Clinical Features of BoDV-1 Encephalitis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
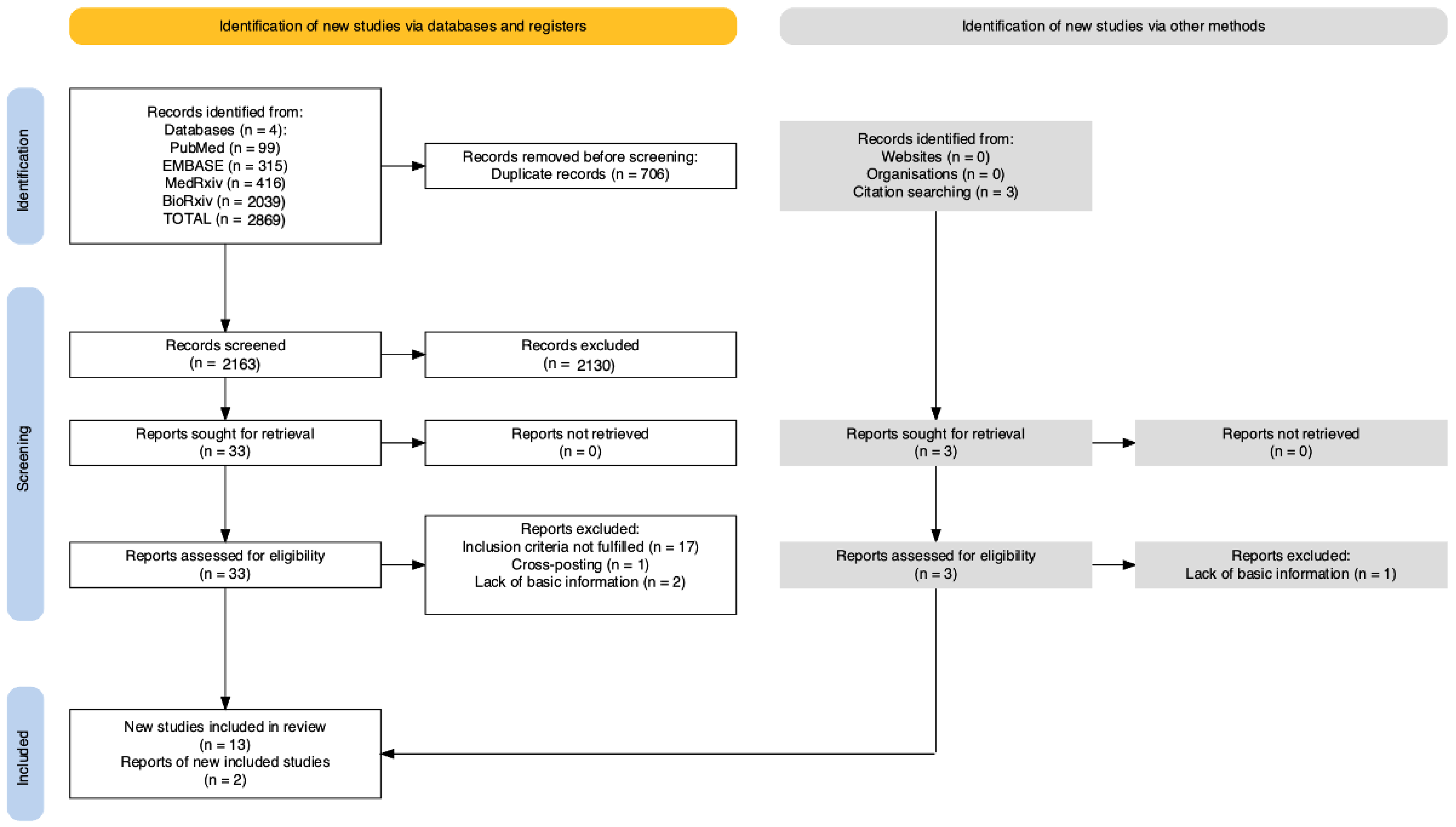
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Selection, Inclusion, and Exclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Availability of the full text;
- (2)
- Diagnosis of viral encephalitis and or meningoencephalitis;
- (3)
- Status of “probable” or “confirmed” BoDV-1 case according to RKI definition [25], that is: (a) Confirmed case: encephalitis or encephalopathy AND detection of BoDV-1 RNA in Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) or Central Nervous System (CNS) tissue, OR detection of BoDV-1 antigen by immunohistochemical analysis with virus-specific monoclonal antibodies in CNS tissue; (b) Probable case: Encephalitis or encephalopathy AND detection of bornavirus-reactive IgG in a serum or CSF sample by screening test (with full virus antigen, for example by immunofluorescence test), and suitable confirmation assay detecting antibodies against individual bornavirus antigens (derived from infected cells or recombinant antigens, e.g., the western blot, immunoblot, or ELISA).
2.2. Data Extraction
- (a)
- Settings of the case: year, month or season, geographic region;
- (b)
- Age and gender of the reported cases;
- (c)
- Pre-existing clinical features, if any; in particular, previous solid organ transplantation(s), were taken into account;
- (d)
- Potential risk factors: living in urban vs. rural areas; whether the patient worked as a farmer and/or with animal(s) and/or livestock; whether the patient(s) had any documented interaction with pets and/or livestock and/or rodents;
- (e)
- Clinical characteristics at the onset of the symptoms. According to the clinical features reported by the original reports from Schlottau et al. [42], by Korn et al. [50], and by the case series of Niller et al. [12], the following signs and symptoms were specifically taken into account: flu-like syndrome (general aches and a fever); headache; fever (body temperature > 38 °C); apathy (loss of motivation, decreased initiative, and emotional blunting) [51]; asthenia; malaise, nausea and/or vomiting; any altered state of consciousness; any progressive loss of consciousness up to eventual coma; seizures; aphasia and/or blurred speech; hemiplegia or tetraplegia; sensorimotor neuropathy;
- (f)
- CSF features at the onset of the symptoms: whether pleocytosis (>5 leucocytes/μL in CSF) [52] increased values of protein and/or lactate according to the normal range values of the parent institution;
- (g)
- Features of electroencephalographic studies: whether focal or general anomalies were reported; signs of slowed rhythm;
- (h)
- Total T1/T2 anomalies reported at magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) studies at the onset of the clinical symptoms;
- (i)
- Outcomes: survival vs. death and weeks of total survival time.
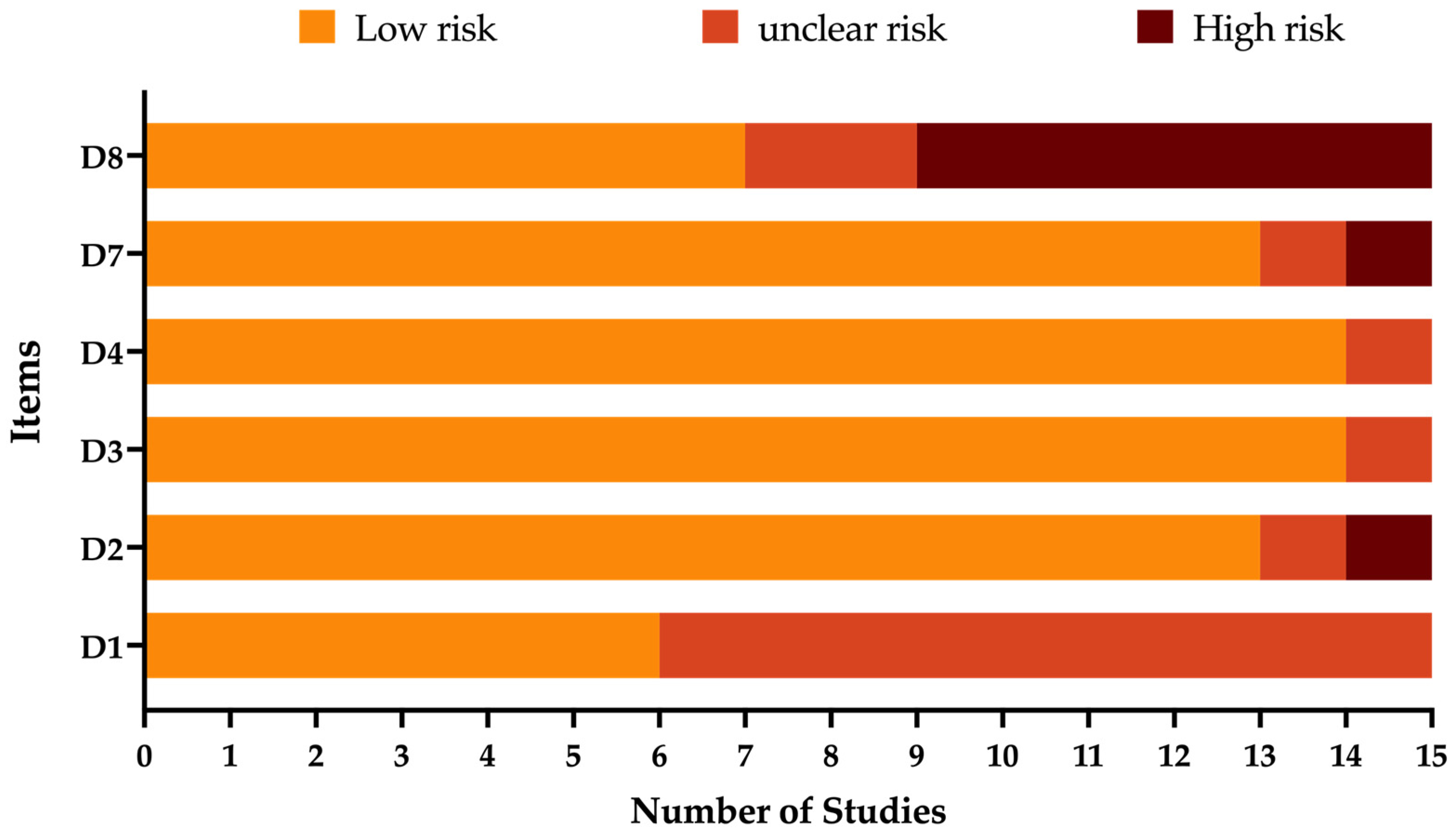
2.3. Qualitative Assessment
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Qualitative Assessment
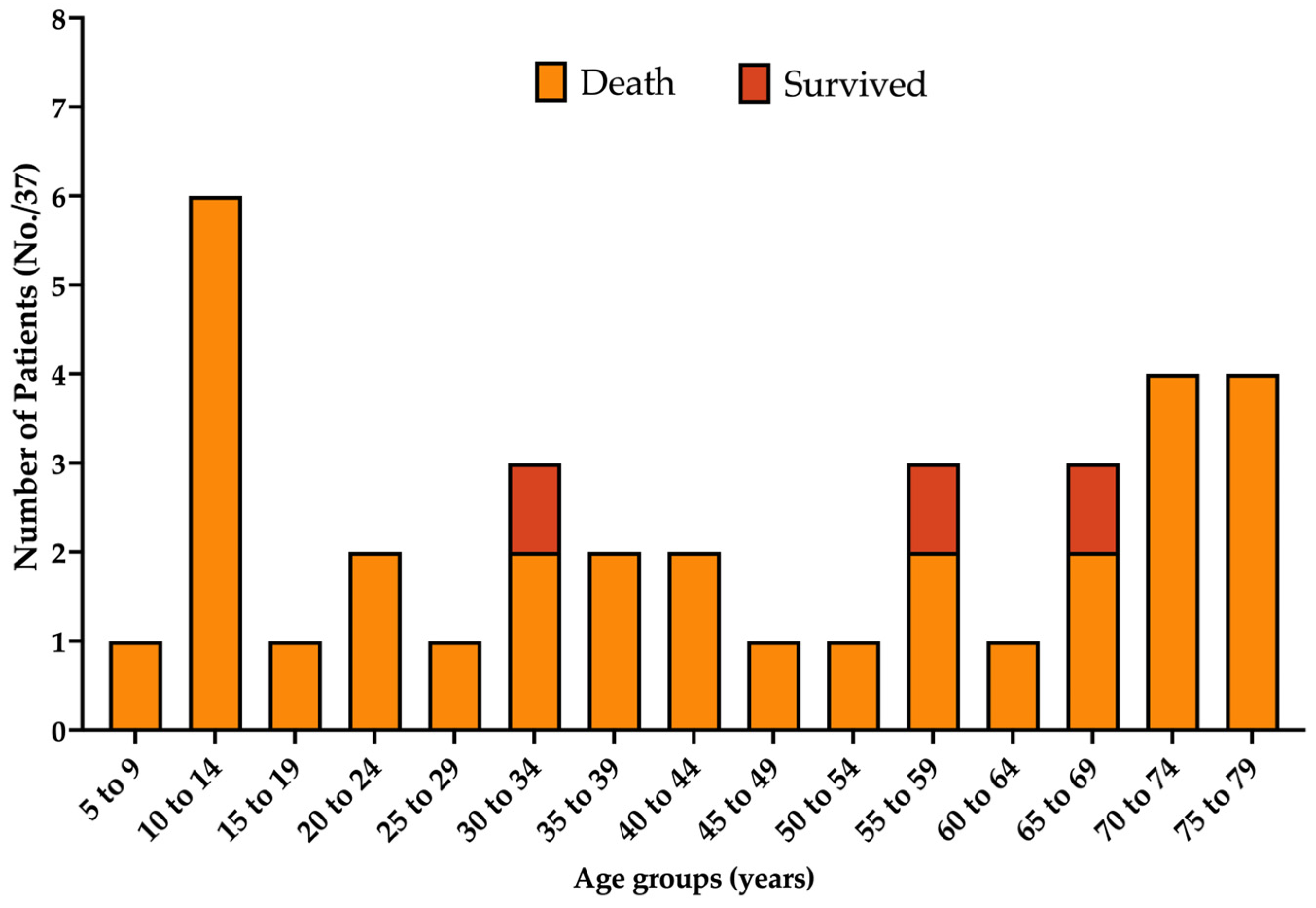
3.2. Demographics
3.3. Pre-Existing Clinical Features
3.4. Natural History
3.5. Clinical Features
3.6. Imaging Features
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Main Findings
4.2. Summary of Clinical Features
4.3. Summary of MRI Studies
4.4. Summary of the CSF Studies
4.5. BoDV-1 Encephalitis as a Zoonosis: Role of Rural and Occupational Exposures
4.6. Limitations of Collected Results and Implication for Future Research
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Database | Keywords Searched | No. of Entries Found |
|---|---|---|
| PubMed [MeSH] | (“Borna Disease”[Mesh] OR “Borna disease virus”[Mesh] OR “Bornaviridae”[Mesh]) AND (“Encephalitis”[Mesh] OR “Encephalitis, Viral”[Mesh] OR “Encephalitis Viruses”[Mesh]) | 99 |
| EMBASE | (‘orthobornavirus’/exp OR ‘orthobornavirus’ OR ‘borna disease’ OR ‘borna disease virus’ OR ‘borna disease virus 1’) AND (‘encephalitis’ OR ‘brain disease’ OR ‘meningoencephalitis’ OR ‘meningitis’ OR ‘infectious meningitis’ OR ‘viral meningoencephalitis’ OR ‘virus meningitis’) | 315 |
| MedRxiv | (“bornavirus” OR “borna disease virus”) AND (“encephalitis” OR “meningitis” OR “meningoencephalitis”) | 436 |
| BioRxiv | 2039 |
| Study | D1 | D2 | D3 | D4 | D7 | D8 | Score (0 to 6) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korn et al., 2018 [50] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 6 |
| Schlottau et al., 2018 [42] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 6 |
| Coras et al., 2019 [61] | ? | ☹ | ☹ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 3 |
| Liesche et al., 2019 [47] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 6 |
| Finck et al., 2020 [60] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ? | 4 |
| Niller et al., 2020 [12] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ? | 5 |
| Eisermann et al., 2021 [25] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | 5 |
| Schimmel et al., 2021 [58] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | 4 |
| Tappe et al., 2021 [38] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 5 |
| Bourgade et al., 2022 [62] | ? | ? | ☺ | ☹ | ? | ☹ | 1 |
| Frank et al., 2022 [39] | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | 5 |
| Liesche-Starnecker et al., 2022 [59] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | 4 |
| Meier et al., 2022 [9] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 5 |
| Neumann et al., 2022 [46] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☹ | ☹ | 3 |
| Grosse et al., 2023 [26] | ? | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | ☺ | 5 |
| Case | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Coras et al. [61] | On day 5/6 after the onset of neurological symptoms, developed unresponsive state. After 4 months without any documented improvement, the patient was transferred to a local hospital closer to the family. After 6 weeks, the patient was released into the care of family in a palliative situation (mechanical respiration). |
| Frank et al. P1 [39] | The patient developed dysphasia, vigilance decline, and epileptic seizures, with sopor and ocular bulbus divergence. After 11 months, the patient was alive but severely disabled and lives in a nursing home. |
| Schlottau et al. P3 [42] | Developed symptoms associated with BoDV-1 infection 98 days after liver transplantation (facial palsy, anomia, cognitive deficits). After 9 months, the patient was alive with residual optic nerve atrophy. |
| Reported Environmental Risk Factors (N. 17) | |
|---|---|
| Residence in rural area | Eisermann et al. P4 [25] |
| Frank et al. P1, P2 [39] | |
| Korn et al. [50] | |
| Liesche et al. P4 [47] | |
| Niller et al. P3, P4, P5 [12] | |
| Tappe et al. [57] | |
| Outskirts of urban centers | Eisermann et al. P3 [25] |
| Grosse et al. P2 [26] | |
| Niller et al. P1 [12] | |
| Schimmel et al. P1, P2 [58] | |
| Farming activities (any) | Korn et al. [50] |
| Liesche et al. P2, P4 [47] | |
| Tappe et al. [57] | |
| Finck et al. P15 [60] | |
| Suburban activities (any) | Liesche et al. P4 [47] |
| Niller et al. P1, P2 [12] | |
| Any interaction with pets | Liesche et al. P7 [47] |
| Tappe et al. [57] | |
| Any interaction with livestock | Korn et al. [50] |
| Liesche et al. P7 [47] | |
| Meier et al. P2 [9] | |
| Niller et al. P1, P2, P3, P5 [12] | |
| Tappe et al. [57] | |
| Pre-existing comorbidities (N. 27) | |
| Chronic kidney disease | Bourgade et al. P1, P2 [62] |
| Liesche et al. P1 [47] | |
| Niller et al. P3, P4 [12] | |
| Hepatic cell Carcinoma | Schlottau et al. P3 [42] |
| Diabetes | Liesche et al. P8 [47] |
| Niller et al. P3, P4 [12] | |
| Hypertension | Finck et al. P15 [60] |
| Niller et al. P3 [12] | |
| Multiple sclerosis | Finck et al. P15 [60] |
| Congestive heart disease | Niller et al. P3 [12] |
| Obesity | Finck et al. P15 [60] |
| History of solid organ transplantation | Bourgade et al. P1, P2 [62] |
| Liesche et al. P1 [47] | |
| Niller et al. P3, P4 [12] | |
| Schlottau et al. P3 [42] | |
| Kidney | Bourgade et al. P1, P2 [62] |
| Liesche et al. P1 [47] | |
| Niller et al. P3, P4 [12] | |
| Liver | Schlottau et al. P3 [42] |
| Documented Survival (N. 3) | Coras et al. [61] |
| Frank et al. P1 [39] | |
| Schlottau et al. P3 [42] |
References
- Norrild, B. The International Berlin Symposium on Bornavirus Infections—From Animals to Man--50 Years of Development. Introduction. APMIS Suppl. 2008, 124, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Chalmers, R.M.; Thomas, D.R.; Salmon, R.L. Borna Disease Virus and the Evidence for Human Pathogenicity: A Systematic Review. QJM 2005, 98, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tizard, I.; Ball, J.; Stoica, G.; Payne, S. The Pathogenesis of Bornaviral Diseases in Mammals. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2016, 17, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaff, F.; Rubbenstroth, D. Two Novel Bornaviruses Identified in Colubrid and Viperid Snakes. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 2611–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubbenstroth, D. Avian Bornavirus Research—A Comprehensive Review. Viruses 2022, 14, 1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauder, C.; Staeheli, P. Rat Model of Borna Disease Virus Transmission: Epidemiological Implications. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 12886–12890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyding-Lamadé, U.; Craemer, E.; Schnitzler, P. Emerging and Re-Emerging Viruses Affecting the Nervous System. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2019, 1, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmutzhard, E.; Pfausler, B. Rabies and Bornavirus Encephalitis. Fatal Emerging Viral Encephalitis—A Potential Problem for Organ Recipients. Nervenarzt 2018, 89, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, H.; Bauer, C.; Finkenzeller, W.; Nentwich, J.; Städt, M.; Steininger, P.; Korn, K.; Ensser, A.; Erbguth, F. Bornavirus Encephalitis as a Differential Diagnosis to Seronegative Autoimmune Encephalitis. Nervenarzt 2022, 93, 835–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauswein, M.; Lampl, B.M.J.; Pregler, M.; Niller, H.H.; Böhmer, M.M.; Schmidt, B. Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1): Aktueller Stand Und Perspektiven. Krankenh. Up2date 2023, 18, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornavirus Associated with Fatal Human Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1880–1881. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niller, H.H.; Angstwurm, K.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Schlottau, K.; Ebinger, A.; Giese, S.; Wunderlich, S.; Banas, B.; Forth, L.F.; Hoffmann, D.; et al. Zoonotic Spillover Infections with Borna Disease Virus 1 Leading to Fatal Human Encephalitis, 1999–2019: An Epidemiological Investigation. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 467–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amarasinghe, G.K.; Bào, Y.; Basler, C.F.; Bavari, S.; Beer, M.; Bejerman, N.; Blasdell, K.R.; Bochnowski, A.; Briese, T.; Bukreyev, A.; et al. Taxonomy of the Order Mononegavirales: Update 2017. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staeheli, P.; Sauder, C.; Rgen Hausmann, J.; Ehrensperger, F.; Schwemmle, M. Epidemiology of Borna Disease Virus. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2123–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipkin, W.I.; Briese, T.; Hornig, M. Borna Disease Virus—Fact and Fantasy. Virus Res. 2011, 162, 162–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlos De La Torre, J. Molecular Biology of Borna Disease Virus and Persistence. Front. Biosci. 2002, 7, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, I.; Lipkin, W.I. Borna Disease Virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2001, 11, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, W.I.; Travist, G.H.; Carbone, K.M.; Wilson, M.C. Isolation and Characterization of Borna Disease Agent CDNA Clones (Limbic System/Behavioral Disorders/Central Nervous System Infection). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 4184–4188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürrwald, R.; Kolodziejek, J.; Weissenböck, H.; Nowotny, N. The Bicolored White-Toothed Shrew Crocidura Leucodon (HERMANN 1780) Is an Indigenous Host of Mammalian Borna Disease Virus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e93659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahlenkamp, T.W.; Enbergs, H.K.; Èller, H.M. Experimental and Natural Borna Disease Virus Infections: Presence of Viral RNA in Cells of the Peripheral Blood. Vet. Microbiol. 2000, 76, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igata-Yi, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Yoshiki, K.; Takemoto, S.; Yamasaki, H.; Matsuoka, M.; Miyakawa, T. Borna Disease Virus and the Consumption of Raw Horse Meat. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 948–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L.; Xie, P.; Dietrich, D.E.; Zaliunaite, V.; Ludwig, H. Are Human Borna Disease Virus 1 Infections Zoonotic and Fatal? Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 650–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnunen, P.M.; Billich, C.; Ek-Kommonen, C.; Henttonen, H.R.K.; Kallio, E.; Niemimaa, J.; Palva, A.; Staeheli, P.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Serological Evidence for Borna Disease Virus Infection in Humans, Wild Rodents and Other Vertebrates in Finland. J. Clin. Virol. 2007, 38, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinnunen, P.M.; Palva, A.; Vaheri, A.; Vapalahti, O. Epidemiology and Host Spectrum of Borna Disease Virus Infections. J. Gen. Virol. 2013, 94, 247–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisermann, P.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Cadar, D.; Thomé-Bolduan, C.; Eggert, P.; Schlaphof, A.; Leypoldt, F.; Stangel, M.; Fortwängler, T.; Hoffmann, F.; et al. Active Case Finding of Current Bornavirus Infections in Human Encephalitis Cases of Unknown Etiology, Germany, 2018–2020. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2021, 27, 1371–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosse, L.; Lieftüchter, V.; Vollmuth, Y.; Hoffmann, F.; Olivieri, M.; Reiter, K.; Tacke, M.; Heinen, F.; Borggraefe, I.; Osterman, A.; et al. First Detected Geographical Cluster of BoDV-1 Encephalitis from Same Small Village in Two Children: Therapeutic Considerations and Epidemiological Implications. Infection 2023, 51, 1383–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, K.; Wilking, H.; Frank, C.; Böhmer, M.M.; Stark, K.; Tappe, D. Risk Factors for Borna Disease Virus 1 Encephalitis in Germany—A Case-Control Study. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2023, 12, e2174778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, L. Human Bornavirus Infection—Towards a Valid Diagnostic System. APMIS Suppl. 2008, 116, 21–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferszt, R.; Severus, E.; Bode, L.; Brehm, M.; Kühl, K.P.; Berzewski, H.; Ludwig, H. Activated Borna Disease Virus in Affective Disorders. Pharmacopsychiat 1999, 32, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azami, M.; Jalilian, F.A.; Khorshidi, A.; Mohammadi, Y.; Tardeh, Z. The Association between Borna Disease Virus and Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Asian J. Psychiatr. 2018, 34, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bode, L.; Fersztz, R.; Czech, G. Borna Disease Virus Infection and Affective Disorders in Man. Arch. Virol. 1993, 7, 159–167. [Google Scholar]
- Bode, L.; Riegel, S.; Lange, W.; Ludwig, H. Human Infections with Borna Disease Virus: Seroprevalence in Patients with Chronic Diseases and Healthy Individuals. J. Med. Virol. 1992, 36, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaliunaite, V.; Steibliene, V.; Bode, L.; Podlipskyte, A.; Bunevicius, R.; Ludwig, H. Primary Psychosis and Borna Disease Virus Infection in Lithuania: A Case Control Study. BMC Psychiatry 2016, 16, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L.; Guo, Y.; Xie, P. Molecular Epidemiology of Human Borna Disease Virus 1 Infection Revisited. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Alwin Prem Anand, A.; Bode, L.; Ludwig, H.; Emrich, H.M.; Dietrich, D.E. Word Recognition Memory and Serum Levels of Borna Disease Virus Specific Circulating Immune Complexes in Obsessive–Compulsive Disorder. BMC Psychiatry 2022, 22, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dürrwald, R.; Kolodziejek, J.; Herzog, S.; Nowotny, N. Meta-Analysis of Putative Human Bornavirus Sequences Fails to Provide Evidence Implicating Borna Disease Virus in Mental Illness. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 181–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, B.; Tappe, D.; Höper, D.; Herden, C.; Boldt, A.; Mawrin, C.; Niederstraßer, O.; Müller, T.; Jenckel, M.; van der Grinten, E.; et al. A Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus Associated with Fatal Human Encephalitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 154–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, D.; Schlottau, K.; Cadar, D.; Hoffmann, B.; Balke, L.; Bewig, B.; Hoffmann, D.; Eisermann, P.; Fickenscher, H.; Krumbholz, A.; et al. Occupation-Associated Fatal Limbic Encephalitis Caused by Variegated Squirrel Bornavirus 1, Germany, 2013. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 978–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, C.; Wickel, J.; Brämer, D.; Matschke, J.; Ibe, R.; Gazivoda, C.; Günther, A.; Hartmann, C.; Rehn, K.; Cadar, D.; et al. Human Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1) Encephalitis Cases in the North and East of Germany. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubbenstroth, D.; Schlottau, K.; Schwemmle, M.; Rissland, J.; Beer, M. Human Bornavirus Research: Back on Track! PLoS Pathog. 2019, 15, e1007873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allartz, P.; Hotop, S.K.; Muntau, B.; Schlaphof, A.; Thomé-Bolduan, C.; Gabriel, M.; Petersen, N.; Lintzel, M.; Behrens, C.; Eggert, P.; et al. Detection of Bornavirus-Reactive Antibodies and BoDV-1 RNA Only in Encephalitis Patients from Virus Endemic Areas: A Comparative Serological and Molecular Sensitivity, Specificity, Predictive Value, and Disease Duration Correlation Study. Infection 2023. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlottau, K.; Forth, L.; Angstwurm, K.; Höper, D.; Zecher, D.; Liesche, F.; Hoffmann, B.; Kegel, V.; Seehofer, D.; Platen, S.; et al. Fatal Encephalitic Borna Disease Virus 1 in Solid-Organ Transplant recipients. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1377–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauswein, M.; Eidenschink, L.; Knoll, G.; Neumann, B.; Angstwurm, K.; Zoubaa, S.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Lampl, B.M.J.; Pregler, M.; Niller, H.H.; et al. Human Infections with Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1) Primarily Lead to Severe Encephalitis: Further Evidence from the Seroepidemiological BoSOT Study in an Endemic Region in Southern Germany. Viruses 2023, 15, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, B.; Hierl, A.; Wunderlich, S.; Meier, H.; Bauer, C.; Gerner, S.T.; Rieder, G.; Geis, T.; Kunkel, J.; Bauswein, M.; et al. Cerebrospinal Fluid in Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1) Encephalitis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 446, 120568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eidenschink, L.; Knoll, G.; Tappe, D.; Offner, R.; Drasch, T.; Ehrl, Y.; Banas, B.; Banas, M.C.; Niller, H.H.; Gessner, A.; et al. IFN-γ-Based ELISpot as a New Tool to Detect Human Infections with Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1): A Pilot Study. Viruses 2023, 15, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neumann, B.; Angstwurm, K.; Linker, R.A.; Knoll, G.; Eidenschink, L.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Schlottau, K.; Beer, M.; Schreiner, P.; Soutschek, E.; et al. Antibodies against Viral Nucleo-, Phospho-, and X Protein Contribute to Serological Diagnosis of Fatal Borna Disease Virus 1 Infections. Cell Rep. Med. 2022, 3, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesche, F.; Ruf, V.; Zoubaa, S.; Kaletka, G.; Rosati, M.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Herden, C.; Goehring, L.; Wunderlich, S.; Wachter, M.F.; et al. The Neuropathology of Fatal Encephalomyelitis in Human Borna Virus Infection. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 653–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Altman, D.; Antes, G.; Atkins, D.; Barbour, V.; Barrowman, N.; Berlin, J.A.; et al. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses: The PRISMA Statement. PLoS Med. 2009, 6, e1000097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rethlefsen, M.L.; Kirtley, S.; Waffenschmidt, S.; Ayala, A.P.; Moher, D.; Page, M.J.; Koffel, J.B. PRISMA-S: An Extension to the PRISMA Statement for Reporting Literature Searches in Systematic Reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, K.; Coras, R.; Bobinger, T.; Herzog, S.M.; Lücking, H.; Stöhr, R.; Huttner, H.B.; Hartmann, A.; Ensser, A. Fatal Encephalitis Associated with Borna Disease Virus 1. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 1375–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, S.; Viswanathan, M.A.; Godin, O.; Dufouil, M.C.; Benisty, S.; Hernandez, K.; Kurtz, M.A.; Jouvent, E.; O’sullivan, M.; Czernecki, V.; et al. Apathy A Major Symptom in CADASIL. Neurology 2009, 72, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Østergaard, A.A.; Sydenham, T.V.; Nybo, M.; Andersen, Å.B. Cerebrospinal Fluid Pleocytosis Level as a Diagnostic Predictor? A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2017, 17, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murad, M.H.; Sultan, S.; Haffar, S.; Bazerbachi, F. Methodological Quality and Synthesis of Case Series and Case Reports. Evid. Based Med. 2018, 23, 60–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- United States Department of Health and Human Services. Handbook for Conducting a Literature-Based Health Assessment Using OHAT Approach for Systematic Review and Evidence Integration; United States Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2019.
- Eick, S.M.; Goin, D.E.; Chartres, N.; Lam, J.; Woodruff, T.J. Assessing Risk of Bias in Human Environmental Epidemiology Studies Using Three Tools: Different Conclusions from Different Tools. Syst. Rev. 2020, 9, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Development Core Team. R a Language and Environment for Statistical Computing: Reference Index; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2010; ISBN 3900051070. [Google Scholar]
- Tappe, D.; Pörtner, K.; Frank, C.; Wilking, H.; Ebinger, A.; Herden, C.; Schulze, C.; Muntau, B.; Eggert, P.; Allartz, P.; et al. Investigation of Fatal Human Borna Disease Virus 1 Encephalitis Outside the Previously Known Area for Human Cases, Brandenburg, Germany—A Case Report. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schimmel, M.; Vollert, K.; Märkl, B.; Schenk, W.; Liesche-Starnecker, F.; Buheitel, G.; Frühwald, M.C. Overwhelming Bornavirus Encephalitis Resulting in a Lethal Outcome. Neuropediatrics 2021, 52, S1–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liesche-Starnecker, F.; Schifferer, M.; Schlegel, J.; Vollmuth, Y.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Delbridge, C.; Gempt, J.; Lorenzl, S.; Schnurbus, L.; Misgeld, T.; et al. Hemorrhagic Lesion with Detection of Infected Endothelial Cells in Human Bornavirus Encephalitis. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 144, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finck, T.; Liesche-Starnecker, F.; Probst, M.; Bette, S.; Ruf, V.; Wendl, C.; Dorn, F.; Angstwurm, K.; Schlegel, J.; Zimmer, C.; et al. Bornavirus Encephalitis Shows a Characteristic Magnetic Resonance Phenotype in Humans. Ann. Neurol. 2020, 88, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coras, R.; Korn, K.; Kuerten, S.; Huttner, H.B.; Ensser, A. Severe Bornavirus-Encephalitis Presenting as Guillain–Barré-Syndrome. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 137, 1017–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgade, K.; Thouard, A.; Abravanel, F.; Hebral, A.L.; Del Bello, A.; Viguier, A.; Gonzalez-Dunia, D.; Kamar, N. Fatal Encephalitis and Borna Disease Virus-1 Seropositivity in Two Kidney-Transplant Patients Living in the Same Nonendemic Area. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2021, 23, e13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropper, A.H.; Samuels, M.A.; Klein, J.P.; Prasad, S. Chapter 32. Viral Infections of the Nervous System and Prion Diseases. In Adams and Victor’s Principles of Neurology; Ropper, A.H., Samuels, M.A., Klein, J.P., Prasad, S., Eds.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2023; pp. 739–771. [Google Scholar]
- George, B.P.; Schneider, E.B.; Venkatesan, A. Encephalitis Hospitalization Rates and Inpatient Mortality in the United States, 2000–2010. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redenbaugh, V.; Flanagan, E.P. Understanding the Etiology and Epidemiology of Meningitis and Encephalitis: Now and into the Future. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pacific 2022, 20, 100380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofrit, S.G.; Pikkel, Y.Y.; Levine, H.; Fraifeld, S.; Kahana Merhavi, S.; Friedensohn, L.; Eliahou, R.; Ben-Hur, T.; Honig, A. Characterization of Meningitis and Meningoencephalitis in the Israeli Defense Forces From 2004 to 2015: A Population-Based Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 887677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungureanu, A.; van der Meer, J.; Bicvic, A.; Abbuehl, L.; Chiffi, G.; Jaques, L.; Suter-Riniker, F.; Leib, S.L.; Bassetti, C.L.A.; Dietmann, A. Meningitis, Meningoencephalitis and Encephalitis in Bern: An Observational Study of 258 Patients. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode, L.; Reckwald, P.; Stoyloff, R.; Ferszt, R.; Dietrich, D.E.; Ludwig, H. Borna Disease Virus-Specific Circulating Immune Complexes, Antigenemia, and Free Antibodies-the Key Marker Triplet Determining Infection and Prevailing in Severe Mood Disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 2001, 6, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Scholbach, T.; Bode, L. Borna Disease Virus Infection in Young Children. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2008, 116, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.M.; Vulcano, A.; Candelori, E.; Ludwig, H.; Bode, L. Borna Virus Disease Infection in the Population of Latium (Italy). Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2008, 116, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patti, A.; Vulcano, A.; Candelori, E.; Donfrancesco, R.; Ludwig, H.; Bode, L. Borna Disease Virus Infection in Italian Children. A Potential Risk for the Developing Brain? Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 2008, 116, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tappe, D.; Frank, C.; Offergeld, R.; Wagner-Wiening, C.; Stark, K.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Giese, S.; Lattwein, E.; Schwemmle, M.; Beer, M.; et al. Low Prevalence of Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1) IgG Antibodies in Humans from Areas Endemic for Animal Borna Disease of Southern Germany. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 20154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puorger, M.E.; Hilbe, M.; Müller, J.P.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N.; Zlinszky, K.; Ehrensperger, F. Distribution of Borna Disease Virus Antigen and Rna in Tissues of Naturally Infected Bicolored White-Toothed Shrews, Crocidura Leucodon, Supporting Their Role as Reservoir Host Species. Vet. Pathol. 2010, 47, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilbe, M.; Herrsche, R.; Kolodziejek, J.; Nowotny, N.; Zlinszky, K.; Ehrensperger, F. Shrews as Reservoir Hosts of Borna Disease Virus. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 675–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatalski, C.G.; Lewis, A.J.; Lipkin, W.I. Borna Disease. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 1997, 3, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riccó, M.; Signorelli, C.; Pistelli, E.; Cattani, S. Quantitative Olfactory Disorders and Occupational Exposure to Phenolic Resins | Ilościowe Zaburzenia Węchu a Narażenie Zawodowe Na Żywice Fenolowe. Med. Pract. 2016, 67, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cain, M.; Ly, H. Increasing Evidence of Human Infections by the Neurotropic Borna Disease Virus 1 (BoDV-1). Virulence 2023, 14, 2218075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauch, J.; Steffen, J.F.; Muntau, B.; Gisbrecht, J.; Pörtner, K.; Herden, C.; Niller, H.H.; Bauswein, M.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Mehlhoop, U.; et al. Human Borna Disease Virus 1 Encephalitis Shows Marked Pro-Inflammatory Biomarker and Tissue Immunoactivation during the Course of Disease. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 1843–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, R.G.; Drewes, S.; Haring, V.; Panajotov, J.; Pfeffer, M.; Rubbenstroth, D.; Dreesman, J.; Beer, M.; Dobler, G.; Knauf, S.; et al. Viral Zoonoses in Germany: A One Health Perspective. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundh. Gesundh. 2023, 66, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, J.W.; Toklu, H.Z.; Ye, F.; Mazza, J.; Yale, S. Case Reports, Case Series—From Clinical Practice to Evidence-Based Medicine in Graduate Medical Education. Cureus 2017, 9, e1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitze, B.; Herzog, S.; Rieckmann, P.; Poser, S.; Richt, J. No Evidence of Borna Disease Virus-Specific Antibodies in Multiple Sclerosis Patients in Germany. J. Neurol. 1996, 243, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study | Country | Reported Cases (No.) | Cross Reported Cases | Included Cases (No.) | Cases Included in the Pooled Analyses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Korn et al., 2018 [50] | Germany | 1 | Yes | 1 | P1 |
| Schlottau et al., 2018 [42] | Germany | 3 | Partially | 1 | P3 |
| Coras et al., 2019 [61] | Germany | 1 | Yes | 1 | P1 |
| Liesche et al., 2019 [47] | Germany | 6 | Partially | 5 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5 |
| Finck et al., 2020 [60] | Germany | 19 | Partially | 11 | P1, P2, P3, P5, P6, P10, P12, P13, P15, P18; P19 |
| Niller et al., 2020 [12] | Germany | 8 | Partially | 5 | P1, P2, P3, P4, P5 |
| Eisermann et al., 2021 [25] | Germany | 4 | Partially | 2 | P3, P4 |
| Schimmel et al., 2021 [58] | Germany | 2 | No | 2 | P1, P2 |
| Tappe et al., 2021 [38] | Germany | 1 | Yes | 1 | P1 |
| Bourgade et al., 2022 [62] | France | 2 | No | 2 | P1, P2 |
| Frank et al., 2022 [39] | Germany | 3 | Partially | 2 | P1, P2 |
| Liesche-Starnecker et al., 2022 [59] | Germany | 1 | No | 1 | P1 |
| Meier et al., 2022 [9] | Germany | 2 | No | 1 | P2 |
| Neumann et al., 2022 [46] | Germany | 1 | No | 1 | P1 |
| Grosse et al., 2023 [26] | Germany | 2 | Partially | 1 | P2 |
| Characteristic | No./37, % |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Male | 8, 21.6% |
| Female | 15, 40.5% |
| Not reported | 14, 37.8% |
| Age Group | |
| <20 years | 8, 21.6% |
| 20–50 years | 11, 29.7% |
| 50 years or more | 16, 43.2% |
| Not reported | 2, 5.4% |
| Region of origin | |
| Germany | |
| Bavaria | 32, 86.5% |
| Saxony-Anhalt | 1, 2.7% |
| Brandenburg | 1, 2.7% |
| Thuringia | 1, 2.7% |
| France | |
| Occitanie | 2, 5.4% |
| Reported environmental risk factors | 17, 45.9% |
| Residence in rural area | 9, 24.3% |
| Outskirts of urban centers | 5, 13.5% |
| Farming activities (any) | 5, 13.5% |
| Suburban activities (any) | 3, 8.1% |
| Any interaction with pets | 8, 21.6% |
| Any interaction with livestock | 2, 5.4% |
| Season (onset of symptoms) | |
| Winter | 4, 10.8% |
| Spring | 3, 8.1% |
| Summer | 8, 21.6% |
| Autumn | 2, 5.4% |
| Not reported | 20, 54.1% |
| Deaths | 34, 91.9% |
| Survival < 4 weeks | 6, 16.2% |
| Survival 4 to 9 weeks | 20, 54.1% |
| Survival ≥ 10 weeks | 4, 10.8% |
| Length of survival not reported | 4, 10.8% |
| Comorbidities | No./27, % |
|---|---|
| Pre-existing comorbidities (any) | 8, 29.6% |
| Chronic Kidney disease | 5, 18.5% |
| Hepatic Cells carcinoma | 1, 3.7% |
| Diabetes | 3, 11.1% |
| Hypertension | 2, 7.4% |
| Multiple sclerosis | 1, 3.7% |
| Congestive heart disease | 1, 3.7% |
| Obesity | 1, 3.7% |
| History of solid organ transplantation | 6, 22.2% |
| Kidney | 5, 18.5% |
| Liver | 1, 3.7% |
| Sign(s)/Symptom(s) | Total No./37, % | Age < 18 years (No./8, %) | Age ≥ 18 years (No./27, %) | Fisher’s Test p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Flu-like syndrome | 12, 32.4% | 2, 25.0% | 10, 37.0% | 0.685 |
| Headache | 18, 48.6% | 5, 50.0% | 12, 44.4% | 1.000 |
| Fever (at onset) | 21, 56.8% | 8, 100% | 11, 40.7% | 0.004 |
| Nausea/Vomiting | 4, 10.8% | 2, 25.0% | 2, 7.4% | 0.218 |
| Malaise | 4, 10.8% | 1, 12.5% | 3, 11.1% | 1.000 |
| Asthenia | 2, 5.4% | 0, - | 2, 7.4% | 1.000 |
| Apathy | 4, 10.8% | 0, - | 4, 14.8% | 0.553 |
| Drowsiness | 22, 59.5% | 4, 50.0% | 17, 63.0% | 0.685 |
| Progressive loss of consciousness | 10, 27.0% | 4, 50.0% | 4, 14.8% | 0.060 |
| Dysphagia | 3, 8.1% | 2, 25.0% | 1, 3.7% | 0.124 |
| Visual hallucinations | 1, 2.7% | 0, - | 1, 3.7% | 1.000 |
| Seizures | 8, 21.6% | 2, 25.0% | 5, 18.5% | 0.648 |
| Speech disturbances, including aphasia | 8, 21.6% | 1, 12.5% | 7, 25.9% | 0.648 |
| Hemiparesis | 2, 5.4% | 0, - | 2, 7.4% | 1.000 |
| Memory deficits | 4, 10.8% | 0, - | 4, 14.8% | 0.553 |
| Coma | 6, 16.2% | 0, - | 5, 18.5% | 0.315 |
| Meningism | 4, 10.8% | 1, 12.5% | 2, 7.4% | 0.553 |
| Polyneuropathy | 4, 10.8% | 0, - | 4, 14.8% | 0.553 |
| Gait Ataxia | 10, 27.0% | 5, 62.5% | 4, 14.8% | 0.015 |
| Enuresis | 1, 2.7% | 1, 12.5% | 0, - | 0.229 |
| Tetraplegia | 2, 5.4% | 0, - | 2, 7.4% | 1.000 |
| Weight loss | 1, 2.7% | 0, - | 1, 3.7% | 1.000 |
| Arthralgia | 1, 2.7% | 0, - | 1, 3.7% | 1.000 |
| Cerebrospinal fluid features | ||||
| Pleocytosis (>5 leucocytes/μL) | 29, 78.4% | 8, 100% | 19, 70.4% | 0.154 |
| High lactate levels * | 9, 24.3% | 3, 37.5% | 4, 14.8% | 0.312 |
| High protein levels * | 9, 24.3% | 1, 12.5% | 6, 22.2% | 1.000 |
| EEG abnormalities | ||||
| Slowed | 10, 27.0% | - | - | - |
| General abnormalities | 2, 5.4% | - | - | - |
| Negative | 2, 5.4% | - | - | - |
| Not reported | 23, 62.2% | - | - | - |
| Region | No./33, % |
|---|---|
| Telencephalon | |
| Temporal pole | 10, 30.3% |
| Insular cortex | 10, 30.3% |
| Operculum | 6, 18.2% |
| Hippocampus | 6, 18.2% |
| Parahippocampal gyrus | 6, 18.2% |
| Gyrus rectus | 3, 9.1% |
| Occipital pole | 1, 3.0% |
| Deep white matter | 1, 3.0% |
| Optic nerves | 1, 3.0% |
| Diencephalon | |
| Head of the caudate nucleus | 14, 42.4% |
| Thalamus | 11, 33.3% |
| Putamen | 4, 12.1% |
| Brainstem | |
| Mesencephalon | 3, 9.1% |
| Pons | 3, 9.1% |
| Medulla oblongata | 3, 9.1% |
| Cerebellar hemisphere | 1, 3.0% |
| Pineal gland | 1, 3.0% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riccò, M.; Corrado, S.; Marchesi, F.; Bottazzoli, M. Clinical Features of BoDV-1 Encephalitis: A Systematic Review. Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 3, 279-300. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040023
Riccò M, Corrado S, Marchesi F, Bottazzoli M. Clinical Features of BoDV-1 Encephalitis: A Systematic Review. Zoonotic Diseases. 2023; 3(4):279-300. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040023
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiccò, Matteo, Silvia Corrado, Federico Marchesi, and Marco Bottazzoli. 2023. "Clinical Features of BoDV-1 Encephalitis: A Systematic Review" Zoonotic Diseases 3, no. 4: 279-300. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040023
APA StyleRiccò, M., Corrado, S., Marchesi, F., & Bottazzoli, M. (2023). Clinical Features of BoDV-1 Encephalitis: A Systematic Review. Zoonotic Diseases, 3(4), 279-300. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040023







