Green Hydrogen Production from Biogas or Landfill Gas by Steam Reforming or Dry Reforming: Specific Production and Energy Requirements
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To identify the optimal operating conditions for SMR and DMR processes using biogas/LFG with varying compositions;
- To evaluate and compare the hydrogen yield and energy consumption of each process under different process parameters (e.g., S/C and S/CO ratios, temperature, pressure);
- To simulate and analyze the complete reforming processes under equilibrium conditions to assess overall energy requirements;
- To incorporate CO2 separation and heat recovery integration into the process models for a more realistic and sustainable performance evaluation;
- To ensure application of results for both biogas/LFG by using representative compositions in the simulations.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Simulation Model and Validation
2.2. Description of the Simulations
2.3. Calculated Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Preliminary Simulations
3.1.1. Effect of Temperature
3.1.2. Preliminary Simulations—Effect of Pressure
3.2. Second-Step Simulations
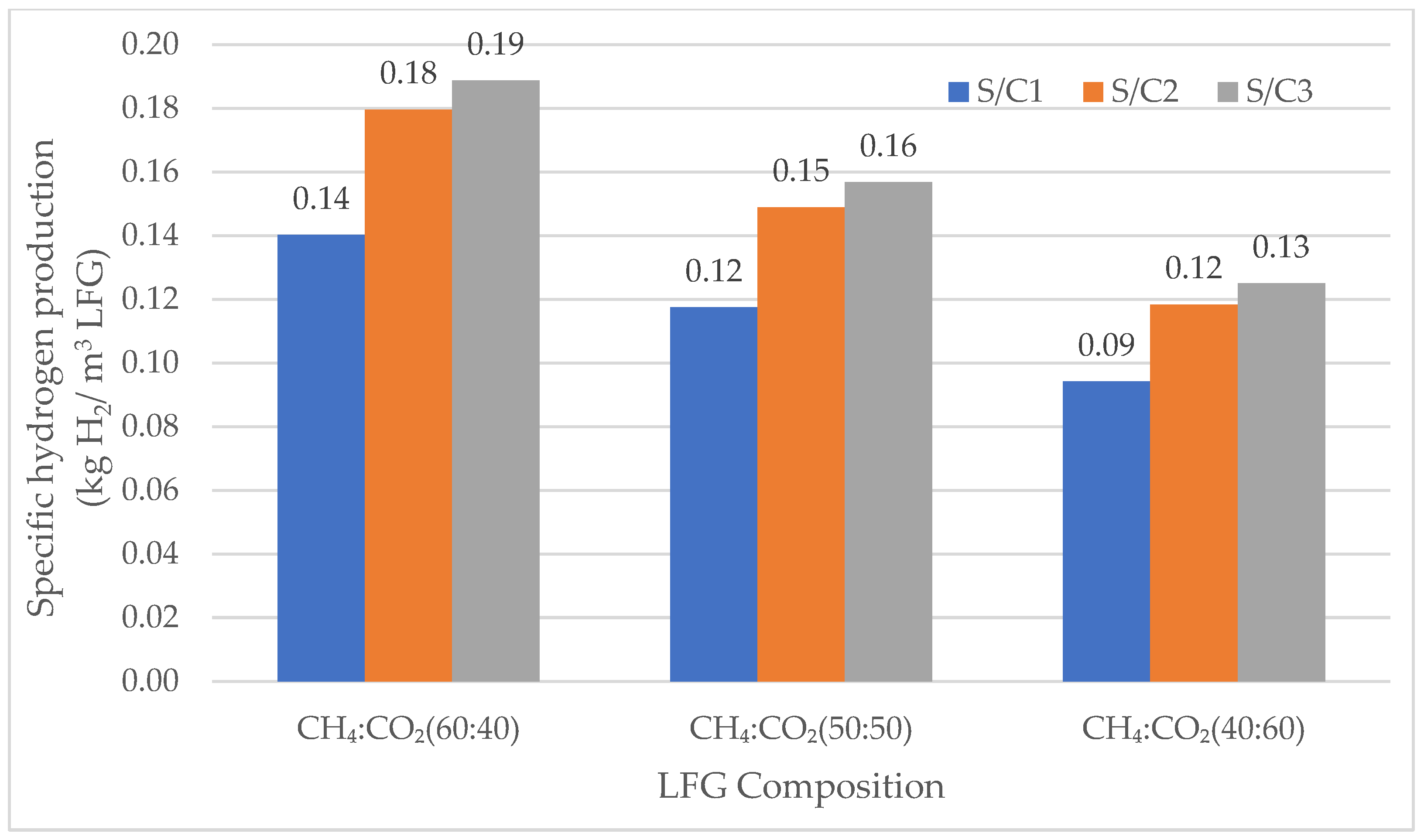
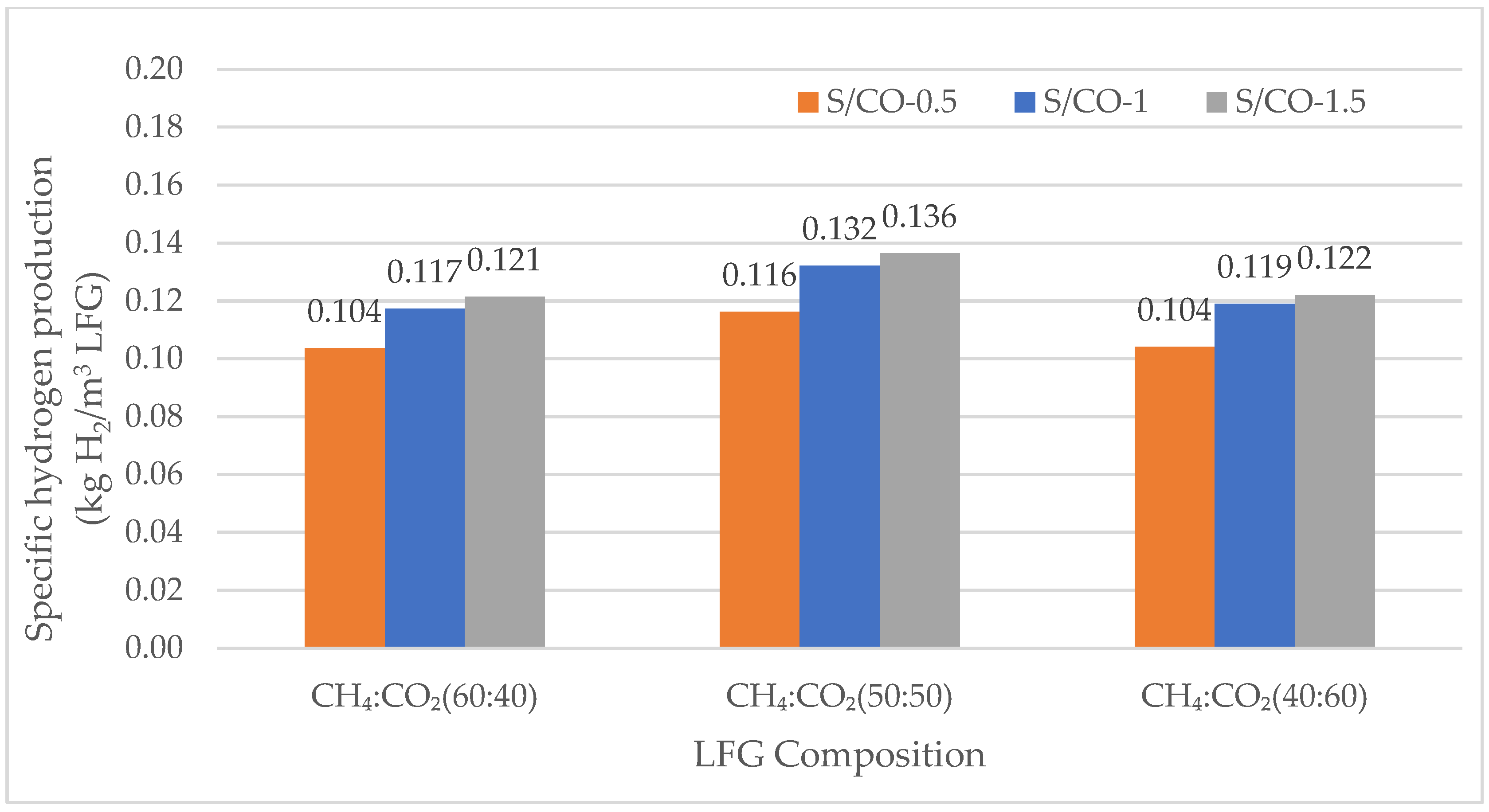
3.2.1. Specific Hydrogen Production
Specific Hydrogen Production for SMR
Specific Hydrogen Production for DMR
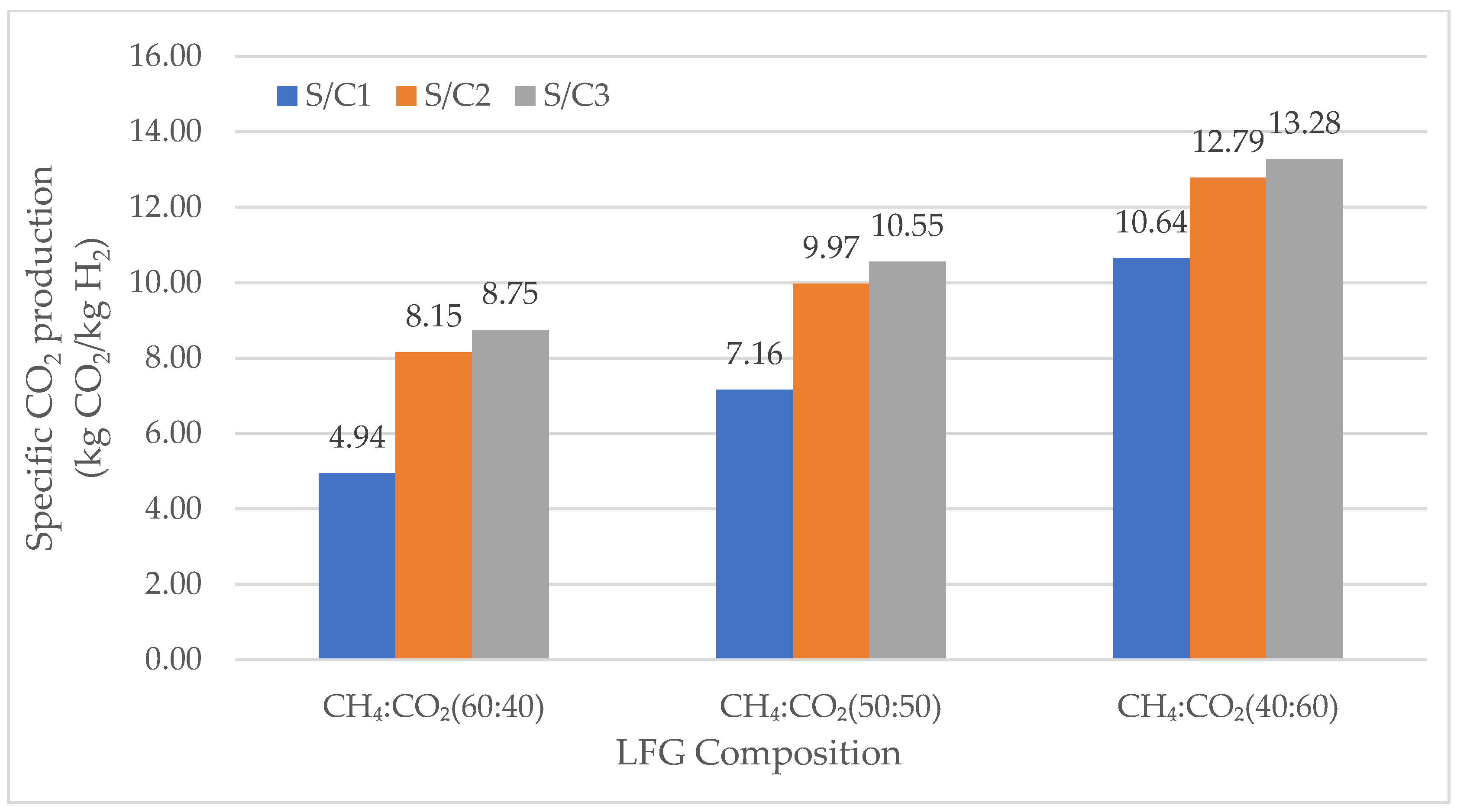
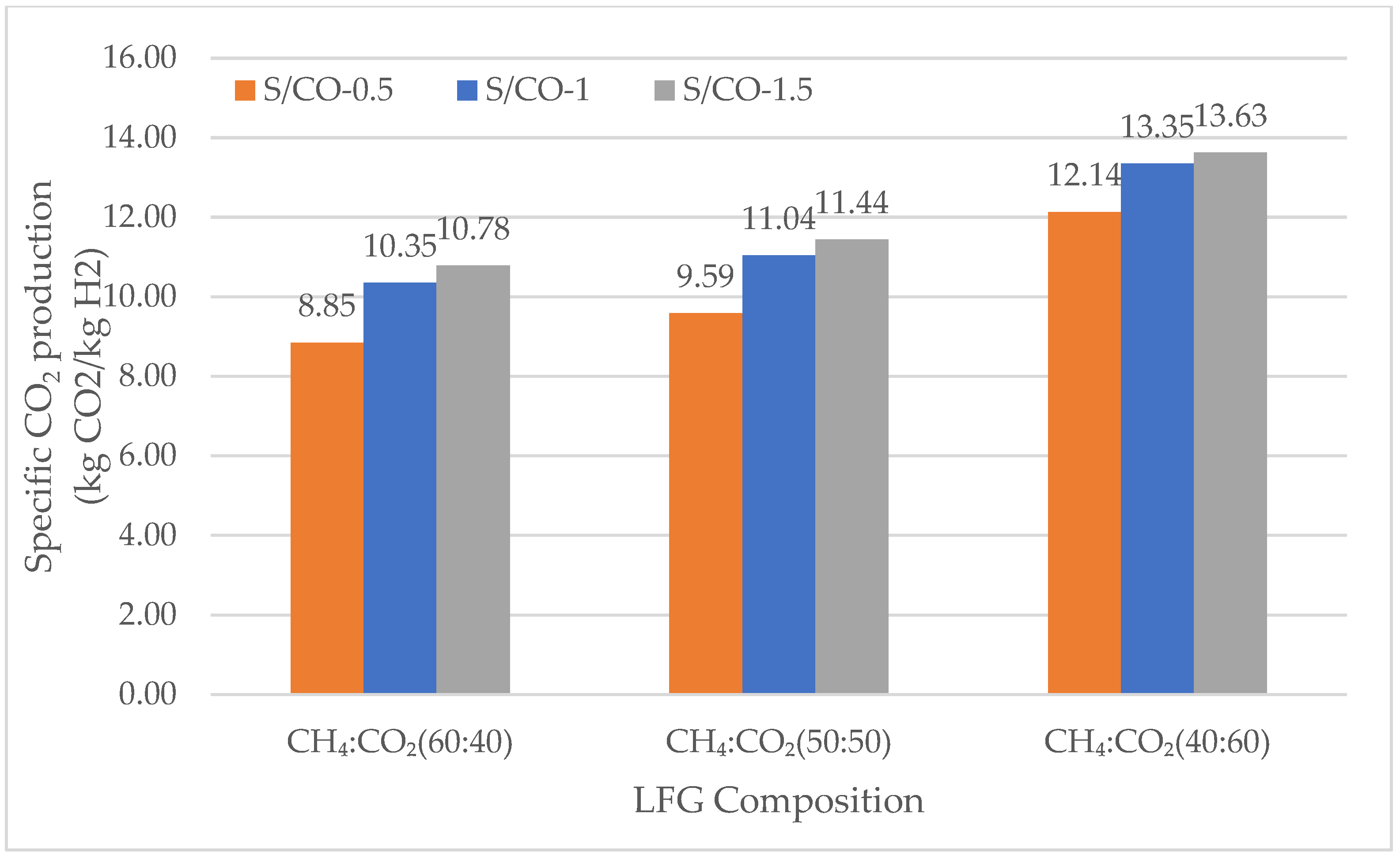
3.2.2. Specific Carbon Dioxide Production
Specific Carbon Dioxide Production in SMR
Specific Carbon Dioxide Production in DMR
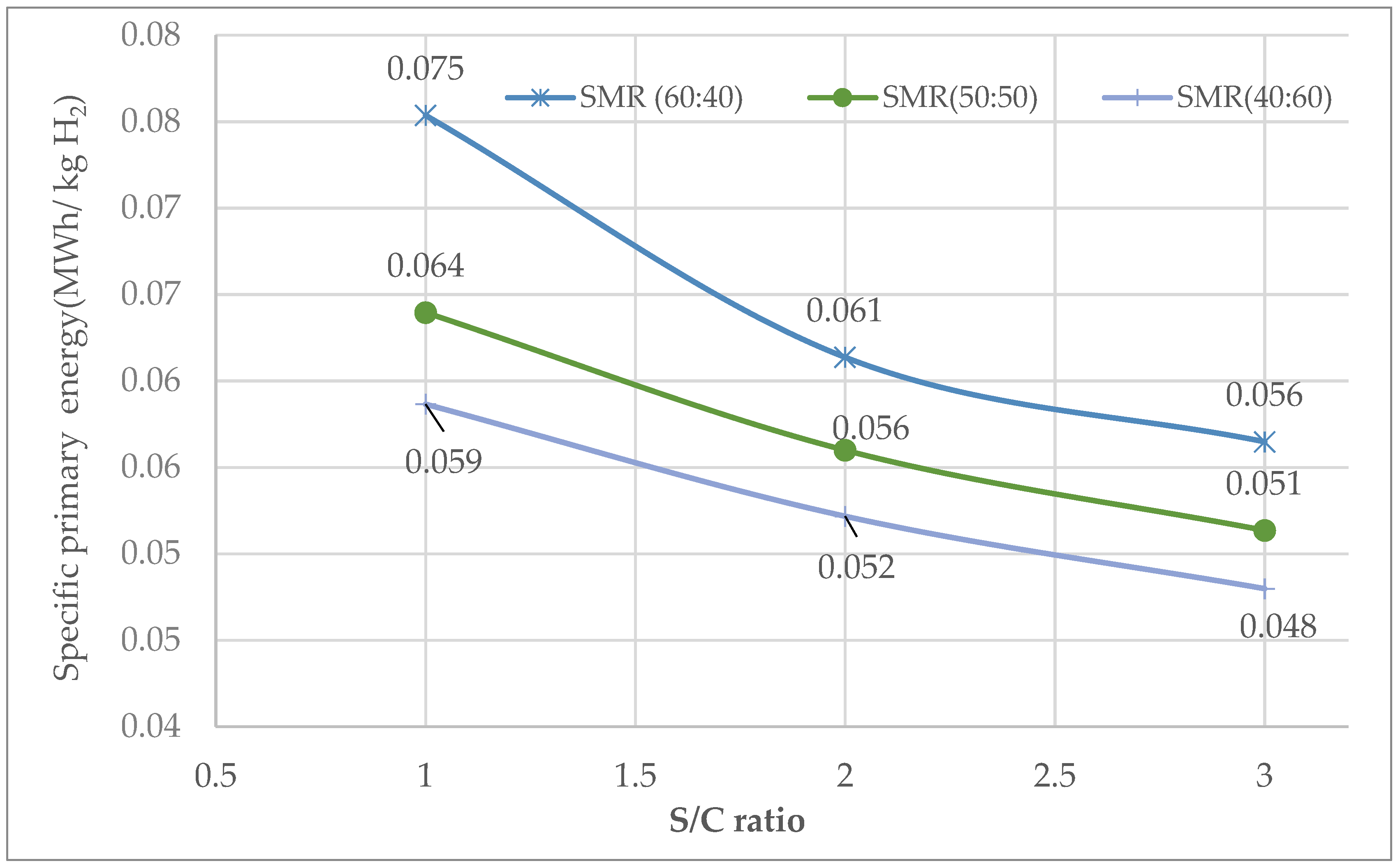
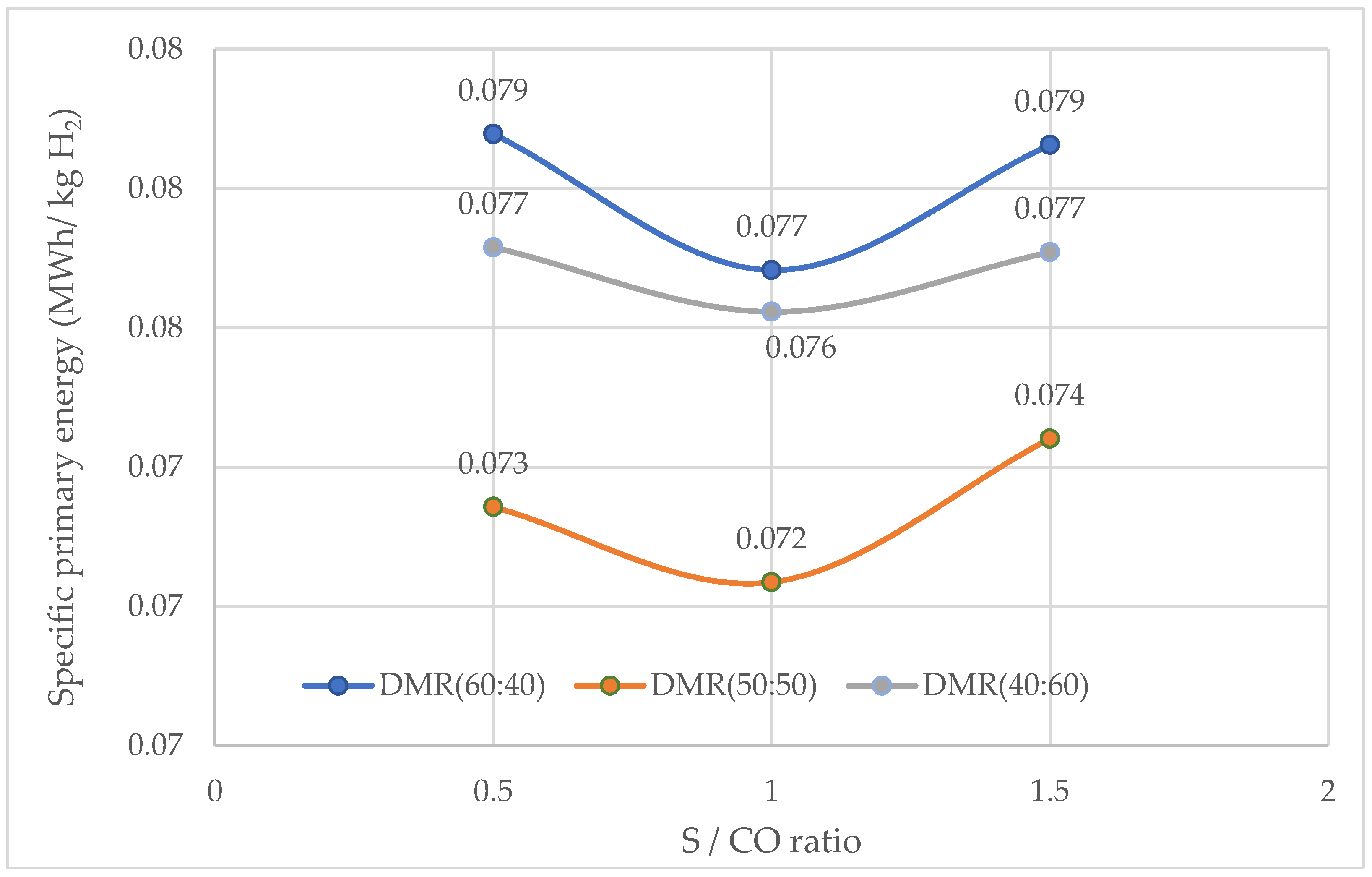
3.2.3. Specific Primary Energy Consumption
Specific Primary Energy Consumption for SMR
Specific Primary Energy Consumption for DMR
3.2.4. CH4 and CO2 Conversion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madurai Elavarasan, R.; Pugazhendhi, R.; Irfan, M.; Mihet-Popa, L.; Khan, I.A.; Campana, P.E. State-of-the-Art Sustainable Approaches for Deeper Decarbonization in Europe—An Endowment to Climate Neutral Vision. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 159, 112204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd, A.A.; Othman, M.R.; Majdi, H.S.; Helwani, Z. Green Route for Biomethane and Hydrogen Production via Integration of Biogas Upgrading Using Pressure Swing Adsorption and Steam-Methane Reforming Process. Renew. Energy 2023, 210, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Laurentiis, V.; Biganzoli, F.; Valenzano, A.; Sala, S. Estimating Food Waste Generated and Packaging Placed on the Market at National Level; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What a Waste 2.0. Available online: https://datatopics.worldbank.org/what-a-waste/ (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- Rapportorifiutiurbani_ed-2024_n406_versione_integrale. Available online: https://www.rinnovabili.it/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/rapportorifiutiurbani_ed-2024_n406_versione_integrale.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2025).
- Wei, Y.; Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Peng, Y.; Ke, H.; Zhan, L.; Lan, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of Greenhouse Gas Emission and Reduction Potential of High-Food-Waste-Content Municipal Solid Waste Landfills: A Case Study of a Landfill in the East of China. Waste Manag. 2024, 189, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council Directive 1999/31/EC of 26 April 1999 on the Landfill of Waste. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:31999L0031 (accessed on 25 January 2025).
- DIRECTIVE 2008/98/EC OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 19 November 2008 on Waste and Repealing Certain Directives (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32008L0098 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- DIRECTIVE (EU) 2018/851 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL of 30 May 2018 Amending Directive 2008/98/EC on Waste (Text with EEA Relevance). Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32018L0851 (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- BIOGAS BAROMETER. Available online: https://www.eurobserv-er.org/biogas-barometer-2023/ (accessed on 21 February 2025).
- Mou, Z.; Scheutz, C.; Kjeldsen, P. Evaluation and Application of Site-Specific Data to Revise the First-Order Decay Model for Estimating Landfill Gas Generation and Emissions at Danish Landfills. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2015, 65, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, P.; Samanta, S.K. Overview of Biogas Reforming Technologies for Hydrogen Production: Advantages and Challenges. In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Recent Advances in Bioenergy Research; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2016; pp. 227–243. [Google Scholar]
- Nahar, G.; Mote, D.; Dupont, V. Hydrogen Production from Reforming of Biogas: Review of Technological Advances and an Indian Perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 1032–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.M.; Trably, E.; Latrille, E.; Carrre, H.; Steyer, J.P. Hydrogen Production from Agricultural Waste by Dark Fermentation: A Review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 10660–10673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, I.P. Hydrogen the Fuel for 21st Century. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 7368–7378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.N.; Yang, Y.C.; Yoshikawa, K. Hydrogen Generation from Biogas Reforming Using a Gliding Arc Plasma-Catalyst Reformer. Catal. Today 2009, 148, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calbry-Muzyka, A.; Madi, H.; Rüsch-Pfund, F.; Gandiglio, M.; Biollaz, S. Biogas Composition from Agricultural Sources and Organic Fraction of Municipal Solid Waste. Renew. Energy 2022, 181, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.-F.; Wagner, J.-F.; Rettenberger, G.; Reinert, P. Modern landfill technology-landfill behavior of mechanical-biological pre-treated waste. In Proceedings of the 11th International Waste Management and Landfill Symposium, S. Margherita di Pula-Cagliari, Sardinia, Italy, 1–5 October 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Borisova, D.; Kostadinova, G.; Petkov, G.; Dospatliev, L.; Ivanova, M.; Dermendzhieva, D.; Beev, G. Assessment of CH4 and CO2 Emissions from a Gas Collection System of a Regional Non-Hazardous Waste Landfill, Harmanli, Bulgaria, Using the Interrupted Time Series ARMA Model. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horikawa, M.S.; Rossi, F.; Gimenes, M.L.; Costa, C.M.M.; Da Silva, M.G.C. Chemical Absorption of H 2 S for Biogas Purification. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2004, 21, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, M.D.; Özcan, O.; Akın, A.N. Effect of H2S on Oxidative Steam Reforming of Biogas for Syngas Production over MgAl-Supported Ni–Ce-Based Catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpaz, R.; Konrad, O.; Cândido da Silva Cyrne, C.; Panis Barzotto, H.; Hasan, C.; Guerini Filho, M. Using Biogas for Energy Cogeneration: An Analysis of Electric and Thermal Energy Generation from Agro-Industrial Waste. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2020, 40, 100774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardolino, F.; Cardamone, G.F.; Parrillo, F.; Arena, U. Biogas-to-Biomethane Upgrading: A Comparative Review and Assessment in a Life Cycle Perspective. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 139, 110588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkouri, L.P.; Ahmet, H.; Ramirez Reina, T.; Duyar, M.S. The Direct Synthesis of Dimethyl Ether (DME) from Landfill Gas: A Techno-Economic Investigation. Fuel 2022, 319, 123741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Zhang, M.H.; Singh Chauhan, B.; Elsiddieg, A.M.A.; Abdelghany Elkotb, M.; Zhu, P.; Tian, R.; Abouelela, M. Comprehensive Analysis of a Novel Power and Methanol Coproduction Process Using Landfill Gas Reforming and Renewable Hydrogen Generation by an Alkaline Electrolyzer. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 418, 138131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.; Sirini, P.; Lombardi, L. Review of Reforming Processes for the Production of Green Hydrogen from Landfill Gas. Energies 2024, 18, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, Z.; Khataee, A.; Han, N.; Orooji, Y. Hydrogen Production through Methane Reforming Processes Using Promoted-Ni/Mesoporous Silica: A Review. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 107, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, J.F.; Álvez-Medina, C.M.; Nogales-Delgado, S. Biogas Steam Reforming in Wastewater Treatment Plants: Opportunities and Challenges. Energies 2023, 16, 6343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armor, J.N. The Multiple Roles for Catalysis in the Production of H2. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 1999, 176, 159–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yan, C.F.; Guo, C.Q.; Lu, Z.X.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Z.D. Synthesis of GO-Modified Cu2O Nanosphere and the Photocatalytic Mechanism of Water Splitting for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 85, 4007–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Teng, F.; McLellan, B.C. A Critical Review on Deployment Planning and Risk Analysis of Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) toward Carbon Neutrality. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2022, 167, 112537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wodołażski, A.; Magdziarczyk, M.; Smoliński, A. Techno-Economic Analysis of Hydrogen Production from Swine Manure Biogas via Steam Reforming in Pilot-Scale Installation. Energies 2023, 16, 6389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Full, J.; Hohmann, S.; Ziehn, S.; Gamero, E.; Schließ, T.; Schmid, H.P.; Miehe, R.; Sauer, A. Perspectives of Biogas Plants as BECCS Facilities: A Comparative Analysis of Biomethane vs. Biohydrogen Production with Carbon Capture and Storage or Use (CCS/CCU). Energies 2023, 16, 5066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barelli, L.; Bidini, G.; Gallorini, F.; Servili, S. Hydrogen Production through Sorption-Enhanced Steam Methane Reforming and Membrane Technology: A Review. Energy 2008, 33, 554–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carapellucci, R.; Giordano, L. Steam, Dry and Autothermal Methane Reforming for Hydrogen Production: A Thermodynamic Equilibrium Analysis. J. Power Sources 2020, 469, 228391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Wan Daud, W.M.A.; Abbas, H.F. Dry Reforming of Methane: Influence of Process Parameters—A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 45, 710–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, D.; King, K.D. Reforming of CH4 by Partial Oxidation: Thermodynamic and Kinetic Analyses. Fuel 2001, 80, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscherini, M.; Storione, A.; Minelli, M.; Miccio, F.; Doghieri, F. New Perspectives on Catalytic Hydrogen Production by the Reforming, Partial Oxidation and Decomposition of Methane and Biogas. Energies 2023, 16, 6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvagno, A.; Chiodo, V.; Urbani, F.; Freni, F. Biogas as Hydrogen Source for Fuel Cell Applications. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2013, 38, 3913–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Wu, J.; Huang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Hu, W.; Tang, Y.; Tan, H.; Zhang, H.; Zairov, R.; Pan, Z. Biogas to Chemicals: A Review of the State-of-the-Art Conversion Processes. Biomass Convers. Biorefin 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Li, J.; Zhang, X.; Jin, X.; Xiong, B.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; et al. Industrial Status, Technological Progress, Challenges, and Prospects of Hydrogen Energy. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2022, 9, 427–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cormos, C.C. Techno-Economic and Environmental Assessment of Green Hydrogen Production via Biogas Reforming with Membrane-Based CO2 Capture. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 101, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katebah, M.; Al-Rawashdeh, M.; Linke, P. Analysis of Hydrogen Production Costs in Steam-Methane Reforming Considering Integration with Electrolysis and CO2 Capture. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2022, 10, 100552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedorov, M.; Maslikov, V.; Korablev, V.; Politaeva, N.; Chusov, A.; Molodtsov, D. Production of Biohydrogen from Organ-Containing Waste for Use in Fuel Cells. Energies 2022, 15, 8019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajak, M.; Brus, G.; Kimijima, S.; Szmyd, J.S. Enhancing Hydrogen Production from Biogas through Catalyst Rearrangements. Energies 2023, 16, 4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, D.J.; Simbeck, D.R.; Karp, A.D.; Dickenson, R.L. Syngas Production for Gas-to-Liquids Applications: Technologies, Issues and Outlook. Fuel Process. Technol. 2001, 71, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangadharan, P.; Kanchi, K.C.; Lou, H.H. Evaluation of the Economic and Environmental Impact of Combining Dry Reforming with Steam Reforming of Methane. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2012, 90, 1956–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarkhoon, F.; Rezaei, M.; Alavi, S.M. Structure-Activity Relationships in NiO–MgO Solid Solution Catalysts for Biogas Dry Reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2025, 126, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, A.; Yamada, S.; Ichii, R.; Ichikawa, M.; Hayakawa, T.; Kolhe, M.L. Hydrogen Yield Enhancement in Biogas Dry Reforming with a Ni/Cr Catalyst: A Numerical Study. Energies 2024, 17, 5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, G.; Varitis, S.; Zhumabek, M.; Karanasios, K.; Vekinis, G.; Tungatarova, S.A.; Baizhumanova, T.S. Direct Reduction in Greenhouse Gases by Continuous Dry (CO2) Reforming of Methane over Ni-Containing Shs Catalysts. Energies 2021, 14, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Saché, E.; Johnson, S.; Pastor-Pérez, L.; Horri, B.A.; Reina, T.R. Biogas Upgrading via Dry Reforming over a Ni-Sn/CeO2-Al2O3 Catalyst: Influence of the Biogas Source. Energies 2019, 12, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Swift, J.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, L.S.; Tong, A. Biogas to H2 Conversion with CO2 Capture Using Chemical Looping Technology: Process Simulation and Comparison to Conventional Reforming Processes. Fuel 2020, 279, 118479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajizadeh, A.; Mohamadi-Baghmolaei, M.; Cata Saady, N.M.; Zendehboudi, S. Hydrogen Production from Biomass through Integration of Anaerobic Digestion and Biogas Dry Reforming. Appl. Energy 2022, 309, 118442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, D.P.; Siang, T.J.; Vo, D.V.N.; Phan, T.S.; Ridart, C.; Nzihou, A.; Grouset, D. Hydrogen Production From Biogas Reforming: An Overview of Steam Reforming, Dry Reforming, Dual Reforming, and Tri-Reforming of Methane. Hydrog. Supply Chain Des. Deploy. Oper. 2018, 111–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balat, M. Possible Methods for Hydrogen Production. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2008, 31, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hajj Chehade, A.M.; Daher, E.A.; Assaf, J.C.; Riachi, B.; Hamd, W. Simulation and Optimization of Hydrogen Production by Steam Reforming of Natural Gas for Refining and Petrochemical Demands in Lebanon. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 33235–33247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro Camacho, Y.S.; Bensaid, S.; Lorentzou, S.; Vlachos, N.; Pantoleontos, G.; Konstandopoulos, A.; Luneau, M.; Meunier, F.C.; Guilhaume, N.; Schuurman, Y.; et al. Development of a Robust and Efficient Biogas Processor for Hydrogen Production. Part 1: Modelling and Simulation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 22841–22855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamilselvan, R.; Selwynraj, A.I. Model Development for Biogas Generation, Purification and Hydrogen Production via Steam Methane Reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 50, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marcoberardino, G.; Vitali, D.; Spinelli, F.; Binotti, M.; Manzolini, G. Green Hydrogen Production from Raw Biogas: A Techno-Economic Investigation of Conventional Processes Using Pressure Swing Adsorption Unit. Processes 2018, 6, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.S.; Pham Minh, D.; Espitalier, F.; Nzihou, A.; Grouset, D. Hydrogen Production from Biogas: Process Optimization Using ASPEN Plus®. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 42027–42039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Hur, K.-B.; Lee, N.-H. Effects of Hydrogen Sulfide and Siloxane on Landfill Utility Facilities. Environ. Eng. Res. 2011, 16, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattanathan, S.A.; Adhikari, S.; McVey, M.; Fasina, O. Hydrogen Production from Biogas Reforming and the Effect of H2S on CH4 Conversion. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 19905–19911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Rosen, M.A.; Dincer, I. Assessment of CO2 Capture Options from Various Points in Steam Methane Reforming for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 20266–20275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipitì, F.; Barbera, O.; Briguglio, N.; Giacoppo, G.; Italiano, C.; Vita, A. Design of a Biogas Steam Reforming Reactor: A Modelling and Experimental Approach. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 11577–11583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, P.L.; Navas-Anguita, Z.; Iribarren, D.; Dufour, J. Exergy Analysis of Hydrogen Production via Biogas Dry Reforming. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 11688–11695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosha, P.; Mohapatra, S.K.; Mahla, S.K.; Dhir, A. Catalytic Reforming of Synthetic Biogas for Hydrogen Enrichment over Ni Supported on ZnOCeO2 Mixed Catalyst. Biomass Bioenergy 2019, 125, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wylock, C.E.; Budzianowski, W.M. Performance Evaluation of Biogas Upgrading by Pressurized Water Scrubbing via Modelling and Simulation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 170, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, X.F.; Nair, J. The impact of landfilling and composting on greenhouse gas emissions–a review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3792–3798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.; Xie, X.; Yu, Z.; von Gadow, K.; Xu, J.; Zhao, S.; Yang, Y. Analysis of the Global Warming Potential of Biogenic CO2 Emission in Life Cycle Assessments. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Nabavi, S.A.; Clough, P.T. Intrinsic Kinetics of Steam Methane Reforming over a Monolithic Nickel Catalyst in a Fixed Bed Reactor System. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2024, 299, 120482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Bousiffi, M.A.; Gunn, D.J. A Dynamic Study of Steam-Methane Reforming. Int. J. Heat. Mass. Transf. 2007, 50, 723–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pashchenko, D. Experimental Investigation of Synthesis Gas Production by Methane Reforming with Flue Gas over a NiO-Al2O3 Catalyst: Reforming Characteristics and Pressure Drop. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 7073–7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Pal, A. Simulation Modelling of Hydrogen Production from Steam Reforming of Methane and Biogas. Fuel 2024, 362, 130742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras Bilbao, D.; Blanco Machin, E.; Travieso Pedroso, D. Operating Parameters’ Influence on Hydrogen Production Performance in Microwave-Induced Plasma. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 80, 956–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzara, A.; Heracleous, E.; Bukur, D.B.; Lemonidou, A.A. Thermodynamic Analysis of Hydrogen Production via Chemical Looping Steam Methane Reforming Coupled with in Situ CO2 Capture. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control 2015, 32, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-Lotina, A.; Daza, L. Influence of the Operating Parameters over Dry Reforming of Methane to Syngas. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 4089–4094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, K.; Sinha, S.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S. Simulation of Steam Reforming of Biogas in an Industrial Reformer for Hydrogen Production. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 26809–26824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- le Saché, E.; Alvarez Moreno, A.; Reina, T.R. Biogas Conversion to Syngas Using Advanced Ni-Promoted Pyrochlore Catalysts: Effect of the CH4/CO2 Ratio. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 672419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, K.; Liu, J.L.; Li, X.S.; Zhu, A.M. Effect of CO2/CH4 Ratio on Biogas Reforming with Added O2 through an Unique Spark-Shade Plasma. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 13902–13908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, Y.; Yao, L.; Hu, C. Temperature Hysteresis in Dry Reforming of Methane on Ni/SBA-15 Catalyst: Low Temperature Activity Originated from the Synergy of Ni0 and Carbon Nanotubes. Appl. Catal. B Environ. Energy 2023, 333, 122756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
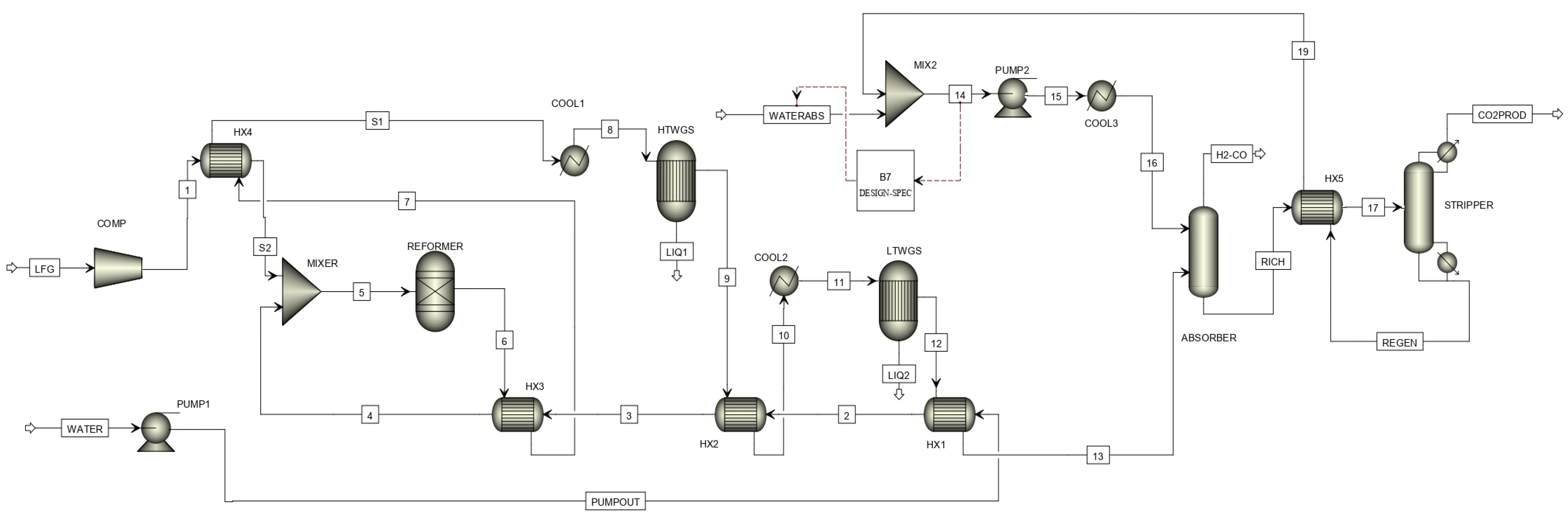
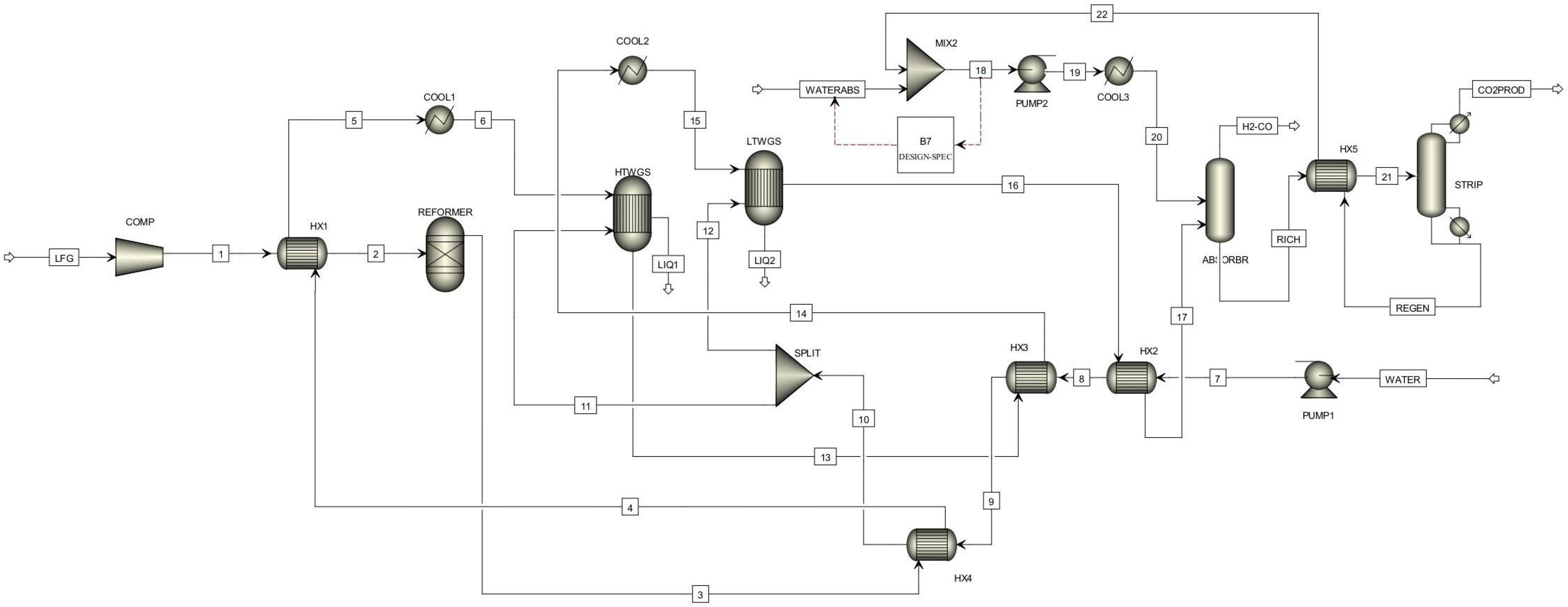
| Preliminary Simulations (SMR and DMR) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simulation | LFG Composition | Temperature | Pressure | S/C or S/CO ratio | |
| CH4 | CO2 | °C | bar | ||
| Temperature analysis | 60 | 40 | 500–1000 | 5 | 1 |
| Pressure analysis | 60 | 40 | 900 | 0–50 | 1 |
| Second-step simulations | |||||
| LFG Composition | Temperature | Pressure | S/C ratio | ||
| SMR | CH4 | CO2 | [°C] | [bar] | |
| 60 | 40 | 900 | 5 | 1, 2, 3 | |
| 50 | 50 | 900 | 5 | 1, 2, 3 | |
| 40 | 60 | 900 | 5 | 1, 2, 3 | |
| LFG Composition | Temperature | Pressure | S/CO ratio | ||
| DMR | CH4 | CO2 | [°C] | [bar] | |
| 60 | 40 | 900 | 5 | 0.5, 1, 1.5 | |
| 50 | 50 | 900 | 5 | 0.5, 1, 1.5 | |
| 40 | 60 | 900 | 5 | 0.5, 1, 1.5 | |
| Unit in Aspen Plus | Module | SMR Specification | DMR Specification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reformer | Rgibbs | Operating temperature: 900 °C | Operating temperature: 900 °C |
| Operating pressure: 5 bar | Operating pressure: 5 bar | ||
| HTWGS | REquil | Operating temperature: 350 °C | Operating temperature: 350 °C |
| Operating pressure: 5 bar | Operating pressure: 5 bar | ||
| LTWGS | REquil | Operating temperature: 250 °C | Operating temperature: 250 °C |
| Operating pressure: 5 bar | Operating pressure: 5 bar | ||
| Absorber | RadFrac | Condenser pressure: 4 bar | Condenser pressure: 4 bar |
| No of stages: 4 | No of stages: 4 | ||
| Stripper | RadFrac | Operating pressure: 1 bar | Operating pressure: 1 bar |
| No of stages: 3 | No of stages: 3 | ||
| Comp | compr | Discharge pressure: 5 bar | Discharge pressure: 5 bar |
| efficiency: 0.85 | efficiency: 0.85 | ||
| PUMP1 | pump | Discharge pressure: 5 bar | Discharge pressure: 5 bar |
| efficiency: 0.85 | efficiency: 0.85 | ||
| PUMP2 | pump | Discharge pressure: 5 bar | Discharge pressure: 5 bar |
| efficiency: 0.85 | efficiency: 0.85 | ||
| COOL1 | Cooler | Operating temperature: 350 °C | Operating temperature: 350 °C |
| Operating pressure: 5 bar | Operating pressure: 5 bar | ||
| COOL2 | Cooler | Operating temperature: 250 °C | Operating temperature: 250 °C |
| Operating pressure: 5 bar | Operating pressure: 5 bar | ||
| COOL3 | Cooler | Operating temperature: 40 °C | Operating temperature: 40 °C |
| Operating pressure: 5 bar | Operating pressure: 5 bar | ||
| HX1 | HeatX | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 86 °C | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 165 °C |
| HX2 | HeatX | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 103 °C | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 39 °C |
| HX3 | HeatX | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 210 °C | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 101 °C |
| HX4 | HeatX | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 25 °C | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 536 °C |
| HX5 | HeatX | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 25 °C | Hot Outlet cold inlet temperature difference: 25 °C |
| Process | CH4:CO2 | S/C Ratio | CH4 Conv. | CO2 Conv. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMR | 60–40 | 1 | 96.54 | 66.96 |
| 60–40 | 2 | 98.93 | 57.33 | |
| 60–40 | 3 | 99.51 | 10.08 | |
| 50–50 | 1 | 97.93 | 63.48 | |
| 50–50 | 2 | 99.20 | 39.78 | |
| 50–50 | 3 | 99.60 | 22.16 | |
| 40–60 | 1 | 99.30 | 73.34 | |
| 40–60 | 2 | 99.47 | 41.27 | |
| 40–60 | 3 | 99.70 | 28.48 | |
| DMR | CH4:CO2 | S/CO ratio | CH4 conv. | CO2 conv. |
| 60–40 | 0.5 | 79.69 | 99.01 | |
| 60–40 | 1 | 79.69 | 99.01 | |
| 60–40 | 1.5 | 79.69 | 99.01 | |
| 50–50 | 0.5 | 92.69 | 96.61 | |
| 50–50 | 1 | 92.69 | 96.61 | |
| 50–50 | 1.5 | 92.69 | 96.61 | |
| 40–60 | 0.5 | 98.09 | 89.75 | |
| 40–60 | 1 | 98.09 | 89.75 | |
| 40–60 | 1.5 | 98.09 | 89.75 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, D.; Sirini, P.; Lombardi, L. Green Hydrogen Production from Biogas or Landfill Gas by Steam Reforming or Dry Reforming: Specific Production and Energy Requirements. Energies 2025, 18, 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102631
Singh D, Sirini P, Lombardi L. Green Hydrogen Production from Biogas or Landfill Gas by Steam Reforming or Dry Reforming: Specific Production and Energy Requirements. Energies. 2025; 18(10):2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102631
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Dhruv, Piero Sirini, and Lidia Lombardi. 2025. "Green Hydrogen Production from Biogas or Landfill Gas by Steam Reforming or Dry Reforming: Specific Production and Energy Requirements" Energies 18, no. 10: 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102631
APA StyleSingh, D., Sirini, P., & Lombardi, L. (2025). Green Hydrogen Production from Biogas or Landfill Gas by Steam Reforming or Dry Reforming: Specific Production and Energy Requirements. Energies, 18(10), 2631. https://doi.org/10.3390/en18102631






