Diet–Microbiome Relationships in Prostate-Cancer Survivors with Prior Androgen Deprivation-Therapy Exposure and Previous Exercise Intervention Enrollment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subject Recruitment, Study Design, and Study Participants
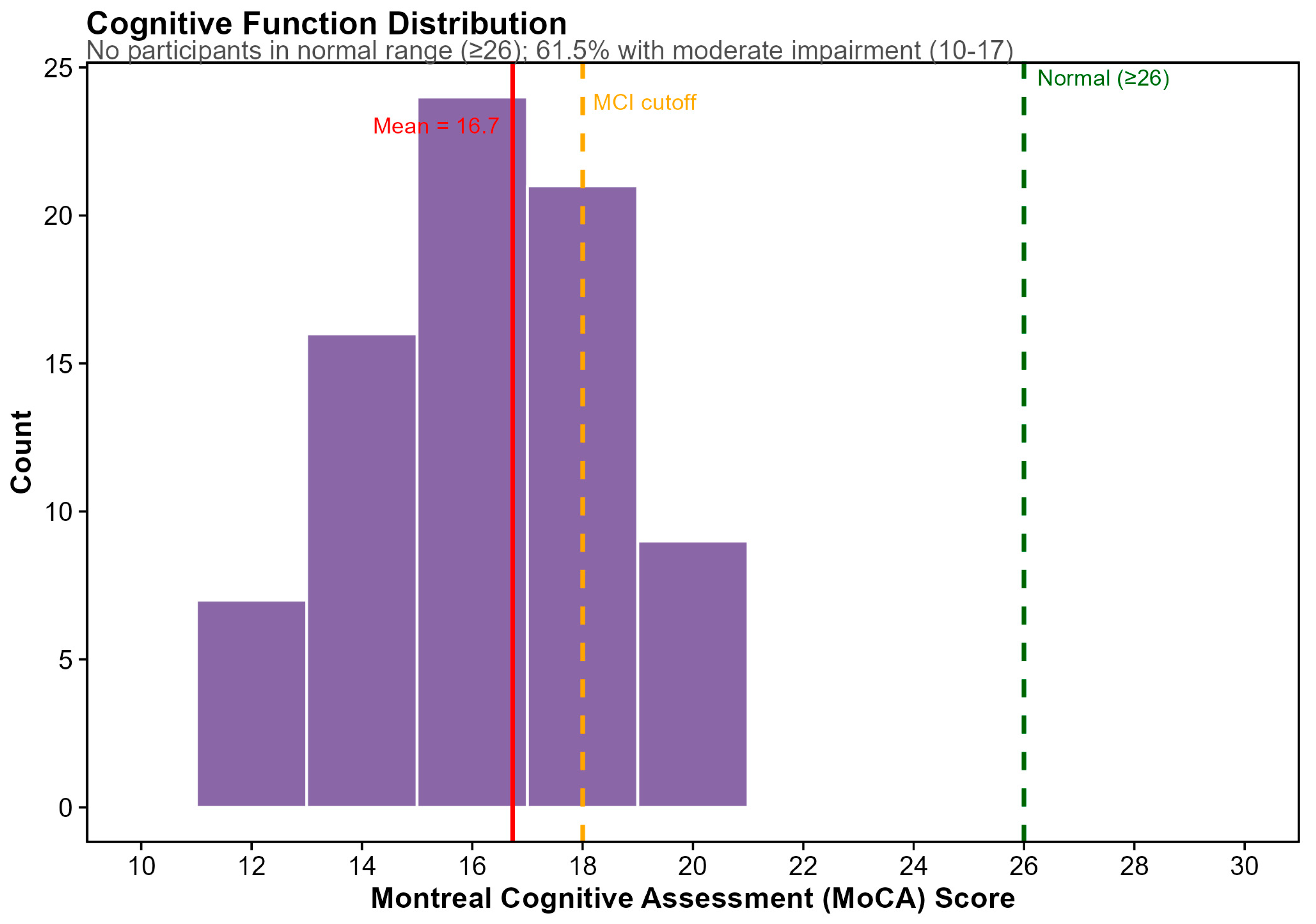
2.2. Cognitive Testing
2.3. Dietary Assessment
2.4. Sample Collection of Saliva and Stool Samples
2.5. Bioinformatic Processing
2.6. Host Factor Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
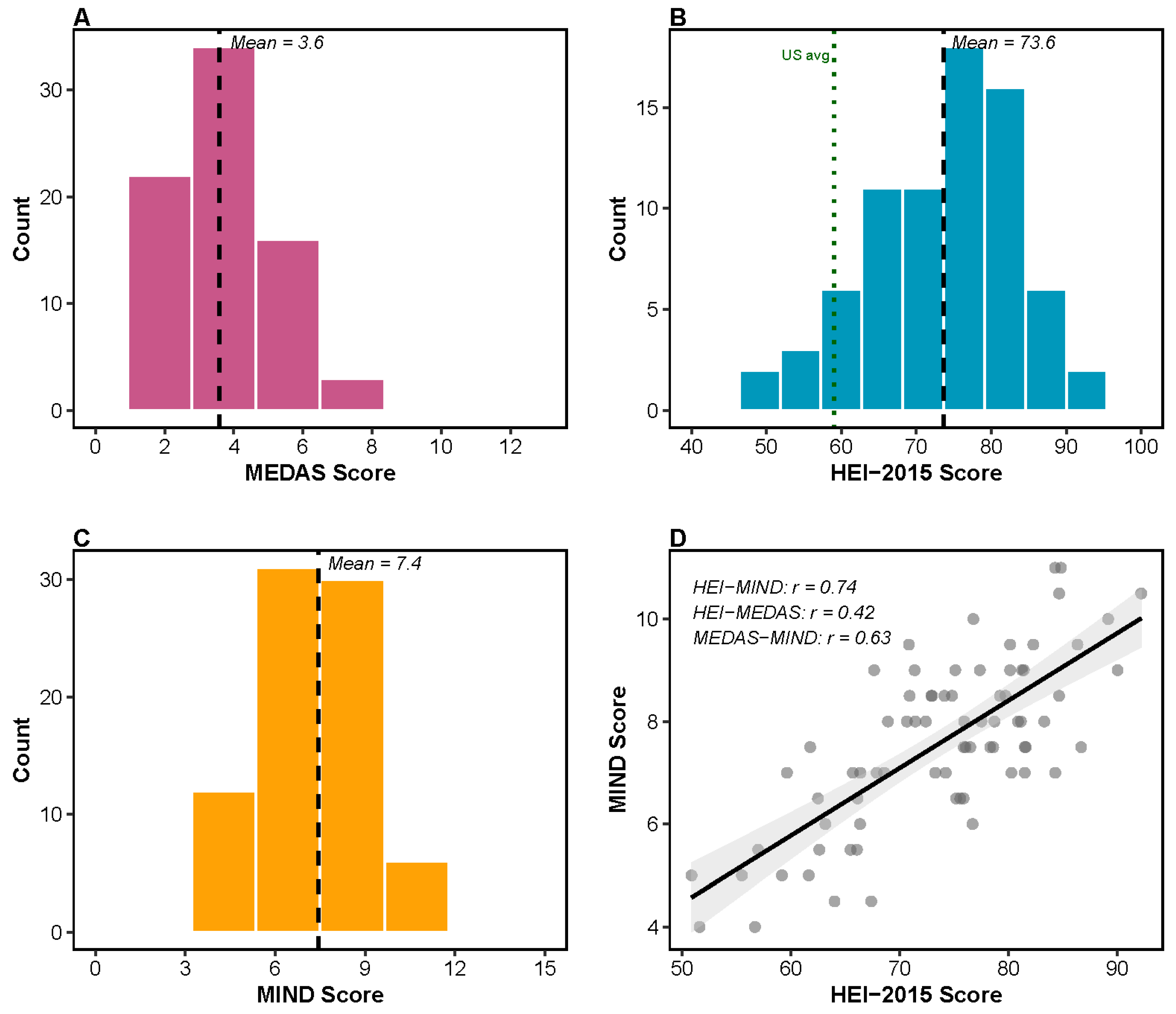
3.1. Cohort Characteristics and Baseline Assessments
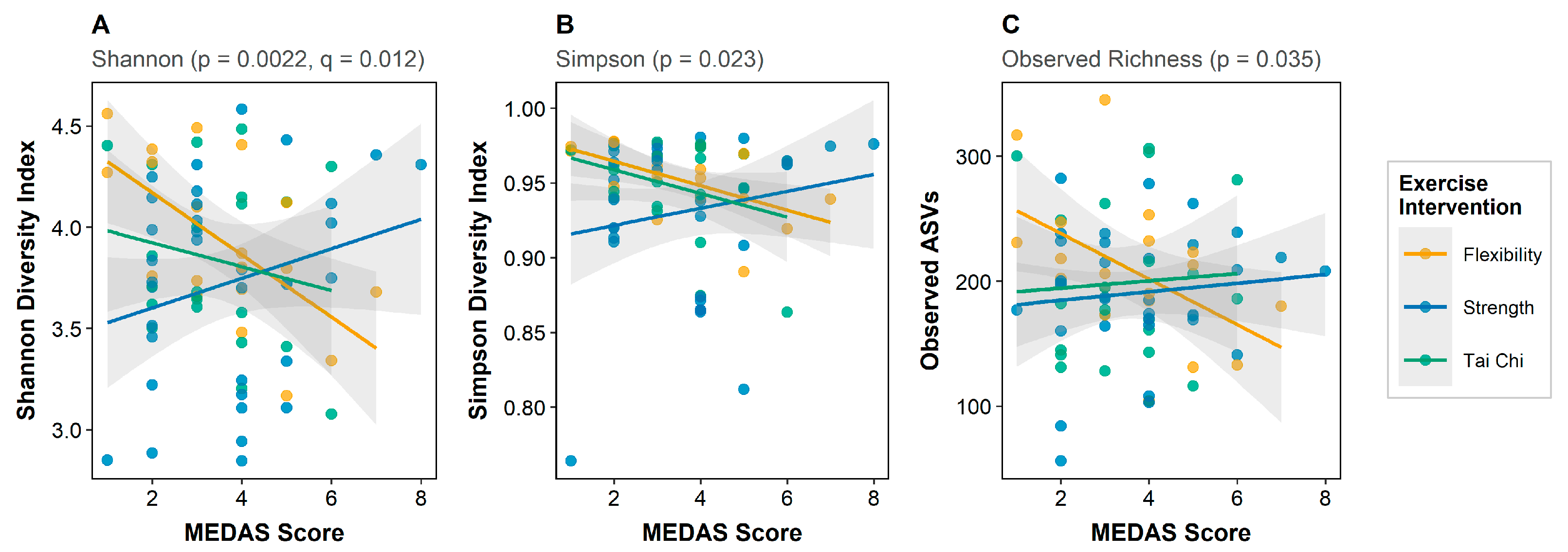
3.2. Diet–Microbiome Associations: Alpha Diversity
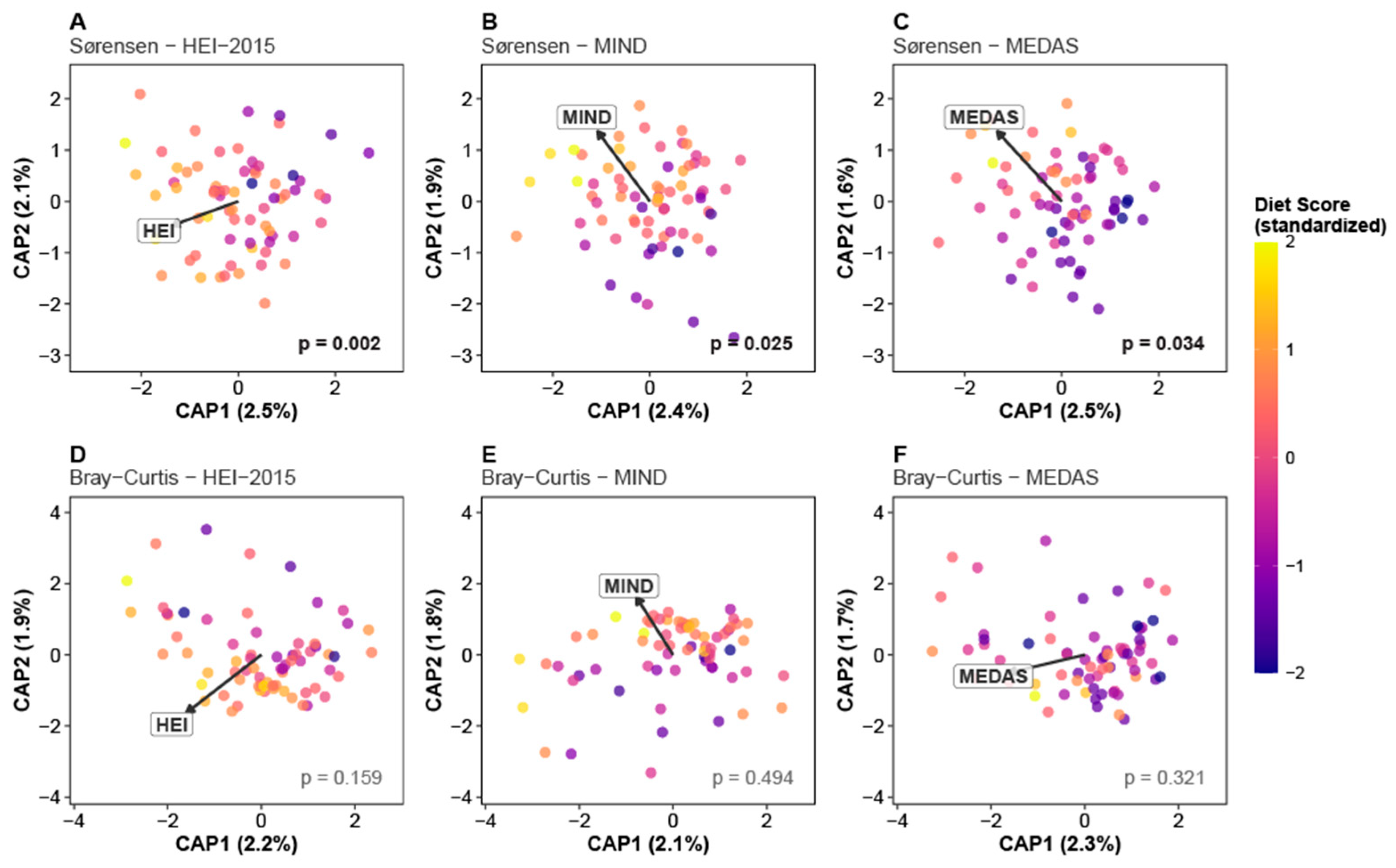
3.3. Diet–Microbiome Associations: Beta Diversity
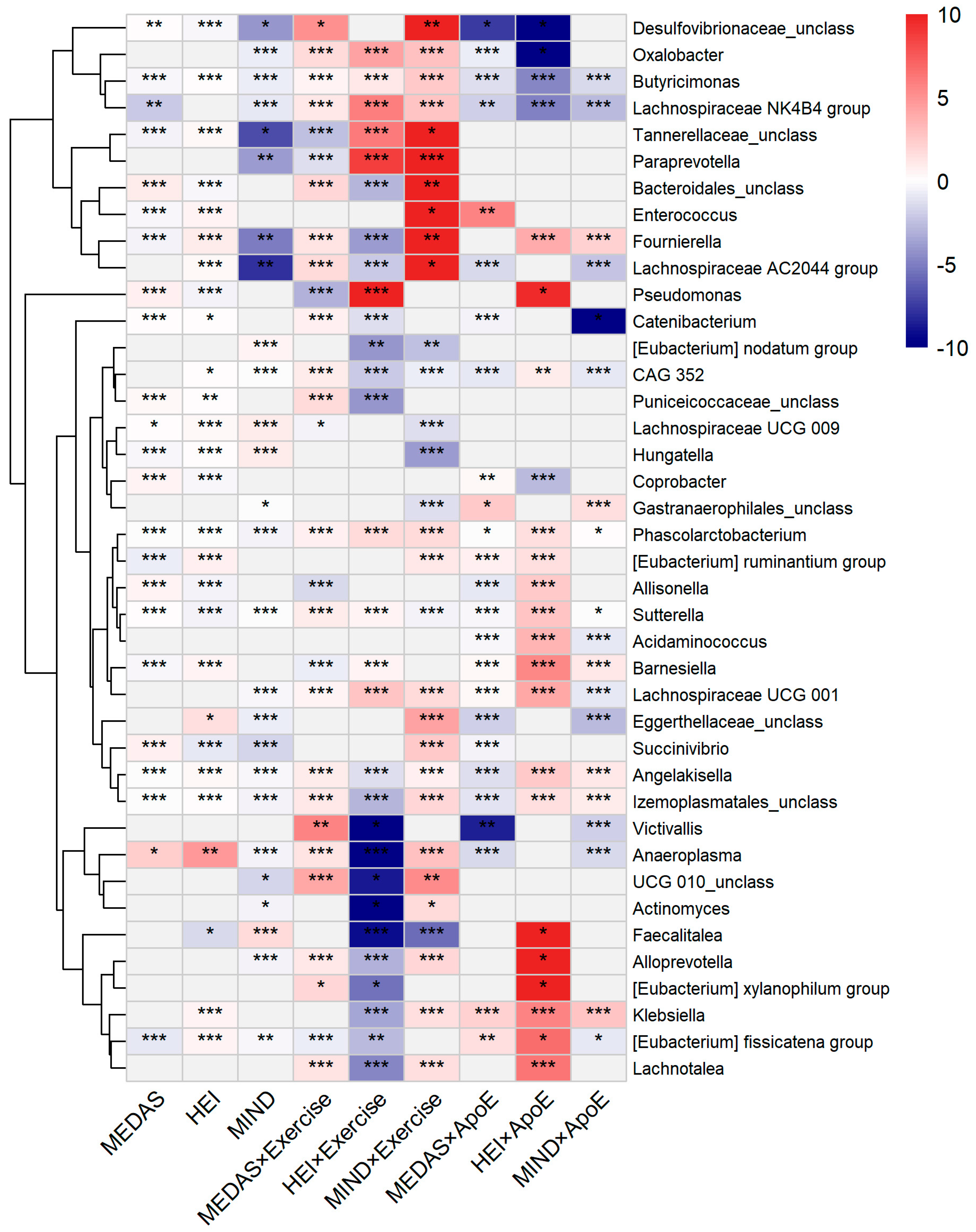
3.4. Taxon-Level Associations
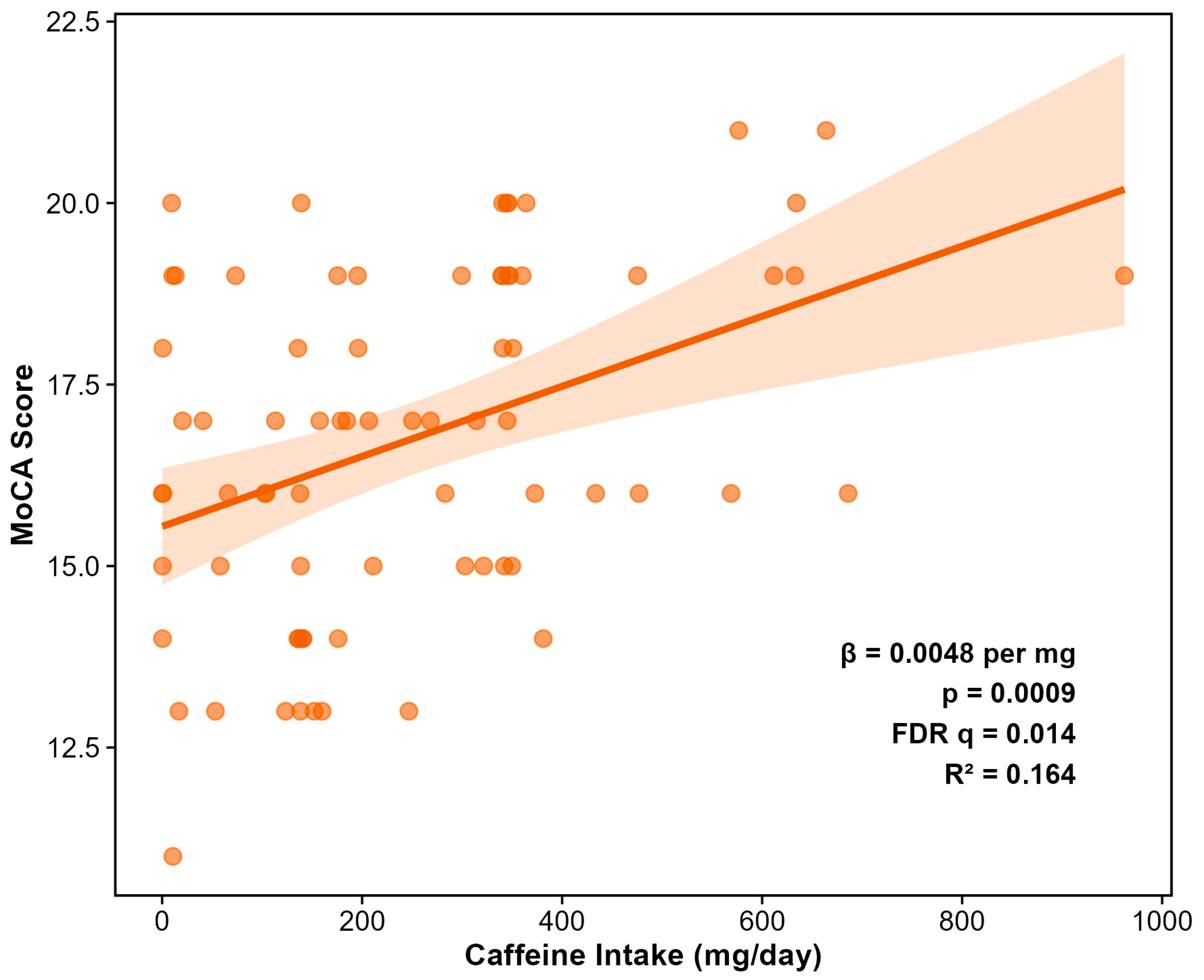
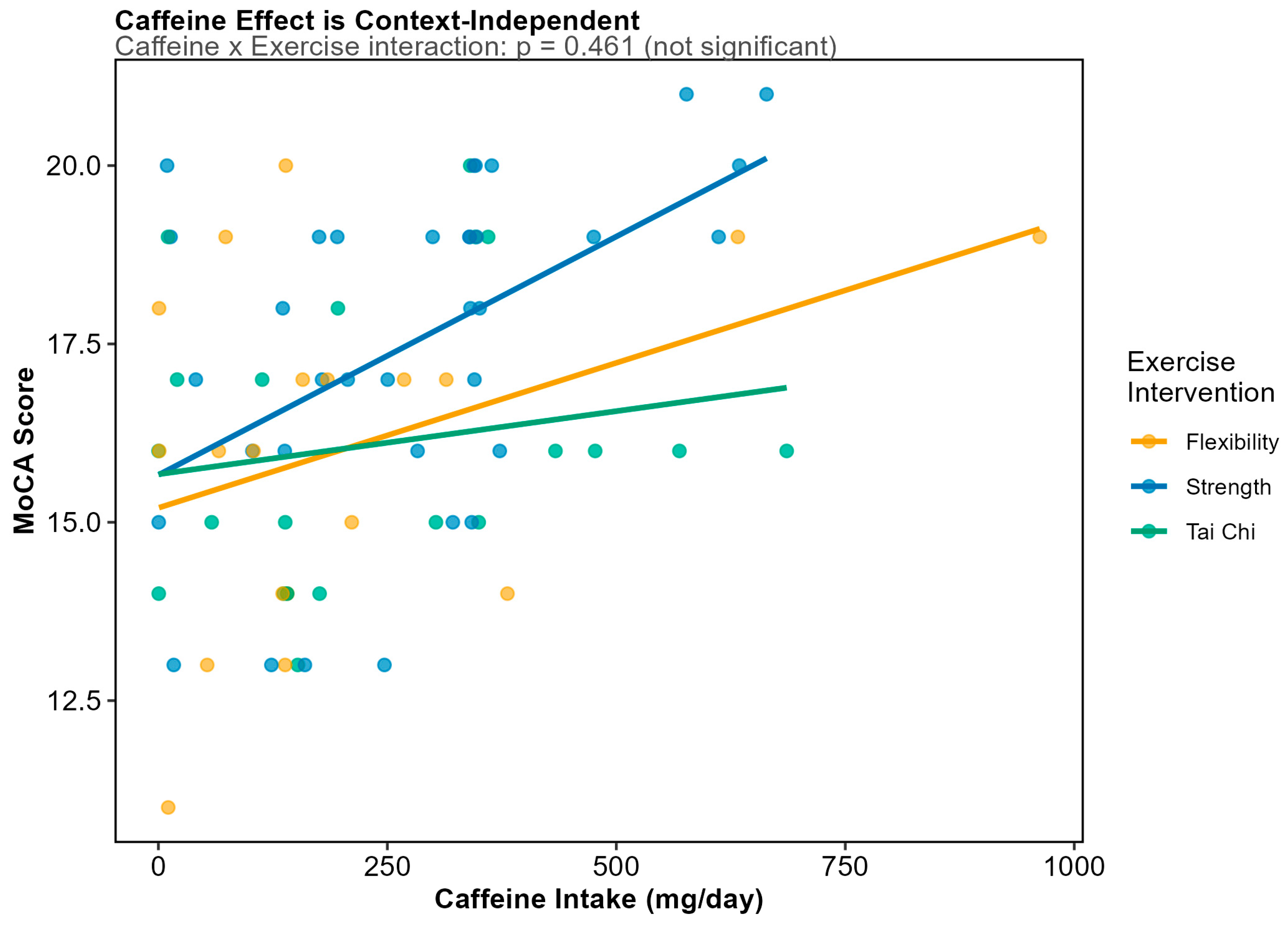
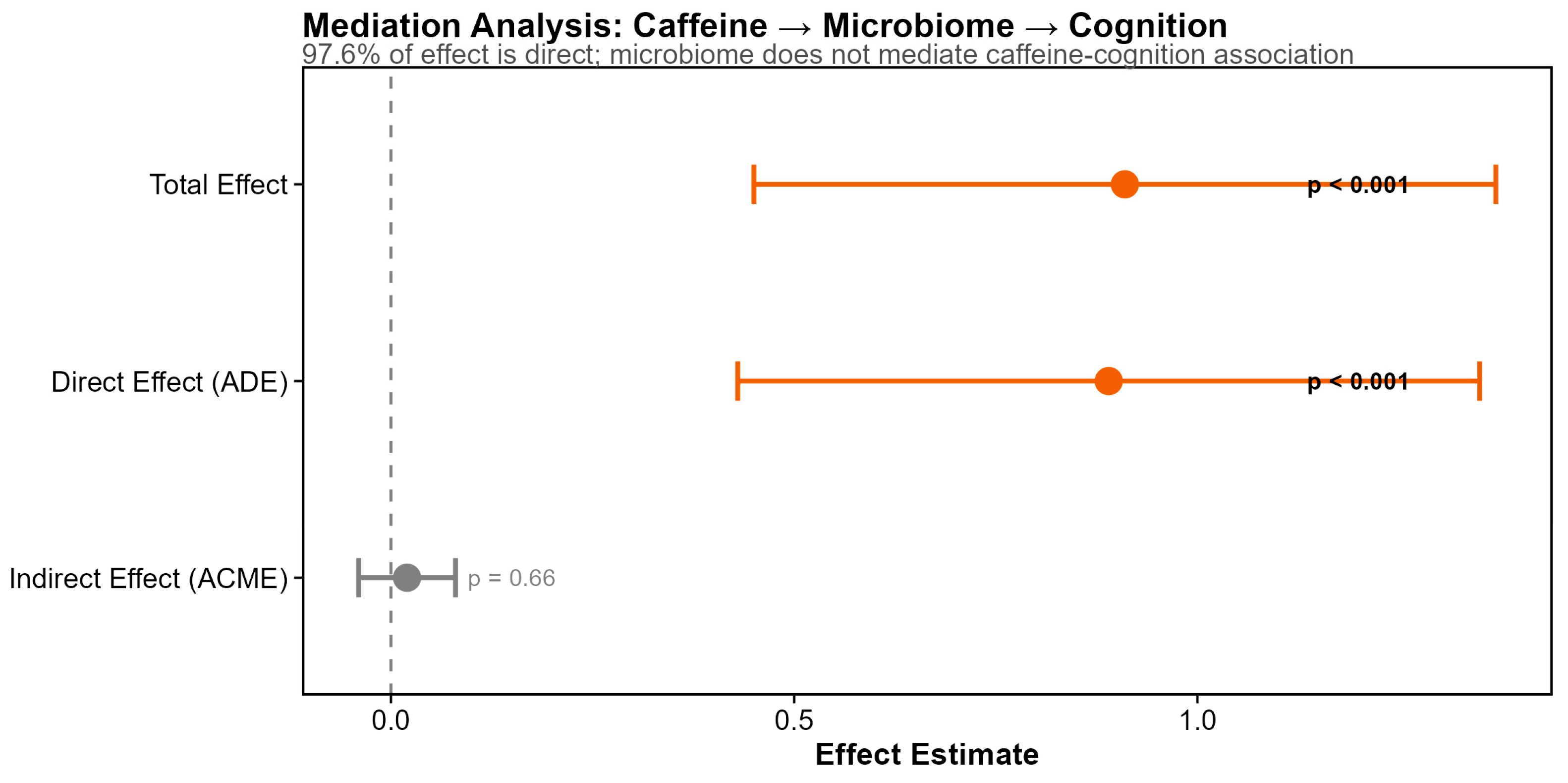
3.5. Dietary Predictors of Cognitive Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| ADT | androgen-deprivation therapy |
| APOE | APOLIPOPROTEIN E |
| ASV | amplicon sequence variant |
| ACME | average causal mediation effect |
| ADE | average direct effect |
| bp | base pair |
| CV | coefficient of variance |
| DHQ | Diet Questionnaire |
| E2 | apolipoprotein E2 |
| E3 | apolipoprotein E3 |
| E4 | apolipoprotein E4 |
| FDR | False Discovery Rate |
| HEI-2015 | Healthy Eating Index-2015 |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| MCI | Mild Cognitive Impairment |
| MaAsLin2 | Microbiome Multivariable Associations with Linear Models |
| MEDAS | Mediterranean Diet Adherence Score |
| MIND | Mediterranean-Dash Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay |
| MoCA | Montreal Cognitive Assessment |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational Multivariate Analysis of Variance |
| rRNA | ribosomal RNA |
| SNP | single-nucleotide polymorphism |
References
- Bower, J.; Ganz, P.A.; Tao, M. Inflammatory biomarkers and fatigue during radiation therapy for breast and prostate cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5534–5540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Von Ah, D. Cancer-related cognitive impairment: Updates to treatment, the need for more evidence, and impact on quality of life—A narrative review. Ann. Pal. Med. 2024, 13, 1265–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettridge, K.A.; Bowden, J.A.; Chambers, S.K.; Smith, D.P.; Murphy, M.; Evans, S.M.; Roder, D.; Miller, C.L. Prostate cancer is far more hidden…”: Perceptions of stigma, social isolation and help-seeking among men with prostate cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 27, e12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raber, J.; Huang, Y.; Ashford, J. ApoE genotype accounts for the vast majority of AD risk and AD pathology. Neurobiol. Aging 2004, 25, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Holtzman, D. Interplay between innate immunity and Alzheimer disease: APOE and TREM2 in the spotlight. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancaro, N.; Calì, B.; Troiani, M.; Elia, A.R.; Arzola, R.A.; Attanasio, G.; Lai, P.; Crespo, M.; Gurel, B.; Pereira, R.; et al. Apolipoprotein E induces pathogenic senescent-like myeloid cells in prostate ca. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 602–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahles, T.A.; Saykin, A.J.; Noll, W.W.; Furstenberg, C.T.; Guerin, S.; Cole, B.; Mott, L.A. The relationship of APOE genotype to neuropsychological performance in long-term cancer survivors treated with standard dose chemotherapy. Psycho-Oncol. J. Psychol. Soc. Behav. Dimens. Cancer 2003, 12, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayan, V.; Ross, A.E.; Parikh, R.B.; Nohria, A.; Morgans, A.K. How to Treat Prostate Cancer With Androgen Deprivation and Minimize Cardiovascular Risk. JACC Cardio Oncol. 2021, 3, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, M.; Bang, W.J.; Oh, C.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Cho, J.S. Androgen deprivation therapy and risk of cognitive dysfunction in men with prostate cancer: Is there a possible link? Prostate Int. 2022, 10, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowsky, J.S.; Oviatt, S.K.; Orwoll, E.S. Testosterone influences spatial cognition in older men. Behav. Neurosci. 1994, 108, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowsky, J.S.; Chavez, B.; Orwoll, E. Sex steroids modify working memory. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motlagh, R.; Quhal, F.; Mori, K.; Miura, N.; Aydh, A.; Laukhtina, E.; Pradere, B.; Karakiewicz, P.; Enikeev, D.; Deuker, M.; et al. The Risk of New Onset Dementia and/or Alzheimer Disease among Patients with Prostate Cancer Treated with Androgen Deprivation Therapy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Urol. 2021, 205, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, A.V.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Moore, S.C.; Hayes, S.C.; Silver, J.K.; Campbell, K.L.; Winters-Stone, K.; Gerber, L.H.; George, S.M.; Fulton, J.E.; et al. American College of Sports Medicine Roundtable Report on Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Cancer Prevention and Control. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2019, 51, 2391–2402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardia, A.; Arieas, E.T.; Zhang, Z.; DeFilippis, A.; Tarpinian, K.; Jeter, S.; Nguyen, A.; Henry, N.L.; Flockhart, D.A.; Hayes, D.F.; et al. Comparison of breast cancer recurrence risk and cardiovascular disease incidence risk among postmenopausal women with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 131, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaul, S.; Miller, J.G.; Grayburn, P.A.; Hashimoto, S.; Hibberd, M.; Holland, M.R.; Houle, H.C.; Klein, A.L.; Knoll, P.; Lang, R.M.; et al. A suggested roadmap for cardiovascular ultrasound research for the future. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2011, 24, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pernigoni, N.; Zagato, E.; Calcinotto, A.; Troiani, M.; Mestre, R.P.; Calì, B.; Attanasio, G.; Troisi, J.; Minini, M.; Mosole, S.; et al. Commensal bacteria promote endocrine resistance in prostate cancer through androgen biosynthesis. Science 2021, 374, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzaal, M.; Saeed, F.; Shah, Y.A.; Hussain, M.; Rabail, R.; Socol, C.T.; Hassoun, A.; Pateiro, M.; Lorenzo, J.M.; Rusu, A.V.; et al. Human gut microbiota in health and disease: Unveiling the relationship. Front. Microbol. 2022, 10, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemi, M.; Hakkinen, T.; Karttunen, T.; Eskelinen, S.; Kervinen, K.; Savolainen, M.; Lehtola, J.; Makela, J.; Yla-Herttula, S.; Kesaniemi, Y. Apolipoprotein E and colon cancer: Expression in normal and malignant human intestine and effect on cultured human colonic adenocarcinoma cells. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2002, 13, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.; Corsini, S.; Kellinggray, L.; Hegarty, C.; Le Gail, C.; Narbad, A.; Muller, M.; Tereja, N.; O’Toole, P.; Minihane, A.-M.; et al. APOE genotype influences the gut microbiome structure and function in humans and mice: Relevance for Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8221–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pencheva, N.; Tran, H.; Buss, C.; Huh, D.; Drobnjak, M.; Busam, K.; Tavazoie, S.F. Convergent Multi-miRNA Targeting of ApoE Drives LRP1/LRP8-Dependent Melanoma Metastasis and Angiogenesis. Cell 2012, 151, 1068–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostendorf, B.N.; Bilanovic, J.; Adaku, N.; Tafreshian, K.N.; Tavora, B.; Vaughan, R.D.; Tavazoie, S.F. Common germline variants of the human APOE gene modulate melanoma progression and survival. Nat. Med. 2020, 26, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailing, L.J.; Allen, J.M.; Buford, T.W.; Fields, C.J.; Woods, J.A. Exercise and the Gut Microbiome: A Review of the Evidence, Potential Mechanisms, and Implications for Human Health. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2019, 47, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, M.; Gerard, P.; Mosca, A.; Leclerc, M. Interplay Between Exercise and Gut Microbiome in the Context of Human Health and Performance. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 637010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raber, J.; O’Niel, A.; Kasschau, K.; Pederson, A.; Robinson, N.; Guidarelli, C.; Chalmers, C.; Winters-Stone, K.; Sharpton, T. Exercise, APOE genotype, and testosterone modulate gut microbiome-cognition associations in prostate cancer survivors. Genes 2025, 16, 1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Kaser, A. Gut microbiome, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohland, C.; Kish, L.; Bell, H.C.; Thiesen, A.; Hotte, N.; Pankiv, E.; Madsen, K. Effects of Lactobacillus helveticus on murine behavior are dependent on diet and genotype and correlate with alterations in the gut microbiome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2013, 38, 1738–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, S.; Ohno, H. Gut microbiome and metabolic diseases. Semin. Immunopathol. 2014, 36, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatch, A.; Horne, J.A.; Toma, R.; Twibell, B.; Somerville, K.; Pelle, B.; Candfield, K.; Genkin, M.; Banavar, G.; Perlina, A.; et al. A Robust Metatranscriptomic Technology for Population-Scale Studies of Diet, Gut Microbiome, and Human Health. Int. J. Genom. 2019, 2019, 1718741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koblinsky, N.; Power, K.; Middleton, L.; Ferland, G.; Anderson, N. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Diet and Exercise Effects on Cognition: A Review of the Intervention Literature. J. Gerontol. 2023, 78, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCI. Diet History Questionnaire III. 2025. Available online: https://epi.grants.cancer.gov/dhq3/ (accessed on 15 January 2026).
- Fransen, H.; Ocke, M. Indices of diet quality. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2008, 11, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourlaba, G.; Panagiotakos, D. Dietary quality indicaes and human health: A review. Maturitas 2009, 62, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrone, P.; D’Angelo, S. Gut Microbiota Modulation Through Mediterranean Diet Foods: Implications for Human Health. Nutrients 2025, 17, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, Q.; Gao, M.; Luo, M. The long-term neuroprotective effect of MIND and Mediterranean diet on patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 32725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.H.; Burwell, A.D.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Loeb, S.; Chan, J.M.; Tuttle, B.; De Nunzio, C.; Bjartell, A.; Aronson, W.; Freedland, S.J. Dietary patterns in prostate cancer prevention and management: A systematic review of prospective cohort studies and randomized clinical trials. Eur. Urol. 2025, 88, 571–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, S.; Ritchie, C.; Ritchie, K.; Shannon, O.; Stevenson, E.; Muniz-Terrera, G. Mediterranean diet score is associated with greater allocentric processing in the EPAD LCS cohort: A comparative analysis by biogeographical region. Front. Aging 2022, 3, 10125298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H. Higher HEI-2015 score is associated with reduced risk of Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide population-based study. Clin. Nutr. 2025, 12, 1541271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Garcia, A.; Soldevila-Domenech, N.; Yi, S.-Y.; de la Torre, R. Diet patterns associated with cognitive decline: Methods to harmonize data from European and US cohort studies. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1379531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Dunk, M.; Wang, B.; Zhao, M.; Shen, J.; Zong, G.; Pan, Y.; Tong, L.; Xu, W.; Yuan, C. Associations of the Mediterranean-DASH Intervention for Neurodegenerative Delay diet with brain structural markers and their changes. Alzheimer Dement. 2024, 20, 1190–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Simpson-Yap, S.; Lerede, A.; Nicholas, R.; Coe, S.; Tektonidis, T.G.; Martinez Solsona, E.; Middleton, E.; Probst, J.; Hampshire, A.; et al. Mediterranean and MIND Dietary Patterns and Cognitive Performance in Multiple Sclerosis: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of the UK Multiple Sclerosis Register. Nutrients 2025, 17, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, S.K.; Babio, N.; Gómez-Martínez, C.; Martínez-González, M.Á.; Ros, E.; Corella, D.; Castañer, O.; Alfredo Martínez, J.; Alonso-Gómez, A.M.; Wärnberg, J.; et al. Mediterranean, DASH, and MIND Dietary Patterns and Cognitive Function: The 2-Year Longitudinal Changes in an Older Spanish Cohort. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 782067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winters-Stone, K.; Lyons, K.; Dieckmann, N.; Lee, C.; Mitri, Z.; Beer, T. Study protocol for the Exercising Together© trial: A randomized, controlled trial of partnered exercise for couples coping with cancer. Trials 2021, 22, 579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasreddine, Z.S.; Phillips, N.A.; Bédirian, V.; Charbonneau, S.; Whitehead, V.; Collin, I.; Cummings, J.L.; Chertkow, H. The Montreal Cognitive Assessment, MoCA: A brief screening tool for mild cognitive impairment. J. Am. Ger. Soc. 2005, 53, 695–699, Erratum in J. Am. Ger. Soc. 2019, 67, 1991.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, H.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Martínez-González, M.A.; Corella, D.; Salas-Salvadó, J.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.; Ros, E.; Salaverría, I.; Fiol, M.; et al. A short screener is valid for assessing Mediterranean diet adherence among older Spanish men and women. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 1140–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs-Smith, S.M.; Pannucci, T.E.; Subar, A.F.; Kirkpatrick, S.I.; Lerman, J.L.; Tooze, J.A.; Wilson, M.M.; Reedy, J. Update of the Healthy Eating Index: HEI-2015. J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2018, 118, 1591–1602, Erratum in J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2019, 119, 1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Tangney, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.T. MIND diet associated with reduced incidence of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer Dement. 2015, 11, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, J.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. Regularization paths for generalized linear models via coordinate descent. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 33, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.; McDurdie, P.; Rosen, M.; AW, H.; Johnson, A.; Holmes, S. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Meth. 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadept removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequences reads. EMBnet J. 2011, 17, 10–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nuc. Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, M.; Dehal, P.; Arkin, A. FastTree 2—Approximately Maximum-Likelihood Trees for Large Alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMurdie, P.; Holmes, S. phyloseq: An R package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cribari-Neto, F.; Zeileis, A. Beta regression in R. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 34, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Simpson, G.L.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, R.B.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Szoecs, E.; et al. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.6-4. 2022. Available online: https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan (accessed on 15 January 2026).
- Anderson, M. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral. Ecol. 2001, 26, 32–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick, H.; Rahnavard, A.; McIver, L.J.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Nguyen, L.H.; Tickle, T.L.; Weingart, G.; Ren, B.; Schwager, E.H.; et al. Multivariable association discovery in population-scale meta-omics studies. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1009442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B (Methodol.) 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingley, D.; Yamamori, T.; Hirose, K.; Keele, L.; Imai, K. mediation: R package for causal mediation analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2014, 59, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, A.E.; Jäger, R.; Carpenter, K.C.; Kerksick, C.M.; Purpura, M.; Townsend, J.R.; West, N.P.; Black, K.; Gleeson, M.; Pyne, D.B.; et al. The athletic gut microbiota. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2020, 17, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Steege, R.; Kolkman, J. Review article: The pathophysiology and management of gastrointestinal symptoms during physical exercise, and the role of splanchnic blood flow. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 35, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, A.M.; Keulemans, Y.C.; Peters, H.P.; Akkermans, L.M.; Smout, A.J.; De Vries, W.R.; Van Berge-Henegouwen, G.P. Effects of regular physical activity on defecation pattern in middle-aged patients complaining of chronic constipation. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 40, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, A.; Pedersen, B. The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 2005, 98, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codella, R.; Luzi, L.; Terruzi, I. Exercise has the guts: How physical activity may positively modulate gut microbiota in chronic and immune-based diseases. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeevi, D.; Korem, T.; Zmora, N.; Israeli, D.; Rothschild, D.; Weinberger, A.; Ben-Yacov, O.; Lador, D.; Avnit-Sagi, T.; Lotan-Pompan, M.; et al. Personalized nutrition by prediction of glycemic responses. Cell 2015, 163, 1079–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zmora, N.; Suez, J.; Elinav, E. You are what you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 35–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, J.; Sebastiao, A.M. Caffeine and adenosine. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, S3–S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eskelinen, M.; Kivipelto, M. Caffeine as a protective factor in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, S167–S174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.; Costa, J.; Santos, J.; Vaz-Carneiro, A.; Lunet, N. Caffeine intake and dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, S187–S204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehlig, A. Is caffeine a cognitive enhancer? J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, S85–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, R.; Agostinho, P. Chronic caffeine consumption prevents memory disturbance in different animal models of memory decline. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, S95–S116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nead, K.T.; Gaskin, G.; Chester, C.; Swisher-McClure, S.; Dudley, J.T.; Leeper, N.J.; Shah, N.H. Androgen deprivation therapy and future Alzheimer’s disease risk. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 566–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, B.D.; Jim, H.S.; Booth-Jones, M.; Small, B.J.; Sutton, S.K.; Lin, H.Y.; Park, J.Y.; Spiess, P.E.; Fishman, M.N.; Jacobsen, P.B. Course and predictors of cognitive function in patients with prostate cancer receiving androgen-deprivation therapy: A controlled comparison. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2021–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Tangney, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.T. MIND diet slows cognitive decline with aging. Alzheimer Dement. 2015, 11, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Raber, J.; O’Niel, A.; Kasschau, K.D.; Pederson, A.; Robinson, N.; Guidarelli, C.; Chalmers, C.; Winters-Stone, K.; Sharpton, T.J. Diet–Microbiome Relationships in Prostate-Cancer Survivors with Prior Androgen Deprivation-Therapy Exposure and Previous Exercise Intervention Enrollment. Microorganisms 2026, 14, 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010251
Raber J, O’Niel A, Kasschau KD, Pederson A, Robinson N, Guidarelli C, Chalmers C, Winters-Stone K, Sharpton TJ. Diet–Microbiome Relationships in Prostate-Cancer Survivors with Prior Androgen Deprivation-Therapy Exposure and Previous Exercise Intervention Enrollment. Microorganisms. 2026; 14(1):251. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010251
Chicago/Turabian StyleRaber, Jacob, Abigail O’Niel, Kristin D. Kasschau, Alexandra Pederson, Naomi Robinson, Carolyn Guidarelli, Christopher Chalmers, Kerri Winters-Stone, and Thomas J. Sharpton. 2026. "Diet–Microbiome Relationships in Prostate-Cancer Survivors with Prior Androgen Deprivation-Therapy Exposure and Previous Exercise Intervention Enrollment" Microorganisms 14, no. 1: 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010251
APA StyleRaber, J., O’Niel, A., Kasschau, K. D., Pederson, A., Robinson, N., Guidarelli, C., Chalmers, C., Winters-Stone, K., & Sharpton, T. J. (2026). Diet–Microbiome Relationships in Prostate-Cancer Survivors with Prior Androgen Deprivation-Therapy Exposure and Previous Exercise Intervention Enrollment. Microorganisms, 14(1), 251. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms14010251







