Investigations on Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Characteristics in Micro-Turning of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Workpiece and Cutting Tool Material
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Surface Roughness Measurement
2.4. Design of Experiment
2.5. Response Surface Methodology
3. Results and Discussions
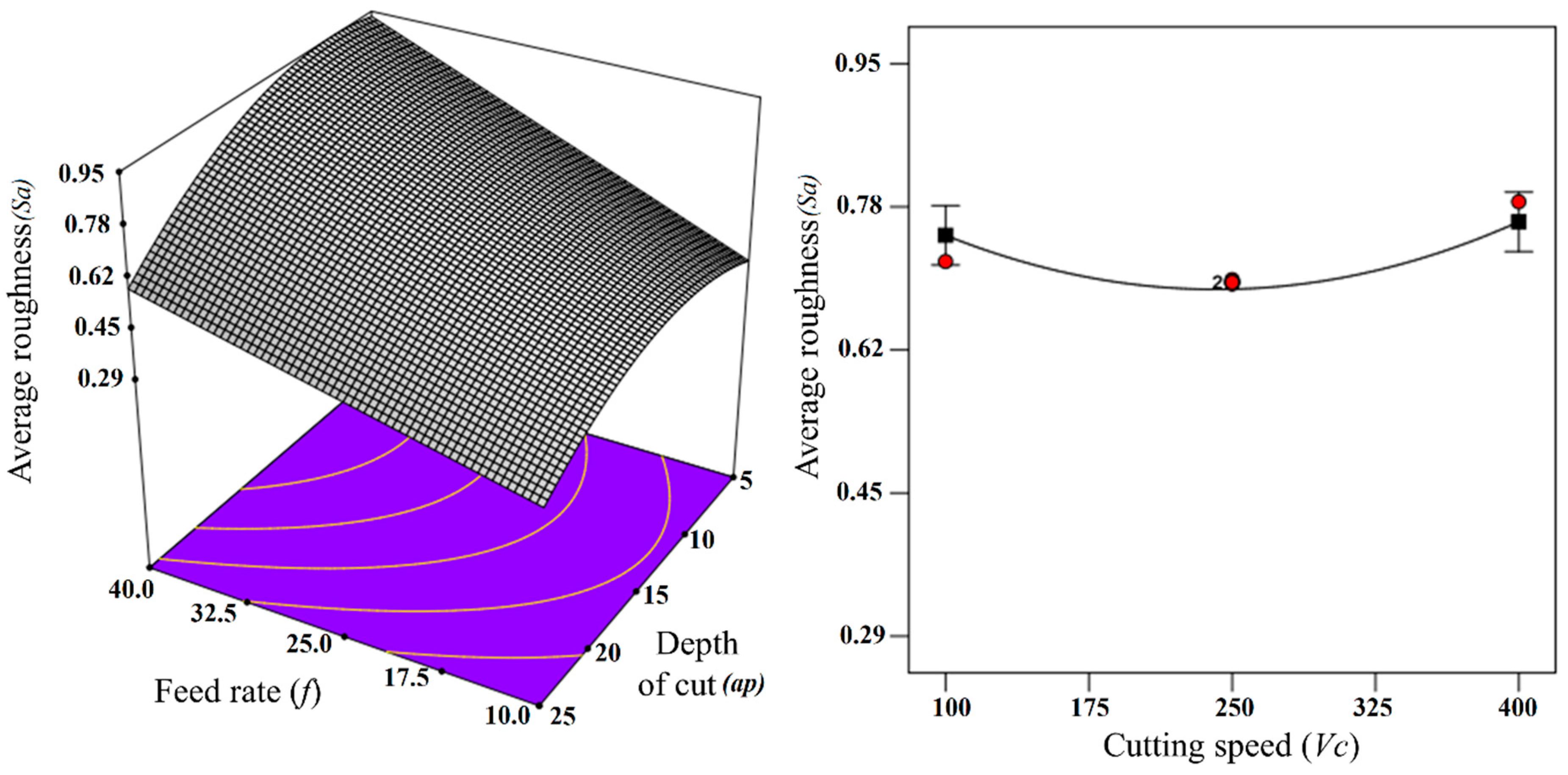
3.1. Model of Average Roughness (Sa)
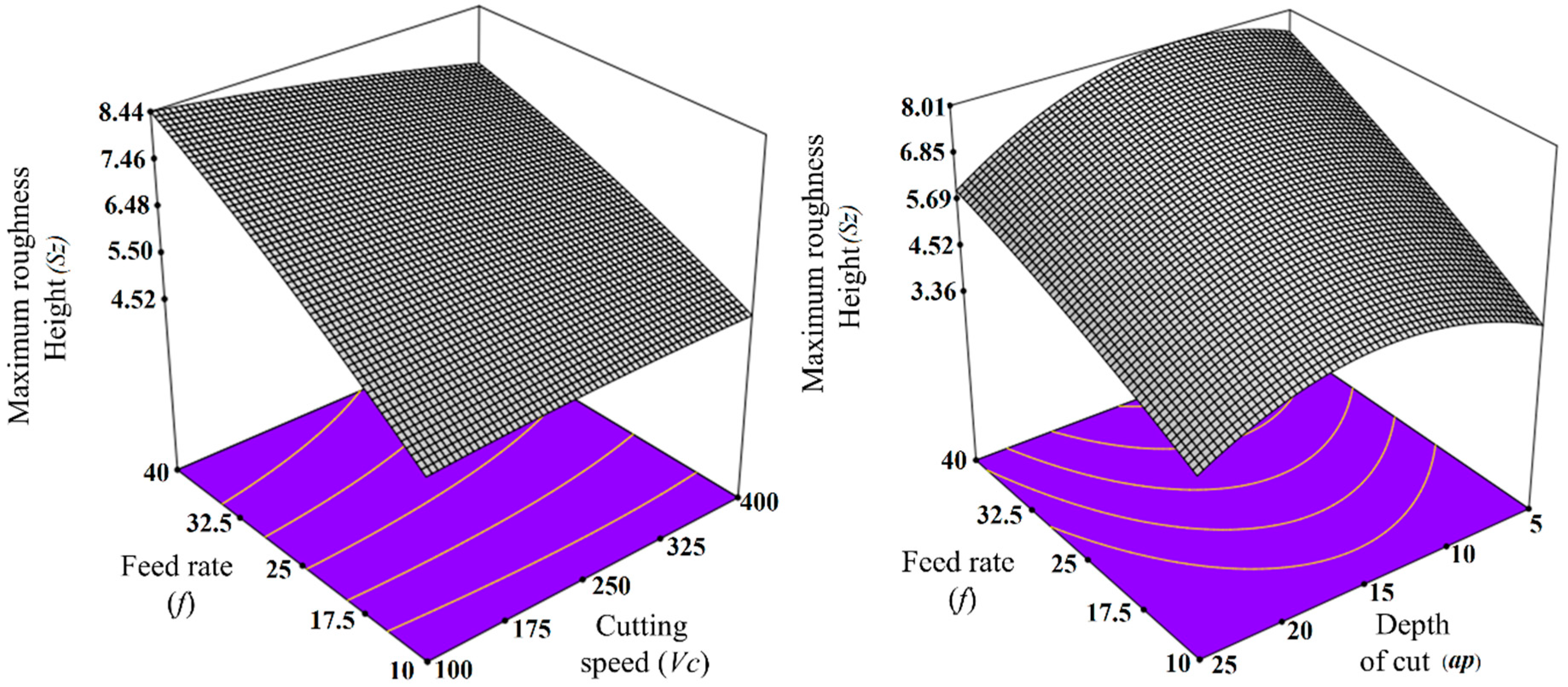
3.2. Model for Maximum Roughness Height (Sz)
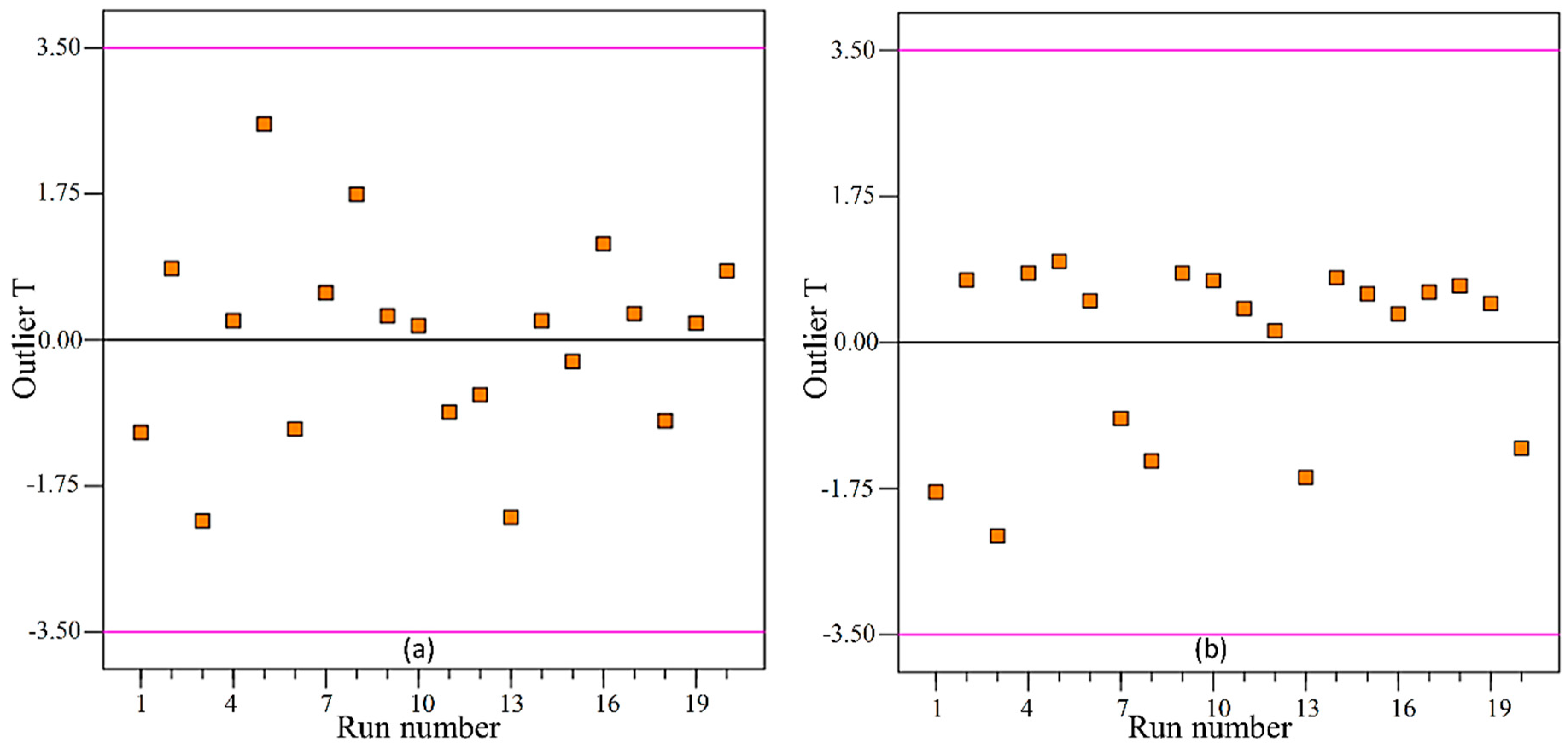
3.3. Adequacy Tests
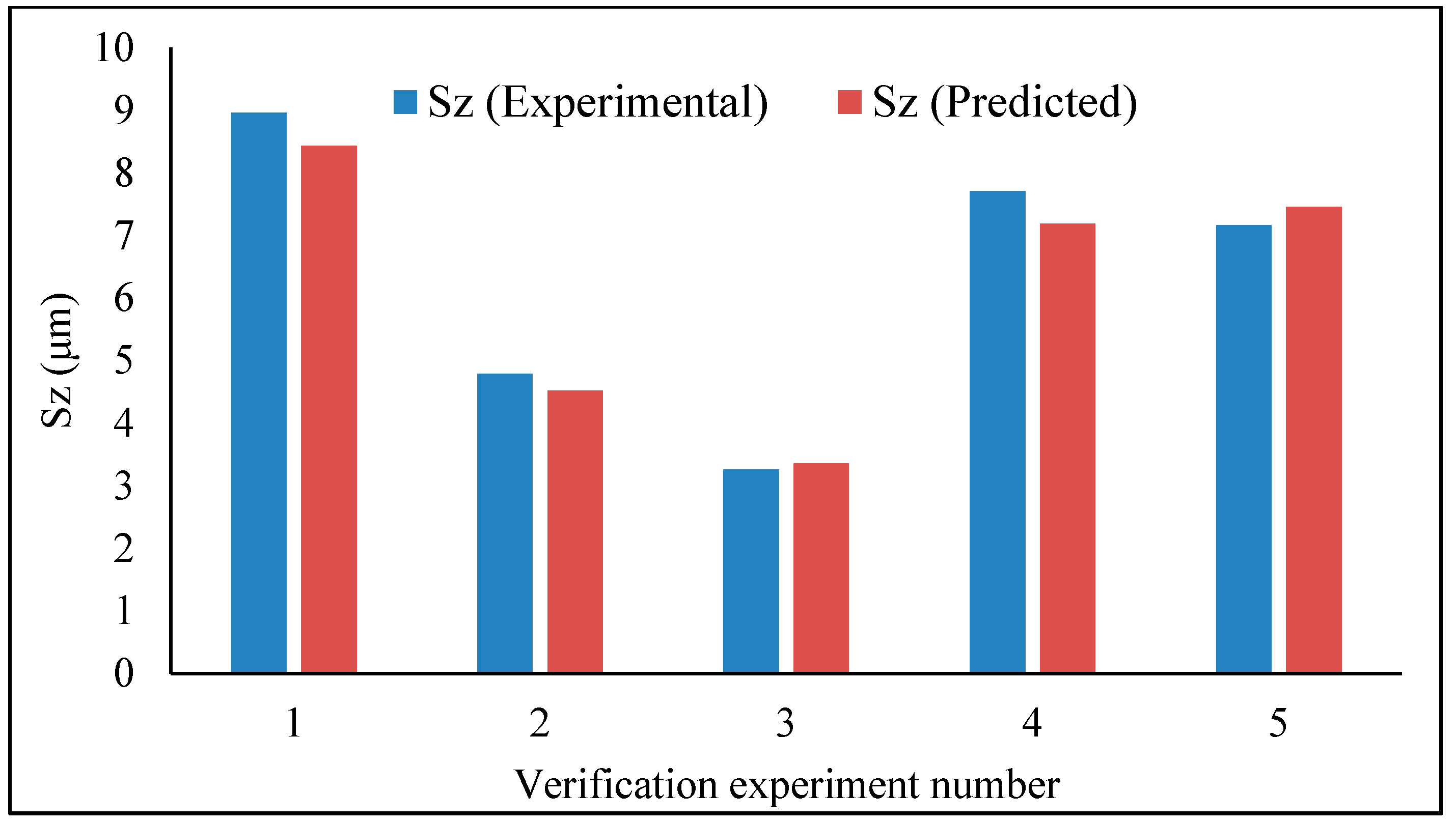
3.4. Experimental Verification Test
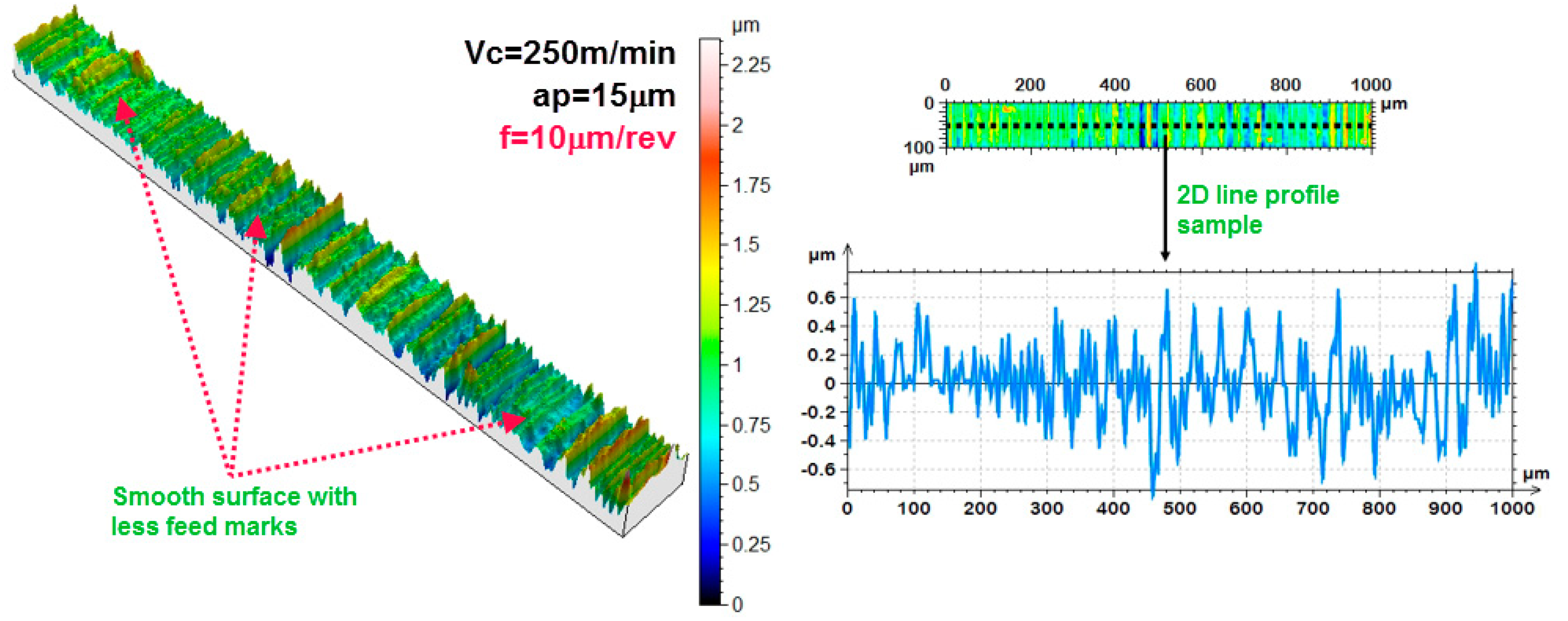
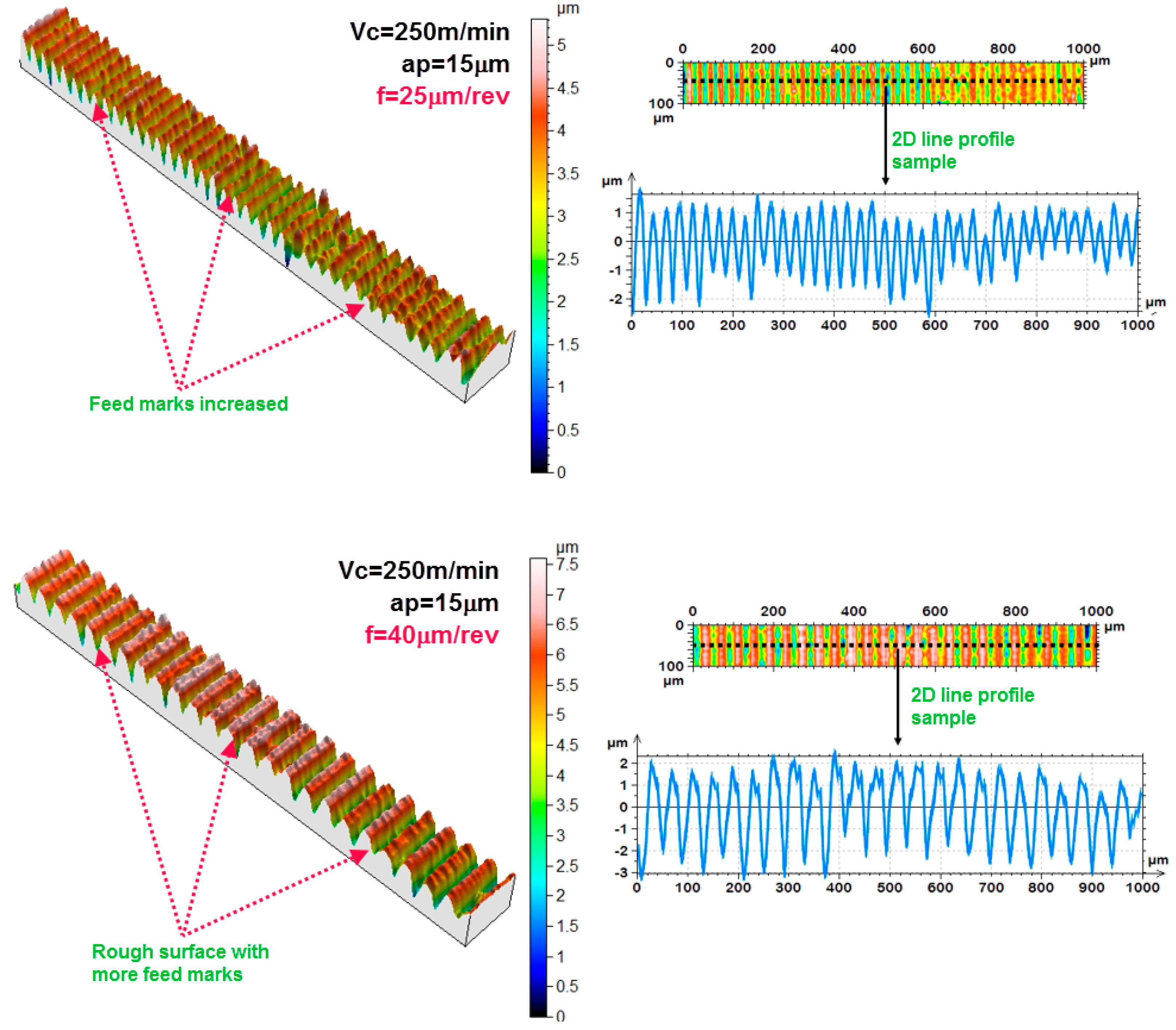
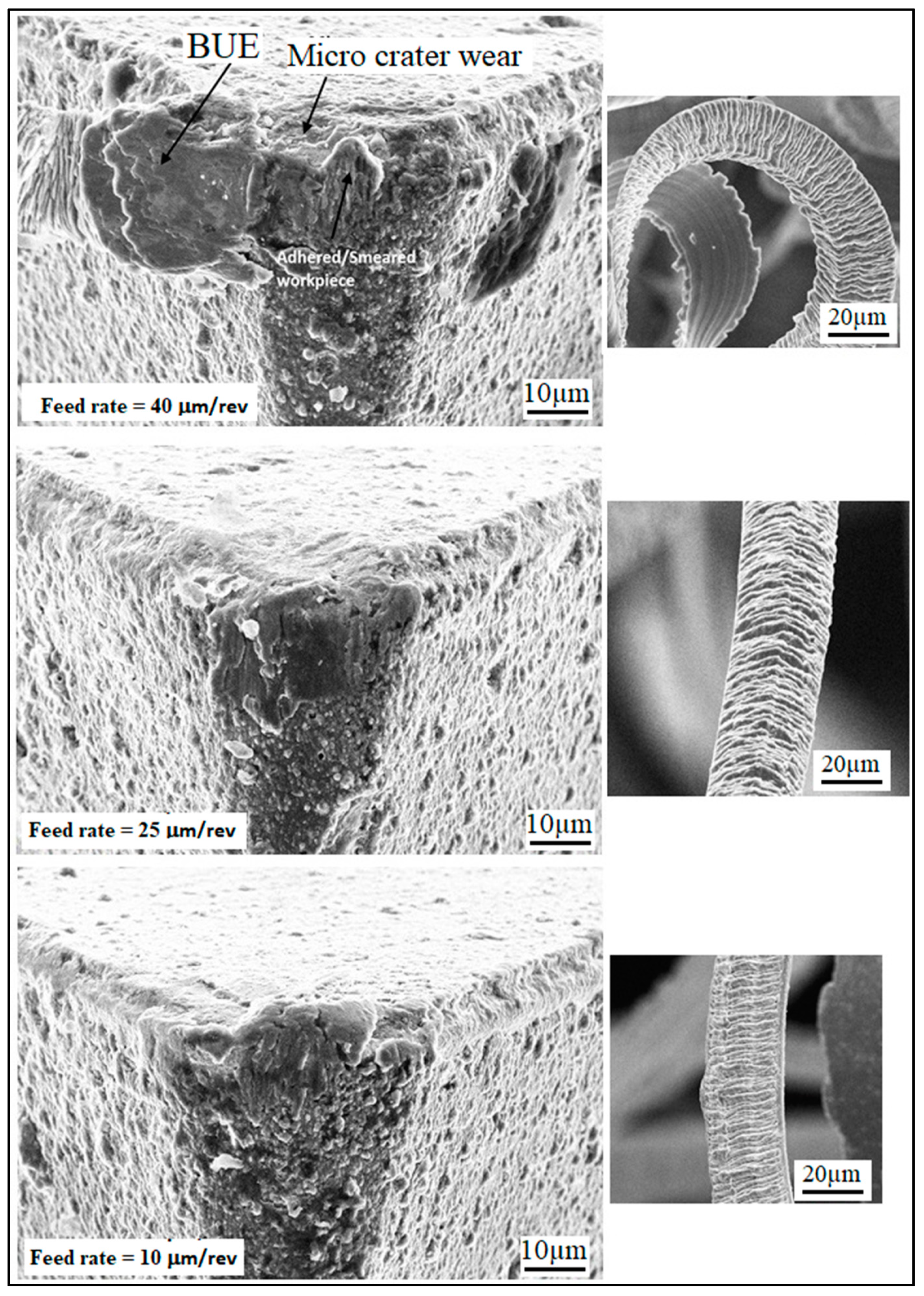
3.5. 3D Response Surface, One Factor Plots and Analysis by SEM
3.6. Optimization of Surface Roughness Parameters and Material Removal Rate
- For minimum Sa;
- For minimum Sz;
- For minimization of both Sa and Sz simultaneously;
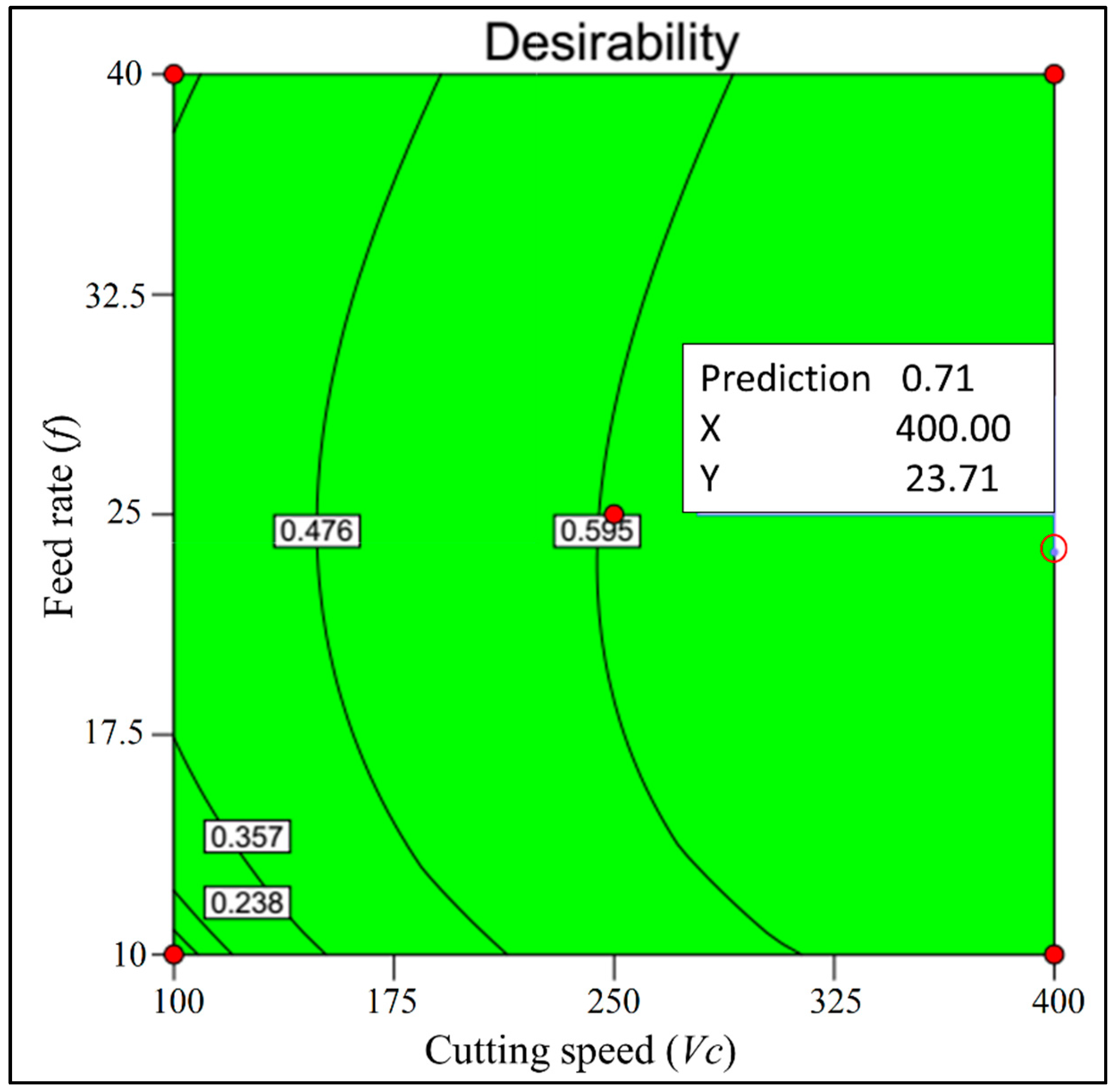
- For minimum of surface roughness (Sa and Sz) and maximum MRR at the same time.
4. Conclusions
- Empirical relations between cutting parameters and surface roughness (Sa and Sz) of the TiAl4V alloy was successfully developed using RSM for the micro-turning process;
- The efficiency of both models was checked according to the different R2 terms. The developed models showed good accuracy in terms of correlation coefficient, close to unity. The residual plots and the outliers plot showed the adequacy of the models. Last but not least, the verification test showed superior accuracy, an error value of less than 7% for both the average roughness parameter and maximum height roughness parameter;
- With the increase in feed rate, both the Sa and Sz of the TiAl4V alloy were found to be increased, while a mixed trend was observed for other cutting parameters. Overall, the most dominant factor which affects the Sa and Sz of the micro-turned TiAl4V was found to be the feed rate;
- The tool wear results show that the crater wear is the dominant wear for micro-turned Ti-6Al-4V alloys. Moreover, the higher serrations in the chips were observed at high feed rate values, which is also the reason for the poor surface roughness values;
- All optimization results are as follows:
- Minimum Sa optimization: Vc = 156.14 m/min, f =10.44 μm /rev and ap = 24.92 μm;
- Minimum Sz optimization: Vc = 339.67 m/min, f =10.55 μm /rev and ap = 24.87 μm;
- Minimum Sa and Sz optimization: Vc = 340.49 m/min, f = 10.24 μm /rev and ap = 24.87 μm;
- For minimum of surface roughness (Sa and Sz) and maximum MRR at the same time: Vc = 400 m/min, f = 23.71 μm/rev and ap = 25 μm;
- The optimized values for Sa, Sz and MRR obtained by the multi-objective optimization approach were 0.50 μm, 4.16 μm and 239.03 mm3/min, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, D.; Wang, B.; Fang, F. Effects of tool wear on surface micro-topography in ultra-precision turning. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 102, 4397–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojciechowski, S.; Matuszak, M.; Powałka, B.; Madajewski, M.; Maruda, R.W.; Królczyk, G.M. Prediction of cutting forces during micro end milling considering chip thickness accumulation. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2019, 147, 103466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuff, C.M.; Danish, M.; Ho, E.T.W.; Basha, K.; Hussain, I.; Hamid, N.H.B. Study on the optimum cutting parameters of an aluminum mold for effective bonding strength of a PDMS microfluidic device. Micromachines 2017, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boswell, B.; Islam, M.N.; Davies, I.J. A review of micro-mechanical cutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 94, 789–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ginta, T.L.; Abdul Rani, A.M.; Carou, D.; Davim, J.P.; Rubaiee, S. Investigation of surface integrity induced on AZ31C magnesium alloy turned under cryogenic and dry conditions. Procedia Manuf. 2019, 41, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piotrowska, I.; Brandt, C.; Karimi, H.R.; Maass, P. Mathematical model of micro turning process. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2009, 45, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Melkote, S.N. Effect of plastic side flow on surface roughness in micro-turning process. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, Z.; Shi, Z.; Xu, C. Size effect on surface roughness in micro turning. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2013, 14, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; He, N.; Li, L.; Liu, Z.Q.; Wu, W.F.; Zheng, K.B. Analyses of Size Effect on Surface Roughness in Micro Turning Process. In Materials Science Forum. Trans Tech. Publ. 2012, 723, 389–393. [Google Scholar]
- Danish, M.; Yasir, M.; Mia, M.; Nazir, K.; Ahmed, T.; Rani, A.M.A. High speed machining of magnesium and its alloys. In High Speed Mach; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2020; pp. 263–282. [Google Scholar]
- Mia, M.; Morshed, M.S.; Kharshiduzzaman, M.; Razi, M.H.; Mostafa, M.R.; Rahman, S.M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Hafiz, M.T.; Kamal, A.M. Prediction and optimization of surface roughness in minimum quantity coolant lubrication applied turning of high hardness steel. Measurement 2018, 118, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.; Dhar, N.R. Prediction of surface roughness in hard turning under high pressure coolant using Artificial Neural Network. Measurement 2016, 92, 464–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Rahman, M.; Kumar, A.S.; Lim, H.S.; Asad, A. Development of micropin fabrication process using tool based micromachining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 27, 939–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alauddin, M.; El Baradie, M.A.; Hashmi, M.S.J. Optimization of surface finish in end milling Inconel 718. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 1996, 56, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Jia, Z.; Jia, X.; Li, G.; Wu, W. Research on the prediction model of micro-milling surface roughness. Int. J. Nanomanuf. 2013, 9, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuram, E.; Ozcelik, B. Multi-objective optimization using Taguchi based grey relational analysis for micro-milling of Al 7075 material with ball nose end mill. Measurement 2013, 46, 1849–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vipindas, K.; Kuriachen, B.; Mathew, J. Investigations into the effect of process parameters on surface roughness and burr formation during micro end milling of TI-6AL-4V. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 100, 1207–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslantas, K.; Ekici, E.; Çiçek, A. Optimization of process parameters for micro milling of Ti-6Al-4V alloy using Taguchi-based gray relational analysis. Measurement 2018, 128, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ucun, İ.; Aslantaş, K.; Gökçe, B.; Bedir, F. Effect of tool coating materials on surface roughness in micromachining of Inconel 718 super alloy. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 2014, 228, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepsonthi, T.; Özel, T. Multi-objective process optimization for micro-end milling of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2012, 63, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.P.L. Measurement and uncertainty analysis of surface roughness and material removal rate in micro turning operation and process parameters optimization. Measurement 2019, 140, 538–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Yahya, S.; Saha, B.B. Modelling and optimization of thermophysical properties of aqueous titania nanofluid using response surface methodology. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 139, 3051–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshtegar, B.; Mert, C.; Kisi, O. Comparison of four heuristic regression techniques in solar radiation modeling: Kriging method vs RSM, MARS and M5 model tree. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 330–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danish, M.; Ginta, T.L.; Habib, K.; Carou, D.; Rani, A.M.A.; Saha, B.B. Thermal analysis during turning of AZ31 magnesium alloy under dry and cryogenic conditions. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 91, 2855–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabbi, A.; Yallese, M.A.; Meddour, I.; Nouioua, M.; Mabrouki, T.; Girardin, F. Predictive modeling and multi-response optimization of technological parameters in turning of Polyoxymethylene polymer (POM C) using RSM and desirability function. Measurement 2017, 95, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groover, M.P. Fundamentals of Modern Manufacturing: Materials Processes, and Systems; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; ISBN 8126512660. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, G.; Gupta, M.K.; Mia, M.; Sharma, V.S. Modeling and optimization of tool wear in MQL-assisted milling of Inconel 718 superalloy using evolutionary techniques. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 97, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M.; Singh, G.; Gupta, M.K.; Sharma, V.S. Influence of Ranque-Hilsch vortex tube and nitrogen gas assisted MQL in precision turning of Al 6061-T6. Precis. Eng. 2018, 53, 289–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popov, A.; Dugin, A. Effect of uncut chip thickness on the ploughing force in orthogonal cutting. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 76, 1937–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mia, M. Multi-response optimization of end milling parameters under through-tool cryogenic cooling condition. Measurement 2017, 111, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Sood, P.K.; Sharma, V.S. Optimization of machining parameters and cutting fluids during nano-fluid based minimum quantity lubrication turning of titanium alloy by using evolutionary techniques. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 135, 1276–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Mia, M.; Singh, G.R.; Pimenov, D.Y.; Sarikaya, M.; Sharma, V.S. Hybrid cooling-lubrication strategies to improve surface topography and tool wear in sustainable turning of Al 7075-T6 alloy. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 101, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
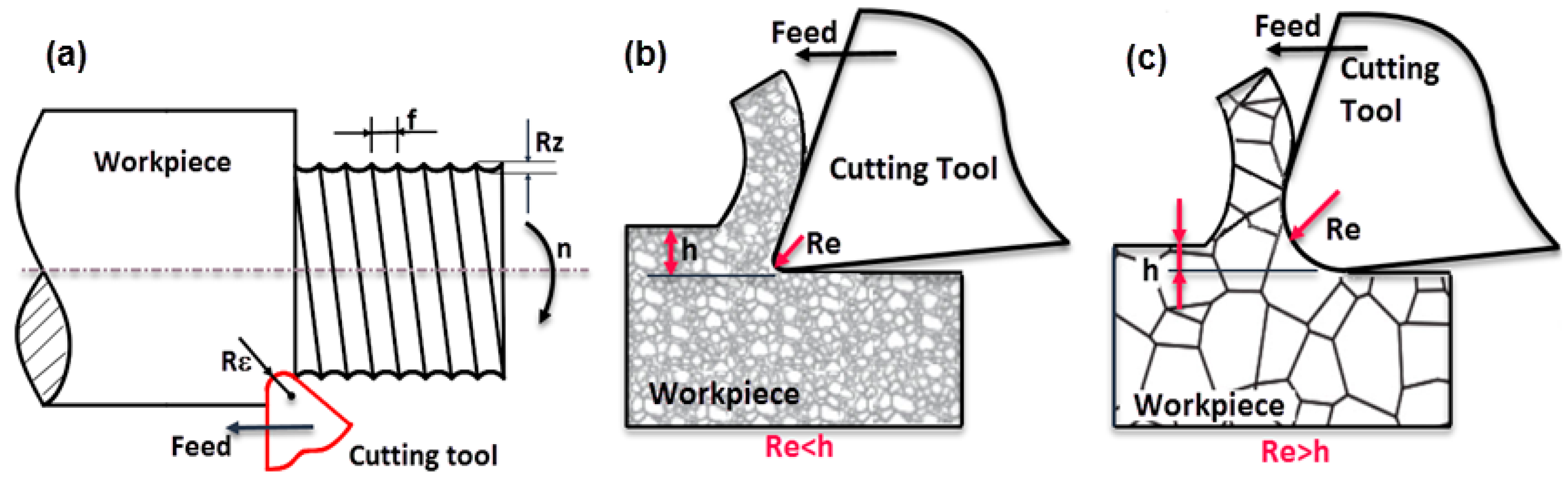
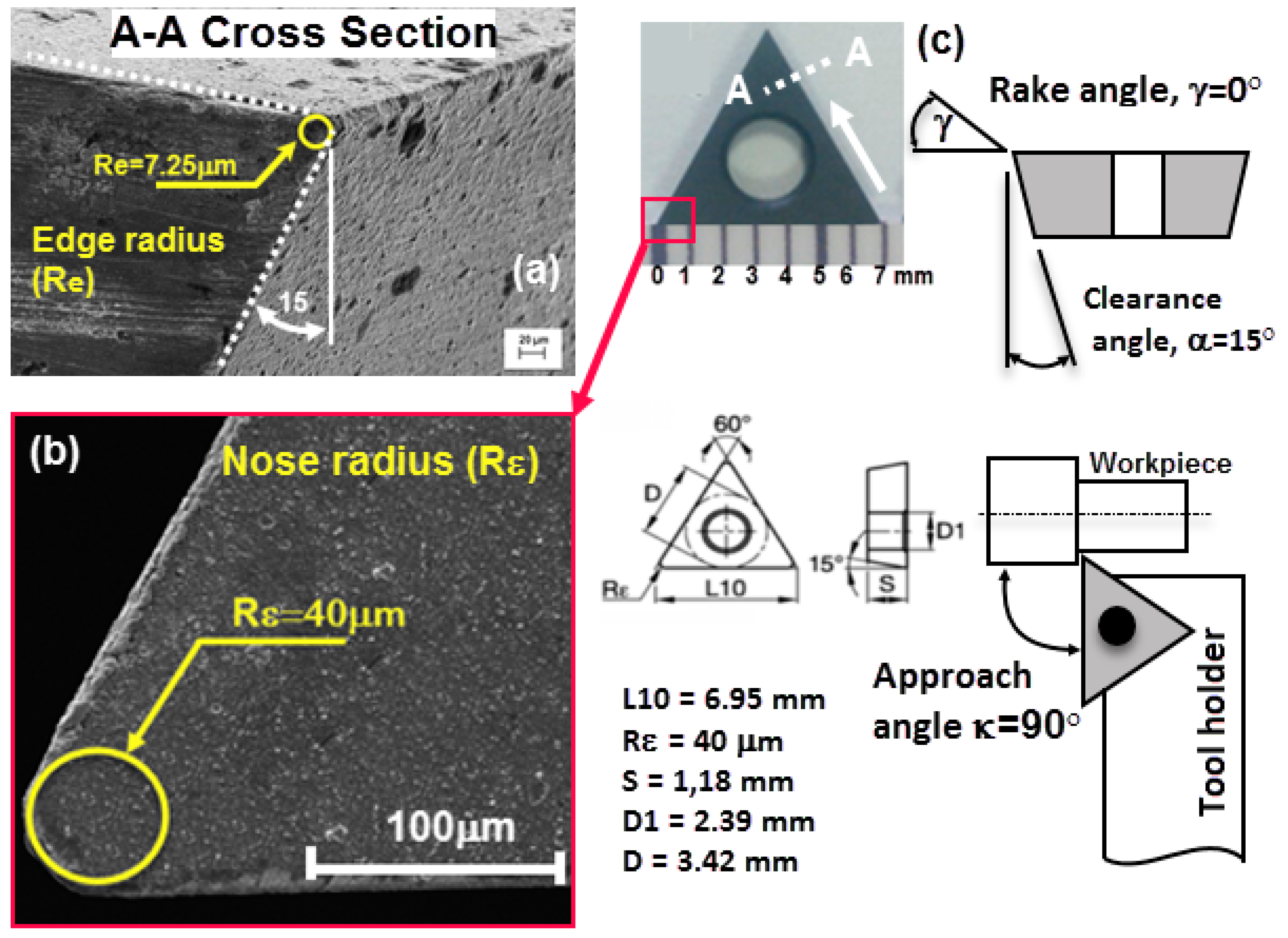
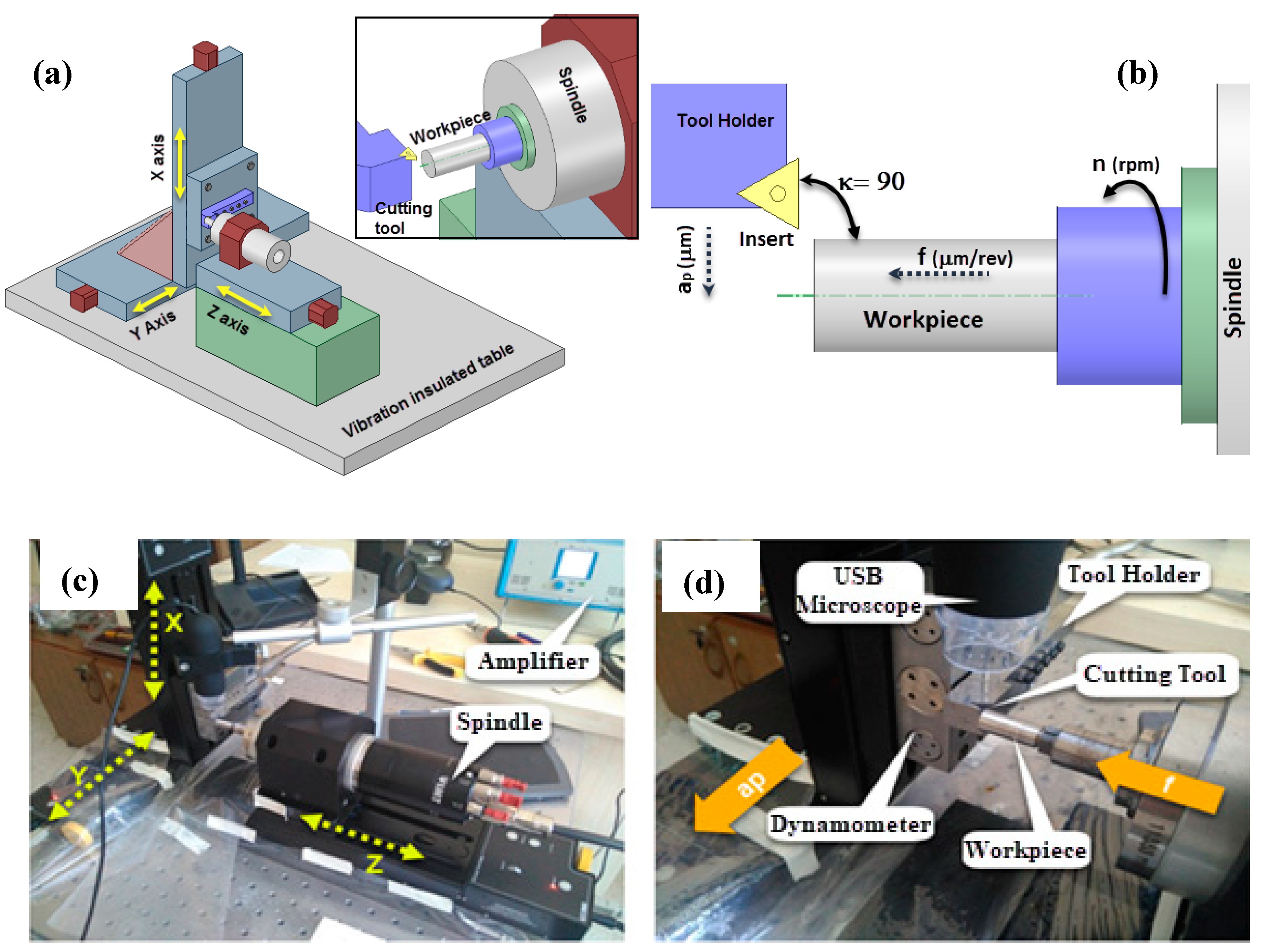





| Element | Al | V | Fe | C | O | N | H | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt % | 6.40 | 4.16 | 0.16 | 0.028 | 0.154 | 0.017 | 0.001 | Balance |
| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 900–1000 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 830–910 |
| Elongation (%) | 10–18 |
| Elastic Modulus (GPa) | 114 |
| Hardness (Brinell) | 330–340 |
| Levels | Cutting Speed (Vc) (m/min) | Feed Rate (f) (μm/rev) | Depth of Cut (ap) (μm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 100 | 25 | 5 |
| 2 | 250 | 10 | 15 |
| 3 | 400 | 40 | 25 |
| Sr. NO | Inputs | Outputs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting Speed (Vc) (m/min) | Feed Rate (f) (μm/rev) | Depth of Cut (ap) (μm) | Average Roughness (Sa) (μm) | Maximum Roughness Height (Sz) (μm) | Material Removal Rate (mm3/min) | |
| 1 | 100.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.72 | 5.94 | 37.50 |
| 2 | 400.00 | 10.00 | 25.00 | 0.39 | 3.35 | 100.00 |
| 3 | 250.00 | 10.00 | 15.00 | 0.42 | 3.83 | 37.50 |
| 4 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.70 | 6.98 | 93.75 |
| 5 | 100.00 | 10.00 | 5.00 | 0.52 | 3.48 | 05.00 |
| 6 | 100.00 | 40.00 | 25.00 | 0.62 | 6.87 | 100.00 |
| 7 | 250.00 | 40.00 | 15.00 | 0.91 | 7.48 | 150.00 |
| 8 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 25.00 | 0.48 | 4.23 | 156.25 |
| 9 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.70 | 6.98 | 93.75 |
| 10 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.69 | 6.93 | 93.75 |
| 11 | 400.00 | 40.00 | 5.00 | 0.99 | 7.12 | 80.00 |
| 12 | 400.00 | 40.00 | 25.00 | 0.64 | 5.02 | 400.00 |
| 13 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 5.00 | 0.62 | 5.06 | 31.25 |
| 14 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.70 | 6.95 | 93.75 |
| 15 | 400.00 | 10.00 | 5.00 | 0.48 | 4.07 | 20.00 |
| 16 | 100.00 | 40.00 | 5.00 | 1.02 | 7.85 | 20.00 |
| 17 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.70 | 6.85 | 93.75 |
| 18 | 100.00 | 10.00 | 25.00 | 0.33 | 3.63 | 25.00 |
| 19 | 250.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.69 | 6.77 | 93.75 |
| 20 | 400.00 | 25.00 | 15.00 | 0.79 | 5.59 | 150.00 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | Dominance of Factor | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.657 | 9 | 0.072 | 56.69 | 99.55% | <0.0001 |
| Vc | 6.084 × 10−4 | 1 | 6.084 × 10−4 | 0.48 | 0.09% | 0.5040 |
| f | 0.42 | 1 | 0.42 | 330.95 | 63.64% | <0.0001 |
| ap | 0.14 | 1 | 0.14 | 108.67 | 21.21% | <0.0001 |
| Vc2 | 0.015 | 1 | 0.015 | 12.16 | 2.27% | 0.0059 |
| f2 | 4.423 × 10−4 | 1 | 4.423 × 10−4 | 0.35 | 0.07% | 0.5676 |
| ap2 | 0.047 | 1 | 0.047 | 37.09 | 7.12% | 0.0001 |
| Vcf | 7.812 × 10−5 | 1 | 7.812 × 10−5 | 0.062 | 0.01% | 0.8088 |
| Vcap | 3.240 × 10−3 | 1 | 3.240 × 10−3 | 2.56 | 0.49% | 0.1407 |
| f ap | 0.026 | 1 | 0.026 | 20.26 | 3.94% | 0.0011 |
| Residual | 0.013 | 10 | 1.266 × 10−3 | - | 1.97% | - |
| Total | 0.66 | 19 | - | - | 100% | - |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | Dominance of Factor | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 0.64 | 6 | 0.11 | 84.73 | 96.97% | <0.0001 |
| Vc | 6.084 × 10−4 | 1 | 6.084 × 10−4 | 0.48 | 0.09% | 0.4999 |
| f | 0.42 | 1 | 0.42 | 331.71 | 63.64% | <0.0001 |
| ap | 0.14 | 1 | 0.14 | 108.92 | 21.21% | <0.0001 |
| Vc2 | 0.016 | 1 | 0.016 | 12.44 | 2.42% | 0.0037 |
| a2 | 0.059 | 1 | 0.059 | 46.47 | 8.94% | <0.0001 |
| f ap | 0.026 | 1 | 0.026 | 20.31 | 3.94% | 0.0006 |
| Residual | 0.016 | 13 | 1.263 × 10−3 | - | 2.42% | - |
| Total | 0.66 | 19 | - | - | 100% | - |
| Parameter | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| R2 (overall) | 0.98 | 0.98 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.96 | 0.96 |
| Predicted R2 | 0.85 | 0.92 |
| Adeq Precision | 27.44 | 31.37 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | Dominance of Factor | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 40.00 | 9 | 4.44 | 11.29 | 91.03% | 0.0004 |
| Vc | 0.69 | 1 | 0.69 | 1.74 | 1.57% | 0.2161 |
| F | 25.54 | 1 | 25.54 | 64.87 | 58.12% | <0.0001 |
| ap | 2.01 | 1 | 2.01 | 5.10 | 4.57% | 0.0475 |
| Vc2 | 0.018 | 1 | 0.018 | 0.045 | 0.04% | 0.8368 |
| f2 | 0.099 | 1 | 0.099 | 0.25 | 0.23% | 0.6264 |
| ap2 | 3.96 | 1 | 3.96 | 10.06 | 9.01% | 0.0100 |
| Vcf | 1.04 | 1 | 1.04 | 2.65 | 2.37% | 0.1345 |
| Vcap | 0.50 | 1 | 0.50 | 1.26 | 1.14% | 0.2883 |
| f ap | 0.79 | 1 | 0.79 | 2.00 | 1.80% | 0.1876 |
| Residual | 3.94 | 10 | 0.39 | - | 8.97% | - |
| Total | 43.94 | 19 | - | - | 100% | - |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F-Value | Dominance of Factor | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 36.82 | 3 | 12.27 | 27.57 | 83.80% | <0.0001 |
| f | 25.54 | 1 | 25.54 | 57.37 | 58.13% | <0.0001 |
| ap | 2.01 | 1 | 2.01 | 4.51 | 4.57% | 0.0497 |
| a2 | 9.28 | 1 | 9.28 | 20.84 | 21.12% | 0.0003 |
| Residual | 7.12 | 16 | 0.45 | - | 16.20% | - |
| Total | 43.94 | 19 | - | - | 100% | - |
| Parameter | Before | After |
|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.91 | 0.84 |
| Adjusted R2 | 0.83 | 0.81 |
| Predicted R2 | 0.61 | 0.73 |
| Adequate Precision | 10.73 | 16.78 |
| Name | Goal | Lower Limit | Upper Limit | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cutting speed (Vc) | is in range | 100 | 400 | - |
| Feed rate (f) | is in range | 10 | 40 | - |
| Depth of cut (ap) | is in range | 5 | 25 | - |
| Average roughness (Sa) | Minimize | 0.325 | 1.02 | 5 |
| Maximum roughness height (Sz) | Minimize | 3.35 | 7.85 | 5 |
| Material removal rate (MMR) | Maximize | 5 | 400 | 5 |
| Sr. No. | Vc | f | ap | Sa | Sz | MMR | Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 400.00 | 23.71 | 25.00 | 0.50 | 4.16 | 239.03 | 0.714 Selected |
| 2 | 400.00 | 23.88 | 25.00 | 0.50 | 4.17 | 240.45 | 0.714 |
| 3 | 400.00 | 23.18 | 25.00 | 0.49 | 4.13 | 234.525 | 0.713 |
| 4 | 400.00 | 22.24 | 24.97 | 0.49 | 4.08 | 226.261 | 0.712 |
| 5 | 400.00 | 22.56 | 24.94 | 0.49 | 4.11 | 228.645 | 0.710 |
| 6 | 400.00 | 33.41 | 25.00 | 0.59 | 4.70 | 321.503 | 0.700 |
| 7 | 400.00 | 10.31 | 25.00 | 0.37 | 3.16 | 125.099 | 0.659 |
| 8 | 100.00 | 10.00 | 5.01 | 0.47 | 3.21 | 27.4834 | 0.356 |
| Optimization Cases | Vc (m/min) | f (μm/rev) | ap (μm) | Sa (μm) | Sz (μm) | MMR (mm3/min) | Desirability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum Sa | 156.14 | 10.44 | 24.92 | 0.32 | - | - | 1.000 |
| Minimum Sz | 339.67 | 10.55 | 24.87 | - | 3.34 | - | 1.000 |
| Minimization of both Sa and Sz | 340.49 | 10.24 | 24.87 | 0.32 | 3.30 | - | 1.000 |
| Minimization of Sa and Sz and maximization of MMR | 400.00 | 23.71 | 25.00 | 0.50 | 4.16 | 239.03 | 0.714 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aslantas, K.; Danish, M.; Hasçelik, A.; Mia, M.; Gupta, M.; Ginta, T.; Ijaz, H. Investigations on Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Characteristics in Micro-Turning of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials 2020, 13, 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132998
Aslantas K, Danish M, Hasçelik A, Mia M, Gupta M, Ginta T, Ijaz H. Investigations on Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Characteristics in Micro-Turning of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials. 2020; 13(13):2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132998
Chicago/Turabian StyleAslantas, Kubilay, Mohd Danish, Ahmet Hasçelik, Mozammel Mia, Munish Gupta, Turnad Ginta, and Hassan Ijaz. 2020. "Investigations on Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Characteristics in Micro-Turning of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy" Materials 13, no. 13: 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132998
APA StyleAslantas, K., Danish, M., Hasçelik, A., Mia, M., Gupta, M., Ginta, T., & Ijaz, H. (2020). Investigations on Surface Roughness and Tool Wear Characteristics in Micro-Turning of Ti-6Al-4V Alloy. Materials, 13(13), 2998. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132998








