Dynamic Modeling and Validation of Peak Ability of Biomass Units
Abstract
1. Introduction
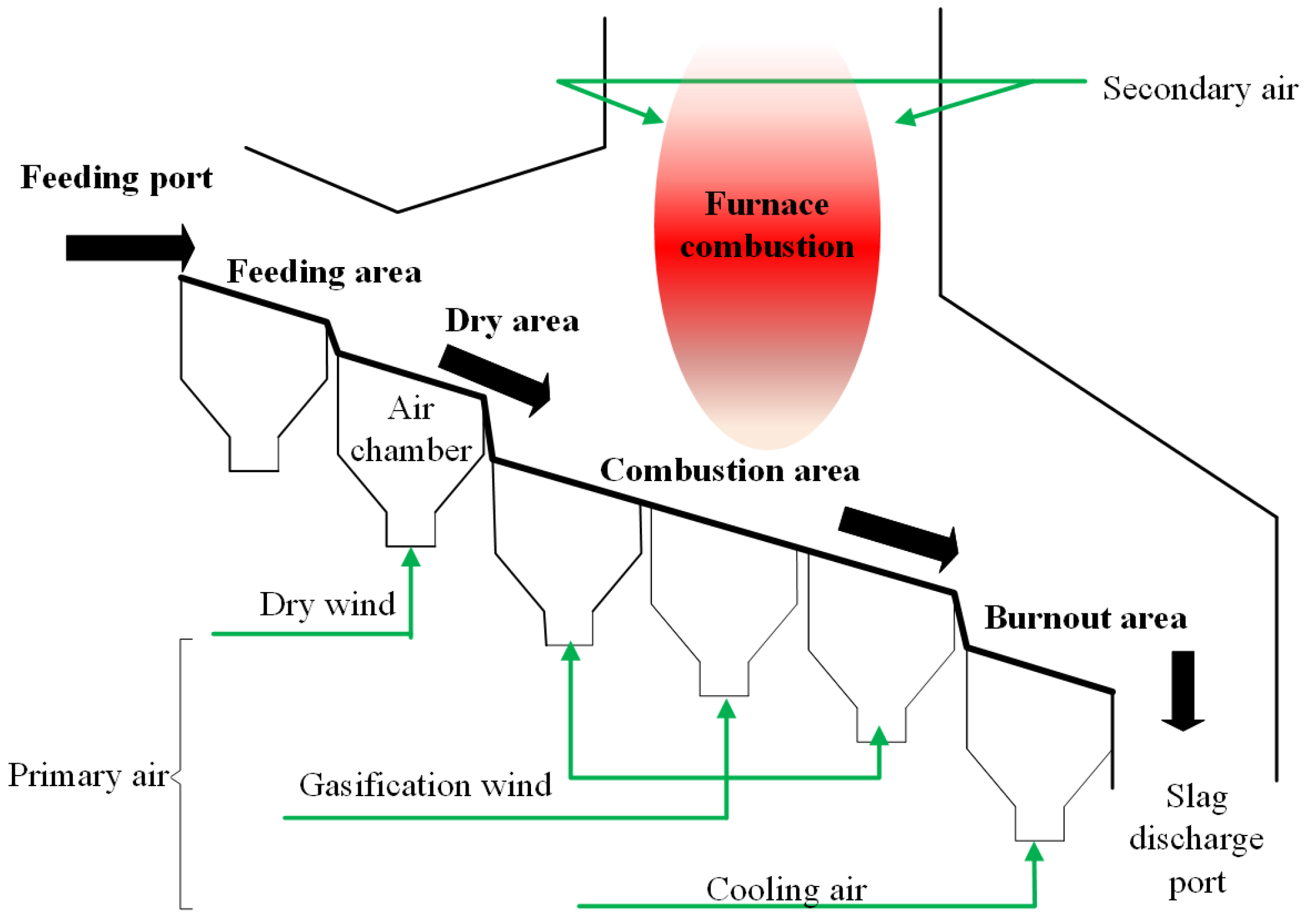
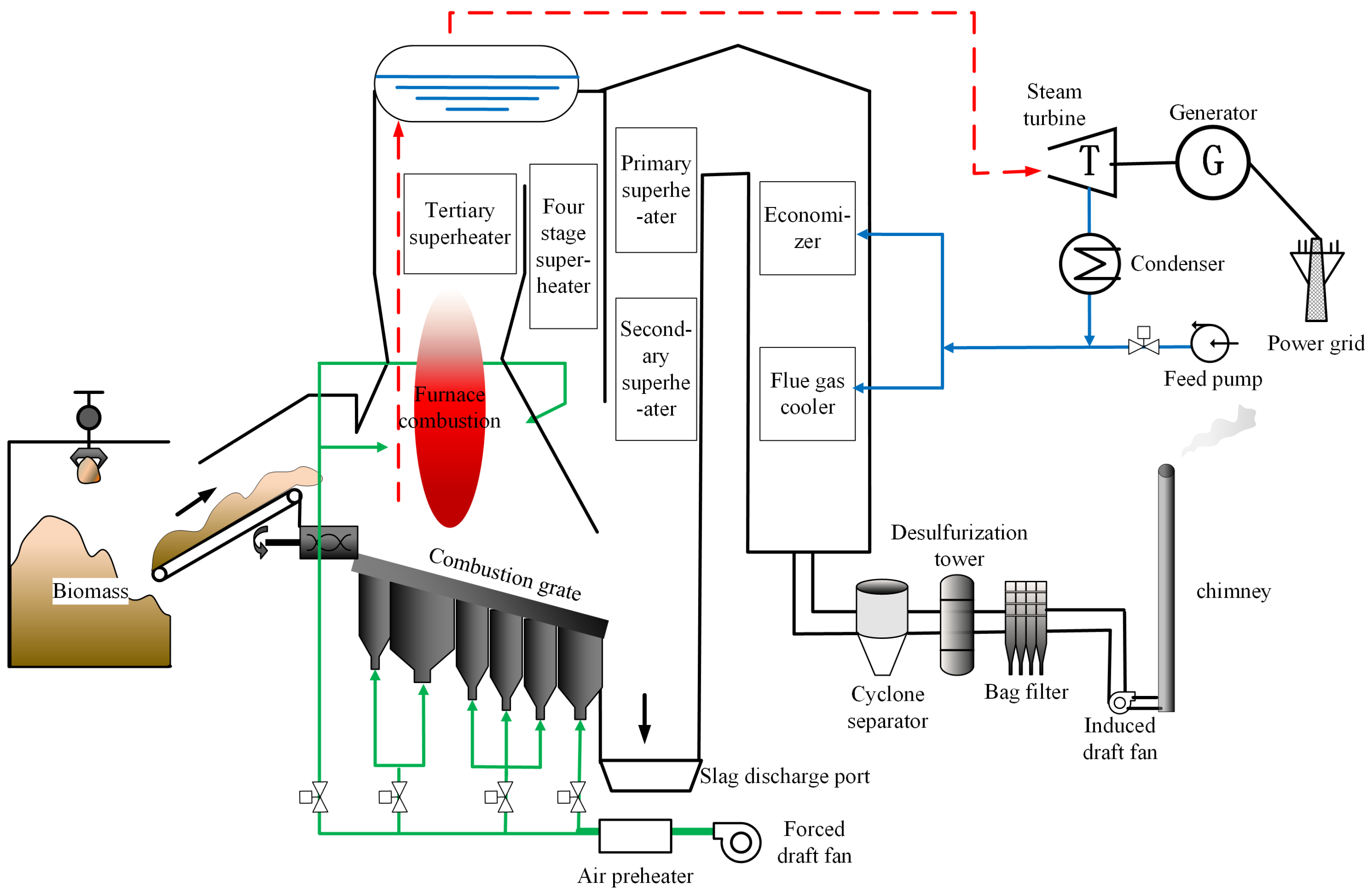
2. Biomass Power Generation Process
3. Dynamic Modeling of Biomass Unit Peak Ability
3.1. Feed–Heat Model
3.2. Heat–Pressure Model
3.3. Pressure–Power Model
4. Dynamic Model Validation
4.1. Data Preprocessing
4.2. Model Validation
5. Conclusions
- According to the characteristics of a biomass grate furnace unit, a modular modeling method is proposed. It divides the process from biomass unit feed quantity to unit power into three modules based on the first principles: feed–heat module, heat–main steam pressure module and main steam pressure–power module.
- A “two-input and two-output” (TITO) dynamic model framework based on biomass combustion characteristics was constructed, using the feed rate and the steam turbine valve opening as inputs, and the main steam pressure and steam turbine output power as outputs.
- The actual operation data of a 30 MW biomass unit were used to verify the model and the open-loop step response of the model. Experiments show that the model has good fitting effect. The RMSE values of the two output parameters turbine output power and main steam pressure were 0.2201 MW and 0.4655 MPa, respectively. The MAE values were 0.1520 MW and 0.4017 MPa, respectively. The model demonstrates high accuracy, with the steam turbine output power and main steam pressure output exhibiting minor deviations from actual operation data.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Biomass Energy Industry Branch of China Association for the Promotion of Industrial Development. Blue Book on the Development Potential of Zero Carbon Biomass Energy in 3060; Biomass Energy Industry Branch of China Association for the Promotion of Industrial Development: Beijing, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.M.; Cao, K.; Li, P.K.; Xu, S.S.; Wu, Z.Q. Effects of Several Chief Parameters on the NOx Emission of a MILD Burner Firing Biogas. J. Zhengzhou Univ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 42, 105–110. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13705/j.issn.1671-6833.2020.06.003 (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Mao, J.X.; Guo, H.N.; Wu, Y.X. Road to Low-Carbon Transformation of Coal Power in China: A Review of Biomass Co-Firing Policies and Technologies for Coal Power Abroad and Its Inspiration on Biomass Utilization. Clean Coal Technol. 2022, 28, 1–11. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13226/j.issn.1006-6772.cc22021701 (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- Fu, P.; Xu, G.P.; Li, X.H.; Zhu, L.T.; Zhang, Z. Analysis of the development status and trends of China’s biomass power industry and carbon emission reduction potential. Ind. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 47, 48–52. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.L.; He, T.; Liu, Y.H.; Li, D.H.; Chen, Y.Q. Physics-informed energy-balanced modeling and active disturbance rejection control for circulating fluidized bed units. Control Eng. Pract. 2021, 116, 104934. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Li, D.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Xue, Y. Control-oriented modeling and analysis of direct energy balance in coal-fired boiler-turbine unit. Control Eng. Pract. 2016, 55, 38–55. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, Y.L.; Zhou, H.C. A mathematical model suitable for simulation of fast cut back of coal-fired boiler-turbine plant. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 108, 546–554. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, N.C.; Pan, L.; Liu, Z.X.; Lee, K.Y.; Song, Y.; Si, P. Dynamic modeling of thermal-supply system for two-by-one combined-cycle gas and steam turbine unit. Fuel Process. Technol. 2020, 209, 106549. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Lu, Y.; Wei, Q.; Xu, H. Research on Dynamic Modeling Method of Waste Incinerator Combustion Process. Proc. CSEE 2025, 45, 1–13. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.232316 (accessed on 10 February 2025).
- Jiang, H.W.; Gao, M.M.; Li, J.; Yu, H.Y.; Yue, G.X.; Huang, Z. Modeling and dynamic characteristic analysis of combustion process of biomass vibrating grate furnace. Power Gener. Technol. 2024, 45, 250–259. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.Q.; Wang, Z.W.; Li, J.H. Simulation Research of Biomass Boiler Based on Virtual DPU. Autom. Instrum. 2023, 38, 89–93. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19557/j.cnki.1001-9944.2023.08.019 (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Yang, X.Y.; Wang, L.; Qi, K.; Wang, Z.K.; Zhu, C. Simulation of Biomass Vibrating-Grate Boiler. Proc. CSEE 2009, 29, 101–107. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2009.s1.013 (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Gao, M.M.; Liu, B.T.; Zhang, H.F.; Wang, Y.K.; Yue, G.X. Research on a coordination system model for biomass circulating fluidized bed unit. J. Chin. Soc. Power Eng. 2024, 44, 292–300. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, W.T. Pressure Reducing and Pipe Blowing Process of 60 MW Biomass Chain Grate Furnace. Electr. Eng. 2021, 14, 171–172. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19768/j.cnki.dgjs.2021.14.063 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhai, G.X.; Chen, R.Y. Analysis on the Characteristics of Biomass Fuel Direct Combustion Process. J. Northeast Agric. Univ. 2001, 32, 290–294. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19720/j.cnki.issn.1005-9369.2001.03.015 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Fan, J.L.; Li, J.; Yan, S.P.; Yu, C.J.; Xiao, P.; Wang, T.; Zeng, Z.H.; Shen, S.; Ma, X.S.; Fang, M.X. Application Potential Analysis for Bioenergy Carbon Capture and Storage Technology in China. Therm. Power Gener. 2021, 50, 7–17. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19666/j.rlfd.202007204 (accessed on 1 January 2025).
- Rathour, K.R.; Behl, M.; Sakhuja, D.; Kumar, N.; Sharma, N.; Walia, A.; Bhatt, A.K.; Bhatia, R.K. Recent updates in biomass pretreatment techniques for a sustainable biofuel industry: A comprehensive review. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2025; prepublish. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, C.X.; Meng, X.Z.; Thygesen, L.G.; Sheng, K.; Pu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ragauskas, A.; Zhang, X.; Thomsen, S.T. The significance of biomass densification in biological-based biorefineries: A critical review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2023, 183, 113520. [Google Scholar]
- Su, X.Q.; Ma, L.; Fang, Q.Y.; Yin, C.; Zhuang, H.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, C.; Chen, G. Optimizing biomass combustion in a 130 t/h grate boiler: Assessing gas-phase reaction models and primary air distribution strategies. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 238, 122043. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Sun, X.B.; Wang, J.; Xie, G.H. Differences and correlations between ash content and calorific value in waste biomass and their determination methods. J. China Agric. Univ. 2022, 27, 160–172. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Y.J.; Zhou, A.Q.; Xu, M.C.; Yang, W.; Siah, K.B.; Subbaiah, P. NOx reduction in a 40 t/h biomass fired grate boiler using internal flue gas recirculation technology. Appl. Energy 2018, 220, 962–973. [Google Scholar]
- Marangwanda, G.T.; Madyira, D.M.; Babarinde, T.O. Combustion models for biomass: A review. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 664–672. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.L.; Lu, B.N.; Zhong, S.K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z. Multiscale modeling of ozone decomposition in fluidized bed reactors: Integrating dynamic structural mass transfer analysis. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 306, 121248. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Y.; Zhang, X.Z.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, T. Calculation on Water Wall Temperature in a 1000 MW USC Boiler. Energy Res. Inf. 2014, 30, 209–213. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.13259/j.cnki.eri.2014.04.006 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Gao, M.M.; Liu, B.T.; Zhang, K.P.; Wang, Y.K.; Yue, G.X. Study on Dynamic Bed Temperature Model of Biomass Circulating Fluidized Bed Boiler. Therm. Power Gener. 2023, 52, 72–81. Available online: https://link.cnki.net/doi/10.19666/j.rlfd.202212138 (accessed on 3 January 2025).
- Wang, X.H.; Sheng, W.; Liu, Q.S. Study on technical scheme of flue gas waste heat utilization in utility boiler. Power Gener. Technol. 2019, 40, 276–280. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.R.; Wang, L.M.; Guo, Y.L.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.; Che, D. Progress in dynamic modeling and simulation of coal-fired utility boiler. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2023, 44, 1737–1752. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, M.; Yan, H.; Yan, J. Optimization on coordinate control strategy assisted by high-pressure extraction steam throttling to achieve flexible and efficient operation of thermal power plants. Energy 2022, 244, 122676. [Google Scholar]
- Porto-Hernandez, L.A.; Vargas, J.V.C.; Munoz, M.N.; Galeano-Cabral, J.; Ordonez, J.C.; Balmant, W.; Mariano, A.B. Fundamental optimization of steam Rankine cycle power plants. Energy Convers. Manag. 2023, 289, 117148. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.M.; Zhang, K.S. Multi-objective optimal dispatching of microgrid containing biomass energy. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2019, 35, 49–53, 67. [Google Scholar]









| Fuel Name | Average Moisture Content (%) | Average Ash Content (%) | Calorific Value (kcal) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peanut Shell | 15.53 | 17.63 | 3100.63 |
| Wheat Straw | 18.75 | 13.89 | 2758.72 |
| Wheat Husk | 9.39 | 20.02 | 2805.56 |
| Bark | 43.28 | 14.80 | 2000.44 |
| Whole Template | 3350 | ||
| Waste Veneer Strip | 15.84 | 5.42 | 3329.15 |
| Corn Straw | 14.66 | 21.85 | 2500.07 |
| Chili Stalks | 18.83 | 10.32 | 3044.81 |
| Corncob | 18.98 | 3.52 | 3222.11 |
| Branch | 37.42 | 8.77 | 2278.48 |
| Steady State Parameters | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| 1.0000 | |
| 6.8143 × 10−6 | |
| 7.1550 × 10−5 | |
| 1.1500 | |
| 0.0615 | |
| 63.6531 | |
| 39.7832 | |
| 0.0082 | |
| 5.6358 | |
| 0.8758 |
| Dynamic Parameters | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| 80.0000 | |
| 0.4100 | |
| 148.5761 | |
| 0.4523 | |
| 31.9593 | |
| 37.5900 | |
| 1.8463 | |
| 1.0325 | |
| 10.0000 |
| Dynamic Parameters | Numerical Value |
|---|---|
| 51.3606 | |
| 4.1577 | |
| 225.2294 | |
| 0.6818 | |
| 32.6523 | |
| 25.9014 | |
| 2.1168 | |
| 1.3462 | |
| 16.1684 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xia, D.; Cao, G.; Pan, J.; Wang, X.; Meng, K.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Z. Dynamic Modeling and Validation of Peak Ability of Biomass Units. Algorithms 2025, 18, 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070423
Xia D, Cao G, Pan J, Wang X, Meng K, Sun Y, Wu Z. Dynamic Modeling and Validation of Peak Ability of Biomass Units. Algorithms. 2025; 18(7):423. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070423
Chicago/Turabian StyleXia, Dawei, Guizhou Cao, Jiayao Pan, Xinghai Wang, Kai Meng, Yuancheng Sun, and Zhenlong Wu. 2025. "Dynamic Modeling and Validation of Peak Ability of Biomass Units" Algorithms 18, no. 7: 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070423
APA StyleXia, D., Cao, G., Pan, J., Wang, X., Meng, K., Sun, Y., & Wu, Z. (2025). Dynamic Modeling and Validation of Peak Ability of Biomass Units. Algorithms, 18(7), 423. https://doi.org/10.3390/a18070423






