Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Effects on Metallic Brackets and Wires: Does It Alter the Temperature and Bonding Efficacy of Orthodontic Devices?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Specimen Preparation
- Group 1: No MRI—No Wire
- Group 2: 1.5 T MRI—No wire
- Group 3: 1.5 T MRI—0.014 inch stainless steel wire
- Group 4: 1.5 T MRI—0.019 × 0.025 inch stainless steel wire
- Group 5: 1.5 T MRI—0.014 inch nickel titanium wire
- Group 6: 1.5 T MRI—0.019 × 0.025 inch nickel titanium wire
- Group 7: 3 T MRI—No wire
- Group 8: 3 T MRI—0.014 inch stainless steel wire
- Group 9: 3 T MRI—0.019 × 0.025 inch stainless steel wire
- Group 10: 3 T MRI—0.014 inch nickel titanium wire
- Group 11: 3 T MRI—0.019 × 0.025 inch nickel titanium wire
2.2. Temperature Test and MRI
2.3. Shear Bond Strength Test
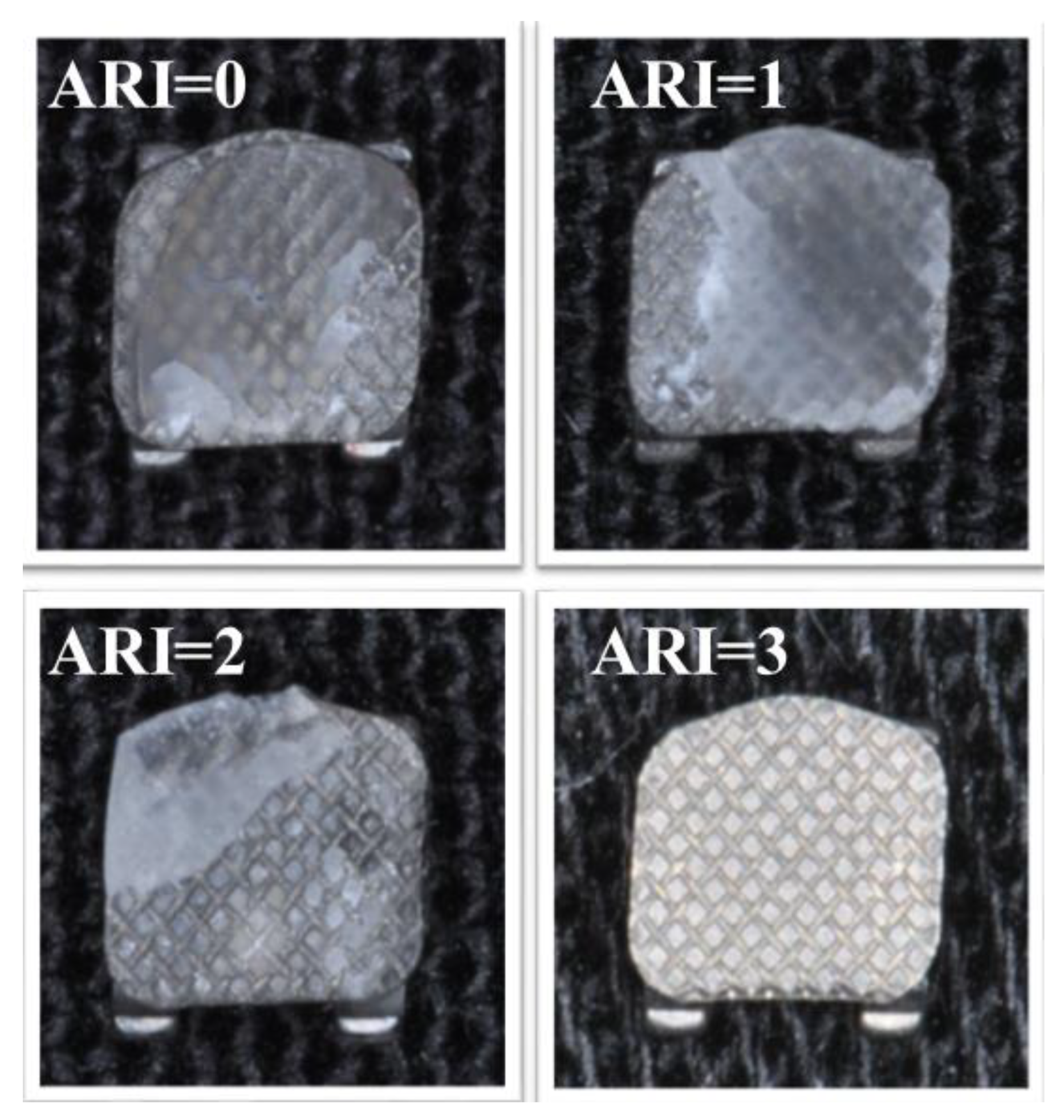
2.4. Adhesive Remnant Index Test
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
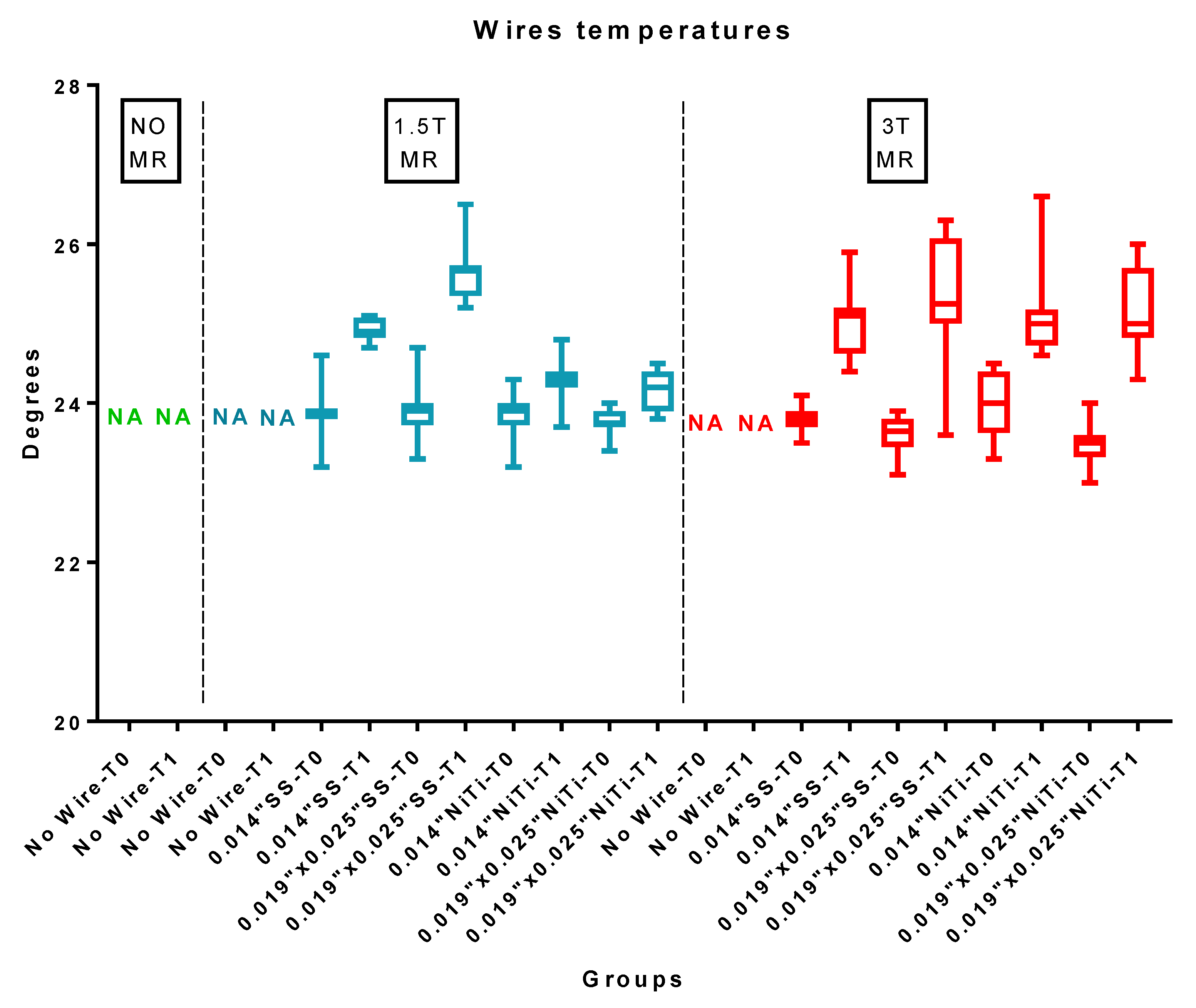
3.1. Temperature Test
3.2. Shear Bond Strength Test
3.3. ARI Score Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oshagh, M.; Hematian, M.R.; Shahidi, S.; Feizi, N.; Bayani, F.; Pishbin, L. Effect of MRI on the mechanical properties of stainless steel orthodontic wires. World J. Orthod. 2010, 11, e72–e77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Poorsattar-Bejeh Mir, A.; Rahmati-Kamel, M. Should the orthodontic brackets always be removed prior to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)? J. Oral Biol. Craniofacial Res. 2016, 6, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafiei, F.; Honda, E.; Takahashi, H.; Sasaki, T. Artifacts from dental casting alloys in magnetic resonance imaging. J. Dent. Res. 2003, 82, 602–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shellock, F.G. Biomedical implants and devices: Assessment of magnetic field interactions with a 3.0-Tesla MR system. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2002, 16, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanin, M.; Kaplan, S.E.F.; Hohlen, B.; Lai, C.; Nagshabandi, R.; Zhu, X.; Al-Jewair, T. Effects of orthodontic appliances on the diagnostic capability of magnetic resonance imaging in the head and neck region: A systematic review. Int. Orthod. 2019, 17, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Rollins, N.K.; Liang, H.; Park, Y.J. Induced magnetic moment in stainless steel components of orthodontic appliances in 1.5 T MRI scanners. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 5871–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.L.; Appenzeller, S.; Yasuda, C.L.; Pereira, F.R.; Zanardi, V.A.; Cendes, F. Artifacts in brain magnetic resonance imaging due to metallic dental objects. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2009, 14, E278–E282. [Google Scholar]
- Blankenstein, F.H.; Asbach, P.; Beuer, F.; Glienke, J.; Mayer, S.; Zachriat, C. Magnetic permeability as a predictor of the artefact size caused by orthodontic appliances at 1.5 T magnetic resonance imaging. Clin. Oral Investig. 2017, 21, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degrazia, F.W.; Genari, B.; Ferrazzo, V.A.; Santos-Pinto, A.D.; Grehs, R.A. Enamel Roughness Changes after Removal of Orthodontic Adhesive. Dent. J. 2018, 6, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassaei, S.; Aghili, H.; KhanPayeh, E.; Goldani Moghadam, M. Comparison of shear bond strength of rebonded brackets with four methods of adhesive removal. Lasers Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 1563–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribante, A.; Vallittu, P.K.; Özcan, M. Fiber-Reinforced Composites for Dental Applications. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4734986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maekawa, M.; Kanno, Z.; Wada, T.; Hongo, T.; Doi, H.; Hanawa, T.; Ono, T.; Uo, M. Mechanical properties of orthodontic wires made of super engineering plastic. Dent. Mater. J. 2015, 34, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Calderoni, G.; Vitale, M.C.; Gandini, P.; Scribante, A. Is laser conditioning a valid alternative to conventional etching for aesthetic brackets? Eur. J. Paediatr. Dent. 2018, 19, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, D.J.; Walker, M.P.; Kula, K.; Williams, K.B.; Eick, J.D. Fluoride Prophylactic Agents Effect on Ceramic Bracket Tie-Wing Fracture Strength. Angle Orthod. 2008, 78, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, M. A comparison of treatment effectiveness between clear aligner and fixed appliance therapies. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Gandini, P.; Castroflorio, T.; Garino, F.; Mergati, L.; D’Anca, K.; Trovati, F.; Scribante, A. Buccolingual Inclination Control of Upper Central Incisors of Aligners: A Comparison with Conventional and Self-Ligating Brackets. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 9341821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassir, Y.A.; McIntyre, G.T.; Bearn, D.R. Variation in bracket slot sizes, ligation methods and prescriptions: UK national survey. Int. Orthod. 2019, 17, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Gatti, S.; Scribante, A. Effect of blood contamination on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets and disinclusion buttons. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 49, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görgülü, S.; Ayyildiz, S.; Kamburoglu, K.; Gökçe, S.; Ozen, T. Effect of orthodontic brackets and different wires on radiofrequency heating and magnetic field interactions during 3-T MRI. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2014, 43, 20130356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribante, A.; Sfondrini, M.F.; Gatti, S.; Gandini, P. Disinclusion of unerupted teeth by mean of self-ligating brackets: Effect of blood contamination on shear bond strength. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal 2013, 18, e162–e167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfondrini, M.F.; Gatti, S.; Scribante, A. Shear bond strength of self-ligating brackets. Eur. J. Orthod. 2011, 33, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beltrami, R.; Chiesa, M.; Scribante, A.; Allegretti, J.; Poggio, C. Comparison of shear bond strength of universal adhesives on etched and nonetched enamel. J. Appl. Biomater. Funct. Mater. 2016, 14, e78–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scribante, A.; Sfondrini, M.F.; Fraticelli, D.; Daina, P.; Tamagnone, A.; Gandini, P. The influence of no-primer adhesives and anchor pylons bracket bases on shear bond strength of orthodontic brackets. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 315023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artun, J.; Bergland, S. Clinical trials with crystal growth conditioning as an alternative to acid-etch enamel pretreatment. Am. J. Orthod. 1984, 85, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, M.; Miyata, K.; Abe, Y.; Ishigami, T. Radiofrequency heating of metallic dental devices during 3.0 T MRI. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2013, 42, 20120234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassi, K.; Ziane, F.; Bardinet, E.; Moinard, M.; Veyret, B.; Chateil, J.F. Evaluation of the risk of overheating and displacement of orthodontic devices in magnetic resonance imaging. J. Radiol. 2007, 88, 263–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regier, M.; Kemper, J.; Kaul, M.G.; Feddersen, M.; Adam, G.; Kahl-Nieke, B.; Klocke, A. Radiofrequency-induced heating near fixed orthodontic appliances in high field MRI systems at 3.0 Tesla. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2009, 70, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubálková, H.; Hora, K.; Seidl, Z.; Krásenský, J. Dental materials and magnetic resonance imaging. Eur. J. Prosthodont. Restor. Dent. 2002, 10, 125–130. [Google Scholar]
- El-Bediwi, A.B.; El-Fallal, A.; Saker, S.; Ozcan, M. Effect of non-ionizing radio frequency signals of magnetic resonance imaging on physical properties of dental alloys and metal-ceramic adhesion. J. Adhes. Dent. 2014, 16, 407–413. [Google Scholar]
- Kemper, J.; Klocke, A.; Kahl-Nieke, B.; Adam, G. Orthodontic brackets in high field MR imaging: Experimental evaluation of magnetic field interactions at 3.0 Tesla. Rofo 2005, 177, 1691–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scribante, A.; Contreras-Bulnes, R.; Montasser, M.A.; Vallittu, P.K. Orthodontics: Bracket Materials, Adhesives Systems, and Their Bond Strength. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 1329814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montasser, M.A.; Drummond, J.L. Reliability of the adhesive remnant index score system with different magnifications. Angle Orthod. 2009, 79, 773–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tymofiyeva, O.; Vaegler, S.; Rottner, K.; Boldt, J.; Hopfgartner, A.J.; Proff, P.C.; Richter, E.J.; Jakob, P.M. Influence of dental materials on dental MRI. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2013, 42, 20120271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhylich, D.; Krishnan, P.; Muthusami, P.; Rayner, T.; Shroff, M.; Doria, A.; Tompson, B.; Lou, W.; Suri, S. Effects of orthodontic appliances on the diagnostic quality of magnetic resonance images of the head. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2017, 151, 484–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalish, M.; Dykstein, N.; Friedlander-Barenboim, S.; Ben-David, E.; Gomori, J.M.; Chaushu, S. Influence of common fixed retainers on the diagnostic quality of cranial magnetic resonance images. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2015, 147, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, E.; Honda, E.I.; Parakonthun, K.N.; Ohmori, H.; Shimazaki, K.; Kurabayashi, T.; Ono, T. Influence of orthodontic appliance-derived artifacts on 3-T MRI movies. Prog. Orthod. 2018, 19, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beau, A.; Bossard, D.; Gebeile-Chauty, S. Magnetic resonance imaging artefacts and fixed orthodontic attachments. Eur. J. Orthod. 2015, 37, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainz, W. MR heating tests of MR critical implants. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 450–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
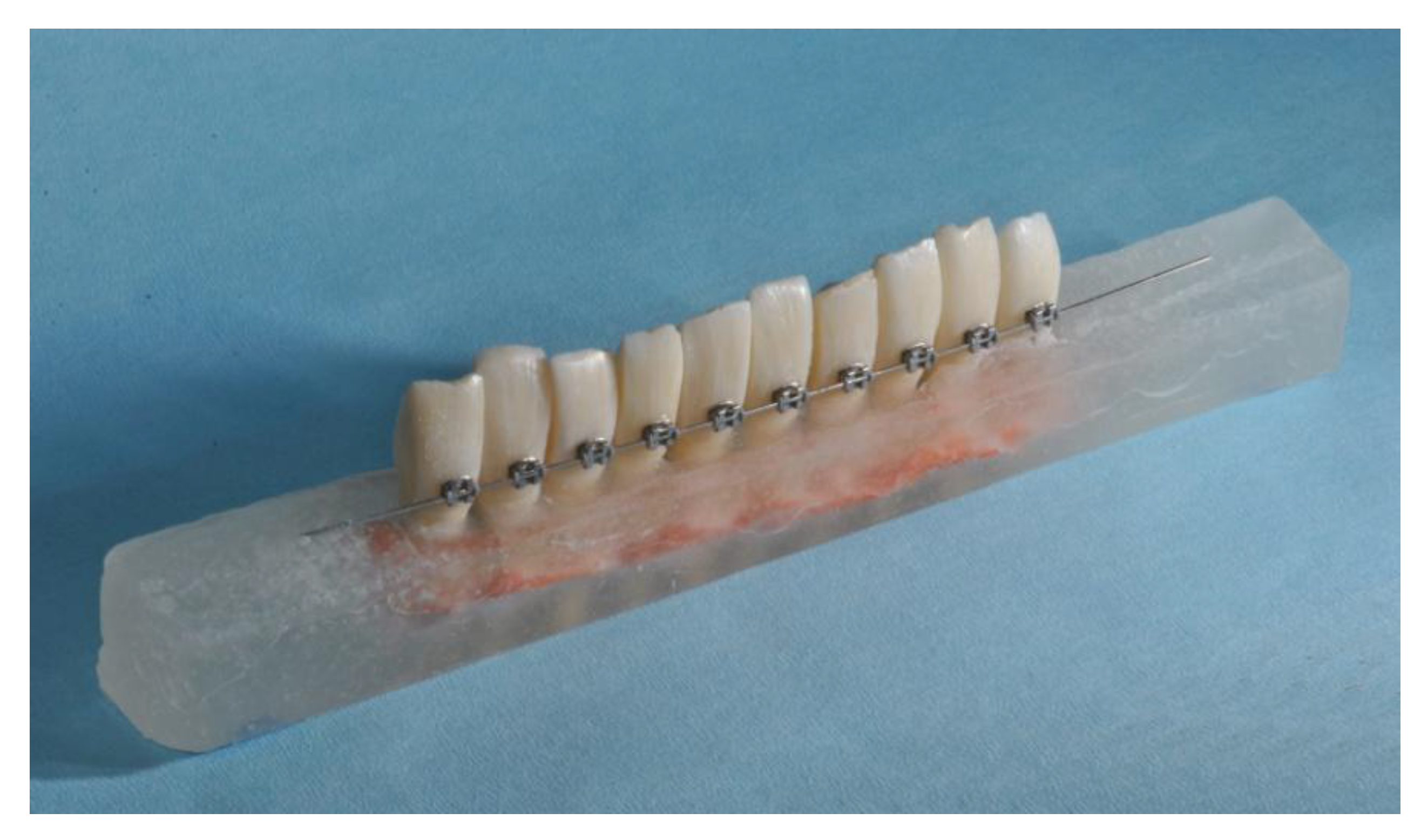
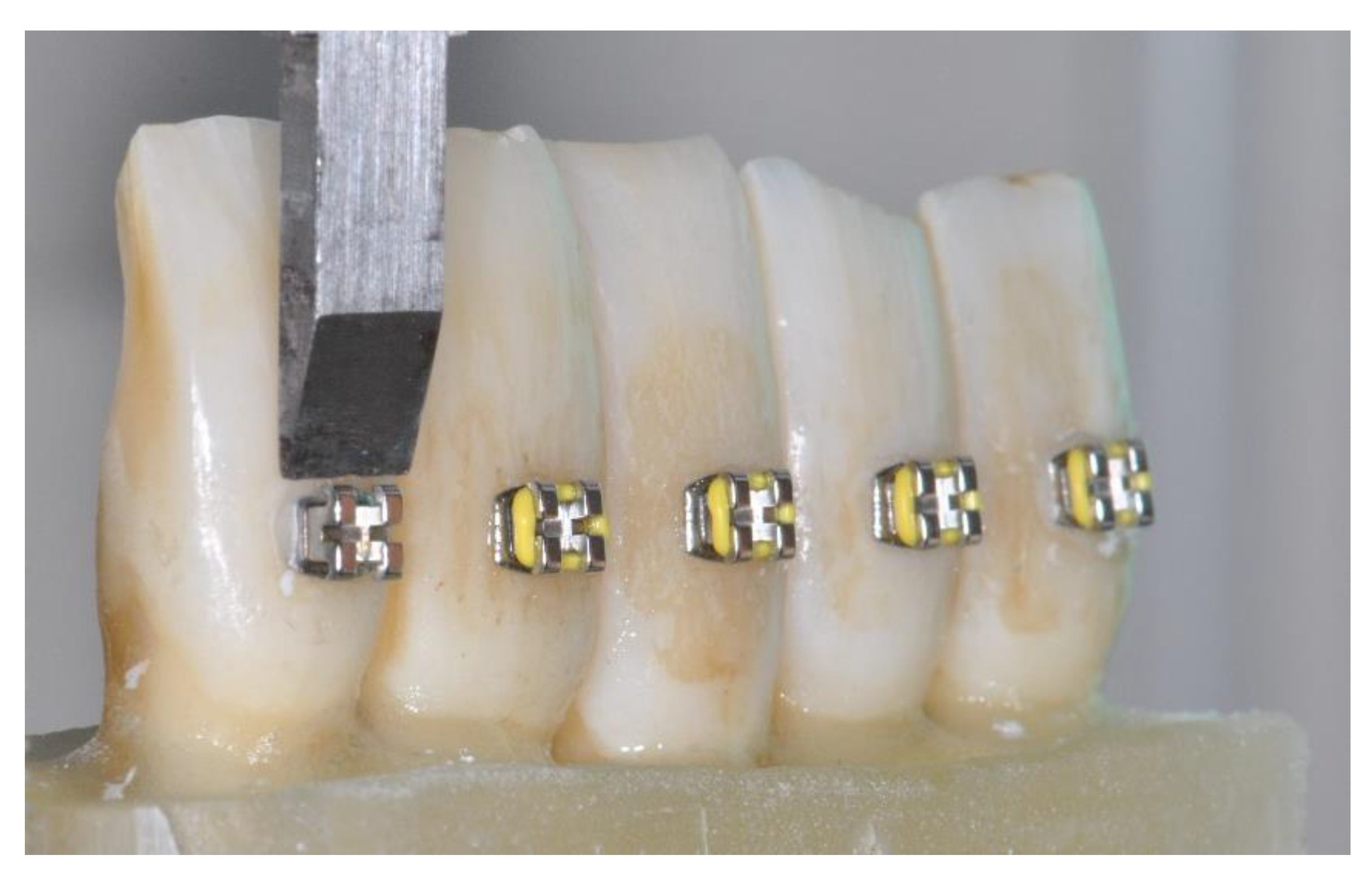

| Material | Commercial Name | Manufacturer | Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.014″ Orthodontic Stainless Steel Wire | Stainless steel wire, 0.014″ | Ormco, Glendora, CA, USA | 17–20% chromium, 8–12% nickel, and 0.08–0.15% carbon, with iron forming the balance |
| 0.019 × 0.025″ Orthodontic Stainless Steel Wire | Stainless steel wire, 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Ormco, Glendora, CA, USA | 17–20% chromium, 8–12% nickel, and 0.08–0.15% carbon, with iron forming the balance |
| 0.014″ Orthodontic Nickel Titanium Wire | Nickel Titanium wire, 0.014″ | Ormco, Glendora, CA, USA | 55% Nickel and 45% Titanium |
| 0.019 × 0.025″ Orthodontic Nickel Titanium Wire | Nickel Titanium wire, 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Ormco, Glendora, CA, USA | 55% Nickel and 45% Titanium |
| Orthodontic bracket | Victory MBT | 3M Unitek Monrovia, CA, USA | 18–20% chromium, 8–12% nickel, and 0.08–0.15% carbon, with iron forming the balance |
| Orthodontic adhesive | Transbond XT primer | 3M Unitek Monrovia, CA, USA | TEGDMA, Bis-GMA, and camphorquinone |
| Orthodontic paste | Transbond XT resin | 3M Unitek Monrovia, CA, USA | Bis-GMA, silane, n-dimethylbenzocaine, and phosphorus hexafluoride, 77% by weight of the inorganic filler (silica) |
| - | T2W-TSE AXIAL | T2W-TSE CORONAL | T2-FLAIR AXIAL | T1 VIBE 3D FS |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOV (mm) | 210 × 210 | 200 × 200 | 235 × 185 | 200 × 200 |
| Voxel Size (mm) | 0.5 × 0.5 × 2.0 | 0.7 × 0.5 × 2.0 | 1.2 × 0.7 × 5.0 | 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 |
| Slice Thickness (mm) | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 |
| Slices | 24 | 28 | 20 | 128 (slices per slab) |
| Time of Echo (ms) | 84 | 81 | 107 | 2.66 |
| Repetition Time (ms) | 3000 | 3000 | 9000 | 6.72 |
| Scan Time (min:s) | 6:32 | 7:20 | 4:59 | 6:24 |
| SAR whole body (W/kg) | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 |
| - | T2W-TSE AXIAL | T2W-TSE CORONAL | T2W-FLAIR AXIAL | T1 VIBE 3D FS | T2W-FL2D HEMO AXIAL | T2W-TIRM AXIAL | EP2D DIFF 5 mm AXIAL | EP2D DIFF 3 mm AXIAL | PDw AXIAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FOV (mm) | 210 | 200 | 235 | 200 | 210 | 210 | 260 | 190 | 210 |
| Voxel Size (mm) | 0.5 × 0.5 × 2.0 | 0.7 × 0.5 × 2.0 | 1.2 × 0.7 × 5.0 | 1.0 × 1.0 × 1.0 | 0.8 × 0.5 × 3.0 | 0.7 × 0.7 × 2.0 | 2.2 × 2.2 × 5.0 | 2.5 × 2.5 × 3.0 | 0.8 × 0.7 × 3.0 |
| Slice Thickness (mm) | 2 | 2 | 5 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 3 |
| Slices | 25 | 28 | 20 | 128 | 24 | 24 | 15 | 10 | 25 |
| Time of Echo (ms) | 84 | 81 | 108 | 2.14 | 19.90 | 57 | 75 | 69 | 9.1 |
| Repetition Time (ms) | 3260 | 3000 | 9000 | 6.72 | 650 | 5070 | 7300 | 4700 | 3000 |
| Turbo Inversion Recovery (ms) | - | - | - | - | - | 220 | 220 | 220 | - |
| Scan Time (min:s) | 3:24 | 2:32 | 3:18 | 1:39 | 3:13 | 2:23 | 2:55 | 1:53 | 2:53 |
| SAR whole body (W/kg) | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 | <0.5 |
| Variable | Coefficients | Estimate | Std. Error | t value | Pr(>|t|) | Confidence Intervals | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.5% | 97.5% | ||||||
| Bracket temperature | Intercept | 0.88 | 0.07 | 12.34 | <0.0001 | 0.74 | 1.02 |
| WireMaterial | 0.54 | 0.10 | 5.41 | <0.0001 | 0.35 | 0.74 | |
| Intercept | 0.94 | 0.07 | 12.59 | <0.0001 | 0.79 | 1.08 | |
| WireSize | 0.0002 | 0.00005 | 4.08 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | |
| Intercept | 0.33 | 0.16 | 2.07 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.64 | |
| Power | 0.37 | 0.07 | 5.45 | <0.0001 | 0.23 | 0.50 | |
| Wire Temperature | Intercept | 0.88 | 0.07 | 12.34 | <0.0001 | 0.74 | 1.02 |
| WireMaterial | 0.55 | 0.10 | 5.42 | <0.0001 | 0.35 | 0.74 | |
| Intercept | 0.94 | 0.07 | 12.59 | <0.0001 | 0.79 | 1.08 | |
| WireSize | 0.0002 | 0.0002 | 4.08 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 0.0003 | |
| Intercept | 0.33 | 0.16 | 2.07 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.64 | |
| Power | 0.37 | 0.07 | 5.45 | <0.0001 | 0.23 | 0.50 | |
| Shear Bond Strength | Intercept | 24.34 | 0.54 | 45.23 | <0.0001 | 23.28 | 25.39 |
| WireMaterial | 0.19 | 0.76 | 0.25 | 0.8 | −1.30 | 1.68 | |
| Intercept | 24.68 | 0.41 | 60.16 | <0.0001 | 23.87 | 25.48 | |
| WireSize | −0.00001 | 0.0003 | −0.04 | 0.97 | −0.0007 | 0.0007 | |
| Intercept | 25.66 | 0.76 | 33.74 | <0.0001 | 24.17 | 27.15 | |
| Power | −0.48 | 0.34 | −1.44 | 0.15 | −1.14 | 0.17 | |
| Group | Wire Size | Wire Material | MRI | Time | Mean | SD | Min | Mdn | Max | ΔT (T1-T0) | Significance * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No Wire | No Wire | No MRI | T0 | 23.84 | 0.13 | 23.50 | 23.90 | 24.10 | - | A |
| - | No Wire | No Wire | No MRI | T1 | 23.73 | 0.25 | 23.00 | 23.80 | 23.90 | −0.11 | A |
| 2 | No Wire | No Wire | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.69 | 0.27 | 23.10 | 23.80 | 24.00 | - | A |
| - | No Wire | No Wire | 1.5 T | T1 | 23.79 | 0.28 | 23.00 | 23.85 | 24.20 | 0.10 | A |
| 3 | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.83 | 0.27 | 23.40 | 23.80 | 24.50 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T1 | 25.02 | 0.20 | 24.80 | 25.00 | 25.30 | 1.20 | B |
| 4 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.79 | 0.14 | 23.50 | 23.80 | 24.10 | - | A |
| - | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T1 | 25.95 | 0.52 | 25.10 | 26.00 | 27.60 | 2.16 | C |
| 5 | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.71 | 0.30 | 23.20 | 23.80 | 24.10 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T1 | 23.76 | 0.25 | 23.30 | 23.75 | 24.20 | 0.05 | A |
| 6 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.67 | 0.32 | 23.00 | 23.80 | 24.10 | - | A |
| - | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T1 | 23.76 | 0.29 | 23.40 | 23.80 | 24.40 | 0.09 | A |
| 7 | No Wire | No Wire | 3 T | T0 | 23.84 | 0.20 | 23.40 | 23.85 | 24.20 | - | A |
| - | No Wire | No Wire | 3 T | T1 | 24.81 | 0.56 | 24.00 | 24.80 | 25.90 | 0.97 | B |
| 8 | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T0 | 23.81 | 0.26 | 23.10 | 23.85 | 24.10 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T1 | 24.50 | 0.42 | 23.90 | 24.50 | 25.60 | 0.69 | B |
| 9 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T0 | 23.66 | 0.43 | 23.00 | 23.65 | 24.40 | - | A |
| - | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T1 | 25.60 | 0.24 | 25.10 | 25.55 | 26.00 | 1.94 | C |
| 10 | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T0 | 23.73 | 0.31 | 23.00 | 23.70 | 24.20 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T1 | 24.50 | 0.30 | 24.10 | 24.50 | 25.40 | 0.78 | B |
| 11 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T0 | 23.66 | 0.39 | 22.70 | 23.70 | 24.20 | - | A |
| 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T1 | 26.05 | 0.61 | 24.60 | 26.20 | 26.70 | 2.40 | C |
| Group | Wire Size | Wire Material | MRI | Time | Mean | SD | Min | Mdn | Max | ΔT (T1-T0) | Significance * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No Wire | No Wire | No MRI | T0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| - | No Wire | No Wire | No MRI | T1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 2 | No Wire | No Wire | 1.5 T | T0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| - | No Wire | No Wire | 1.5 T | T1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 3 | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.91 | 0.33 | 23.20 | 23.90 | 24.60 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T1 | 24.92 | 0.13 | 24.70 | 24.90 | 25.10 | 1.02 | B |
| 4 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.94 | 0.35 | 23.30 | 23.90 | 24.70 | - | A |
| - | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 1.5 T | T1 | 25.63 | 0.34 | 25.20 | 25.70 | 26.50 | 1.69 | C |
| 5 | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.89 | 0.25 | 23.20 | 23.90 | 24.30 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T1 | 24.31 | 0.25 | 23.70 | 24.30 | 24.80 | 0.42 | D |
| 6 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T0 | 23.78 | 0.14 | 23.40 | 23.75 | 24.00 | - | A |
| - | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 1.5 T | T1 | 24.17 | 0.24 | 23.80 | 24.20 | 24.50 | 0.39 | D |
| 7 | No Wire | No Wire | 3 T | T0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| - | No Wire | No Wire | 3 T | T1 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| 8 | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T0 | 23.80 | 0.16 | 23.50 | 23.80 | 24.10 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T1 | 25.06 | 0.47 | 24.40 | 25.10 | 25.90 | 1.26 | B,C |
| 9 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T0 | 23.63 | 0.21 | 23.10 | 23.65 | 23.90 | - | A |
| - | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Stainless Steel | 3 T | T1 | 25.37 | 0.68 | 23.60 | 25.25 | 26.30 | 1.74 | B,C |
| 10 | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T0 | 23.98 | 0.39 | 23.30 | 24.00 | 24.50 | - | A |
| - | 0.014″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T1 | 25.04 | 0.46 | 24.60 | 25.00 | 26.60 | 1.07 | B,C |
| 11 | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T0 | 23.48 | 0.28 | 23.00 | 23.50 | 24.00 | - | A |
| - | 0.019″ × 0.025″ | Nickel Titanium | 3 T | T1 | 25.12 | 0.51 | 24.30 | 25.00 | 26.00 | 1.65 | B,C |
| Group | MRI | Wire | Wire Material | Mean | SD | Min | Mdn | Max | Significance * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No MRI | No wire | No wire | 26.45 | 4.64 | 18.44 | 25.26 | 33.44 | A |
| 2 | 1.5 T | No wire | No wire | 25.07 | 4.36 | 16.35 | 25.13 | 33.29 | A |
| 3 | 1.5 T | 0.014’’ | Stainless Steel | 24.91 | 3.56 | 18.02 | 24.64 | 33.81 | A |
| 4 | 1.5 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Stainless Steel | 24.49 | 4.30 | 18.23 | 24.85 | 31.99 | A |
| 5 | 1.5 T | 0.014’’ | Nickel Titanium | 23.33 | 4.78 | 15.98 | 23.02 | 31.07 | A |
| 6 | 1.5 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Nickel Titanium | 25.29 | 5.14 | 18.20 | 24.69 | 35.43 | A |
| 7 | 3 T | No wire | No wire | 24.39 | 5.56 | 14.76 | 24.68 | 33.95 | A |
| 8 | 3 T | 0.014’’ | Stainless Steel | 24.21 | 4.71 | 16.20 | 24.01 | 34.62 | A |
| 9 | 3 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Stainless Steel | 24.51 | 5.52 | 12.04 | 24.52 | 33.13 | A |
| 10 | 3 T | 0.014’’ | Nickel Titanium | 24.38 | 5.44 | 14.18 | 23.82 | 34.83 | A |
| 11 | 3 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Nickel Titanium | 24.34 | 5.24 | 14.94 | 24.77 | 31.85 | A |
| Group | MRI | Wire | Wire Material | ARI = 0 | ARI = 1 | ARI = 2 | ARI = 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | No MRI | No wire | No wire | 15 | 75 | 5 | 5 |
| 2 | 1.5 T | No wire | No wire | 50 | 45 | 5 | 0 |
| 3 | 1.5 T | 0.014’’ | Stainless Steel | 55 | 30 | 10 | 5 |
| 4 | 1.5 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Stainless Steel | 55 | 40 | 5 | 0 |
| 5 | 1.5 T | 0.014’’ | Nickel Titanium | 45 | 30 | 25 | 0 |
| 6 | 1.5 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Nickel Titanium | 45 | 40 | 15 | 0 |
| 7 | 3 T | No wire | No wire | 55 | 45 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 3 T | 0.014’’ | Stainless Steel | 55 | 35 | 10 | 0 |
| 9 | 3 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Stainless Steel | 55 | 45 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 3 T | 0.014’’ | Nickel Titanium | 50 | 45 | 5 | 0 |
| 11 | 3 T | 0.019’’ × 0.025’’ | Nickel Titanium | 60 | 35 | 5 | 0 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sfondrini, M.F.; Preda, L.; Calliada, F.; Carbone, L.; Lungarotti, L.; Bernardinelli, L.; Gandini, P.; Scribante, A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Effects on Metallic Brackets and Wires: Does It Alter the Temperature and Bonding Efficacy of Orthodontic Devices? Materials 2019, 12, 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233971
Sfondrini MF, Preda L, Calliada F, Carbone L, Lungarotti L, Bernardinelli L, Gandini P, Scribante A. Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Effects on Metallic Brackets and Wires: Does It Alter the Temperature and Bonding Efficacy of Orthodontic Devices? Materials. 2019; 12(23):3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233971
Chicago/Turabian StyleSfondrini, Maria Francesca, Lorenzo Preda, Fabrizio Calliada, Lorenzo Carbone, Luca Lungarotti, Luisa Bernardinelli, Paola Gandini, and Andrea Scribante. 2019. "Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Effects on Metallic Brackets and Wires: Does It Alter the Temperature and Bonding Efficacy of Orthodontic Devices?" Materials 12, no. 23: 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233971
APA StyleSfondrini, M. F., Preda, L., Calliada, F., Carbone, L., Lungarotti, L., Bernardinelli, L., Gandini, P., & Scribante, A. (2019). Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Effects on Metallic Brackets and Wires: Does It Alter the Temperature and Bonding Efficacy of Orthodontic Devices? Materials, 12(23), 3971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12233971








