Abstract
Over the last two decades, the use of DNA barcodes has transformed our ability to identify and assess life on our planet. Both strengths and weaknesses of the method have been exemplified through thousands of peer-reviewed scientific articles. Given the novel sequencing approaches, currently capable of generating millions of reads at low cost, we reflect on the questions: What will the future bring for DNA barcoding? Will identification of species using short, standardized fragments of DNA stand the test of time? We present reflected opinions of early career biodiversity researchers in the form of a SWOT analysis and discuss answers to these questions.
1. Introduction
The use of short, standardized DNA sequences to identify species (i.e., DNA barcoding [1]) has considerably changed how we assess, analyze, and monitor biodiversity within all ecosystems (e.g., [2,3]). Since its initiation, DNA barcoding has significantly contributed to our understanding of species boundaries and the composition of biological communities across the world [4]. In addition, it has paved the way for national and international biodiversity research programs. Notable examples include biodiversity biomonitoring [5], food industry surveillance [6], and detecting substitution in the herbal medicine industry [7].
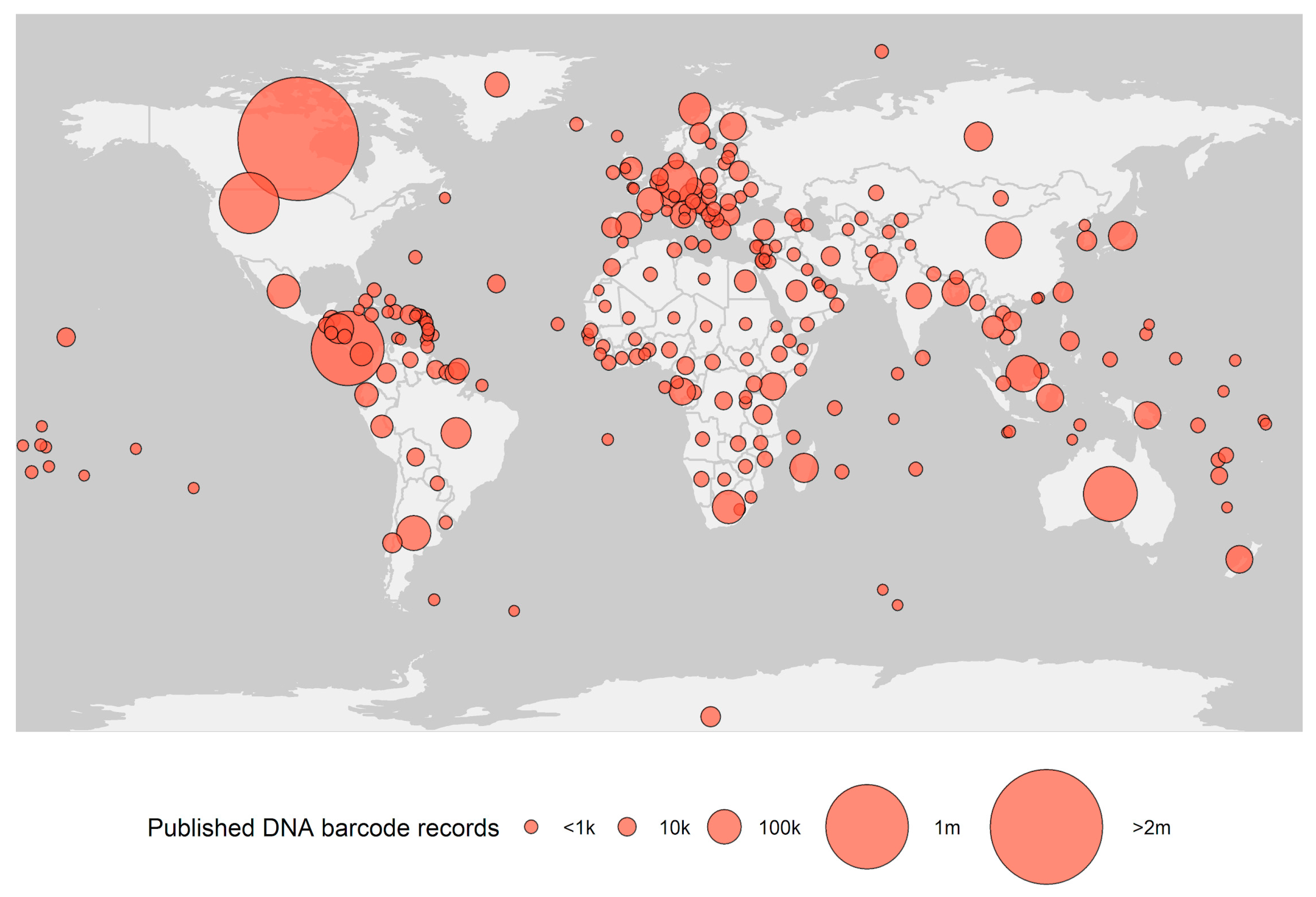
The foundation of species identification by DNA barcoding is a curated barcode reference library, enabling comparisons of DNA sequences from unidentified organisms to sequences from previously identified taxa. The largest database for this purpose is the Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD [8]) containing more than nine million DNA barcodes (Figure 1). The reference library is continuously expanding, with ~60% of the entries published during the last decade. This effort has been primarily driven by research projects promoted by the International Barcode of Life consortium (iBOL), such as Barcode 500K (completed in 2015) and BIOSCAN, launched June 2019 [9,10]. Other initiatives, such as the Earth Biogenome Project, aim to genome sequence all eukaryotic biodiversity in the upcoming decade, which will further expand DNA barcode coverage. The vast majority of organisms still lack DNA barcodes, and much of the current work has been carried out in Europe and North America, resulting in a bias in barcoded biota (Figure 1).
Figure 1.
Number of public DNA barcodes available in Barcode of Life Data Systems (BOLD) by country (obtained 1 January, 2021).
A review by DeSalle and Goldstein [4] highlighted that DNA barcoding is a widely applied contemporary tool that has diversified paradigms and practices. The adoption of high-throughput sequencing (HTS) technologies has further decreased costs and increased the range of applications for DNA barcoding [5,11]. Despite differences in the choice of target DNA marker and challenges with generating barcodes for some taxa [12], DNA barcoding is now routinely used across the tree of life and functions as an integrated and standard methodology in biodiversity studies. The essential value of DNA barcoding as an identification tool is obvious: many species would remain unidentified, hidden, or cryptic by other means of identification. The added value of DNA barcodes for identification is that they elucidate species boundaries and provide information on relationships and interactions. A list of scientific advances was accomplished through the use of DNA barcodes and DNA barcoding (e.g., [6,13]).
Two major advances in DNA barcoding have been the development of approaches for sequencing mixtures of samples, and high-throughput sequencing of PCR amplicons with generic primers (DNA metabarcoding). The metabarcoding approach enables the analysis of entire communities in complex samples [14,15], and has expanded the utility of DNA barcoding and associated libraries to microbiomes (e.g., [16]), diets (e.g., [17]), bulk sample biomonitoring (e.g., [2]), sequencing environmental samples (eDNA, e.g., [18]), and paleogenomics (e.g., [19]). DNA metabarcoding contributes to the molecular toolbox for studying both temporal and spatial species dynamics [20].
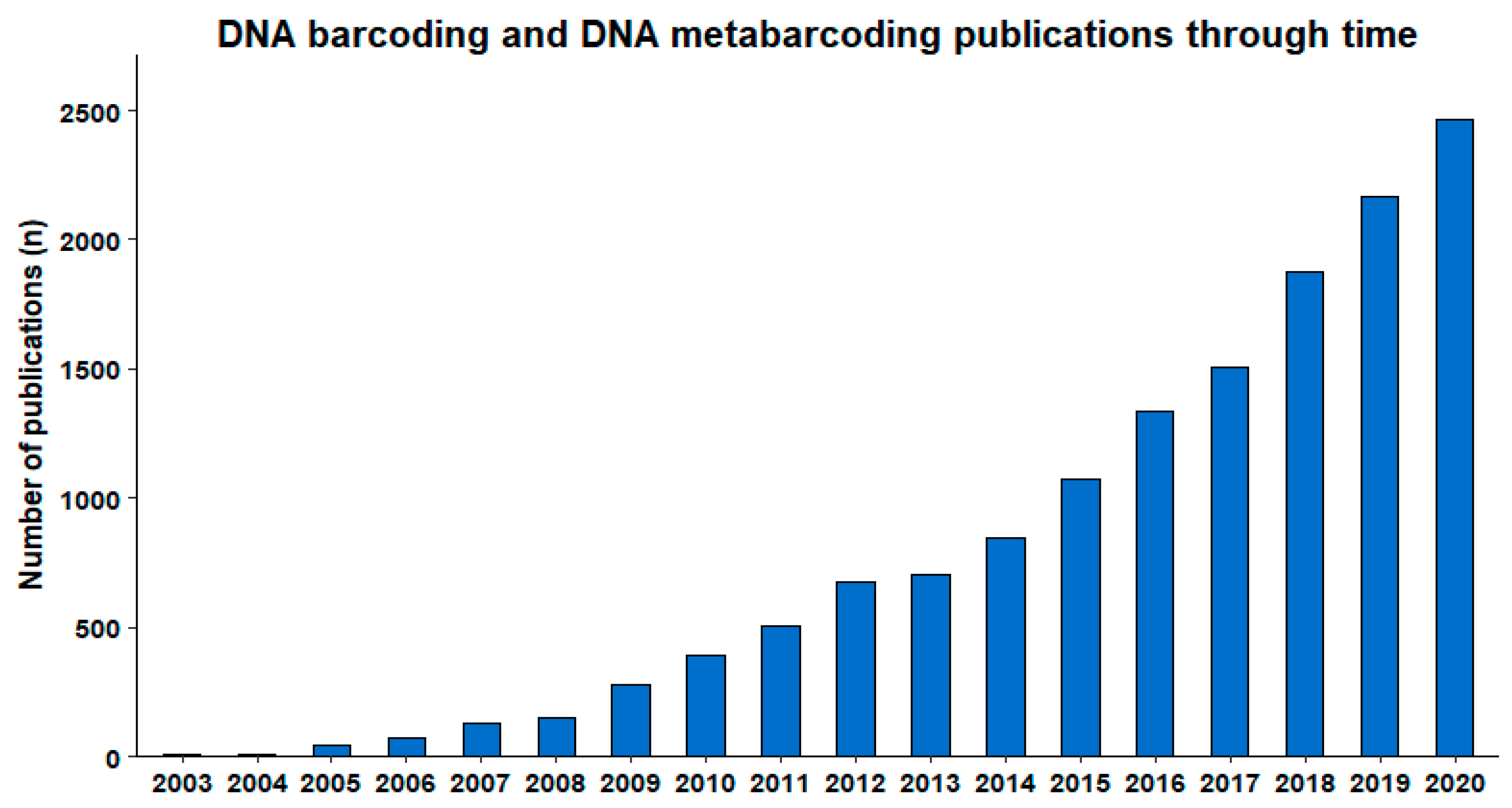
Beyond the above-mentioned large-scale initiatives and widespread global engagement, a measure of the impact of DNA barcoding can be deduced from the steep curve of the annual number of scientific publications on this topic. Our search (21 January 2021) in Scopus® for publications with ‘DNA barcod*’ or ‘DNA metabarcod*’ in the title, abstract, or keywords for the period 2003–2020 returned 14,229 publications from a variety of journals, representing extensive scientific diversity and applications. The publication numbers on these topics have been steadily growing since their introduction (Figure 2).
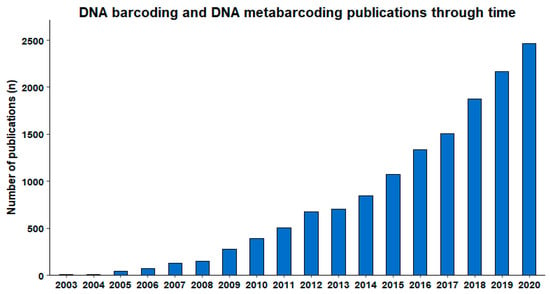
Figure 2.
Publications per year registered in Scopus®, containing ‘DNA barcod*’ or ‘DNA metabarcod*’ in the title, abstract, or keywords (obtained 21 January 2021).
Nearly two decades after DNA barcodes were first proposed, we reflect upon their future utility and value. In a world of rapid scientific progress, technology has introduced not only novel research avenues, but also rapidly evolving scientific practices. We pose the following two key, overarching questions: (1) Will DNA barcoding stand the test of time as technological progress enables relatively easy access to large-scale genomic data? (2) Will DNA barcoding alter how we describe, assess, and investigate biodiversity?
To answer these questions and contemplate the future of DNA barcoding, we organized a discussion on this topic among early career researchers during the ForBio course, DNA barcoding—from sequences to species, held online 21–25 September 2020. The course covered multiple theoretical and practical aspects of the use of molecular tools to delimit and identify species. To prime the discussion, arguments were organized through a SWOT analysis, and were facilitated by tutors in the course. This allowed us to develop and collate opinions on the key aspects, current state (strengths and weaknesses), and future prospects (opportunities and threats) of DNA barcoding. This analysis served as a starting point for a comprehensive discussion with flexible category boundaries. For instance, an opportunity may be seen as a threat and vice-versa. The main objective of this opinion paper is to communicate views and perspectives on the future of DNA barcoding from early career researchers, following comprehensive discussions and literature reviews.
2. SWOT Analysis and Early Career Opinions
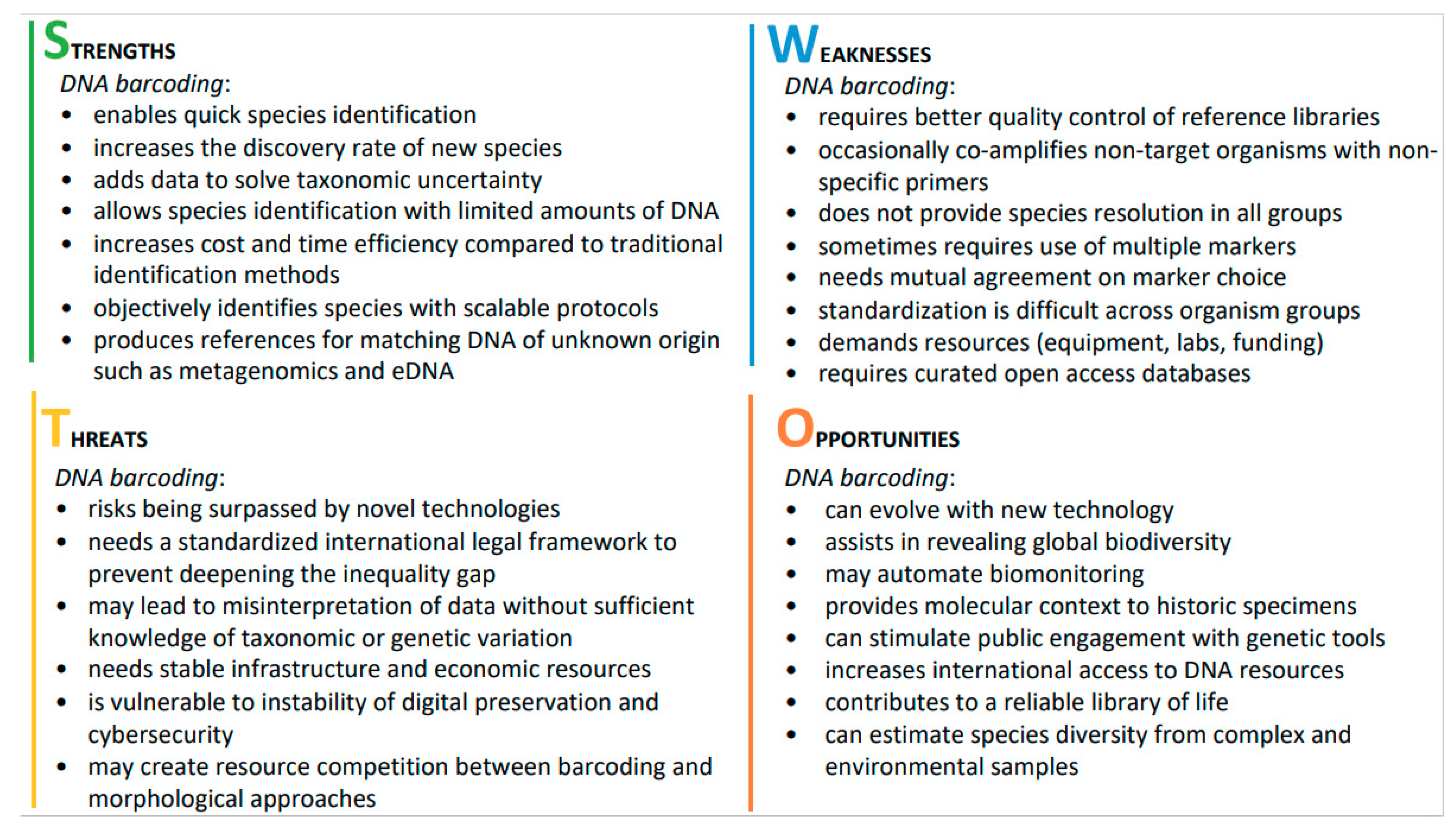
Our SWOT analysis, led by early career researchers, identified several current characteristics and prospects for DNA barcoding (Figure 3). In the following, we discuss the most important aspects related to the future of DNA barcoding in biodiversity research and management.
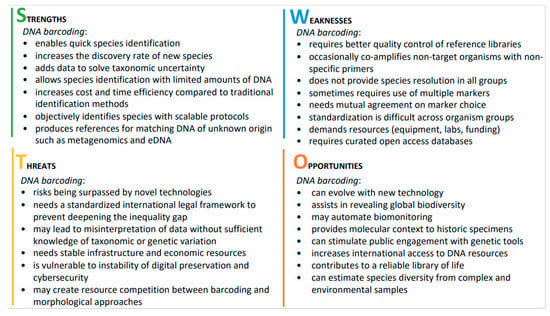
Figure 3.
Major strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats for DNA barcoding, resulting from the SWOT analysis.
2.1. DNA Barcoding Offers Efficient, Affordable, and High-Throughput Solutions
For most biological diversity, DNA barcoding can be more efficient and require less expertise compared to traditional morphological methods for species identification. It can also be more affordable, particularly for large sample sizes, since the price of generating a single barcode sequence can be as low as USD 0.10 if workflows are scaled efficiently [21]. However, the present costs and efficiency of DNA barcoding vary depending on the research question, taxonomic target group, and project scale, and may not be optimal for all studies. The uneven distribution of infrastructure required for DNA barcoding must also be considered in cost calculations. For regions with limited access to DNA technology, the more realistic identification option for individual specimens may still be morphology. Such scenarios have spurred collaborations, in which local knowledge on species identification has been coupled with sequencing capacity, generating barcoding “hubs” (e.g., [22]). As the international DNA barcoding program continues to expand, key priorities include ensuring equitable global access to technologies, and that samples, knowledge, and benefits are treated in line with the Nagoya Protocol. Inclusive collaboration should be a priority for established and early career researchers alike.
With the advent of various HTS platforms, whole-genome sequencing and metagenomics have become more affordable in recent years. Such big data sequencing approaches have been considered a threat to DNA barcoding [23]. Although genomic data may provide deeper insights for some biodiversity-related questions, DNA barcoding remains more scalable when species identifications are needed. The analysis of genomic data is time-consuming, requires considerable bioinformatic competence compared to standardized DNA barcodes, demands more energy for data computation and storage, and is challenging for quality control when shared [24]. There is an inherent complementarity in DNA barcoding and genomics, with “sequencing a small amount of DNA from vast sample sizes”, appropriate for species identification and biomonitoring, and “sequencing a vast amount of nucleotides from smaller sample sizes”, appropriate for understanding genomic complexity, diversity, and function. Within this continuum between whole genomes and DNA barcoding, there are organism groups that benefit from deeper sequencing strategies to better address species-level diversity, such as plants [25]. In plant studies, whole-plastid sequencing has some potential to increase taxonomic resolution in species identifications [26,27], and the development of extended barcoding using the nuclear genome is underway [28]. Thus, the question is less about which method is better for discriminating between species and more about which is appropriate for a specific application. There are also clear mutual benefits between barcoding and genome sequencing, with DNA barcoding providing a framework for well-identified samples in genome sequencing projects, and genomic studies contributing insights that may identify new barcode regions in groups where the standard regions are suboptimal.
2.2. DNA Barcoding will Survive and Thrive with Accessible and Curated Reference Libraries
Public biological databases that contain sequence information (e.g., BOLD and GenBank) are pivotal for biodiversity science and equal opportunities in academia. The usefulness of open databases can, however, be compromised by erroneous or ambiguous sequence data [29]. For instance, certain primer sets can lead to accidental co-amplification of non-target organisms [30]. From the start, quality control measures have been implemented in BOLD, for instance, highlighting records that are not barcode compliant, display stop codons, or result from contamination or misidentifications [8,31]. Despite quality control measures, mistakes can still arise from specimen misidentification or errors during one of the many workflow steps [32,33]. Mislabeling of sequences, cross-contamination, low-quality sequences, and sequencing errors may be unnoticed and become potential liabilities for downstream applications [29,34].
The necessity of comprehensive and accurate reference libraries for DNA (meta)barcoding is well-understood, as is the importance of record curation [35]. Despite this understanding, there is admittedly little incentive for researchers producing the data to also curate their shared data. It is our view that there should be incentives (funding and/or recognition) to encourage the development and curation of reference libraries. BOLD is especially useful as it incorporates several pieces of information (trace files, metadata, photos, etc.) and cross-shares data with other repositories [36]. BOLD holds approximately 9 million barcode compliant sequences, although only ~2.2 million are publicly available (BOLD, accessed 11 February 2021). Private records can be made public at any time and shared among researchers in private projects. Researchers that publicly share DNA barcodes bolster the extent and quality of public databases, enabling use and quality control. Machine learning is already in use for the detection of technical and biological errors in sequence data [37] and has the potential to further enhance quality assessments of public data repositories. Another opportunity to strengthen DNA barcode reference libraries is to invest in the production of barcodes for vouchered specimens in curated natural history collections. Obtaining DNA barcode data from these well-curated samples offers the potential to increase the confidence and quality of reference libraries for many taxonomic groups. Another potential step would be to move to routine inclusion of reference barcodes as part of new species descriptions, although it would be premature to make this mandatory as it may prevent many new species from being described (due to lack of access to technology, failed sequencing, degraded DNA, or requiring destructive sampling methods).
2.3. DNA Barcoding Enhances Biodiversity Discovery and Monitoring
The importance of species discovery, species identification, and biodiversity monitoring cannot be overstated, as these are the only means to quantitatively and qualitatively measure the impacts of climate change, habitat degradation, ecosystem management, and other anthropogenic impacts on the biosphere. DNA barcode data can provide a comprehensive basis for organizing and recognizing species-rich groups in the tree of life, providing good starting points for taxonomy as well as biodiversity assessments and biomonitoring (e.g., [38]).
The application of DNA barcoding to species discovery and identification is well-established, including the ability of the methodology to cope with different life stages and provide insights into cryptic species diversity [39]. Since these initial applications, rapid species identification with DNA barcodes has been deployed in several fields, including forensic science [40], control of the food supply chain [6], and understanding disease [41]. Its use in biodiversity characterisation and descriptive taxonomy remains important [38], and acceleration of species discovery is increasingly crucial, given the current threats to biodiversity and elevated rates of extinction [42].
Biomonitoring is a major application of DNA barcoding, and although the term is most often used to refer to ecological assessments, it also encompasses biological identifications to support border control, food authenticity, pharmaceutical monitoring, etc., with sample characterization and identification as the common base task (e.g., [43,44,45]). Increased knowledge of community composition and species interactions can lead to more precise biomonitoring and allow for the tracking and tracing of particularly important taxa, including endangered and invasive species (e.g., [46]). For instance, DNA barcoding of a single specimen’s symbiome, through targeted sequencing of all coexisting organismal DNA, may shed new light on species interactions (e.g., food webs, microbiomes, and parasites) and provide information for environmental management decisions. Detailed mapping of organisms’ symbiomes may even be an effective tool to intercept future pandemics [47].
Biomonitoring is often performed at the species level, but DNA barcoding also enables population-level research, assessing, for example, intraspecific genetic structure, population segregation, and phylogeographic patterns (e.g., [48]). As reference databases are compiled, multiple sequences per species will accumulate. This represents a natural foundation for inquisition into population-level dynamics. Sequencing of barcode markers is often the starting point in a phylogeographic study design due to low initial commitment costs before focusing on additional nuclear DNA regions, which is the preferred target in systematics due to their biparental inheritance [48,49]. In recent years, metabarcoding approaches on environmental and fecal samples have yielded insights into population structure in multiple species [50,51,52]. Likewise, metabarcoding of stream water can help elucidate the ecological impacts of environmental stressors by analyzing the haplotype richness and perseverance of selected macroinvertebrate species [53]. The application of eDNA (meta)barcoding for biomonitoring at the population-level has just begun, and there is considerable expansion potential [54]. As distinct populations are typically handled as separate entities, for example, in estimating quotas and making stock assessments for commercial fish species (e.g., [55]), expanding the reference databases to include wider population coverage per species will also expand applications into population-level inferences.
There are also interdisciplinary avenues that use DNA barcoding and metabarcoding. For example, paleo-reconstructions utilize ancient DNA metabarcoding to better understand past biodiversity, climate boundary conditions and response, past ocean conditions, and even past species distribution (e.g., [19]). The use of paleo-records is well-established, but the inclusion of DNA (meta)barcoding provides more resolution for these past environments compared to traditional methods [56]. The potential for recovering soft-bodied biota typically lost in the geological record creates a compelling argument for the implementation of metabarcoding and eDNA methods.
2.4. DNA Barcoding Methodology Is the Foundation for Automation and Accelerated Biodiversity Assessments
Every methodology has its limitations and challenges. Those that utilize DNA barcoding for species identification must acknowledge the challenges in order to mitigate them. Some species may not be well-discriminated by standard barcodes due to the absence of a clear barcode gap (i.e., maximum intraspecific distance lower than minimum interspecific distance), and this can be particularly problematic in groups that have recently diverged, show extensive hybridization, and/or have slow mutation rates relative to rates of speciation [28]. To overcome the limited discriminatory efficiency for standard barcodes, multiple alternative markers or even approaches are suggested, exemplified by the conundrum of plant DNA barcoding where no single DNA barcode marker separates all or most plant species [26,57]. Moreover, established universal primers may bind to a variety of templates but fail to amplify a specific target group, hence establishing a need for either more degenerative or target-specific primers [58]. Yet another challenge includes barcode pseudogenes (i.e., non-functional copies of barcode regions), which can result in the overestimation of species diversity and misidentifications [59].
DNA metabarcoding has a particular set of challenges, as the outcome of studies is influenced by several variables and decisions made in the experimental setup; this includes the choice of primers, marker specificity, and taxonomic resolution [5]. The requirements of metabarcoding protocols have resulted in the use of additional or alternative DNA barcoding regions more suitable for specific taxa or applications (e.g., 12S for fish eDNA [60] and the trnL intron for plants [61]). This utilization of alternative barcoding regions can increase recoverability and resolution (and thus provides clear benefits) while maintaining similarity to a standardized system, using a common set of loci for the molecular identification of species.
Fully accepting the challenges and limitations outlined above, ongoing technological developments are considerably improving the efficiency of DNA barcoding and metabarcoding. One example of this is the use of the PacBio Sequel platform for extensively multiplexing samples and reducing costs [11]. Another innovation is where single-species biomonitoring techniques have been developed based on barcoding primers designed to detect target species in complex samples with a dip-stick. Doyle and Uthicke [62] designed the tool by combining a lateral flow assay with species-specific primers to successfully detect the presence of crown-of-thorn starfish on the Great Barrier Reef. This dip-stick method may potentially detect a wide variety of species from environmental samples, requiring little scientific training or laboratory access, making it well-suited for citizen science and remote conservation projects. Another future prospect is the potential for closed-tube PCR and automation, such as FASTFISH-ID [63], aiming to complete DNA barcoding in the field. When automated, these set-ups can become remote, real-time sensors. Deployment of such devices can efficiently provide unprecedented detail of real-time species movement, migration, and distribution. These tools, as well as other technological advancements for automatic sampling and processing, may be used for policy development, conservation, and biosecurity applications.
2.5. DNA Barcoding for Everyone, Everywhere
The DNA barcoding community contributes to networks, collaborative projects, data sharing, citizen science initiatives, and informed policy design. For instance, iBOL estimates 29,000 users of the Barcode of Life Data Systems database from 200 nations, which includes ~9 million barcodes, and the ambitious goal to expand by another 2 million barcoded taxa by 2026 (iBOL, http://ibol.org; access on 1 January 2021). Access to these and other reference barcodes is pivotal for well-rounded science and academic inclusivity. Researchers and organizations planning international collaborations should acknowledge funding bias and implement benefit-sharing with regions identified to have less barcoding capacity. In addition to academic projects, DNA barcoding is accessible to the public and suitable for citizen science. Citizen science projects such as the School Malaise Trap Program can result in data collection, education opportunities, and two-way collaboration between scientists and the general public [64,65].
The effectiveness of collaboration efforts relies on improved and continued open access to sequence information. However, freely accessible DNA barcode data can be targeted by commercial and exploitative research [66,67]. Thus, the delicate discussion of DNA barcodes as a form of digital sequence information (DSI, [68]), is needed. Digital sequence information is not yet regulated by the Nagoya Protocol on Access and Benefit-sharing that came into effect in 2014, despite ongoing discussions regarding DSI inclusion. Some support open-access DSI as a form of benefit-sharing, while others propose tighter restrictions [66]. The outcome of these discussions will have ramifications for DNA barcoding and metabarcoding and should be considered by anyone working directly or indirectly with DNA barcodes.
From our reflections, as long as a focus on data quality is prioritized and the methodological and technological advancements remain aligned, DNA (meta)barcoding will continue to impact, shape, and respond to changes in biological sciences, and DNA barcoding will continue to grow and increase our knowledge of global biodiversity. The scalability, accessibility, and automation potential of DNA (meta)barcoding methods strengthen biodiversity investigations. Beyond biodiversity monitoring, the knowledge provided by DNA barcoding can help mitigate threats to global biodiversity through improved environmental management and informed conservation measures.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed to the conceptualization, discussion and writing of this article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The Research School in Biosystematics (ForBio) is supported by a grant from the Norwegian Biodiversity Information Centre.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no research data were generated or analysed during the current study.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Research School for Biosystematics (https://www.forbio.uio.no/, accessed on 13 June 2021), for organizing the course ‘DNA Barcoding—from sequences to species’.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Cywinska, A.; Ball, S.L.; deWaard, J.R. Biological identifications through DNA barcodes. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2003, 270, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, A.; Monk, A.W.; Compson, G.Z.; Peters, D.L.; Porter, M.T.; Shokralla, S.; Wright, G.T.M.; Hajibabaei, M.; Baird, J.D. DNA metabarcoding reveals metacommunity dynamics in a threatened boreal wetland wilderness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 8539–8545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennisi, E. DNA barcodes jump-start search for new species. Science 2019, 364, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSalle, R.; Goldstein, P. Review and interpretation of trends in DNA barcoding. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Bonin, A.; Zinger, L.; Coissac, E. Environmental DNA: For Biodiversity Research and Monitoring; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Galimberti, A.; Casiraghi, M.; Bruni, I.; Guzzetti, L.; Cortis, P.; Berterame, N.M.; Labra, M. From DNA barcoding to personalized nutrition: The evolution of food traceability. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2019, 28, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Boer, H.J.; Ichim, M.C.; Newmaster, S. DNA barcoding and pharmacovigilance of herbal medicines. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD: The Barcode of Life Data System (http://www.barcodinglife.org). Mol. Ecol. Notes 2007, 7, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobern, D. BIOSCAN: DNA barcoding to accelerate taxonomy and biogeography for conservation and sustainability. Genome 2021, 64, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobern, D.; Hebert, P.D.N. BIOSCAN-revealing eukaryote diversity, dynamics, and interactions. Biodivers. Inf. Sci. Stand. 2019, 3, e37333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebert, P.D.N.; Braukmann, T.W.; Prosser, S.W.; Ratnasingham, S.; DeWaard, J.R.; Ivanova, N.V.; Janzen, H.D.; Hallwachs, W.; Sones, E.J.; Zakharov, E. A Sequel to Sanger: Amplicon sequencing that scales. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kress, W.J. Plant DNA barcodes: Applications today and in the future. J. Syst. Evol. 2017, 55, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, A.; Willows-Munro, S. The utility of DNA barcoding as a tool to assess the success of ecological restoration using Hemiptera as a biological indicator. Restor. Ecol. 2019, 27, 1409–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Brochmann, C.; Willerslev, E. Towards next-generation biodiversity assessment using DNA metabarcoding. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beng, K.C.; Corlett, R.T. Applications of environmental DNA (eDNA) in ecology and conservation: Opportunities, challenges and prospects. Biodivers. Conserv. 2020, 29, 2089–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yatsunenko, T.; Rey, F.E.; Manary, M.J.; Trehan, I.; Dominguez-Bello, M.G.; Contreras, M.; Magris, M.; Hidalgo, G.; Baldassano, N.R.; Anokhin, P.A.; et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature 2012, 486, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, O.; Bulman, C.; Bunce, M.; Coghlan, M.; Murray, D.C.; Ward, R.D. Comparison of morphological and DNA metabarcoding analyses of diets in exploited marine fishes. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 540, 167–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiner, K.; Bik, H.M.; Machler, E.; Seymour, M.; Lacoursiere-Roussel, A.; Altermatt, F.; Creer, S.; Bista, I.; Lodge, M.D.; de Vere, N.; et al. Environmental DNA metabarcoding: Transforming how we survey animal and plant communities. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5872–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsos, I.G.; Lammers, Y.; Yoccoz, N.G.; Jørgensen, T.; Sjögren, P.; Gielly, L.; Edwards, M.E. Plant DNA metabarcoding of lake sediments: How does it represent the contemporary vegetation. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creer, S.; Deiner, K.; Frey, S.; Porazinska, D.; Taberlet, P.; Thomas, W.K.; Potter, C.; Bik, H.M. The ecologist’s field guide to sequenceh-based identification of biodiversity. Methods Ecol. Evol. 2016, 7, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivathsan, A.; Lee, L.; Katoh, K.; Hartop, E.; Kutty, S.N.; Wong, J.; Yeo, D.; Meier, R. MinION barcodes: Biodiversity discovery and identification by everyone, for everyone. bioRxiv 2021, 434692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W.; Pereira, G.; Blanco, R.; Masis, A.; Chavarria, M.M.; Chavarria, F.; Guadamuz, A.; Araya, M.; Smith, M.A.; et al. Using DNA-barcoded Malaise trap samples to measure impact of a geothermal energy project on the biodiversity of a Costa Rican old-growth rainforest. Genome 2020, 63, 407–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joly, S.; Davies, T.J.; Archambault, A.; Bruneau, A.; Derry, A.; Kembel, S.W.; Peres-Neto, P.; Vamosi, J.; Wheeler, T.A. Ecology in the age of DNA barcoding: The resource, the promise and the challenges ahead. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2014, 14, 221–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obringer, R.; Rachunok, B.; Maia-Silva, D.; Arbabzadeh, M.; Nateghi, R.; Madani, K. The overlooked environmental footprint of increasing Internet use. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Graham, S.W.; Little, D.P. Choosing and using a plant DNA barcode. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.-F.; Ma, H.; Ci, X.-Q.; Li, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, H.W.; Wang, S.L.; Qu, X.J.; Hu, J.L.; et al. Can plastid genome sequencing be used for species identification in Lauraceae? Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 2021, boab018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollingsworth, P.M.; Li, D.-Z. van der Bank, M. Twyford, A.D. Telling plant species apart with DNA: From barcodes to genomes. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150338. [Google Scholar]
- Fontes, J.T.; Vieira, P.E.; Ekrem, T.; Soares, P.; Costa, F.O. BAGS: An automated Barcode, Audit & Grade System for DNA barcode reference libraries. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2021, 21, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siddall, M.E.; Fontanella, F.M.; Watson, S.C.; Kvist, S.; Erséus, C. Barcoding bamboozled by bacteria: Convergence to metazoan mitochondrial primer targets by marine microbes. Syst. Biol. 2009, 58, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnasingham, S.; Hebert, P.D.N. A DNA-based registry for all animal species: The Barcode Index Number (BIN) system. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigand, H.; Beermann, A.J.; Čiampor, F.; Costa, F.O.; Csabai, Z.; Duarte, S.; Geiger M., F.; Grabowski, M.; Rimet, F.; Rulik, B.; et al. DNA barcode reference libraries for the monitoring of aquatic biota in Europe: Gap-analysis and recommendations for future work. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 678, 499–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigand, A.M.; Jochum, A.; Pfenninger, M.; Steinke, D.; Klussmann-Kolb, A. A new approach to an old conundrum—DNA barcoding sheds new light on phenotypic plasticity and morphological stasis in microsnails (Gastropoda, Pulmonata, Carychiidae). Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2011, 11, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pentinsaari, M.; Ratnasingham, S.; Miller, S.E.; Hebert, P.D.N. BOLD and GenBank revisited—Do identification errors arise in the lab or in the sequence libraries? PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimet, F.; Aylagas, E.; Borja, A.; Bouchez, A.; Canino, A.; Chauvin, C.; Chonova, T.; Ciampor, F., Jr.; Costa, F.О.; Ferrari, B.J.D.; et al. Metadata standards and practical guidelines for specimen and DNA curation when building barcode reference libraries for aquatic life. Metabarcoding Metagenom. 2021, 5, e58056. [Google Scholar]
- Porter, T.M.; Hajibabaei, M. Over 2.5 million COI sequences in GenBank and growing. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0200177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krachunov, M.; Nisheva, M.; Vassilev, D. Machine learning models for error detection in metagenomics and polyploid sequencing data. Information 2019, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharkey, M.J.; Janzen, D.H.; Hallwachs, W.; Chapman, E.G.; Smith, M.A.; Dapkey, T.; Brown, A.; Ratnasingham, S.; Naik, S.; Manjunath, R.; et al. Minimalist revision and description of 403 new species in 11 subfamilies of Costa Rican braconid parasitoid wasps, including host records for 219 species. ZooKeys 2021, 1013, 1–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montes-Ortiz, L.; Elías-Gutiérrez, M. Water mite diversity (Acariformes: Prostigmata: Parasitengonina: Hydrachnidiae) from karst ecosystems in southern of Mexico: A barcoding approach. Diversity 2020, 12, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buenaventura, E.; Valverde-Castro, C.; Wolff, M.; Triana-Chavez, O.; Gómez-Palacio, A. DNA barcoding for identifying synanthropic flesh flies (Diptera, Sarcophagidae) of Colombia. Acta Tropica 2018, 182, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ćelepirović, N.; Novak Agbaba, S.; Karija Vlahović, M. DNA Barcoding of Fungi in the Forest Ecosystem of the Psunj and Papuk Mountains in Croatia. South-East Eur. For. 2020, 11, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPBES. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental; IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Madden, M.J.L.; Young, R.G.; Brown, J.W.; Miller, S.E.; Frewin, A.J.; Hanner, R.H. Using DNA barcoding to improve invasive pest identification at U.S. ports-of-entry. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raclariu, A.C.; Heinrich, M.; Ichim, M.C.; de Boer, H. Benefits and limitations of DNA barcoding and metabarcoding in herbal product authentication. Phytochem. Anal. 2018, 29, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, J.; Anabalón, L.; Figueroa, A.; Gangitano, D. ITS barcoding using high resolution melting analysis of Cannabis sativa drug seizures in Chile: A forensic application. Forensic Sci. Int. 2020, 316, 110550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuzmina, M.L.; Braukmann, T.W.A.; Zakharov, E.V. Finding the pond through the weeds: eDNA reveals underestimated diversity of pondweeds. Appl. Plant. Sci. 2018, 6, e01155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kress, J.W.; Mazet, J.A.K.; Hebert, P.D.N. Intercepting pandemics through genomics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13852–13855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, P.E.; Desiderato, A.; Holdich, D.M.; Soares, P.; Creer, S.; Carvalho, G.R.; Costa, F.O.; Queiroga, H. Deep segregation in the open ocean: Macaronesia as an evolutionary hotspot for low dispersal marine invertebrates. Mol. Ecol. 2019, 28, 1784–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hupało, K.; Teixeira, M.A.L.; Rewicz, T.; Sezgin, M.; Iannilli, V.; Karaman, G.S.; Grabowski, M.; Costa, F.O. Persistence of phylogeographic footprints helps to understand cryptic diversity detected in two marine amphipods widespread in the Mediterranean basin. Mol. Phylogen. Evol. 2019, 132, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Nielsen, I.B.; Carl, H.; Krag, M.A.; Knudsen, S.W.; Xing, Y.; Holm-Hansen, H.T.; Møller, P.R.; Thomsen, P.F. Seawater environmental DNA reflects seasonality of a coastal fish community. Mar. Biol. 2017, 164, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, K.M.; Everett, M.; Dahlheim, M.; Park, L. Water, water everywhere: Environmental DNA can unlock population structure in elusive marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2018, 5, 180537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohmann, K.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Nielsen, M.; Nielsen, L.D.S.B.; Jones, G.; Streicker, D.G.; Gilbert, M.T.P. Using DNA metabarcoding for simultaneous inference of common vampire bat diet and population structure. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2018, 18, 1050–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zizka, V.M.; Geiger, M.F.; Leese, F. DNA metabarcoding of stream invertebrates reveals spatio-temporal variation but consistent status class assessments in a natural and urban river. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 115, 106383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigsgaard, E.E.; Jensen, M.R.; Winkelmann, I.E.; Møller, P.R.; Hansen, M.M.; Thomsen, P.F. Population-level inferences from environmental DNA—current status and future perspectives. Evol. Appl. 2020, 13, 245–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stransky, C.; Baumann, H.; Fevolden, S.E.; Harbitz, A.; Høie, H.; Nedreaas, K.H.; Salberg, A.-B.; Skarstein, T.H. Separation of Norwegian coastal cod and Northeast Arctic cod by outer otolith shape analysis. Fish. Res. 2008, 90, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zobel, M.; Davison, J.; Edwards, M.E.; Brochmann, C.; Coissac, E.; Taberlet, P.; Willerslev, E.; Moora, M. Ancient environmental DNA reveals shifts in dominant mutualisms during the late Quaternary. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsos, I.G.; Lavergne, S.; Merkel, M.K.F.; Boleda, M.; Lammers, Y.; Alberti, A.; Pouchon, C.; Denoeud, F.; Pitelkova, I.; Pușcaș, M. The treasure vault can be opened: Large-scale genome skimming works well using herbarium and silica gel dried material. Plants 2020, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, J.; Costa, P.M.; Teixeira, M.A.; Ferreira, M.S.; Costa, M.H.; Costa, F.O. Enhanced primers for amplification of DNA barcodes from a broad range of marine metazoans. BMC Ecol. 2013, 13, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leite, L.A.R. Mitochondrial pseudogenes in insect DNA barcoding: Differing points of view on the same issue. Biota Neotrop. 2012, 12, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miya, M.; Sato, Y.; Fukunaga, T.; Sado, T.; Poulsen, J.Y.; Sato, K.; Minamoto, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Yamanaka, H.; Araki, H.; et al. MiFish, a set of universal PCR primers for metabarcoding environmental DNA from fishes: Detection of more than 230 subtropical marine species. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2015, 2, 150088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taberlet, P.; Coissac, E.; Pompanon, F.; Gielly, L.; Miquel, C.; Valentini, A.; Vermat, T.; Corthier, G.; Brochmann, C.; Willerslev, E. Power and limitations of the chloroplast trnL (UAA) intron for plant DNA barcoding. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.; Uthicke, S. Sensitive environmental DNA detection via lateral flow assay (dipstick)-A case study on corallivorous crown-of-thorns sea star (Acanthaster cf. solaris) detection. Environ. DNA 2021, 3, 323–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naaum, A.M.; Cusa, M.; Singh, M.; Bleicher, Z.; Elliott, C.; Goodhead, I.B.; Hanner, R.H.; Helyar, S.J.; Mariani, S.; Rice, J.E.; et al. Validation of FASTFISH-ID: A new commercial platform for rapid fish species authentication via universal closed-tube barcoding. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobori, H.; Dickinson, J.L.; Washitani, I.; Sakurai, R.; Amano, T.; Komatsu, N.; Kitamura, W.; Takagawa, S.; Koyama, K.; Ogawara, T.; et al. Citizen science: A new approach to advance ecology, education, and conservation. Ecol. Res. 2016, 31, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinke, D.; Breton, V.; Berzitis, E.; Hebert, P.D.N. The School Malaise Trap Program: Coupling educational outreach with scientific discovery. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2001829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, M.E. The Nagoya Protocol: The conundrum of defining digital sequence information. Bioscience 2019, 69, 480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bond, M.R.; Scott, D. Digital biopiracy and the (dis)assembling of the Nagoya Protocol. Geoforum 2020, 117, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houssen, W.; Sara, R.; Jaspars, M. Digital Sequence Information on Genetic Resources: Concept, Scope and Current Use; Convention on Biological Conservation CBD/DSI/AHTEG: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2020. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).