Smart Humidly Adaptive Yarns and Textiles from Twisted and Coiled Viscose Fiber Artificial Muscles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Fabrication of Viscose Muscles
2.2. Characterizations
2.3. Measurement of Actuation Performance
3. Results and Discussion
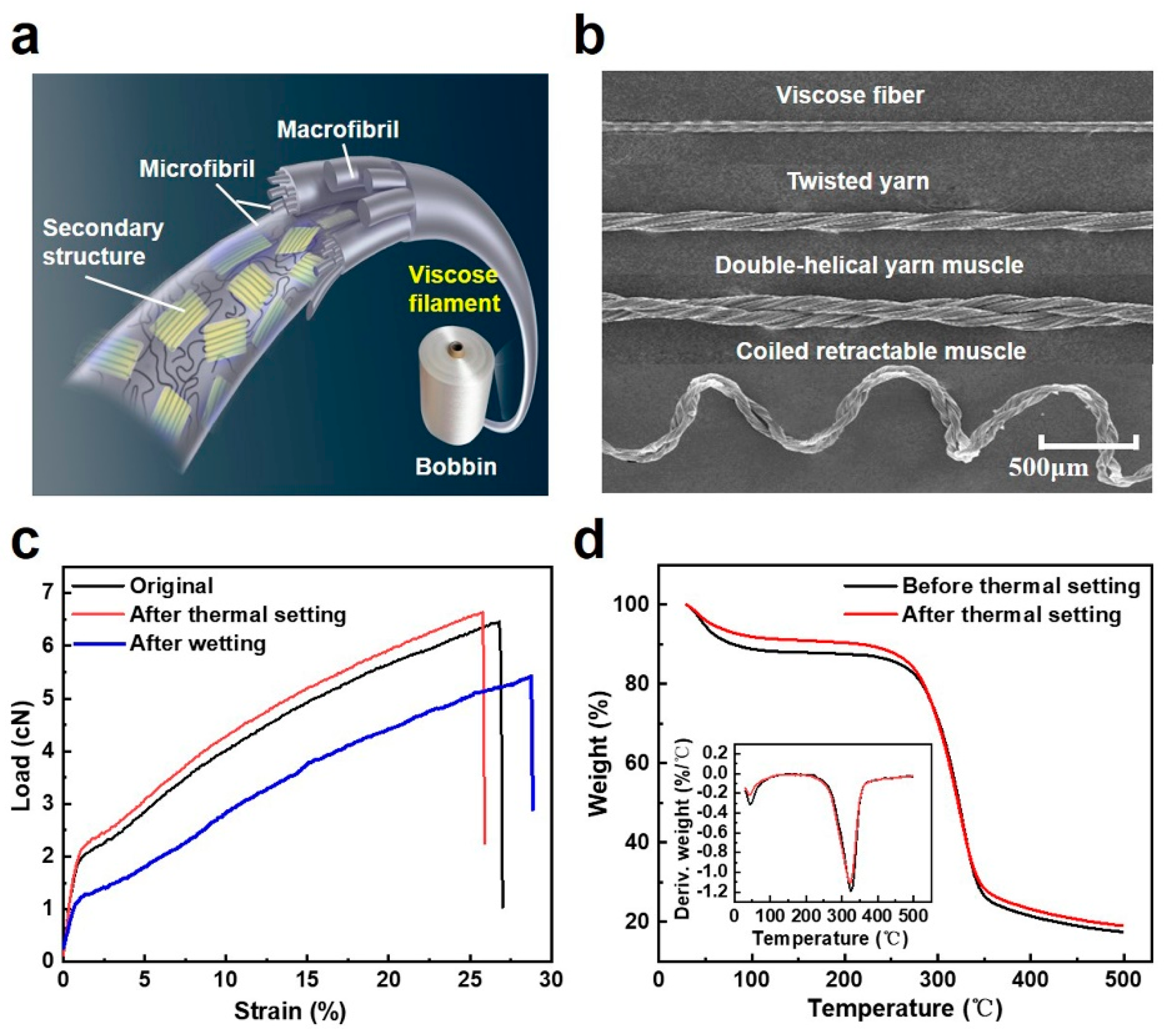
3.1. Structures and Properties of Viscose Filaments
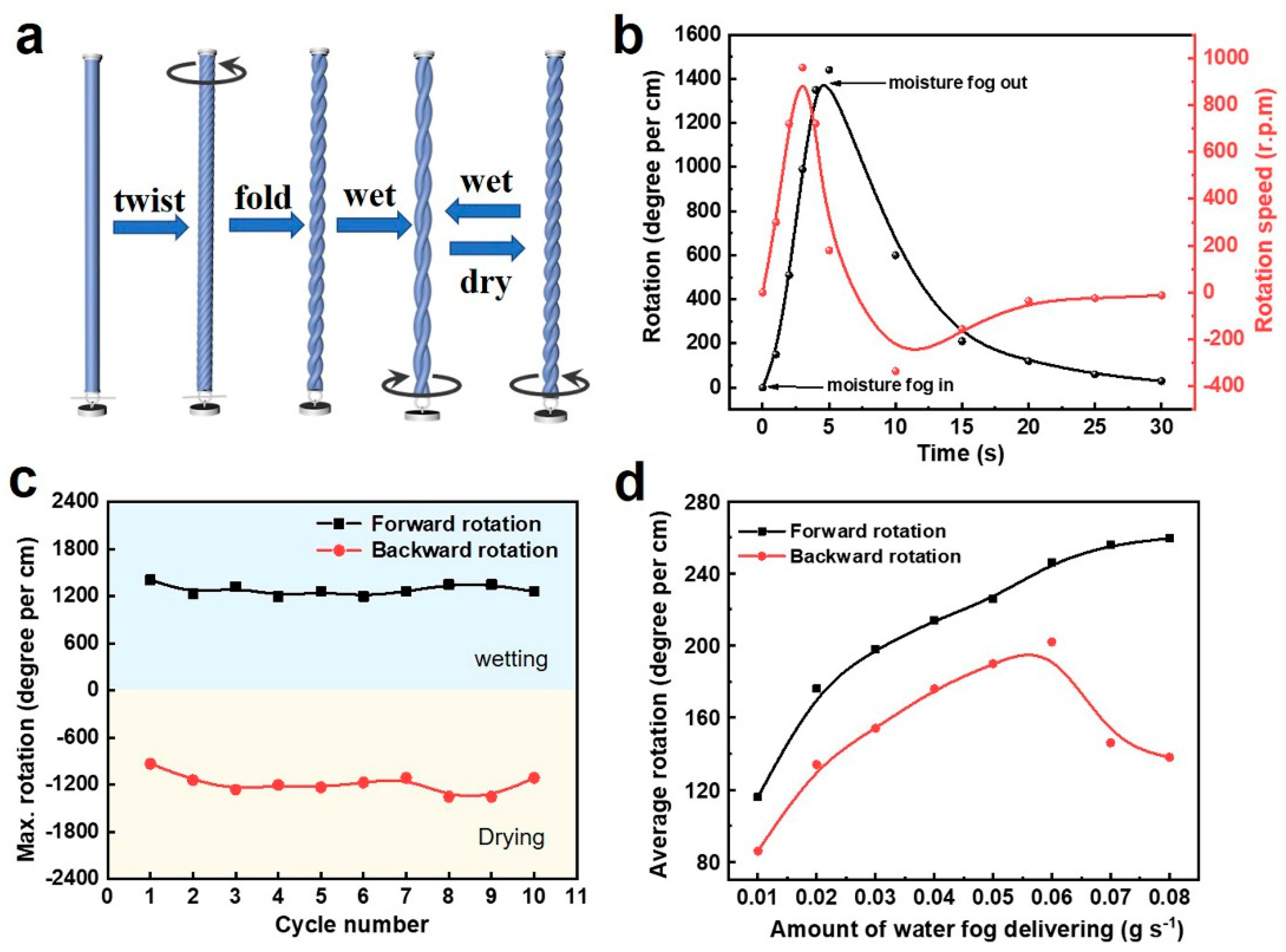
3.2. Torsional Yarn Artificial Muscles
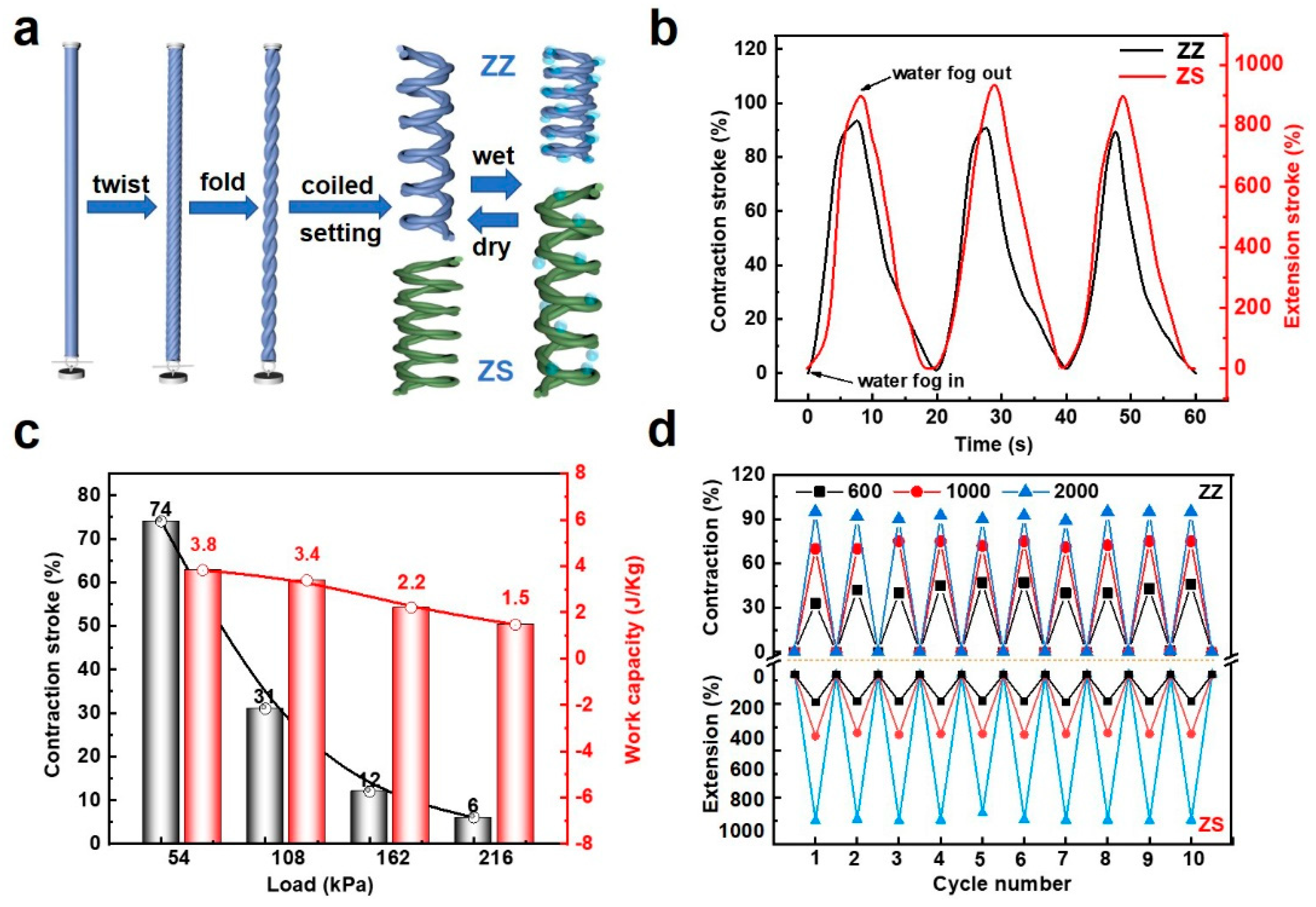
3.3. Tensile Yarn Artificial Muscles
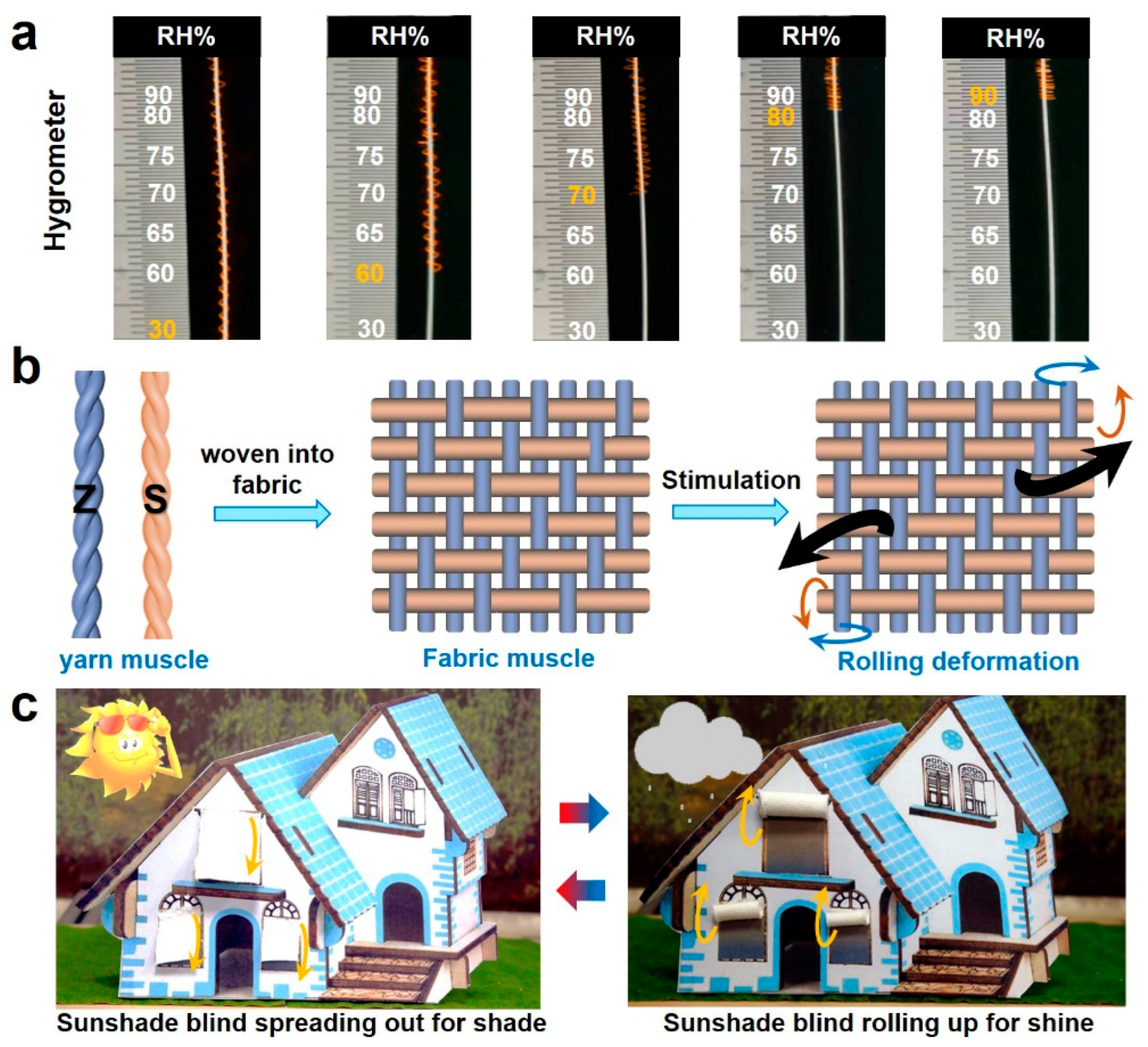
3.4. Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ebi, K.L.; Vanos, J.; Baldwin, J.W.; Bell, J.E.; Hondula, D.M.; Errett, N.A.; Hayes, K.; Reid, C.E.; Saha, S.; Spector, J.; et al. Extreme Weather and Climate Change: Population Health and Health System Implications. Annu. Rev. Public. Health 2021, 42, 293–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xue, B.; Li, Y.; Xiao, X.; Xia, J.C.; He, B. Contribution of urban ventilation to the thermal environment and urban energy demand: Different climate background perspectives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, P.C.; Song, A.Y.; Catrysse, P.B.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y.; Xie, J.; Fan, S.; Cui, Y. Radiative human body cooling by nanoporous polyethylene textile. Science 2016, 353, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Pian, S.; Su, M.; Wang, Z.; Wu, M.; Liu, X.; Ma, Y.; Tao, G. Hierarchical-morphology metafabric for scalablepassive daytime radiative cooling. Science 2021, 373, 692–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Ye, C.; Pei, Y.; Ling, S. Thermochromic Silks for Temperature Management and Dynamic Textile Displays. Nanomicro Lett. 2021, 13, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Yang, Z.; Pei, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Yang, B.; Hu, L. Designing Textile Architectures for High Energy-Efficiency Human Body Sweat- and Cooling-Management. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2019, 1, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Yang, Z.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Fu, K.; Dai, J.; Hitz, E.M.; Xie, H.; Liu, B.; Song, J.; et al. Three-Dimensional Printed Thermal Regulation Textiles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11513–11520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabor, J.; Chatterjee, K.; Ghosh, T.K. Smart Textile-Based Personal Thermal Comfort Systems: Current Status and Potential Solutions. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 1901155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Irfan Iqbal, M.; Sun, F. Wool Can Be Cool: Water-Actuating Woolen Knitwear for Both Hot and Cold. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 2005033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wei, L.; Sun, F. Simultaneous-integrated evaluation of mechanical–thermal sensory attributes of woven fabrics in considering practical wearing states. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 2872–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yu, X.; Liu, R.; Zhi, C.; Liu, Y.; Fan, W.; Meng, J. Shape memory active thermal-moisture management textiles. Composites Part A 2022, 160, 107037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, M.; Augustine, E.; Konerman, S.; Shin, M. Biorobotics: An overview of recent innovations in artificial muscles. Actuators 2022, 11, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.H.; Haines, C.S.; Li, N.; Km, K.J.; Mun, T.J.; Choi, C.; Di, J.; Oh, Y.J.; Oviedo, J.P.; Bykova, J.; et al. Harvesting electrical energy from carbon nanotube yarn twist. Science 2017, 357, 773–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di, J.; Fang, S.; Moura, F.A.; Galvao, D.S.; Bykova, J.; Aliev, A.; de Andrade, M.J.; Lepro, X.; Li, N.; Haines, C.; et al. Strong, Twist-Stable Carbon Nanotube Yarns and Muscles by Tension Annealing at Extreme Temperatures. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6598–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirvakili, S.M.; Hunter, I.W. Fast Torsional Artificial Muscles from NiTi Twisted Yarns. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 16321–16326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, F.; Dong, Z.; Wang, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhang, Z.; Qu, L. Moisture-activated torsional graphene-fiber motor. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 2909–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, C.S.; Lima, M.D.; Li, N. Artificial Muscles from Fishing Line and Sewing Thread. Science 2014, 343, 868–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, J.; Andrade, M.J.D.; Fang, S.; Wang, X.; Gao, E.; Li, N.; Kim, S.H.; Wang, H.; Hou, C.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Sheath-run artificial muscles. Science 2019, 365, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Di, J.; Liu, X.; Qin, J.; Cheng, P. Coiled polymer fibers for artificial muscle and more applications. Matter 2022, 5, 1092–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, T.; Wang, Y.; Dou, Y.; Li, Y.; Jung de Andrade, M.; Wang, R.; Fang, S.; Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Qiao, R.; et al. Moisture Sensitive Smart Yarns and Textiles from Self-Balanced Silk Fiber Muscles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1808241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, Z.; Jung de Andrade, M.; Fang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, J.; Baughman, R.H. Humidity- and Water-Responsive Torsional and Contractile Lotus Fiber Yarn Artificial Muscles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 6642–6649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Miao, M. Moisture-Responsive Natural Fiber Coil-Structured Artificial Muscles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 32256–32264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J.; Sheng, N.; Yang, M.; Sun, F. Free-standing single-helical woolen yarn artificial muscles with robust and trainable humidity-sensing actuation by eco-friendly treatment strategies. Smart Mater. Struct. 2022, 31, 095017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Bai, Y.; Chen, X.; Liu, W. A review on raw materials, commercial production and properties of lyocell fiber. J. Bioresour. Bioprod. 2020, 5, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Sun, F.; Xiao, C.; Iqbal, M.I.; Sun, Z.; Guo, M.; Gao, W.; Hu, X. Hierarchically Structured and Scalable Artificial Muscles for Smart Textiles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 54386–54395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Miao, M. Water-responsive artificial muscles from commercial viscose fibers without chemical treatment. Mater. Res. Lett. 2020, 8, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.D.; Li, N.; Andrade, M.J.D.; Fang, S.; Oh, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Kozlov, M.E.; Haines, C.S.; Suh, D.; Foroughi, J.; et al. Electrically, Chemically, and Photonically Powered Torsional and Tensile Actuation of Hybrid Carbon Nanotube Yarn Muscles. Science 2012, 338, 928–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, X.; Hu, X.; Zhao, W.; An, B.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z. Recent Advances in Twisted-Fiber Artificial Muscles. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2020, 3, 2000185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroka, B.; Noisternig, M.; Griesser, U.J.; Bechtold, T. Characterization of cellulosic fibers and fabrics by sorption/desorption. Carbohydr. Res. 2008, 343, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Huang, W.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Pang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H. Structure and properties of regenerated cellulose fibers from different technology processes. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, T. Effect of bound water on structural change of regenerated cellulose. Die Makromol. Chem. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1987, 188, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreze, T.; Malej, S. Structural characteristics of new and conventional regenerated cellulosic fibers. Text. Res. J. 2003, 73, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Leng, X.; Sun, J.; Zhou, X.; Wu, W.; Chen, H.; Liu, Z. Moisture-sensitive torsional cotton artificial muscle and textile. Chin. Phys. B 2020, 29, 048103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Kim, Y.T.; Spinks, G.M.; Suh, D.; Lepro, X.; Lima, M.D.; Baughman, R.H.; Kim, S.J. All-solid-state carbon nanotube torsional and tensile artificial muscles. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2664–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.A.; Li, N.; Haines, C.S.; Kim, K.J.; Lepro, X.; Ovalle-Robles, R.; Kim, S.J.; Baughman, R.H. Electrochemically Powered, Energy-Conserving Carbon Nanotube Artificial Muscles. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guo, M.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Sheng, N.; Sun, F. Smart Humidly Adaptive Yarns and Textiles from Twisted and Coiled Viscose Fiber Artificial Muscles. Materials 2022, 15, 8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238312
Guo M, Peng Y, Chen Z, Sheng N, Sun F. Smart Humidly Adaptive Yarns and Textiles from Twisted and Coiled Viscose Fiber Artificial Muscles. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238312
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Mingrui, Yangyang Peng, Zihan Chen, Nan Sheng, and Fengxin Sun. 2022. "Smart Humidly Adaptive Yarns and Textiles from Twisted and Coiled Viscose Fiber Artificial Muscles" Materials 15, no. 23: 8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238312
APA StyleGuo, M., Peng, Y., Chen, Z., Sheng, N., & Sun, F. (2022). Smart Humidly Adaptive Yarns and Textiles from Twisted and Coiled Viscose Fiber Artificial Muscles. Materials, 15(23), 8312. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238312




