Electrochemical Sensing: Technologies, Applications and Challenges
A special issue of Sensors (ISSN 1424-8220). This special issue belongs to the section "Chemical Sensors".
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 25 August 2026 | Viewed by 192
Special Issue Editor
Special Issue Information
Dear Colleagues,
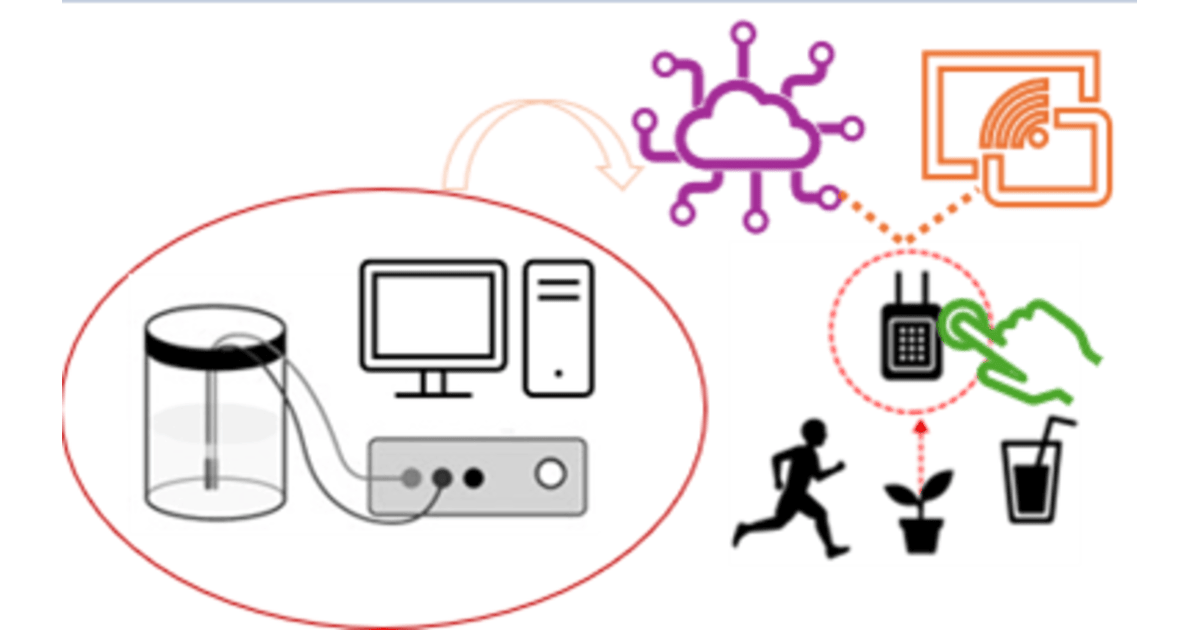
Electrochemical sensors constitute a transformative class of analytical tools that convert chemical interactions into measurable electrical signals. These signals are detected through various architectures such as potentiometric, amperometric, voltammetric, and field-effect transistor-based systems. The design of tailored electrode interfaces plays a crucial role in achieving the sensitivity and selectivity required for a wide range of biomedical and environmental applications. By leveraging miniaturized electrodes and nanostructured surfaces, these sensors enhance signal-to-noise ratios and response times. Despite their advantages, reproducibility remains a key challenge that must be addressed for reliable implementation. Among the different types, amperometric sensors, known for measuring current generated by redox reactions at electrode surfaces, have emerged as the very standard in enzymatic biosensing, as evidenced by their widespread use in commercial monitoring strips. These sensors effectively translate biochemical signals into quantifiable electrical outputs using conventional electronic systems. Potentiometric devices, typically ion-selective electrodes, are essential for monitoring electrolyte concentrations and pH levels, particularly in clinical diagnostics. Voltammetric techniques, on the other hand, offer robust analytical capabilities and enable multi-analyte discrimination, though they demand more sophisticated instrumentation for consistent signal acquisition.
Recent advancements in electrochemical sensing have led to the integration of miniaturized electrodes and microfabricated arrays, facilitating rapid data acquisition in small sample volumes and complex in situ environments. However, achieving high selectivity in physiologically complex matrices remains critical for accurate in vivo and wearable applications, especially under electrocatalytic conditions. In biomedical applications, electrochemical sensors are increasingly used in wearable technologies, point-of-care diagnostics, and clinical analysis, where portability, cost-effectiveness, and direct molecular interaction are vital. Modern wearable systems now incorporate flexible electrochemical bioelectronics, including ion-selective potentiometry, enzymatic amperometry, and affinity-based sensors embedded in usual substrates, allowing real-time monitoring of biomarkers in sweat and interstitial fluids.
This Special Issue focuses on new and exciting research that helps solve current problems in electrochemical sensors. It highlights creative designs for electrodes, improved materials for signal detection, and smart combinations of sensing methods. The goal is to develop advanced sensor systems that are small, multifunctional, and able to use data more effectively. By bringing together these studies, the issue hopes to encourage fresh ideas and teamwork across different fields to build the next generation of electrochemical sensors.
Dr. Shatrudhan Palsaniya
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. Manuscripts can be submitted until the deadline. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the special issue website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Sensors is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript. The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 2600 CHF (Swiss Francs). Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- electrochemical sensors
- biomedical devices
- low-cost electronic materials
- IoTs with sustainable routes
Benefits of Publishing in a Special Issue
- Ease of navigation: Grouping papers by topic helps scholars navigate broad scope journals more efficiently.
- Greater discoverability: Special Issues support the reach and impact of scientific research. Articles in Special Issues are more discoverable and cited more frequently.
- Expansion of research network: Special Issues facilitate connections among authors, fostering scientific collaborations.
- External promotion: Articles in Special Issues are often promoted through the journal's social media, increasing their visibility.
- Reprint: MDPI Books provides the opportunity to republish successful Special Issues in book format, both online and in print.
Further information on MDPI's Special Issue policies can be found here.






