Exclusive Papers Collection of Editorial Board Members of Disabilities
A topical collection in Disabilities (ISSN 2673-7272).
Viewed by 74053
Share This Topical Collection
Editor
 Prof. Dr. Reinie Cordier
Prof. Dr. Reinie Cordier
 Prof. Dr. Reinie Cordier
Prof. Dr. Reinie Cordier
E-Mail
Website
Guest Editor
Curtin School of Allied Health, Faculty of Health Sciences, Curtin University, Perth, WA 6102, Australia
Interests: social inclusion; measurement; instrument development; developmental disability; child mental health; development of psychosocial interventions
Topical Collection Information
Dear Colleagues,
As the Editor-in-Chief of Disabilities, I am pleased to announce this Special Issue titled “Exclusive Papers Collection of Editorial Board Members of Disabilities”. This Special Issue will be a collection of high-quality papers from only the Editorial Board Members of Disabilities. Both original research articles and comprehensive review papers are welcome. The papers will be published free of charge and with full open access after peer review.
Prof. Dr. Reinie Cordier
Guest Editor
Manuscript Submission Information
Manuscripts should be submitted online at www.mdpi.com by registering and logging in to this website. Once you are registered, click here to go to the submission form. All submissions that pass pre-check are peer-reviewed. Accepted papers will be published continuously in the journal (as soon as accepted) and will be listed together on the collection website. Research articles, review articles as well as short communications are invited. For planned papers, a title and short abstract (about 250 words) can be sent to the Editorial Office for assessment.
Submitted manuscripts should not have been published previously, nor be under consideration for publication elsewhere (except conference proceedings papers). All manuscripts are thoroughly refereed through a single-blind peer-review process. A guide for authors and other relevant information for submission of manuscripts is available on the Instructions for Authors page. Disabilities is an international peer-reviewed open access semimonthly journal published by MDPI.
Please visit the Instructions for Authors page before submitting a manuscript.
The Article Processing Charge (APC) for publication in this open access journal is 1200 CHF (Swiss Francs).
Submitted papers should be well formatted and use good English. Authors may use MDPI's
English editing service prior to publication or during author revisions.
Keywords
- disability theory
- social inclusion
- participation
- enabling practices
- human rights
Published Papers (14 papers)
Open AccessConcept Paper
Reflections on the Quality of Life of Adults with Down Syndrome from an International Congress
by
Rachel Spencer, Robin Gibson, Leigh Creighton, Catherine Watson and Roy McConkey
Viewed by 656
Abstract
People with Down Syndrome often experience more barriers to achieving a good quality of life compared to people without disabilities. A lot of the existing research has focused on the views of parents and professionals, rather than directly including the voices and perspectives
[...] Read more.
People with Down Syndrome often experience more barriers to achieving a good quality of life compared to people without disabilities. A lot of the existing research has focused on the views of parents and professionals, rather than directly including the voices and perspectives of people with Down Syndrome themselves. We wanted to find out how this might be done. At the 2024 World Down Syndrome Conference, over 140 adults with Down Syndrome came together at a one-day Forum to talk about their lives—aspects that are going well and what could be better. The goal was to hear directly from them. This article explains how the Forum was run so that others with Down Syndrome can use a similar process. We describe how Artificial Intelligence (AI) was used to assist the authors in organising and sharing the information from participants, such as grouping what people said into different themes and helping to create plain language reports. This process worked. Eight key themes were found that could help people to have a good life, such as having good relationships with family and friends; having a job; making personal choices; and being respected and included. The list was longer than previously reported in other studies. The Forum gave valuable insights and helped us think of new ideas for supporting people with Down Syndrome to speak up for themselves. Used thoughtfully, AI (Artificial Intelligence) could be a helpful tool in the future to help these people share their experiences and needs. More research is needed to understand how people with Down Syndrome can be more involved in making changes through advocacy projects where they take an active role.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Perspectives on Mainstreaming Special Education: How Principals’ and Counselors’ Attitudes Relate to Their Professional Well-Being
by
Galia Taller Azulay, Tali Heiman and Dorit Olenik Shemesh
Viewed by 915
Abstract
The current study examined the attitudes of elementary and middle school principals and school counselors toward including students with special needs in regular classrooms. 243 participants completed questionnaires on their self-efficacy, job satisfaction, stress, and attitudes toward inclusion. Additionally, 22 semi-structured interviews were
[...] Read more.
The current study examined the attitudes of elementary and middle school principals and school counselors toward including students with special needs in regular classrooms. 243 participants completed questionnaires on their self-efficacy, job satisfaction, stress, and attitudes toward inclusion. Additionally, 22 semi-structured interviews were conducted to gain a deeper understanding of how principals and counselors deal with the inclusion of students with special needs in their school. The study’s findings reveal a difference between middle school counselors and principals and those in elementary schools in terms of the desire for inclusion. It was also found that the less the counselors believe in themselves, the less they are in favor of inclusion, while the more satisfied they are with their work, the more they support inclusion. Qualitative analysis brought up various difficulties in the inclusion process.
Full article
Open AccessReview
College Students with ADHD: A Selective Review of Qualitative Studies
by
Shira L. Cohen, Katie Shavel and Benjamin J. Lovett
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 18229
Abstract
Diagnoses of ADHD in adults continue to increase, and the number of college students with ADHD has risen in particular. Qualitative research on this population has been common, but it is not clear what conclusions can be drawn from this research base. We
[...] Read more.
Diagnoses of ADHD in adults continue to increase, and the number of college students with ADHD has risen in particular. Qualitative research on this population has been common, but it is not clear what conclusions can be drawn from this research base. We conducted a review of the qualitative research on college students with ADHD over a 20-year period (2002–2021). A systematic search yielded 41 papers that were reviewed in detail. Studies were grouped into four topic areas, with the most researched area being the college experience for these students. Most sample sizes were small, with a median of 10 participants, and most studies used students’ self-reports of having ADHD as the sole method of diagnosis identification/verification. Very few studies (7.3%) included a comparison group of students without disabilities. These results suggest that the qualitative research base on college students with ADHD has significant limitations, including difficulties with generalization, uncertainty regarding diagnostic accuracy, and an inability to make comparative statements about students with vs. without ADHD.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessStudy Protocol
Strategies for Increasing Accessibility and Equity in Health and Human Service Educational Programs: Protocol for a National, Mixed Methods Study
by
Tal Jarus, Lindsay Stephens, Tracey Edelist, Erika Katzman, Cheryl Holmes, Stuart Kamenetsky, Iris Epstein and Shahbano Zaman
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 3017
Abstract
Introduction: Despite legislation mandating accommodation policies in higher education, support for learners with disabilities is often not implemented within health and human services (HHS) education programs, particularly in fieldwork settings. This paper will describe the protocol of a study aimed to (a) explore
[...] Read more.
Introduction: Despite legislation mandating accommodation policies in higher education, support for learners with disabilities is often not implemented within health and human services (HHS) education programs, particularly in fieldwork settings. This paper will describe the protocol of a study aimed to (a) explore challenges and opportunities of current practices for supporting learners living with disabilities in a fieldwork context, across 10 HHS programs; and (b) develop, pilot and evaluate innovative accessibility practices to decrease existing barriers faced by educators and learners. Method: Using a critical disability studies framework, we designed a national, multi-profession, mixed methods design. Data are collected through interviews (qualitative) and an online survey (quantitative) that participants complete prior to the interview. Additionally, an online mapping diary is used to facilitate the understanding of accessibility in fieldwork education from the perspective of the learners. Participants include learners living with disabilities, academic fieldwork coordinators, fieldwork educators, accessibility advisors and professional organizations representatives. Implications: Learners living with disabilities navigate systemic barriers: (a) the additional “work of being a disabled learner”, during a rigorous academic program, and (b) absent or inadequate fieldwork accommodations. Exploring those systemic barriers as faced by all partners offers the potential to develop strategies and tools to foster inclusive and accessible HHS education.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Feasibility of a Peer-Led Leisure Time Physical Activity Program for Manual Wheelchair Users Delivered Using a Smartphone
by
Krista L. Best, Shane N. Sweet, Jaimie F. Borisoff, Kelly P. Arbour-Nicitopoulos and François Routhier
Cited by 1 | Viewed by 2037
Abstract
Active living lifestyles for wheelchair users (ALLWheel) was developed to improve leisure time physical activity (LTPA). The purpose of this study was to assess the feasibility of the ALLWheel program. In a pilot pre-post design, 12 manual wheelchair users in three Canadian cities
[...] Read more.
Active living lifestyles for wheelchair users (ALLWheel) was developed to improve leisure time physical activity (LTPA). The purpose of this study was to assess the feasibility of the ALLWheel program. In a pilot pre-post design, 12 manual wheelchair users in three Canadian cities completed the ALLWheel program (containing 14 sessions over 10 weeks delivered by a peer using a smartphone). Feasibility indicators were collected for process, resources, management, and intervention—before, during, and after ALLWheel. Exploratory outcomes were collected for LTPA (primary outcome), motivation, self-efficacy, and satisfaction with autonomy support and goal attainment—at baseline, immediately following ALLWheel, and three months later. Feasibility was evaluated using a priori criteria for success (yes/no), and within-subjects comparisons were made to explore the change in exploratory outcomes. The participants were 48.9 ± 15.1 years of age and women (66.7%), and had spinal cord injury (41.7%) or multiple sclerosis (16.7%). Feasibility was achieved in 11 of 14 indicators, with suggestions to consider subjective reports of LTPA as the primary outcome in a future randomized controlled trial to overcome limitations with device-based measures and to use strategies to enhance recruitment. Mild-intensity LTPA and satisfaction with goal attainment improved after the completion of ALLWheel. With minor modifications, it is feasible that ALLWheel can be administered to wheelchair users by a peer using a smartphone.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Methods for Estimating the Impact of Disability Costs for Designing Inclusive Policies
by
Daniel Mont, Lena Morgon Banks, Ludovico Carraro, Alex Cote, Jill Hanass-Hancock, Sophie Mitra, Zachary Morris, Mercoledi Nasiir and Monica Pinilla-Roncancio
Cited by 3 | Viewed by 5043
Abstract
The impact of disability on people’s lives is often underestimated because the extra costs of living with a disability are not accounted for. This paper analyzes several different methodologies for estimating those costs and explores their usefulness in designing inclusive social policies. For
[...] Read more.
The impact of disability on people’s lives is often underestimated because the extra costs of living with a disability are not accounted for. This paper analyzes several different methodologies for estimating those costs and explores their usefulness in designing inclusive social policies. For example, one approach is to measure what is currently being spent, while another is to estimate what would need to be spent for equal participation. These can be measured using statistical techniques or through a more qualitative methodology. Each of these methods has its advantages and disadvantages. The paper concludes with recommendations for which methodology fits which purpose, and how they can be used together to obtain a full accounting of the extra costs incurred by people with disabilities.
Full article
Open AccessReview
Re-Imagining Education for All Children
by
Roy McConkey and Judith McKenzie
Viewed by 2832
Abstract
Universal education is an elusive goal in many countries, especially for disabled children. Nonetheless, determined efforts around the globe have shown that it can become a reality once existing systems were re-imagined by practitioners who arguably have been to the fore more so
[...] Read more.
Universal education is an elusive goal in many countries, especially for disabled children. Nonetheless, determined efforts around the globe have shown that it can become a reality once existing systems were re-imagined by practitioners who arguably have been to the fore more so than academic researchers. Their efforts have identified new ways of thinking about children’s disabilities, the introduction of new practices in schools, forging partnerships between teachers and parents and mobilising community resources. Societal change is both a consequence of and a support to these local systems. The complexity of creating education for all may be daunting, but it is achievable when driven by committed, creative and inspirational leadership from practitioners, as is evident from the examples provided in this paper, which were further validated by research and evaluation into their efforts.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
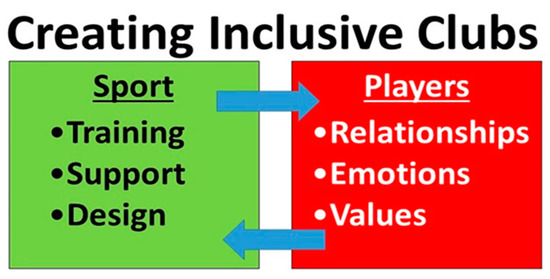
The Involvement of Athletes with Intellectual Disability in Community Sports Clubs
by
Florian Pochstein, Gemma Diaz Garolera, Sabine Menke and Roy McConkey
Cited by 11 | Viewed by 8892
Abstract
People with intellectual disability lack opportunities to engage in sports, although the benefits of doing so may be even greater for them. One option is to encourage their inclusion in mainstream sports clubs that exist in nearly all European communities. Although there is
[...] Read more.
People with intellectual disability lack opportunities to engage in sports, although the benefits of doing so may be even greater for them. One option is to encourage their inclusion in mainstream sports clubs that exist in nearly all European communities. Although there is a growing knowledge base within organisations such as Special Olympics in adjusting sports to meet the needs of people with intellectual disability, inclusion in community clubs raises additional challenges. This exploratory study aimed to garner the experiences of coaches alongside those of clubs members—with and without disabilities—in 12 community sports clubs in three European countries. In all 20 coaches and 51 members took part in semi-structured interviews. A thematic content analysis was used to devise a conceptual model describing an inclusive sports club. The overarching theme was that inclusive clubs require an ongoing balancing between a focus on sporting skills and performance, with managing the needs and characteristics of the players and the inter-relationships among them. Six subthemes were identified that described the core strategies to the effective functioning of the clubs. However, the vision and commitment of coaches was crucial and their recruitment was the main challenge the clubs faced. In addition, new opportunities for training coaches are needed to support the extension of inclusive clubs across a range of sports and locations. Continuing research could usefully identify the benefits to club members and identify sport-specific adaptations required to make clubs more fully inclusive.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Applying the ‘Human Rights Model of Disability’ to Informed Consent: Experiences and Reflections from the SHAPES Project
by
Richard Lombard-Vance, Evelyn Soye, Delia Ferri, Emma McEvoy, Malcolm MacLachlan and Sari Sarlio-Siintola
Cited by 10 | Viewed by 8399
Abstract
Understanding the complexity of informed consent processes is critically important to the success of research that requires participants to test, develop, or inform research data and results. This is particularly evident in research involving persons experiencing neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, dementia) that
[...] Read more.
Understanding the complexity of informed consent processes is critically important to the success of research that requires participants to test, develop, or inform research data and results. This is particularly evident in research involving persons experiencing neurodegenerative diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, dementia) that impair cognitive functioning, who according to national law are considered to have a diminished capacity, or to lack the capacity, to consent to research participation. Those who would potentially benefit most from applied research participation may be excluded from participating and shaping data and outcomes. This article offers insights into challenges faced by the Smart and Healthy Ageing through People Engaging in Supportive Systems (SHAPES) Project in obtaining the consent of older persons, including older persons with disabilities. The promotion of continuing health, active ageing, and independent living is central to SHAPES, requiring project partners to reflect on traditional informed consent approaches to encourage the full, cognisant participation of older persons with disabilities. We examine how this issue may be addressed, with reference to the inclusive approach of SHAPES. In respecting the inalienable legal capacity of all legal persons, SHAPES uses the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD) and the human rights model of disability as part of the theoretical framework. A novel, inclusive, representative informed consent framework was designed and is detailed herein. This framework provides significant opportunity to advance the inclusion of persons with disabilities or those experiencing neurodegenerative diseases in innovative research and is readily transferable to other research studies. The SHAPES approach is a substantial contribution to research on informed consent, demonstrating the utility of the human rights model of disability in facilitating the full research participation of target populations.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessArticle
Evaluation of Smiles for Life: A Caregiver Focused Oral Health Education Programme
by
Nathan J. Wilson, Tiffany Patterson-Norrie, Cheryl Bedford, Natalie Bergstedt, Lia Marri Mendoza, Amy R. Villarosa, Ajesh George and Avanti Karve
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 3780
Abstract
Background: People with an intellectual and/or developmental disability are at increased risk of adverse oral health outcomes and often require support from caregivers to assist in maintaining or seeking treatment for their oral health needs. However, caregivers and support workers are often
[...] Read more.
Background: People with an intellectual and/or developmental disability are at increased risk of adverse oral health outcomes and often require support from caregivers to assist in maintaining or seeking treatment for their oral health needs. However, caregivers and support workers are often family members with limited formal oral health training. Hence, the aim of this pilot study was to review the outcomes of the ‘Smiles for Life’ oral health education workshop with reference to their knowledge, attitudes, and practices of caregivers of people with an intellectual or developmental disability.
Methods: A single group pre-test post-test intervention design was used to explore the preliminary effectiveness and appropriateness of the Smiles for Life oral health education workshop.
Results: A total of 244 participants completed both the pre and post knowledge test. Oral health literacy scores decreased following the post test. Those with higher levels of education achieved higher post-training knowledge scores. Overall, caregivers reported satisfaction on the material presented however, it could be improved with more practical demonstrations.
Conclusion: Providing an oral health education tool that caters to the diverse caregiver audience presents a unique set of challenges, despite oral health education in this professional group being vital. Future studies may benefit from reviewing the efficacy of a more tailored educational intervention.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
Traversing Disability: Employers’ Perspectives of Disability Inclusion
by
Adèle Ebrahim, Theresa Lorenzo and Harsha Kathard
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 4507
Abstract
Persons with disabilities still experience challenges in obtaining employment even though obligations associated with their employment are in place in legislative frameworks that strive to support transformation within the labour market. This paper explores employers’ perspectives on the employment of persons with disabilities
[...] Read more.
Persons with disabilities still experience challenges in obtaining employment even though obligations associated with their employment are in place in legislative frameworks that strive to support transformation within the labour market. This paper explores employers’ perspectives on the employment of persons with disabilities in South Africa identified in a case study. The influence of social capital on disability inclusive employment was explored from the perspective of two employers who employed trainees who completed an auxiliary training programme for persons with disabilities, which provides opportunities to facilitate pathways to economic inclusion and/or employment. Findings reveal that despite the call for increased labour inclusivity, the development of social capital is not clearly apparent when persons with disabilities are considered for employment. Organisational attitudes and beliefs seem to stem from the obligatory standpoint of the organisations. The paper highlights the need for employers to look beyond impairments so that employment goals are shared and re-enforced by understanding and possibly re-evaluating their views on their organisation’s obligations, norms, values and mission, and goals. Insights can guide employers to think more holistically about ways to facilitate the economic inclusion of persons with disabilities.
Full article
Open AccessArticle
The Perceived Role of Healthcare Providers and Systems in the Development of Secondary Health Conditions among Adults with Spinal Cord Injury
by
Michelle A. Meade, Karla Reed, Melinda Jarnecke, Kristian Manley and James S. Krause
Viewed by 2560
Abstract
Individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), with high healthcare utilization rates and costs, require special attention and tailored care protocols to meet their healthcare needs. This qualitative study collected narrative information from adults with SCI and their family members and/or caregivers to examine
[...] Read more.
Individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), with high healthcare utilization rates and costs, require special attention and tailored care protocols to meet their healthcare needs. This qualitative study collected narrative information from adults with SCI and their family members and/or caregivers to examine the perceived role of healthcare providers and systems in the development and treatment of secondary health conditions (SHCs). After personal information was collected, individuals participated in focus groups which were recorded and transcribed; transcripts were then reviewed, cleaned, and uploaded to NVivo10 software to facilitate the analysis. An initial stage of coding was conducted which identified potential categories and themes; afterwards, the perceived role of healthcare providers in the development and management of secondary health conditions (SHC) was prioritized and transcripts were re-coded. Two overlapping themes emerged: (1) Iatrogenic and nosocomial factors; and (2) Relationships with healthcare providers. Iatrogenic and nosocomial factors had three subthemes: (1) Misdiagnosis; (2) Perceived mistreatment or mistakes made during treatment; and (3) Unintended consequences of medical treatment; while three subthemes were identified for Relationships with healthcare providers: (1) Respect; (2) Knowledge and experience; and (3) Patient Expertise. To improve safety, reduce healthcare costs, and facilitate more favorable perceived outcomes for individuals with SCI, healthcare providers, organizations and systems need to implement principles of high reliability organizations to improve outcomes through the treatment and prevention of SHC.
Full article
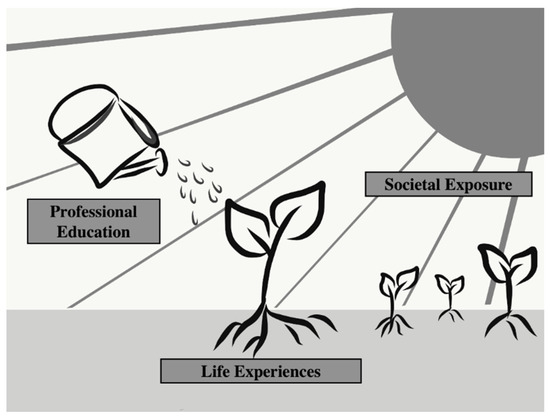
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
“Someone Like Anyone Else”: A Qualitative Exploration of New Zealand Health Professional Students’ Understanding of Disability
by
Sadhana Ravichandran, Allyson Calder, Tristram Ingham, Bernadette Jones and Meredith Perry
Cited by 2 | Viewed by 6182
Abstract
Background: One in four New Zealanders identify as disabled. Disabled people, including Māori (the indigenous people of New Zealand (NZ)), experience health disparities. Systemic and individual health professional (HP) biases are factors that may affect health outcomes. Disability education is a means for
[...] Read more.
Background: One in four New Zealanders identify as disabled. Disabled people, including Māori (the indigenous people of New Zealand (NZ)), experience health disparities. Systemic and individual health professional (HP) biases are factors that may affect health outcomes. Disability education is a means for improving attitudes and behaviors towards disabled people. The objective of this study was to explore NZ HP students’ understanding of disability and health-related concepts. Methods: HP students from one tertiary institution in NZ were interviewed through Zoom video call about their understanding of disability and health. A relativism paradigm and contextualism epistemology (underpinned by the socio-ecological model) shaped the reflexive thematic analysis. Transcripts were analyzed at a deductive and latent level. Results: Nine HP participants, from different professional courses and cultural backgrounds, were interviewed. Three main themes influenced participants’ understanding of disability: life experiences, professional education, and societal exposure. Participants who had more experience with disabled people had a deeper and more nuanced appreciation of the challenges disabled people face in accessing health services and obtaining equitable health outcomes. Cultural background also influenced the participants’ understanding of disability. Participants preferred more experiential learning methods to improve their knowledge of disability concepts. Lastly, expectations of inclusion are determined by observing social norms. Conclusion: Participants reported learning just a few models of disability. The HP students predominantly came from a perspective of ensuring equality rather than equity. There was limited recognition of the systemic biases that exist within multiple social determinants and how these perpetuate health inequities for disabled people. A socio-ecological consideration of disability throughout the curricula, self-reflection, acknowledging systemic bias, and proactively including disabled people as HP students and teachers are potential means for addressing health inequities.
Full article
►▼
Show Figures
Open AccessFeature PaperArticle
Changing Children’s Attitudes to Disability through Music: A Learning Intervention by Young Disabled Mentors
by
Eamonn McCarron, Erica Curran and Roy McConkey
Cited by 5 | Viewed by 4283
Abstract
Children with disabilities are at greater risk of social exclusion. In part, this results from the negative perceptions of disability held by their peers. An innovative, school-based project used creative music-making sessions facilitated by young disabled musicians to nurture more positive attitudes among
[...] Read more.
Children with disabilities are at greater risk of social exclusion. In part, this results from the negative perceptions of disability held by their peers. An innovative, school-based project used creative music-making sessions facilitated by young disabled musicians to nurture more positive attitudes among children aged 9 years in four schools, with two classes from each. In all, around 200 pupils were involved in weekly sessions totalling 16 h. Their attitudes to disability were assessed before and after participating in the project, along with the reactions of parents and teachers. Pupils were significantly more disposed to interacting with children with disabilities and to persons with disabilities more generally as well as to having a teacher with a disability. Parents and teachers confirmed the pupils’ enthusiasm for the project and the impact it had on them. A core driver for change appeared to be sharing enjoyable musical activities with competent musicians who had disabilities. Further research should explore the potential of mentoring by disabled persons in other arts activities and sports to provide further validation of this approach.
Full article