Abstract
The present work describes the synthesis of a Schiff base, 3-{4-[4-(benzylidene-amino)benzenesulfonyl]phenyl}-2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-one from a novel quinazolin-one, 3-[4-(4-aminobenzenesulfonyl)phenyl]-2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-one. The quin-azolinone was prepared by reacting 2-phenyl-4H-3,1-benzoxazin-4-one with dapsone. The structure of the synthesized Schiff base is confirmed by IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, MS and elemental analysis.
Introduction
Fused nitrogen-containing heterocycles are structural fragments of many natural compounds and are important for various vital processes. Quinazolinones have been frequently used in medicine because of their wide spectrum of biological activities [1,2,3,4,5,6]. Different quinazolinone derivatives have been reported for their antibacterial, antifungal, anti-HIV, anthelmintic, CNS depressant and antitubercular activities. Schiff bases have also gained importance in recent days due to their potential biological activities [7]. In this paper, we want to report the synthesis of a novel Schiff base from a quinazolinone.
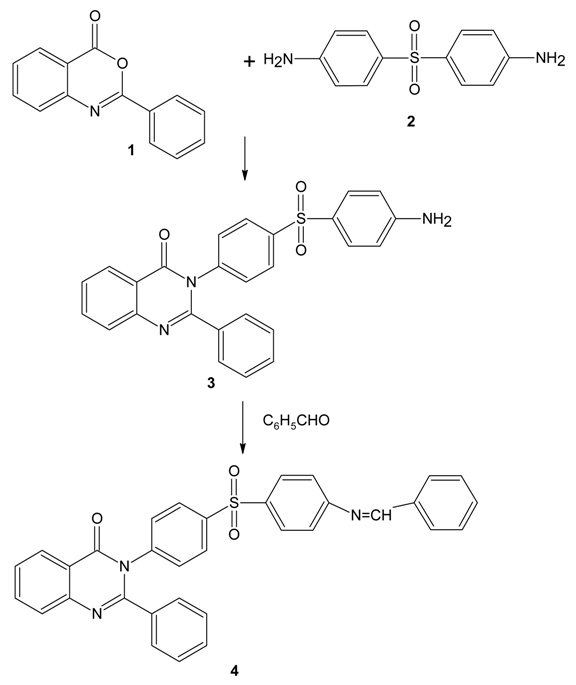
Synthesis
Preparation of 3-[4-(4-aminobenzenesulfonyl)phenyl]-2-phenylquinazolin-4(3H)-one 3
2-Phenyl-4H-3,1-benzoxazine-4-one (1) was prepared according to the literature [8]. Compound 1 (3.34 g, 0.01 mol) was dissolved in 20 ml of ethanol and then Dapsone 2 (7.44 g, 0.03 mol) was added to it. The mixture was refluxed for 4 h and cooled. The separated solid 3 was recrystallized from ethanol; yield: 61%, m.p.:148oC.
Preparation of Schiff Base 4
A mixture of compound 3 (4.55 g, 0.01 mol), benzaldehyde (1.06 g, 0.01 mol) and ethanol (20 ml) was refluxed for 6 h. The resulting mixture was cooled and poured into ice-water. The separated solid was filtered and washed with water. Recrystallization of the crude product from ethanol afforded colorless crystals of 4. The yield of the product is 68%.
Melting point: sublimation above 190oC
IR (KBr pellet, cm-1): 1631 (C=N), 1764 (N-C=O, quinazolinone)
1H NMR (500 MHz, MeOD): 7.2-7.9 (m, 22H, Ar-H), 8.5 (s, 1H, -N=CH-)
13C NMR: 121.2, 126.4, 126.8, 127.8, 127.9, 128.1, 128.6, 130.3, 132.3, 136.5, 146.9, 152.8, 157.1, 164.0.
MS (m/z): 541 (M+, 8%), 119 (100%)
Elemental Analysis: Calculated: C, 73.18; H, 4.28; N, 7. 76; S,5.92;
Found: C, 73.08; H, 4.24; N, 7. 72 ; S,5.91.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2Supplementary File 3Acknowledgement
The authors wish to thank the management of SRM University for providing financial assistance for carrying out the pilot project.
References
- Spirkova, K.; Stankovsky, S.; Mrvova, A.; Cipak, L. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Some 2 Substituted Quinazolin-4-ones. Chem. Pap. 1999, 53, 272–275. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Srivastava, V.K.; Singh, A.; Gucati, A.; Shankar, K. Antiparkinsonian agent from quinazolinyl thiozolidinones and azetidinones. Indian J. Chem. 1987, 26, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Gupta, D.P.; Ahamed, S.; Kumar, A.; Shankar, K. Newer Quinazolinone Derivatives as Antihelmintic Agents. Indian J. Chem. 1988, 27, 1060–1062. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yale, H.J.; Kalkstein, M. Substituted 2, 3-dihydro-4(1H)-quinazolinones, a new class of inhibitors of cell multiplication. J. Med. Chem. 1967, 10, 334–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshi, V.; Chaurasia, R.P. Synthesis of Some New 4-Quinazolinone-2-Carboxylhydrazides and their Tosyl Derivatives having potential Biological Activity. Indian J. Chem. 1987, 26, 602–604. [Google Scholar]
- Nanda, A.K.; Ganguli, S.; Chakraborty, R. Antibacterial Activity of Some 3-(Arylideneamino)-2-phenylquinazoline-4(3H)-ones: Synthesis and Preliminary QSAR Studies. Molecules 2007, 12, 2413–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendran, S.P.; Karvembu, R. Synthesis and antifungal activities of Schiff bases derived from 3-amino-2H-pyrano [2, 3]-quinolin-2-ones. Indian J. Chem. 2002, 41, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sain, B.; Sandhu, J.S. An efficient one-pot synthesis of 1,3,4-oxadiazoles and 4H-3,1-benzoxazin-4- ones. Indian J. Chem. 1992, 31, 768–770. [Google Scholar]
© 2009 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).