Journal Description
Psychoactives
Psychoactives
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on psychoactive substances published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 27.8 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the first half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
- Psychoactives is a companion journal of Pharmaceuticals.
Latest Articles
Cautions on the Notion of Moral Enhancement with Psychedelics. Reply to Kähönen, J. Subjective Effects of Psychedelics Are the Plausible Mechanism of Psychedelic Moral Enhancement Rather than a Risk. Comment on “Tang, B.L. Psychedelics for Moral Bioenhancement in Healthy Individuals—A Violation of the Non-Maleficence Principle? Psychoactives 2025, 4, 5”
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 44; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040044 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
Kähönen argued that the harms associated with psychedelics have been overstated, while evidence for the latter’s moral enhancing effects was disregarded, in my earlier commentary. Here, I respond to these arguments and maintain that the notion of moral enhancement with psychedelics needs substantially
[...] Read more.
Kähönen argued that the harms associated with psychedelics have been overstated, while evidence for the latter’s moral enhancing effects was disregarded, in my earlier commentary. Here, I respond to these arguments and maintain that the notion of moral enhancement with psychedelics needs substantially more scientific evidence and extended bioethical debates.
Full article
Open AccessComment
Subjective Effects of Psychedelics Are the Plausible Mechanism of Psychedelic Moral Enhancement Rather than a Risk. Comment on Tang, B.L. Psychedelics for Moral Bioenhancement in Healthy Individuals—A Violation of the Non-Maleficence Principle? Psychoactives 2025, 4, 5
by
Juuso Kähönen
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 43; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040043 - 17 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
In a recent Psychoactives article, Bor Luen Tang argues against psychedelic moral bioenhancement (PMBE)—the use of classic psychedelics such as psilocybin to foster moral growth in healthy individuals [...]
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
A Systematic Review of the Prevalence of Substance Abuse in the South Pacific Region
by
Wole Akosile, Daniel McDonald, Henry Aghanwa and Bola Ola
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 42; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040042 - 3 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Background: This review examines the prevalence of substance abuse and related disorders in South Pacific nations. Methods: The review focused on data included in reports published since 2000 from countries like Samoa, Papua New Guinea, Fiji, and French Polynesia, excluding Hawaii, New Zealand,
[...] Read more.
Background: This review examines the prevalence of substance abuse and related disorders in South Pacific nations. Methods: The review focused on data included in reports published since 2000 from countries like Samoa, Papua New Guinea, Fiji, and French Polynesia, excluding Hawaii, New Zealand, Australia, and American Samoa. Prevalence studies indexed in Medline, CINAHL, PsycInfo, Embase, and Cochrane were screened and retrieved. Joanna Briggs Institute critical appraisal tools were used to assess included studies. Results: Ten studies with diverse methods, such as national surveys, were analysed. Results show high variability in prevalence across countries, sexes, and ethnicities. Notably, tobacco and betel nut use are prevalent. Indigenous populations and men face higher SUD burdens. Discussion: inconsistencies in study methods and reliance on self-reporting limit direct comparison. Data on co-occurring disorders and polysubstance use are limited, highlighting research gaps. The review emphasises the need for culturally sensitive, standardised research to monitor emerging trends like synthetic drug use. Policy suggestions call for targeted interventions and improved surveillance to reduce disparities and support vulnerable populations in Pacific Island communities.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
A Comparative Neurophenomenology of the Psychedelic State and Autism: Predictive Processing as a Unifying Lens
by
William Roseby and Catriona Osborn Moar
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 41; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040041 - 14 Nov 2025
Abstract
Serotonergic psychedelics, particularly psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), and dimethyltryptamine (DMT), are increasingly recognised as powerful tools to advance the understanding of consciousness and its relation to brain activity. Psychedelic research has informed neuroscientific theories that attempt to map neural observations of network
[...] Read more.
Serotonergic psychedelics, particularly psilocybin, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), and dimethyltryptamine (DMT), are increasingly recognised as powerful tools to advance the understanding of consciousness and its relation to brain activity. Psychedelic research has informed neuroscientific theories that attempt to map neural observations of network connectivity and signal diversity to phenomenological qualities like psychological flexibility. Thus far, however, there have been relatively limited efforts to bridge the gap between psychedelic-informed theory and the experiential differences observed in neurodevelopmental conditions such as autism. In this narrative review and conceptual synthesis, we compare the psychedelic state and autism in adults from a neurophenomenological perspective. Predictive processing is invoked as a unifying framework. This procedure highlights both phenomena as involving a shift towards sensory information relative to prior knowledge, but potentially implicating alterations at opposite ends of the cortical hierarchy. This contrastive approach also reveals opportunities for refining concepts—including psychological flexibility—as well as interpretations of results across fields. However, neurobiological findings, especially in autism, are heterogeneous and there are inherent restrictions in comparing transient state and lifelong trait phenomena. Conclusions of this comparison are primarily conceptual and offer testable hypotheses for the neurophenomenology of the psychedelic state, autism, and their interaction.
Full article
Open AccessReview
A Bibliometric Review of Genetic Research on Methamphetamine
by
Caroline Anastasia Fernando, Akila Randika Jayamaha, Nafeesa Noordeen, Tibutius Thanesh Pramanayagam Jayadas, Chinthika Gunasekara, Chandima Jeewandara and Neluka Fernando
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 40; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040040 - 13 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Methamphetamine is a highly addictive stimulant with severe health and psychosocial consequences. Over recent decades, genetic and molecular research on methamphetamine use disorders has expanded considerably, yet a comprehensive synthesis of this growing body of literature is lacking. This study conducted a bibliometric
[...] Read more.
Methamphetamine is a highly addictive stimulant with severe health and psychosocial consequences. Over recent decades, genetic and molecular research on methamphetamine use disorders has expanded considerably, yet a comprehensive synthesis of this growing body of literature is lacking. This study conducted a bibliometric analysis to map the scientific landscape of genetic and molecular biology research on methamphetamine use, identifying key contributors, influential publications, publication trends, and co-occurring keywords and citations. A systematic search of the Scopus database retrieved 1550 documents. After applying the inclusion criteria and manual screening, 449 peer-reviewed articles published between 1993 and 2025 were included. Performance analysis and scientific mapping were conducted using VOSviewer software through bibliographic coupling and keyword co-occurrence. The study followed the BIBLIO checklist for reporting bibliometric reviews in biomedical literature. Publication output increased markedly after 2005, peaking in 2022, followed by a decline that may reflect a shift in research priorities. The United States, China, and Japan emerged as leading contributors, underscoring their significant investment in addiction and molecular research. Keyword co-occurrence revealed strong emphasis on addiction, dopamine, neurotoxicity, gene expression, and genetic polymorphisms, highlighting their central role in the pathophysiology of methamphetamine use disorders. This bibliometric analysis demonstrates substantial growth and influence of genetic research on methamphetamine use. Despite a recent decline in publications, the field provides a solid foundation for future interdisciplinary research and funding priorities in addiction genetics.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Hormonal Influences on Psilocybin Responsivity Across the Female Lifespan: Toward Personalized Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy
by
Faith Ekoh, Shanice Rerrie, James Angud and Ersilia Mirabelli
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 39; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040039 - 2 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Today’s research highlights the therapeutic potential of the hallucinogen psilocybin in the treatment of pathologies associated with mood, cognitive, and affective dysregulation. These domains of function are regulated by the serotonergic system, which can be influenced by sex hormones, like estrogen and testosterone,
[...] Read more.
Today’s research highlights the therapeutic potential of the hallucinogen psilocybin in the treatment of pathologies associated with mood, cognitive, and affective dysregulation. These domains of function are regulated by the serotonergic system, which can be influenced by sex hormones, like estrogen and testosterone, and psychedelic compounds including psilocybin. Current evidence supports a higher prevalence of affective disorders in females, and a growing awareness of sex-based differences in response to drug therapy. Estrogen’s influence on serotonin physiology is an aspect that must be accounted for when planning a treatment regimen that includes a psychoactive drug such as psilocybin. A review of the current literature was conducted, and an analysis of how the fluid hormonal states in females across their different reproductive phases may impact serotonin dynamics, synaptic plasticity, and therapeutic timing of psilocybin use is discussed. Future research should focus on the influence of sex hormones on psychedelic-assisted therapy in the effort to further personalize treatment plans for these pathologies.
Full article
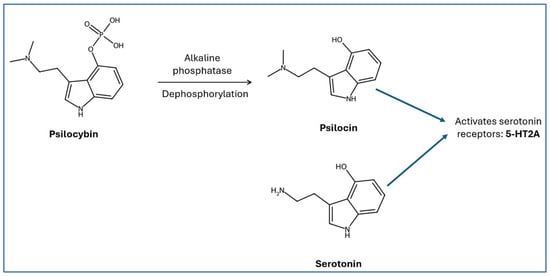
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Suicidal Ideation, Suicide Attempts, and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Associated with Opioid Misuse Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the USA: A Scoping Review of Emerging Patterns and Risks
by
Sharmistha Roy, Ashis Kumar Biswas and Manoj Sharma
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 38; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040038 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Opioid misuse and suicide among youth remain pressing public health challenges. This scoping review examined studies published between 2020 and 2024 on associations between opioid misuse and suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, or non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) among adolescents and young adults aged 12–30, emphasizing
[...] Read more.
Opioid misuse and suicide among youth remain pressing public health challenges. This scoping review examined studies published between 2020 and 2024 on associations between opioid misuse and suicidal ideation, suicide attempts, or non-suicidal self-injury (NSSI) among adolescents and young adults aged 12–30, emphasizing sex and racial or ethnic differences. Guided by Arksey and O’Malley’s framework and PRISMA-ScR, we searched MEDLINE (PubMed), PsycINFO, Scopus, Embase, and CINAHL for peer-reviewed cross-sectional studies in English. Eligible studies assessed nonmedical prescription or illicit opioid use and excluded clinical or incarcerated samples and those with older participants. Seventeen studies met the inclusion criteria. Fifteen analyzed U.S. national or state data, one examined youth in the Northern Mariana Islands, and one used Canadian data. Sixteen studies identified a positive association between opioid misuse and suicide-related outcomes, while one showed a recency gradient, with current misuse carrying the highest risk. Other findings showed that frequent misuse increased risk, multiple substance use heightened danger, and females and youth from racial and ethnic minority groups were more vulnerable. Opioid misuse is strongly associated with suicide risk. Integrated, sex- and culturally responsive prevention strategies are needed, alongside further research clarifying mechanisms and protective factors.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Profound Opioid and Medetomidine Withdrawal: A Case Series and Narrative Review of Available Literature
by
Phil Durney, Elise Paquin, Gamal Fitzpatrick, Drew Lockstein, TaReva Warrick-Stone, Maeve Montesi, Sejal H. Patel-Francis, Jamal Rashid, Oluwarotimi Vaughan-Ogunlusi, Kelly Goodsell, Jennifer L. Kahoud, Christopher Martin, Keira Chism, Paul Goebel, Karen Alexander, Dennis Goodstein and Kory S. London
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 37; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040037 - 23 Oct 2025
Abstract
Medetomidine, a potent central acting α2 agonist, has emerged as a fentanyl adulterant in the non-medical opioid supply. Its use has been linked to a novel withdrawal syndrome that is often resistant to conventional treatment protocols. Four cases are presented exemplifying extreme, but
[...] Read more.
Medetomidine, a potent central acting α2 agonist, has emerged as a fentanyl adulterant in the non-medical opioid supply. Its use has been linked to a novel withdrawal syndrome that is often resistant to conventional treatment protocols. Four cases are presented exemplifying extreme, but increasingly common forms of this withdrawal syndrome. A literature review is provided demonstrating both the paucity of available literature as well as potential avenues for treatment and future research. As adulterants continue to proliferate in the illicit drug supply, clinicians should anticipate atypical withdrawal phenotypes and consider early intervention.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue New Psychoactive Substances and Emerging Trends: Pharmacology, Neurotoxicity and Public Health Implications)
►▼
Show Figures
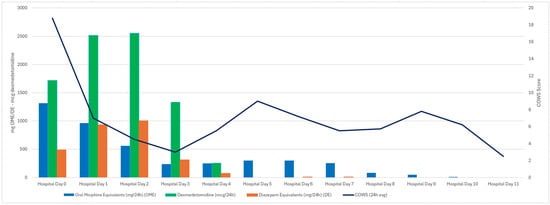
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Cannabis Use Motives Associated with Mental Health Screening Among Older Adults
by
Rachel E. Thayer, Juliamaria Coromac-Medrano and Adrianna C. Neiderman
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 36; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040036 - 5 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Cannabis use (CU) motives among older adults (OA) could be an important indicator of broader mental health. OA ages 60+ (N = 78) reported on CU, alcohol consumption, and mood and anxiety. Coping, enhancement, social, conformity, expansion, and routine motives were assessed.
[...] Read more.
Cannabis use (CU) motives among older adults (OA) could be an important indicator of broader mental health. OA ages 60+ (N = 78) reported on CU, alcohol consumption, and mood and anxiety. Coping, enhancement, social, conformity, expansion, and routine motives were assessed. Relationships among CU, alcohol consumption, and screenings for Cannabis Use Disorder (CUD), Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD), depression, and anxiety were examined. OA who screened positive for CUD were not different in CU frequency or alcohol consumption, but did endorse higher routine, social, coping, and conformity motives than OA endorsing non-harmful CU (d = 1.01 to 1.70). Participants who screened positive for depression or anxiety endorsed higher coping (d = 1.87, 2.18) and routine (d = 0.83, 0.85) motives in the absence of higher alcohol or CU. Higher routine motives were particularly associated with positive CUD screening, beyond other motives and CU frequency. Healthcare providers serving OA with CU should ask about motives to help determine if further mental health evaluation is warranted.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessSystematic Review
Digital Enablement of Psychedelic-Assisted Therapy in Non-Clinical Settings: A Systematic Review of Safety, Efficacy, and Implementation Models
by
Brendan Driscoll and Shaheen E. Lakhan
Psychoactives 2025, 4(4), 35; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4040035 - 1 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Psychedelic-assisted therapy offers rapid and profound benefits for treatment-resistant psychiatric conditions but remains constrained by the need for intensive, clinic-based administration. Concurrently, advances in digital health technologies have introduced scalable tools. This systematic review evaluates the safety, efficacy, and implementation of digitally enabled
[...] Read more.
Psychedelic-assisted therapy offers rapid and profound benefits for treatment-resistant psychiatric conditions but remains constrained by the need for intensive, clinic-based administration. Concurrently, advances in digital health technologies have introduced scalable tools. This systematic review evaluates the safety, efficacy, and implementation of digitally enabled psychedelic-assisted therapy delivered in non-clinical settings. A comprehensive search of five databases, registered in PROSPERO (CRD420251020968) and conducted in accordance with PRISMA guidelines, identified six eligible studies including real-world analyses, clinical trials, qualitative research, and case reports, representing a total of 12,731 participants. Most studies examined at-home ketamine or esketamine therapy supported by telehealth platforms or mobile applications. Data were synthesized narratively given the heterogeneity of designs and outcomes. Digital enablement was associated with high response rates (ranging from 56.4% to 62.8% for depression) and rapid symptom improvement, particularly in depression and anxiety. Remote monitoring and digital tools demonstrated feasibility and acceptability, but serious safety concerns—including psychiatric adverse events and one unintentional overdose—underscore the need for strict oversight. Risk of bias was moderate to serious across non-randomized studies, limiting confidence in the findings. One study on virtual ayahuasca rituals highlighted the sociocultural potential and limitations of online practices. Despite promising preliminary findings, the field is marked by low methodological rigor and absence of controlled trials. Digitally supported at-home psychedelic therapy represents a transformative but high-stakes frontier, requiring robust research and safeguards to ensure safe, equitable, and effective implementation. No funding was received for this review, and the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessEssay
The Legal Perspective on Psilocybin for Medical Use in Czechia: A Key Milestone and the Case for Broader Consideration Beyond the Clinical Setting
by
Tereza Dlestikova
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 34; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030034 - 11 Sep 2025
Cited by 2
Abstract
Czechia has recently approved the medical use of psilocybin, marking a pivotal shift in the country’s drug policy landscape. This development paves the way for regulated therapeutic applications of psilocybin within clinical settings, while simultaneously prompting a timely discussion on the potential uses
[...] Read more.
Czechia has recently approved the medical use of psilocybin, marking a pivotal shift in the country’s drug policy landscape. This development paves the way for regulated therapeutic applications of psilocybin within clinical settings, while simultaneously prompting a timely discussion on the potential uses of psychedelics beyond strictly medical contexts. This commentary first outlines the legal status of psilocybin for therapeutic use in Czechia and situates this reform within broader international policy trends. Drawing on the publication How to Regulate Psychedelics and qualitative findings from a ketamine-assisted therapy program conducted as part of the Czech Destigmatizing the Therapeutic Use of Psychedelics in Psychiatry project, it then examines the regulation of non-clinical psychedelic use, while also highlighting the persistent legal ambiguity surrounding the Czech offence of “spreading toxicomania.” The commentary advocates for a rational, evidence-based regulatory approach, arguing that while the medicalization of psilocybin constitutes a significant legal milestone, the framework will remain incomplete without clear pathways for non-clinical use to ensure safety and legal clarity.
Full article
Open AccessSystematic Review
Neuroimmune Mechanisms in Alcohol Use Disorder: Microglial Modulation and Therapeutic Horizons
by
Jiang-Hong Ye, Wanhong Zuo, Faraz Chaudhry and Lawrence Chinn
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 33; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030033 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) profoundly impacts individuals and society, driven by neurobiological adaptations that sustain chronicity and relapse. Emerging research highlights neuroinflammation, particularly microglial activation, as a central mechanism in AUD pathology. Ethanol engages microglia—the brain’s immune cells—through key signaling pathways such as
[...] Read more.
Alcohol Use Disorder (AUD) profoundly impacts individuals and society, driven by neurobiological adaptations that sustain chronicity and relapse. Emerging research highlights neuroinflammation, particularly microglial activation, as a central mechanism in AUD pathology. Ethanol engages microglia—the brain’s immune cells—through key signaling pathways such as Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and the NLRP3 inflammasome, triggering the release of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6). These mediators alter synaptic plasticity in addiction-related brain regions, including the ventral tegmental area, nucleus accumbens, amygdala, and lateral habenula, thereby exacerbating cravings, withdrawal symptoms, and relapse risk. Rodent models reveal that microglial priming disrupts dopamine signaling, heightening impulsivity and anxiety-like behaviors. Human studies corroborate these findings, demonstrating increased microglial activation markers in postmortem AUD brains and neuroimaging analyses. Notably, sex differences influence microglial reactivity, complicating AUD’s neuroimmune landscape and necessitating sex-specific research approaches. Microglia-targeted therapies—including minocycline, ibudilast, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and P2X7 receptor antagonists—promise to mitigate neuroinflammation and reduce alcohol intake, yet clinical validation remains limited. Addressing gaps such as biomarker identification, longitudinal human studies, and developmental mechanisms is critical. Leveraging multi-omics tools and advanced neuroimaging can refine microglia-based therapeutic strategies, offering innovative avenues to break the self-sustaining cycle of AUD.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Feature Papers in Psychoactives)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Psychedelics and Mental Health Treatment Seeking Among Asians and Hawaiians
by
Sean Matthew Viña
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 32; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030032 - 4 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
States like Hawai‘i are decriminalizing psychedelics based on emerging evidence linking their use to improved psychological well-being. Yet, in many cultural contexts, stigma surrounding mental illness may lead individuals to pursue non-traditional forms of healing, including psychedelics, in place of formal care. This
[...] Read more.
States like Hawai‘i are decriminalizing psychedelics based on emerging evidence linking their use to improved psychological well-being. Yet, in many cultural contexts, stigma surrounding mental illness may lead individuals to pursue non-traditional forms of healing, including psychedelics, in place of formal care. This study examines how psychedelic use relates to mental health treatment-seeking behaviors among Asians and Native Hawaiians and Other Pacific Islanders (NHOPIs). Using the National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) data from 2008 to 2019 (n = 458,372), the analysis compares Non-Hispanic Whites with Asian and NHOPI respondents to assess associations between MDMA and lifetime classic psychedelic use, psychological distress (K6 scale), and formal mental health service utilization. Nested logistic regression models conducted in Stata 18 indicate that psychedelic use among White individuals is associated with a lower likelihood of seeking formal treatment. In contrast, among NHOPI individuals, psychedelic use is associated with increased odds of accessing mental health care. These findings suggest that psychedelic use may serve culturally distinct roles in coping with distress, shaped by structural stigma and the perceived trustworthiness of formal treatment systems.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Neuroplasticity and Neuro-Generation: The Promise of Psychedelics in Dementia Care
by
Kerem Kemal Soylemez, Emma Marie de Boo, Aysil Susuzlu and Joanne Lusher
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 31; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030031 - 2 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Dementia is a progressive neurodegenerative disease which is characterised by cognitive decline, memory loss, and behavioural changes. Patients suffering from dementia often experience emotional distress, sadness and depression which also impacts the wellbeing of their caregivers. Recent research has explored the potential of
[...] Read more.
Dementia is a progressive neurodegenerative disease which is characterised by cognitive decline, memory loss, and behavioural changes. Patients suffering from dementia often experience emotional distress, sadness and depression which also impacts the wellbeing of their caregivers. Recent research has explored the potential of psychedelics, such as psilocybin and LSD, when treating various mental health conditions. Psychedelics are known to alter perception, mood and cognition by affecting serotonin receptors in the brain. Studies suggest that psychedelics may be a promising treatment for dementia patients and promote neuroplasticity, reduce neuroinflammation and enhance cognitive flexibility. These effects could potentially lead to a reduction in the progression of neurodegenerative diseases and improve the patients’ quality of life. Additionally, psychedelics might contribute to the prevention of dementia by fostering brain health and resilience against age-related decline. The application of psychedelics in dementia care might pose significant safety and ethical concerns. The present paper provides a narrative review of the existing literature on the use of psychedelics in treatment of dementia and its different types (Alzheimer’s) with the aim to raise awareness on the topic from a critical perspective.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
Psilocybin-Assisted Psychotherapy for Chronic Somatoform Pain Disorder: A Case Report
by
Mathilda Mercier, Cedric Mabilais, Vasileios Chytas, Leonice Furtado, Federico Seragnoli, Albert Buchard, Tatiana Aboulafia-Brakha, Gabriel Thorens, Daniele Zullino and Louise Penzenstadler
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 30; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030030 - 1 Sep 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Psychedelic substances have experienced a resurgence of clinical interest in recent years, particularly for their promising effects in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety. While evidence regarding their role in chronic pain management remains limited, emerging studies suggest potential
[...] Read more.
Psychedelic substances have experienced a resurgence of clinical interest in recent years, particularly for their promising effects in the treatment of psychiatric disorders such as depression and anxiety. While evidence regarding their role in chronic pain management remains limited, emerging studies suggest potential therapeutic benefits. This case report describes a patient with persistent somatoform pain disorder and recurrent depressive disorder who underwent four sessions of psilocybin-assisted psychotherapy. The intervention was associated with a reduction in the negative impact of pain on daily life, increased pain acceptance, improved quality of life, and reduction in depressive symptoms. These findings contribute to the growing body of literature suggesting that psychedelics, when combined with psychotherapy, may offer a novel and holistic approach to the treatment of chronic pain. Further controlled studies are needed to explore the safety, efficacy, and underlying mechanisms.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Critical Windows of Vulnerability: Behavioral Dysregulation After Prenatal vs. Adolescent THC Exposure
by
Erica Holliday, Kawsar Ullah Chowdhury, Kai Chen, Bilal Saleem, Abhinav Yenduri and Vishnu Suppiramaniam
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 29; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030029 - 20 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review synthesizes preclinical evidence on the behavioral and neurobiological effects of cannabis exposure during prenatal and adolescent developmental periods, with a focus on anxiety, social behavior, learning and memory, and associated brain changes. Understanding the differential impact of cannabis exposure across these
[...] Read more.
This review synthesizes preclinical evidence on the behavioral and neurobiological effects of cannabis exposure during prenatal and adolescent developmental periods, with a focus on anxiety, social behavior, learning and memory, and associated brain changes. Understanding the differential impact of cannabis exposure across these windows is critical, given the increasing prevalence of cannabis use and the rising potency of its primary psychoactive component, delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). Both prenatal and adolescent periods represent vulnerable windows for disruption of the endocannabinoid system, which plays a central role in typical neurodevelopment. Exogenous activation of this system via THC can lead to atypical brain maturation and subsequent behavioral impairments. These impairments are associated with region-specific alterations in cortical and subcortical structures and are highly dependent on the timing of exposure. For instance, prenatal exposure may disrupt medial prefrontal cortex development, leading to long-term social deficits while sparing memory function. In contrast, adolescent exposure tends to impair hippocampal function, resulting in learning and memory deficits. The manuscript is organized developmentally, beginning with the effects of prenatal exposure and then discussing consequences of adolescent exposure. By delineating the distinct behavioral and neurobiological outcomes associated with the timing of cannabis exposure, this review highlights the importance of developmental stage in assessing the risks of exogenous cannabinoid use and identifies critical periods for targeted research and intervention.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
“Becoming Your Own Psychologist”: Novel Psychoactive Substances (NPSs) for Mood and Anxiety Disorder Self-Medication
by
Tayler Holborn, Fabrizio Schifano, Emma Smith and Paolo Deluca
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 28; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030028 - 20 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Numerous individuals suffer from mental health issues including depression and anxiety, resulting in substantial societal burden. Data suggests individuals are choosing to self-medicate with Novel Psychoactive Substances (NPS); however, this phenomenon is poorly understood. We aimed to investigate which NPS are being used
[...] Read more.
Numerous individuals suffer from mental health issues including depression and anxiety, resulting in substantial societal burden. Data suggests individuals are choosing to self-medicate with Novel Psychoactive Substances (NPS); however, this phenomenon is poorly understood. We aimed to investigate which NPS are being used to self-medicate, evaluate their perceived effectiveness and examine influencing factors. Data from respondents (n = 274) (Mean Age [SD] = 29.8 ± 9.1, Male = 71%, Female = 18%, non-binary 5%) were collected via an online survey, with five participants (male = 2; nonbinary = 3) undertaking further semi-structured interviews and the data examined using a Framework analysis. NPS used included bromazolam, etizolam, clonazolam, 1P-LSD and 2-FDCK. Individuals perceived self-medication to be more effective than conventional treatment (p < 0.001). A Framework analysis identified the following themes surrounding mood and anxiety disorder self-medication: (1) depression being chronic, treatment resistant and often comorbid; (2) individuals attempting to mimic existing treatments; (3) individuals having high levels of pharmacological knowledge; (4) difficulties in controlling benzodiazepine self-medication. This study brings important insight into self-medication practices with NPSs, adding to data demonstrating an increase in bromazolam use. Data suggests self-medication follows conventional treatment and, therefore, we outline the importance of affordable emerging treatment options for depression and anxiety.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Co-Use of Alcohol and Cannabis During COVID-19: Associations Between Sociodemographic Factors and Self-Reported Mental Health Symptoms and Heavy Episodic Drinking in Canadian Adults
by
Nibene H. Somé, Sameer Imtiaz, Yeshambel T. Nigatu, Samantha Wells, Claire de Oliveira, Shehzad Ali, Tara Elton-Marshall, Jürgen Rehm, Kevin D. Shield and Hayley A. Hamilton
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 27; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030027 - 6 Aug 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
This study estimates the prevalence of co-use of alcohol and cannabis, assesses the sociodemographic risk factors of co-use, and examines the associations between mental health and heavy episodic drinking (HED) and alcohol–cannabis co-use in Canada during the early years of the COVID-19 pandemic.
[...] Read more.
This study estimates the prevalence of co-use of alcohol and cannabis, assesses the sociodemographic risk factors of co-use, and examines the associations between mental health and heavy episodic drinking (HED) and alcohol–cannabis co-use in Canada during the early years of the COVID-19 pandemic. Nine successive cross-sectional surveys, held from May 2020 to January 2022, of adults (aged ≥18 years) living in Canada were pooled for 9011 participants. The prevalence of co-use was calculated across sociodemographic groups. Logistic regressions were used to assess associations. Alcohol–cannabis co-use was associated with a greater likelihood of engaging in HED and experiencing symptoms of anxiety, depression, and loneliness. The prevalence of co-use of alcohol was different across sociodemographic groups. The highest prevalence was among TGD people (35.5%), followed by individuals aged 18–39 years (14.5%). Additionally, being TGD (aOR = 3.61, 95% CI 2.09–6.25), separated/divorced/widowed (aOR = 1.60, 95% CI 1.23–2.07), living in an urban area (aOR = 1.26, 95% CI 1.07–1.56), and having a high household income (aOR = 1.41, 95% CI 1.09–1.82) increased the likelihood of reporting alcohol–cannabis co-use. These findings underscore the fact that developing public health and clinical interventions for preventing and treating excessive alcohol or cannabis use must consider both alcohol and cannabis use patterns and should be tailored to the highest-risk TGD and young adults.
Full article
Open AccessBrief Report
Pilot Data on Salivary Oxytocin as a Biomarker of LSD Response in Patients with Major Depressive Disorder
by
Laure Cazorla, Sylvie Alaux, Caroline Amberger, Cédric Mabilais, Leonice Furtado, Albert Buchard, Gabriel Thorens, Louise Penzenstadler, Daniele Zullino and Tatiana Aboulafia Brakha
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 26; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030026 - 1 Aug 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Despite growing evidence supporting the efficacy of LSD-assisted psychotherapy in treating major depressive disorder (MDD), identifying reliable psychopharmacological biomarkers remains necessary. Oxytocin, a neuropeptide implicated in social bonding and flexibility, is a promising candidate due to its release following serotonergic psychedelic administration in
[...] Read more.
Despite growing evidence supporting the efficacy of LSD-assisted psychotherapy in treating major depressive disorder (MDD), identifying reliable psychopharmacological biomarkers remains necessary. Oxytocin, a neuropeptide implicated in social bonding and flexibility, is a promising candidate due to its release following serotonergic psychedelic administration in healthy individuals; however, its dynamics in psychiatric populations are currently unexplored. This observational pilot study aimed to characterize salivary oxytocin dynamics during a single LSD-assisted psychotherapy session in our patients with treatment-resistant MDD. Participants received 100 or 150 µg LSD, and salivary oxytocin was measured at baseline, 60, 90, and 180 min post-LSD. Concurrently, participants rated subjective drug intensity (0–10 scale) at 60, 90, and 180 min. A linear mixed model revealed significant variation of oxytocin levels over time. Perceived psychedelic intensity also significantly varied over time. This supports oxytocin as a potential biomarker. Larger, controlled trials are warranted to replicate these findings and clarify the mechanistic links between oxytocin dynamics and clinical outcomes, including changes in depressive symptoms and mental flexibility.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessCase Report
‘Crystal Meth’ Use in an Addiction Outpatient Clinic in Italy: A Multifaceted Challenge
by
Filippo Besana, Stefano Pasquariello, Attilio Negri and Valentina Costa
Psychoactives 2025, 4(3), 25; https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4030025 - 16 Jul 2025
Abstract
Shaboo is a street name commonly used in parts of Asia, particularly the Philippines and Thailand, to refer to methamphetamine, a powerful and highly addictive stimulant. Its long-term effects are related to chronic exposure to the drug effects, primarily neurotoxicity phenomena, which could
[...] Read more.
Shaboo is a street name commonly used in parts of Asia, particularly the Philippines and Thailand, to refer to methamphetamine, a powerful and highly addictive stimulant. Its long-term effects are related to chronic exposure to the drug effects, primarily neurotoxicity phenomena, which could lead to cognitive impairment, or psychiatric symptoms. We aim to present one case of problematic shaboo use in a patient referring to an addiction outpatient clinic in Northern Italy. This case highlights that the treatment of these patients involves careful multidisciplinary management. An accurate knowledge of the physical and psychological effects of New Psychoactive Substances is essential, as well as the implementation of a tailored psychological and social support program.
Full article
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
Topics

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Psychoactives
New Psychoactive Substances and Emerging Trends: Pharmacology, Neurotoxicity and Public Health Implications
Guest Editors: Daniel José Barbosa, Ana Filipa Sobral, Renata Silva, Ricardo Dinis-OliveiraDeadline: 30 June 2026









