Entropy as a Lens: Exploring Visual Behavior Patterns in Architects
Highlights
- Architectural expertise shapes visual attention in image perception.
- Architects exhibit focused, systematic gaze patterns on built structures.
- Their gaze reflects a learned "Grammar of Space" from their training.
- Architects share similar gaze patterns, contrasting with the varied patterns of laypeople.
- Group differences in gaze entropy appear only in scenes with architectural elements.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Expertise Acquired Through Architectural Education and Training
2.2. Some Previous Studies on Expertise
2.3. Entropy in Visual Attention
2.4. Seeing-for-Speaking
3. Materials and Methods
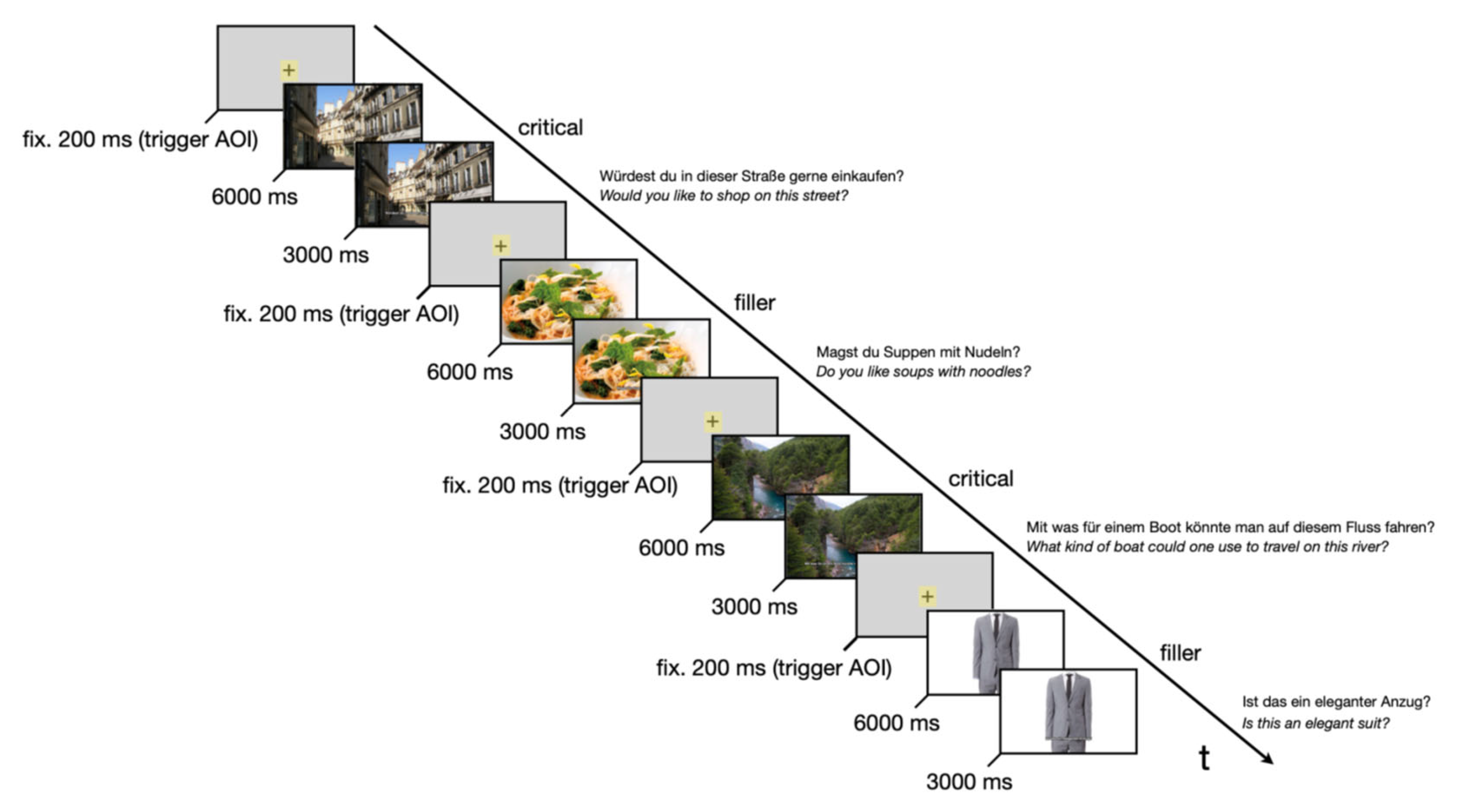
3.1. Stimuli
3.2. Procedure
3.3. Participants
3.4. Methods
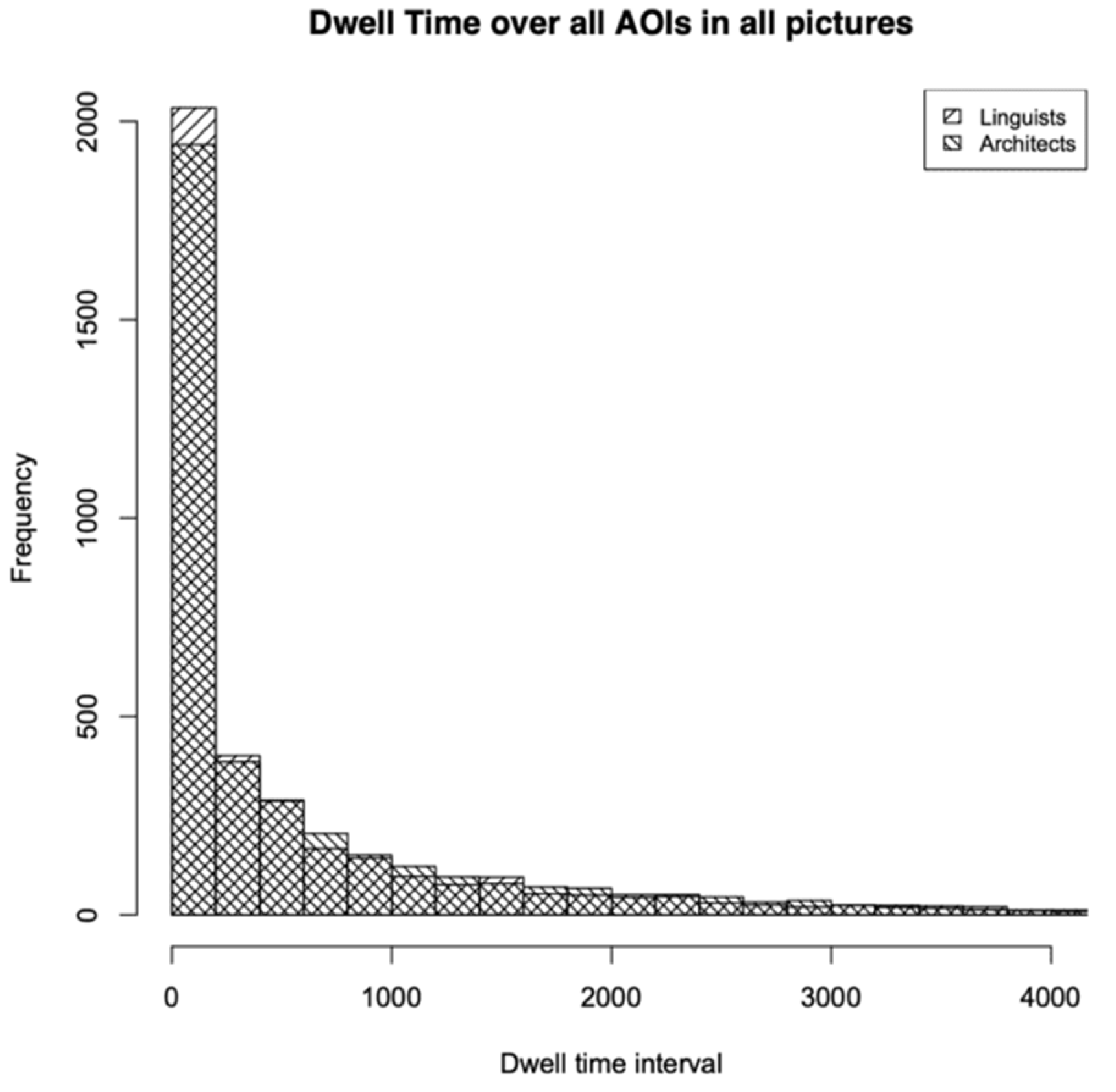
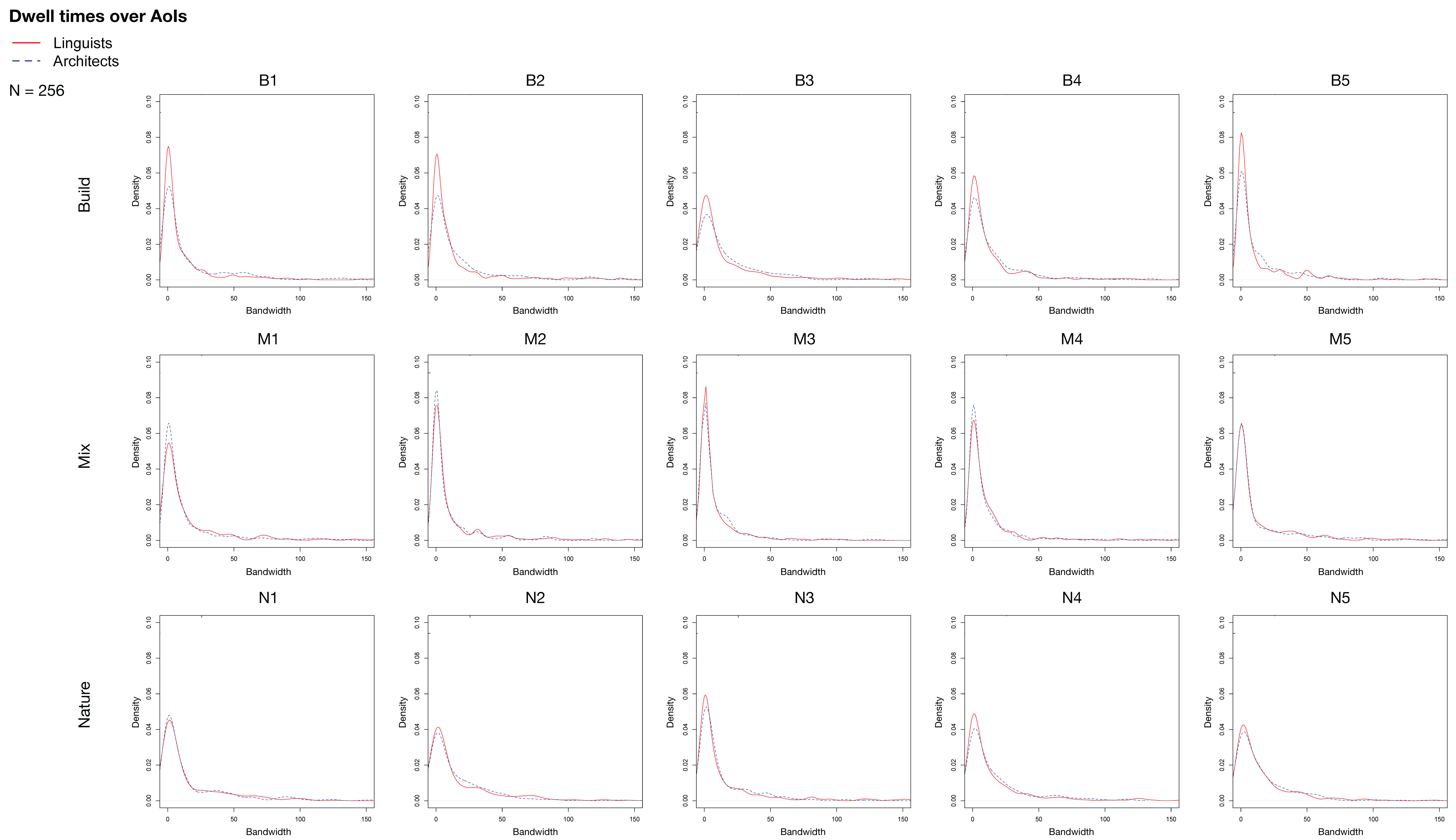
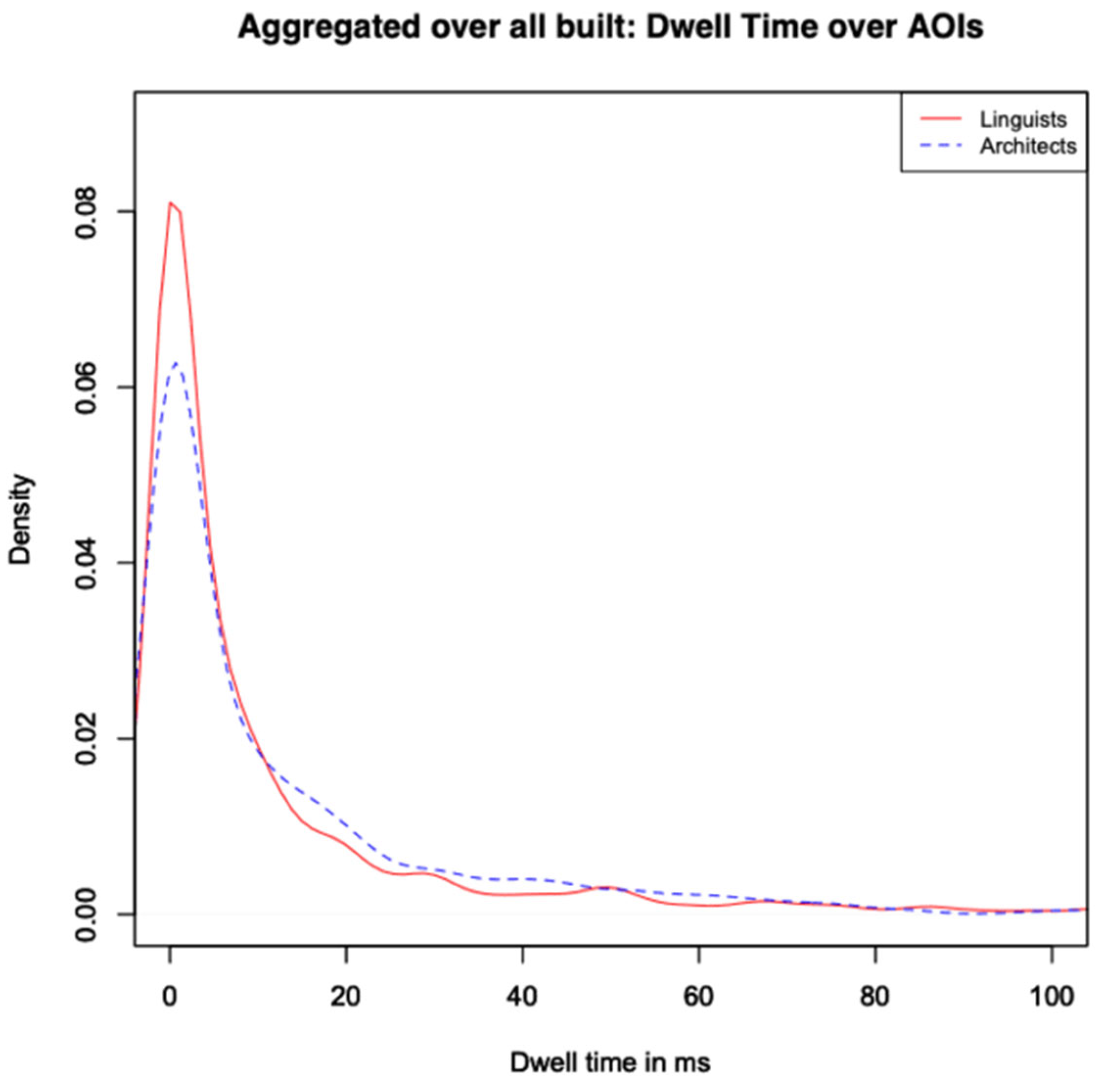
3.4.1. Visualization with Histograms and Densities
3.4.2. Skewness
3.4.3. Kurtosis
4. Results
4.1. Overall Trends
4.2. Individual Stimuli
4.3. Selected Individual Stimuli
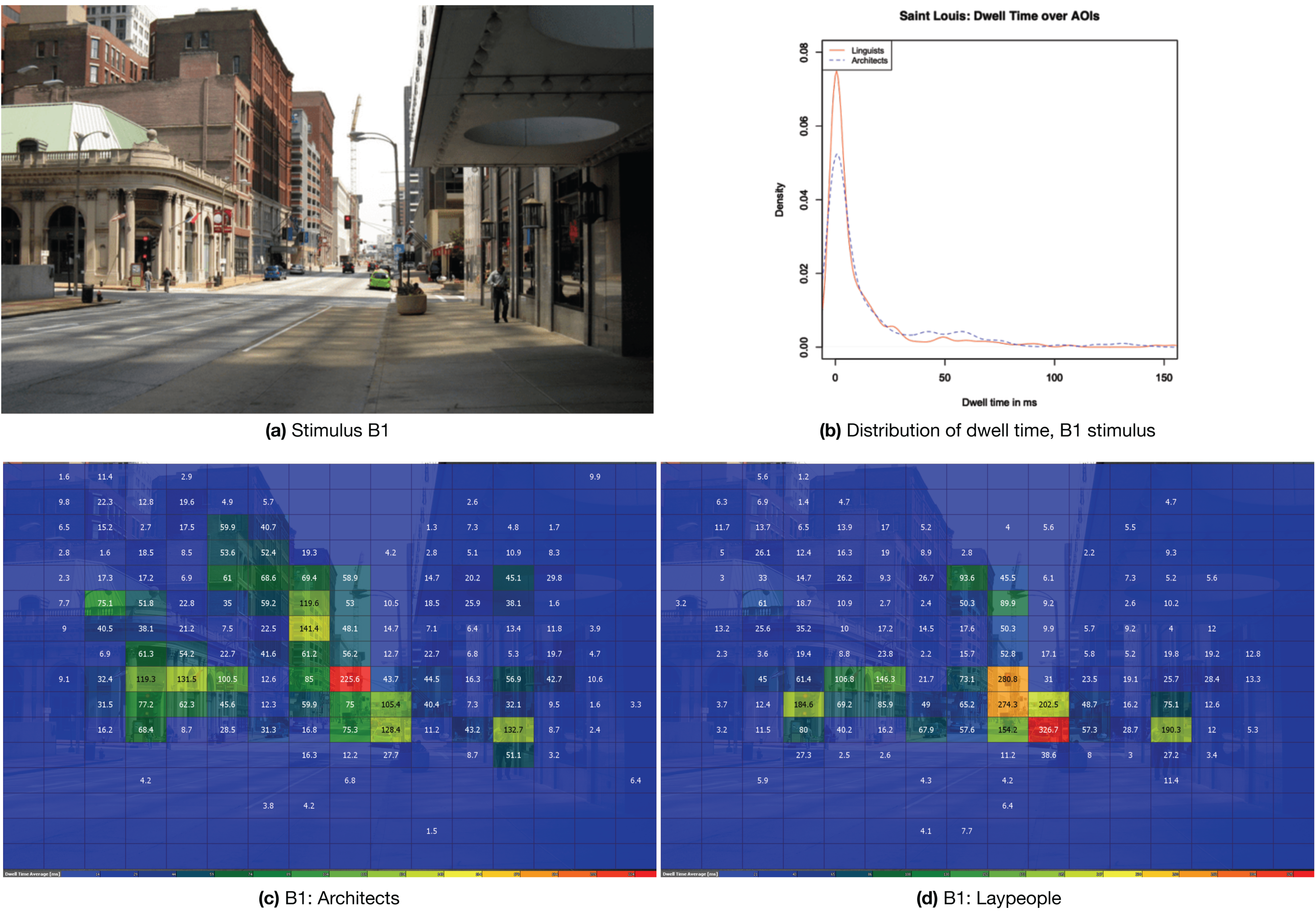
4.3.1. A Picture from the Built Environment Category: B1 (St. Louis)
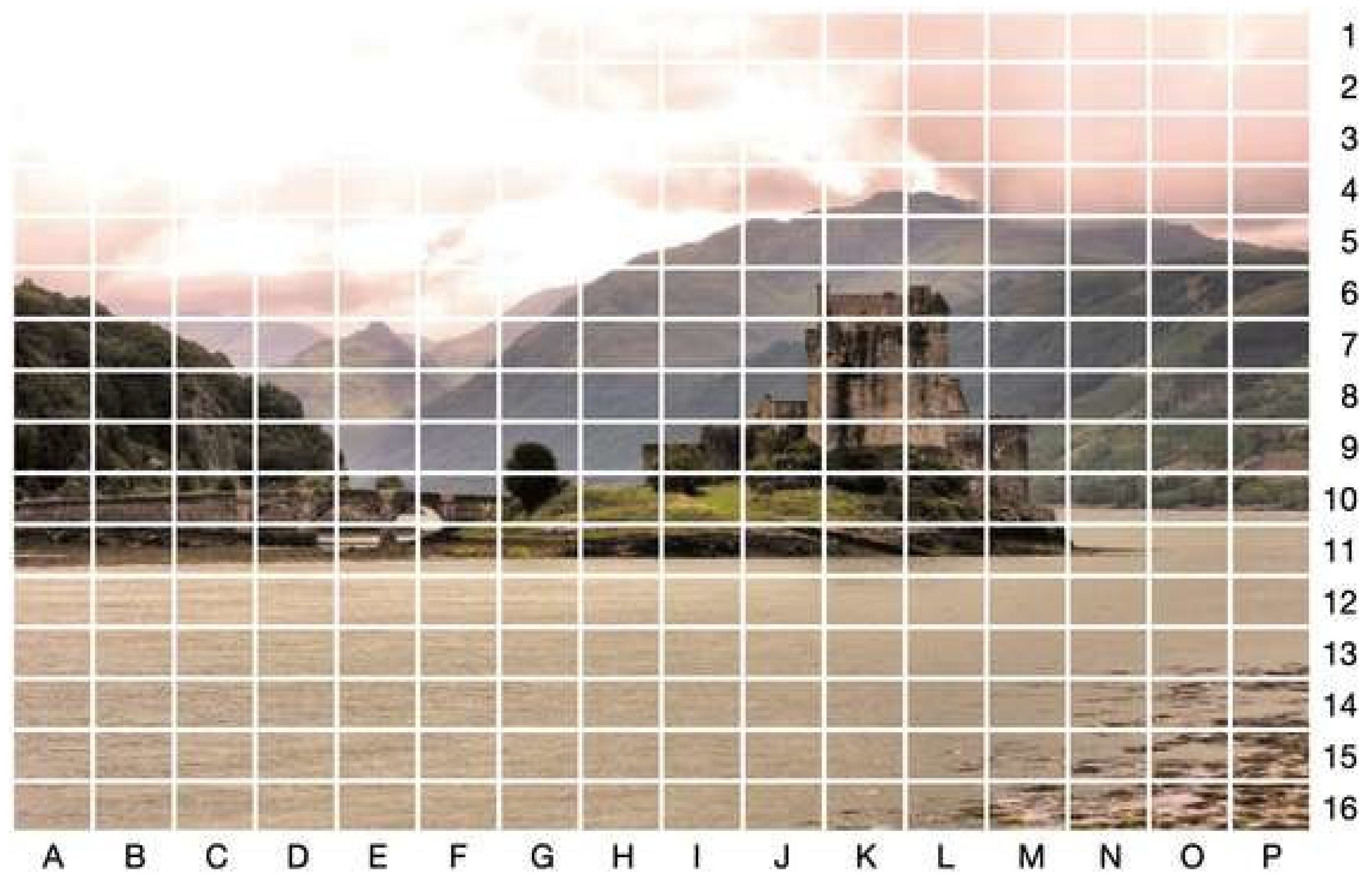
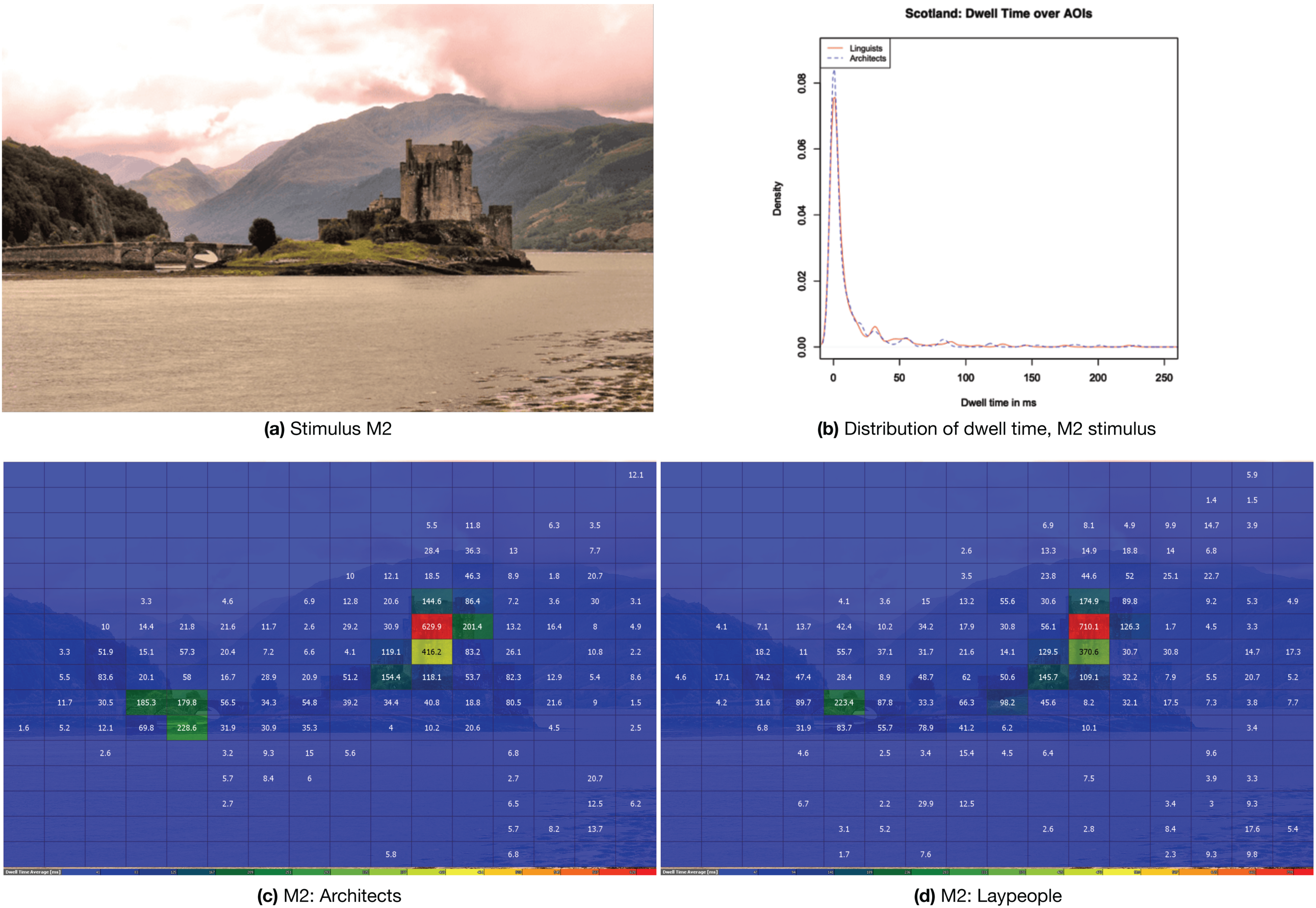
4.3.2. A Picture from the Mixed Environment Category: M2 (Scotland)
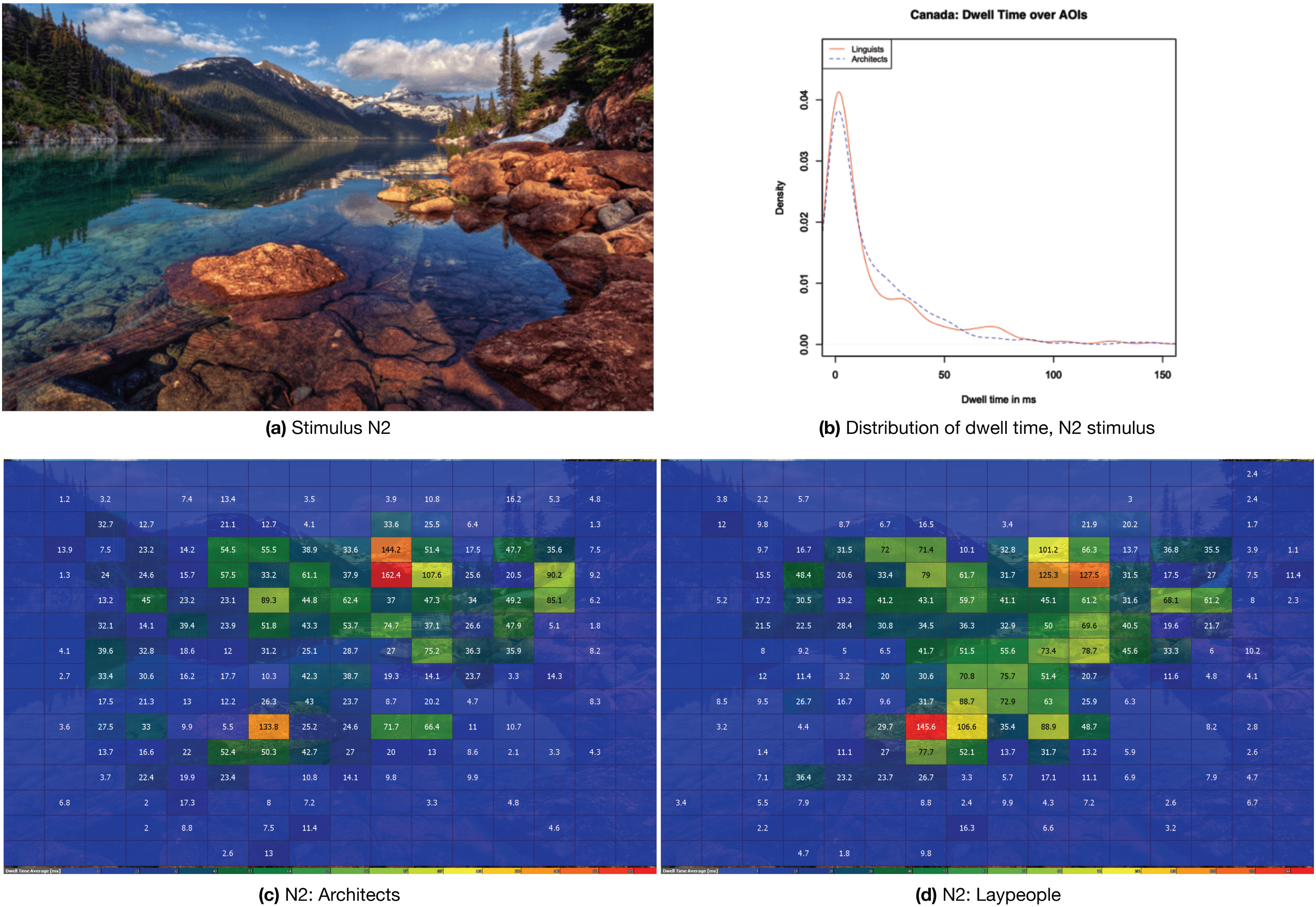
4.3.3. A Picture from the Natural Environment Category: N2 (Canada)
4.4. Significance Testing
4.5. Prediction by Model
5. Discussion
5.1. Summary of Main Findings
5.2. Interpretation of Entropy Measures
5.3. Grammar of Space and Expertise
5.4. Limitations and Future Work
6. Conclusions and Broader Implications
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AOI | Area of Interest |
| CAD | Computer-aided Design |
| VR | Virtual Reality |
| AR | Augmented Reality |
| MRI | Magnetic Resonance Imaging |
| LCD | Liquid-crystal display |
References
- Psarra, S. Architecture and Narrative: The Formation of Space and Cultural Meaning; Routledge: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, N. Narrative Architecture; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Correia, L.G. Spaces and places of education: Prelude. Paedagog. Hist. 2021, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, E.A.; Gadian, D.G.; Johnsrude, I.S.; Good, C.D.; Ashburner, J.; Frackowiak, R.S.J.; Frith, C.D. Navigation-related structural change in the hippocampi of taxi drivers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4398–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benz, I.; Rambow, R. Sichtbeton in der Architektur: Perspektivenunterschiede zwischen ArchitektInnen und Laien. Umweltpsychologie 2011, 15, 112–129. [Google Scholar]
- Mertins, H.; Delucchi Danhier, R.; Mertins, B.; Schulz, A.; Schulz, B. The Role of Expertise in the Perception of Architectural Space. In Research Culture in Architecture; Leopold, C., Robeller, C., Weber, U., Eds.; Birkhäuser: Basel, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Mertins, H.; Mertins, B.; Delucchi Danhier, R.; Schulz, A.; Schulz, B. Architekten haben eine andere Wahrnehmung. Detail 2017, 9, 80–81. [Google Scholar]
- Shannon, C.E. A mathematical theory of communication. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromiley, P.; Thacker, N.; Bouhova-Thacker, E. Shannon entropy, Renyi entropy, and information. Stat. Inf. Ser. 2004, 2004-004, 2–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kosel, C.; Holzberger, D.; Seidel, T. Identifying expert and novice visual scanpath patterns and their relationship to assessing learning-relevant student characteristics. Front. Educ. 2021, 5, 612175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krejtz, K.; Szmidt, T.; Duchowski, A.T.; Krejtz, I. Entropy-based Statistical Analysis of Eye Movement Transitions. In Proceedings of the Eye Tracking Research & Applications (ETRA) Conference, Safety Harbor, FL, USA, 26–28 March 2014; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 159–166. [Google Scholar]
- Melnyk, K.; Friedman, L.; Komogortsev, O.V. What can entropy metrics tell us about the characteristics of ocular fixation trajectories? PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0291823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winawer, J.; Witthoft, N.; Frank, M.C.; Wu, L.; Wade, A.R.; Boroditsky, L. Russian blues reveal effects of language on color discrimination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 7780–7785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberson, D.; Davies, I.; Davidoff, J. Color categories are not universal: Replications and new evidence from a stone-age culture. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2000, 129, 369–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobin, D.I. From “thought and language” to “thinking for speaking”. In Rethinking Linguistic Relativity; Gumperz, J.J., Levinson, S.C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1996; pp. 70–96. [Google Scholar]
- Papafragou, A.; Hulbert, J.; Trueswell, J. Does language guide event perception? Evidence from eye movements. Cognition 2008, 108, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sera, M.D.; Elieff, C.; Forbes, J.; Burch, M.C.; Rodríguez, W.; Dubois, D.P. When language affects cognition and when it does not: An analysis of grammatical gender and classification. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 2002, 131, 377–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, T. The semantics of grammatical gender: A cross-cultural study. J. Psycholinguist. Res. 1993, 22, 519–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, P. Numerical cognition without words: Evidence from Amazonia. Science 2004, 306, 496–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pica, P.; Lemer, C.; Izard, V.; Dehaene, S. Exact and approximate arithmetic in an Amazonian indigene group. Science 2004, 306, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, S.C. Space in Language and Cognition: Explorations in Cognitive Diversity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Majid, A.; Bowerman, M.; Kita, S.; Haun, D.B.; Levinson, S.C. Can language restructure cognition? The case for space. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickmann, M.; Robert, S. Space in Languages: Linguistic Systems and Cognitive Categories; John Benjamins: Amsterdam, The Netherlands; Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, P.; Levinson, S.C. Linguistic and Nonlinguistic Coding of Spatial Arrays: Explorations in Mayan Cognition. Working Paper No. 24, Cognitive Anthropology Research Group, Max Planck Institute for Psycholinguistics. Nijmegen, The Netherlands. 1993. Available online: https://pure.mpg.de/rest/items/item_825550_4/component/file_825551/content (accessed on 26 May 2025).
- von Stutterheim, C.; Andermann, M.; Carroll, M.; Flecken, M.; Schmiedtová, B. How grammaticized concepts shape event conceptualization in language production: Insights from linguistic analysis, eye tracking data and memory performance. Linguistics 2012, 4, 833–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carroll, M.; von Stutterheim, C.; Nuese, R. The language and thought debate: A psycholinguistic approach. In Multidisciplinary Approaches to Language Production; Pechmann, T., Habel, C., Eds.; De Gruyter Mouton: Berlin, Germany, 2004; pp. 183–218. [Google Scholar]
- Schmiedtová, B.; von Stutterheim, C.; Carroll, M. Implications of language-specific patterns in event construal of advanced L2 speakers. In Thinking and Speaking in Two Languages; Pavlenko, A., Ed.; Multilingual Matters: Clevendon, UK, 2011; pp. 66–107. [Google Scholar]
- Mertins, B. Sprache und Kognition: Ereigniskonzeptualisierung im Deutschen und Tschechischen; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bock, K.; Irwin, D.E.; Davidson, D.J.; Levelt, W.J.M. Minding the clock. J. Mem. Lang. 2003, 48, 653–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuchinsky, S.E.; Bock, K.; Irwin, D.E. Reversing the hands of time: Changing the mapping from seeing to saying. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. Mem. Cogn. 2011, 37, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmiedtová, B. Do L2 speakers think in the L1 when speaking in the L2? Int. J. Appl. Linguist. 2011, 8, 97–122. [Google Scholar]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.-G.; Buchner, A. G*Power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessels, R.S.; Kemner, C.; van den Boomen, C.; Hooge, I.T.C. The area-of-interest problem in eye-tracking research: A noise-robust solution for face and sparse stimuli. Behav. Res. Methods 2016, 48, 1694–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shannon, C.E. Prediction and entropy of printed English. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1951, 30, 50–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, K.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, S.; Ali, A.; Chu, Y.M. New estimation of Zipf–Mandelbrot and Shannon entropies via refinements of Jensen’s inequality. AIP Adv. 2021, 11, 015147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaynes, E.T. Information Theory and Statistical Mechanics. Phys. Rev. 1957, 106, 620–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacKay, D. Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016; Available online: http://www.deeplearningbook.org (accessed on 10 September 2025).
- Levinson, S.C.; Wilkins, D.P. (Eds.) Grammars of Space: Explorations in Cognitive Diversity; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Laguia, A.X. Giving voice to space: The grammar of Northern Alta spatial roots. Folia Linguist. 2022, 56, 351–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delucchi Danhier, R. Weganweisungen im Deutschen und Spanischen. Eine Vergleichsanalyse unter Anwendung von Visualisierungen; Verlag Dr. Hut: München, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]


| Measure | Architects | Laypeople |
|---|---|---|
| Entropy | 7.016 | 6.923 |
| Relative Entropy | 87.71% | 86.54% |
| Mean | 816.6 ms | 817.0 ms |
| Standard Deviation | 2100 ms | 2161 ms |
| Median | 192.0 ms | 163.9 ms |
| Skewness | 13.73 | 11.40 |
| Kurtosis | 358.1 | 246.4 |
| Pearson Correlation | 0.896 | |
| Measure | Architects | Laypeople |
|---|---|---|
| Shannon’s Entropy | 5.796 | 5.581 |
| Relative Entropy | 57.97% | 55.18% |
| Mean | 17.08 ms | 17.15 ms |
| Standard Deviation | 34.38 ms | 44.34 ms |
| Median | 4.1 ms | 3.2 ms |
| Skewness | 4.732 | 5.961 |
| Kurtosis | 33.68 | 48.35 |
| Pearson Correlation | 0.830 | |
| B1: St. Louis | M2: Scotland | N1: Canada | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measure | Architects | Laypeople | Architects | Laypeople | Architects | Laypeople |
| Shannon’s Entropy | 4.420 | 4.090 | 3.831 | 3.901 | 4.667 | 4.595 |
| Relative Entropy | 55.25% | 51.11% | 47.89% | 48.76% | 58.34% | 57.44% |
| Mean | 17.00 ms | 17.11 ms | 17.72 ms | 17.56 ms | 16.40 ms | 16.76 ms |
| Standard Deviation | 30.54 ms | 42.62 ms | 56.39 ms | 56.80 ms | 24.51 ms | 25.83 ms |
| Median | 2.65 ms | 2.2 ms | 0.0 ms | 0.7 ms | 6.6 ms | 4.75 ms |
| Skewness | 2.88 | 4.47 | 7.08 | 8.45 | 2.62 | 2.13 |
| Kurtosis | 10.99 | 23.20 | 63.15 | 90.34 | 9.35 | 4.91 |
| Pearson Correlation | 0.770 | 0.945 | 0.819 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Delucchi Danhier, R.; Mertins, B.; Mertins, H.; Schneider, G. Entropy as a Lens: Exploring Visual Behavior Patterns in Architects. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2025, 18, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jemr18050043
Delucchi Danhier R, Mertins B, Mertins H, Schneider G. Entropy as a Lens: Exploring Visual Behavior Patterns in Architects. Journal of Eye Movement Research. 2025; 18(5):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jemr18050043
Chicago/Turabian StyleDelucchi Danhier, Renate, Barbara Mertins, Holger Mertins, and Gerold Schneider. 2025. "Entropy as a Lens: Exploring Visual Behavior Patterns in Architects" Journal of Eye Movement Research 18, no. 5: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jemr18050043
APA StyleDelucchi Danhier, R., Mertins, B., Mertins, H., & Schneider, G. (2025). Entropy as a Lens: Exploring Visual Behavior Patterns in Architects. Journal of Eye Movement Research, 18(5), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/jemr18050043







