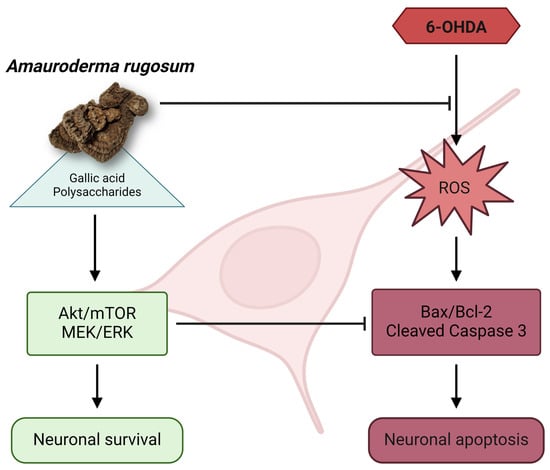
Neuroprotective Effects of Polysaccharides and Gallic Acid from Amauroderma rugosum against 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Chemical Compositions of AR Water Extract (ARW) and Polysaccharide-Rich AR Extract (ARP)
2.2. Antioxidant Capacities of ARW, ARP, and the Different Components in the ARW
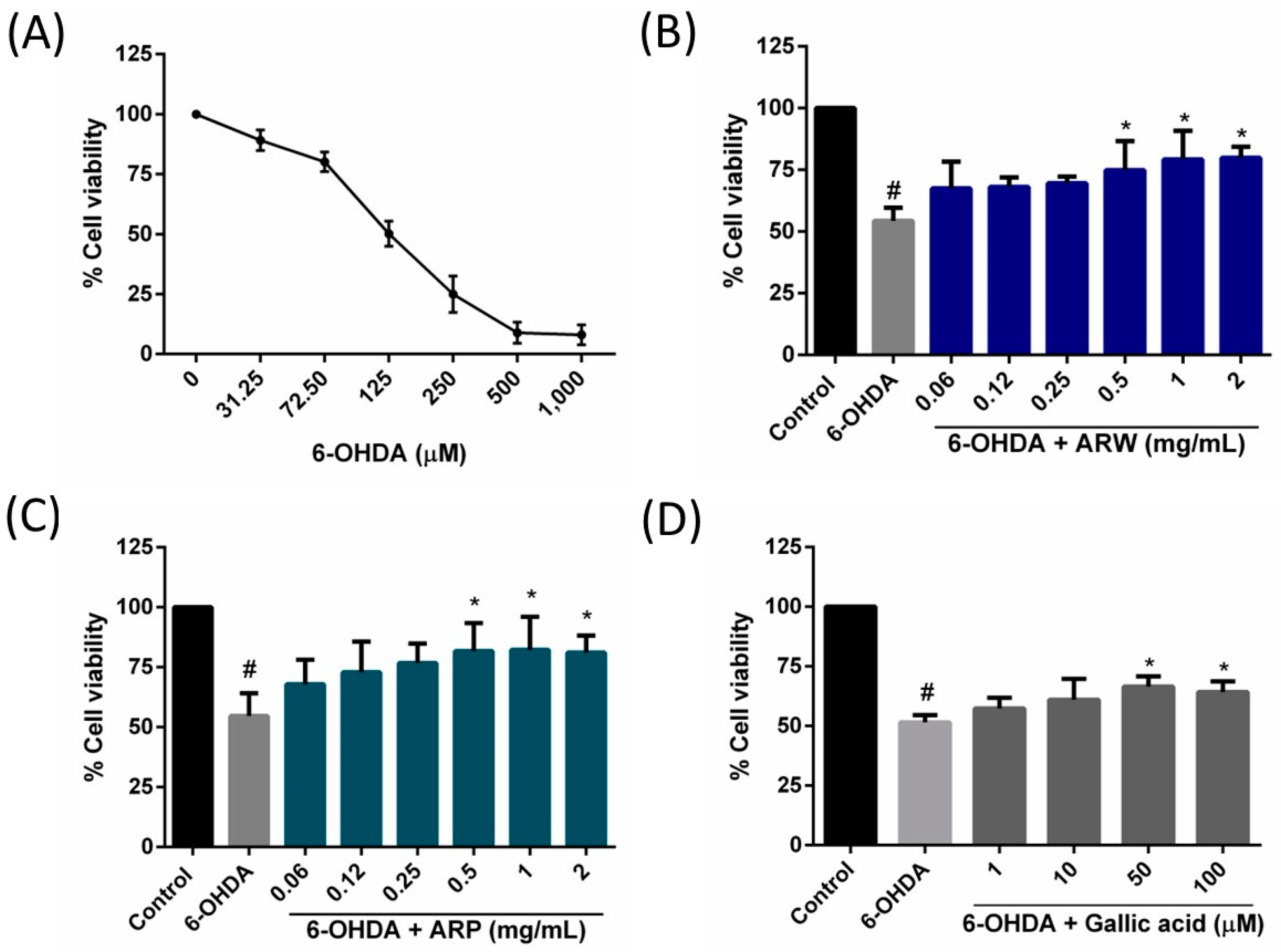
2.3. Protective Effects on ARW, ARP, and Gallic Acid on 6-OHDA-Induced SH-SY5Y Cell Death
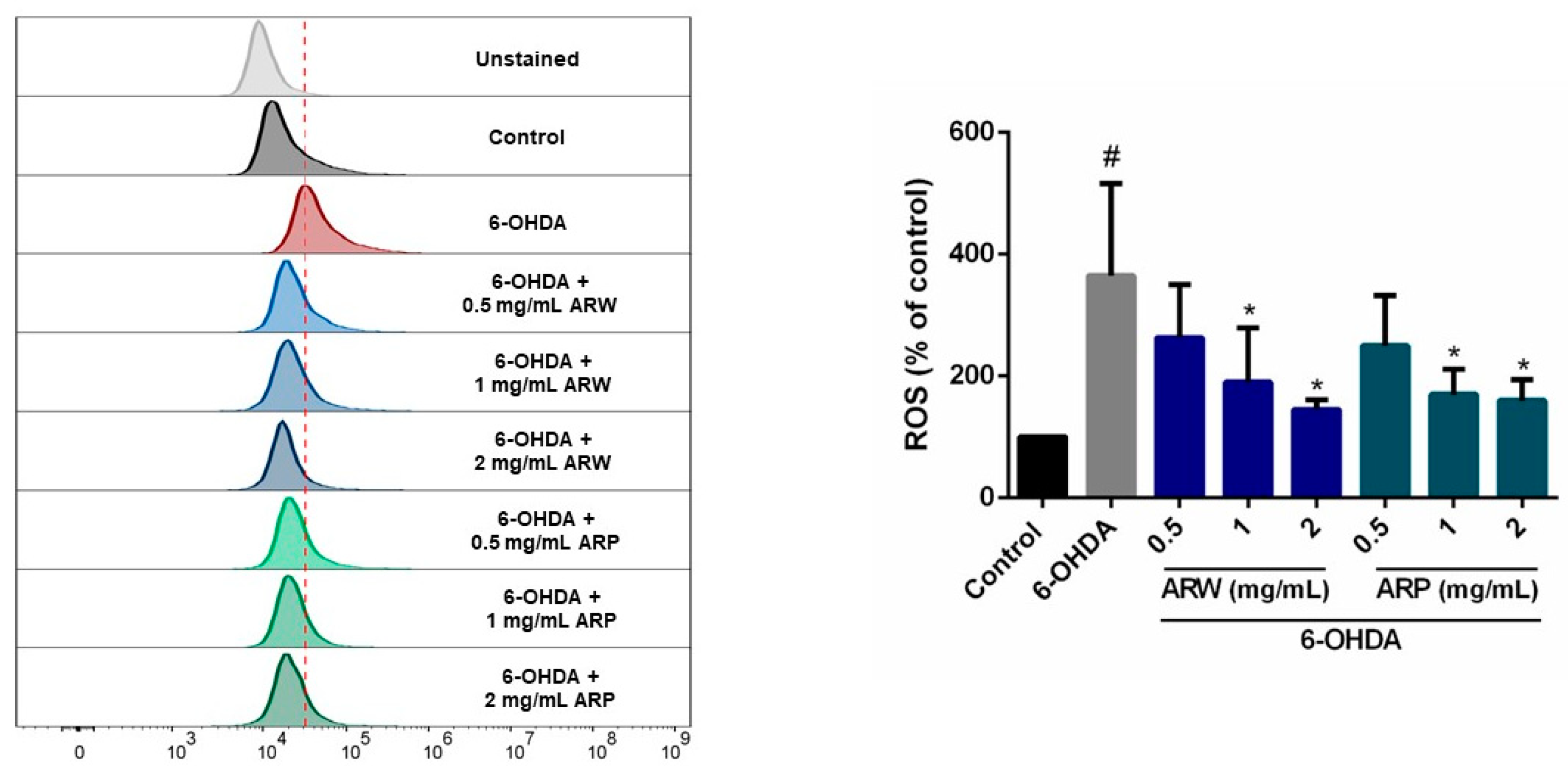
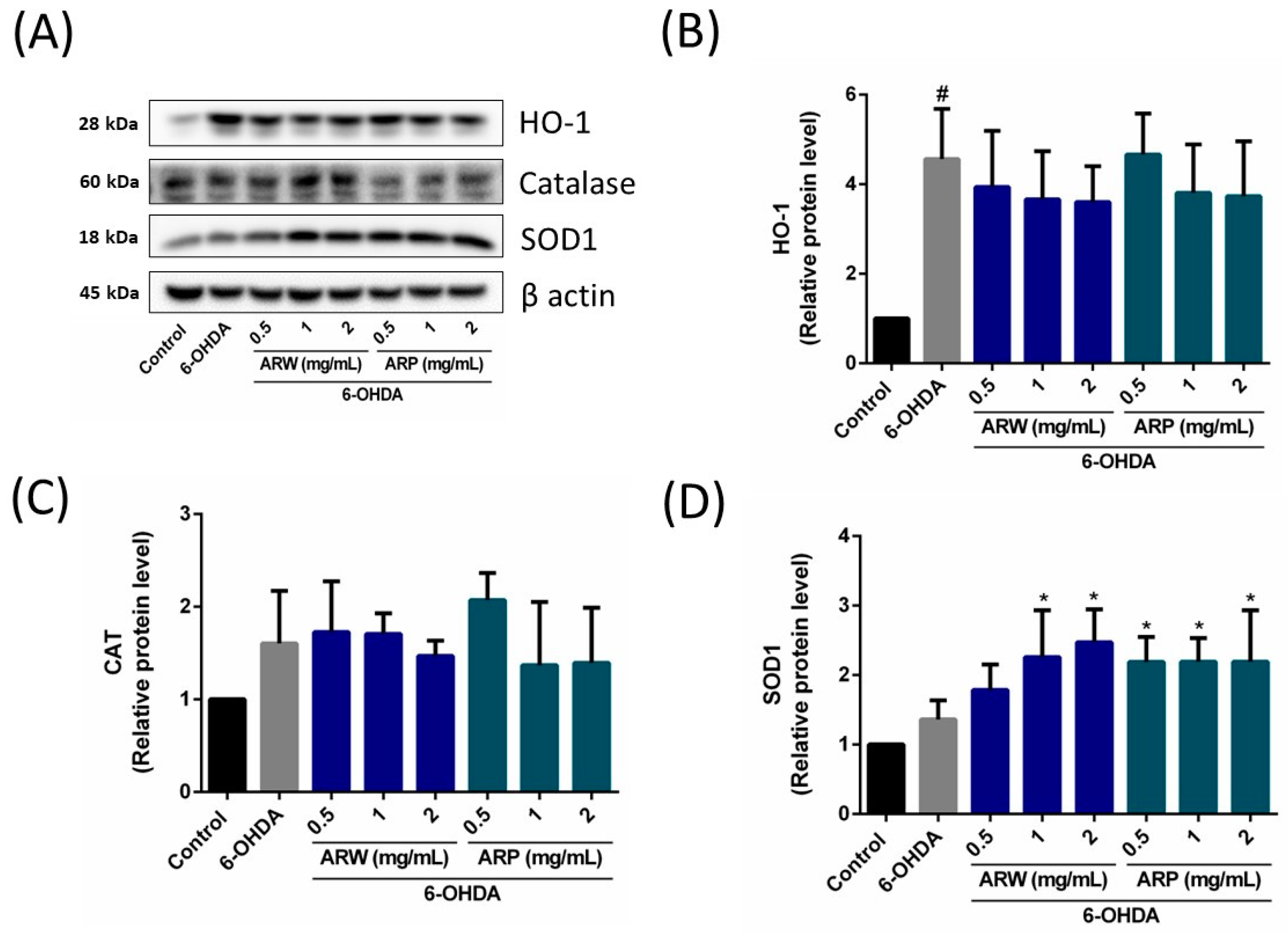
2.4. In Vitro and In Vivo Antioxidant Activities of ARW and ARP
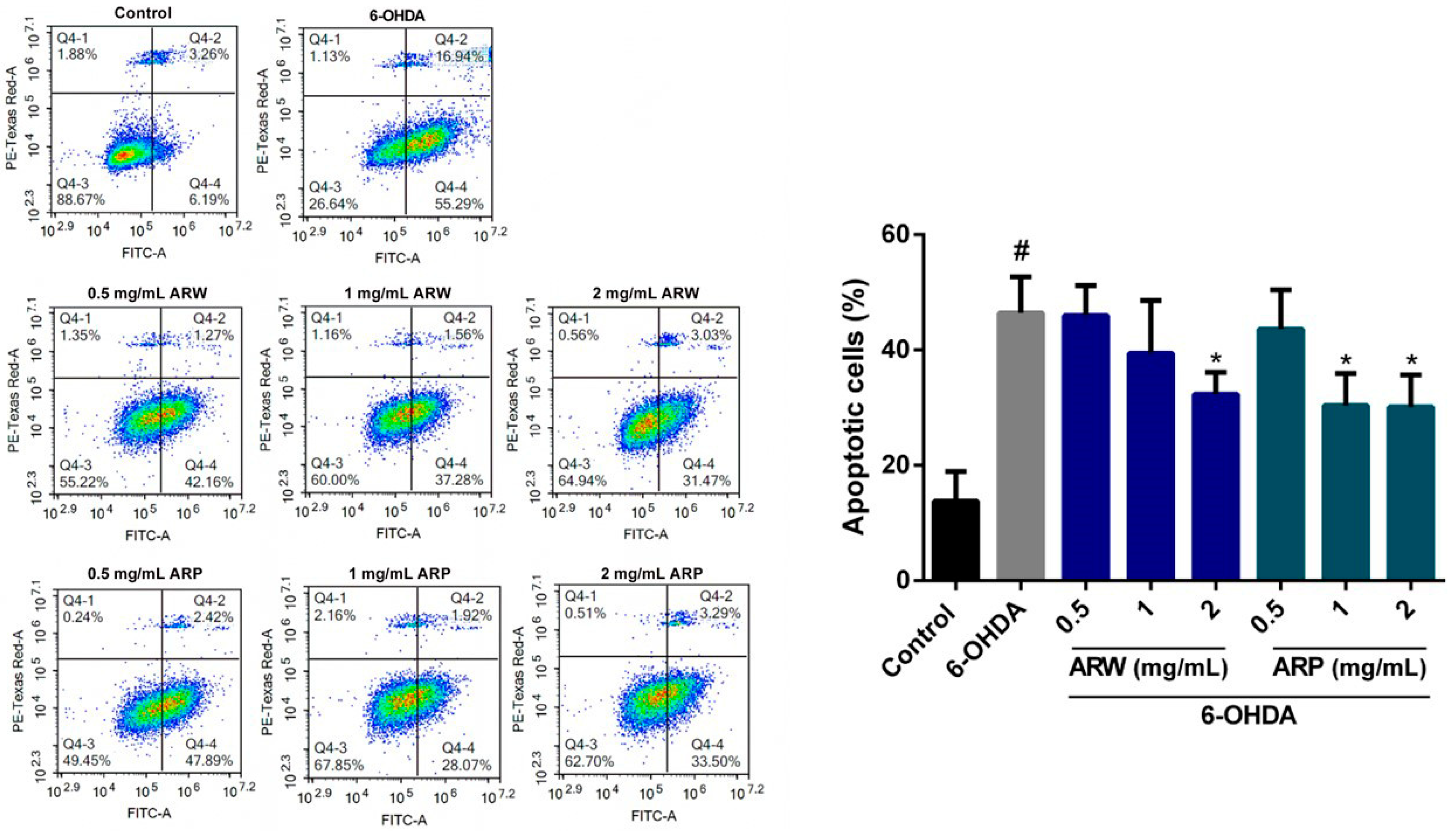
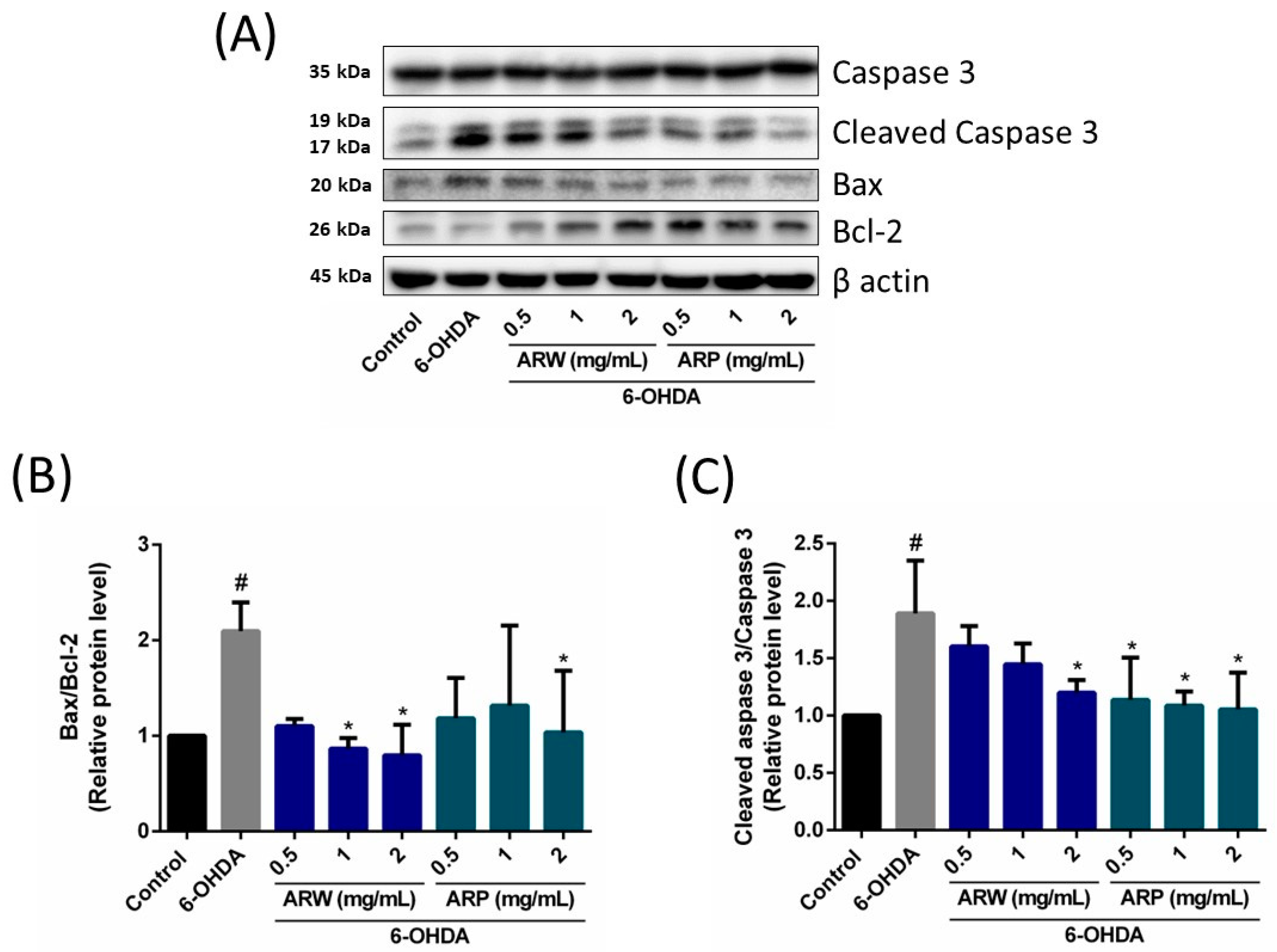
2.5. Anti-Apoptotic Effects of ARW and ARP in SH-SY5Y Cells
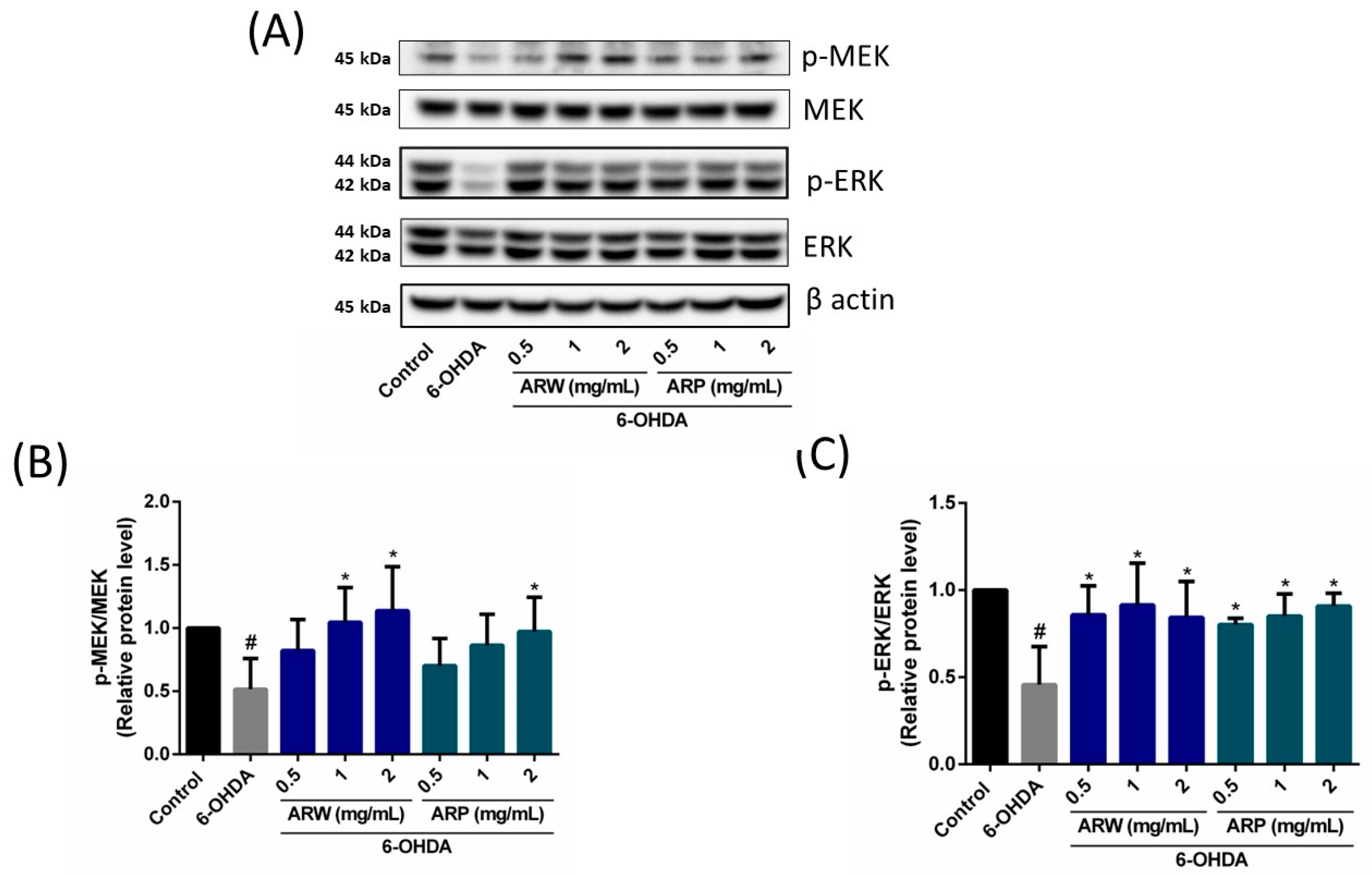
2.6. Effects of ARW and ARP on the Expression of Apoptosis-Related Signaling Pathways and Pro/Antioxidant Enzyme Levels in SH-SY5Y Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of ARW via Reflux Distillation and of ARP via Ethanol Precipitation
4.3. Measurement of Chemical Content
4.4. DPPH Assay
4.5. Strains, Maintenance, and Synchronization of Caenorhabditis elegans
4.6. Survival Assay for C. elegans under Juglone-Induced Oxidative Stress
4.7. Longevity Assay for C. elegans
4.8. Cell Culture
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. Detection of Intracellular ROS Levels
4.11. Annexin V-Fluorescein Isothiocyanate (FITC)/PI Staining
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. Data and Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirsch, L.; Jette, N.; Frolkis, A.; Steeves, T.; Pringsheim, T. The incidence of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neuroepidemiology 2016, 46, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkouzi, A.; Vedam-Mai, V.; Eisinger, R.S.; Okun, M.S. Emerging therapies in Parkinson disease—Repurposed drugs and new approaches. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.D.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.R.; Liu, X.L. Damage to dopaminergic neurons by oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittal, P.; Dhankhar, S.; Chauhan, S.; Garg, N.; Bhattacharya, T.; Ali, M.; Chaudhary, A.A.; Rudayni, H.A.; Al-Zharani, M.; Ahmad, W.; et al. A review on natural antioxidants for their role in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.; Wu, X.; Hoo, R.L.; Lee, S.M.; Cheung, T.M.; Ho, B.S.; Leung, G.P. Amauroderma rugosum protects PC12 Cells against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity through antioxidant and antiapoptotic effects. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 6683270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerink, R.H.; Ewing, A.G. The PC12 cell as a model for neurosecretion. Acta Physiol. 2008, 192, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioghen, O.C.; Ceafalan, L.C.; Popescu, B.O. SH-SY5Y cell line in vitro models for Parkinson disease research-old practice for new trends. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiu, P.H.; Li, J.; Zheng, C.; Rangsinth, P.; Li, R.; Cheung, Q.T.; Lau, A.H.; Chan, J.C.; Kwan, Y.W.; Cheung, T.M.; et al. Amauroderma rugosum extract suppresses inflammatory responses in tumor necrosis factor alpha/interferon gamma-induced HaCaT keratinocytes. Molecules 2022, 27, 6533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Duan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, W.; Wang, L.; Sun, Y.; Lang, M.; Hoi, P.M.; Han, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. The novel tetramethylpyrazine bis-nitrone (TN-2) protects against MPTP/MPP+-induced neurotoxicity via inhibition of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2014, 9, 245–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cui, W.; Li, G.; Yuan, S.; Xu, D.; Hoi, M.P.M.; Lin, Z.; Dou, J.; Han, Y.; Lee, S.M.Y. Baicalein protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity through activation of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 and involving PKC alpha and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8171–8182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiatrak, B.; Balon, K. Protective activity of Aβ on cell cultures (PC12 and THP-1 after differentiation) preincubated with lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 58, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.R.; Hu, L.S.; Li, G.Y. SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cell line: In vitro cell model of dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease. Chin. Med. J. 2010, 123, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Xicoy, H.; Wieringa, B.; Martens, G.J.M. The SH-SY5Y cell line in Parkinson’s disease research: A systematic review. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.W.; Cheung, T.M.; Leung, G.P. A review of the phytochemical and pharmacological properties of Amauroderma rugosum. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2022, 38, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Soto, C.Y.; Villaseca-Flores, M.; Ovalle-Noguez, E.A.; Nava-Osorio, J.; Galván-Arzate, S.; Rangel-López, E.; Maya-López, M.; Retana-Márquez, S.; Túnez, I.; Tinkov, A.A.; et al. Oleamide reduces mitochondrial dysfunction and toxicity in rat cortical slices through the combined action of cannabinoid receptors activation and induction of antioxidant activity. Neurotox. Res. 2022, 40, 2167–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F. Ganoderic Acid A targeting leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 involved in Parkinson’s disease-A computational study. Aging Med. 2022, 6, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.M.; Qiu, H.B.; Wang, S.Q.; Guo, J.; Yang, Z.W.; Zhou, S.B. Ganoderic acid A potentiates the antioxidant effect and protection of mitochondrial membranes and reduces the apoptosis rate in primary hippocampal neurons in magnesium free medium. Pharmazie 2018, 73, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuia, M.S.; Rahaman, M.M.; Islam, T.; Bappi, M.H.; Sikder, M.I.; Hossain, K.N.; Akter, F.; Al Shamsh Prottay, A.; Rokonuzzman, M.; Gürer, E.S.; et al. Neurobiological effects of gallic acid: Current perspectives. Chin. Med. 2023, 18, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Nie, G.; Belton, P.S.; Tang, H.; Zhao, B. Structure-activity relationship analysis of antioxidant ability and neuroprotective effect of gallic acid derivatives. Neurochem. Int. 2006, 48, 263–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekhar, Y.; Phani Kumar, G.; Ramya, E.M.; Anilakumar, K.R. Gallic acid protects 6-OHDA induced neurotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress in human dopaminergic cell line. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1150–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, M.T.; Farbood, Y.; Sameri, M.J.; Sarkaki, A.; Naghizadeh, B.; Rafeirad, M. Neuroprotective effects of oral gallic acid against oxidative stress induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in rats. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sameri, M.J.; Sarkaki, A.; Farbood, Y.; Mansouri, S.M. Motor disorders and impaired electrical power of pallidal EEG improved by gallic acid in animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 14, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Li, Y.; Pei, G. Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum attenuate microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and modulate microglial phagocytosis and behavioural response. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.B.; Lin, S.Q.; Liu, J.H.; Lin, Z.B. Polysaccharide extract isolated from Ganoderma lucidum protects rat cerebral cortical neurons from hypoxia/reoxygenation injury. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2004, 95, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Tang, Y.P.; Xiang, J.; Wua, P.; Jin, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Mori, M.; Cai, D.F. Neuroprotective effects of water-soluble Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on cerebral ischemic injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tello, I.; Campos-Pena, V.; Montiel, E.; Rodriguez, V.; Aguirre-Moreno, A.; Leon-Rivera, I.; Del Rio-Portilla, F.; Herrera-Ruiz, M.; Villeda-Hernandez, J. Anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects of oligosaccharides from lingzhi or Reishi medicinal mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (Higher Basidiomycetes). Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2013, 15, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Ling, Y. Poria cocos polysaccharide attenuates damage of nervus in Alzheimer’s disease rat model induced by D-galactose and aluminum trichloride. Neuroreport 2021, 32, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.X.; Shan, J.L.; Hu, W.Q.; Zeng, J.X.; Shu, J.C. Gallic acid activates hippocampal BDNF-Akt-mTOR signaling in chronic mild stress. Metab. Brain Dis. 2019, 34, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Nie, S.P.; Peng, X.P.; Liu, X.Z.; Li, C.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.E.; Song, W.R.; Xie, M.Y. Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide improves age-related oxidative stress and immune impairment in mice. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.J.; Nie, S.P.; Xie, M.Y.; Yu, Q.; Chen, Y.; He, M. Ganoderma atrum polysaccharide attenuates oxidative stress induced by d-galactose in mouse brain. Life Sci. 2011, 88, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Li, M.; Meng, Z. Polysaccharides: Potential bioactive macromolecules for Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1249018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Wu, S.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Ding, Y. Whole-plant foods and their macromolecules: Untapped approaches to modulate neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 2388–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnihotri, T.G.; Jadhav, G.S.; Sahu, B.; Jain, A. Recent trends of bioconjugated nanomedicines through nose-to-brain delivery for neurological disorders. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2022, 12, 3104–3120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, S.Y.; Tan, N.H.; Kong, B.H.; Lee, S.S.; Tan, Y.S.; Sabaratnam, V. Acute toxicity study and the in vitro cytotoxicity of a black Lingzhi medicinal mushroom, Amauroderma rugosum (Agaricomycetes), from Malaysia. Int. J. Med. Mushrooms 2017, 19, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.A.; Ellis, A.C. Dietary antioxidants and Parkinson’s disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.L.; Wang, C.D.; Wang, T.; Ding, H.; Zhou, M.; Yang, N.; Liu, Y.Y.; Chan, P. Ganoderma lucidum extract ameliorates MPTP-induced parkinsonism and protects dopaminergic neurons from oxidative stress via regulating mitochondrial function, autophagy, and apoptosis. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2019, 40, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Qu, Z.Q.; Zeng, Y.S.; Lin, Y.K.; Li, Y.; Chung, P.; Wong, R.; Hägg, U. Neuroprotective effect of preadministration with Ganoderma lucidum spore on rat hippocampus. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2012, 64, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattarachotanant, N.; Rangsinth, P.; Warayanon, W.; Leung, G.P.H.; Chuchawankul, S.; Prasansuklab, A.; Tencomnao, T. Protective effect of Aquilaria crassna leaf extract against benzo[a]pyrene-induced toxicity in neuronal cells and Caenorhabditis elegans: Possible active constituent includes clionasterol. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Treatment | Mean Lifespan (Day) ± SD | Maximum Lifespan (Day) | p-Value (vs. Control) * | Number of Worms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 15.24 ± 5.11 | 28 | 120 | |
| 1 mg/mL ARW | 14.61 ± 5.36 | 33 | 0.4508 | 137 |
| 2 mg/mL ARW | 14.25 ± 4.99 | 28 | 0.2022 | 100 |
| 1 mg/mL ARP | 14.89 ± 5.72 | 30 | 0.9632 | 125 |
| 2 mg/mL ARP | 14.64 ± 5.82 | 33 | 0.5977 | 121 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rangsinth, P.; Pattarachotanant, N.; Wang, W.; Shiu, P.H.-T.; Zheng, C.; Li, R.; Tencomnao, T.; Chuchawankul, S.; Prasansuklab, A.; Cheung, T.M.-Y.; et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Polysaccharides and Gallic Acid from Amauroderma rugosum against 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. Molecules 2024, 29, 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050953
Rangsinth P, Pattarachotanant N, Wang W, Shiu PH-T, Zheng C, Li R, Tencomnao T, Chuchawankul S, Prasansuklab A, Cheung TM-Y, et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Polysaccharides and Gallic Acid from Amauroderma rugosum against 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. Molecules. 2024; 29(5):953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050953
Chicago/Turabian StyleRangsinth, Panthakarn, Nattaporn Pattarachotanant, Wen Wang, Polly Ho-Ting Shiu, Chengwen Zheng, Renkai Li, Tewin Tencomnao, Siriporn Chuchawankul, Anchalee Prasansuklab, Timothy Man-Yau Cheung, and et al. 2024. "Neuroprotective Effects of Polysaccharides and Gallic Acid from Amauroderma rugosum against 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells" Molecules 29, no. 5: 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050953
APA StyleRangsinth, P., Pattarachotanant, N., Wang, W., Shiu, P. H.-T., Zheng, C., Li, R., Tencomnao, T., Chuchawankul, S., Prasansuklab, A., Cheung, T. M.-Y., Li, J., & Leung, G. P.-H. (2024). Neuroprotective Effects of Polysaccharides and Gallic Acid from Amauroderma rugosum against 6-OHDA-Induced Toxicity in SH-SY5Y Cells. Molecules, 29(5), 953. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29050953