Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Combined with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Reboots the Immune Response Assisted by Immunotherapy in Metastatic Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Lung Cancer and SABR
1.2. The Use of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors (ICI) in Lung Cancer
1.3. Rationale of Radiotherapy and ICI Combination
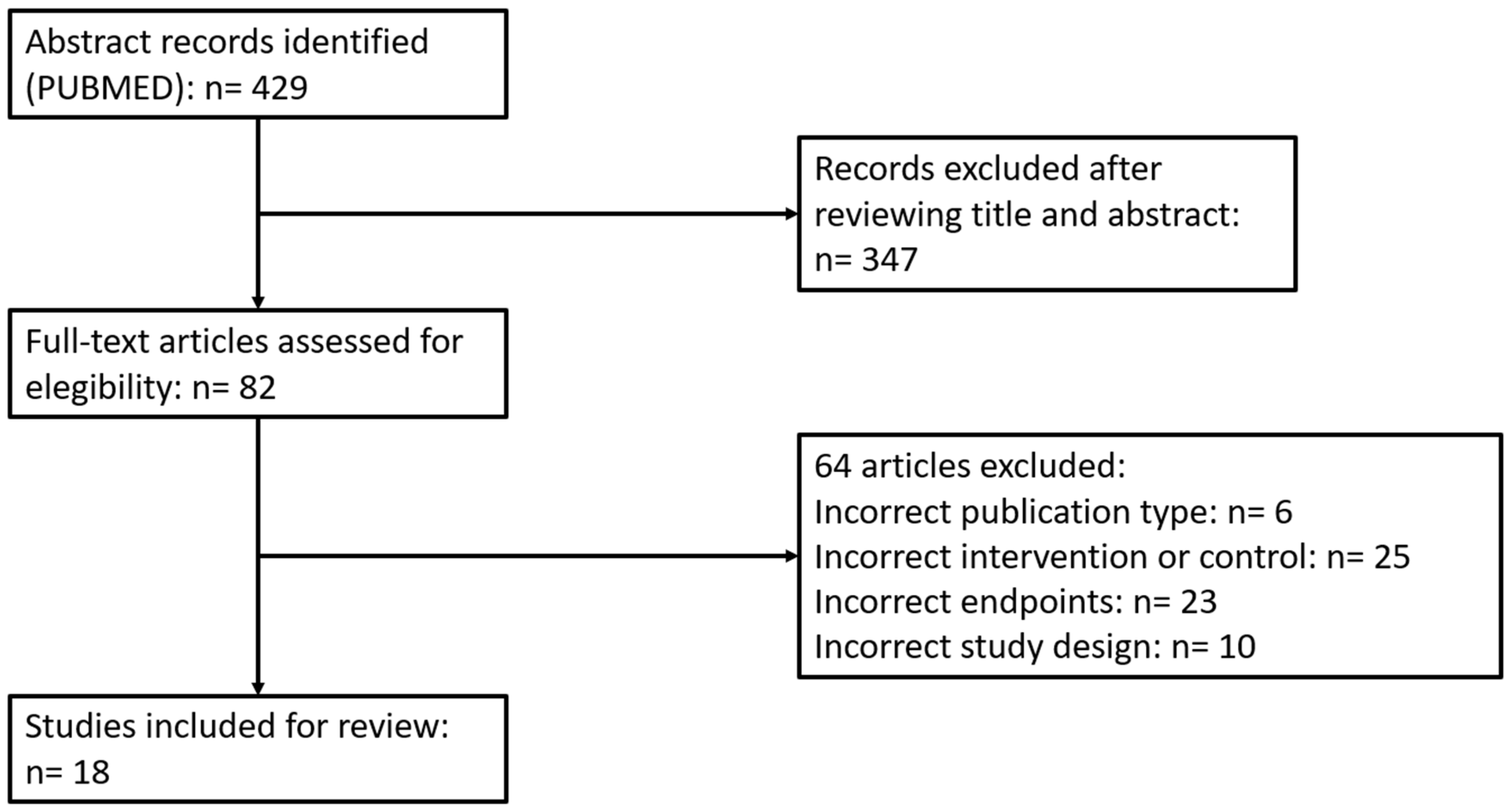
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Selection of Studies and Data Compilation
2.3. Statistical Considerations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Is It Possible to Obtain Target Control with the Combination of RT and ICI?
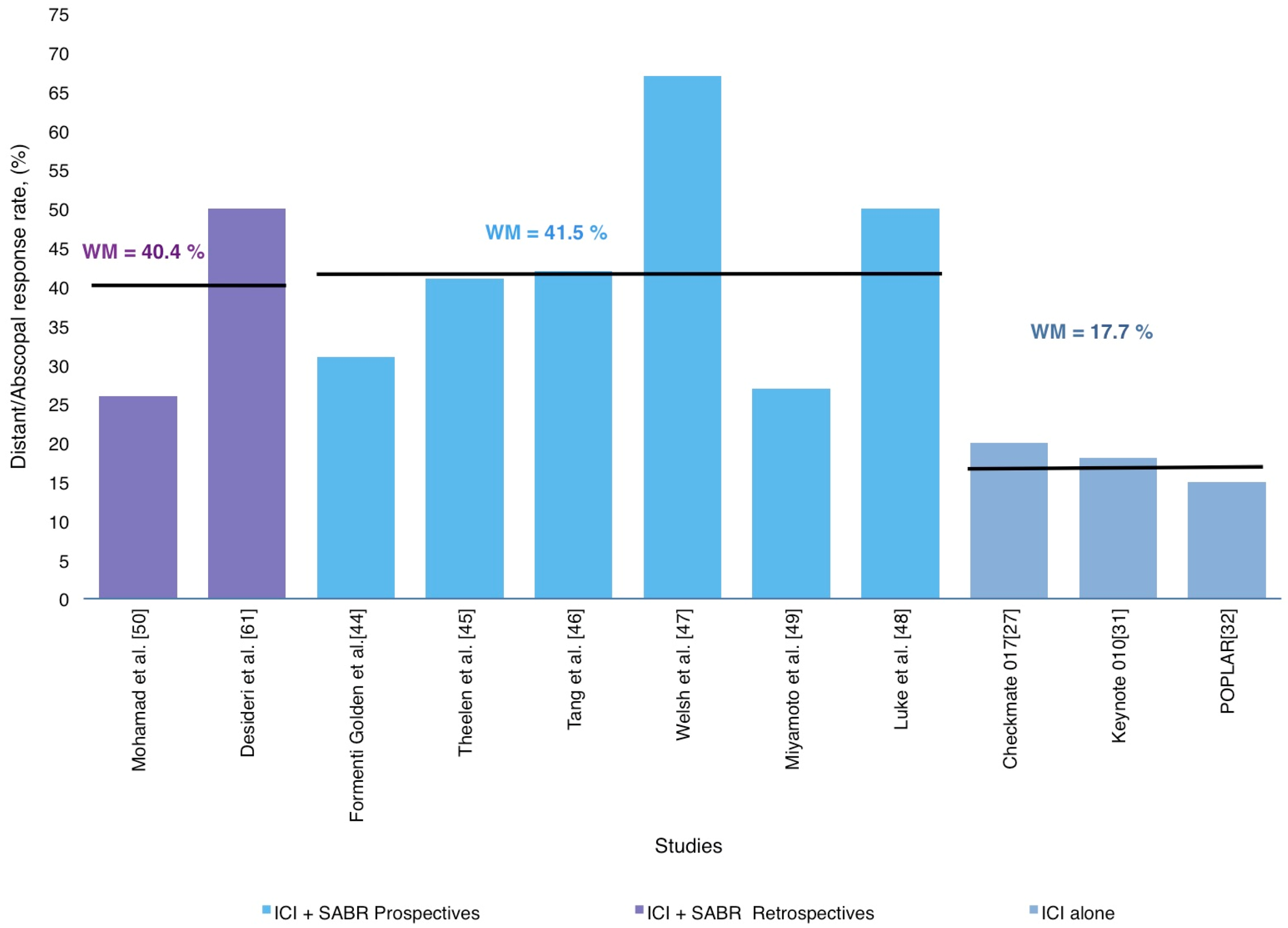
3.2. Using RT-ICI Combination to Improve Systemic Immunotherapy Effects: Abscopal Response in NCSLC
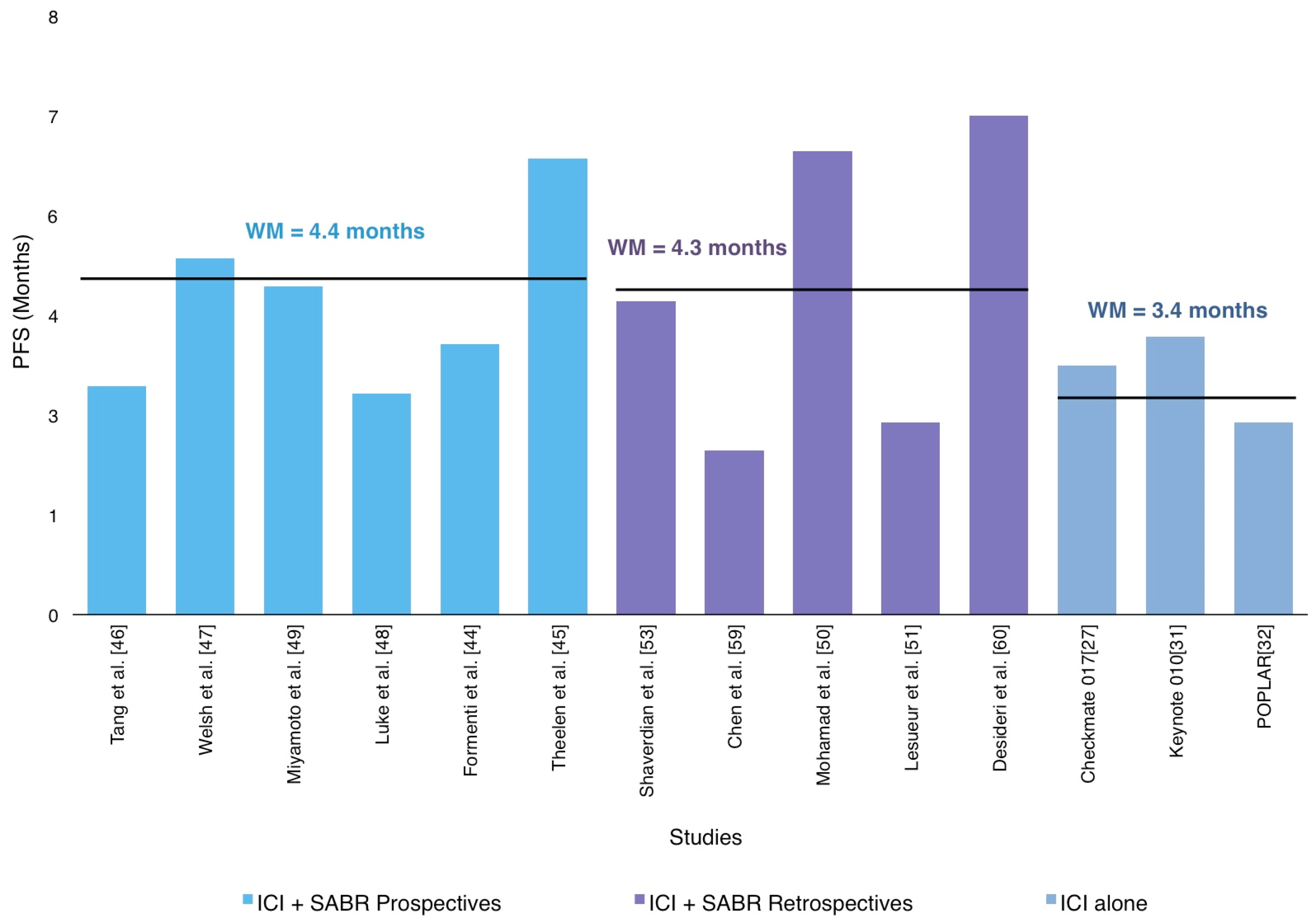
3.3. The Abscopal Response Potentially Delays Disease Progression
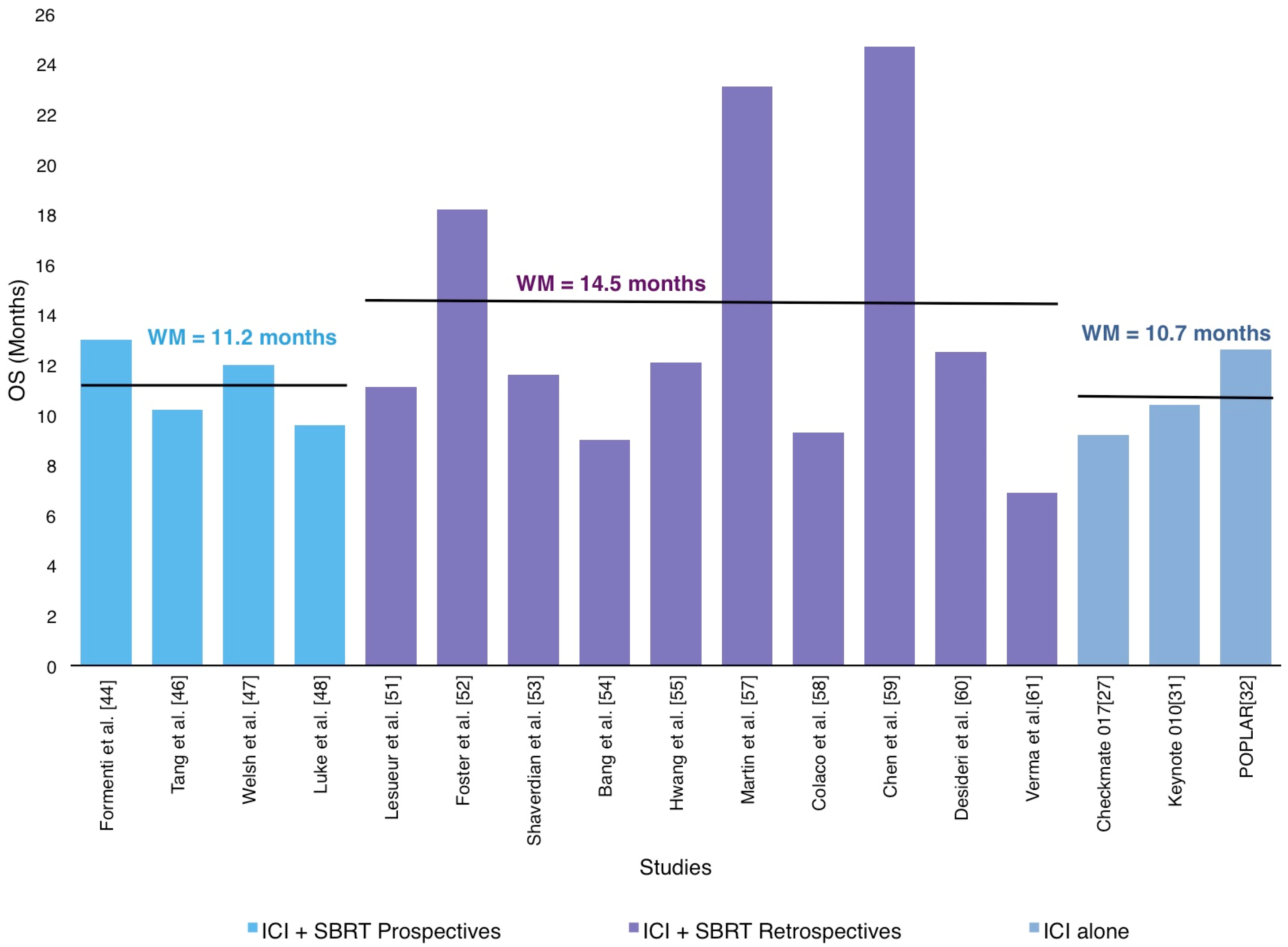
3.4. Could Radiotherapy and ICI Combination Improve Overall Survival in Metastatic NSCLC Patients?
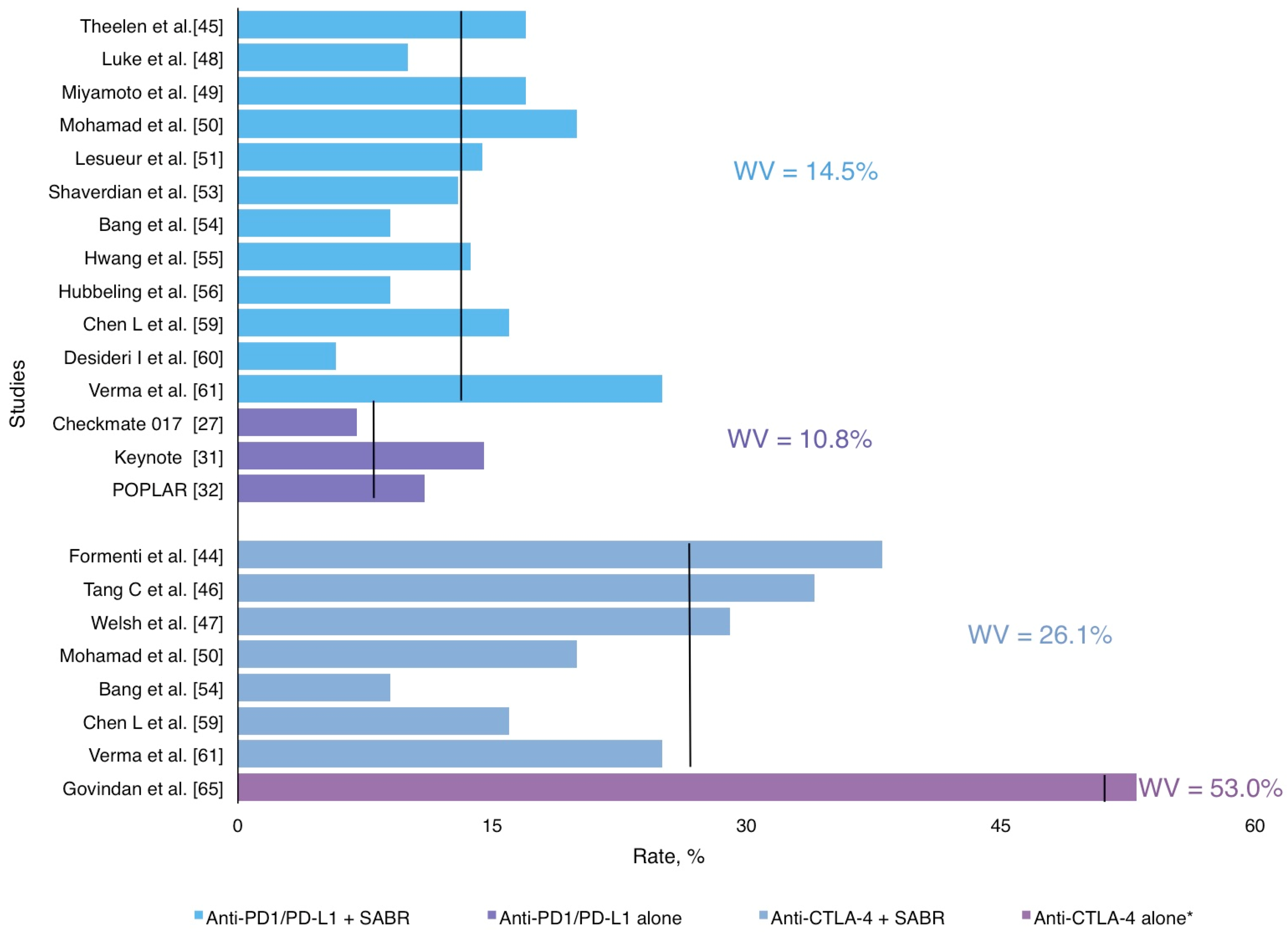
3.5. Radiotherapy and ICI: A Safe Combination
3.6. Futures Perspectives
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2016, 66, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Noone, A.M.; Krapcho, M.; Neyman, N.; Aminou, R.; Waldron, W.; Altekruse, S.F.; Kosary, C.L.; Ruhl, J.; Tatalovich, Z.; et al. (Eds.) SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975-2008; National Cancer Institute: Bethesda, MD, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Goldstraw, P.; Chansky, K.; Crowley, J.; Rami-Porta, R.; Asamura, H.; Eberhardt, W.E.; Nicholson, A.G.; Groome, P.; Mitchell, A.; Bolejack, V. The IASLC lung cancer staging project: Proposals for revision of the TNM stage groupings in the forthcoming (eighth) edition of the TNM Classification for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines): Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Version 3 2019. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/nscl.pdf (accessed on 18 January 2019).
- Videtic, G.M.; Donington, J.; Giuliani, M.; Heinzerling, J.; Karas, T.Z.; Kelsey, C.R.; Lally, B.E.; Latzka, K.; Lo, S.S.; Moghanaki, D.; et al. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: Executive Summary of an ASTRO Evidence-Based Guideline. Pr. Radiat. Oncol. 2017, 7, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, M.; Shioda, A.; Tahara, K.; Fukui, T.; Yamamoto, F.; Tsumatori, G.; Ozeki, Y.; Aoki, T.; Watanabe, M.; Kusano, S. Focal, high dose, and fractionated modified stereotactic radiation therapy for lung carcinoma patients: a preliminary experience. Cancer 1998, 82, 1062–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, P.; Nyman, J.; Hoyer, M.; Wennberg, B.; Gagliardi, G.; Lax, I.; Drugge, N.; Ekberg, L.; Friesland, S.; Johansson, K.-A.; et al. Outcome in a Prospective Phase II Trial of Medically Inoperable Stage I Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 3290–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGarry, R.C.; Papiez, L.; Williams, M.; Whitford, T.; Timmerman, R.D. Stereotactic body radiation therapy of early-stage non–small-cell lung carcinoma: Phase I study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2005, 63, 1010–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakiris, A.J.; McGarry, R.C.; Yiannoutsos, C.T.; Papiez, L.; Williams, M.; Henderson, M.A.; Timmerman, R. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Early-Stage Non–Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma: Four-Year Results of a Prospective Phase II Study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2009, 75, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, R.; Paulus, R.; Galvin, J.; Michalski, J.; Straube, W.; Bradley, J.; Fakiris, A.; Bezjak, A.; Videtic, G.; Johnstone, D.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Inoperable Early Stage Lung Cancer. JAMA 2010, 303, 1070–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, P.; Wardak, Z.; Gerber, D.E.; Tumati, V.; Ahn, C.; Hughes, R.S.; Dowell, J.E.; Cheedella, N.; Nedzi, L.; Westover, K.D.; et al. Consolidative Radiotherapy for Limited Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, e173501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, D.A.; Haasbeek, C.J.; Rodrigues, G.B.; Dahele, M.; Lock, M.; Yaremko, B.; Olson, R.; Liu, M.; Panarotto, J.; Griffioen, G.H.; et al. Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for comprehensive treatment of oligometastatic tumors (SABR-COMET): study protocol for a randomized phase II trial. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, P.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Wardak, Z.; Smith, I.; Ahn, C.; Gerber, D.E.; Dowell, J.; Hughes, R.; Abdulrahman, R.; Camidge, D.R.; et al. Phase II Trial of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Combined With Erlotinib for Patients With Limited but Progressive Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3824–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collen, C.; Christian, N.; Schallier, D.; Meysman, M.; Duchateau, M.; Storme, G.; De Ridder, M. Phase II study of stereotactic body radiotherapy to primary tumor and metastatic locations in oligometastatic nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 1954–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Ruysscher, D.; Wanders, R.; van Baardwijk, A.; Dingemans, A.M.; Reymen, B.; Houben, R.; Bootsma, G.; Pitz, C.; van Eijsden, L.; Geraedts, W.; et al. Radical treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer patients with synchronous oligometastases: long-term results of a prospective phase II trial (Nct01282450). J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Downey, R.J.; Ng, K.K.; Kris, M.G.; Bains, M.S.; A Miller, V.; Heelan, R.; Bilsky, M.; Ginsberg, R.; Rusch, V.W. A phase II trial of chemotherapy and surgery for non-small cell lung cancer patients with a synchronous solitary metastasis. Lung Cancer 2002, 38, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vin, T.; Engels, B.; Gevaert, T.; Storme, G.; De Ridder, M. Stereotactic radiotherapy for oligometastatic cancer: a prognostic model for survival. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasselle, M.D.; Haraf, D.J.; Rusthoven, K.E.; Golden, D.W.; Salgia, R.; Villaflor, V.M.; Shah, N.; Hoffman, P.C.; Chmura, S.J.; Connell, P.P.; et al. Hypofractionated Image-Guided Radiation Therapy for Patients with Limited Volume Metastatic Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2012, 7, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.J.; Mehta, P.S.; Zusag, T.W.; Bonomi, P.D.; Faber, L.P.; Shott, S.; Abrams, R.A. Long term disease-free survival resulting from combined modality management of patients presenting with oligometastatic, non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC). Radiother. Oncol. 2006, 81, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Zhu, X.; Wang, H.; Qiu, M.; Li, N. Should aggressive thoracic therapy be performed in patients with synchronous oligometastatic non-small cell lung cancer? A meta-analysis. J. Thorac. 2017, 9, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.; Hu, Y.; Ouyang, W.; Ma, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, T.; Li, J.; et al. Might radiation therapy in addition to chemotherapy improve overall survival of patients with non-oligometastatic Stage IV non-small cell lung cancer?: Secondary analysis of two prospective studies. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez Guerra, J.L.; Gomez, D.; Zhuang, Y.; Hong, D.; Heymach, J.; Swisher, S.; Lin, S.; Komaki, R.; Cox, J.; Liao, Z. Prognostic impact of radiation therapy to the primary tumor in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and oligometastasis at diagnosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 84, e61–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sheu, T.; Heymach, J.V.; Swisher, S.G.; Rao, G.; Weinberg, J.S.; Mehran, R.; McAleer, M.F.; Liao, Z.; Aloia, T.A.; Gomez, D.R. Propensity Score–Matched Analysis of Comprehensive Local Therapy for Oligometastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer That Did Not Progress After Front-Line Chemotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 90, 850–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, D.R.; Blumenschein, G.R.; Lee, J.J.; Hernandez, M.; Ye, R.; Camidge, D.R.; Doebele, R.C.; Skoulidis, F.; Gaspar, L.E.; Gibbons, D.L.; et al. Local consolidative therapy versus maintenance therapy or observation for patients with oligometastatic non-small-cell lung cancer without progression after first-line systemic therapy: a multicenter, randomized, controlled, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado-Garcia, H.; Romero-Garcia, S.; Aguilar-Cazares, D.; Meneses-Flores, M.; Lopez-Gonzalez, J.S. Tumor-induced CD81T-cell dysfunction in lung cancer patients. Clin. Dev. Immunol. 2012, 2012, 741741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.; Reckamp, K.L.; Baas, P.; Crinò, L.; Eberhardt, W.; Poddubskaya, E.; Antonia, S.; Pluzanski, A.; Vokes, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced squamous-cell nonsmall-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghaei, H.; Paz-Ares, L.; Horn, L.; Spigel, D.; Steins, M.; Ready, N.; Chow, L.; Vokes, E.; Felip, E.; Holgado, E.; et al. Nivolumab versus docetaxel in advanced nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postow, M.A.; Callahan, M.K.; Wolchok, J.D. Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Cancer Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1974–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, D.P.; Reck, M.; Paz-Ares, L.; Creelan, B.; Horn, L.; Steins, M.; Felip, E.; Heuvel, M.M.V.D.; Ciuleanu, T.-E.; Badin, F.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab in Stage IV or Recurrent Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 376, 2415–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.-W.; Felip, E.; Perez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.-Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.-H.; Arvis, C.D.; Ahn, M.-J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D.; Artal-Cortes, A.; Lewanski, C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatloukal, P.; Heo, D.; Park, K.; Kang, J.; Butts, C.; Bradford, D.; Graziano, S.; Huang, B.; Healey, D. Randomized phase II clinical trial comparing tremelimumab (CP- 675,206) with best supportive care (BSC) following first-line platinum-based therapy in patients (pts) with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 8071a. [Google Scholar]
- Lynch, T.J.; Bondarenko, I.; Luft, A.; Kang, J.; Butts, C.; Bradford, D.; Graziano, S.; Huang, B.; Healey, D.; et al. Ipilimumab in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment in stage IIIB/IV non-small-cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized, double blind, multicenter phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 2046–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretero-González, A.; Lora, D.; Ghanem, I.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Castellano, D.; Sepulveda, J.M.; López-Martín, J.A.; Paz-Ares, L.; De Velasco, G. Analysis of response rate with ANTI PD1/PD-L1 monoclonal antibodies in advanced solid tumors: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 8706–8715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buque, A.; Kepp, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Melero, I.; Formenti, S.C.; DeMaria, S. Immunological Mechanisms Responsible for Radiation-Induced Abscopal Effect. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 644–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Liang, H.; Burnette, B.; Beckett, M.; Darga, T.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Fu, Y.-X. Irradiation and anti–PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lara, P.C.; Lopez-Penalver, J.J.; Farias Vde, A.; Ruiz-Ruiz, M.C.; Oliver, F.J.; Ruiz de Amodovar, J.M. Direct and bystander radiation effects: a biophysical model and clinical perpectives. Cancer Lett. 2015, 356, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sologuren, I.; Rodriguez-Gallego, C.; Lara, P.C. Immune effects of high dose radiation treatment: Implications of ionizing radiation on the development of bystander and abscopal effects. Transl. Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Mole, R.J. Whole body irradiation – Radiology or medicine? Br. J. Radiol. 1953, 26, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicas-Sett, R.; Morales-Orue, I.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Lara-Jimenez, P. Combining radiotherapy and ipilimumab induces clinically relevant radiation-induced abscopal effects in metastatic melanoma patients: A systematic review. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 9, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.; Pisani, R.; Purves, R. Statistics, 3rd ed.; WW Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Formenti, S.C.; Rudqvist, N.-P.; Golden, E.; Cooper, B.; Wennerberg, E.; Lhuillier, C.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Friedman, K.; De Andrade, L.F.; Wucherpfennig, K.W.; et al. Radiotherapy induces responses of lung cancer to CTLA-4 blockade. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1845–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theelen, W.; Lalezari, F.; De Vries, J.; De Langen, J.; Aerts, J.; Monkhorst, K.; Baas, P. Randomized phase II study of pembrolizumab after stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) versus pembrolizumab alone in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The PEMBRO-RT study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Welsh, J.W.; de Groot, P.; Massarelli, E.; Chang, J.Y.; Hess, K.R.; Basu, S.; Curran, M.A.; Cabanillas, M.E.; Subbiah, V.; et al. Ipilimumab with stereotactic ablative radiation therapy: Phase I results and immunologic correlates from peripheral T cells. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 1388–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.W.; Tang, C.; de Groot, P.; Naing, A.; Raju, U.; Shaaban, S.; Chang, J.Y.; Cushman, T.; Heymach, J.; Dadu, R.; et al. Phase II 5-arm trial of ipilimumab plus lung or liver stereotactic radiation for patients with advanced malignancies. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luke, J.J.; Lemons, J.M.; Karrison, T.G.; Pitroda, S.P.; Melotek, J.M.; Zha, Y.; Al-Hallaq, H.A.; Arina, A.; Khodarev, N.N.; Janisc, L.; et al. Safety and clinical activity of pembrolizumab and multisite stereotactic body radiotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1611–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, S.; Nomura, R.; Sato, K.; Awano, N.; Kuse, N.; Inomata, M.; Izumo, T.; Terada, Y.; Furuhata, Y.; Bae, Y.; et al. Nivolumab and stereotactic radiation therapy for the treatment of patients with Stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer. Jpn. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 49, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, O.; De Leon, A.D.; Schroeder, S.; Leiker, A.; Christie, A.; Zhang-Velten, E.; Trivedi, L.; Khan, S.; Desai, N.B.; Laine, A.; et al. Safety and efficacy of concurrent immune checkpoint inhibitors and hypofractionated body radiotherapy. OncoImmunology 2018, 7, e1440168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lesueur, P.; Escande, A.; Thariat, J.; Vauléon, E.; Monnet, I.; Cortot, A.; Lerouge, D.; Danhier, S.; Dô, P.; Dubos-Arvis, C.; et al. Safety of combined PD-1 pathway inhibition and radiation therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicentric retrospective study from the GFPC. Cancer Med. 2018, 7, 5505–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, C.C.; Sher, D.J.; Rusthoven, C.G.; Verma, V.; Spiotto, M.T.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; Koshy, M. Overall survival according to immunotherapy and radiation treatment for metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer: A National Cancer Database analysis. Radiat. Oncol. 2019, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaverdian, N.; E Lisberg, A.; Bornazyan, K.; Veruttipong, D.; Goldman, J.W.; Formenti, S.C.; Garon, E.B.; Lee, P. Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: a secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, A.; Wilhite, T.J.; Pike, L.R.G.; Cagney, D.N.; Aizer, A.A.; Taylor, A.; Spektor, A.; Krishnan, M.; Ott, P.A.; Balboni, T.A.; et al. Multicenter evaluation of the tolerability of combined treatment with PD-1 and CTLA-4 immune ckeckpoint inhibitors and palliative radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 98, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.L.; Niemierko, A.; Hwang, K.L.; Hubbeling, H.; Schapira, E.; Gainor, J.F.; Keane, F.K. Clinical outcomes in patients with metastatic lung cancer treated with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and thoracic radiotherapy. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 253–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbeling, H.G.; Schapira, E.F.; Horick, N.K.; Goodwin, K.E.; Lin, J.J.; Oh, K.S.; Shaw, A.T.; Mehan, W.A.; Shih, H.A.; Gainor, J.F. Safety of Combined PD-1 Pathway Inhibition and Intracranial Radiation Therapy in Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.M.; Cagney, D.N.; Catalano, P.J.; Alexander, B.M.; Redig, A.J.; Schoenfeld, J.D.; Aizer, A.A. Immunotherapy and Symptomatic Radiation Necrosis in Patients With Brain Metastases Treated With Stereotactic Radiation. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1123–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colaco, R.J.; Martin, P.; Kluger, H.M.; Yu, J.B.; Chiang, V.L. Does immunotherapy increase the rate of radiation necrosis after radiosurgery treatment of brain metastases? J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Douglass, J.; Kleinberg, L.; Ye, X.; Marciscano, A.E.; Forde, P.M.; Brahmer, J.; Lipson, E.; Sharfman, W.; Hammers, H.; et al. oncurrent immune checkpoint inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 916–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desideri, I.; Francolini, G.; Scotti, V.; Pezzulla, D.; Becherini, C.; Terziani, F.; Paoli, C.D.; Olmetto, E.; Visani, L.; Meattini, I.; et al. Benefit of ablative versus palliative-only radiotherapy in combination with nivolumab in patients affected by metastatic kidney and lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Cushman, T.R.; Selek, U.; Tang, C.; Welsh, J.W. Safety of Combined Immunotherapy and Thoracic Radiation Therapy: Analysis of 3 Single-Institutional Phase I/II Trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 101, 1141–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmerman, R.D.; Paulus, R.; I Pass, H.; Gore, E.M.; Edelman, M.J.; Galvin, J.; Straube, W.L.; A Nedzi, L.; McGarry, R.C.; Robinson, C.G.; et al. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Operable Early-Stage Lung Cancer: Findings From the NRG Oncology RTOG 0618 Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 1263–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marciscano, A.E.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Lee, P.; Tran, P.T.; Tomé, W.A.; Guha, C.; Kong, F.-M.; Sahgal, A.; El Naqa, I.; Rimner, A.; et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: Preclinical Insights and Clinical Opportunities. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gide, T.N.; Wilmott, J.S.; Scoyler, R.A.; Long, V.G. Primary and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic melanoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, L.R.G.; Bang, A.; Ott, P.; Balbonic, T.; Taylor, A.; Catalano, P.; Rawal, B.; Spektor, A.; Krishnan, M.; Cagney, D.; et al. Radiation and PD-1 inhibition: favorable outcomes after brain-directed radiation. Radiother. Oncol. 2017, 124, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindan, R.; Szczesna, A.; Ahn, M.-J.; Schneider, C.-P.; Mella, P.F.G.; Barlesi, F.; Han, B.; Ganea, D.E.; Von Pawel, J.; Vladimirov, V.; et al. Phase III Trial of Ipilimumab Combined With Paclitaxel and Carboplatin in Advanced Squamous Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 3449–3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after chemotherapy in stage III non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Orue, I.; Chicas-Sett, R.; Lara, P.C. Nanoparticles as a promising method to enhance the abscopal effect in the era of new targeted therapies. Rep. Pr. Oncol. Radiother. 2019, 24, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author | Study Type | N | Cancer Histology | RT Target | RT Dose Gy/Fraction | Treatment Sequencing | IT Agent | IT Dose | Local Control Rate (CR+PR+S) % | Median OS (months) | PFS (months) | Distant/Abscopal Response Rate (CR+PR+S)% | Toxicity ≥ Grade 3 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Formenti et al. 2018 [44] | Phase I-II | 39 | NSCLC | NR | 28.5–30/ 3–5 | Concurrent | Ipi | 3 mg/Kg/ 3w | NR | 13 | 3.8 | 31% (Abscopal) | 38 |
| Theelen et al. 2018 [45] | Phase II | 74 | NSCLC | NR | 24/3 | Sequential | Pembro | 200 mg q3w | NR | NR | 6.4 | 41% | 17 |
| Tang et al. 2017 [46] | Phase I | 35 Lung: 14 | Various | Lung, liver | 50/4 | Concurrent Sequential | Ipi | 3 mg/Kg/ 3w | 90% | 10.2 | 3.2 | 42% | 34 |
| Welsh et al. 2017 [47] | Phase II | 100 | Various | Lung, liver | 50/4 | Concurrent Sequential | Ipi | 3 mg/Kg/ 3w | NR | 12 | 5.0 | 67% | 29% |
| Luke et al. 2018 [48] | Phase I | 79 Lung: 7 | Various | Lung, liver, bone, abdomen, pelvis | 30–50/ 3–5 | Sequential | Pembro | 200 mg q3w | NR | 9.6 | 3.1 | 26.9% (Abscopal) Systemic: 13% | 10 |
| Miyamoto et al. 2018 [49] | Prospective | 6 | NSCLC | Lung | 25–48/ 3–4 | Sequential | Nivo | 3 mg/kg q2w | NR | NR | 4.6 | 50% | 17 |
| Mohamad et al. 2018 [50] | Retrospective | 59 Lung; 5 | Various | Extracranial | >5 Gy perfx/ 1–5 | Concurrent Sequential | Nivo, Pembro Atezo, Ipi | NR | NR | Not reached | 6.5 | 26% | 20 |
| Lesueur et al. 2018 [51] | Retrospective | 104 | NSCLC | Bone, brain, lung, others | RT3D: 20–30/ 5–10 SABR: 20–36/ 1–6 | Concurrent (n = 45) Sequential (n = 59) | Nivo | NR | 2 y-LC: 64.4% | 11.1 | 2.7 | NR | 14.4 |
| Foster et al. 2019 [52] | Retrospective | 228 | NSCLC | Intracranial | 18–50/ 1–5 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 18.2 | NR | NR | NR |
| Shaverdian et al. 2017 [53] | Retrospective | 42 | NSCLC | Thoracic | NR | Sequential | Pembro | 2 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg q3w; 10 mg/kg q2w | NR | 11.6 | 4.4 | NR | 13 |
| Bang et al. 2017 [54] | Retrospective | 133 Lung: 71 | NSCLC | Lung, bowel, brain, neck | 8–37.5/ 1–15 | Concurrent Sequential | Anti-CTLA-4 Anti-PD-1 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 9 |
| Hwang et al. 2017 [55] | Retrospective | 164 | NSCLC SCLC | Lung | 8–60/ 1–30 | Concurrent Sequential | Anti-PD-1 Anti-PD-L1 | NR | NR | 12.1 | NR | NR | 13.7 |
| Hubbelling et al. 2018 [56] | Retrospective | 50 | NSCLC | Intracranial | 20–37.5/10–15 SRS: 10–22/1 | Concurrent Sequential | Nivo; Pembro; Atezo | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 9 |
| Martin et al. 2018 [57] | Retrospective | 115 | Various | Intracranial | 25–30/5 SRS: 18–20/1 | NR | Ipi; Nivo; Pembro | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR |
| Colaco et al. 2016 [58] | Retrospective | 180; Lung: 71 | Various | Intracranial | 15–24/1 | Sequential | Anti CTLA-4; Anti-PD-1 | NR | NR | 9.3 | NR | NR | NR |
| Chen et al. 2017 [59] | Retrospective | 260; Lung 157 | Various | Intracranial | 15–25/ 1–5 | Concurrent (n = 28) Sequential (n = 51) | Anti-CTLA-4 Anti-PD-1 | NR | Concurrent: 1y-LC: 88% Sequential: 1y-LC: 79% | Concurrent 24.7 Sequential14.5 | 2.3 | NR | 16 |
| Desideri et al. 2018 [60] | Retrospective | 20 Lung: 17 | Various | Intracranial | 20–30/ 5–10 SRS: 18–40/ 1–5 | Concurrent | Nivo | NR | NR | 12.5 | 7.0 | 50% | 5.8 |
| Verma et al. 2018 [61] | Retrospective | 60 Lung: 41 | Various | Extracranial | 45/2x/day 54/15 SABR: 50-60/4 | Concurrent | Ipi, Pembro | Ipi: 3 mg/kg q3w Pembro: 100 mg q3w | NR | NR | NR | NR | 25 |
| 18 Studies | 1736 patients | Overall Weighted Mean | 70.7% | 12.4 months | 4.6 months | 41.3% | 20.0% | ||||||
| Study Design | Follow-Up in Months, Median, Range | Toxicity ≥ Grade 3 %, Weighted Median | Most Common irAEs |
|---|---|---|---|
| AntiPD1/antiPD-L1 + SABR | 14.0 (2,9–33) | 14,5% | Pneumonitis, asthenia, breakthrough pain, colitis, neurological and hepatic toxicity |
| Anti CTLA4 + SABR | 20.0 (2–38) | 26,0% | Pneumonitis, fatigue, liver enzymes increase, colitis and neurological |
| AntiPD1/AntiPD-L1 alone | 11.0 (7–14,5) | 10,8% | Pneumonia, increased aspartate aminotransferase, skin reactions, pneumonitis, neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, diarrhea |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chicas-Sett, R.; Morales-Orue, I.; Castilla-Martinez, J.; Zafra-Martin, J.; Kannemann, A.; Blanco, J.; Lloret, M.; Lara, P.C. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Combined with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Reboots the Immune Response Assisted by Immunotherapy in Metastatic Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092173
Chicas-Sett R, Morales-Orue I, Castilla-Martinez J, Zafra-Martin J, Kannemann A, Blanco J, Lloret M, Lara PC. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Combined with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Reboots the Immune Response Assisted by Immunotherapy in Metastatic Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(9):2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092173
Chicago/Turabian StyleChicas-Sett, Rodolfo, Ignacio Morales-Orue, Juan Castilla-Martinez, Juan Zafra-Martin, Andrea Kannemann, Jesus Blanco, Marta Lloret, and Pedro C Lara. 2019. "Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Combined with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Reboots the Immune Response Assisted by Immunotherapy in Metastatic Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 9: 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092173
APA StyleChicas-Sett, R., Morales-Orue, I., Castilla-Martinez, J., Zafra-Martin, J., Kannemann, A., Blanco, J., Lloret, M., & Lara, P. C. (2019). Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy Combined with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Reboots the Immune Response Assisted by Immunotherapy in Metastatic Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(9), 2173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20092173





