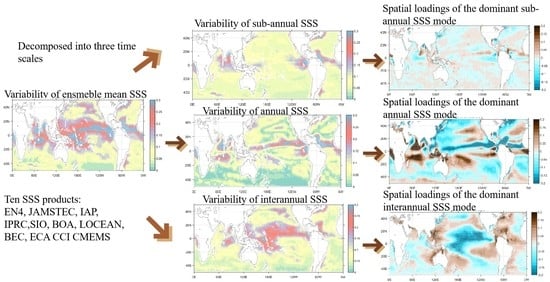
Intercomparison of Global Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Datasets over 2011–2018
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SMOS Satellite-Based Product
2.1.1. SMOS LOCEAN
2.1.2. SMOS BEC
2.1.3. ESA CCI SSS
2.1.4. CMEMS SSS
2.2. In Situ-Based SSS Products
2.2.1. EN4
2.2.2. JAMSTEC Argo
2.2.3. IAP
2.2.4. IPRC
2.2.5. SIO
2.2.6. BOA
2.3. Methods
3. Results
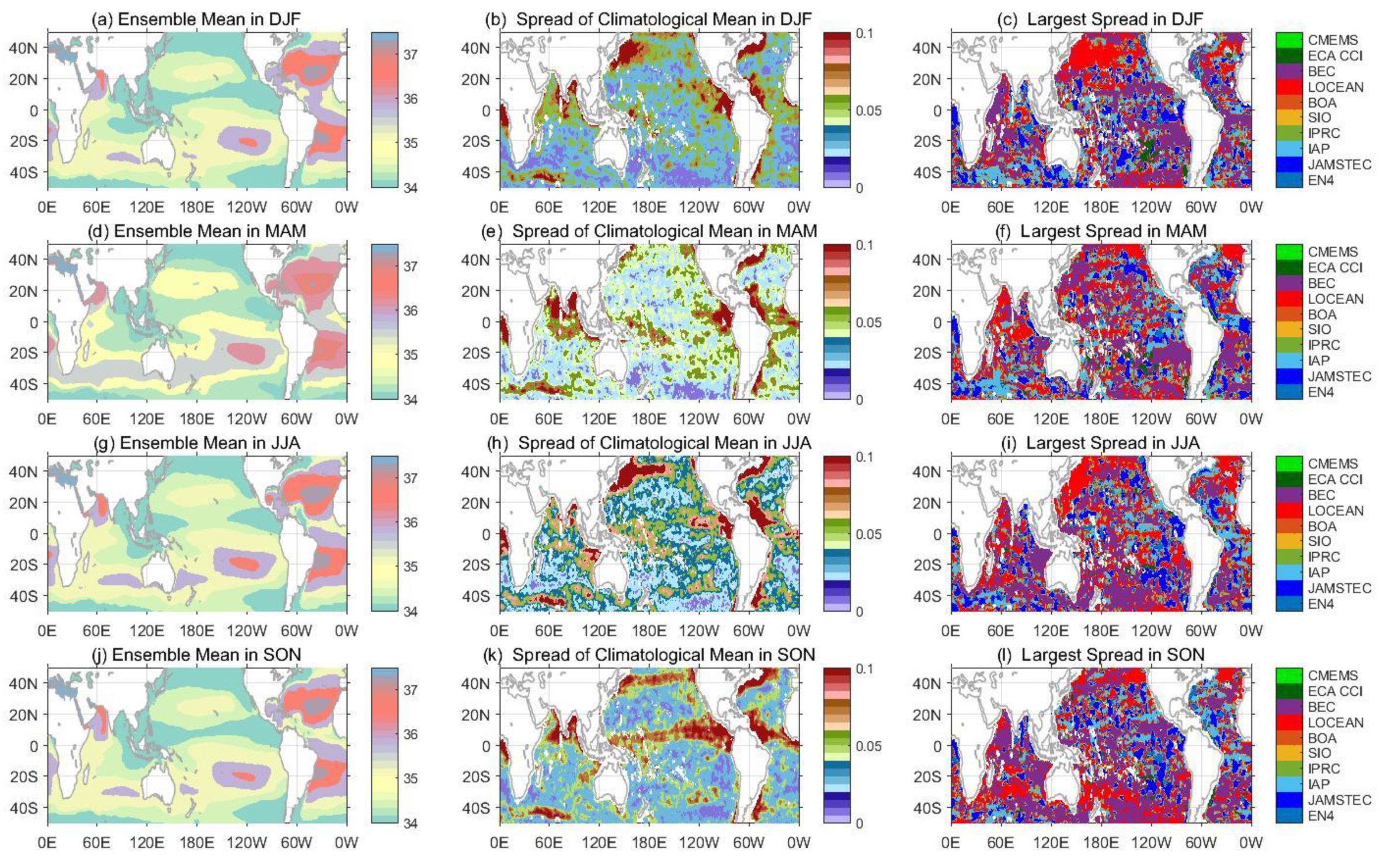
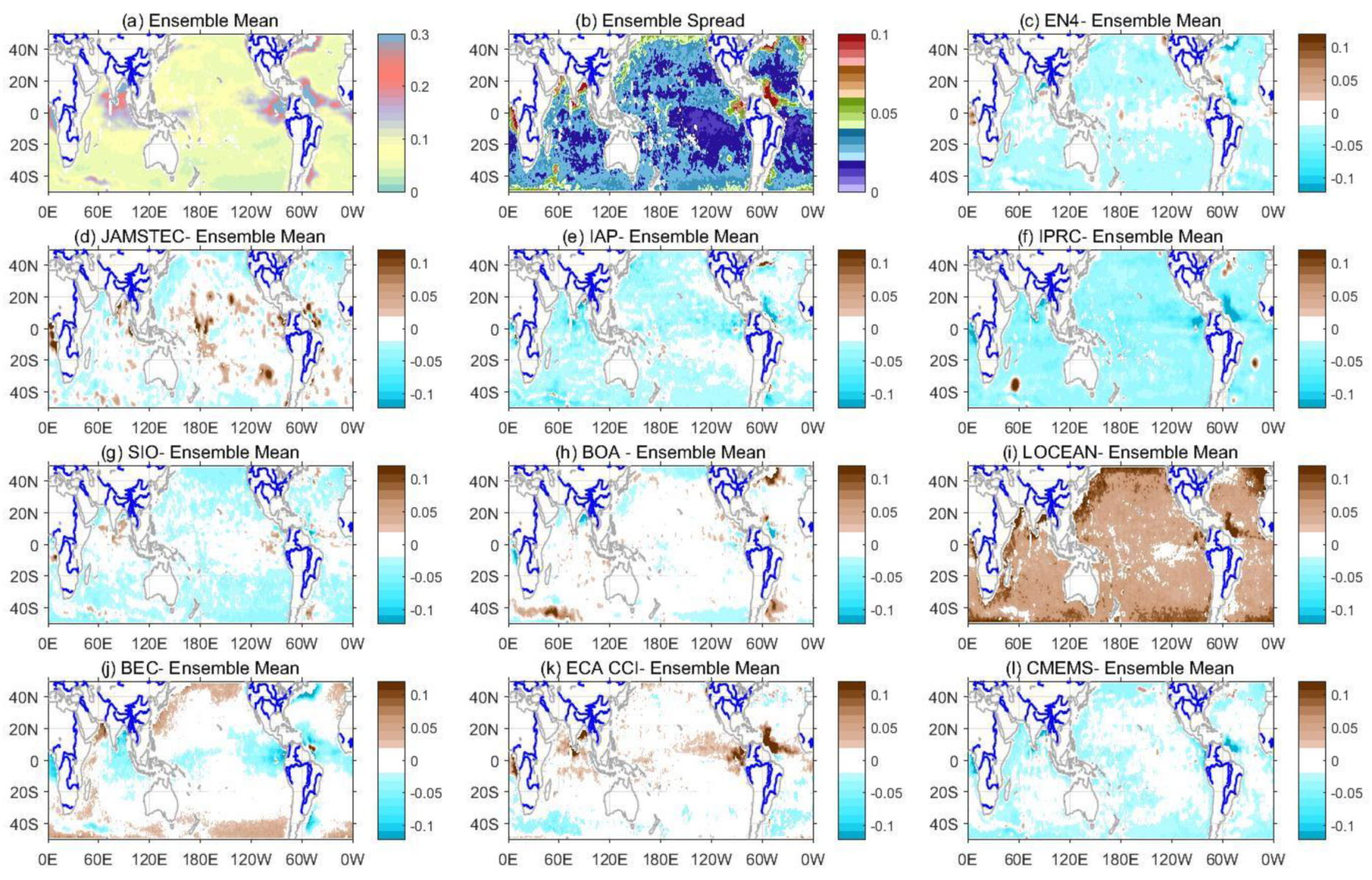
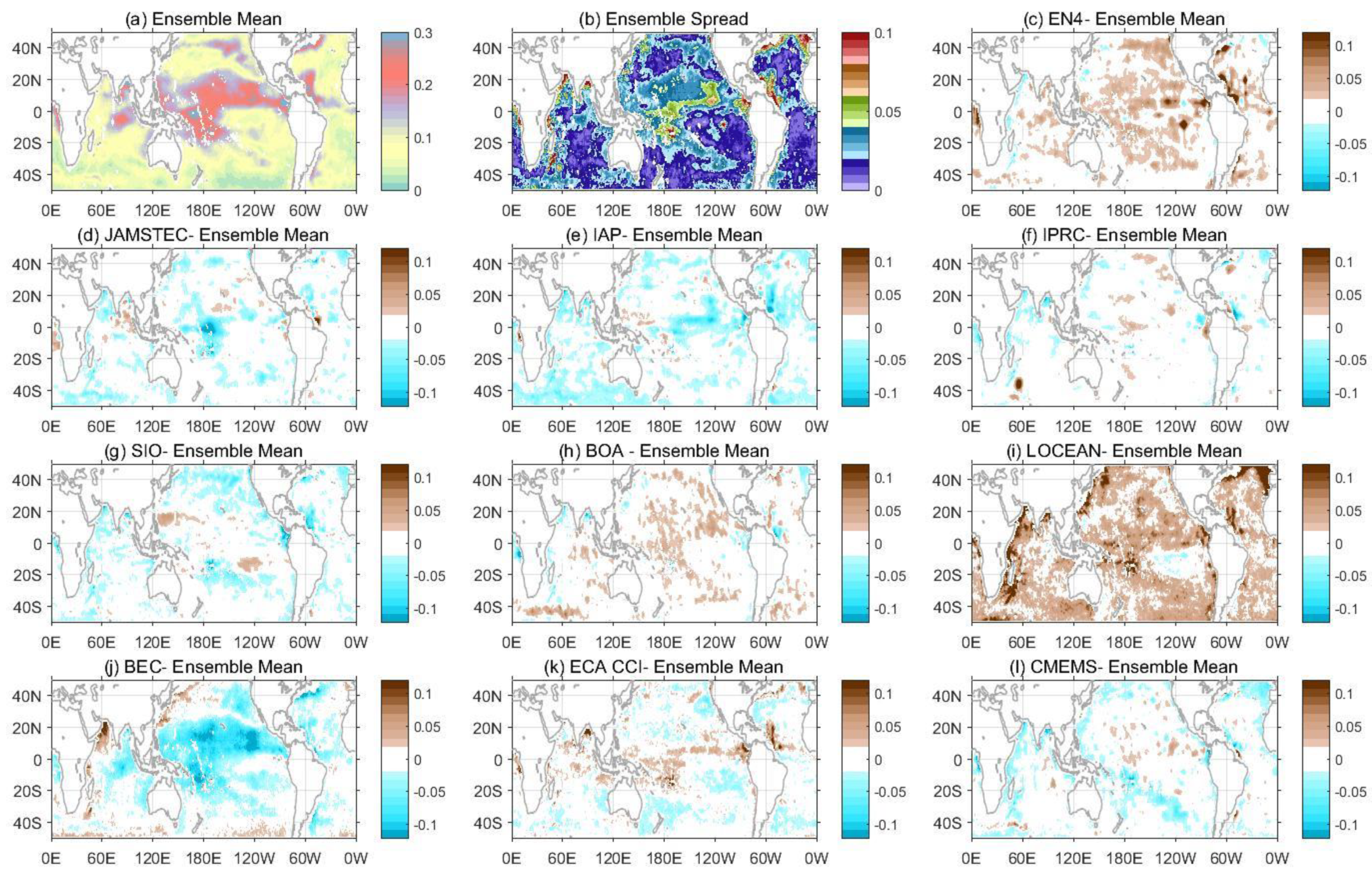
3.1. Mean State and Variability
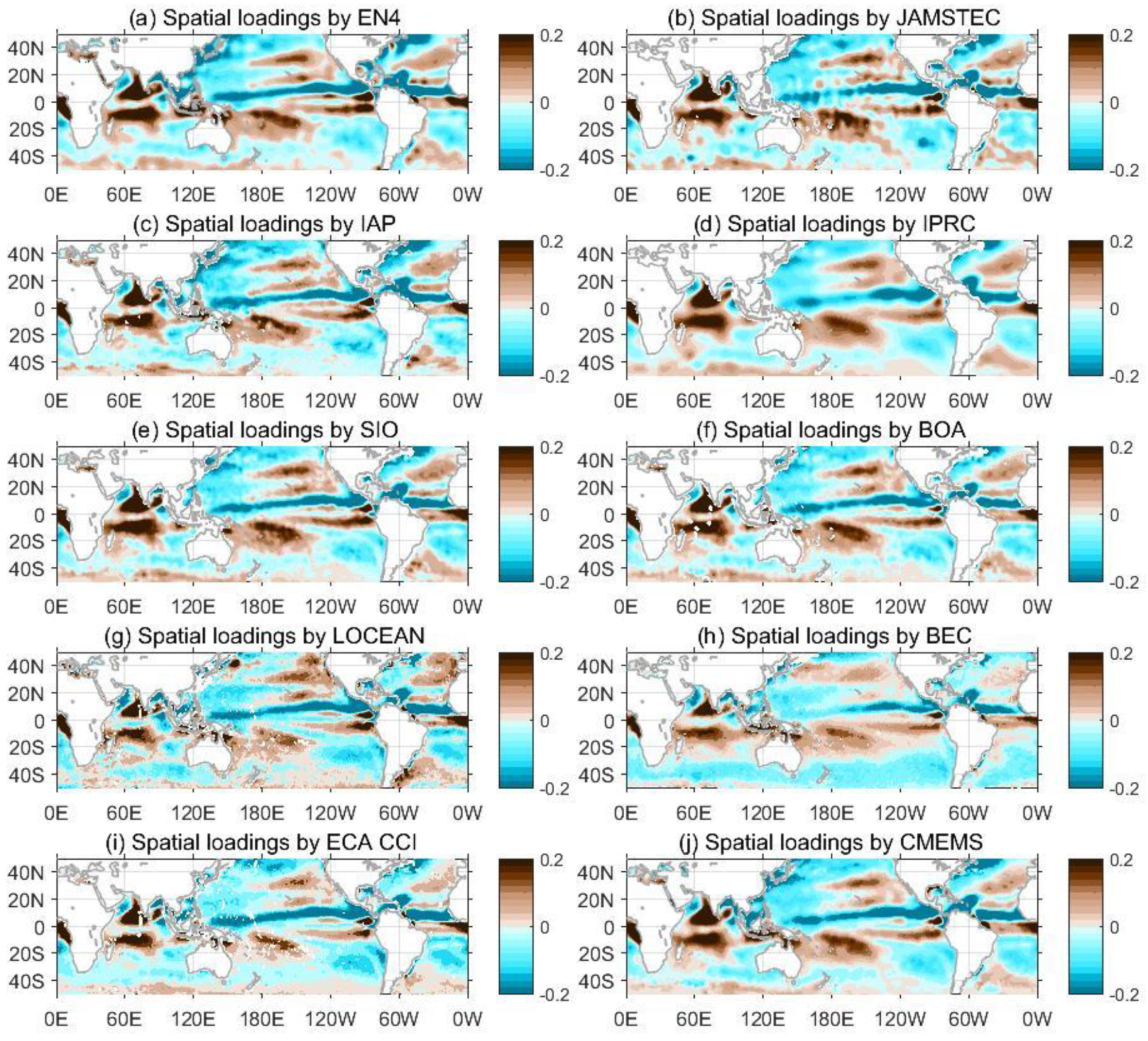
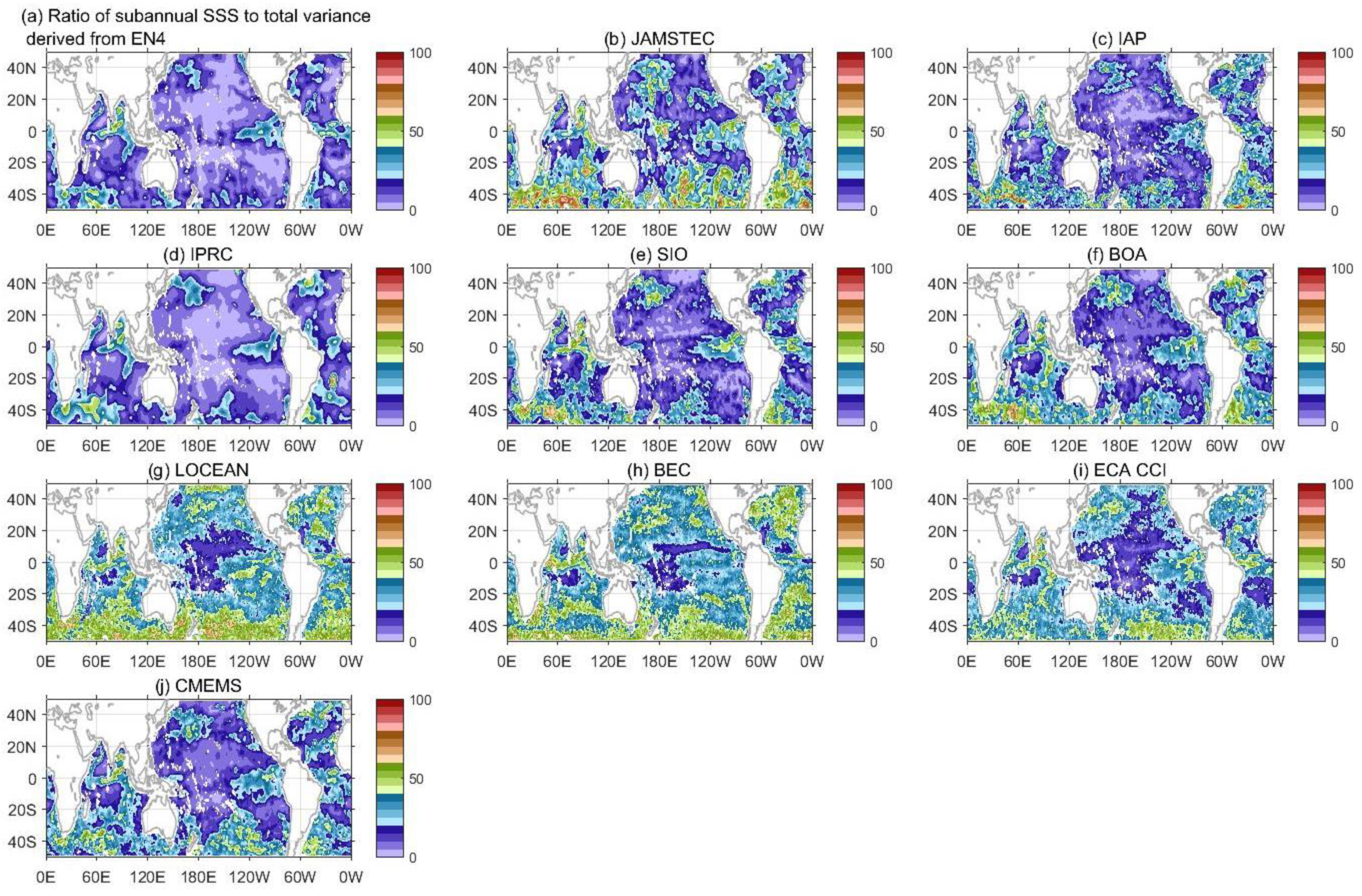
3.2. Sub-Annual SSS Variability
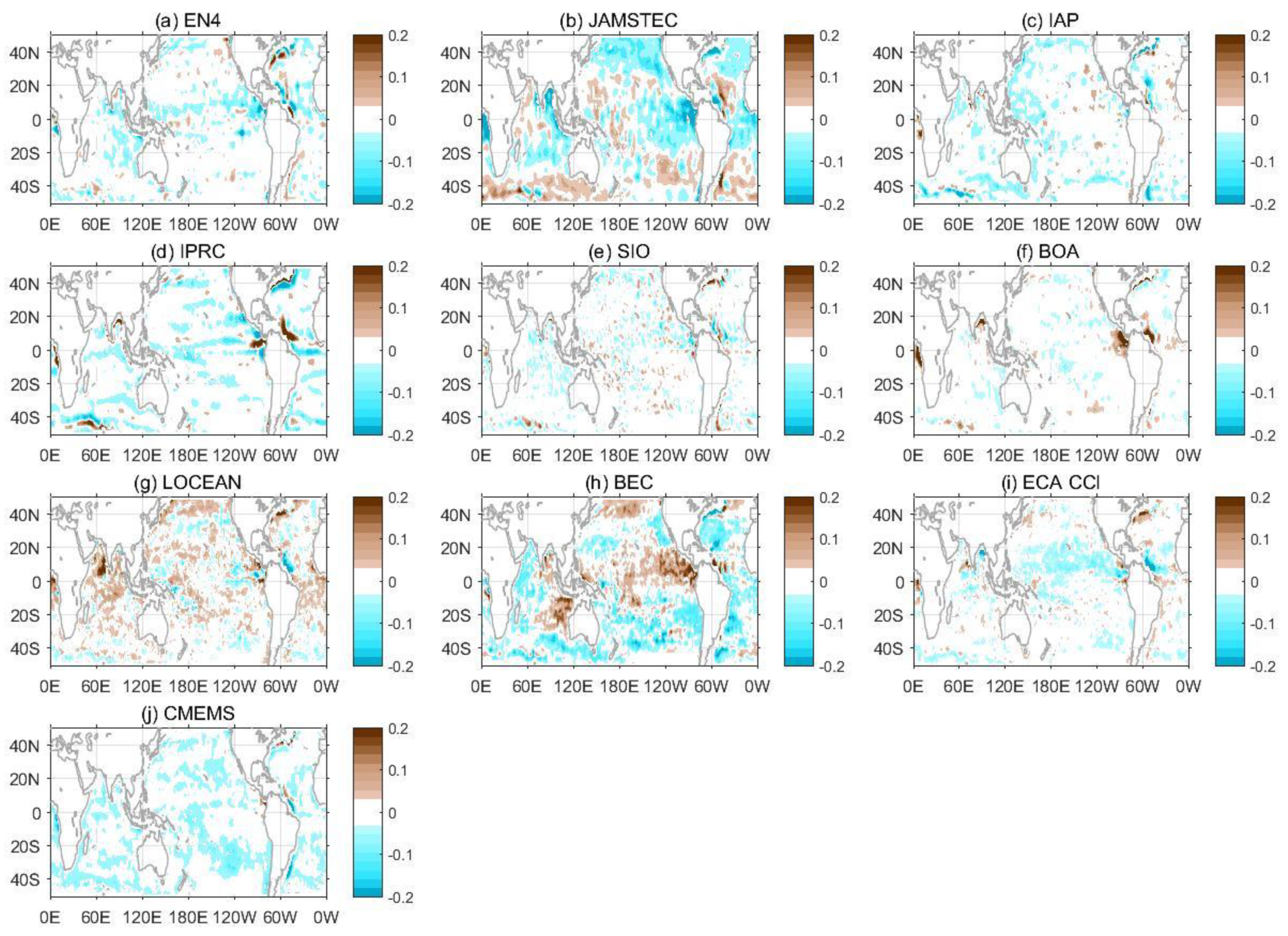
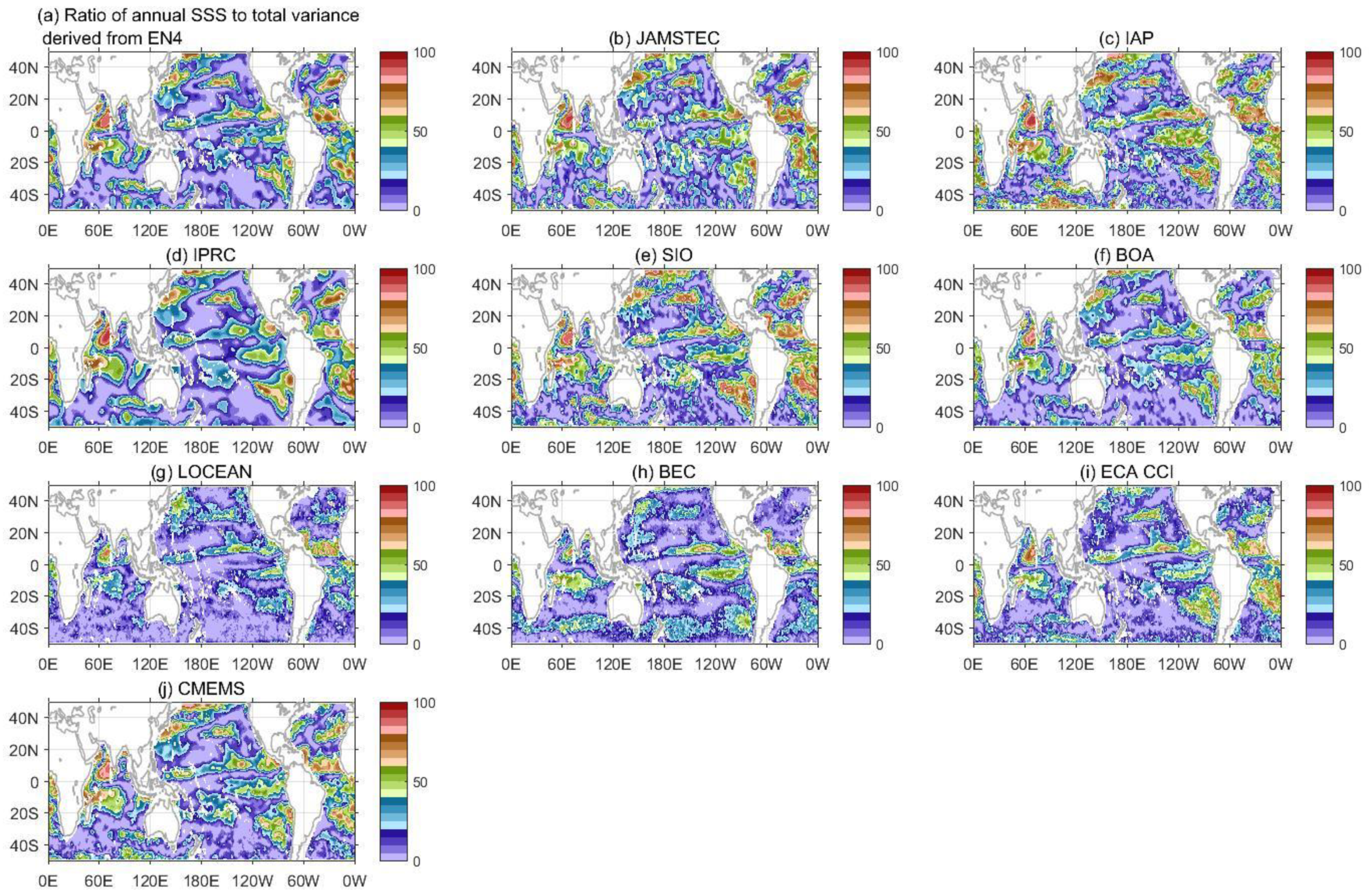
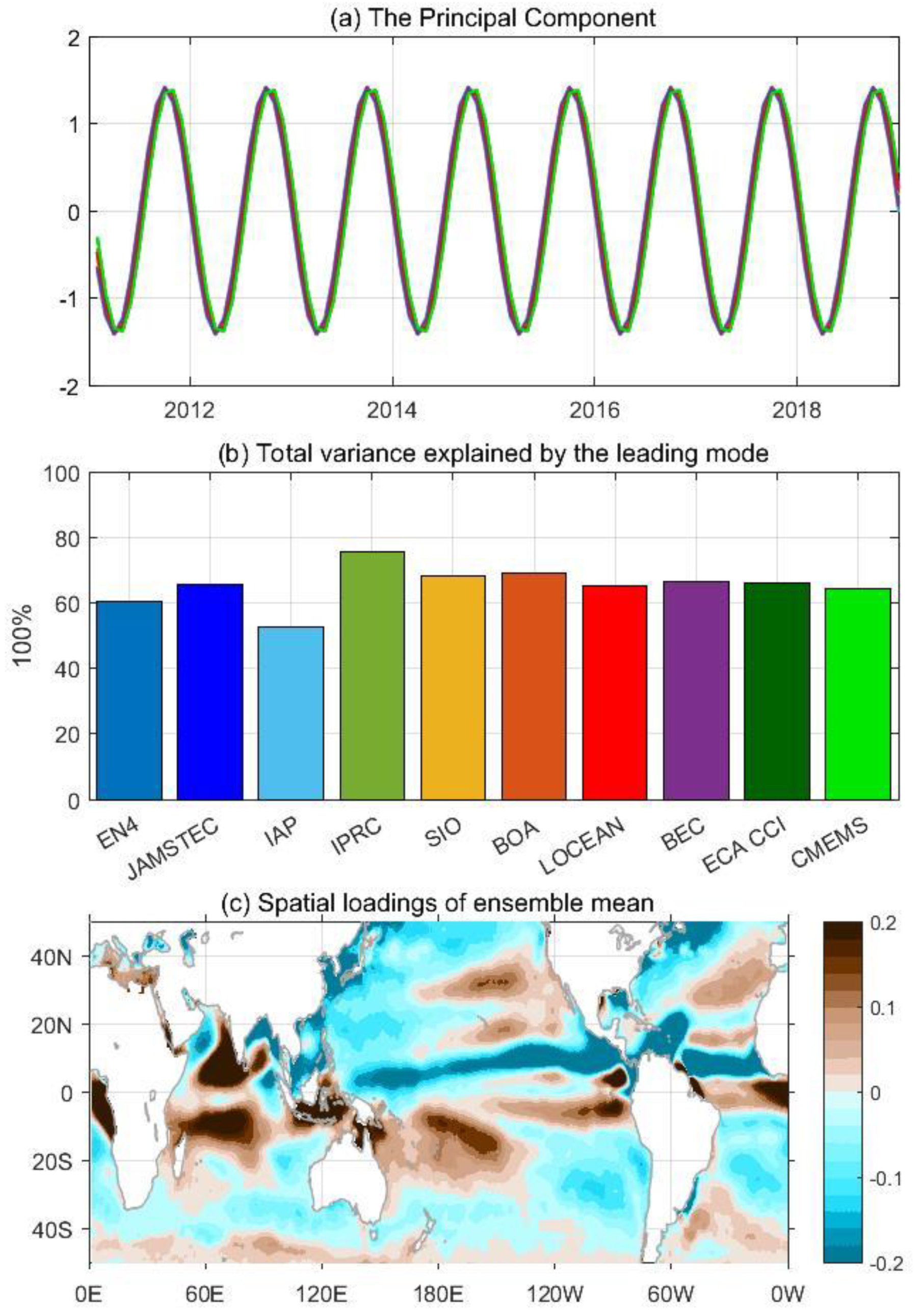
3.3. The Annual Cycle of SSS
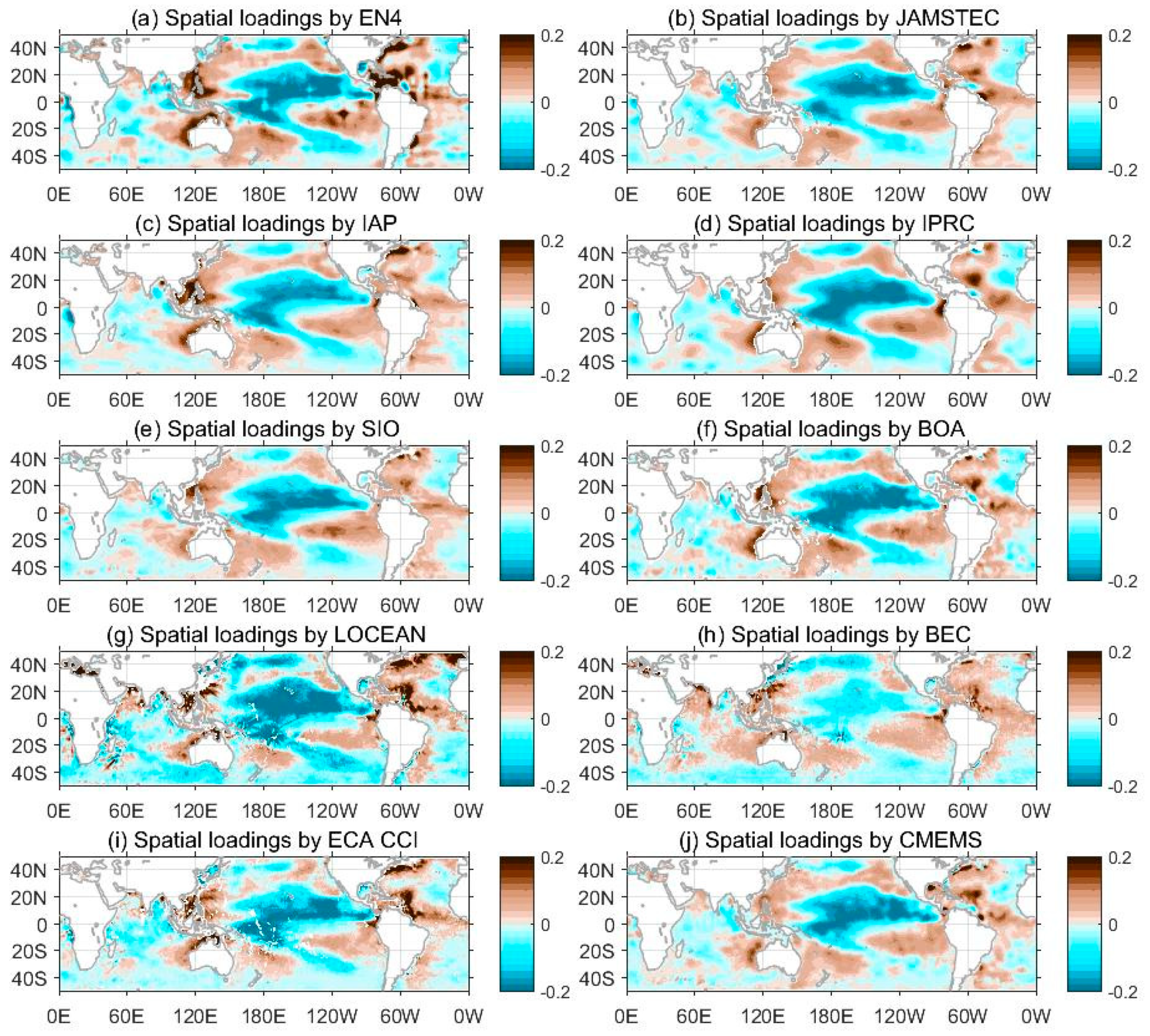
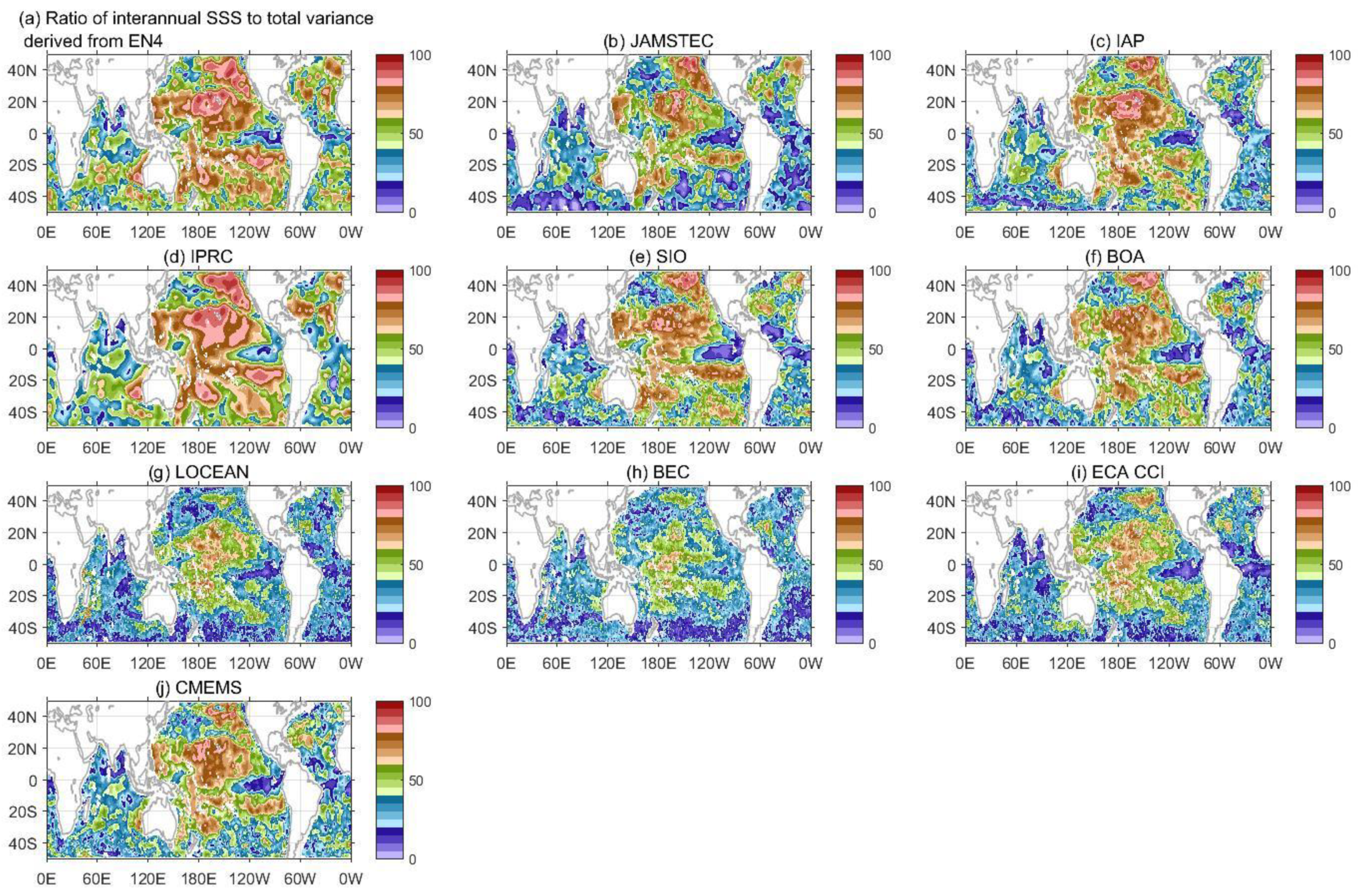
3.4. Interannual Variability in SSS
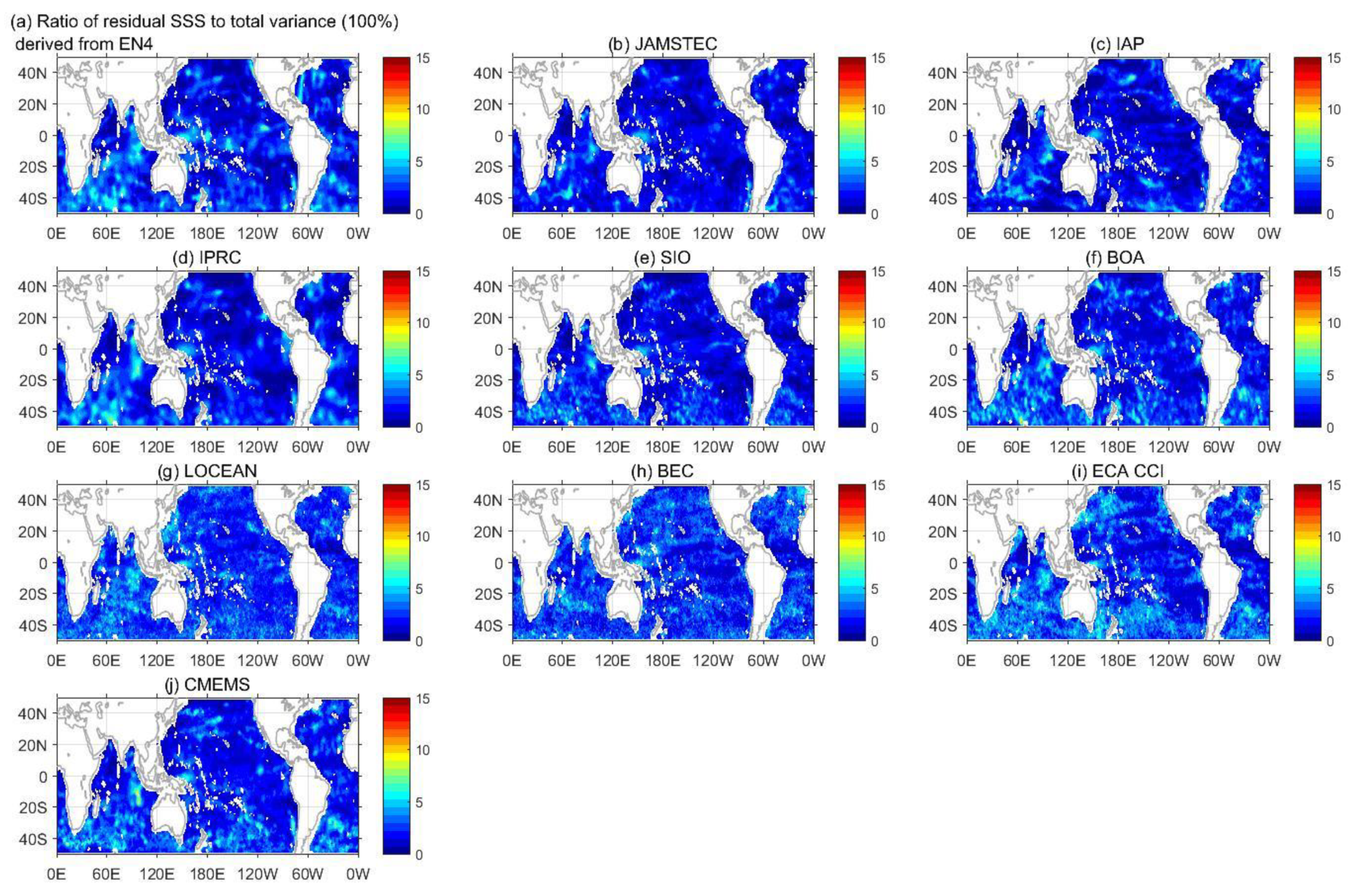
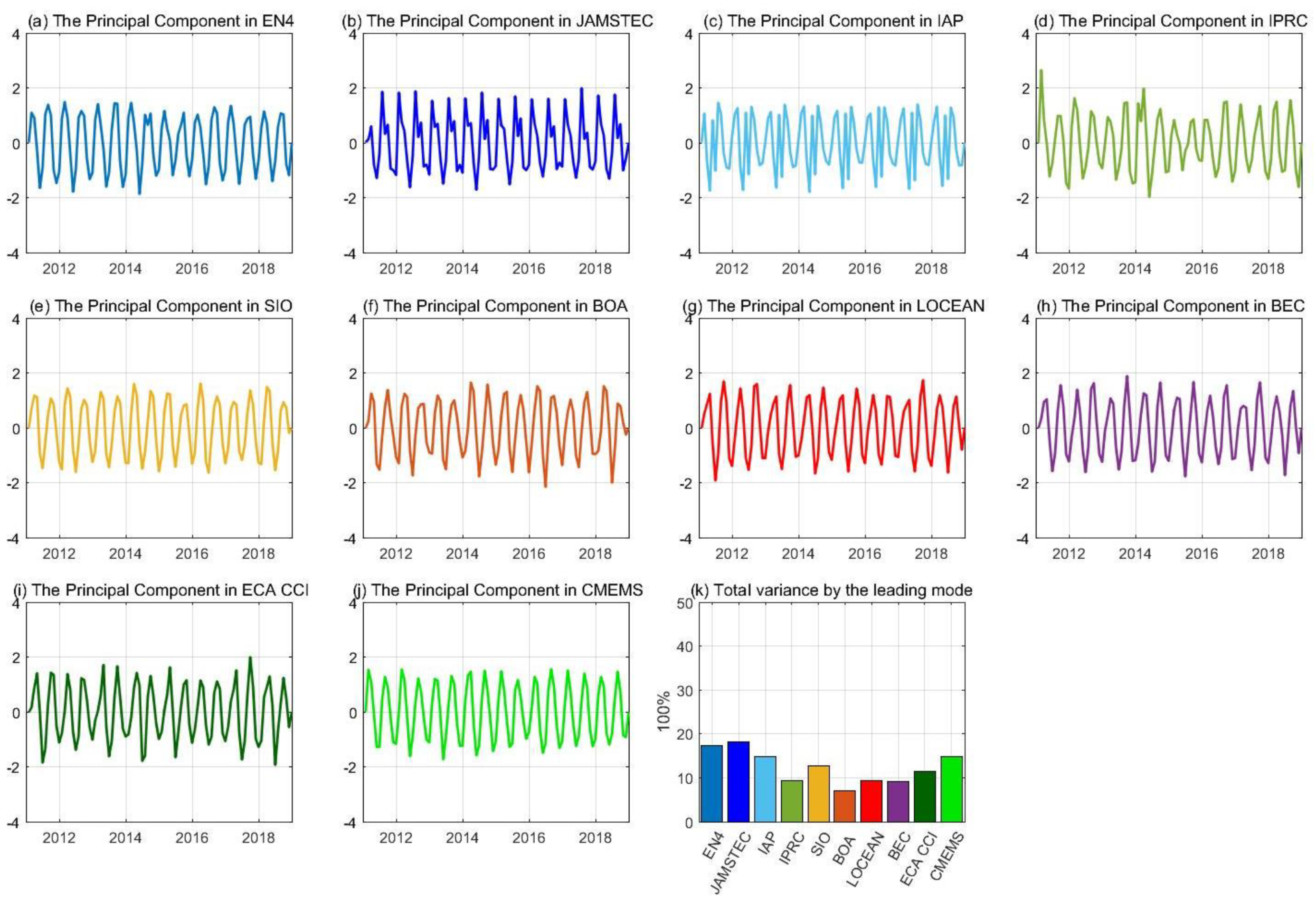
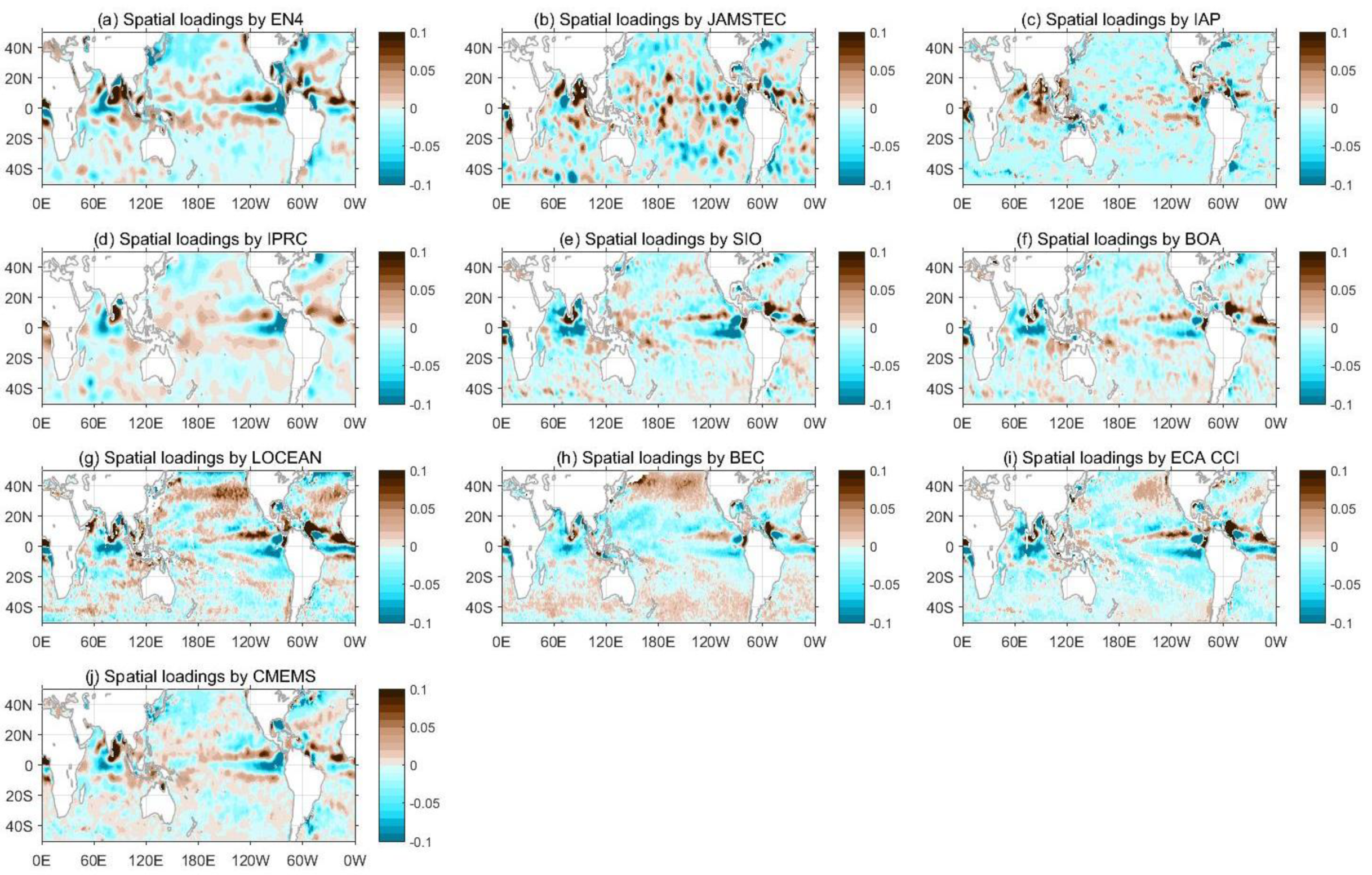
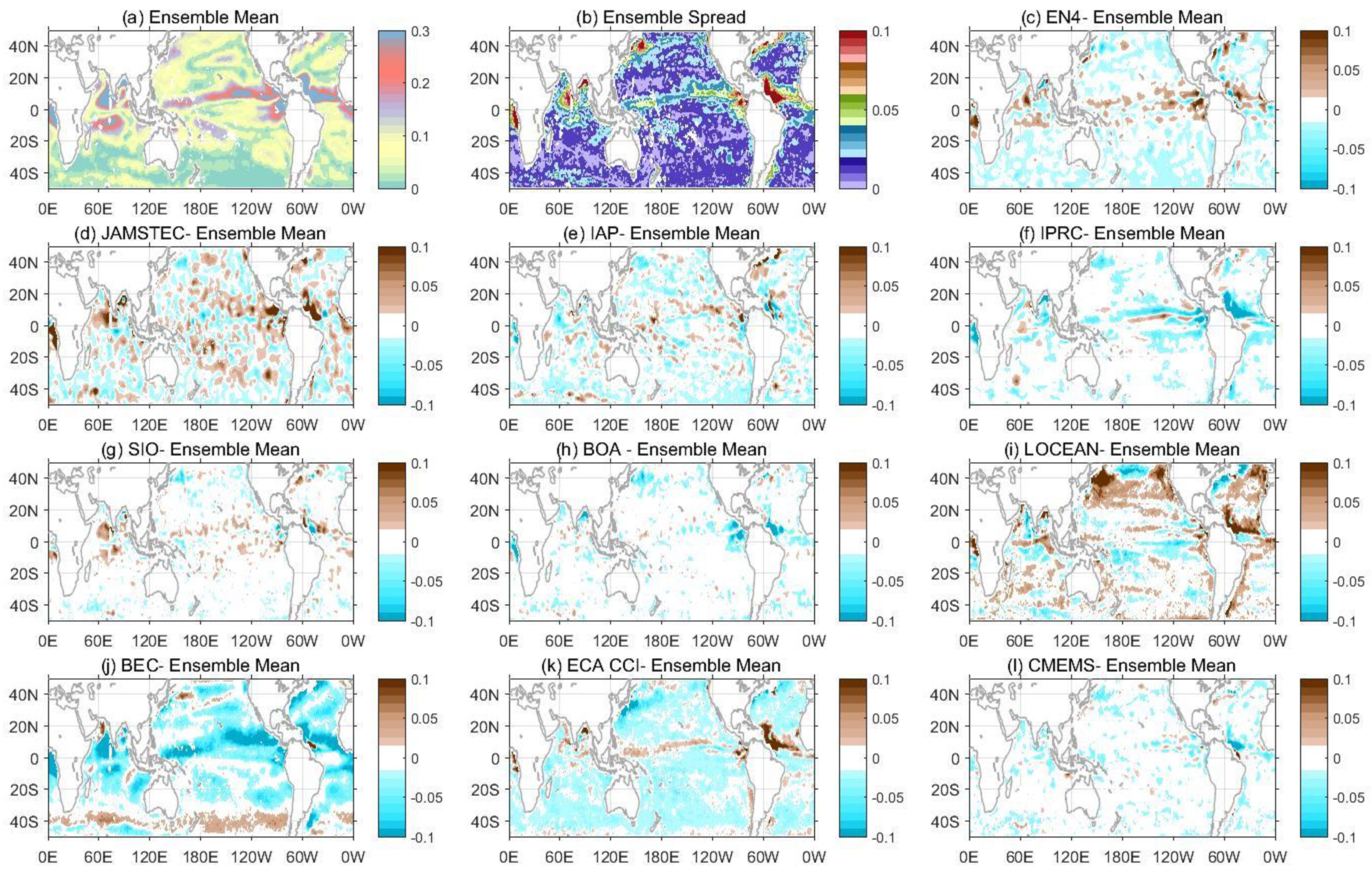
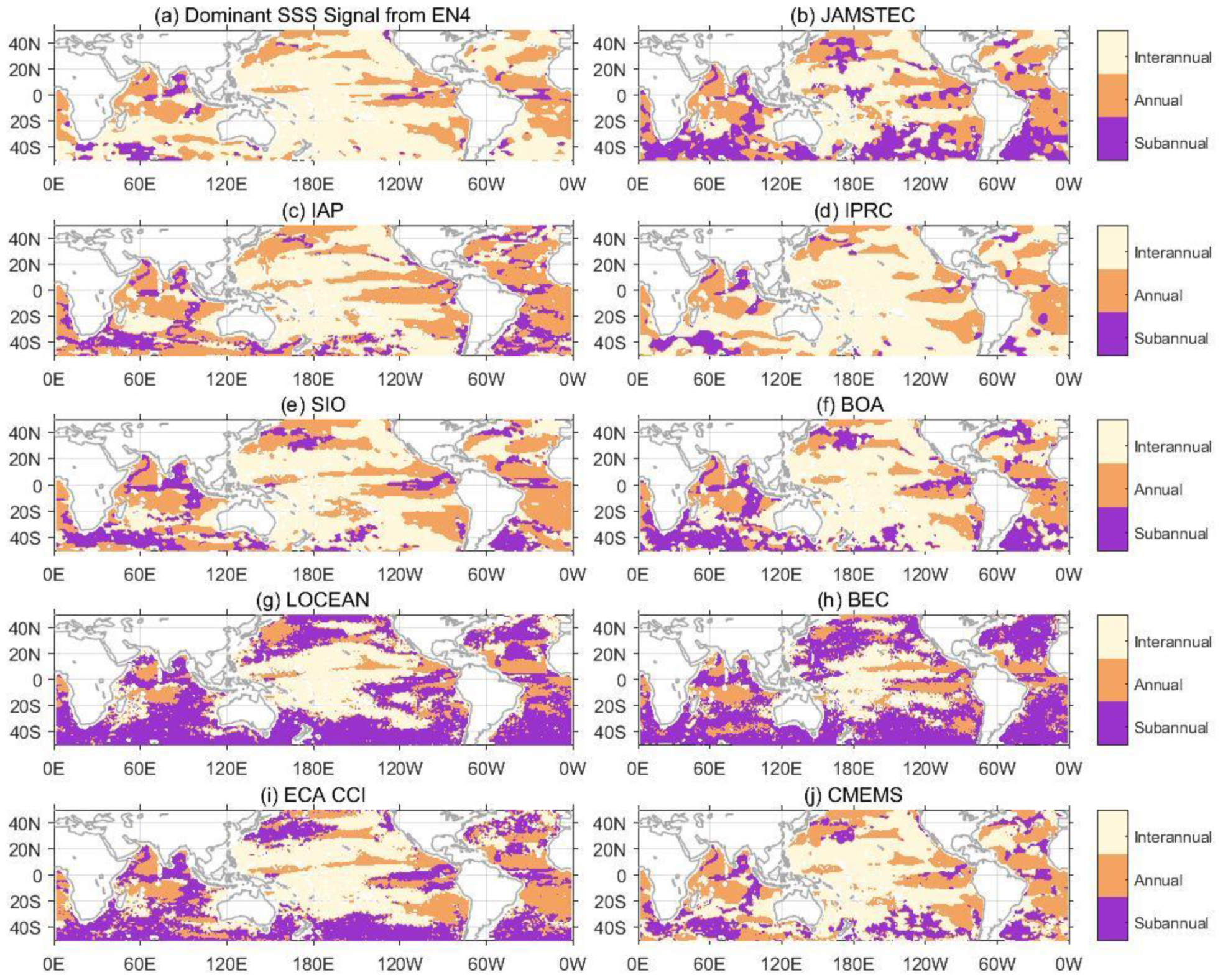
3.5. The Dominant SSS Signal
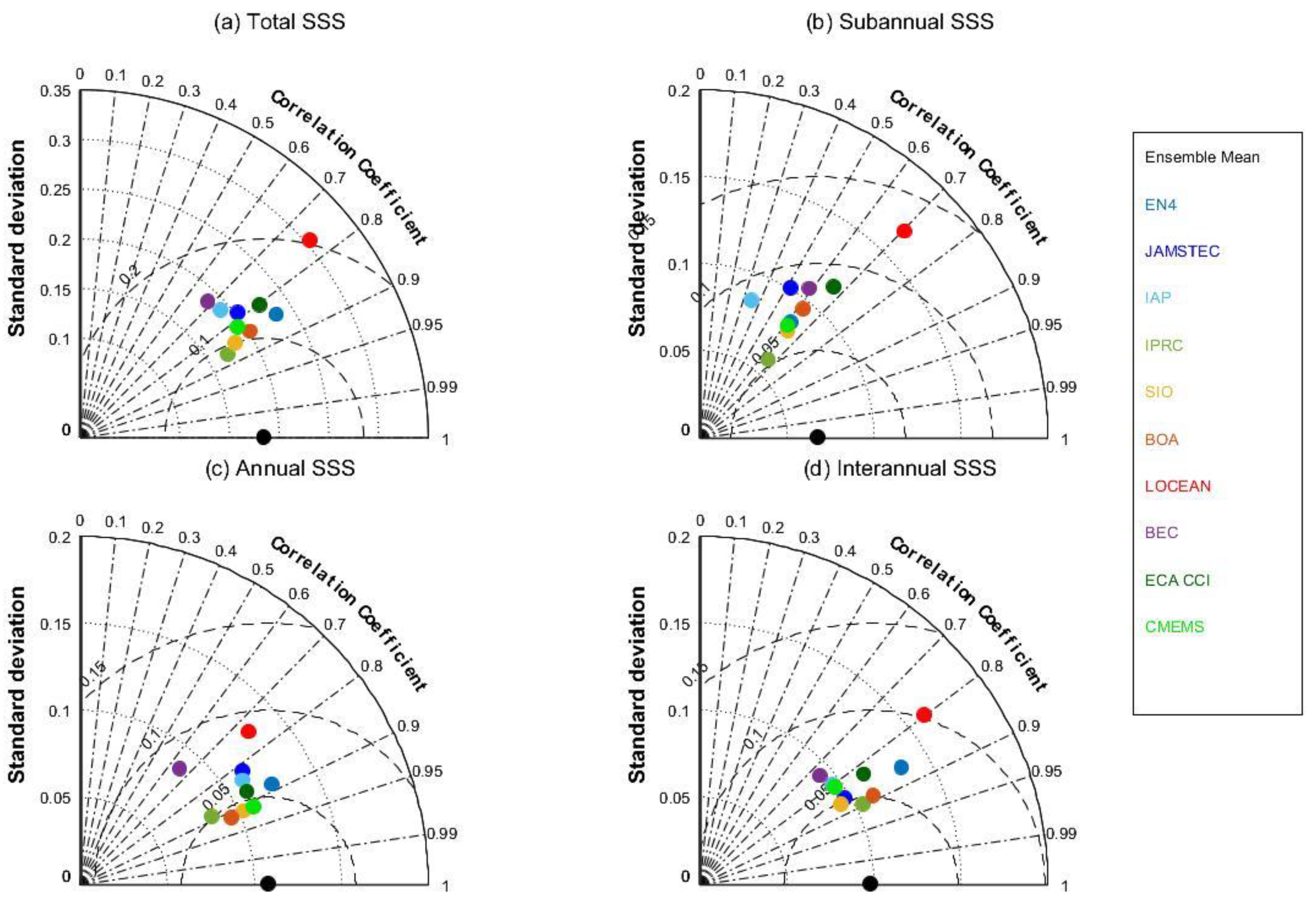
3.6. The Statistical Summary
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A

References
- Schmitt, R. Salinity and the Global Water Cycle. Oceanography 2008, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, K.P.; Bindoff, N.L.; Church, J.A. Changes in the global hydrological-cycle inferred from ocean salinity. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durack, P.J.; Wijffels, S.E. Fifty-year trends in global ocean salinities and their relationship to broad-scale warming. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 4342–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skliris, N.; Marsh, R.; Josey, S.A.; Good, S.A.; Liu, C.; Allan, R.P. Salinity changes in the World Ocean since 1950 in relation to changing surface freshwater fluxes. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 709–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Cheng, L.; Boyer, T.P.; Li, C. Halosteric Sea Level Changes during the Argo Era. Water 2017, 9, 484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lagerloef, G.; Gierach, M.M.; Kao, H.Y.; Yueh, S.; Dohan, K. Aquarius reveals salinity structure of tropical instability waves. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Boutin, J.; Reverdin, G.; Lee, T.; Arnault, S.; Martin, N. SMOS S ea S urface S alinity signals of tropical instability waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 7811–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, V.V.; Vianna, M.L.; Phillips, H.E. Aquarius sea surface salinity in the South Indian Ocean: Revealing annual-period planetary waves. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 3883–3908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcroix, T. Observed surface oceanic and atmospheric variability in the tropical Pacific at seasonal and ENSO timescales: A tentative overview. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 1998, 103, 18611–18633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballabrera-poy, J.; Murtugudde, R.; Busalacchi, A.J. On the potential impact of sea surface salinity observations on ENSO predictions. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 8007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, C.; Picaut, J.; Belamari, S. Salinity barrier layer and onset of El Nino in a Pacific coupled model. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Huang, B.; Zhang, R.-H.; Hu, Z.-Z.; Kumar, A.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Marx, L.; Kinter III, J.L. Salinity anomaly as a trigger for ENSO events. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, T.; Yu, J.-Y. ENSO indices from sea surface salinity observed by Aquarius and Argo. J. Oceanogr. 2014, 70, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverdin, G.; Kestenare, E.; Frankignoul, C.; Delcroix, T. Surface salinity in the Atlantic Ocean (30 S–50 N). Prog. Oceanogr. 2007, 73, 311–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, A.R.; Reverdin, G.; Khodri, M.; Gastineau, G. A new record of Atlantic sea surface salinity from 1896 to 2013 reveals the signatures of climate variability and long-term trends. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 1866–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argo. Argo Float Data and Metadata from Global Data Assembly Centre (Argo GDAC). Available online: https://www.seanoe.org/data/00311/42182/ (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Stammer, D.; Martins, M.S.; Köhler, J.; Köhl, A. How good do we know ocean salinity and its changes? Prog. Oceanogr. 2020, 109, 102478. [Google Scholar]
- Lagerloef, G.S.; Swift, C.T.; Le Vine, D.M. Sea surface salinity: The next remote sensing challenge. Oceanography 1995, 8, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droppleman, J.; Mennella, R.; Evans, D. An airborne measurement of the salinity variations of the Mississippi River outflow. J. Geophys. Res. 1970, 75, 5909–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Font, J.; Lagerloef, G.S.; Le Vine, D.M.; Camps, A.; Zanife, O.-Z. The determination of surface salinity with the European SMOS space mission. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2196–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reul, N.; Grodsky, S.; Arias, M.; Boutin, J.; Catany, R.; Chapron, B.; d’Amico, F.; Dinnat, E.; Donlon, C.; Fore, A. Sea surface salinity estimates from spaceborne L-band radiometers: An overview of the first decade of observation (2010–2019). Remote Sens. Environ. 2020, 242, 111769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.; Lee, T.; Boutin, J.; Drushka, K.; Fournier, S.; Sabia, R.; Stammer, D.; Bayler, E.; Reul, N.; Gordon, A. Satellite salinity observing system: Recent discoveries and the way forward. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Waldteufel, P.; Martin, N.; Caudal, G.; Dinnat, E. Surface salinity retrieved from SMOS measurements over the global ocean: Imprecisions due to sea surface roughness and temperature uncertainties. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2004, 21, 1432–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinnat, E.P.; Le Vine, D.M.; Boutin, J.; Meissner, T.; Lagerloef, G. Remote sensing of sea surface salinity: Comparison of satellite and in situ observations and impact of retrieval parameters. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Chao, Y.; Asher, W.E.; Delcroix, T.; Drucker, R.; Drushka, K.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Lee, T.; Reul, N.; Reverdin, G. Satellite and in situ salinity: Understanding near-surface stratification and subfootprint variability. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2016, 97, 1391–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Alves, O.; Wedd, R.; Balmaseda, M.; Chang, Y.; Chepurin, G.; Ferry, N.; Fujii, Y.; Gaillard, F.; Good, S. An assessment of upper ocean salinity content from the Ocean Reanalyses Inter-comparison Project (ORA-IP). Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 1009–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carton, J.A.; Penny, S.G.; Kalnay, E. Temperature and salinity variability in the SODA3, ECCO4r3, and ORAS5 ocean reanalyses, 1993–2015. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 2277–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liang, X.; Chambers, D.P.; Ponte, R.M. Global Patterns of Spatial and Temporal Variability in Salinity from Multiple Gridded Argo Products. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 8751–8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, T.; Domingues, C.M.; Good, S.A.; Johnson, G.C.; Lyman, J.M.; Ishii, M.; Gouretski, V.; Willis, J.K.; Antonov, J.; Wijffels, S. Sensitivity of global upper-ocean heat content estimates to mapping methods, XBT bias corrections, and baseline climatologies. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 4817–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan, J.; Boyer, T.; Antonov, J.; Zweng, M. Comparison analysis between Aquarius sea surface salinity and World Ocean Database in situ analyzed sea surface salinity. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2014, 119, 8122–8140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, R.; Yan, H.; Chen, J. Comparison of Satellite-Derived Sea Surface Salinity Products from SMOS, Aquarius, and SMAP. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemmich, D.; Gilson, J. The 2004–2008 mean and annual cycle of temperature, salinity, and steric height in the global ocean from the Argo Program. Prog. Oceanogr. 2009, 82, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, C.T.; Mcintosh, R.E. Considerations for microwave remote sensing of ocean-surface salinity. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1983, 4, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.-L.; Marchand, S.; d’Amico, F.; Hasson, A.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Reul, N.; Reverdin, G.; Vialard, J. New SMOS Sea Surface Salinity with reduced systematic errors and improved variability. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 214, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, S.A.; Martin, M.J.; Rayner, N.A. EN4: Quality controlled ocean temperature and salinity profiles and monthly objective analyses with uncertainty estimates. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 6704–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoda, S.; Suga, T.; Shikama, N.; Mizuno, K. Global surface layer salinity change detected by Argo and its implication for hydrological cycle intensification. J. Oceanogr. 2009, 65, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Trenberth, K.E.; Gruber, N.; Abraham, J.P.; Fasullo, J.T.; Li, G.; Mann, M.E.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, J. Improved estimates of changes in upper ocean salinity and the hydrological cycle. J. Clim. 2020, 33, 10357–10381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Xu, F.; Zhou, W.; Wang, D.; Wright, J.S.; Liu, Z.; Lin, Y. Development of a global gridded A rgo data set with B arnes successive corrections. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2017, 122, 866–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.; Thouvenin-Masson, C.; Supply, A.; Khvorostyanov, D. SMOS SSS L3 Maps Generated by CATDS CEC LOCEAN; Debias V4.0; Seanoe: Ancona, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Olmedo, E.; Martínez, J.; Turiel, A.; Ballabrera-Poy, J.; Portabella, M. Debiased non-Bayesian retrieval: A novel approach to SMOS Sea Surface Salinity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 193, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardelli, B.B.; Droghei, R.; Santoleri, R. Multi-dimensional interpolation of SMOS sea surface salinity with surface temperature and in situ salinity data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 392–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Droghei, R.; Nardelli, B.B.; Santoleri, R. Combining in situ and satellite observations to retrieve salinity and density at the ocean surface. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2016, 33, 1211–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, V.A. SMOS OS Level 3: The Algorithm Theoretical Basis Document (v300). CATDS. 2017. Available online: http://doi.org/10.17882/52804#69293 (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Boutin, J.; Vergely, J.; Reul, N.; Catany, R.; Koehler, J.; Martin, A.; Rouffi, F.; Arias, M.; Chakroun, M.; Corato, G.; et al. ESA Sea Surface Salinity Climate Change Initiative (Sea_Surface_Salinity_cci): Weekly and Monthly Sea Surface Salinity Products, v2. 31, for 2010 to 2019. Available online: https://catalogue.ceda.ac.uk/uuid/4ce685bff631459fb2a30faa699f3fc5 (accessed on 7 September 2020).
- Cheng, L.; Zhu, J. Benefits of CMIP5 multimodel ensemble in reconstructing historical ocean subsurface temperature variations. J. Clim. 2016, 29, 5393–5416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, F.M.; Foltz, G.R.; McPhaden, M.J. Seasonal cycles of surface layer salinity in the Pacific Ocean. Ocean Sci. 2010, 6, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, E.N. Empirical Orthogonal Functions and Statistical Weather Prediction. Available online: https://eapsweb.mit.edu/sites/default/files/Empirical_Orthogonal_Functions_1956.pdf (accessed on 10 February 2021).
- Yu, L. A global relationship between the ocean water cycle and near-surface salinity. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2011, 116, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, A.L.; Giulivi, C.F.; Busecke, J.; Bingham, F.M. Differences among subtropical surface salinity patterns. Oceanography 2015, 28, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinogradova, N.T.; Ponte, R.M. Clarifying the link between surface salinity and freshwater fluxes on monthly to interannual time scales. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2013, 118, 3190–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Pan, D.; Bai, Y.; He, X.; Chen, X.; Chen, C.-T.A.; Wang, D. Areas of the global major river plumes. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2013, 32, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, W.; Lee, T. Intraseasonal sea surface salinity variability in the equatorial I ndo-P acific O cean induced by M adden-J ulian oscillations. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 2233–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bingham, F.M.; Foltz, G.; McPhaden, M. Characteristics of the seasonal cycle of surface layer salinity in the global ocean. Ocean Sci. 2012, 8, 915–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Bingham, F.M.; Dinnat, E.; Fournier, S.; Lee, T.; Melnichenko, O. Seasonality in Sea Surface Salinity Revisited. J. Geophys.Res. Ocean. 2020. in review. [Google Scholar]
- Boyer, T.P.; Levitus, S. Harmonic analysis of climatological sea surface salinity. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2002, 107, SRF 7-1–SRF 7-14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durand, F.; Alory, G.; Dussin, R.; Reul, N. SMOS reveals the signature of Indian Ocean Dipole events. Ocean Dyn. 2013, 63, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Du, Y.; Qu, T. A sea surface salinity dipole mode in the tropical Indian Ocean. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 47, 2573–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaitanya, A.V.S.; Durand, F.; Mathew, S.; Gopalakrishna, V.V.; Papa, F.; Lengaigne, M.; Vialard, J.; Kranthikumar, C.; Venkatesan, R. Observed year-to-year sea surface salinity variability in the Bay of Bengal during the 2009–2014 period. Ocean Dyn. 2015, 65, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchilibou, M.; Delcroix, T.; Alory, G.; Arnault, S.; Reverdin, G. Variations of the tropical Atlantic and Pacific SSS minimum zones and their relations to the ITCZ and SPCZ rain bands (1979–2009). J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2015, 120, 5090–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boutin, J.; Martin, N.; Kolodziejczyk, N.; Reverdin, G. Interannual anomalies of SMOS sea surface salinity. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 180, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, Y.; Farrara, J.D.; Schumann, G.; Andreadis, K.M.; Moller, D. Sea surface salinity variability in response to the Congo river discharge. Cont. Shelf Res. 2015, 99, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, M.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Wijffels, S. Decadal trends of the upper ocean salinity in the tropical Indo-Pacific since mid-1990s. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnichenko, O.; Hacker, P.; Bingham, F.M.; Lee, T. Patterns of SSS variability in the eastern tropical pacific. Oceanography 2019, 32, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subrahmanyam, B.; Trott, C.B.; Murty, V. Detection of intraseasonal oscillations in SMAP salinity in the Bay of Bengal. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 7057–7065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, C.B.; Subrahmanyam, B.; Roman-Stork, H.L.; Murty, V.; Gnanaseelan, C. Variability of intraseasonal oscillations and synoptic signals in sea surface salinity in the Bay of Bengal. J. Clim. 2019, 32, 6703–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, A.; Farrar, J.T.; Boutin, J.; Bingham, F.; Lee, T. Intraseasonal variability of surface salinity in the eastern tropical Pacific associated with mesoscale eddies. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2019, 124, 2861–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| SSS Product | Data Source | First Guess | Objective Analysis or Correction Method | Temporal Coverage | Domain | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EN4 | ARGO, GTSPP, others | WOA98 | Optimal interpolation (OI) algorithm | 1900–2019 | 83°S–89°N 180°W–180°E | Good et al. [35] |
| JAMSTEC Argo | Argo, CTD, and moorings | WOA01 | OI algorithm | 2001–2019 | 60.5°S–70.5°N 180°W–180°E | Hosoda et al. [36] |
| IAP | Argo, CTD, and Bottles | An ensemble of CMIP5 simulations | Ensemble OI algorithms | 1940–2019 | 89°S–89°N 180°W–180°E | Cheng et al. [37] |
| IPRC | Argo, Dynamic Height | WOA01 | Variational interpolation | 2005–2020.4 | 62.5°S–63.5°N 180°W–180°E | http://apdrc.soest.hawaii.edu/projects/argo (accessed on 20 February 2021) |
| SIO | Argo | Argo | OI algorithm | 2004–2019 | 64.5°S–79.5°N 180°W–180°E | Roemmich and Gilson [32] |
| BOA | Argo | Argo | Barnes successive correction method | 2004–2019 | 79.5°S–79.5°N 180°W–180°E | Li et al. [38] |
| SMOS LOCEAN | Satellite | In situ-sea surface salinity gridded fields (ISAS) | Ocean target transformation | 2010–2019.9 | 83.5°S–83.5°N 180°W–180°E | Boutin et al. [39] |
| SMOS BEC | Satellite | WOA 2013 | Non-Bayesian retrieval of SSS | 2011–2019 | 89°S–89°N, 180°W–180°E | Olmedo et al. [40] |
| ESA CCI | Satellite | None | Multiple error corrections steps | 2010–2019 | 83.5°S–83.5°N 180°W–180°E | https://climate.esa.int/ (accessed on 20 February 2021) |
| CMEMS | Satellite CTD, and Argo | “MULTIOBS_GLO_PHY_REP_015_002” from CMEMS | Multidimensional OI algorithm | 1993–2019 | 89.875°S–89.875°N, 0.125–359.875°E | Nardelli et al. [41]; Droghei et al. [42] |
| Methods | Sub-Annual (g/kg) | Interannual (g/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| Hanning | 0.068 ± 0.029 | 0.098 ± 0.022 |
| Butterworth | 0.078 ± 0.031 | 0.109 ± 0.025 |
| Running Mean | none | 0.095 ± 0.022 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Wei, Z. Intercomparison of Global Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Datasets over 2011–2018. Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040811
Liu H, Wei Z. Intercomparison of Global Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Datasets over 2011–2018. Remote Sensing. 2021; 13(4):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040811
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Hao, and Zexun Wei. 2021. "Intercomparison of Global Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Datasets over 2011–2018" Remote Sensing 13, no. 4: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040811
APA StyleLiu, H., & Wei, Z. (2021). Intercomparison of Global Sea Surface Salinity from Multiple Datasets over 2011–2018. Remote Sensing, 13(4), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs13040811