changes from 9:00 to 16:00 h were not prominent in this study (Table 2), making a direct influence of temperature less likely.
Stability of vegetation indices were influenced by time of day among the eight vegetation indices evaluated, the most stable indices throughout the day were the NIR/Red edge ratio, the water index, and the REIP index. In previous work, it was shown that the REIP index was insensitive to the solar elevation angle [24]; this could partly explain why this index showed excellent temporal stability with differences of less than 2% throughout the day in the current work.
The normalized vegetation indices evaluated (i.e., NDVI and GNDVI) were generally the second most stable group of indices throughout the different measurement times. Padilla et al. (2019) [27] reported similar results in sweet pepper; NDVI and GNDVI indices were not affected by the time of day.
In the current work, the indices most affected by the time of day were simple ratio vegetation indices such as NIR/Red, Red edge/Red, and NIR/Green; within this category, the NIR/Red was the most affected, and the NIR/Green less affected. These results agree with Padilla et al. (2019) [27], who found that the Green Ratio Vegetation Index (GVI) was less affected by the time of day, and the Red Ratio Vegetation Index (RVI) was significantly affected. This study and previous work suggest that green reflectance is more stable under different irradiation conditions. Differences between normalized and simple ratio vegetation indices in response to the time of day could be attributed to measurement variability. Bannari et al. (1995) [8] have proposed that the normalized vegetation indices enable compensation for non-uniform illumination effects compared to simple ratio indices. Within the different vegetation indices evaluated in the present work, the vegetation indices based on the Green or Red edge band seem to be more stable throughout the day than the indices based on the Red band. Similar findings were reported for tomatoes [7].
4.2. Sensor Specific Performance Influenced by Time of Day
Within the active sensors used in the current work, the indices calculated from the Crop Circle ACS-470 sensor showed smaller differences between measurement times than indices calculated from the active sensor Greenseeker RT100. This observation agrees with the findings of Oliveira and Scharf (2014) [12], who noticed that the average coefficient of variation for the Greenseeker was larger than for the Crop Circle for visible/near-infrared (Vis/NIR) (p = 0.01) and the normalized difference vegetative index (NDVI) as well (p = 0.15). Overall, the results are consistent with the long-stated assumption that active canopy reflectance sensors can be used under any irradiance conditions without substantial alterations in vegetation indices measured [26,27]. However, despite the Greenseeker RT100 being an active sensor, differences between measurement times were found for the NIR/Red ratio and, to a smaller degree, for the NDVI. This result agrees with previous works that reported slight solar irradiance effects on measurements with the Greenseeker sensor [38,39]. In the present study, the NDVI measured with the Greenseeker RT100 was slightly lower at 14:00 than at 9:00 and 16:00 h, but this decline in NDVI values at 14:00 h was not observed with the Crop Circle ACS-470 sensor. The decline of the NDVI values measured with the Greenseeker sensor at midday has also been reported by Oliveira and Scharf (2014) [12] and Allen et al. (2009) [28] in cotton crops, thus suggesting that the decline of NDVI values is not due to plant properties; instead, it is probable that environmental conditions influenced the Greenseeker.
Big differences between paired time measurements were found for the vegetation indices measured with the UAV, particularly for the NIR/Red ratio at 9:00 compared to 14:00 h, with a difference of approximately 36%. The variation throughout the day in the vegetation indices calculated from UAVs has been reported in previous works. Rasmussen et al. (2016) [30] and Verger et al. (2014) [29] found that vegetation indices based on UAV imagery had the same capability to quantify crop responses as ground-based sensors. However, it is necessary to consider the angular variation in reflectance [29] and ambient light fluctuations [30]. These shortcomings could be partly responsible for the differences found in the present study between measurement times in the vegetation indices calculated from UAV imagery, mainly for the ratio vegetation indices. This means it is necessary to consider the time effect on UAVs measurements considering sun elevation angles.
Within the passive hyperspectral sensors used in the current work, the bidirectional vehicle-based spectrometer showed smaller differences between paired time measurements than the HandySpec sensor. However, differences between paired time measurements were less than 5% for the NIR/Red edge, water index, and REIP in both sensors, plus NDVI and GNDVI for the HandySpec sensor. Overall, the hyperspectral bidirectional passive sensors, whether being vehicle-based or handheld, delivered the best performance regarding the stability over time with differences lower than 2% and 4%, respectively, for the indices NIR/Red edge ratio, REIP, and the water index. These results are important for a practical application of these sensors since they suggest that it could be feasible to use these passive sensors at any time of day from 9:00 to 16:00 h without large impacts on measurement values. Previous research carried out over many years in different locations agrees with this observation; in narrow row crops such as wheat or barley grown in high-yielding environments, even better performance could be achieved with bidirectional hyperspectral passive sensors compared with active sensors [17,40,41]. It is important to notice that this study’s hyperspectral sensors simultaneously measured the incident radiation and reflectance, making them exceptionally robust to changes over time. This conclusion may not apply to passive sensors measuring only reflectance hence requiring frequent calibrations. In contrast, a major advantage of active sensors is the possibility of carrying out reliable measurements even outside the investigated daytime windows and particularly at night. Since sensors are now also used at early or late daytime and even in the night for fertilizing or pesticide spraying, optimized atmospheric conditions with lower wind speed and extended working slots can be used to make better use of the soil trafficability.
4.3. Evaluation of Sky Condition Effects
The differences detected between a completely sunny and overcast day in the vegetation indices measured with the active Crop Circle ACS-470 sensor can be considered small since the differences between both sky conditions were less than 5%. Similar results were found by Fitzgerald (2010) [25] in wheat, where the Crop Circle sensor was insensitive to light conditions (cloudy versus clear sky).
There were deviating values observed on the overcast day, relative to the succeeding sunny day, measured with the Greenseeker RT100, mainly for the NDVI index. This agrees with the findings of Allen et al. (2009) [28], where a reduction of solar radiation due to cloud covering led to increased NDVI values.
Regarding the passive hyperspectral sensors used, the differences between measurements conducted on a sunny and overcast day were more dependent on the vegetation indices evaluated than on the kind of sensor. Within both passive sensors evaluated, the differences between sky conditions were slightly higher for the vegetation indices measured with the HandySpec sensor than the vehicle-carried spectrometer. Therefore, in practical terms, the vehicle-based bidirectional spectrometer could be more reliable for farming to assess the biomass and plant health status. The fixed position on a carrier vehicle seems to allow for higher stability in reflectance measurements than handheld measurements.
This study has investigated the influence of daytime and sky conditions on reflectance indices of the narrow row crop winter wheat using several ground-based sensors and an aerial UAV sensor. Possible reflectance changes due to daytime might be more pronounced in tall row crops such as maize, where shadowing effects are expected to play a larger role. All sensors in this study were oriented Nadir downwards in contrast to obliquely oriented sensors also used in precision farming. Interaction of the sensor orientation and the radiation source’s orientation might be relevant and deserve further attention in future studies. It is also evident that bidirectional sensors used in this study can better cope with possible frequent radiation changes throughout the day, e.g., due to varying cloudiness, which was not investigated in this study by choosing days with full sunshine except one measurement conducted under overcast condition. This study’s results have further indicated that daytime effects might be particularly relevant in multispectral UAV imagery sensing. This might also be due to the first generation of light sensors embedded in the current version of the camera used and might open room for further improvements.
5. Conclusions
Regardless of the sensors used (active or passive sensors), the effect of the measurement time or sky conditions on the sensor measurements depended on the vegetation indices considered. In general, the most stable indices over time of day and contrasting sky conditions were the NIR/Red edge ratio, water index, and REIP index. On the other hand, the vegetation indices more variable throughout the day and under varying sky conditions were the simple ratios NIR/Red and NIR/Green.
The most stable measurements throughout the day and sky conditions were obtained by the passive hyperspectral sensors and the active Crop Circle ACS470 sensor. A comparison of a vehicle-based and a handheld passive spectrometer, both measuring bidirectionally, showed that the handheld sensor was slightly more dependent on the time of measurement and sky conditions. Handheld systems are frequently used in agronomic plot experimentation, whereas vehicle-based sensing is standard in practical farming. Some differences between the two active sensors might partly be due to the higher flexibility in choosing optimized indices since the Crop Circle ACS470 allows for a user-specific choice of filters. The time effect on UAV measurements should further be researched considering the angular variation in reflectance.
In practical terms, these results confirm that by choosing optimized indices, ground-based passive and active sensors could be used to measure on-farm at any time of day.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.S. and R.d.S.; methodology, U.S., R.d.S., J.P., and C.B.; investigation U.S. and R.d.S.; data curation, R.d.S., J.P., and C.B.; data analysis, R.d.S., F.M.P., and K.H.; writing—original draft preparation, R.d.S., and F.M.P.; writing—review and editing, R.d.S., F.M.P., and U.S..; funding acquisition, U.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research work was supported by funds of the Federal Ministry of Food and Agriculture (BMEL) based on a decision of the Parliament of the Federal Republic of Germany via the Federal Office for Agriculture and Food (BLE) under the innovation support program for the project 28-1-B3.030-16. R.d.S. was supported by an FPI grant (BES-2016-076706) and F.M.P. by a Ramón y Cajal grant (RYC-2014-15815), both from the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff of the Dürnast research station of the Technical University of Munich for conducting the trials. Pertinent and constructive comments made by the reviewers are highly acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Thompson, R.B.; Tremblay, N.; Fink, M.; Gallardo, M.; Padilla, F.M. Tools and strategies for sustainable nitrogen fertilisation of vegetable crops. In Advances in Research on Fertilization Management in Vegetable Crops; Tei, F., Nicola, S., Benincasa, P., Eds.; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 11–63. [Google Scholar]
- Scharf, P.C.; Shannon, D.K.; Palm, H.L.; Sudduth, K.A.; Drummond, S.T.; Kitchen, N.R.; Mueller, L.J.; Hubbard, V.C.; Oliveira, L.F. Sensor-based nitrogen applications out-performed producer-chosen rates for corn in on-farm demonstrations. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, J.S.; Blackmer, T.M.; Wilhelm, W.W.; Resende, M. Transmittance and reflectance measurements of corn leaves from plants with different nitrogen and water supply. J. Plant Physiol. 1996, 148, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Goffart, J.P.; Ledent, J.F. Threshold value for chlorophyll meter as decision tool for nitrogen management of potato. Agron. J. 2006, 98, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira Martins, R.; Marcus Fialho e Moraes, H.; Fagundes Portes, M.; Orlando Junior, W.d.A.; Furtado Ribeiro Junior, M. Do optical sensor readings change throughout the day? An evaluation of two sensor systems. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1689–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, F.M.; Gallardo, M.; Peña-Fleitas, M.T.; de Souza, R.; Thompson, R.B. Proximal optical sensors for nitrogen management of vegetable crops: A review. Sensors 2018, 18, 2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianquinto, G.; Orsini, F.; Pennisi, G.; Bona, S. Sources of variation in assessing canopy reflectance of processing tomato by means of multispectral radiometry. Sensors 2019, 19, 4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Morin, D.; Bonn, F.; Huete, A.R. A review of vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 13, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Berjón, A.; López-Lozano, R.; Miller, J.R.; Martín, P.; Cachorro, V.; González, M.R.; De Frutos, A. Assessing vineyard condition with hyperspectral indices: Leaf and canopy reflectance simulation in a row-structured discontinuous canopy. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 99, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, J.M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, K.; Yao, X.; Tian, Y.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Improved estimation of leaf chlorophyll content of row crops from canopy reflectance spectra through minimizing canopy structural effects and optimizing off-noon observation time. Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 248, 111985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogirou, S.A. Environmental Characteristics. In Solar Energy Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 49–120. ISBN 978-0-12-374501-9. [Google Scholar]
- Oliveira, L.F.; Scharf, P.C. Diurnal variability in reflectance measurements from cotton. Crop Sci. 2014, 54, 1769–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ollinger, S. V Sources of variability in canopy reflectance and the convergent properties of plants. New Phytol. 2011, 189, 375–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usha, K.; Singh, B. Potential applications of remote sensing in horticulture—A review. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 153, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tremblay, N. Sensing technologies in horticulture: Options and challenges. Chron. Hortic. 2013, 53, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Gitelson, A.A.; Schepers, J.S.; Walthall, C.L. Application of spectral remote sensing for agronomic decisions. Agron. J. 2008, 100, S117–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdle, K.; Mistele, B.; Schmidhalter, U. Comparison of active and passive spectral sensors in discriminating biomass parameters and nitrogen status in wheat cultivars. Field Crop. Res. 2011, 124, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quemada, M.; Gabriel, J.L.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J. Airborne Hyperspectral Images and Ground-Level Optical Sensors As Assessment Tools for Maize Nitrogen Fertilization. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 2940–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Knapp, S.; Schmidhalter, U. Advancing high-throughput phenotyping of wheat in early selection cycles. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña, J.M.; Torres-Sánchez, J.; de Castro, A.I.; Kelly, M.; López-Granados, F. Weed Mapping in Early-Season Maize Fields Using Object-Based Analysis of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) Images. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelong, C.C.D.; Burger, P.; Jubelin, G.; Roux, B.; Labbé, S.; Baret, F. Assessment of unmanned aerial vehicles imagery for quantitative monitoring of wheat crop in small plots. Sensors 2008, 8, 3557–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haboudane, D.; Miller, J.R.; Pattey, E.; Zarco-Tejada, P.J.; Strachan, I.B. Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 90, 337–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza, E.G.; Scharf, P.C.; Sudduth, K.A. Sun position and cloud effects on reflectance and vegetation indices of corn. Agron. J. 2010, 102, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broge, N.H.; Thomsen, A.G.; Andersen, P.B. Comparison of selected vegetation indices as indicators of crop status. Geoinf. Eur. Integr. 2003, 591–596. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/265814721_Comparison_of_selected_vegetation_indices_as_indicators_of_crop_status (accessed on 23 April 2021).
- Fitzgerald, G.J. Characterizing vegetation indices derived from active and passive sensors. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 4335–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kipp, S.; Mistele, B.; Schmidhalter, U. The performance of active spectral reflectance sensors as influenced by measuring distance, device temperature and light intensity. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 100, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla, F.M.; de Souza, R.; Peña-Fleitas, M.T.; Grasso, R.; Gallardo, M.; Thompson, R.B. Influence of time of day on measurement with chlorophyll meters and canopy reflectance sensors of different crop N status. Precis. Agric. 2019, 20, 1087–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, P.; Wilkerson, J.; Benitez Ramirez, M. Evaluating Temporal Variation in Active-Light Plant Sensors. In Proceedings of the Beltwide Cotton Conferences, San Antonio, TX, USA; 2009; pp. 367–373. [Google Scholar]
- Verger, A.; Vigneau, N.; Chéron, C.; Gilliot, J.M.; Comar, A.; Baret, F. Green area index from an unmanned aerial system over wheat and rapeseed crops. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, J.; Ntakos, G.; Nielsen, J.; Svensgaard, J.; Poulsen, R.N.; Christensen, S. Are vegetation indices derived from consumer-grade cameras mounted on UAVs sufficiently reliable for assessing experimental plots? Eur. J. Agron. 2016, 74, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmeier, G.; Schmidhalter, U. High-throughput field phenotyping of leaves, leaf sheaths, culms and ears of spring barley cultivars at anthesis and dough ripeness. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellers, P.J. Canopy reflectance, photosynthesis and transpiration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1985, 6, 1335–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.L.; Morrison, M.J.; Dwyer, L.M. Canopy light reflectance and field greenness to assess nitrogen fertilization and yield of maize. Agron. J. 1996, 88, 915–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birth, G.S.; McVey, G.R. Measuring the color of growing turf with a reflectance spectrophotometer. Agron. J. 1968, 60, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Gritz, Y.; Merzlyak, M.N. Relationships between leaf chlorophyll content and spectral reflectance and algorithms for non-destructive chlorophyll assessment in higher plant leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 160, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Biel, C.; Serrano, L.; Savé, R. The reflectance at the 950–970 nm region as an indicator of plant water status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1887–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyot, G.; Baret, F.; Major, D.J. High spectral resolution: Determination of spectral shifts between the red and infrared. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1988, 11, 750–760. [Google Scholar]
- Teixeira Crusiol, L.G.; Corrêa Carvalho, J.F.; Ribeiro Sibaldelli, R.N.; Neiverth, W.; Do Rio, A.; Ferreira, L.C.; de Oliveira Procópio, S.; Mertz-Henning, L.M.; Lima Nepomuceno, A.; Neumaier, N.; et al. NDVI variation according to the time of measurement, sampling size, positioning of sensor and water regime in different soybean cultivars. Precis. Agric. 2017, 18, 470–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Glenn, D.M.; Park, J.; Ngugi, H.K.; Lehman, B.L. Characteristics of active spectral sensor for plant sensing. Trans. ASABE 2012, 55, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmeier, G.; Schmidhalter, U. High-throughput phenotyping of wheat and barley plants grown in single or few rows in small plots using active and passive spectral proximal sensing. Sensors 2016, 16, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, E.; Schmidhalter, U. Evaluation of yield and drought using active and passive spectral sensing systems at the reproductive stage in wheat. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).