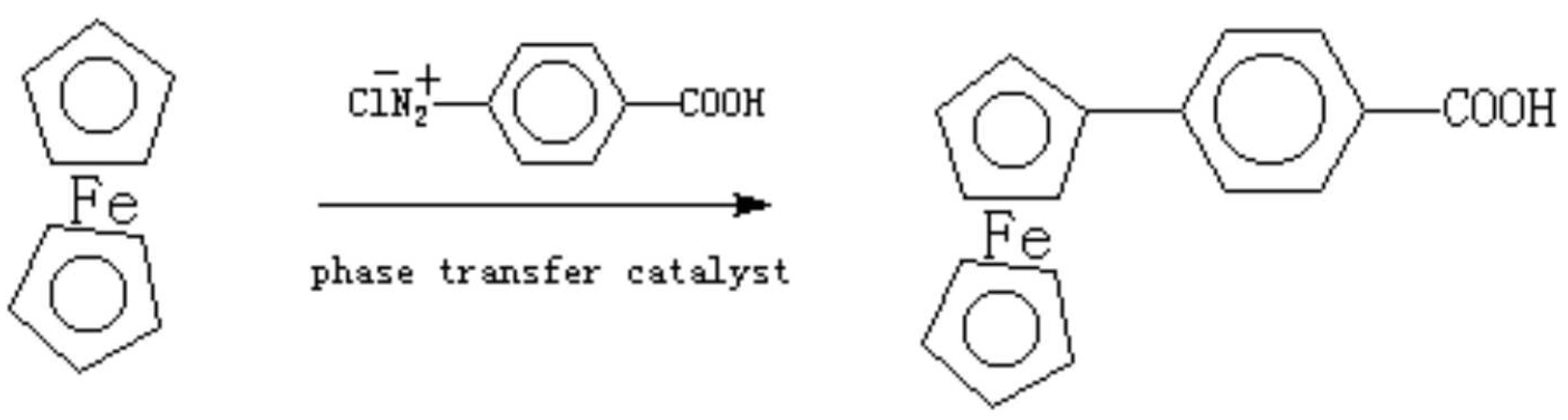
Ferrocene-containing liquid crystals, non-linear optical materials and magnetic materials are of considerable interests for their high thermal stability, tunable redox characteristics and structural variability [1]. 4-Ferrocenebenzoic acid is an important intermediate because it can be transferred into ester-type liquid crystal. The reported method of synthesis has very low yield [2]. We report a modified synthetic method using the reaction of ferrocene with diazonium salt of 4-aminobenzoic acid under the phase transfer catalysis. A mixture of 4-aminobenzoic acid (7.0 g, 50 mmol), 80 ml water, and 12 ml concentrated hydrochloric acid is cooled to 0-5°C with an ice-salt bath. A 20 ml aqueous solution of sodium nitrite (3.5g, 50 mmol) is added dropwise under stirring. After the addition is finished, it was stirred further for 30 min and the solution is kept in a temperature less than 5°C for use.
Ferrocene (10 g, 50 mmol) is dissolved in 100 ml ethyl ether, and 0.5 g hexadecyltrimethyl-ammonium bromide added and the mixture is cooled to 0-5°C under stirring. The above prepared diazonium salt solution is dropwise added with stirring. After addition is finished, it was further reacted 2 h in room temperature. Then ethyl ether is rotary evaporated to give red solid. The solid is dissolved in 500 ml water containing 5 g NaOH at 90°C and is filtrated while it was hot. The solid is the recovered, un-reacted ferrocene. The filtrate is cooled and the sodium salt of 4-ferrocenylbenzoic acid is precipitated. Filtration and acidification of the salt give 4-ferrocenylbenzoic acid as a red solid. Yield: 65%.
M.p., 240-241°C (decompose).
IR (KBr, cm-1): 3200-2500, 1679, 1606, 1567, 1105, 1003.
1HNMR: 4.02(s, 5H, C5H5), 4.3(s, 2H of C5H4), 4.7(s, 2H, C5H4), 7.2(d, 2H, C6H4), 7.9(d, 2H, C6H4).
Microanalysis for C17H14FeO2: calculated, C, 66.61; H, 4.50%. Found: C, 66.67; H, 4.58%.
Supplementary materials
Supplementary File 1Supplementary File 2References
- Togni, A.; Hayashi, T. Ferrocene; VCH: NewYork, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Weinmayr, V. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 3012.
- Sample Availability: Available from the authors and from MDPI.
© 2001 MDPI. All rights reserved. Molecules website http://www.mdpi.org/molecules/