Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Identification of Ginsenosides in Russian and North Korean Ginseng by HPLC with Tandem Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
1. Introduction
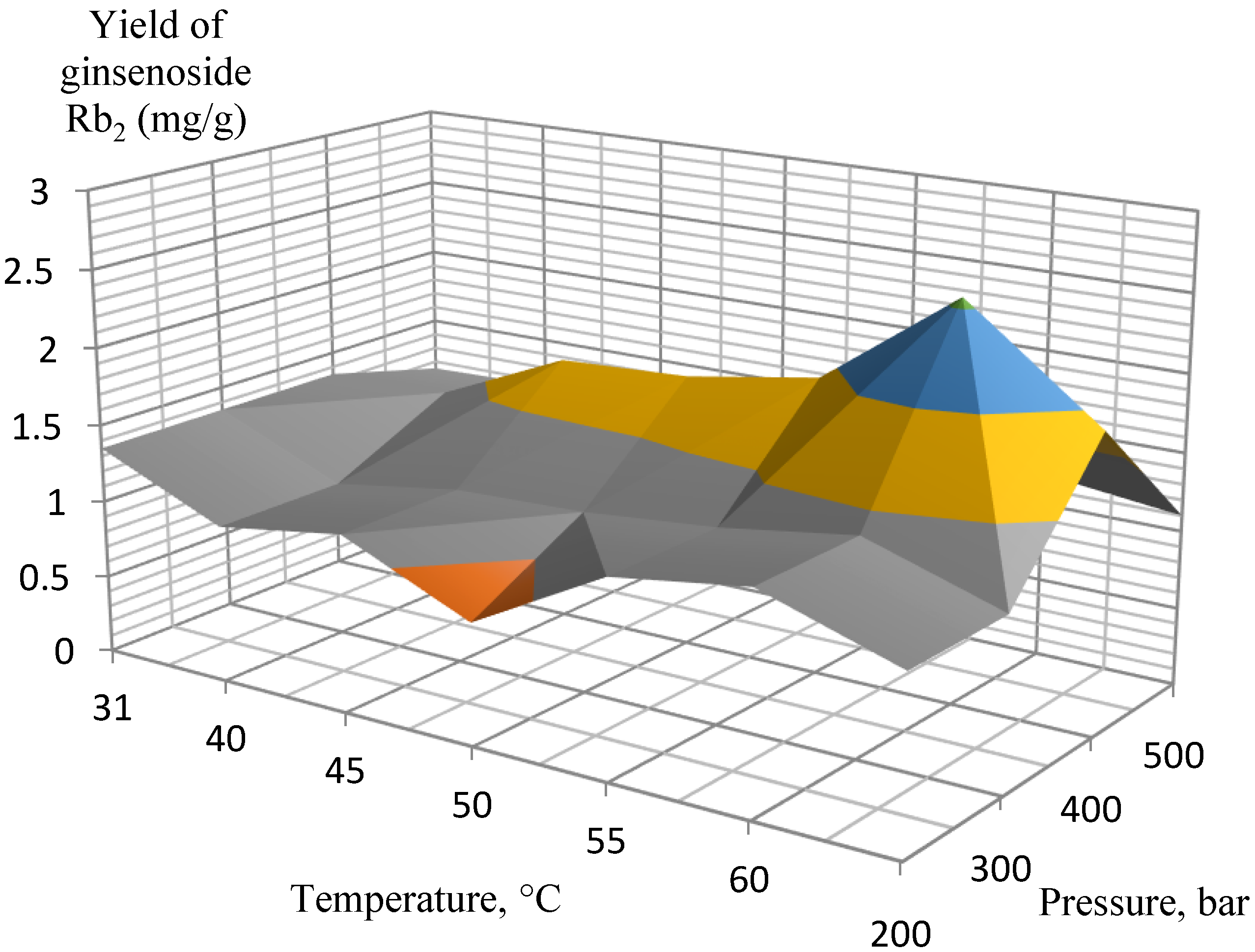
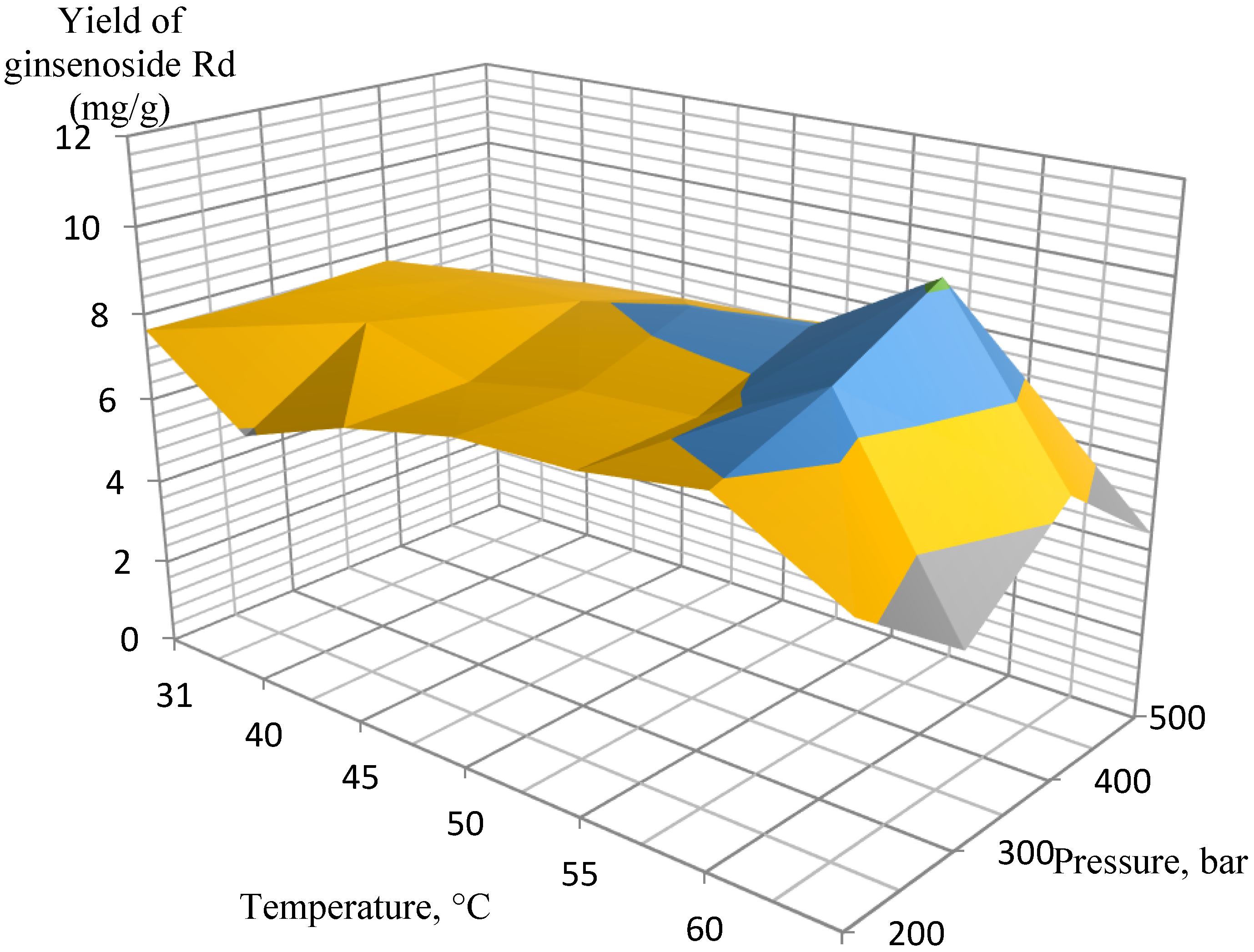
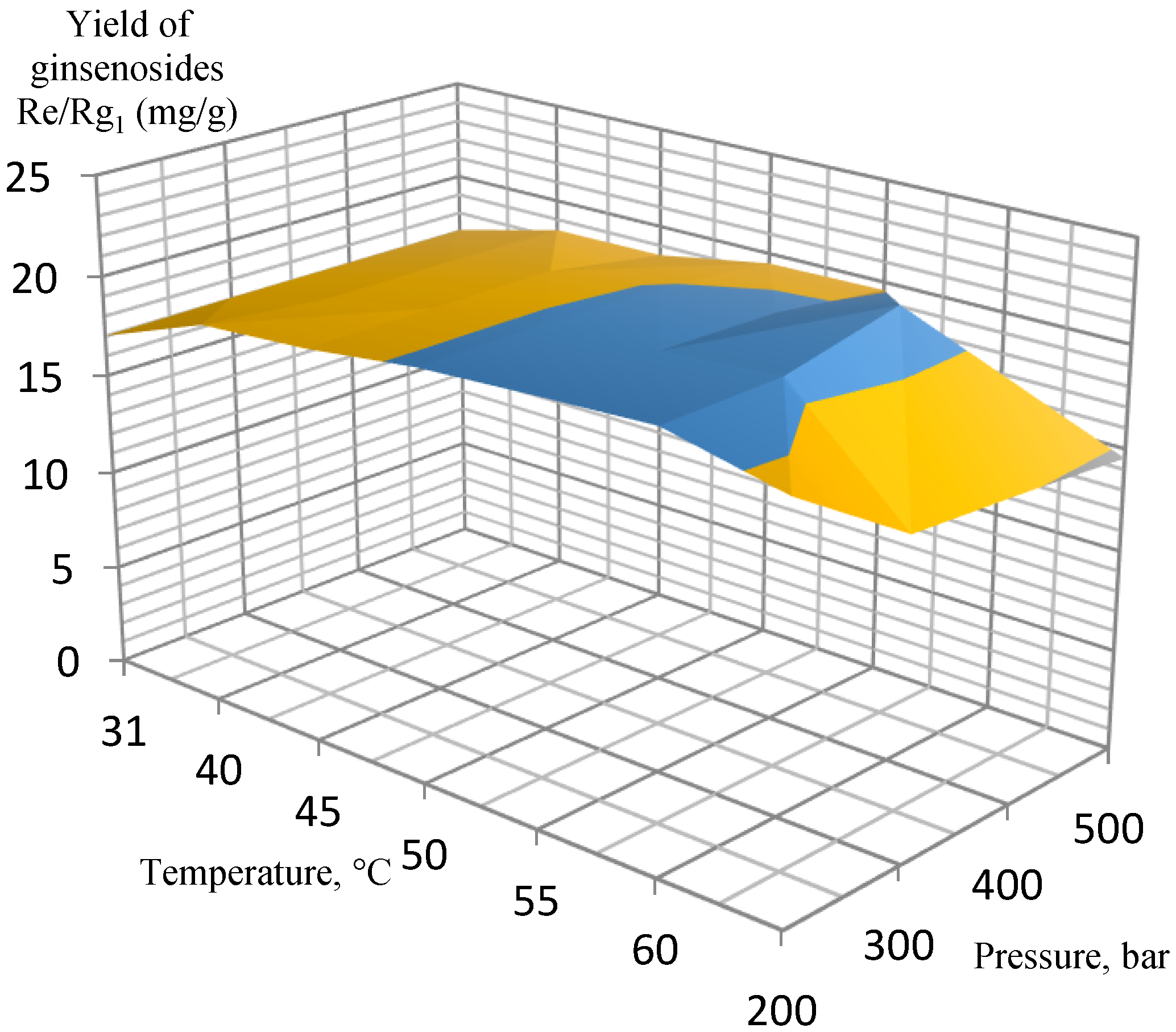
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Chemicals and Reagents
3.3. Liquid Chromatography
3.4. Supercritical Fluid Extraction
3.5. Mass Spectrometry
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subra, P.; Castellani, S.; Jestin, P.; Aoufi, A. Extraction of β-carotene with supercritical fluids. J. Supercrit. Fluids 1998, 12, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, L.; Mantell, C.; Rodríguez, M.; Torres, A.; Macías, F.A.; De La Ossa, E.M.; Cardoso, L.C. Extraction of natural compounds with biological activity from sunflower leaves using supercritical carbon dioxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 152, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, M.; Mendiola, J.A.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Supercritical fluid extraction: Recent advances and applications. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 2495–2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaza, M.; Herrero, M.; Cifuentes, A.; Ibáñez, E. Innovative natural functional ingredients from microalgae. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 7159–7170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.H.; Kim, J.; Jeon, S.H.; Yoo, K.-P.; Lee, H.-K. Optimum SFE condition for lignans of Schisandra chinensis fruits. Chromatographia 1998, 48, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Sánchez, M.D.; Serrano, C.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, M.; De La Ossa, E.M.; Lubián, L.M.; Montero, O. Extraction of carotenoids and chlorophyll from microalgae with supercritical carbon dioxide and ethanol as cosolvent. J. Sep. Sci. 2008, 31, 1352–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouveia, L.; Nobre, B.; Marcelo, F.; Mrejen, S.; Cardoso, M.; Palavra, A.; Mendes, R. Functional food oil coloured by pigments extracted from microalgae with supercritical CO2. Food Chem. 2007, 101, 717–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehariya, S.; Iovine, A.; Di Sanzo, G.; LaRocca, V.; Martino, M.; Leone, G.P.; Casella, P.; Karatza, D.; Marino, T.; Musmarra, D.; et al. Supercritical fluid extraction of lutein from Scenedesmus almeriensis. Molecules 2019, 24, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahena, F.; Zaidul, I.S.M.; Jinap, S.; Karim, A.A.; Abbas, K.A.; Norulaini, N.A.N.; Omar, A.K.M. Application of supercritical CO2 in lipid extraction—A review. J. Food Eng. 2009, 95, 240–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonthubthimthong, P.; Douglas, P.L.; Douglas, S.; Luewisutthichat, W.; Teppaitoon, W.; Pengsopa, L.-E. Extraction of nimbin from neem seeds using supercritical CO2 and a supercritical CO2–methanol mixture. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2004, 30, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepez, B.; Espinosa, M.; López, S.; Bolaños, G. Producing antioxidant fractions from herbaceous matrices by supercritical fluid extraction. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2002, 194, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zancan, K.C.; Marques, M.O.M.; Petenate, A.J.; Meireles, M.A. Extraction of ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) oleoresin with CO2 and co-solvents: A study of the antioxidant action of the extracts. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2002, 24, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, D.-W.; Zhou, D.; Wang, N.; Liu, Q.; Fan, S. Chemical composition, antibacterial activity and related mechanism of the essential oil from the leaves of Juniperus rigida Sieb. et Zucc against Klebsiella pneumoniae. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 194, 698–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Melo, M.; Oliveira, E.; Silvestre, A.; Silva, C.M. Supercritical fluid extraction of triterpenic acids from Eucalyptus globulus bark. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 70, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elyakov, G.B.; Strigina, L.I.; Khorlin, A.Y.; Kochetkov, H.K. Glycosides of ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Mey). Russ. Chem. Bull. 1962, 11, 1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brekhman, I.; Dardymov, I.V.; Dobriakov, I. On the pharmacology of individual glycosides from the roots of Panax ginseng C.A. Mey. Farmakol. Toksikol. 1966, 29, 167–171. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.-K.; Shin, Y.-W.; Lee, H.-U.; Kim, S.-S.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lee, B.-Y.; Kim, N.-H. Inhibitory effect of ginsenoside Rb1 and compound K on NO and prostaglandin E2 biosyntheses of RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide. Boil. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 652–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; Wang, Y.; Min, H.; Zhang, M.; Du, X.; Han, R.; Liu, X. Combination of ginsenoside Rg1 and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury in rats. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, J.; Bernards, M.A.; Wan, W.-K.; Charpentier, P.A. Extraction of ginsenosides from North American ginseng using modified supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2006, 39, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Weller, C.L. Recent advances in extraction of nutraceuticals from plants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochkin, D.V.; Kachala, V.V.; Shashkov, A.S.; Chizhov, A.O.; Chirva, V.Y.; Nosov, A.M. Malonyl-ginsenoside content of a cell-suspension culture of Panax japonicus var. repens. Phytochemistry 2013, 93, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavrianidi, A.; Baygildiev, T.M.; Stekolshchikova, E.A.; Shpigun, O.A.; Rodin, I.A. New approaches to the determination and group identification of physiologically active compounds in plant materials and commercial products by high-performance liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Chem. 2019, 74, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.C.; Harkey, M.R.; Henderson, G.L.; Gershwin, M.E.; Stern, J.S.; Hackman, R.M. Quantitative determination of ginsenosides by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2001, 12, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ligor, T.; Ludwiczuk, A.; Wolski, T.; Buszewski, B. Isolation and determination of ginsenosides in American ginseng leaves and root extracts by LC-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Sakuma, T.; Asafu-Adjaye, E.; Shiu, G.K. Determination of ginsenosides in plant extracts from Panax ginseng and Panax quinquefolius L. by LC/MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 1999, 71, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kite, G.C.; Howes, M.-J.R.; Leon, C.J.; Simmonds, M.S. Liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry of malonyl-ginsenosides in the authentication of ginseng. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2003, 17, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.N. Determination of ginsenoside content in Asian and North American ginseng raw materials and finished products by high-performance liquid chromatography: Single-laboratory validation. J. AOAC Int. 2011, 94, 1391–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Buckingham, J. Dictionary of Natural Products; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group: London, UK, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Li, C.-L.; Cheng, Y.-Y.; Tsai, T.-H.; Tsai, T.-H. Development of a validated UPLC-MS/MS method for analyzing major ginseng saponins from various ginseng species. Molecules 2019, 24, 4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.-D.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, J.-C. Critical properties of carbon dioxide + methanol, + ethanol, + 1-propanol, and + 1-butanol. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2000, 45, 932–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, G.; Machado, N. Process design methodology for fractionation of fatty acids from palm fatty acid distillates in countercurrent packed columns with supercritical CO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2012, 66, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, H.; Tang, G.; Fillet, M.; Crommen, J.; Jiang, Z. Simultaneous analysis of nucleobases, nucleosides and ginsenosides in ginseng extracts using supercritical fluid chromatography coupled with single quadrupole mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 144, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samimi, R.; Xu, W.Z.; AlSharari, Q.; Charpentier, P.A. Supercritical fluid chromatography of North American ginseng extract. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2014, 86, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.-Y.; Luo, D.; Cheng, Y.-J.; Ma, J.-F.; Wang, Y.-M.; Liang, Q.; Luo, G.-A. Steaming-induced chemical transformations and holistic quality assessment of red ginseng derived from Panax ginseng by means of HPLC-ESI-MS/MSn-based multicomponent quantification fingerprint. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8213–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Lee, N.Y.; Kang, K.B.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, S.O.; Yoo, Y.H.; Sung, S.H. Identification of ginsenoside markers from dry purified extract of Panax ginseng by a dereplication approach and UPLC–QTOF/MS analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 109, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, B.-R.; Kim, Y.-C.; Choi, D.J.; Lee, Y.-S.; Kim, G.-S.; Baek, N.-I.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, D. Comprehensive profiling and quantification of ginsenosides in the root, stem, leaf, and berry of Panax ginseng by UPLC-QTOF/MS. Molecules 2017, 22, 2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Yi, T.; Qin, M.; Liang, Z. Chemical differentiation and quality evaluation of commercial Asian and American ginsengs based on a UHPLC-QTOF/MS/MS metabolomics approach. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 26, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-P.; Zhang, Y.-B.; Yang, X.; Zhao, D.; Wang, Y.-P. Rapid characterization of ginsenosides in the roots and rhizomes of Panax ginseng by UPLC-DAD-QTOF-MS/MS and simultaneous determination of 19 ginsenosides by HPLC-ESI-MS. J. Ginseng Res. 2015, 40, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lv, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Song, D.; Liu, P.; Zhang, D.; Lu, J. Chemical and bioactive comparison of flowers of Panax ginseng Meyer, Panax quinquefolius L., and Panax notoginseng Burk. J. Ginseng Res. 2016, 41, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Cui, M.; Liu, Z.; Song, F.; Mo, W. Structural analysis of saponins from medicinal herbs using electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.-L.; Zhu, D.-N.; Yang, X.; Xu, W.; Wang, Y.-P. Development and validation of a UFLC–MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of sixty-six saponins and their six aglycones: Application to comparative analysis of red ginseng and white ginseng. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpova, R.V.; Shevchenko, V.E.; Bocharov, E.V.; Sheychenko, O.P.; Bocharova, O.A.; Kucheryanu, V.G.; Bykov, V.A. Ginsenosides definition in plant extracts by means of high through liquid chromatography with tandem mass-spectrometry. Russ. J. Biother. 2016, 15, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-L.; Lai, S.-F.; Song, J.-Z.; Qiao, C.-F.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cai, H.; Cai, B.; Xu, H.-X. Decocting-induced chemical transformations and global quality of Du–Shen–Tang, the decoction of ginseng evaluated by UPLC–Q-TOF-MS/MS based chemical profiling approach. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 946–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russia State Pharmacopoeia XII; Scientific Center of Expertise of Medical Products: Moscow, Russia, 2008; pp. 26–121.
Sample Availability: Samples of the compounds are not available from the authors. |

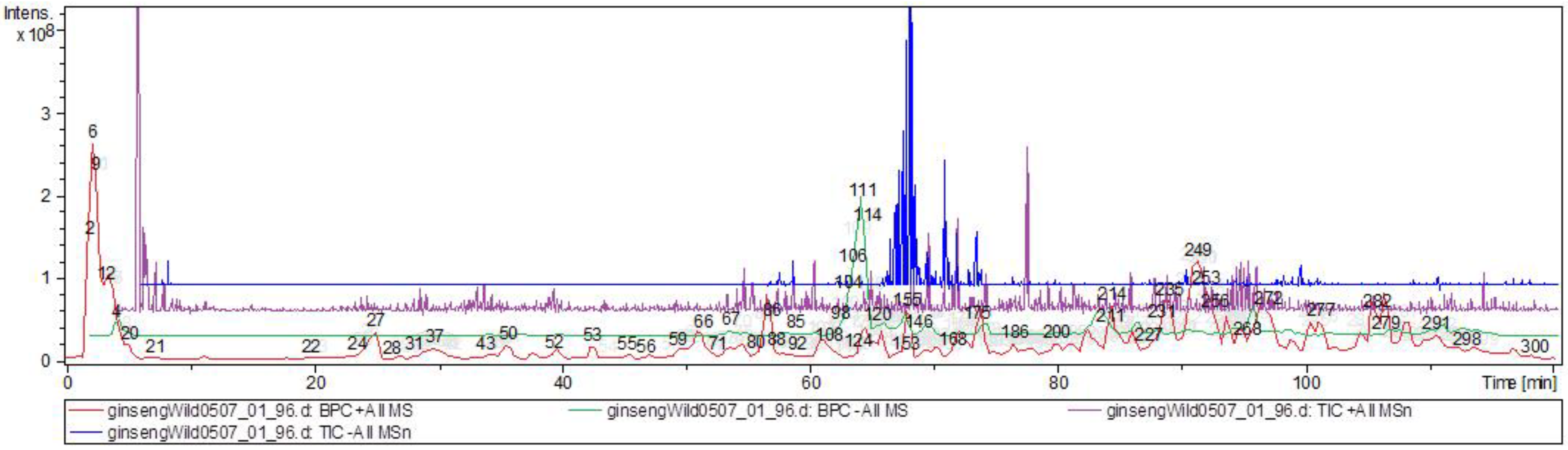
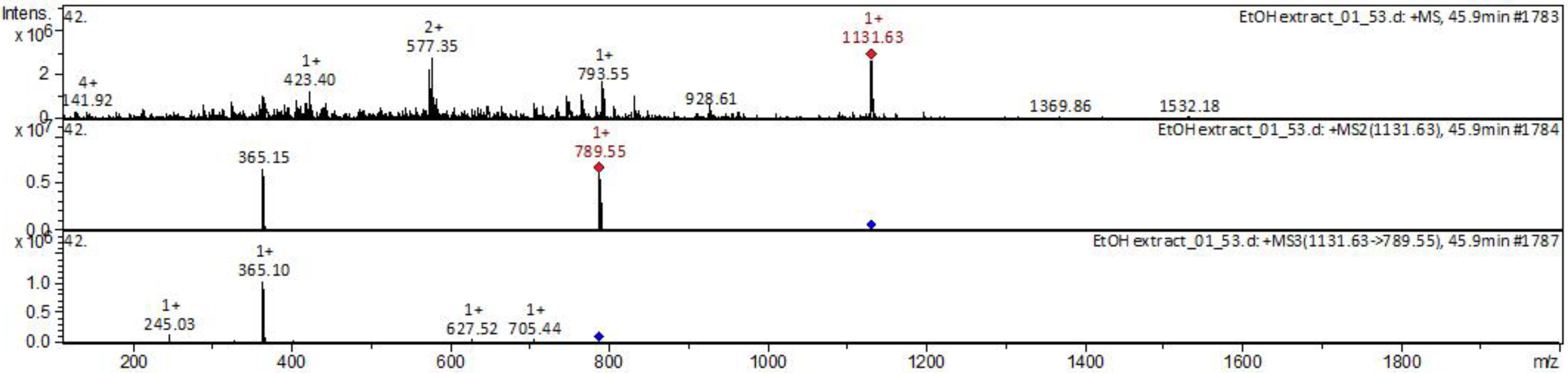
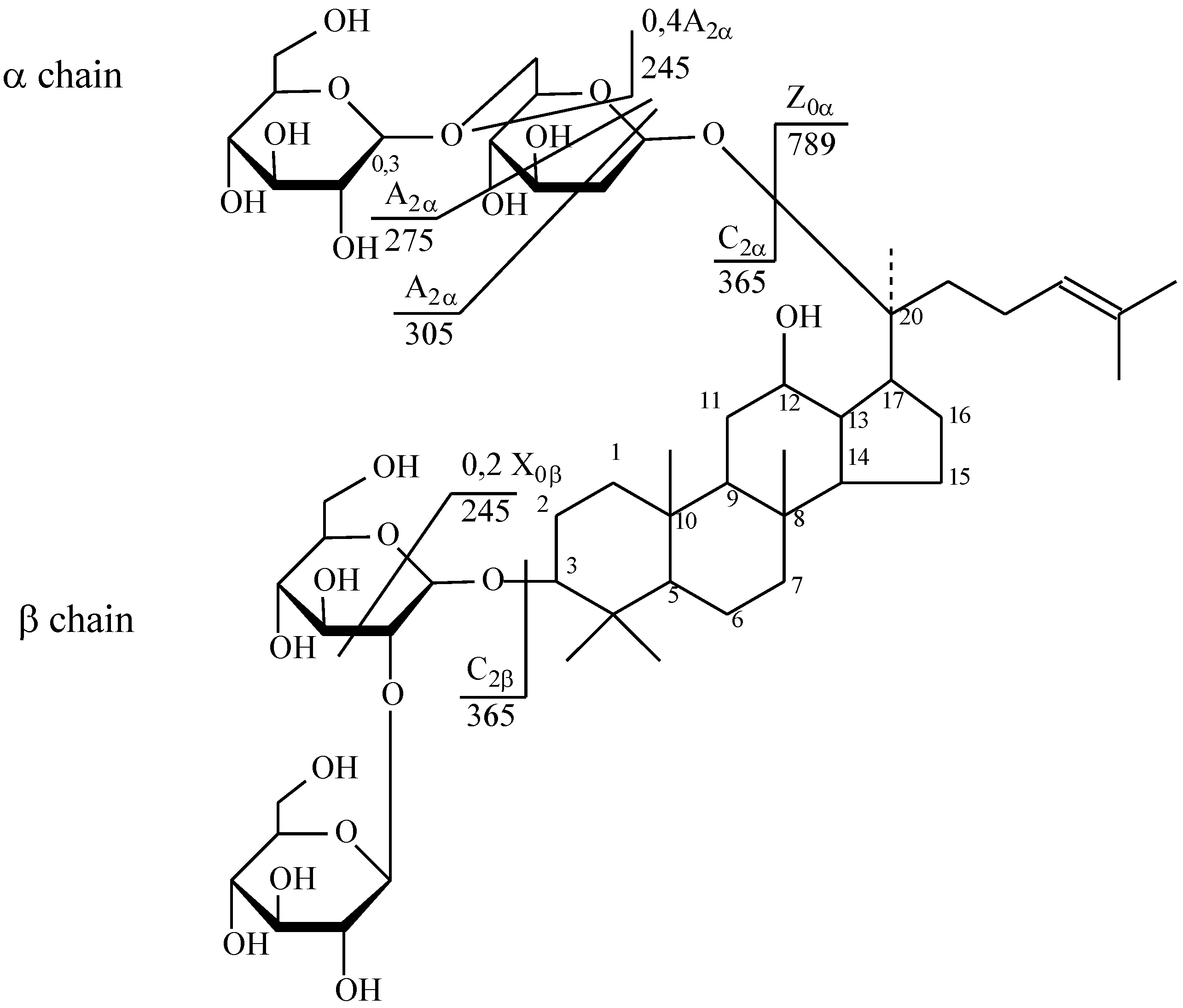
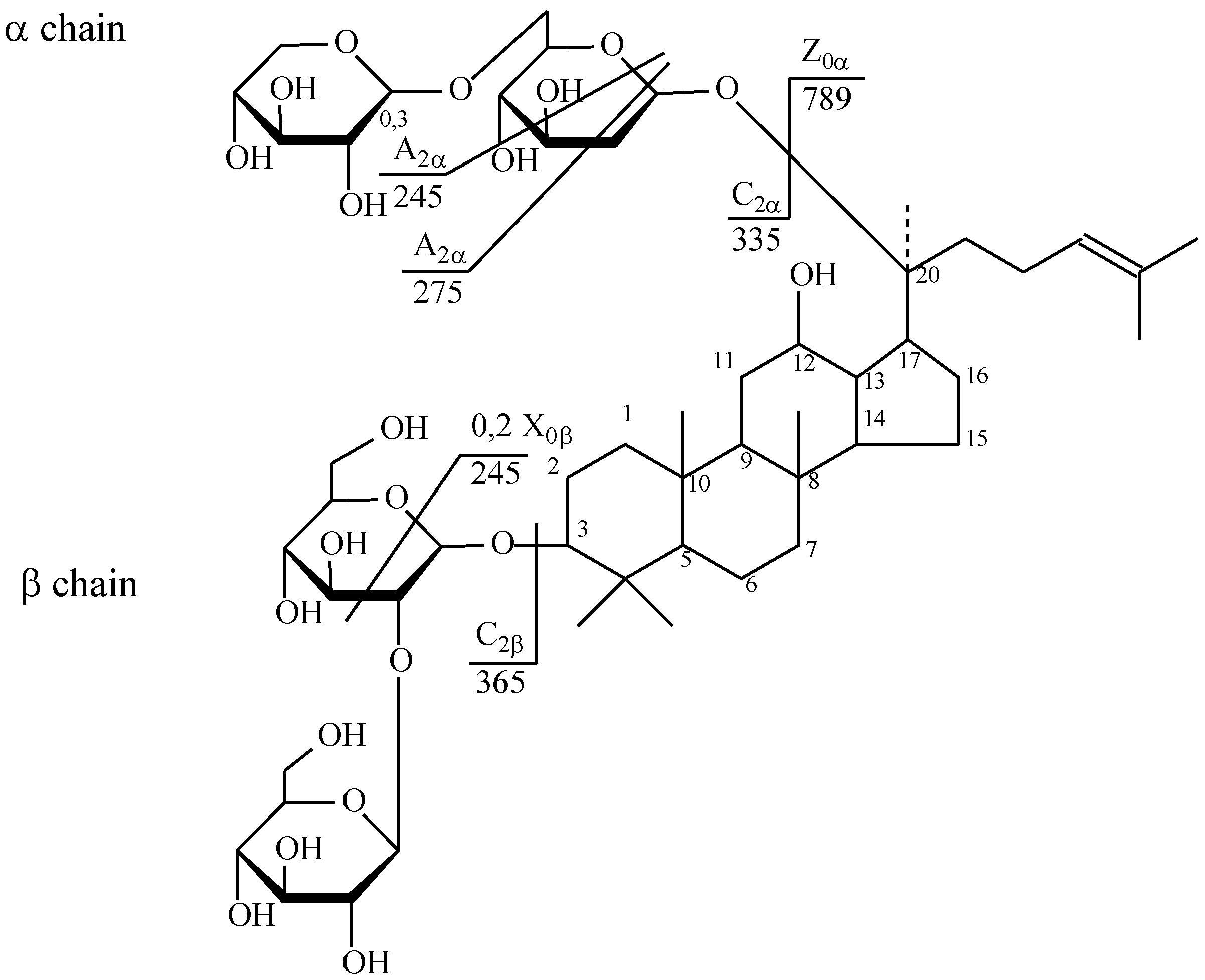
| № | Identity | Molecular Formula | Adducts | MS (m/z) | MS2 (m/z) | MS3 (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triterpene Glycosides (Dammarane Type) | ||||||
| 1 | Ginsenoside Rk3 | C36H60O8 | [M − H]− | 619.21 | 421.22 | 229.06; 347.07; 403.19 |
| 2 | Malonyl ginsenoside Rb1 | C57H94O26 | [M − H]− | 1149.81 | 1107.65 | 459.31; 621.44; 783.46; 945.52 |
| 3 | Malonyl ginsenoside Rb1 isomer | C57H94O26 | [M − H]− | 1193.7 | 1151.72 | 604.33; 826.59; 946.58; 1109.59 |
| 4 | Ginsenoside Rg1 | C42H72O14 | [M − H + HCOOH]− | 845.79 | 799.65 | 475.45; 637.61 |
| 5 | Ginsenoside Rd isomer | C48H82O18 | [M − H + HCOOH]− | 991.83 | 945.73 | 391.43; 475.5; 637.62; 783.68 |
| 6 | Ginsenoside Rg6 | C42H70O12 | [M + Na]+ | 765.41 | 405.39 | 171.07; 281.12 |
| 7 | Acetyl ginsenoside Rg1 isomer | C44H74O15 | [M + Na]+ | 841.55 | 661.5 | 481.53; 573.28; 643.32 |
| 8 | Ginsenoside Rf | C42H72O14 | [M − H]− | 846.81 | 799.65 | 391.34; 475.46; 545.54; 637.55 |
| 9 | (Yesanchinoside d isomer | C44H74O15 | [M + Na]+ | 841.62 | 661.47 | 481.48; 541.46; 571.59; 601.27; 643.42 |
| 10 | Ginsenoside Rb1 | C54H92O23 | [M − H]− | 1107.88 | 783.7 | 621.57; 460.52 |
| Ginsenoside Rb1 | C54H92O23 | [M + Na]+ | 1131.63 | 789.55 | 245.03; 365.10; 627.52; 705.44 | |
| 11 | Ginsenoside Rd | C48H82O18 | [M − H]− | 945.93 | 783.65 | 621.63; 459.39 |
| 12 | Ginsenoside 20-glc-Rf | C48H82O19 | [M − H]− | 961.84 | 915.76 | 292.31; 375.99; 459.51; 621.51; 783.75 |
| 13 | Ginsenoside 25-OH-Rh4 | C36H62O9 | [M − H]− | 637.6 | 239.14 | |
| 14 | Ginsenoside 20(R)-Rh1 | C36H62O9 | [M − H]− | 683.65 | 475.4 | 375.38 |
| 15 | Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rh1 | C36H62O9 | [M − H]− | 683.64 | 637.59 | 375.42; 475.48; 549.31 |
| 16 | Ginsenoside Rc | C53H90O22 | [M − H]− | 1077.86 | 783.59 | 621.66 |
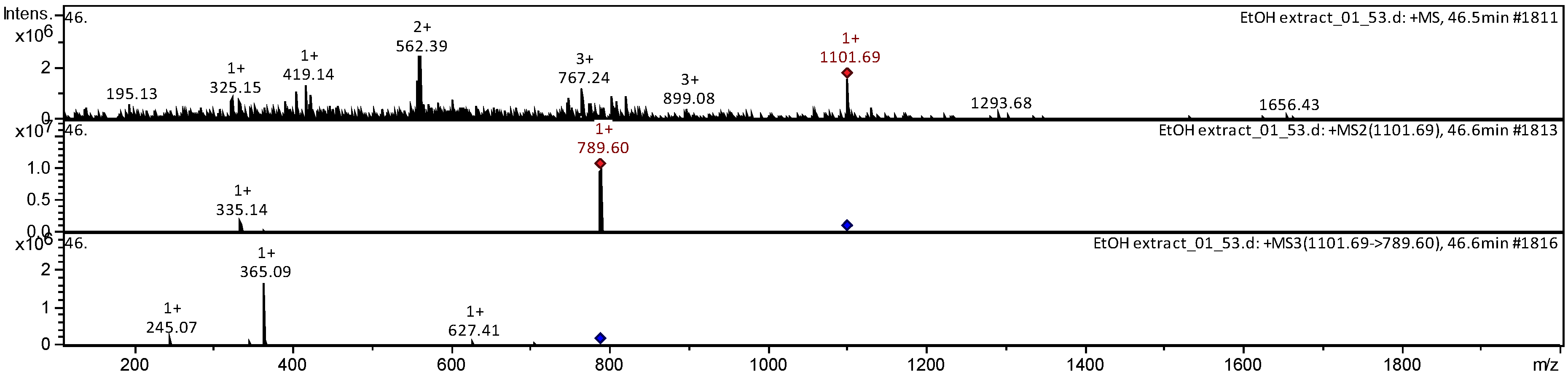
| 17 | Ginsenoside Rb2 | C53H90O22 | [M + Na]+ | 1101.69 | 789.60 | 245.07; 365.09 |
| 18 | Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rf | C42H72O14 | [M + Na]+ | 800.94 | 782.93 | 474.96; 307.83 |
| 19 | Ginsenoside Rk2 | C42H72O15 | [M + Na]+ | 663.20 | 543.26 | 287.04; 367.26; 499.21 |
| 20 | 3,12-dihydroxydammar-20(22)E,24-diene-6-o--d-xylopyranosyl-(12)-O--d-glucopyranoside (DHDXG) | C42H70O12 | [M + Na]+ | 751.19 | 631.31 | 243.08; 367.12; 455.2; 587.21 |
| 21 | Ginsenoside Rg9 | C42H72O13 | [M + Na]+ | 781.79 | 707.44 | 377.14; 671.18 |
| Oleanolic Acid Pentaterpene Glycosides | ||||||
| 22 | Ro | C48H76O19 | [M − H]− | 955.57 | 793.41 | 455.29; 613.38; 731.42 |
| 23 | Methyl ester Ro | C49H78O19 | [M + Na]+ | 969.48 | 364.96 | 304.95 |
| 24 | Chikusetsusaponin IVA | C42H66O14 | [M − H]− | 793.36 | 334.97 | 274.94 |
| 25 | Methyl ester chikusetsusaponin IVA | C42H66O14 | [M + Na]+ | 807.38 | 627.34 | 203.05; 285.14; 361.77; 488.93 |
| 26 | Silphioside G | C42H66O14 | [M − H]− | 793.7 | 613.49 | 483.3 |
| 27 | Zingibroside R1 | C42H66O14 | [M − H]− | 793.56 | 481.43 | 275.07 |
| № | Identity | Molecular Formula | Adducts | MS (m/z) | MS2 (m/z) | MS3 (m/z) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Triterpene Glycosides (Dammarane Type) | ||||||
| 1 | Ginsenoside 20(R)-Rh1 | C36H62O9 | [M − H]− | 637.38 | 597.32 | 375.42; 475.48 |
| 2 | Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rh1 | C36H62O9 | [M − H]− | 637.39 | 597.33 | 375.42; 475.49 |
| 3 | Ginsenoside 20(R)-Rh2 | C36H62O8 | [M − H]− | 621.32 | 580.2 | 390.33 |
| 4 | Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rh2 | C36H63O10 | [M − H]− | 621.32 | 580.24 | 390.34 |
| 5 | Ginsenoside 25-OH-(S)-Rh1 | C36H63O10 | [M − H]− | 654.41 | 375.15 | 332.26 |
| 6 | Ginsenoside Rg1 | C42H72O14 | [M + HCOO]− | 845.26 | 501.18 | 485.17 |
| 7 | Ginsenoside F2 | C42H72O13 | [M + H]+ | 785.55 | 783.6 | 375.27; 459.33; 537.37; 621.36 |
| 8 | Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rf2 | C42H74O14 | [M − H]− | 801.80 | 767.68 | 378.21; 671.55 |
| 9 | Ginsenoside 20-glu-Rf | C48H82O19 | [M − H]− | 961.59 | 681.45 | 637.44; 357.14; 401.12 595.46 |
| 10 | Ginsenoside 20(R/S)-Rg2 | C42H72O13 | [M − H]− | 783.54 | 529.38 | 429.21 |
| 11 | Ginsenoside 20(R/S)-Rg3 | C42H72O13 | [M − H]− | 783.68 | 737.87 | 694.71 |
| 12 | Ginsenoside 20(R/S)-Rf | C42H72O14 | [M − H]− | 799.80 | 544.49 | 227.21; 280.18; 379.14 |
| 13 | Notoginsenoside Rw2 | C41H70O14 | [M + Na]− | 809.81 | 544.50 | 227.21; 280.18; 379.15 |
| Oleanolic Acid Pentaterpene Glycosides | ||||||
| 14 | Silphioside G | C42H66O14 | [M − H]− | 793.49 | 613.3 | 407.21; 509.33 |
| 15 | Chikusetsusaponin IVA | C42H66O14 | [M + H]+ | 795.67 | 631.39 | 511.18 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Razgonova, M.; Zakharenko, A.; Shin, T.-S.; Chung, G.; Golokhvast, K. Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Identification of Ginsenosides in Russian and North Korean Ginseng by HPLC with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules 2020, 25, 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061407
Razgonova M, Zakharenko A, Shin T-S, Chung G, Golokhvast K. Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Identification of Ginsenosides in Russian and North Korean Ginseng by HPLC with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2020; 25(6):1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061407
Chicago/Turabian StyleRazgonova, Mayya, Alexander Zakharenko, Tai-Sun Shin, Gyuhwa Chung, and Kirill Golokhvast. 2020. "Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Identification of Ginsenosides in Russian and North Korean Ginseng by HPLC with Tandem Mass Spectrometry" Molecules 25, no. 6: 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061407
APA StyleRazgonova, M., Zakharenko, A., Shin, T.-S., Chung, G., & Golokhvast, K. (2020). Supercritical CO2 Extraction and Identification of Ginsenosides in Russian and North Korean Ginseng by HPLC with Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules, 25(6), 1407. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25061407









