The Scientific Advances in Psychoactives Versus Artifacts in Amphetamine Analysis
Abstract
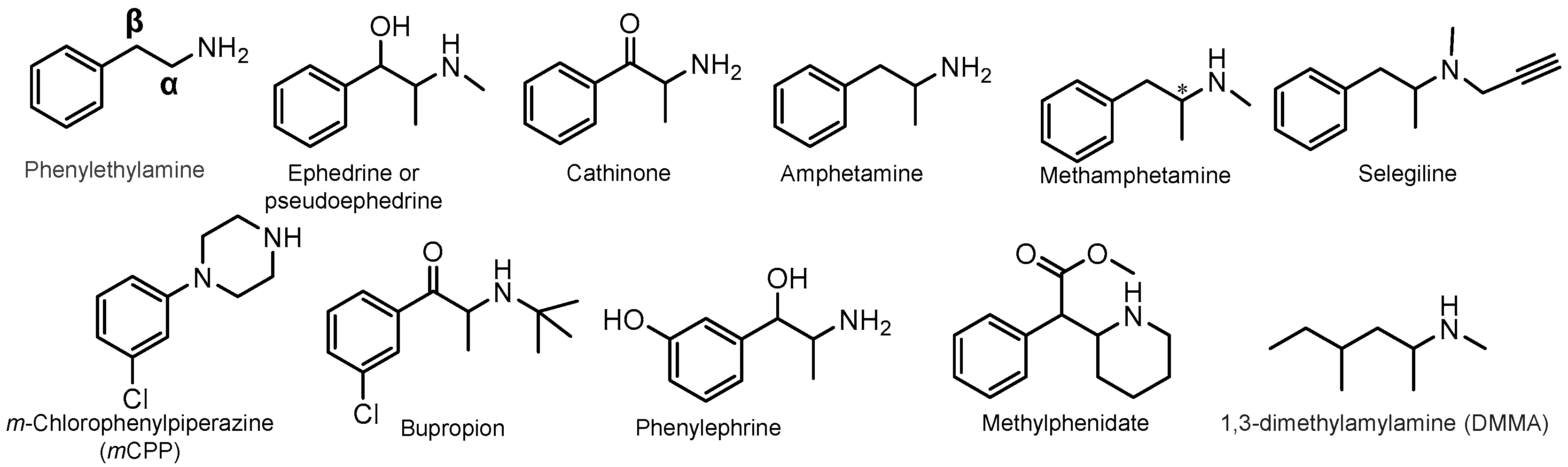
1. Perspective
2. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Carvalho, F.; Bastos, M.L. Toxicologia Forense [Forensic Toxicology]; Lidel, Edições Técnicas LDA: Lisboa, Portugal, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Docherty, J.R. Pharmacology of stimulants prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 154, 606–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boghosian, T.; Mazzoni, I.; Barroso, O.; Rabin, O. Investigating the Use of Stimulants in Out-of-Competition Sport Samples. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 613–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkholtz, H.M.; Hadzima, R.; Miles, A. Pharmacology of R-(-)-Methamphetamine in Humans: A Systematic Review of the Literature. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2023, 6, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulus, M.P.; Stewart, J.L. Neurobiology, Clinical Presentation, and Treatment of Methamphetamine Use Disorder: A Review. JAMA Psychiatry 2020, 77, 959–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Heterogeneous and homogeneous immunoassays for drug analysis. Bioanalysis 2014, 6, 2877–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DePriest, A.Z.; Knight, J.L.; Doering, P.L.; Black, D.L. Pseudoephedrine and false-positive immunoassay urine drug tests for amphetamine. Pharmacotherapy 2013, 33, e88–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, P.R.; Klette, K.L.; Horn, C.K. Evaluation of ephedrine, pseudoephedrine and phenylpropanolamine concentrations in human urine samples and a comparison of the specificity of DRI amphetamines and Abuscreen online (KIMS) amphetamines screening immunoassays. J. Forensic Sci. 2004, 49, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Nicuola, J.; Jones, R.; Levine, B.; Smith, M.L. Evaluation of six commercial amphetamine and methamphetamine immunoassays for cross-reactivity to phenylpropanolamine and ephedrine in urine. J. Anal. Toxicol. 1992, 16, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.N.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Pharmacokinetic and Toxicological Aspects of 1,3-Dimethylamylamine with Clinical and Forensic Relevance. Psychoactives 2023, 2, 222–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorce, S.P.; Holler, J.M.; Cawrse, B.M.; Magluilo, J., Jr. Dimethylamylamine: A drug causing positive immunoassay results for amphetamines. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Paoloni, R.; Szekely, I. Sustained-release bupropion overdose: A new entity for Australian emergency departments. Emerg. Med. 2002, 14, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weintraub, D.; Linder, M.W. Amphetamine positive toxicology screen secondary to bupropion. Depress. Anxiety 2000, 12, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, E.R.; Scott, M.G.; Tang, S.; Mullins, M.E. Frequency of false positive amphetamine screens due to bupropion using the Syva EMIT II immunoassay. J. Med. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reidy, L.; Walls, H.C.; Steele, B.W. Crossreactivity of bupropion metabolite with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays designed to detect amphetamine in urine. Ther. Drug Monit. 2011, 33, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, R.; Oliveira, N.G.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic of bupropion: Integrative overview of relevant clinical and forensic aspects. Drug Metab. Rev. 2019, 51, 293–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, J.M.; Griggs, D.A.; Nixon, A.L.; Long, W.H.; Flood, J.G. The trazodone metabolite meta-chlorophenylpiperazine can cause false-positive urine amphetamine immunoassay results. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2011, 35, 364–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Costa Alegre, M.D.; Barbosa, D.J.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Metabolism of m-CPP, trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone: Clinical and forensic aspects. Drug Metab. Rev. 2025, 57, 115–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtin, L.B.; Cawley, M.J. Immunoassay cross-reactivity of phenylephrine and methamphetamine. Pharmacotherapy 2012, 32, e98–e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romberg, R.W.; Needleman, S.B.; Snyder, J.J.; Greedan, A. Methamphetamine and amphetamine derived from the metabolism of selegiline. J. Forensic Sci. 1995, 40, 1100–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, I.; Choi, H.; Kang, S.; Kim, J.; Park, Y.; Yang, W. Detection of l-Methamphetamine and l-Amphetamine as Selegiline Metabolites. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2021, 45, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, A.; Görgens, C.; Guddat, S.; Piper, T.; Garzinsky, A.-M.; Krug, O.; Thevis, M. Chiral analysis of selected enantiomeric drugs relevant in doping controls. J. Chromatogr. Open 2021, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bickel, J.; Szewczyk, A.; Aboutara, N.; Jungen, H.; Müller, A.; Ondruschka, B.; Iwersen-Bergmann, S. Chiral analysis of amphetamine, methamphetamine, MDMA and MDA enantiomers in human hair samples. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2024, 48, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borg, D.; Kolb, E.; Lantigua, C.; Stripp, R. Chiral Analysis of Methamphetamine in Oral Fluid Samples: A Method to Distinguish Licit from Illicit Drug Use. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2017, 42, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martyny, J.W.; Arbuckle, S.L.; McCammon, C.S.; Erb, N.; Van Dyke, M. Methamphetamine contamination on environmental surfaces caused by simulated smoking of methamphetamine. J. Chem. Health Saf. 2008, 15, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dyke, M.; Martyny, J.W.; Serrano, K.A. Methamphetamine residue dermal transfer efficiencies from household surfaces. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2014, 11, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Symons, B.; Angell, J.; Ross, K.E.; Walker, S. Current practices underestimate environmental exposures to methamphetamine: Inhalation exposures are important. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2021, 31, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, G.; Shakila, N.V.; Parker, K. Accumulation of gas-phase methamphetamine on clothing, toy fabrics, and skin oil. Indoor Air 2015, 25, 405–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Han, G.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Liang, B. Distribution and Contamination Assessment of Soil Heavy Metals in the Jiulongjiang River Catchment, Southeast China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaudreau, M.; Srikanth, P.; Zuidema, C.; Cohen, M.A.; Seto, E.; Simpson, C.D.; Baker, M.G. Assessing fentanyl and methamphetamine in air and on surfaces of transit vehicles. J. Occup. Environ. Hyg. 2025, 22, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naviaux, W.; Hedman, C.; Barkholtz, H. Strategies to detect trace methamphetamine contamination on hard surfaces: Assessing realistic performance of commercially available presumptive tests and a laboratory-based LC-MS/MS method. J. Forensic Sci. 2024, 69, 1011–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.; Kenneally, M.E.; Edwards, J.W.; Walker, G.S. Adverse Health Effects Associated with Living in a Former Methamphetamine Drug Laboratory-Victoria, Australia, 2015. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2017, 65, 1470–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Nair, M.; Miskelly, G. Chemical decontamination of methamphetamine and ephedrine using an activated peroxide-containing cleaning solution. Forensic Sci. Int. 2023, 351, 111816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.; Miskelly, G. A review on the current methods of methamphetamine remediation, their limitations, and chemical degradation techniques that have been investigated. Forensic Chem. 2022, 27, 100399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, M.; Nicolle, S.; Mayo, E.; Chappell, A. Deposition of methamphetamine residues produced by simulated smoking. Forensic Sci. Int. 2022, 338, 111407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boles, T.H.; Wells, M.J. Analysis of amphetamine and methamphetamine in municipal wastewater influent and effluent using weak cation-exchange SPE and LC-MS/MS. Electrophoresis 2016, 37, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponce-Arguello, M.; Abad-Sarango, V.; Crisanto-Perrazo, T.; Toulkeridis, T. Removal of METH through Tertiary or Advanced Treatment in a WWTP. Water 2022, 14, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodayan, A.; Afana, S.; Segura, P.A.; Sultana, T.; Metcalfe, C.D.; Yargeau, V. Linking drugs of abuse in wastewater to contamination of surface and drinking water. Env. Toxicol. Chem. 2016, 35, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borova, V.L.; Maragou, N.C.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Pistos, C.; Thomaidis, N.S. Highly sensitive determination of 68 psychoactive pharmaceuticals, illicit drugs, and related human metabolites in wastewater by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 4273–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Mao, K.; Du, W.; Cai, M.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X. Diluted concentrations of methamphetamine in surface water induce behavior disorder, transgenerational toxicity, and ecosystem-level consequences of fish. Water Res. 2020, 184, 116164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Vieira, D.N.; Magalhães, T. Guidelines for Collection of Biological Samples for Clinical and Forensic Toxicological Analysis. Forensic Sci. Res. 2016, 1, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahmanabadi, L.; Akhgari, M.; Jokar, F.; Sadeghi, H. Quantitative determination of methamphetamine in oral fluid by liquid–liquid extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, R.J.F.; Oyler, J.M.; Joseph, R.E., Jr.; Cone, E.J.; Moolchan, E.T.; Huestis, M.A. Methamphetamine and Amphetamine Pharmacokinetics in Oral Fluid and Plasma after Controlled Oral Methamphetamine Administration to Human Volunteers. Clin. Chem. 2003, 49, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cone, E.J. Saliva testing for drugs of abuse. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1993, 694, 91–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Sanz, J.M.; Sospedra, I.; Ortiz, C.M.; Baladía, E.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Ortiz-Moncada, R. Intended or Unintended Doping? A Review of the Presence of Doping Substances in Dietary Supplements Used in Sports. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen-Meyer, J.; Skotland, T.; Boye, E. Are doping tests in sports trustworthy?: Athletes suffer from insufficiently defined criteria for doping tests: Athletes suffer from insufficiently defined criteria for doping tests. EMBO Rep. 2022, 23, e54431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, A.B.M.; Lobigs, L.; Piper, T.; Champod, C.; Robinson, N. Unravelling the threat of contamination in elite sports: Exploring diverse sources impacting adverse analytical findings and the risk of inadvertent exposure to prohibited substances. Forensic Sci. Int. 2024, 365, 112240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNODC—United Nations Office on Drug and Crime. World Drug Report 2024; United Nations Publications: Vienna, Austria, 2024. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. The Scientific Advances in Psychoactives Versus Artifacts in Amphetamine Analysis. Psychoactives 2025, 4, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4020012
Dinis-Oliveira RJ. The Scientific Advances in Psychoactives Versus Artifacts in Amphetamine Analysis. Psychoactives. 2025; 4(2):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4020012
Chicago/Turabian StyleDinis-Oliveira, Ricardo Jorge. 2025. "The Scientific Advances in Psychoactives Versus Artifacts in Amphetamine Analysis" Psychoactives 4, no. 2: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4020012
APA StyleDinis-Oliveira, R. J. (2025). The Scientific Advances in Psychoactives Versus Artifacts in Amphetamine Analysis. Psychoactives, 4(2), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/psychoactives4020012





