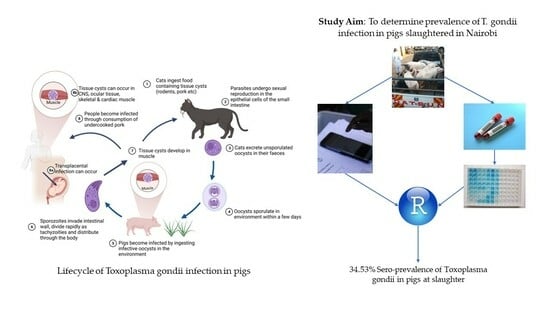
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slaughtered Pigs in Kiambu, Kenya
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site, Design and Sampling Method
2.2. Blood Collection and Processing
2.3. Serological Testing
2.4. Data Management and Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, J.; Wang, W.; Song, P.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; Guo, J.; Hao, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, Q.; Du, X.; et al. Structural predication and antigenic analysis of Toxoplasma gondii ROP20. Acta Parasitol. 2018, 63, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, L.M.; Dubey, J.P. Toxoplasmosis: A history of clinical observations. Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Havelaarid, A.H.; Hoffmannid, S.; Hald, T.; Kirk, M.D.; Torgerson, P.R.; Devleesschauwer, B. Global disease burden of pathogens in animal source foods, 2010. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0216545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, J.P.; Cerqueira-Cézar, C.K.; Murata, F.H.A.; Kwok, O.C.H.; Hill, D.; Yang, Y.; Su, C. All about Toxoplasma gondii infections in pigs: 2009–2020. Vet. Parasitol. 2020, 288, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, M.; Fakhri, Y.; Riahi, S.M.; Ebrahimpour, S.; Namroodi, S.; Taghipour, A.; Spotin, A.; Gamble, H.R.; Rostami, A. The global seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pigs: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Vet. Parasitol. 2019, 269, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sentamu, D.N.; Onono, J.O.; Muinde, P.; Bor, N.; Chepyatich, D.; Thomas, L.F. Prevalence of gross lesions and handling practices in pigs and their association with pork quality, Kiambu, Kenya. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0272951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murungi, M.K.; Muloi, D.M.; Muinde, P.; Githigia, S.M.; Akoko, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Rushton, J.; Alarcon, P. The Nairobi Pork Value Chain: Mapping and Assessment of Governance, Challenges, and Food Safety Issues. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 581376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohoo, I.R.; Martin, S.W.; Stryhn, H. Veterinary Epidemiologic Research; VER, Inc.: Kenosha, WI, USA, 2009; ISBN 978-0-91901-360-5/0-91-901360-0. [Google Scholar]
- Basso, W.; Hartnack, S.; Pardini, L.; Maksimov, P.; Koudela, B.; Venturini, M.C.; Schares, G.; Sidler, X.; Lewis, F.I.; Deplazes, P. Assessment of diagnostic accuracy of a commercial ELISA for the detection of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pigs compared with IFAT, TgSAG1-ELISA and Western blot, using a Bayesian latent class approach. Int. J. Parasitol. 2013, 43, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Development Team. “R: A language and environment for statistical computing, 3.2.1,” Doc. Free. 2015. Available online: http://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 7 September 2021).
- Signorell, A. Tools for Descriptive Statistics [R package DescTools version 0.99.43]. 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/package=DescTools (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Ethan, A.; Atkinson, E.; Dougherty, G.; Lennon, R.; Hanson, A.; Goergen, K.; Lundt, E.; Broderick, B.; Mccullough, M.; Heinzen, M.E. Package “arsenal” R topics documented: 1; 2021. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/arsenal/arsenal.pdf (accessed on 4 August 2021).
- Ishaku, B.S.; Abdullahi, M.; Nalong, D.; Jonah, R.; Mayowa, O. Seroprevalence and Risk Factors for Toxoplasma gondii in Pigs, Sheep and Goats at Slaughter in Jos Municipal Abattoir, Nigeria. Vet. Sci. Res. Rev. 2018, 4, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebremedhin, E.Z.; Kebeta, M.M.; Asaye, M.; Ashenafi, H.; Di Marco, V.; Vitale, M. First report on seroepidemiology of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pigs in Central Ethiopia. BMC Vet. Res. 2015, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Sungirai, M.; Masaka, L.; Benhura, T.M. Validity of weight estimation models in pigs reared under different management conditions. Vet. Med. Int. 2014, 2014, 530469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TE, O.; IO, A. Seroprevalence of anti-Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in cattle and pigs in Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Parasit. Dis. 2015, 39, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halová, D.; Mulcahy, G.; Rafter, P.; Turčeková, L.; Grant, T.; de Waal, T. Toxoplasma gondii in Ireland: Seroprevalence and Novel Molecular Detection Method in Sheep, Pigs, Deer and Chickens. Zoonoses Public Health 2013, 60, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assadi-Rad, A.M.; New, J.C.; Patton, S. Risk factors associated with transmission of Toxoplasma gondii to sows kept in different management systems in Tennessee. Vet. Parasitol. 1995, 57, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villari, S.; Vesco, G.; Petersen, E.; Crispo, A.; Buffolano, W. Risk factors for toxoplasmosis in pigs bred in Sicily, Southern Italy. Vet. Parasitol. 2009, 161, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guide to Good Dairy Farming Practice. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/ba0027e/ba0027e00.htm (accessed on 13 May 2021).
| Categorical Variables | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Category | Category Frequency (n) | Percent by Category (n/N 1) | 95% C.I 2 | Number Positive for T. gondii Antibodies | Percentage Positive for T. gondii Antibodies | 95% C. I 3 | p-Values |
| Sex | Female | 243 | 54.86 | 50.08–59.54 | 85 | 34.98 | 29.06–41.38 | 0.744 |
| Male | 200 | 45.15 | 40.46–49.92 | 67 | 33.50 | 27.07–40.55 | ||
| County of origin of the pig | Nairobi | 56 | 12.81 | 9.90–16.40 | 24 | 42.86 | 29.97–56.73 | 0.083 |
| Kiambu | 342 | 78.26 | 74.03–81.99 | 120 | 35.09 | 30.08–40.44 | ||
| Makueni | 4 | 0.92 | 0.29–2.49 | 1 | 25.00 | 1.32–78.06 | ||
| Kajiado | 15 | 3.43 | 2.00–5.72 | 3 | 20.00 | 5.31–48.44 | ||
| Nakuru | 14 | 3.20 | 1.83–5.45 | 1 | 7.14 | 0.37–35.83 | ||
| Homabay | 4 | 0.92 | 0.30–2.50 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–60.42 | ||
| Murang’a | 2 | 0.45 | 0.08–1.82 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.00–60.42 | ||
| Husbandry type | Housed | 425 | 97.70 | 95.67–98.83 | 146 | 34.35 | 29.88–39.11 | 0.344 |
| Outdoor | 10 | 2.30 | 1.17–4.32 | 2 | 20.00 | 3.54–55.78 | ||
| Farm size (number of pigs) | <10 | 270 | 62.07 | 57.31–66.62 | 110 | 40.74 | 34.87–46.88 | <0.001 4 |
| >100 | 45 | 10.34 | 7.72–13.69 | 4 | 8.89 | 2.89–22.13 | ||
| 10 < 50 | 114 | 26.21 | 22.19–30.65 | 33 | 28.95 | 21.03.38.31 | ||
| 50 < 100 | 6 | 1.38- | 0.56–3.13 | 1 | 16.67 | 0.88–63.52 | ||
| Continuous variables | ||||||||
| Variable | Range | Mean | SD 5 | p-value | ||||
| Live weight | 13–230 | 58.87 | 25.54 | p = 0.044 6 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chepyatich, D.; Sentamu, D.N.; Bor, N.; Onono, J.; Gathura, P.B.; Akoko, J.M.; Thomas, L.F. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slaughtered Pigs in Kiambu, Kenya. Zoonotic Dis. 2023, 3, 301-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040024
Chepyatich D, Sentamu DN, Bor N, Onono J, Gathura PB, Akoko JM, Thomas LF. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slaughtered Pigs in Kiambu, Kenya. Zoonotic Diseases. 2023; 3(4):301-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040024
Chicago/Turabian StyleChepyatich, Dorcas, Derrick Noah Sentamu, Nicholas Bor, Joshua Onono, Peter Baaro Gathura, James M. Akoko, and Lian Francesca Thomas. 2023. "Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slaughtered Pigs in Kiambu, Kenya" Zoonotic Diseases 3, no. 4: 301-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040024
APA StyleChepyatich, D., Sentamu, D. N., Bor, N., Onono, J., Gathura, P. B., Akoko, J. M., & Thomas, L. F. (2023). Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in Slaughtered Pigs in Kiambu, Kenya. Zoonotic Diseases, 3(4), 301-306. https://doi.org/10.3390/zoonoticdis3040024