- Article
Categorical Prediction of the Anthropization Index in the Lake Tota Basin, Colombia, Using XGBoost, Remote Sensing and Geomorphometry Data
- Ana María Camargo-Pérez,
- Iván Alfonso Mayorga-Guzmán and
- Yeison Alberto Garcés-Gómez
- + 2 authors
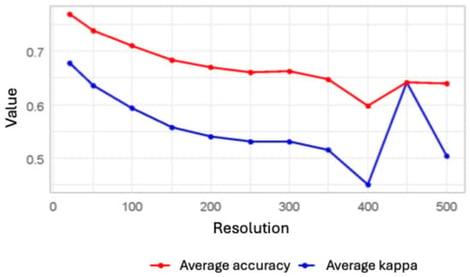
This study presents a machine learning framework to automate the mapping of the Integrated Relative Anthropization Index (INRA, by its Spanish acronym). A predictive model was developed to estimate the degree of anthropization in the basin of Lake Tota, Colombia, using the XGBoost machine learning algorithm and remote sensing data. This research, part of a broader wetland monitoring project, aimed to identify the optimal spatial scale for analysis and the most influential predictor variables. Methodologically, models were tested at resolutions from 20 m to 500 m. The results indicate that a 50 m spatial scale provides the optimal balance between predictive accuracy and computational efficiency, achieving robust performance in identifying highly anthropized areas (sensitivity: 0.83, balanced accuracy: 0.91). SHAP analysis identified proximity to infrastructure and specific Sentinel-2 spectral bands as the most influential predictors in the INRA emulation model. The main result is a robust, replicable model that produces a detailed anthropization map, serving as a practical tool for monitoring human impact and supporting sustainable management strategies in threatened high-Andean ecosystems. Rather than a simple classification exercise, this approach serves to deconstruct the INRA methodology, using SHAP analysis to reveal the latent non-linear relationships between spectral variables and human impact, providing a transferable and explainable monitoring tool.
27 January 2026