Journal Description
Nanoenergy Advances
Nanoenergy Advances
is an international, peer-reviewed, open access journal on all aspects of nanoenergy published quarterly online by MDPI.
- Open Access— free for readers, with article processing charges (APC) paid by authors or their institutions.
- High Visibility: indexed within ESCI (Web of Science), Scopus and other databases.
- Journal Rank: CiteScore - Q1 (Materials Science (miscellaneous))
- Rapid Publication: manuscripts are peer-reviewed and a first decision is provided to authors approximately 15.2 days after submission; acceptance to publication is undertaken in 3.8 days (median values for papers published in this journal in the second half of 2025).
- Recognition of Reviewers: APC discount vouchers, optional signed peer review, and reviewer names published annually in the journal.
Latest Articles
Research Progress on the Preparation and Performance of Nickel Oxide Electrochromic Films
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 10; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010010 - 5 Mar 2026
Abstract
►
Show Figures
NiO electrochromic films have significant potential for applications in smart windows, displays, energy-efficient buildings, and portable electronics, owing to their excellent electrochemical stability, favorable optical modulation performance, and environmental friendliness. However, several challenges remain, such as limited long-term durability, stability under extreme environmental
[...] Read more.
NiO electrochromic films have significant potential for applications in smart windows, displays, energy-efficient buildings, and portable electronics, owing to their excellent electrochemical stability, favorable optical modulation performance, and environmental friendliness. However, several challenges remain, such as limited long-term durability, stability under extreme environmental conditions, and the cost-effectiveness of large-scale production. Future research efforts should focus on enhancing the cyclic stability and environmental adaptability of NiO films, developing low-cost fabrication techniques, and advancing multifunctional composite materials for smart devices. This review summarizes recent advances in the preparation and performance optimization of NiO electrochromic films. Several key fabrication methods—including magnetron sputtering, hydrothermal synthesis, electrodeposition, chemical bath deposition, sol–gel processing, and spray pyrolysis—are highlighted, and their effects on film structure, thickness uniformity, and optical properties are analyzed. Furthermore, the critical role of different electrolytes (inorganic, organic, and gel-based) in the electrochromic process is discussed, with a comparative evaluation of their influence on the electrochromic performance of NiO films. This article offers a comprehensive overview of the progress in high-performance NiO electrochromic films and provides theoretical insights and technical support for their broader application in renewable energy and smart home technologies.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Metal-Support Interaction in Ni/Biomass-Derived Carbon Catalyst via Atomic Ni-N4 Sites for Boosting Dye-Sensitized Photocatalytic H2 Production
by
Weiying Zhang, Qi Wu, Tian Liao, Niuniu Guo, Shiyu Liu, Shaoqin Peng and Yuexiang Li
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 9; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010009 - 27 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
It is of great significance to prepare carbon-supported non-noble metal catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) via a sustainable method. Meanwhile, the enhanced metal-support interaction (MSI) is vital for promoting the catalytic activity of metal/carbon catalysts. Herein, we prepare a biomass-derived porous carbon-supported
[...] Read more.
It is of great significance to prepare carbon-supported non-noble metal catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) via a sustainable method. Meanwhile, the enhanced metal-support interaction (MSI) is vital for promoting the catalytic activity of metal/carbon catalysts. Herein, we prepare a biomass-derived porous carbon-supported metal Ni catalyst (Ni/APC) with the enhanced MSI via atomic Ni-N4 sites utilizing agaric as a precursor. The highly dispersed Ni-N4 species preferentially adsorb dye molecules and reactant H2O, beneficial to efficient electron transfer and promoting H2O dissociation. Meanwhile, Ni nanoparticles undertake the active sites for H2 desorption. In virtue of the synergistic effect of metal Ni nanoparticles and atomic Ni-N4 for different roles of active sites, Ni/APC catalysts show more effective dye-sensitized photocatalytic HER activities, compared with pure Ni and pure APC. The Ni/APC catalyst with an optimal Ni loading amount exhibits a high AQY of 41.0% with an excellent long-term stability in terms of both HER activity and structure. It is the first report of an application for biomass-derived carbon catalysts in dye-sensitization hydrogen production, and the synergistic effect of atomic Ni and particled Ni on the dye-sensitized photocatalytic HER is deeply investigated. This work provides new deep insight into the design of new non-noble metal/carbon materials by taking advantage of biomass materials.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Recent Research Progress on the Preparation and Applications of Metallic, Semiconducting, and Carbon-Based Photothermal Nanomaterials
by
Xiaojing Wu, Huijuan Dong, Yingni Zhou, Ce Zhou, Hong Xia, Fushen Lu and Muwei Ji
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 8; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010008 - 14 Feb 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Energy obtained by green ways with releasing environmental pollution is still a challenge for sustainable development for model society. Among energy technologies, photothermal conversion by using solar energy has become a new field and a hot topic in recent years. Based on the
[...] Read more.
Energy obtained by green ways with releasing environmental pollution is still a challenge for sustainable development for model society. Among energy technologies, photothermal conversion by using solar energy has become a new field and a hot topic in recent years. Based on the exploration of nanomaterials in the past decades, photothermal nanomaterials by using nanomaterials bring new chances for expending the utilization of green energy with high efficiency, mainly including metal semiconductors and carbon nanomaterials. Their modulated structure for enhancing light absorption, accelerating transformation of photon into heat, and located heat management were also considered important for promoting the utilization of solar energy and therefore, the strategies for designed and controllable preparing of photothermal nanomaterials were also summarized. The applications of photothermal nanomaterials were also reviewed to reveal the new chances for energy conversion engineering or promoting the solar energy utilization of solar energy in some cold regions or somewhere with low solar irradiation.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Metal–Organic Framework-Derived Electrocatalysts for Rechargeable Zinc–Air Batteries
by
Shiqi Zhong, Zhiqiang Liu, Xiaolong Li, Fancheng Meng, Xiangfeng Wei and Jiehua Liu
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 7; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010007 - 13 Feb 2026
Abstract
Rechargeable zinc–air batteries (ZABs) are still impeded by the intrinsically sluggish kinetics of oxygen reduction and evolution reactions (ORR/OER) and by the instability or prohibitive price of state-of-the-art noble metal catalysts. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have recently emerged as versatile sacrificial templates for next-generation
[...] Read more.
Rechargeable zinc–air batteries (ZABs) are still impeded by the intrinsically sluggish kinetics of oxygen reduction and evolution reactions (ORR/OER) and by the instability or prohibitive price of state-of-the-art noble metal catalysts. Metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) have recently emerged as versatile sacrificial templates for next-generation air–cathode electrocatalysts. By programming pyrolytic or chemical conversion pathways, MOFs can be quantitatively transformed into hierarchically porous, heteroatom-doped carbon scaffolds that embed uniform metal, alloy, or metal-oxide nanodomains. The resulting architectures couple metallic conductivity with molecular-scale active site tunability, delivering exceptional ORR/OER activity, stability, and mass transport properties. This review critically examines the most recent advances in MOF-derived electrocatalysts for ZABs, establishing quantitative structure–composition–performance relationships across mono-, bi-, and multi-metallic systems. Emphasis is placed on deciphering how framework topology, metal–ligand coordination, and post-synthetic parameters dictate the density, electronic structure, and accessibility of surface-active moieties during catalyst evolution. We further dissect engineering strategies that enhance intrinsic activity via electronic modulation, bolster durability through encapsulation effects, and optimize hierarchical porosity for rapid O2/water transport. This article concludes by outlining unresolved challenges and future research directions, including atomically precise active site construction, multi-scale compositional control, long-term reversibility under realistic ZABs cycles, scalable and green synthesis, providing a roadmap for translating MOF-derived catalysts from laboratory curiosities to commercially viable air–cathode materials.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Graphene-Based Memristive and Photomemristive Nanosensors for Energy-Efficient Information Processing
by
Gennady N. Panin
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 6; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010006 - 9 Feb 2026
Abstract
The emergence of advanced low-dimensional materials of the graphene family opens up unique opportunities for energy-efficient and fast processing of electrical and optical signals in a wide spectral range from ultraviolet to infrared. Non-volatile resistive states in memristors based on two-dimensional (2D) crystals,
[...] Read more.
The emergence of advanced low-dimensional materials of the graphene family opens up unique opportunities for energy-efficient and fast processing of electrical and optical signals in a wide spectral range from ultraviolet to infrared. Non-volatile resistive states in memristors based on two-dimensional (2D) crystals, 1D nanoribbons, and 0D quantum dots are accessible for control by light and an electric field due to polarization and rearrangement of sp2-sp3 hybridization of carbon atoms, as well as due to photoinduced phase transitions. Two-dimensional materials possess unique structural and electronic properties required for the development of highly efficient nanoenergy memristor devices for low-energy information technology. This article discusses memristors and photomemristors based on graphene, graphene oxide, diamane, and chalcogenide semiconductors such as MoS2, WSe2, MoS2−xOx, which are structurally similar to graphene and have a 2D layered structure. Memristors based on graphene and graphene oxide, bigraphene, and diamane, fabricated using localized electron irradiation, exhibit nonlinear behavior and well-controlled memristive states associated with sp2-sp3 transitions of carbon atoms under low-power conditions. The review highlights the dual role of graphene as an active material and electrode, as well as the redox control mechanism. Due to a well-controlled redox process, graphene-based devices exhibit the dynamic behavior required for neuromorphic computing directly in the sensor, reducing the energy and time costs associated with data processing. Neuromorphic computing in a photomemristor-based sensor enables the creation of a compact nano-energy system for real-time information recognition in a wide spectral range, similar to biological vision, for use in self-driving cars, personalized medicine, and other applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Materials for Renewable and Sustainable Energy Systems)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Novel TiO2 Nanotube-Based Electrocatalysts for the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction in Alkaline Medium
by
Bogdan-Ovidiu Taranu, Radu Banica and Florina Stefania Rus
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 5; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010005 - 12 Jan 2026
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increasing global energy demand and its negative environmental impact created the need for substantial changes in the energy infrastructure. A hydrogen-based infrastructure appears to be the most promising way to secure a clean and safe energy future. Water electrolysis is a method
[...] Read more.
The increasing global energy demand and its negative environmental impact created the need for substantial changes in the energy infrastructure. A hydrogen-based infrastructure appears to be the most promising way to secure a clean and safe energy future. Water electrolysis is a method that can be used to generate green hydrogen, but suitable electrocatalysts are required for large-scale applications. This work investigates the electrocatalytic activity of electrodes modified with novel TiO2 nanotube-based electrocatalysts for water electrolysis. The focus was on the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and the electrodes that displayed the highest activity were the ones obtained with the procedure consisting of the growth of TiO2 nanotubes on a Ti plate by anodization, the subsequent deposition of MoO2 and Ni(OH)2, and a thermal treatment performed under different conditions. The results of the HER experiments performed in a strong alkaline environment showed that the electrode obtained via vacuum heat treatment exhibited the lowest overpotential value, of 238 mV at i = −10 mA/cm2. Furthermore, the electrode was electrochemically stable, and inter-electrode reproducibility tests revealed only a small variation of the HER overpotential.
Full article

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Nano-Enhanced Binary Eutectic PCM with SiC for Solar HDH Desalination Systems
by
Rahul Agrawal, Kashif Mushtaq, Daniel López Pedrajas, Iqra Irfan and Breogán Pato-Doldán
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 4; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010004 - 9 Jan 2026
Abstract
Freshwater scarcity is increasing day by day and has already reached a threatening level, especially in remotely populated areas. One of the technological solutions to this rising concern could be the use of the solar-based humidification–dehumidification (SHDH) method for water desalination. This technology
[...] Read more.
Freshwater scarcity is increasing day by day and has already reached a threatening level, especially in remotely populated areas. One of the technological solutions to this rising concern could be the use of the solar-based humidification–dehumidification (SHDH) method for water desalination. This technology is a promising solution but has challenges such as solar intermittency. This challenge can be solved by integrating SHDH with the phase change material as a solar energy storage medium. Therefore, a novel nano-enhanced binary eutectic phase change material (NEPCM) was developed in this project. PCM consisting of 70 wt.% stearic acid (ST) and 30 wt.% suberic acid (SBU) with a varying concentration of silicon carbide (SiC) nanoparticles (NPs) (0.1 to 3 wt.%) was synthesized specifically considering the need of SHDH application. The systematic thermophysical characterization was conducted to investigate their energy storage capacity, thermal durability, and performance consistency over repeated cycles. DSC analysis revealed that the addition of SiC NPs preserved the thermal stability of the NEPCM, while the phase transition temperature remained nearly unchanged with a variation of less than 0.74%. The value of latent heat is inversely related to the nanoparticle concentration, i.e., from 142.75 kJ/kg for the base PCM to 131.24 kJ/kg at 3 wt.% loading. This corresponds to reductions in latent heat ranging between 0.98% and 8.06%. The FTIR measurement confirms that no chemical reactions or no new functional groups were formed. All original functional groups of ST and SBU remained intact, showing that incorporating the SiC NP to the PCM lead to physical interactions (e.g., hydrogen bonding or surface adsorption). The TGA analysis showed that the SiC NPs in the NEPCM act as supporting material, and its nano-doping enhanced the final degradation temperature and thermal stability. There was negligible change in thermal conductivity for nanoparticle loadings of 0.1% and 0.4%; however, it increased progressively by 5.2%, 10.8%, 23.12%, and 25.8% at nanoparticle loadings of 0.7%, 1%, 2%, and 3%, respectively, at 25 °C. Thermal reliability was analyzed through a DSC thermal cycling test which confirmed the suitability of the material for the desired applications.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Innovative Materials for Renewable and Sustainable Energy Systems)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Polybenzimidazole Membranes Modified with Porous Aromatic Frameworks: Synthesis, Structure, Mechanical and Transport Properties
by
Dmitry D. Spasov, Ruslan M. Mensharapov, Matvey V. Sinyakov, Darya E. Grineva, Nataliya A. Ivanova, Xiang Li, Chuanyu Sun, Leonid A. Kulikov, Daria A. Makeeva and Sergey A. Grigoriev
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 3; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010003 - 8 Jan 2026
Cited by 1
Abstract
High-temperature proton exchange membrane systems (HT-PEM) based on polybenzimidazole (PBI) membranes are a promising technology offering significant advantages over their low-temperature counterparts. A key challenge limiting its long-term durability is the leaching of phosphoric acid (PA) from the membrane during operation. This work
[...] Read more.
High-temperature proton exchange membrane systems (HT-PEM) based on polybenzimidazole (PBI) membranes are a promising technology offering significant advantages over their low-temperature counterparts. A key challenge limiting its long-term durability is the leaching of phosphoric acid (PA) from the membrane during operation. This work introduces, for the first time, the strategy of modifying polybenzimidazole (PBI) membranes with amino-functionalized porous aromatic frameworks (PAF-20-NH2) to fundamentally enhance their PA retention and operational stability, a critical challenge for high-temperature PEM technologies. We propose that the synergistic combination of the framework’s nanoscale porosity and the specific interaction of its amino groups create an unprecedented network for acid immobilization via reinforced hydrogen bonding. A comprehensive study of the membranes’ physicochemical and structural properties reveals that PAF-20-NH2 modification results in a significant and quantitatively demonstrated improvement in acid retention capacity, directly translating into a notable increase in proton conductivity compared to both pristine PBI and membranes modified with the non-functionalized PAF-20. These findings establish a new, highly effective pathway for the rational design of next-generation high-performance PBI-based membranes.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessReview
Advanced Layer Fabrication Technologies in Solid Oxide Fuel Cells: From Traditional Methods to Additive and Thin-Film Strategies
by
Serikzhan Opakhai, Asset Kabyshev, Marzhan Kubenova, Zhassulan Zeinulla, Bakytbek Mauyey and Saira Sakhabayeva
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 2; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010002 - 25 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This review examines modern approaches to layer formation in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), focusing on traditional, thin-film, and additive manufacturing methods. A systematic comparison of technologies, including slip casting, screen printing, CVD, PLD, ALD, HiPIMS, inkjet, aerosol, and microextrusion printing, is provided.
[...] Read more.
This review examines modern approaches to layer formation in solid oxide fuel cells (SOFCs), focusing on traditional, thin-film, and additive manufacturing methods. A systematic comparison of technologies, including slip casting, screen printing, CVD, PLD, ALD, HiPIMS, inkjet, aerosol, and microextrusion printing, is provided. It is shown that traditional methods remain technologically robust but are limited in their capabilities for miniaturization and interfacial architecture design. Modern thin-film and additive approaches provide high spatial accuracy, improved ion-electron characteristics, and flexibility in the design of multilayer structures; however, they require addressing issues related to scalability, ink stability, interfacial compatibility, and reproducibility. Particular attention is paid to interfacial engineering methods, such as functionally graded layers, nanostructured infiltration, and temperature-controlled 3D printing. Key challenges are discussed, including thermal instability of materials, the limited gas impermeability of ultra-thin electrolytes, and degradation during long-term operation. Development prospects lie in the integration of hybrid methods, the digitalization of deposition processes, and the implementation of intelligent control of printing parameters. The presented analysis forms the basis for further research into the scalable and highly efficient production of next-generation SOFCs designed for low-temperature operation and long-term operation in future energy systems.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Cellulose-Based Sustainable Photo-Triboelectric Hybrid Nanogenerator for High-Performance Energy Harvesting and Smart Control Systems
by
Zhen Tian, Jiacheng Liu, Chang Ding, Changyu Yang, Muqing Chen, Xiaoming Chen, Qiang Liu and Li Su
Nanoenergy Adv. 2026, 6(1), 1; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv6010001 - 23 Dec 2025
Abstract
With the advancement of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, flexible sensors with dual optoelectronic sensing modes have emerged as a research hotspot for next-generation smart devices, further driving the urgent demand for environmentally friendly functional materials. Here, we innovatively integrated wastepaper recycling technology
[...] Read more.
With the advancement of Internet of Things (IoT) technology, flexible sensors with dual optoelectronic sensing modes have emerged as a research hotspot for next-generation smart devices, further driving the urgent demand for environmentally friendly functional materials. Here, we innovatively integrated wastepaper recycling technology with a polyethyleneimine (PEI)-assisted pulping strategy to develop a novel cellulose-based sustainable photo-triboelectric hybrid nanogenerator (PT-HNG). Based on the working mechanism of a freestanding triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG), the PT-HNG can directly convert pressure stimuli into electrical energy and triboelectrification-induced electroluminescence (TIEL) signals. It achieves luminescence brightness of 0.06 mW cm−2 (3.84 cd m−2) and simultaneously delivers excellent electrical output performance (172.4 V, 6.36 μA, 43.7 nC) under sliding motion. More importantly, compatible with existing industrial papermaking processes, the PT-HNG is scalable for large-scale production. By combining PT-HNG with deep learning algorithms, a handwritten e-book system based on trajectory recognition was constructed, with a recognition accuracy of up to 95.5%. In addition, real-time intelligent control of PowerPoint presentations via PT-HNG was demonstrated. This study provides a new pathway for converting wastepaper into intelligent products and presents a novel idea for the interdisciplinary integration of the circular economy and advanced electronic technology.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Comparative Performance Analysis of Fluoride-Decorated Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 as Cathode Materials for Li Batteries
by
Ashraf E. Abdel-Ghany, Somia M. Abbas, Ahmed M. Hashem, Alain Mauger and Christian M. Julien
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 23; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040023 - 17 Dec 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
This work deals with the comparative analysis of fluoride coatings, i.e., 5 wt.% AlF3 and LiF, applied as surface layer of Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 (LNCM) layered oxides synthesized via facile and cost-effective sol–gel route.
[...] Read more.
This work deals with the comparative analysis of fluoride coatings, i.e., 5 wt.% AlF3 and LiF, applied as surface layer of Li-rich Li1.2Ni0.13Co0.13Mn0.54O2 (LNCM) layered oxides synthesized via facile and cost-effective sol–gel route. The detailed structural and morphological characterizations demonstrate that AlF3 and LiF deposits have a pivotal role in enhancing the electrochemical properties of LNCM. These electrochemical properties include galvanostatic charge–discharge (GCD), differential capacity (dQ/dV), electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS), and area-specific impedance (ASI). A much lower decay of the discharge capacity of 0.22 and 0.25 mAh g−1 per cycle was obtained for AlF3- and LiF-coated LMNC, respectively, after 100 charge/discharge cycles at 0.1 C compared with 0.42 mAh g−1 per cycle for pristine LNCM. Results evidence the non-evolution of the charge transfer resistance, enhanced lithium-ion kinetics and stabilization of electrode/electrolyte interface during cycling.
Full article
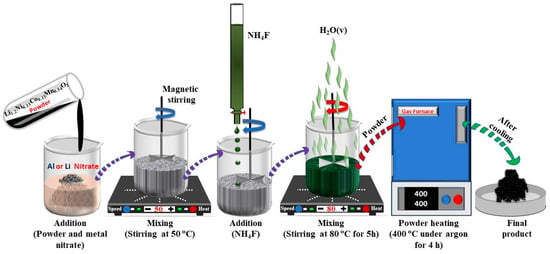
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Layer-by-Layer Hybrid Film of PAMAM and Reduced Graphene Oxide–WO3 Nanofibers as an Electroactive Interface for Supercapacitor Electrodes
by
Vanderley F. Gomes Junior, Danilo A. Oliveira, Paulo V. Morais and José R. Siqueira Junior
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 22; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040022 - 12 Dec 2025
Abstract
Tungsten oxide (WO3) nanostructures have emerged as promising electroactive materials due to their high pseudocapacitance, structural versatility, and chemical stability, while reduced graphene oxide (rGO) provides excellent electrical conductivity and surface area. The strategic combination of these nanomaterials in hybrid electrodes
[...] Read more.
Tungsten oxide (WO3) nanostructures have emerged as promising electroactive materials due to their high pseudocapacitance, structural versatility, and chemical stability, while reduced graphene oxide (rGO) provides excellent electrical conductivity and surface area. The strategic combination of these nanomaterials in hybrid electrodes has gained attention for enhancing the energy storage performance of supercapacitors. In this work, we report the fabrication and electrochemical performance of nanostructured multilayer films based on the electrostatic Layer-by-Layer (LbL) self-assembly of poly (amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers alternated with tungsten oxide (WO3) nanofibers dispersed in reduced graphene oxide (rGO). The films were deposited onto indium tin oxide (ITO) substrates and subsequently subjected to electrochemical reduction. UV-Vis spectroscopy confirmed the linear growth of the multilayers, while atomic force microscopy (AFM) revealed homogeneous surface morphology and thickness control. Electrochemical characterization by cyclic voltammetry (CV) and galvanostatic charge–discharge (GCD) revealed a predominantly electrical double-layer capacitive (EDLC) behavior. From the GCD measurements (PAMAM/rGO-WO3)20 films achieved an areal capacitance of ≈2.20 mF·cm−2, delivering an areal energy density of ≈0.17 µWh·cm−2 and an areal power density of ≈2.10 µW·cm−2, demonstrating efficient charge storage in an ultrathin electrode architecture. These results show that the synergistic integration of PAMAM dendrimers, reduced graphene oxide, and WO3 nanofibers yields a promising strategy for designing high-performance electrode materials for next-generation supercapacitors.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessEditorial
Mechanism-Guided Materials and Structural Design for High-Performance Nanogenerators
by
Ya Yang
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 21; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040021 - 10 Dec 2025
Abstract
The advancement of sensor systems that facilitate our daily lives relies on small, disposable batteries, which contribute to environmental pollution [...]
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Celebrating the 18th Anniversary of the Invention of the First Nanogenerators)
Open AccessArticle
Laser-Fabricated GO/ZIF-67 Hybrid Nanocomposites for High-Performance 3D-Printed Supercapacitors
by
Mahshid Mokhtarnejad, Erick L. Ribeiro, Karen Y. Patino Jaimes, Mariana Milano-Benitez and Bamin Khomami
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 20; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040020 - 4 Dec 2025
Abstract
This study introduces a modified Laser Ablation Synthesis in Solution (LASiS), a surfactant-free and rapid synthesis approach that enables uniform MOF nucleation on graphene oxide (GO) and precise control over crystallinity, for fabricating graphene oxide (GO)-integrated cobalt-based ZIF-67 hybrid nanocomposites tailored for supercapacitor
[...] Read more.
This study introduces a modified Laser Ablation Synthesis in Solution (LASiS), a surfactant-free and rapid synthesis approach that enables uniform MOF nucleation on graphene oxide (GO) and precise control over crystallinity, for fabricating graphene oxide (GO)-integrated cobalt-based ZIF-67 hybrid nanocomposites tailored for supercapacitor applications. By tuning LASiS parameters, we precisely controlled framework size, morphology, and crystallinity, enabling sustainable and scalable production. The incorporation of GO during synthesis markedly enhances the uniform dispersion of ZIF-67 frameworks, minimizing aggregation and establishing interconnected conductive pathways via strong
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Upcycling Medical Tablet Blister Waste into High-Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Sustainable Energy Harvesting
by
Vikram Lakshmi Suneetha, Velpula Mahesh, Khanapuram Uday Kumar and Rajaboina Rakesh Kumar
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 19; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040019 - 1 Dec 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The increasing accumulation of medical waste, especially discarded pharmaceutical blister packs, poses both environmental risks and missed opportunities for resource recovery. In this work, we demonstrate, for the first time, the direct upcycling of tablet blister waste into a potential frictional layer in
[...] Read more.
The increasing accumulation of medical waste, especially discarded pharmaceutical blister packs, poses both environmental risks and missed opportunities for resource recovery. In this work, we demonstrate, for the first time, the direct upcycling of tablet blister waste into a potential frictional layer in triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs). The polymer structure of blister packs, combined with Silicone rubber as a counter frictional layer, enabled the fabrication of durable TENG devices (TS-TENGs). Systematic electrical testing revealed that the TS-TENG achieved an open-circuit voltage of approximately 300 V, a short-circuit current of about 40 μA, and a peak power density of 3.54 W/m2 at an optimal load resistance of 4 MΩ. The devices maintained excellent stability over 10,000 mechanical cycles, confirming their durability. Practical demonstrations included powering 240 LEDs, four LED lamps, and portable electronic devices, such as calculators and hygrometers, through capacitor charging. This study shows that not only can tablet blister waste be used as a triboelectric material but it also presents a sustainable method to reduce pharmaceutical waste while advancing self-powered systems. The approach offers a scalable and low-cost means to integrate medical waste management with renewable energy technologies.
Full article
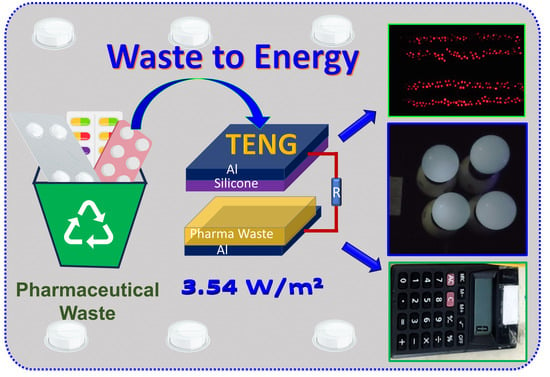
Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
An AI-Driven TiO2-NiFeC-PEM Microbial Electrolyzer for In Situ Hydrogen Generation from POME Using a ZnO/PVA-EDLOSC Nanocomposite Photovoltaic Panel
by
Ataur Rahman Md, Mohamad Qatu, Labib Hasan, Rafia Afroz, Mehdi Ghatus and Sany Ihsan
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 18; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040018 - 26 Nov 2025
Abstract
Electrolysis and biological processes, such as fermentation and microbial electrolysis cells, offer efficient hydrogen production alongside wastewater treatment. This study presents a novel microbial electrolyzer (ME) comprising a titanium dioxide (TiO2) anode, a nickel–iron–carbon (NiFeC) cathode, and a cellulose nanocrystal proton
[...] Read more.
Electrolysis and biological processes, such as fermentation and microbial electrolysis cells, offer efficient hydrogen production alongside wastewater treatment. This study presents a novel microbial electrolyzer (ME) comprising a titanium dioxide (TiO2) anode, a nickel–iron–carbon (NiFeC) cathode, and a cellulose nanocrystal proton exchange membrane (CNC-PEM) designed to generate hydrogen from palm oil mill effluent (POME). The system is powered by a 12 V electric double-layer organic supercapacitor (EDLOSC) integrated with a ZnO/PVA-based solar thin film. Power delivery to the TiO2-NiFeC-PEM electrolyzer is optimized using an Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS). Laboratory-scale pilot tests demonstrated effective degradation of POME’s organic content, achieving a hydrogen yield of approximately 60%. Additionally, the nano-structured ZnO/CuO–ZnO/PVA solar film facilitated stable power supply, enhancing in situ hydrogen production. These results highlight the potential of the EDLOSC-encased ZnO/PVA-powered electrolyzer as a sustainable solution for hydrogen generation and industrial wastewater treatment.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials)
►▼
Show Figures

Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
Electronic Structure Regulation Enhances the Urea Oxidation Reaction Performance of the NiCo-MOF Catalyst
by
Lang Yao, Yanzhi Yang, Sirong Li and Xuechun Xiao
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 17; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040017 - 6 Nov 2025
Cited by 1
Abstract
In this paper, spherical-shaped catalytic materials with needle-like stacking structures were synthesized in situ on the foam nickel substrate using the hydrothermal method, resulting in the NiM (M = Co, Mn, W, Zn)-MOF series. Furthermore, the catalyst with the best performance was obtained
[...] Read more.
In this paper, spherical-shaped catalytic materials with needle-like stacking structures were synthesized in situ on the foam nickel substrate using the hydrothermal method, resulting in the NiM (M = Co, Mn, W, Zn)-MOF series. Furthermore, the catalyst with the best performance was obtained by adjusting the ratio of metal elements. Electrochemical tests show that NiCo-MOF (Ni: Co = 1:2) has the best electrocatalytic performance. During the UOR process, NiCo-MOF exhibits the optimal performance in 1 M KOH and 0.5 M urea solution, with a potential of only 1.33 V at a current density of 10 mA/cm2. The improvement in the activity of NiCo-MOF can be attributed to the synergistic effect between the Ni and Co bimetals, which leads to an increase in the electron transfer rate, the exposure of active sites, and an improvement in conductivity. Moreover, metal–organic framework materials are widely used as electrocatalysts due to their compositional diversity, rich pore structures, and high specific surface areas. Meanwhile, NiCo-MOF was used as a UOR and HER catalyst to assist the overall water decomposition with urea, and it showed relatively excellent performance. Only a voltage of 1.56 V was required to drive the current density of 10 mA/cm2 of the UOR || HER system. Therefore, the synthesized NiCo-MOF catalyst plays an important role in improving the efficiency of hydrogen production from water electrolysis and has promising sustainable application prospects.
Full article
(This article belongs to the Special Issue Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials)
►▼
Show Figures
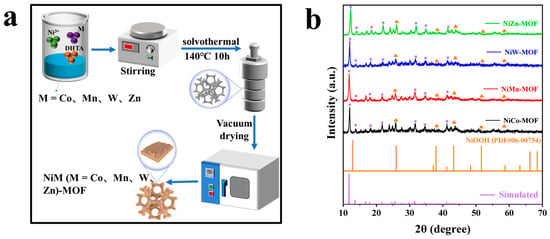
Figure 1
Open AccessReview
Liquid Metal Nanoenergy Systems: Progress and Challenges
by
Yibing Ma, Jianye Gao, Yiyue Tao, Chen Hua, Tangzhen Guan, Cai Cheng, Yujia Song and Jing Liu
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 16; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040016 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
The pursuit of advanced energy technologies has intensified the focus on innovative functional materials. Low-melting-point liquid metals (LMs), particularly Ga-based alloys, have emerged as a promising platform due to their unique combination of metallic conductivity, fluidity, and biocompatibility. Nanoscaling LMs to create nano-liquid
[...] Read more.
The pursuit of advanced energy technologies has intensified the focus on innovative functional materials. Low-melting-point liquid metals (LMs), particularly Ga-based alloys, have emerged as a promising platform due to their unique combination of metallic conductivity, fluidity, and biocompatibility. Nanoscaling LMs to create nano-liquid metals (nano-LMs) further unlocks extraordinary properties, including electrical duality, enhanced surface reactivity, tunable plasmonics, and remarkable deformability, surpassing the limitations of their bulk counterparts. This review provides a comprehensive overview of the recent progress in nano-LM-based energy technology. We begin by delineating the fundamental properties of LMs and the novel characteristics imparted at the nanoscale. Subsequently, we critically analyze mainstream synthesis strategies, such as sonication, mechanical shearing, and microfluidics. The core of the review focuses on innovative applications in energy storage devices, energy harvesting system, and catalysis for energy conversion. Finally, we discuss persistent challenges in stability, scalable synthesis, and mechanistic understanding, while offering perspectives on future research directions aimed at realizing the full potential of nano-LMs in next-generation intelligent and sustainable energy systems.
Full article
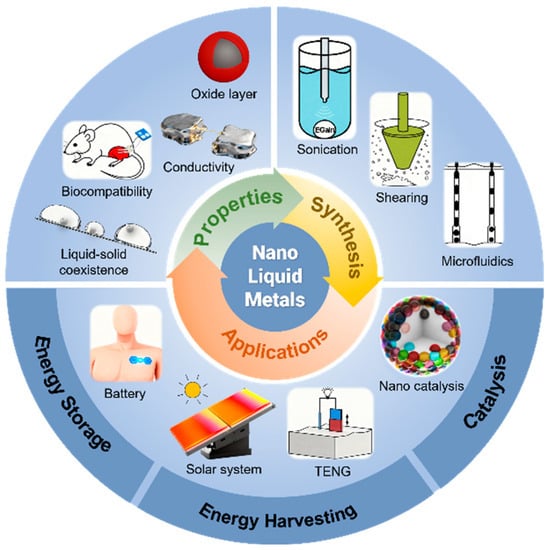
Figure 1
Open AccessArticle
A Layered Electrode Solid–Oil Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Real-Time Monitoring of Oil Leakage and Emulsification
by
Shuyao Li, Yuxuan Lai, Zujian Gong and Huangxuan Zhang
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 15; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040015 - 4 Nov 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Real-time monitoring of lubricants is crucial to the development of transport vehicles. Accidental and fatal failures of components in vehicles occur every day, which threaten the service life of equipment. Inspired by the work of solid–liquid triboelectric nanogenerators (S-L-TENG), we propose a method
[...] Read more.
Real-time monitoring of lubricants is crucial to the development of transport vehicles. Accidental and fatal failures of components in vehicles occur every day, which threaten the service life of equipment. Inspired by the work of solid–liquid triboelectric nanogenerators (S-L-TENG), we propose a method to retrofit a self-powered sensor for real-time monitoring of lubricating oil leakage. The previous work does not have a systematic study on the influence of various modification methods on the electrification signal of oil-solid contact. This study identifies an optimal modification method with the highest electrification performance by comparing the energizing signals of different modification methods, which provides a new approach for the real-time monitoring of lubricating oil leakage and the detection of lubricating oil impurities.
Full article

Graphical abstract
Open AccessArticle
Enhanced Performance of TiO2 Composites for Solar Cells and Photocatalytic Hydrogen Production
by
Xue Bai, Jian Chen, Shengxi Du and Yan Xiong
Nanoenergy Adv. 2025, 5(4), 14; https://doi.org/10.3390/nanoenergyadv5040014 - 28 Oct 2025
Abstract
►▼
Show Figures
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is widely used in solar cells and photocatalysts, given its excellent photoactivity, low cost, and high structural, electronic, and optical stability. Here, a novel TiO2 composite was prepared by coating TiO2 inverse opal (IO) with TiO
[...] Read more.
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is widely used in solar cells and photocatalysts, given its excellent photoactivity, low cost, and high structural, electronic, and optical stability. Here, a novel TiO2 composite was prepared by coating TiO2 inverse opal (IO) with TiO2 nanorods (NRs). With a porous three-dimensional network structure, the composite exhibited higher light absorption; enhanced the separation of the electron–hole pairs; deepened the infiltration of the electrolyte; better transported and collected charge carriers; and greatly improved the power conversion efficiency (PCE) of the quantum-dot sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs) based on it, while also boosting its own photocatalytic hydrogen generation efficiency. A very high PCE of 12.24% was achieved by QDSSCs utilizing CdS/CdSe sensitizer. Furthermore, the TiO2 composite exhibited high photocatalytic activity with a H2 release rate of 1080.2 μ mol h−1 g−1, several times that of bare TiO2 IO or TiO2 NRs.
Full article

Figure 1
Highly Accessed Articles
Latest Books
E-Mail Alert
News
6 November 2025
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science
MDPI Launches the Michele Parrinello Award for Pioneering Contributions in Computational Physical Science

9 October 2025
Meet Us at the 3rd International Conference on AI Sensors and Transducers, 2–7 August 2026, Jeju, South Korea
Meet Us at the 3rd International Conference on AI Sensors and Transducers, 2–7 August 2026, Jeju, South Korea

Topics
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Materials, Micromachines, Nanoenergy Advances, Sensors
Advanced Energy Harvesting Technology, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Mengying Xie, Kean C. Aw, Junlei Wang, Hailing Fu, Wee Chee GanDeadline: 30 June 2026
Topic in
Applied Sciences, Energies, Materials, Nanoenergy Advances, Nanomaterials
Nanomaterials for Energy and Environmental Applications, 2nd Edition
Topic Editors: Robert A. Varin, Tao ChenDeadline: 31 October 2026

Conferences
Special Issues
Special Issue in
Nanoenergy Advances
Hybrid Energy Storage Systems Based on Nanostructured Materials
Guest Editor: Verónica Montes GarcíaDeadline: 30 June 2026
Special Issue in
Nanoenergy Advances
Innovative Materials for Renewable and Sustainable Energy Systems
Guest Editors: Carmen M. Rangel, Joao Ventura, Elby TitusDeadline: 31 December 2026









