Abstract
The steel strip is an important and ideal material for the automotive and aerospace industries due to its superior machinability, cost efficiency, and flexibility. However, surface defects such as inclusions, spots, and scratches can significantly impact product performance and durability. Accurately identifying these defects remains challenging due to the complex texture structures and subtle variations in the material. In order to tackle this challenge, we propose a Differentiable Edge-guided Pyramid Aggregation Network (DEPANet) to utilize edge information for improving segmentation performance. DEPANet adopts an end-to-end encoder-decoder framework, where the encoder consisting of three key components: a backbone network, a Differentiable Edge Feature Pyramid network (DEFP), and Edge-aware Feature Aggregation Modules (EFAMs). The backbone network is designed to extract overall features from the strip steel surface, while the proposed DEFP utilizes learnable Laplacian operators to extract multiscale edge information of defects across scales. In addition, the proposed EFAMs aggregate the overall features generating from the backbone and the edge information obtained from DEFP using the Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM), which combines channel attention and spatial attention mechanisms, to enhance feature expression. Finally, through the decoder, implemented as a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN), the multiscale edge-enhanced features are progressively upsampled and fused to reconstruct high-resolution segmentation maps, enabling precise defect localization and robust handling of defects across various sizes and shapes. DEPANet demonstrates superior segmentation accuracy, edge preservation, and feature representation on the SD-saliency-900 dataset, outperforming other state-of-the-art methods and delivering more precise and reliable defect segmentation.
1. Introduction
Strip steel is a vital component of the steel industry, widely used in automobile manufacturing, home appliance production, and construction structures [1]. During manufacturing, strip steel may develop various surface defects, such as scratches, cracks, oxide scales, pits, roll marks, and scabs [2]. These defects not only degrade the appearance but also potentially compromise the mechanical properties and service life of the material [3]. For instance, scratches and cracks can weaken the material’s strength, while oxide scales and scabs may negatively impact subsequent processing steps, leading to quality degradation [4]. Therefore, precise and prompt segmentation and the effective addressing of these defects are essential for guaranteeing product quality [5].
Advancements in deep learning have led to remarkable progress in segmenting steel surface defects [6]. For example, Liu et al. [7] proposed the multiscale context segmentation network to segment multiscale defects on strip steel surfaces. Built on Faster R-CNN, the network incorporates a parallel atrous convolution architecture to effectively capture multiscale context and minimize confusion. Du et al. [8] proposed AFF-Net for strip steel defect segmentation, tackling challenges from size variations, complexity, and diversity. AFF-Net introduces AFF-Block for adaptive feature weighting of segments and Foc-FPN to improve multiscale fusion and semantic balance.
As mentioned above, deep learning approaches have made remarkable strides in strip steel surface defect segmentation. However, according to the available information, these approaches have failed to fully recognize a crucial role of edge information in strip steel surface defect segmentation. In fact, in other practical applications, edge information has proven to greatly boost the model’s segmentation accuracy. For example, Dong et al. [9] presented CGTD-Net, a dual-branch network utilizing a channel-wise global transformer for strip steel defect segmentation. They enhanced edge information with the SCGA module and optimized feature fusion using the CGT module, improving the accuracy of small or narrow-edge defect segmentation. Hui et al. [10] proposed a model called EMC-UNet to enhance the accuracy of pulmonary nodule segmentation. EMC-UNet utilizes the Sobel operator to enhance edge information, improving the perception of pulmonary nodule boundaries, and employs a multiscale feature extraction module to capture features at different scales.
Based on the discussion above, we propose a Differentiable Edge-guided Feature Pyramid Aggregation Network (DEPANet) within an encoder–decoder framework, leveraging edge information from strip steel surface defects to enhance segmentation performance. This edge information inherently exhibits distinctive characteristics, such as intensity discontinuities and boundary contrasts, which can be exploited to guide precise segmentation. The encoder comprises three key components: a backbone network, a Differentiable Edge Feature Pyramid Network (DEFP), and Edge-aware Feature Aggregation Modules (EFAMs). Considering that ResNet possesses both strong feature extraction capabilities and high execution efficiency, we selected ResNet34 [11] as the backbone to extract the overall features of the input image. In contrast, DEFP is proposed to improve the model’s ability to extract edge components, consisting of a series of stacked Adaptive Feature Smoothing Filters (AFSFs). Each AFSF leverages a learnable Laplacian operator for edge feature extraction and a learnable Gaussian blurring mechanism for feature smoothing and enhancement. The multiple proposed EFAMs are employed to generate edge-enhanced features, with each EFAM designed to integrate the backbone-extracted global features along with the edge components from DEFP at the corresponding level. A Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) is employed to ensure the effective integration of both global information and fine-grained edge details, thereby enhancing the network’s ability to accurately segment defects. For the decoding stage, a Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) is employed to extract multi-level features and fuse them hierarchically, ensuring precise defect localization and robustly handling defects of different sizes and shapes.
The main innovations of this paper are as follows:
- We propose a novel DEFP network consisting of stacked AFSFs to extract multiscale edge components from strip steel surface defects. Each AFSF utilizes a learnable Laplacian operator for edge feature extraction and a learnable Gaussian blurring mechanism for feature smoothing and enhancement.
- We propose EFAMs to generate edge-enhanced features, with each EFAM designed to integrate the backbone features with the edge components obtained from DEFP using a CBAM to enhance defect segmentation accuracy.
- Based on DEFP and EFAM, a novel network called DEPANet is proposed. Experimental results show that DEPANet achieves superior performance in segmenting and localizing complex defects on strip steel surfaces.
The organization of this paper is as follows. Section 2 reviews previous studies. Section 3 elaborates on the proposed methodology, encompassing the overall architecture, DEFP, EFAMs, and the loss function (Section 3.4). Section 4 provides the experimental results, and Section 5 concludes this study.
2. Related Work
2.1. ResNet-Based Methods
ResNet-based methods have been widely adopted for strip steel surface defect segmentation, particularly due to their ability to learn very deep architectures while overcoming the problem of vanishing gradients [12]. For example, Fan et al. [13] introduced ResAt-UNet, an enhanced U-Net to build image segmentation, which leverages ResNet’s residual module and attention mechanisms to boost segmentation accuracy. Sahli et al. [14] developed a ResNet-based glioma segmentation method and support vector machines to segment and classify tumor regions, improving diagnostic efficiency and accuracy. Abdelrahman et al. [15] developed a kidney tumor diagnosis model that combines a squeeze-and-excitation ResNet with a pyramid network feature for improved performance. Yang et al. [16] introduced FRPNet, a lightweight network for real-time semantic segmentation in unstructured scenes. FRPNet employs an enhanced Faster-ResNet encoder and a Partial Spatial Pyramid Pooling (PASPP) module to accurately extract semantic information and address irregular boundaries and similar categories.
2.2. Edge Enhancement
Edge enhancement plays a critical role in image segmentation, especially for tasks such as defect detection [17] and medical image segmentation [18]. Traditional edge enhancement techniques often rely on methods like Sobel, Canny, or Laplacian operators to highlight the edges, but they struggle in complex environments with low signal-to-noise ratios. In recent years, deep learning-based techniques have gained widespread recognition, excelling over traditional methods by automatically learning hierarchical edge features from data. Models such as U-Net and its variants have demonstrated great promise in enhancing edge details through multiscale feature extraction and refinement. For example, Allah et al. [19] introduced Edge U-Net, a deep convolutional neural network that improves the precision of brain tumor segmentation through integration of edge information. Jin et al. [20] proposed ESGNet, a fusion network combining multiple modalities for semantic segmentation of high-resolution remote sensing images. ESGNet improves segmentation accuracy by digital surface models with an edge segmentation guidance module and a multi-modal adaptive fusion module. Wang et al. [21] proposed a new approach for muscle shape modeling and inference, which improves segmentation accuracy and efficiency by combining probabilistic shape modeling with deep edge segmentation. In contrast, our proposed DEPANet achieves edge-aware segmentation through two novel modules: (1) DEFP for enhancing spatial detail via multi-scale edge feature propagation, and (2) EFAM for adaptive fusion of semantic and edge information without external edge annotations. Unlike CGTD-Net and EMC-UNet, DEPANet focuses on efficiently integrating edge and semantic features under purely internal supervision, achieving comparable or superior accuracy on challenging datasets with lower computational cost.
Existing methods have advanced strip steel defect segmentation as mentioned above, but they often overlook the critical role of edge information in improving accuracy. DEPANet addresses this issue by introducing a novel Differentiable Edge Feature Pyramid (DEFP) network and Edge-aware Feature Aggregation Modules (EFAMs) within an encoder–decoder framework. Unlike traditional approaches, DEFP dynamically extracts and refines multiscale edge features using learnable Laplacian operators and Gaussian blurring mechanisms. EFAMs then integrate these edge-cues with global backbone features, ensuring precise defect localization and robust performance across varying defect sizes and shapes.
3. Methods
3.1. Overall Architecture
Inspired by the encoder–decoder framework, we propose a novel Differentiable Edge-guided Feature Pyramid Aggregation Network (DEPANet) to aggregate multi-scale features from different stages, as shown in Figure 1.
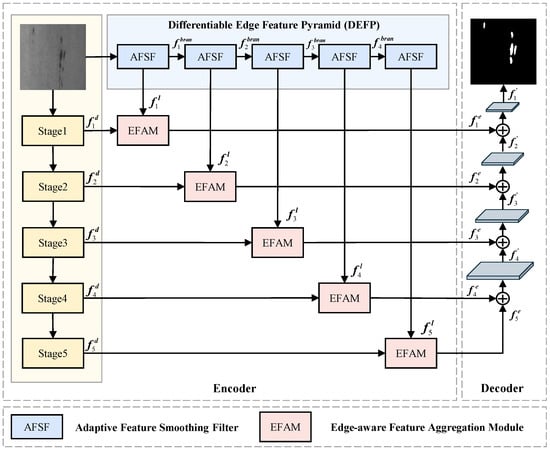
Figure 1.
The architecture of DEPANet.
The encoder consists of three key components: a backbone network, a Differentiable Edge Feature Pyramid Network (DEFP), and Edge-aware Feature Aggregation Modules (EFAMs). We selected ResNet34 [11] as the backbone to extract global characteristics from the steel surface due to its strong feature representation and efficient computational efficiency. Let be the input image, ResNet34 generates five level outputs, i.e., , where represents the i-th layer. The DEFP network consists of five AFSFs, denoted for . Each AFSF applies a learnable filtering operation to generate features and . Formally,
while . The EFAMs integrate the overall features obtained from the backbone network with the edge information from the DEFP to obtain edge-enhanced feature , where . Formally,
In the decoder, we employ the Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) [22] to progressively upsample and fuse edge enhanced multiscale features , ultimately restoring high-resolution segmentation results for precise localization of steel surface defects of various sizes and shapes. Formally,
where denotes the upsampling operation, and represents the feature fusion operation.
Our method was proposed within the framework of an end-to-end encoder–decoder architecture for steel surface defect segmentation. The major contributions of this paper include the overall architecture, named the DEFP network, and the proposed EFAM modules. More details about DEFP and EFAM are presented in Section 3.2 and Section 3.3, respectively.
3.2. Differentiable Edge Feature Pyramid Network (DEFP)
The DEFP network is proposed to extract multiscale edge features through a series of Adaptive Feature Smoothing Filters (AFSFs), as shown in Figure 1. Each AFSF employs a learnable Laplacian operator for edge feature extraction and a learnable Gaussian blur mechanism for feature smoothing and enhancement, as shown in Figure 2.
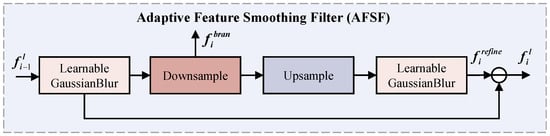
Figure 2.
Architectural diagram of AFSF.
The input feature is first processed through a learnable Gaussian blur module [23] to smooth the feature and suppress high-frequency noise, resulting in the blurred feature . Formally,
where represents the parameter of the Gaussian blur. is downsampled to obtain low-frequency information, denoted . Formally,
is the input of the next AFSF (). In addition, undergoes an upsampling operation, followed by a novel learnable Gaussian blur module to further refine the feature map. Formally,
Finally, the difference between the original input feature and the processed feature is calculated to obtain the edge information .
is used for feature fusion in the EFAM.
3.3. Edge-Aware Feature Aggregation Modules (EFAMs)
The edge information and fine details are helpful for defect segmentation tasks [24]. Therefore, we propose EFAMs to integrate the edge components extracted by DEFP into the global features obtained from the backbone network, ensuring a comprehensive representation of both structural and detailed information. Figure 3 shows the architecture of EFAM.
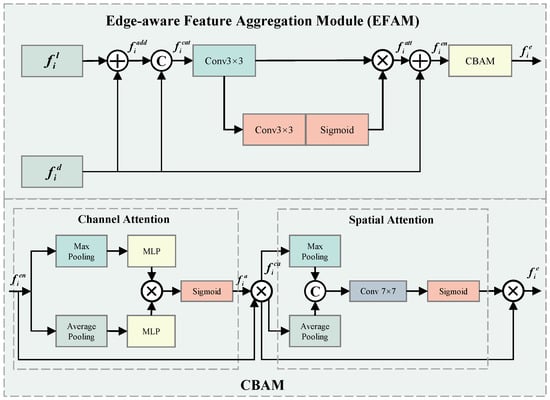
Figure 3.
Architectural diagram of EFAMs.
Each EFAM, , takes the backbone network’s output and DEFP’s edge feature at the i-th level as the inputs, and fuses them through an addition operation to obtain :
The is then concatenated with the , followed by a convolutional layer. Formally,
Then, a spatial attention mechanism is employed to weight the important regions of the aggeragated feature . In particular, a convolutional operation is performed on , followed by a Sigmoid, to obtain the weight matrix a:
where is the Sigmoid function. a is used to weight the to obtain the feature with significant representation. Formally,
where ⊗ indicates the element-wise multiplication. The feature is aggregated with the overall feature obtained from the backbone, obtaining a enhanced feature , and a Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) is applied to to further enhance feature representation by focusing on both channel-wise and spatial-wise attention. Formally,
The details of CBAM are shown in Figure 3(bottom). CBAM integrates channel attention and spatial attention in a cascaded manner. CBAM first applies channel attention to the input . Specifically, undergoes both max pooling as well as average pooling, followed by multilayer perceptrons (MLPs) and an element-wise multiply operation to generate the channel attention feature .
is activated using the Sigmoid function to obtain channel-wise weights, which are element-wise multiplied with to produce the weighted feature. Formally,
Similarly, CBAM applies the spatial attention to the input . In particular, undergoes max pooling and average pooling along the spatial dimension to generate two spatial context descriptors, and concatenates them as :
The spatial weight is obtained by processing through a convolution layer followed by a Sigmoid function. Then, this weight is multiplied in elements with to generate the refined feature .
3.4. Loss Function
The objective functions used to train our proposed DEPANet are a combination of binary cross-entropy loss (BCE) [25] and Dice loss (Dice) [26]. Formally
BCE loss is widely applied in binary classification tasks and is defined as
where N represents the number of samples. is the true label of the sample i, where . The predicted probability for the positive class (i.e., ) is given by .
The Dice loss is used for evaluating segmentation tasks and measures the similarity between two samples. It is given by
where denotes the true label, is the predicted value for the sample i, and N is the total number of samples.
4. Experiment and Results
4.1. Datasets
To assess the effectiveness of DEPANet, experimental evaluations are conducted on the SD-saliency-900 dataset [27], a widely used benchmark for surface defect segmentation in strip steel manufacturing. This dataset contains 900 annotated samples with pixel-accurate masks, partitioned into 540 training images and 360 test images. As illustrated in Figure 4, numerous instances of various defect categories are presented. During training, input images are resized to pixels and standardized using Z-score normalization. During testing, the model processes resized inputs, with the generated segmentation output upscaled to the original resolution using bilinear interpolation for quantitative evaluation. This preprocessing pipeline maintains dimensional consistency while preserving defect characteristics, ensuring accurate performance evaluation.
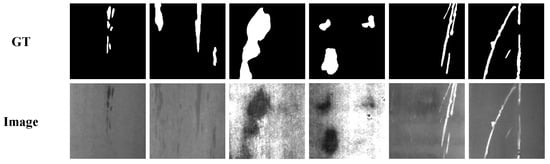
Figure 4.
Visual examples of different types of SD-saliency-900 dataset.
4.2. Experimental Setup
We implement DEPANet using PyTorch version 2.3.1 and conduct experiments on a system equipped with an NVIDIA A100 80 GB PCIe GPU. The backbone is initialized with the parameters of ResNet34 [11] pretrained on ImageNet, while the remaining parameters are initialized using default settings. Adam is selected as the optimizer, with an initial learning rate of and a batch size of 16. The training process is completed over 600 epochs.
4.3. Evaluation Metrics
Nine quantitative metrics are employed to assess the effectiveness of our DEPANet, including MAE [28], S-measure (SM) [29], weighted F-measure (w-), Adaptive F-measure (), Mean F-measure (), Maximum F-measure (), [30], Adaptive E-measure (), Mean E-measure (), and Maximum E-measure () [31].
The MAE quantifies pixel-level discrepancies through absolute differences between the saliency map S and binary annotation T:
where H and W denote spatial dimensions. The SM evaluates structural preservation through dual components:
where measures object-level shape fidelity, assesses regional coherence, and balances their contributions.
The Weighted F-measure, Maximum F-measure, Mean F-measure, and Adaptive F-measure collectively provide a nuanced evaluation of precision and recall in the outcomes of saliency segmentation. These metrics are defined as follows:
where and are computed with threshold-specific strategies. Different values of can correspond to various versions of the F-measure, including the weighted F-measure, Maximum F-measure, Mean F-measure, and Adaptive F-measure.
Adaptive E-measure, Mean E-measure, and Maximum E-measure are metrics used to assess the similarity or matching degree between the predicted saliency map and the ground truth. The formulas are presented as follows:
where denotes an enhancement operator for local contrast adjustment, and determines evaluation mode: The Mean-E-measure averages across thresholds, Maximum E-measure selects optimal thresholds, and Adaptive E-measure uses adaptive thresholding.
4.4. Comparison Results
This section presents a comparative analysis of our DEPANet against 16 other methods on the SD-saliency-900 dataset, i.e., 2LSG [32], BASNet [33], BC [34], BMPM [35], CPD [36], DACNet [37], DSS [38], EDRNet [39], F3Net [40], ITSD [41], MIL [42], MINet [43], NLDF [44], PFANet [45], PiCANet [46], PoolNet [47], R3Net [48], RCRR [49], SAMNet [50], and SMD [51]. For a fair evaluation, we run the original code of the authors or reference their published experimental data. Table 1 compares the methods in the SD-saliency-900 dataset, and Figure 5 visualizes their F-measure and Precision–Recall curves.

Table 1.
Performance comparison of competing methods, with top results highlighted in bold.
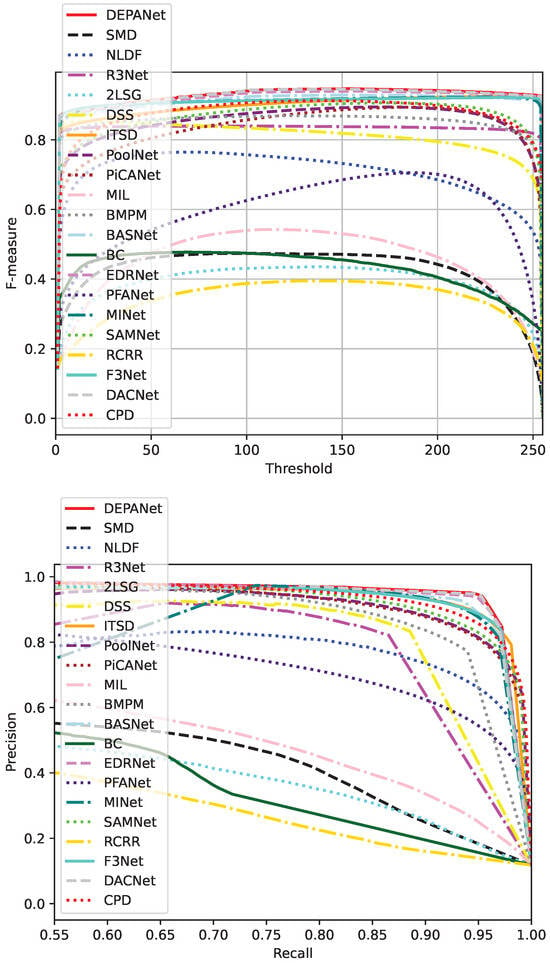
Figure 5.
Comparison of quantitative metrics for different models on SD-saliency-900.
From Table 1, our DEPANet demonstrates significant advantages across multiple metrics, outperforming other comparative methods in overall performance. Firstly, our DEPANet ranks first in terms of structural similarity (SM, 0.9373) and weighted F-measure (, 0.9347), indicating its exceptional ability to capture image structures and details. Secondly, our method also achieves the best results in metrics related to edge detection (, 0.9793; , 0.9765; , 0.9793), further proving its superior capability in edge feature extraction and enhancement. Furthermore, our method reaches the highest level in F-measure (, 0.9223; , 0.9193) and ties with EDRNet in (0.9370), demonstrating its strong competitiveness in comprehensive evaluation metrics. In terms of deployment feasibility, DEPANet has 47.6 million parameters, significantly fewer than models like DACNet (98.2M), which makes it more memory-efficient and suitable for embedded GPU or edge-device deployment.
In addition to segmentation accuracy, inference time is a critical factor for practical deployment in steel production lines, where real-time or near real-time processing is often required. As shown in Table 1, DEPANet achieves a 22.3 FPS on an NVIDIA A100 GPU with a batch size of 16 for images.
Figure 5 shows that DEPANet outperforms all other models, demonstrating a high F-measure at different thresholds and superior precision at various recall rates. The DEPANet precision recall curve is significantly closer to the ideal (1,1) point compared to other models, while its F-measure curve consistently dominates those of alternative approaches. Furthermore, when evaluated against state-of-the-art models, including PiCANet, DACNet, R3Net, and MINet, DEPANet maintains a significant performance advantage. These comprehensive experimental results validate both the effectiveness and reliability of the proposed DEPANet architecture.
4.5. Visualization Analysis
Figure 6 visually compares our DEPANet with competing methods in diverse images. The third column displays our DEPANet segmentation results. Figure 6 shows that DEPANet consistently delivers the highest accuracy in defect segmentation, enabling complete and precise delineation of defect areas. Our method effectively detects and segments defects across a range of sizes and morphological variations, demonstrating robustness to both small and large defects. In the images shown in Rows 1–3, where the contrast between the defect regions and the background is low, existing methods exhibit two typical failure modes. Methods such as BASNet and MINet, being overly sensitive to texture variations, often misclassify background regions as defects. In contrast, methods such as 2LSG and BC, due to their limited feature representation capability, frequently fail to fully segment the defect regions. For images in Rows 4–6, which contain finely detailed defects, certain models yield segmentation results with unclear boundaries. However, DEPANet produces results with sharp and well-defined contours, ensuring precise defect localization. In the last two rows of images, which contain complex backgrounds and challenging scenarios, most existing methods generate saliency maps with poorly defined edges and imprecise highlighting of defect regions. In contrast, DEPANet effectively distinguishes defect regions from the background, demonstrating superior segmentation capability.
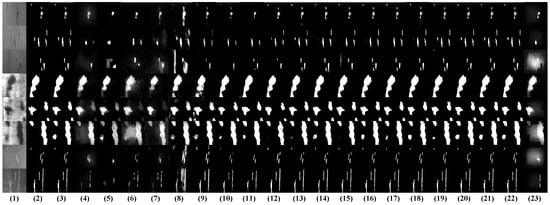
Figure 6.
Visualization comparison of different models on SD-saliency-900. (1) Input images, (2) Ground Truth (GT), (3) ours, (4) 2LSG, (5) BC, (6) SMD, (7) MIL, (8) PFANet, (9) NLDF, (10) DSS, (11) R3Net, (12) BMPM, (13) PoolNet, (14) PiCANet, (15) CPD, (16) BASNet, (17) SAMNet, (18) ITSD, (19) F3Net, (20) MINet, (21) EDRNet, (22) DACNet, and (23) RCRR.
To further illustrate the role of edge information extracted by DEFP, we visualize the intermediate edge maps generated at different stages of DEFP in Figure 7. As shown in Figure 7, Stage 1 and Stage 2 focus on capturing fine-grained textures and noise-like contours, while other stages highlight more semantically meaningful and structurally consistent defect boundaries. These progressive representations demonstrate the hierarchical edge learning ability of our AFSFs and provide insight into how DEPANet progressively refines edge information to assist defect segmentation.

Figure 7.
Visualization results and edge visualization results at different stages of DEPANet.
4.6. Ablation Studies
We conduct ablation studies to evaluate the impact of key components, including the ResNet34 backbone, DEFP, EFAM, and CBAM modules, as well as the BCE and Dice loss functions, using evaluation metrics of MAE, SM, , and .
Table 2 (Rows #1–#3) shows the impact of key components, including the ResNet34 backbone, DEFP, EFAM, and CBAM modules, where Row #1 is used as the baseline. As evidenced in Table 2 (Rows #1–#3), the model exhibits a progressive and substantial performance enhancement with sequential incorporation of each component. Specifically, the model combining DEFP and EFAM (Row #2) achieves improved performance compared to Row #1, demonstrating the complementary effectiveness of the edge-aware mechanism in enhancing feature attention. Finally, Row #3, which integrates all modules (DEFP, EFAM, and CBAM), achieves the best performance with the lowest MAE (0.0132) and highest SM (0.9373), (0.9758), and (0.9396), conclusively proving the synergistic effectiveness of these components in enhancing the overall model performance.

Table 2.
The experimental results of ablation studies conducted using the dataset SD-saliency-900.
Table 2 (Rows #4–#6) shows the impact of the BCE and Dice loss functions on our DEPANet. From Table 2 (row #6), our DEPANet trained with hybrid loss, i.e., BCE and Dice, achieves improvements of 0.22% (0.17%), 3.58% (2.32%), 1.6% (0.84%), and 2.4% (1.76%) over the model trained with BCE (Dice) in terms of MAE, SM, , and , respectively.
4.7. Generalization Experiments
While the SD-saliency-900 dataset provides valuable insight with its three steel surface defect categories, its limited scope may not fully represent all possible defect variations. Potential biases in data collection, particularly from specific production environments, could also impact model generalization across diverse industrial applications.
To comprehensively evaluate the DEPANet’s performance, we performed additional tests on the ESDIs-SOD dataset [52]. Following established protocols, we trained the model on 3600 images (1200 per class) and tested on the remaining 1200 images. Table 3 presents a comparative evaluation of DEPANet against 10 methods. The results demonstrate superior performance across all key metrics (MAE, SM, , , and parameter efficiency), confirming the method’s robustness and effectiveness.

Table 3.
DEPANet is comprehensively evaluated against 10 state-of-the-art methods on the ESDIs-SOD dataset, with optimal results highlighted in bold.
5. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose DEPANet, an encoder–decoder architecture for strip steel surface defect segmentation. The encoder consists of three key components: a backbone, a Differentiable Edge Feature Pyramid (DEFP) network, and Edge-aware Feature Aggregation Modules (EFAMs). The backbone utilizes ResNet34 to extract comprehensive features from the strip steel surface. The DEFP network extracts multi-scale edge features through a series of Adaptive Feature Smoothing Filters (AFSFs). Each AFSF incorporates two learnable components: a Laplacian operator for edge feature extraction and a Gaussian blur mechanism for feature smoothing and enhancement. The multiple proposed EFAMs are employed to generate edge-enhanced features, with each EFAM designed to integrate the global backbone features with the edge components from DEFP at the corresponding level. In addition, we incorporate a Convolutional Block Attention Module (CBAM) to ensure effective fusion of global context and fine edge detail. Experimental results demonstrate that DEPANet effectively enhances defect segmentation accuracy in complex industrial environments.
In future work, we will focus on two key improvements: (1) developing a lightweight variant of DEPANet for real-time defect detection in resource-constrained industrial settings and (2) extending our framework to handle temporal information from production line videos to better capture transient defect patterns.
Author Contributions
Y.S.: conceptualization, methodology, writing—review & editing, supervision; S.G.: validation, formal analysis, writing—original draft, visualization; H.G.: writing—review & editing, supervision; C.Z.: writing—review & editing, supervision; Y.F.: conceptualization, formal analysis, resources, writing—review & editing; C.X.: formal analysis, data curation. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Teacher Education Curriculum Reform Projects of Henan Province under Grant 2024-JSJYZD-008; in part by the Henan Province Key Research and Development Project under Grants 241111212200 and 252102220046; in part by the Henan Joint Fund for Science and Technology Research under Grant 20240012; in part by the Key Scientific Research Projects of Higher Education Institutions in Henan Province under Grant 25B520004; and in part by the Open Fund of the Engineering Research Center of Intelligent Swarm Systems, Ministry of Education under Grant ZZU-CISS-2024004.
Data Availability Statement
Our code and experimental results are available at https://github.com/hpguo1982/DFPANet, accessed on 26 March 2025.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
References
- Wang, Z.; Liu, W. Surface Defect Detection Algorithm for Strip Steel Based on Improved YOLOv7 Model. IAENG Int. J. Comput. Sci. 2024, 51, 308–316. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, L.; Xiao, L.; Liao, B.; Lu, R.; Peng, H. An improved recurrent neural network for complex-valued systems of linear equation and its application to robotic motion tracking. Front. Neurorobotics 2017, 11, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J. Multi-function current differencing cascaded transconductance amplifier (MCDCTA) and its application to current-mode multiphase sinusoidal oscillator. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2016, 86, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Mai, W. VPT: Video portraits transformer for realistic talking face generation. Neural Netw. 2025, 184, 107122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Mo, Z.; Yan, F.; Xia, L.; Shan, F.; Ding, Z.; Song, B.; Gao, W.; Shao, W.; Shi, F.; et al. Adaptive feature selection guided deep forest for COVID-19 classification with chest CT. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2020, 24, 2798–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Wei, J.; Feng, X. TSEDNet:Task-specific encoder–decoder network for surface defects of strip steel. Measurement 2025, 239, 115438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Huang, M.; Gao, Z.; Cao, Z.; Cao, P. MSC-DNet: An efficient detector with multi-scale context for defect detection on strip steel surface. Measurement 2023, 209, 112467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Chen, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, H. AFF-Net: A strip steel surface defect detection network via adaptive focusing features. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2024, 73, 2518514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Li, Y.; Fu, L.; Liu, J. Edge-aware interactive refinement network for strip steel surface defects detection. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2024, 36, 016222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, M.; Yuqin, L.; Tianjiao, H.; Yihua, L. Research on a Multiscale U-Net Lung Nodule Segmentation Model Based on Edge Perception and 3D Attention Mechanism Improvement. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 165458–165471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, K.; Wang, W.; Pan, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, B. Resformer-Unet: A U-shaped Framework Combining ResNet and Transformer for Segmentation of Strip Steel Surface Defects. ISIJ Int. 2024, 64, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xia, M.; Hou, J.; Yan, F.; Zang, Q. ResAt-UNet: A U-shaped network using ResNet and attention module for image segmentation of urban buildings. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote. Sens. 2023, 16, 2094–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, H.; Ben Slama, A.; Zeraii, A.; Labidi, S.; Sayadi, M. ResNet-SVM: Fusion based glioblastoma tumor segmentation and classification. J. X-Ray Sci. Technol. 2023, 31, 27–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelrahman, A.; Viriri, S. FPN-SE-ResNet model for accurate diagnosis of kidney tumors using CT images. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 9802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Yang, S.; Wang, P.; Wang, H.; Jiang, J.; Ni, R.; Yang, C. FRPNet: An improved Faster-ResNet with PASPP for real-time semantic segmentation in the unstructured field scene. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 217, 108623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, T.; Chen, X.; Hauwa, A.S.; Deng, B.; Zhu, Y.; Gao, S.; Zang, H.; Zhao, H. A steel defect detection method based on edge feature extraction via the Sobel operator. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, C.; Zhang, M.; Luo, Y.; Mai, J. DCDLN: A densely connected convolutional dynamic learning network for malaria disease diagnosis. Neural Netw. 2024, 176, 106339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allah, A.M.G.; Sarhan, A.M.; Elshennawy, N.M. Edge U-Net: Brain tumor segmentation using MRI based on deep U-Net model with boundary information. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 213, 118833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Zhou, W.; Yang, R.; Ye, L.; Yu, L. Edge Detection Guide Network for Semantic Segmentation of Remote-Sensing Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote. Sens. Lett. 2023, 20, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, G.; Zhang, T.J.; Wu, N.; Wang, X. An Efficient Muscle Segmentation Method via Bayesian Fusion of Probabilistic Shape Modeling and Deep Edge Detection. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 71, 3263–3274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature Pyramid Networks for Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Gedraite, E.S.; Hadad, M. Investigation on the Effect of a Gaussian Blur in Image Filtering and Segmentation. In Proceedings of the 53rd International Symposium ELMAR-2011, Zadar, Croatia, 14–16 September 2011; pp. 393–396. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Peng, S.; Li, G.; Yin, P. Joint computation offloading and resource allocation for end-edge collaboration in internet of vehicles via multi-agent reinforcement learning. Neural Netw. 2024, 179, 106621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruby, U.; Yendapalli, V. Binary cross entropy with deep learning technique for image classification. Int. J. Adv. Trends Comput. Sci. Eng. 2020, 9, 5393–5397. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Sun, X.; Meng, Y.; Liang, J.; Wu, F.; Li, J. Dice loss for data-imbalanced NLP tasks. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1911.02855. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.; Song, K.; Yan, Y. Saliency Detection for Strip Steel Surface Defects Using Multiple Constraints and Improved Texture Features. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2020, 128, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perazzi, F.; Krähenbühl, P.; Pritch, Y.; Hornung, A. Saliency Filters: Contrast-Based Filtering for Salient Region Detection. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012; pp. 733–740. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.M.; Fan, D.P. Structure-Measure: A New Way to Evaluate Foreground Maps. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2021, 129, 2622–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achanta, R.; Hemami, S.; Estrada, F.; Susstrunk, S. Frequency-Tuned Salient Region Detection. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; pp. 1597–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Gong, C.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Cheng, M.M.; Borji, A. Enhanced-Alignment Measure for Binary Foreground Map Evaluation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10421. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, D. Salient Region Detection Using Diffusion Process on a Two-Layer Sparse Graph. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 5882–5894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, C.; Dehghan, M.; Jagersand, M. BASNet: Boundary-Aware Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7479–7489. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, W.; Liang, S.; Wei, Y.; Sun, J. Saliency Optimization from Robust Background Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 2814–2821. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Dai, J.; Lu, H.; He, Y.; Wang, G. A Bi-Directional Message Passing Model for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 1741–1750. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Su, L.; Huang, Q. Cascaded Partial Decoder for Fast and Accurate Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3907–3916. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Fang, H.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. Dense Attention-Guided Cascaded Network for Salient Object Detection of Strip Steel Surface Defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 71, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M.; Hu, X.; Borji, A.; Tu, Z.; Torr, P.H. Deeply Supervised Salient Object Detection with Short Connections. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 3203–3212. [Google Scholar]
- Song, G.; Song, K.; Yan, Y. EDRNet: Encoder-Decoder Residual Network for Salient Object Detection of Strip Steel Surface Defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2020, 69, 9709–9719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q. F3Net:Fusion, Feedback, and Focus for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 12321–12328. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, H.; Xie, X.; Lai, J.H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, L. Interactive Two-Stream Decoder for Accurate and Fast Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9141–9150. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.; Qi, J.; Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ruan, X. Salient Object Detection Via Multiple Instance Learning. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 26, 1911–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Multi-Scale Interactive Network for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 9413–9422. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.; Mishra, A.; Achkar, A.; Eichel, J.; Li, S.; Jodoin, P.M. Non-Local Deep Features for Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6609–6617. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, T.; Wu, X. Pyramid Feature Attention Network for Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3085–3094. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Han, J.; Yang, M.H. PiCANet: Learning Pixel-Wise Contextual Attention for Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3089–3098. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.J.; Hou, Q.; Cheng, M.M.; Feng, J.; Jiang, J. A Simple Pooling-Based Design for Real-Time Salient Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3917–3926. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhu, L.; Xu, X.; Qin, J.; Han, G.; Heng, P.A. R3Net: Recurrent Residual Refinement Network for Saliency Detection. In Proceedings of the 27th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Stockholm, Sweden, 13–19 July 2018; Volume 684690. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, C.; Kim, J.; Cai, W.; Feng, D.D. Reversion Correction and Regularized Random Walk Ranking for Saliency Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2017, 27, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Bian, J.W.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, M.M. SAMNet: Stereoscopically Attentive Multi-Scale Network for Lightweight Salient Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2021, 30, 3804–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Li, B.; Ling, H.; Hu, W.; Xiong, W.; Maybank, S.J. Salient Object Detection Via Structured Matrix Decomposition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 818–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Song, K.; Feng, H.; Jia, X.; Liu, S.; Yan, Y. Autocorrelation-aware aggregation network for salient object detection of strip steel surface defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N. Context-aware cross-level fusion network for camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.12555. [Google Scholar]
- GongyangLi, Z.; Bai, Z.; Lin, W.; Ling, H. Lightweight salient object detection in optical remote sensing images via feature correlation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2022, 60, 5617712. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).